Analysis of the landslide movement characteristics in Biyi Village, Ganluo County, Sichuan Province, through SPH numerical simulation
-
摘要:
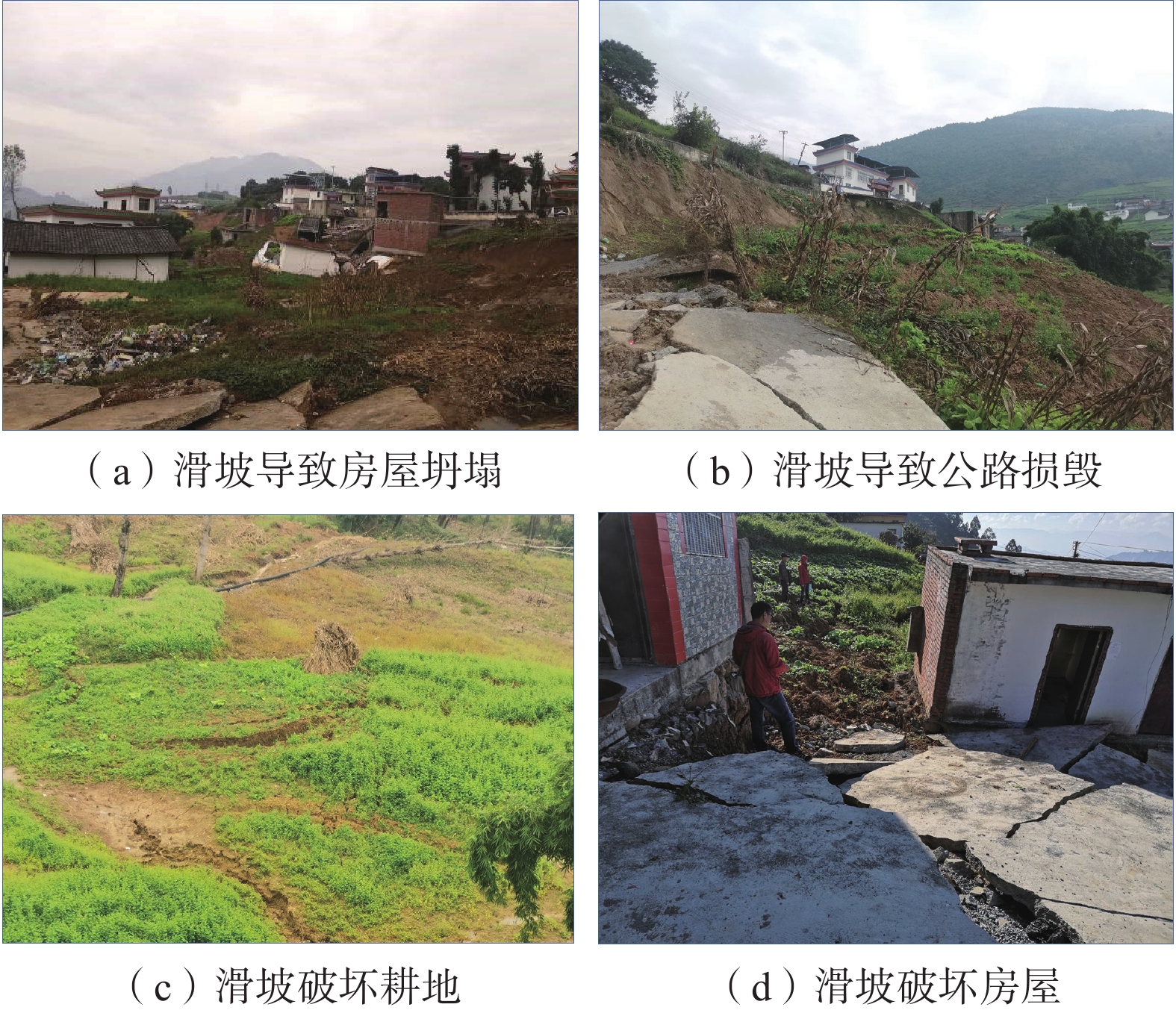
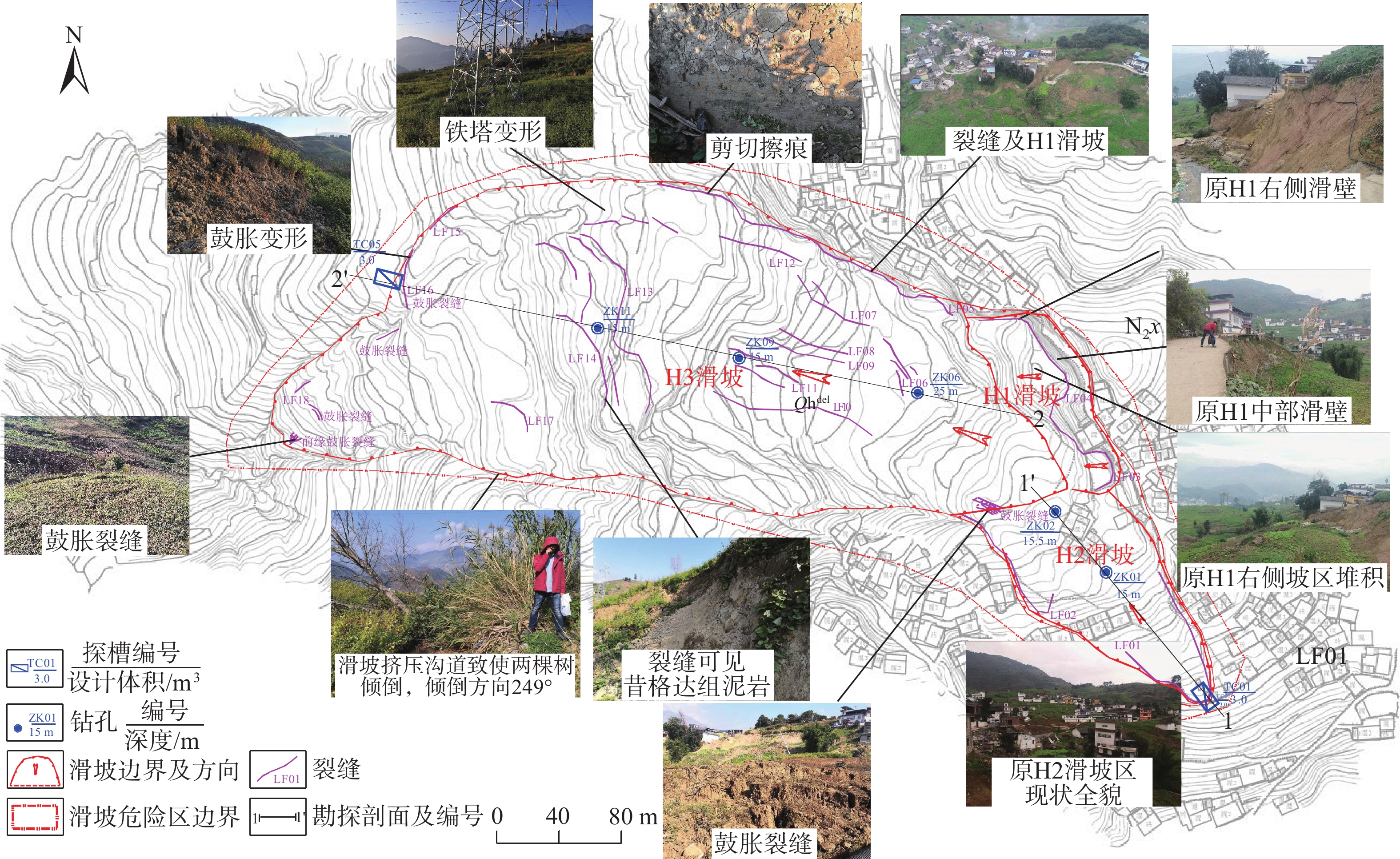
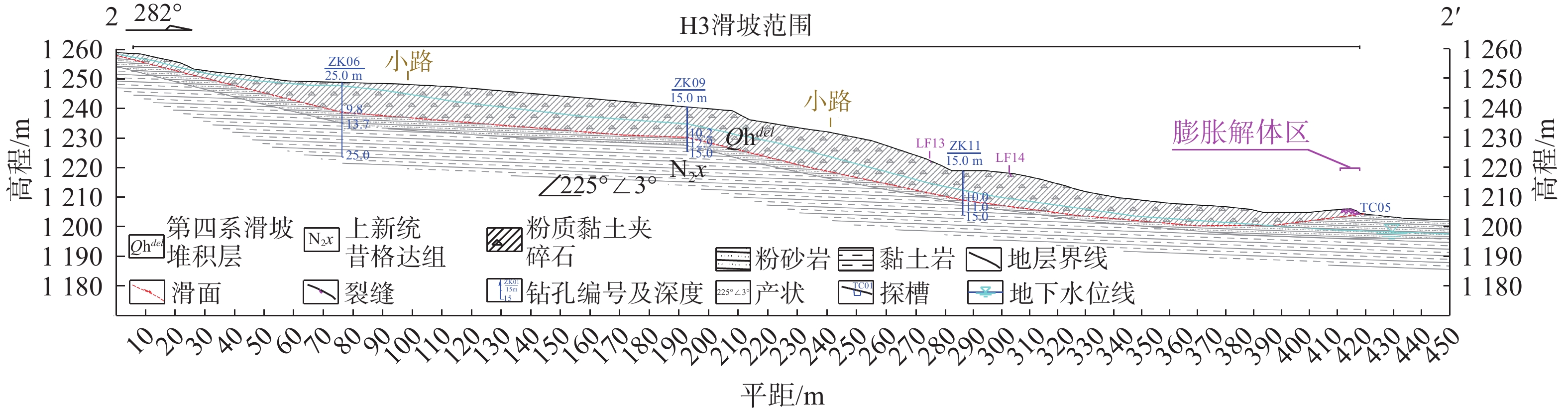
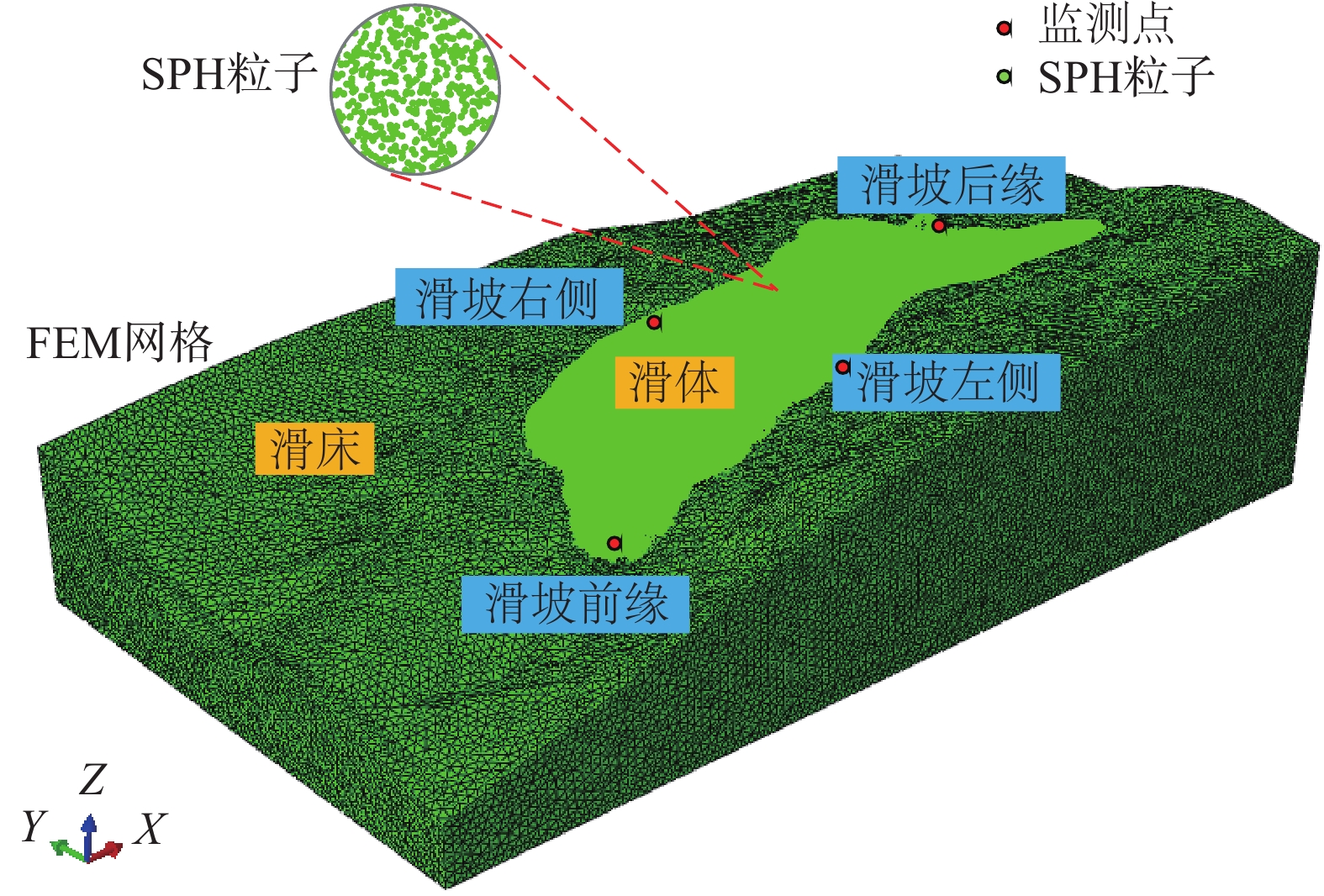
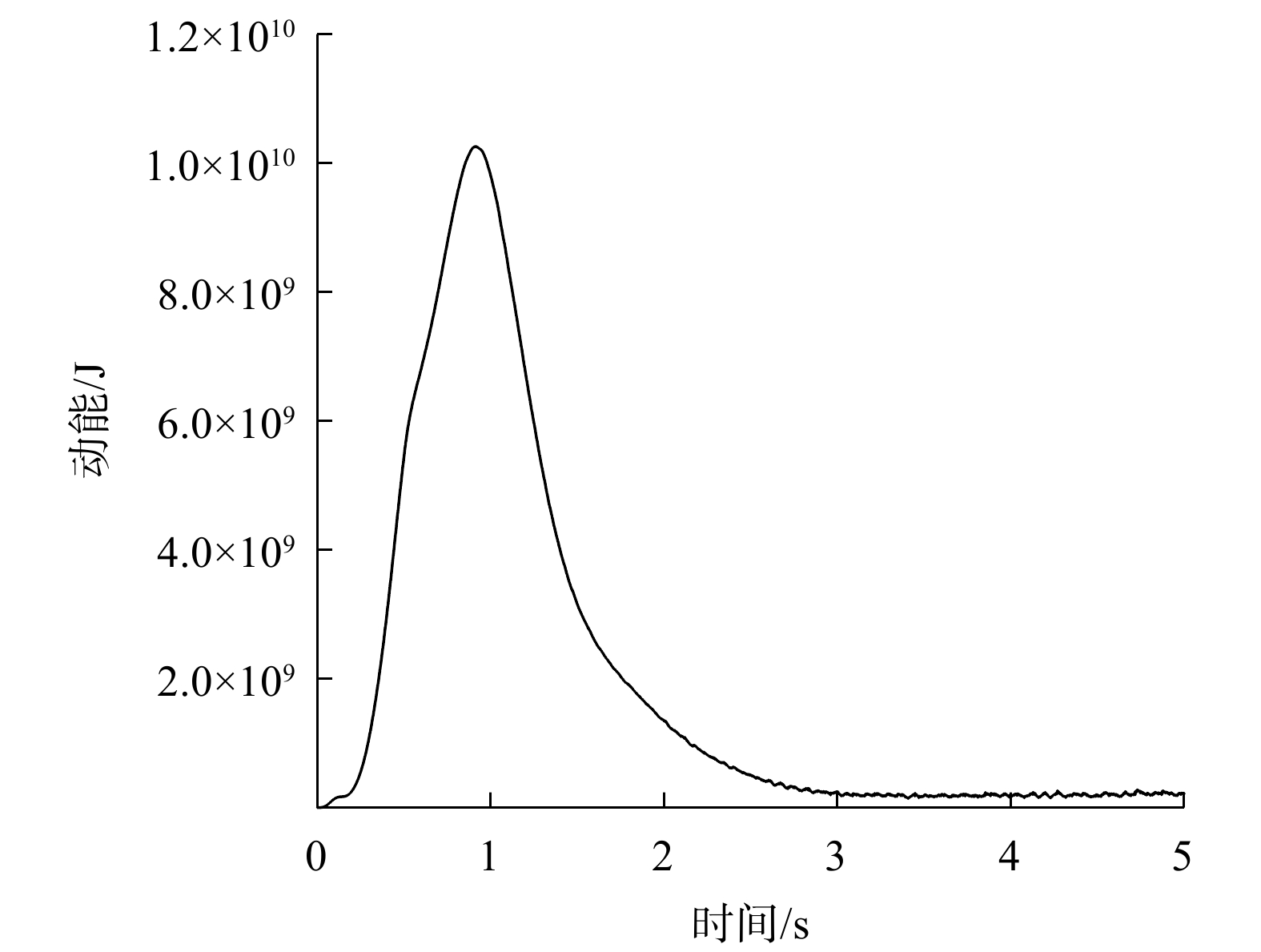
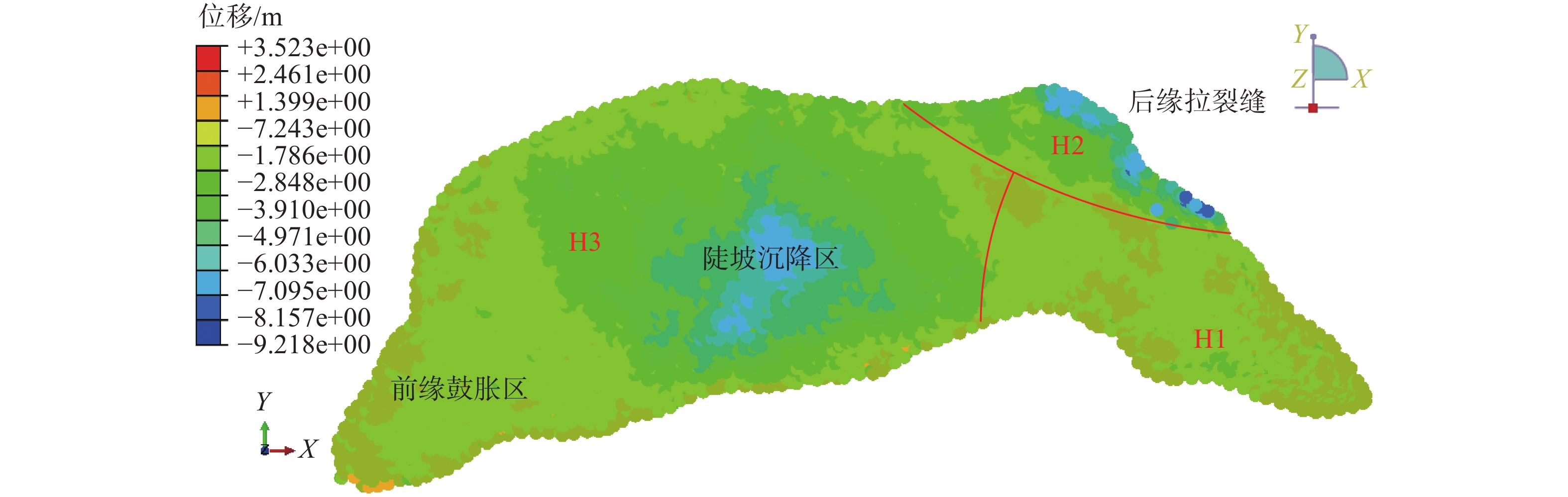
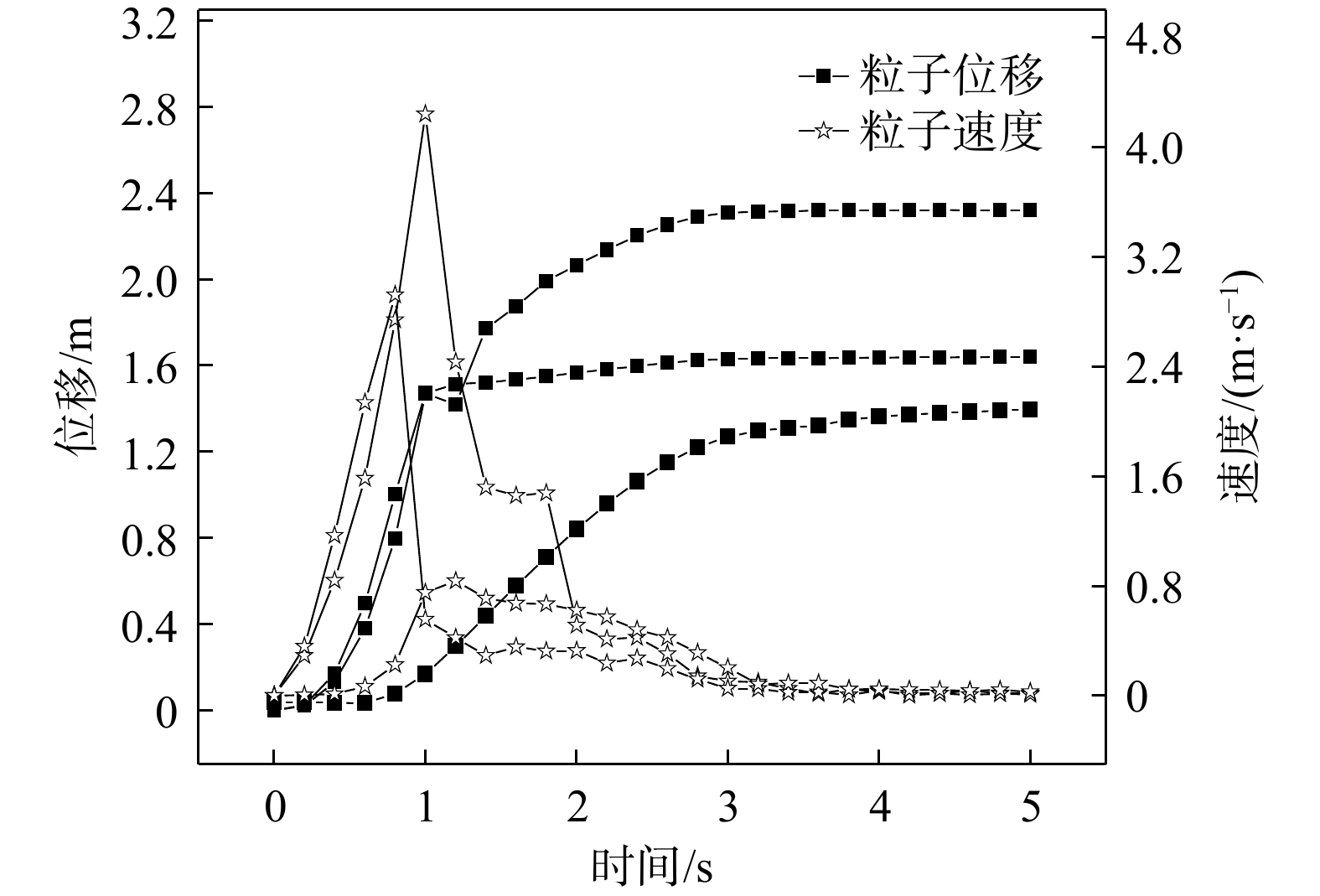
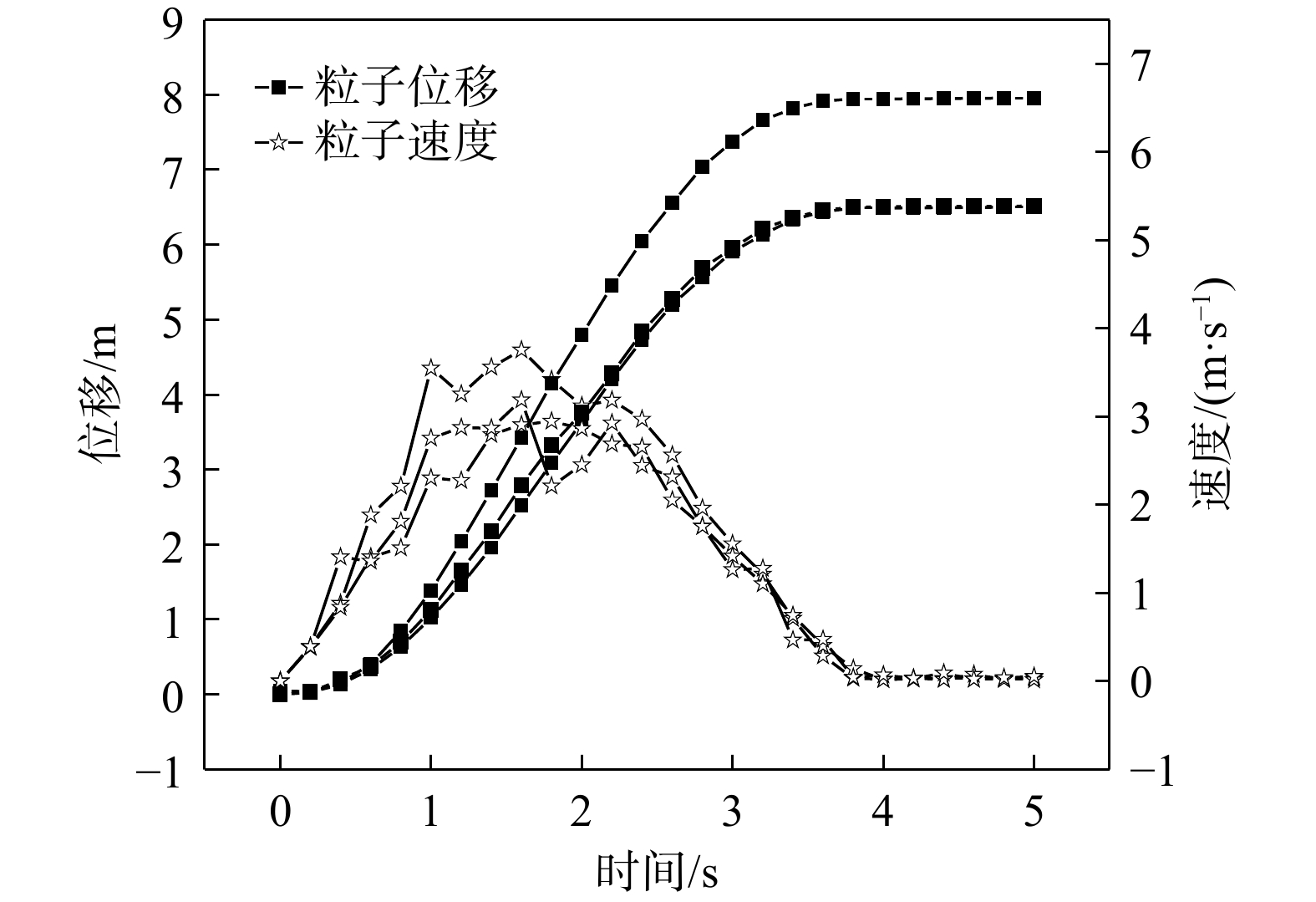
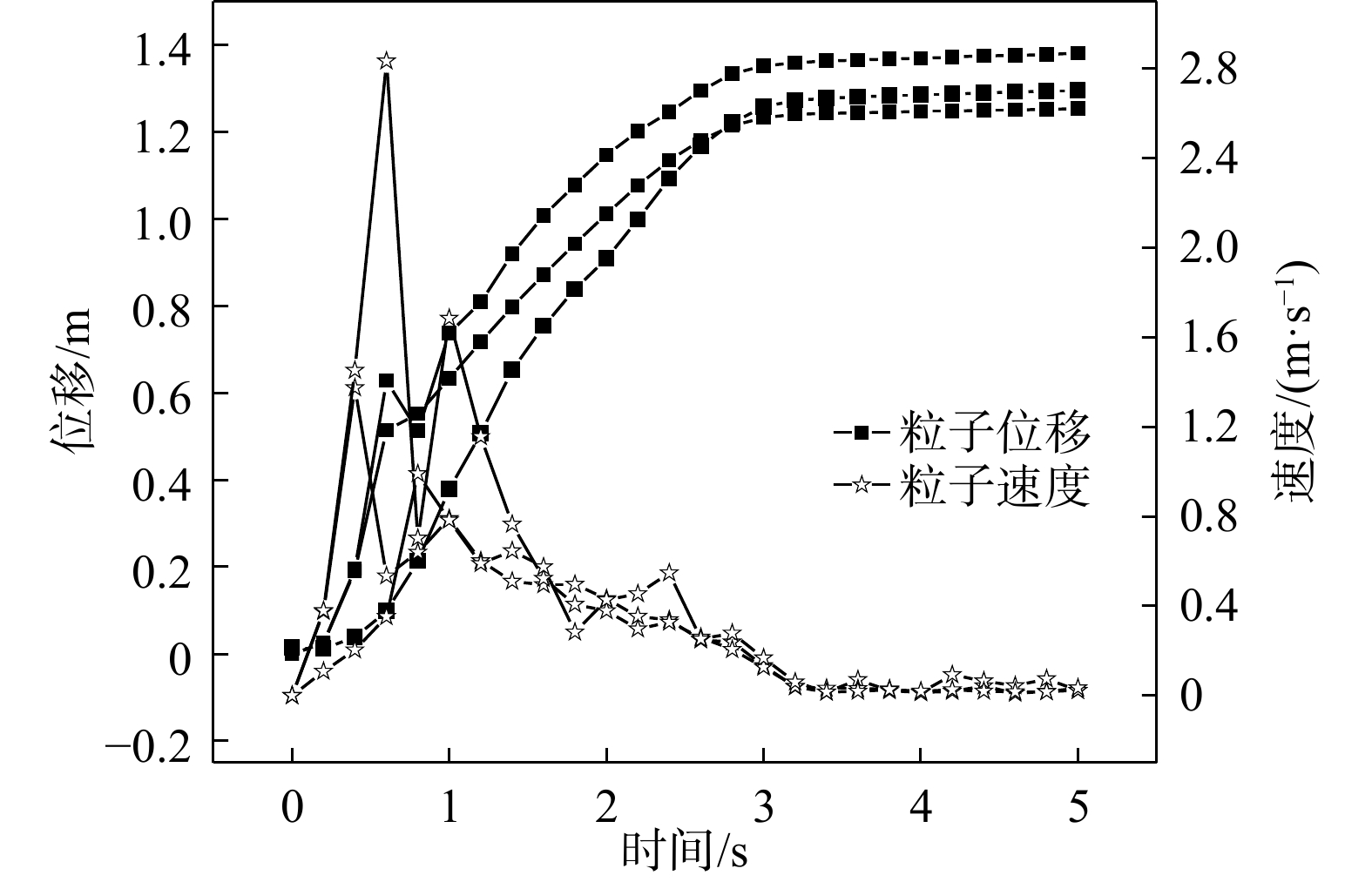
四川甘洛县比依市村受连续强降雨影响下形成滑坡灾害,造成大量财产损失。文章以该滑坡为例,通过工程地质条件探究了比依市村滑坡产生的原因,采用光滑粒子流体动力学(smoothed particle hydrodynamics,SPH)方法对滑坡全过程进行真三维数值模拟,对滑坡关键位置进行位移、速度监测,结果表明:(1)不良地质和长历时、高强度的持续降雨是滑坡的主要诱发因素;(2)SPH方法得到的位移、速度等运动特征参数与实际勘察效果基本一致,具有较好的可靠性;(3)该滑坡是由于滑坡后缘推动滑坡中部导致整体下错,前缘受阻形成鼓胀区,最终破坏模式表现为推移式破坏;(4)比依市村滑坡仍处于蠕变阶段,利用SPH模拟大变形的优势可以为此类灾害的机理研究和工程防治提供新的研究思路。
Abstract:Due to continuous heavy rainfall, landslides were triggered in Biyi Village, Ganluo County, Sichuan Province, resulting in significant property losses. This paper explores the causes of the landslide in Biyi Village by analyzing the local engineering geological conditions, and conducts a true three-dimensional numerical simulations of the entire landslide process using the smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method. Displacement and velocity monitoring were performed at key positions of the landslide. The results indicate that: (1) unfavorable geological conditions and long-duration, high-intensity continuous rainfall were the main triggering factors of the landslide. (2) The SPH method obtained displacement, velocity, and other motion-related parameters that closely aligned with the actual survey results, demonstrating its good reliability and accuracy. (3) The landslide was caused by the sliding of the rear edge of the landslide, pushing the middle part of the landslide, resulting in overall downward movement and blockage at the front edge, ultimately leading to the formation of a bulging zone. The final landslide failure mode was characterized as a translational slide. (4) The Biyi Village landslide is still in the creep stage. Utilizing the capabilities of the SPH method in simulating large deformations opens up new avenues for research in understanding the mechanisms and engineering strategies for the prevention of similar disasters.
-

-
表 1 岩土体参数
Table 1. Rock and soil mass parameters
名称 密度/(kg·m−3) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 滑床 1846 20000 0.25 26 28 滑体 1846 80 0.35 14 18 滑带 - - - 7.51 10.74 -
[1] 郑琅,张欣,王立娟. 四川省甘洛县山体滑坡应急调查与成因机制分析[J]. 人民长江,2022,53(8):117 − 122. [ZHENG Lang,ZHANG Xin,WANG Lijuan. Emergency investigation and formation mechanism of landslide in Ganluo County,Sichuan Province[J]. Yangtze River,2022,53(8):117 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHENG Lang, ZHANG Xin, WANG Lijuan . Emergency investigation and formation mechanism of landslide in Ganluo County, Sichuan Province[J]. Yangtze River,2022 ,53 (8 ):117 −122 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 范刚,聂锐华,陈骎,等. 2020年甘洛县黑西洛沟山洪-滑坡-堰塞湖灾害链成灾机理分析[C]//. 中国水利学会2021学术年会论文集第二分册,2021:291 − 296. [FAN Gang,NIE Ruihua,CHEN Qin,et al. An analysis of the disaster mechanism of the Mountain flood,landslides and barrier Lake disaster chain in Hexiluogou,Ganluo County,in 2020[C]//China water conservancy society 2021 academic conference proceedings of the second volume,2021:291 − 296. (in Chinese)]
FAN Gang, NIE Ruihua, CHEN Qin, et al. An analysis of the disaster mechanism of the Mountain flood, landslides and barrier Lake disaster chain in Hexiluogou, Ganluo County, in 2020[C]//China water conservancy society 2021 academic conference proceedings of the second volume, 2021: 291 − 296. (in Chinese)
[3] ZHOU Jinxing,ZHU Chunyun,ZHENG Jingming,et al. Landslide disaster in the loess area of China[J]. Journal of Forestry Research,2002,13(2):157 − 161. doi: 10.1007/BF02857244
[4] HUANG Da,MENG Qiujie,SONG Yixiang,et al. Dynamic process analysis of the Niumiangou landslide triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake using the finite difference method and a modified discontinuous deformation analysis[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2021,18(4):1034 − 1048. doi: 10.1007/s11629-020-6188-y
[5] LIU Bo, HU Xiewen, HE Kun, et al. The starting mechanism and movement process of the coseismic rockslide:A case study of the Laoyingyan rockslide induced by the “5•12” Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2020,17(5):1188 − 1205.
[6] BERNANDER S,KULLINGSJÖ A,GYLLAND A S,et al. Downhill progressive landslides in long natural slopes:triggering agents and landslide phases modeled with a finite difference method[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2016,53(10):1565 − 1582. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2015-0651
[7] 邹德兵,丁刚,熊瑶,等. 贵州响水水库下汤章滑坡稳定性研究[J]. 水利水电技术,2020,51(增刊1):250 − 255. DOI:10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe. [ZOU Debing,DING Gang,XIONG Yao,et al. Study on the stability of Xiatangzhang landslide in Xiangshui Reservoir,Guizhou Province [J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2020(sup 1):250 − 255. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZOU Debing, DING Gang, XIONG Yao, et al. Study on the stability of Xiatangzhang landslide in Xiangshui Reservoir, Guizhou Province [J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2020(sup 1): 250 − 255. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2020.S1.044
[8] 王伟,王卫,戴雄辉. 四川美姑拉马阿觉滑坡复活特征与影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):9 − 17. [WANG Wei,WANG Wei,DAI Xionghui. Analysis of reactivated characteristics and influencing factors of the Lamajue landslide in Meigu County of Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):9 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Wei, WANG Wei, DAI Xionghui . Analysis of reactivated characteristics and influencing factors of the Lamajue landslide in Meigu County of Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (4 ):9 −17 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 张家勇,邹银先,杨大山. 基于PFC3D的鱼鳅坡滑坡运动过程分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):33 − 39. [ZHANG Jiayong,ZOU Yinxian,YANG Dashan. Analysis of Yuqiupo landslide motion process based on PFC3D[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):33 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Jiayong, ZOU Yinxian, YANG Dashan . Analysis of Yuqiupo landslide motion process based on PFC3D[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (4 ):33 −39 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] 王明辉, 曹熙平, 谯立家. 危岩体精细调查与崩塌过程三维场景模拟——以西南某水电站高边坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(6):86 − 96. [WANG Minghui, CAO Xiping, QIAO Lijia. Comprehensive analysis of hazardous rock mass and simulation of potential rockfall processes using 3D terrain model: A case study of the high cut slope near damsite of a hydropower station in southern China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(6):86 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.01.03
WANG Minghui, CAO Xiping, QIAO Lijia . Comprehensive analysis of hazardous rock mass and simulation of potential rockfall processes using 3D terrain model: A case study of the high cut slope near damsite of a hydropower station in southern China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (6 ):86 −96 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 张龙,唐辉明,熊承仁,等. 鸡尾山高速远程滑坡运动过程PFC3D模拟[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(增刊1):2601 − 2611. [ZHANG Long,TANG Huiming,XIONG Chengren,et al. Movement process simulation of high-speed long-distance Jiweishan landslide with PFC3D[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(Sup 1):2601 − 2611. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Long, TANG Huiming, XIONG Chengren, et al . Movement process simulation of high-speed long-distance Jiweishan landslide with PFC3D[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012 ,31 (Sup 1 ):2601 −2611 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 丛凯, 魏洁, 杨亚兵, 等. 基于坡表变形分析与降雨响应模拟的立节北山滑坡运动特征[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):54 − 65. [CONG Kai, WEI Jie, YANG Yabing, et al. Investigation of the kinematic characteristic of Lijie Beishan landslide through surface displacement monitoring and rainfall response numerical simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):54 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CONG Kai, WEI Jie, YANG Yabing, et al . Investigation of the kinematic characteristic of Lijie Beishan landslide through surface displacement monitoring and rainfall response numerical simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022 ,41 (6 ):54 −65 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 廖德武, 郑冰, 杜艳松, 等. 兴仁“6•10” 彭家洞高速滑坡运动特征与形成机理[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):66 − 76. [LIAO Dewu, ZHENG Bing, DU Yansong, et al. Movement characteristics and formation mechanism of the “6•10” Pengjiadong high speed landslide in Xingren[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):66 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIAO Dewu, ZHENG Bing, DU Yansong, et al . Movement characteristics and formation mechanism of the “6•10” Pengjiadong high speed landslide in Xingren[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022 ,41 (6 ):66 −76 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 张巍,史卜涛,施斌,等. 土质滑坡运动全过程物质点法模拟及其应用[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(3):815 − 823. [ZHANG Wei,SHI Butao,SHI Bin,et al. Material point method for Run-out process simulation of soil landslides and application[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(3):815 − 823. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.03.029
ZHANG Wei, SHI Butao, SHI Bin, et al . Material point method for Run-out process simulation of soil landslides and application[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017 ,25 (3 ):815 −823 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[15] 王升,曾鹏,李天斌,等. 土质滑坡失稳、运动及冲击压力物质点法模拟研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(4):1362 − 1370. [WANG Sheng,ZENG Peng,LI Tianbin,et al. Initiation,movement and impact simulation of soil land-slide with material point method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(4):1362 − 1370. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Sheng, ZENG Peng, LI Tianbin, et al . Initiation, movement and impact simulation of soil land-slide with material point method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022 ,30 (4 ):1362 −1370 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 胡嫚,谢谟文,王立伟. 基于弹塑性土体本构模型的滑坡运动过程SPH模拟[J]. 岩土工程学报,2016,38(1):58 − 67. [HU Man,XIE Mowen,WANG Liwei. SPH simulations of post-failure flow of landslides using elastic-plastic soil constitutive model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2016,38(1):58 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11779/CJGE201601005
HU Man, XIE Mowen, WANG Liwei . SPH simulations of post-failure flow of landslides using elastic-plastic soil constitutive model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2016 ,38 (1 ):58 −67 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] DAI Zili. 3D numerical modeling using smoothed particle hydrodynamics of flow-like landslide propagation triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,180:21 − 33. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.03.018
[18] HUANG Yu,ZHANG Weijie,XU Qiang,et al. Run-out analysis of flow-like landslides triggered by the Ms 8.0 2008 Wenchuan earthquake using smoothed particle hydrodynamics[J]. Landslides,2012,9(2):275 − 283. doi: 10.1007/s10346-011-0285-5
[19] PRAVEEN KUMAR R,DODAGOUDAR G R. Meshfree analysis of two-dimensional contaminant transport through unsaturated porous media using EFGM[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering,2010,26(12):1797 − 1816. doi: 10.1002/cnm.1266
[20] GOODIN C, PRIDDY J D. Comparison of SPH simulations and cone index tests for cohesive soils[J]. Journal of Terramechanics,2016,66:49 − 57.
[21] LIANG Dongfang,HE Xuzhen. A comparison of conventional and shear-rate dependent Mohr-Coulomb models for simulating landslides[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2014,11(6):1478 − 1490. doi: 10.1007/s11629-014-3041-1
[22] BUI H H, SAKO K, FUKAGAWA R. Numerical simulation of soil–water interaction using smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method[J]. Journal of Terramechanics,2007,44(5):339 − 346. doi: 10.1016/j.jterra.2007.10.003
[23] GUO W B,SUN Z W,WANG C S. Slope stability numerical calculation using geotechnical strength yield criterion and sph instability criterion analysis method. Fresenius environmental bulletin. 2020,29(7A):5739 − 5745.
[24] WANG Haibin, YAN Fei, ZHANG Liwei, et al. Mechanism and flow process of debris avalanche in mining waste dump based on improved SPH simulation[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis,2022,138:106345.
[25] FÁVERO NETO A H,ASKARINEJAD A,SPRINGMAN S M,et al. Simulation of debris flow on an instrumented test slope using an updated Lagrangian continuum particle method[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2020,15(10):2757 − 2777. doi: 10.1007/s11440-020-00957-1
[26] DAI Zili, HUANG Yu, CHENG Hualin, et al. 3D numerical modeling using smoothed particle hydrodynamics of flow-like landslide propagation triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,180:21 − 33.
[27] 费康,张建伟. ABAQUS在岩土工程中的应用[M]. 北京:中国水利水电出版社,2010. [FEI Kang,ZHANG Jianwei. Application of ABAQUS in geotechnical engineering[M]. Beijing:China Water & Power Press,2010. (in Chinese)]
FEI Kang, ZHANG Jianwei. Application of ABAQUS in geotechnical engineering[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2010. (in Chinese) -




 下载:
下载: