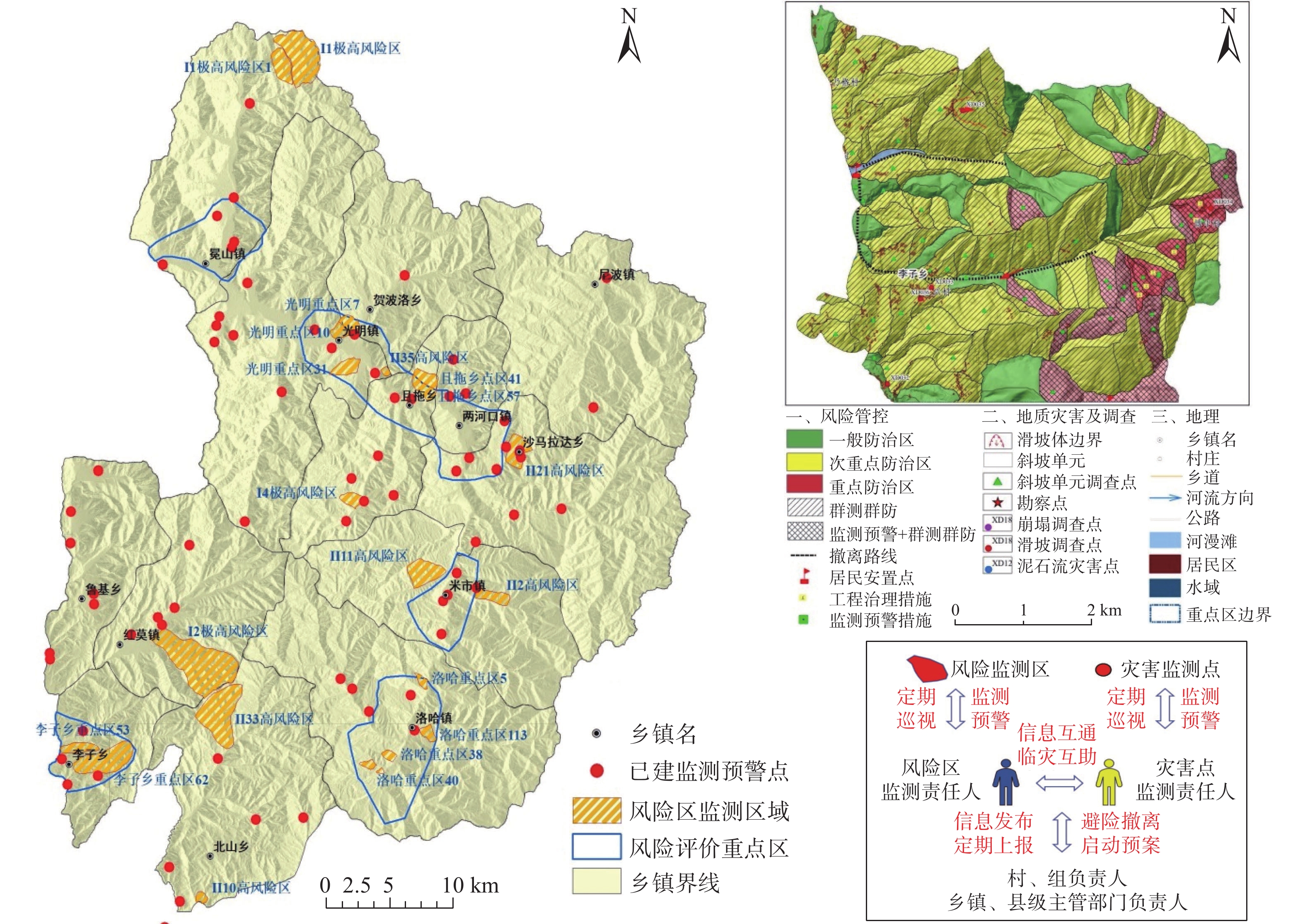
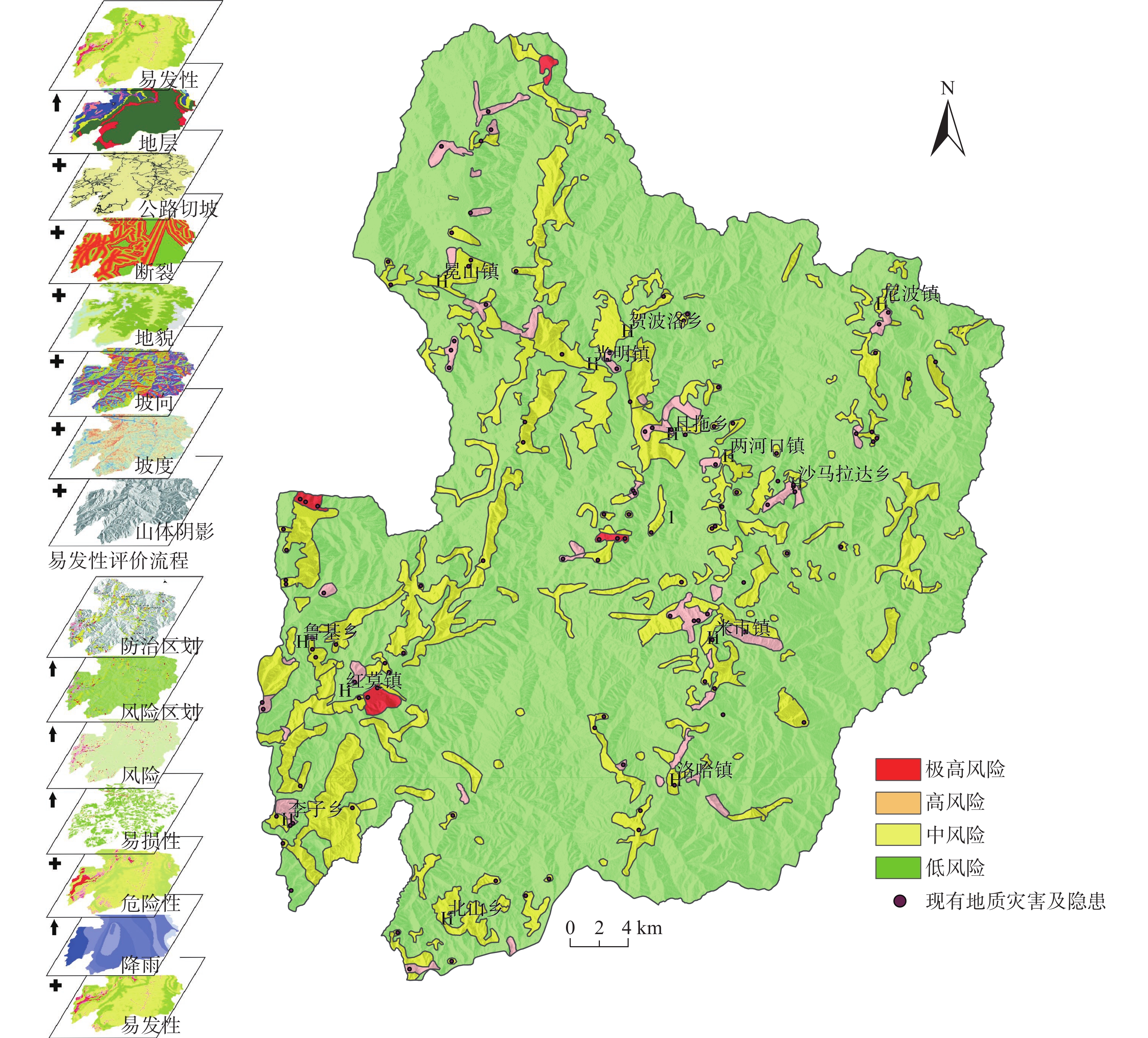
The thoughts on construction of “double-control of point and zone” system of geological hazard risk in southwest China
-
摘要:
西南地区是我国地质灾害发育数量最多、发生频率最高的地区之一,地质灾害隐患点总数约占全国总数的30%,为提升西南地区地质灾害风险管控水平,在总结西南地区地质灾害风险评价及管控现状基础上,分析了目前风险管控中技术层面和管理层面存在的问题与不足,提出了基于地质灾害风险防控专业化、全民化和体系化等模式的地质灾害风险“点面双控”体系构建思路,并对未来西南地区地质灾害风险管控制度化、保险化及智能化趋势进行了展望,成果可为西南地区地质灾害风险系统化防控提供科学参考。
Abstract:Southwest China is one of the regions with the largest number of geological hazards and the highest frequency in China, the total number of geological hazard in this region accounts for about 30% of the national total. In order to improve the ability of geological hazard risk management and control, based on the summary of the current situation of geological hazard risk evaluation and management and control in Southwest China, this paper analyzes the deficiencies existing in the technical level and management level of risk management and control, and puts forward some suggestions based on the specialization of geological hazard risk prevention and control the “double-control of point and zone” system of geological hazard risk in the mode of popularization and systematization, and prospects the future trend of geological hazard risk management, control, insurance and intelligence in southwest China. The results can provide a scientific reference for the systematic prevention and control of geological hazard risk in southwest China.
-

-
[1] 殷跃平. 中国地质灾害减灾回顾与展望—从国际减灾十年到国际减灾战略[J]. 国土资源科技管理,2001,18(3):26 − 29. [YIN Yueping. A review and vision of geological hazards in China[J]. Scientific and Technological Management of Land and Resources,2001,18(3):26 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4210.2001.03.008
Yin Y P. A review and vision of geological hazards inChina[J]. Scientific and Technological Management of Land and Resources, 2001, 18(03): 26-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4210.2001.03.008
[2] 石菊松, 吴树仁, 张永双, 等. 应对全球变化的中国地质灾害综合减灾战略研究[J]. 地质论评,2012,58(2):309 − 318. [SHI Jusong, WU Shuren, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. Study on integrated landslide mitigation strategies for global change in China[J]. Geological Review,2012,58(2):309 − 318. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[Shi J S, Wu S R, Zhang Y S, et al. Study on integrated landslide mitigation strategies for global change in China[J]. Geological Review, 2012, 58(2): 309-318. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
[3] 孙叶. 中国地质灾害类型的划分与减灾对策的战略分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,1991,2(4):12 − 19. [SUNYe. Classification of geological disasters in China and strategic analysis of disaster reduction strategies[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,1991,2(4):12 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sun Ye. Classification of geological disasters in China and strategic analysis of disaster reduction strategies[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1991(4): 12-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张业成, 张梁, 高庆华. 地质灾害减灾指导思想与对策建议[J]. 国土资源科技管理,2000,17(3):34 − 36. [ZHANG Yecheng, ZHANG Liang, GAO Qinghua. Guiding thoughts and countermeasures of geological disaster reduction[J]. Science and Technology Management of Land Resources,2000,17(3):34 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4210.2000.03.010
ZHANG Yecheng, ZHANG Liang, GAO Qinghua. Guiding thoughts and countermeasures of geological disaster reduction[J]. Science and technology management of land resources, 2000, 17(3): 34-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4210.2000.03.010
[5] 张梁. 21世纪中国地质灾害防治形势与减灾战略思考[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2004,15(2):16 − 21. [ZHANG Liang. Thought about the geological hazard control situation and hazard-relief strategy of China in 21st Century[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2004,15(2):16 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.02.003
ZHANG Liang. Thought about the geological hazard control situation and hazard-relief strategy of China in 21st century[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2004, 15(02): 16-21. ( in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.02.003
[6] 铁永波, 强震区城镇泥石流灾害风险评价方法与体系研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009: 17 − 21
TIE Yongbo. Study on risk assessment method and system of urban debris flow disaster in strong earthquake area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2009: 17 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 陈伟. 西南山区城镇建设地质灾害风险管理控制方法研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013: 12 − 23.
CHEN Wei. Study on geohazard risk management methods in southwest mountain towns construction[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2013: 12 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 龚柯. 典型小流域地质灾害风险管控示范研究——以贵州省二塘河流域猴场镇段为例[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019: 66 − 82.
GONG Ke. Demonstration study on risk management and control of geologicaldisasters in typical small watershed: With the second pond river basin in guizhou monkey town as an example[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2019: 66 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] MALONE A W, HO K K S. Learning from landslip disasters in Hong Kong[J]. Built Environment,1995,21(2/3):126 − 144.
[10] 刘传正, 陈春利. 中国地质灾害防治成效与问题对策[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):375 − 383. [LIU Chuanzheng, CHEN Chunli. Achievements and countermeasures in risk reduct-ion of geological disasters in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):375 − 383. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[LIU Chuanzheng, CHEN Chunli. Achievements and countermeasures in risk reduct-ion of geological disasters in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,0, 28(2): 375−383. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
[11] 王雁林, 郝俊卿, 赵法锁, 等. 汶川地震陕西重灾区地质灾害风险区划探讨[J]. 灾害学,2011,26(4):35 − 39. [WANG Yanlin, HAO Junqin, ZHAO Fasuo, et al. The geological disaster risk zoning discuss of Wenchuan earthquake hardest-hit areas in Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2011,26(4):35 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[WANG Yanlin, HAO Junqin, ZHAO Fasuo, et al. TheGeological Disaster risk Zoning Discuss of Wenchuan Earthquake Hardest-hit Areas in Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2011, 26(04): 35-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
[12] 张维宸. 地质灾害防治对策[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2001,12(4):77 − 80. [ZHANG Weicheng. Countermeasures of geological disaster prevention[J]. he Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2001,12(4):77 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
in Chinese with English abstract)]
[13] 马寅生, 张业成, 张春山, 等. 地质灾害风险评价的理论与方法[J]. 地质力学学报,2004,10(1):7 − 18. [MA Yansheng, ZHANG Yecheng, ZHANG Chunshan, et al. Theory and approaches to the risk evaluation of geological hazards[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2004,10(1):7 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2004.01.002
MA Y S, ZHANG Y C, ZHANG C S, et al. 2004. Theory and approaches to the risk evaluation of geological hazards[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2004(1): 7-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2004.01.002
[14] 程太和. 我国西部地区地质灾害保险探讨[J]. 保险研究,2001,6:20 − 21. [CHENG Taihe. Discussion on geological disaster insurance in western China[J]. Insurance Research,2001,6:20 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[CHENG Taihe. Discussion on geological disaster insurance in western ChinaJ]. Insurance research, 2001, (06): 20-21+38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 唐川, 许强. 强震区城市地质灾害风险管理的研究内容与方法探讨[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(1):56 − 61. [TANG Chuan, XU Qiang. Approach on geohazards risk management for urbans in strong seismic zone[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(1):56 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[Tang C Xu Q. Approach on geohazards risk management for56-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)]urbans in strong seismic zone[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(01):
[16] 吴优, 杨根兰, 向喜琼. 景区地质灾害保险支付意愿研究—以南江大峡谷景区为例[J]. 水利科技与经济,2019,25(5):53 − 59. [WU You, YANG Genlan, XIANG Xiqiong. Study on willingness to pay for geological disaster insurance in Scenic spots: A case study of Nanjiang grand canyon scenic area[J]. Water Science and Technology and Economy,2019,25(5):53 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7175.2019.05.011
WU You, YANG Genlan, XIANG Xiqiong. Study on willingness to pay for geological disaster insurance in Scenic spots——A case study of Nanjiang GrandCanyon scenic Area[J]. Water science and technology and economy, 2019, 25(05): 53-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7175.2019.05.011
-



 下载:
下载: