Landslide assessment considering spatial calibration zoning of physical and mechanical parameters of rock and soil mass
-
摘要:
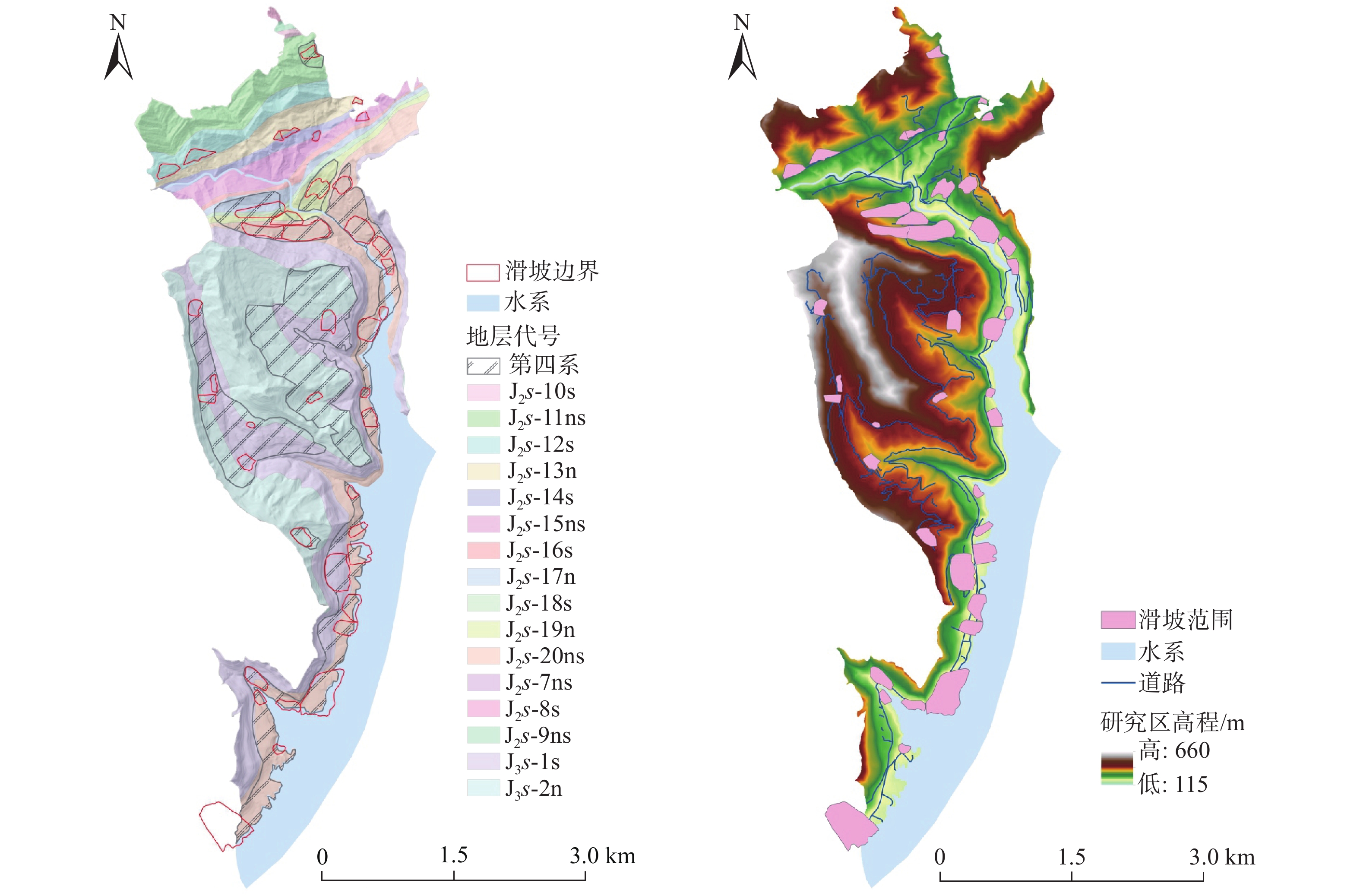
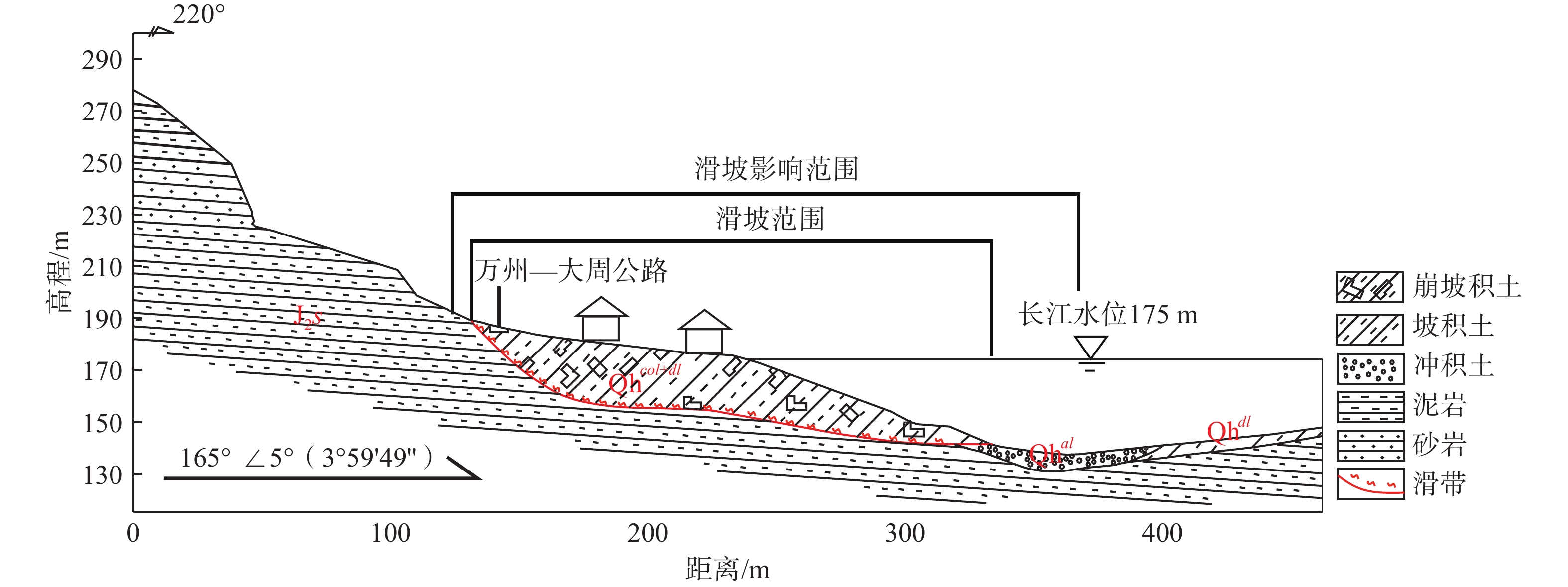
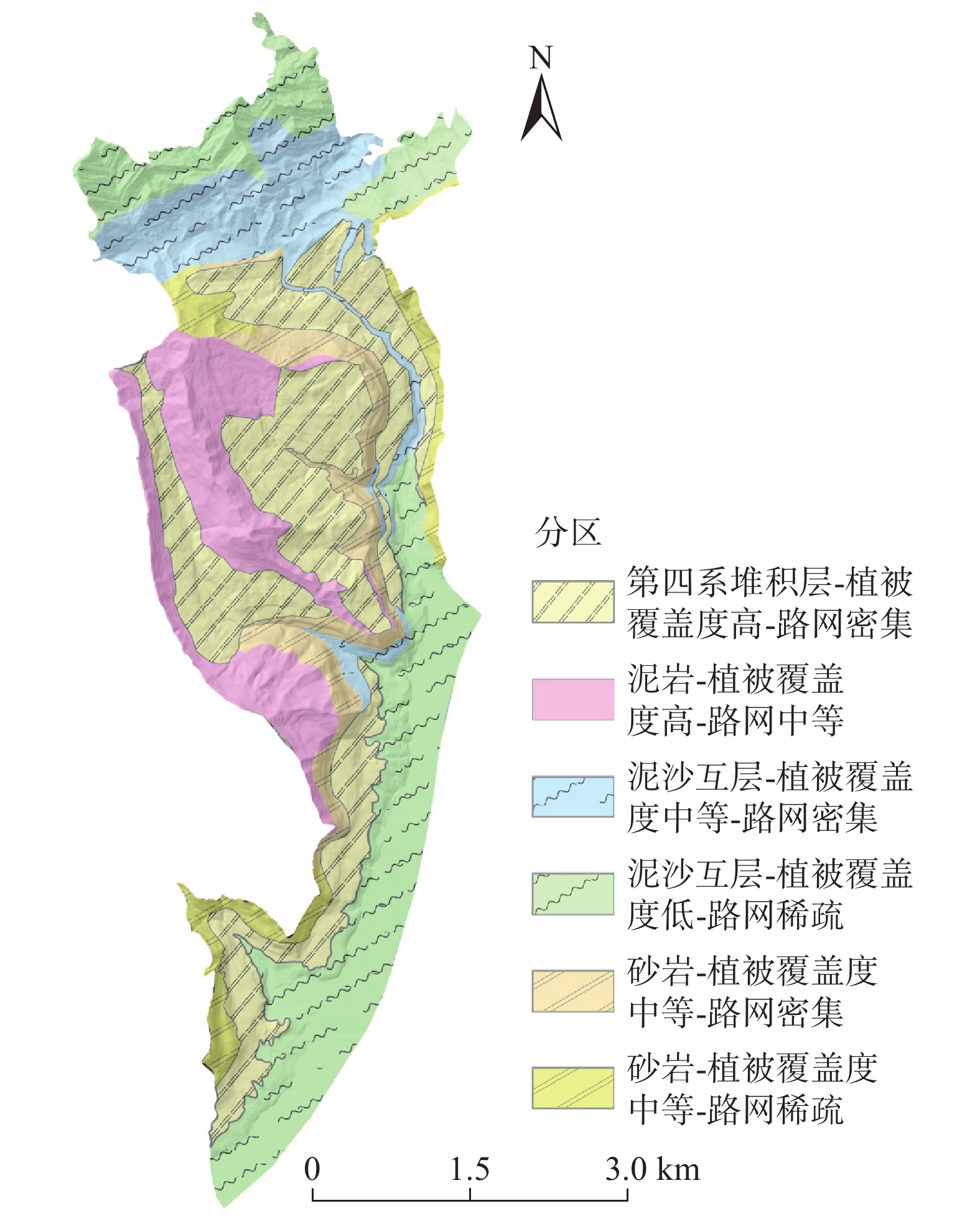
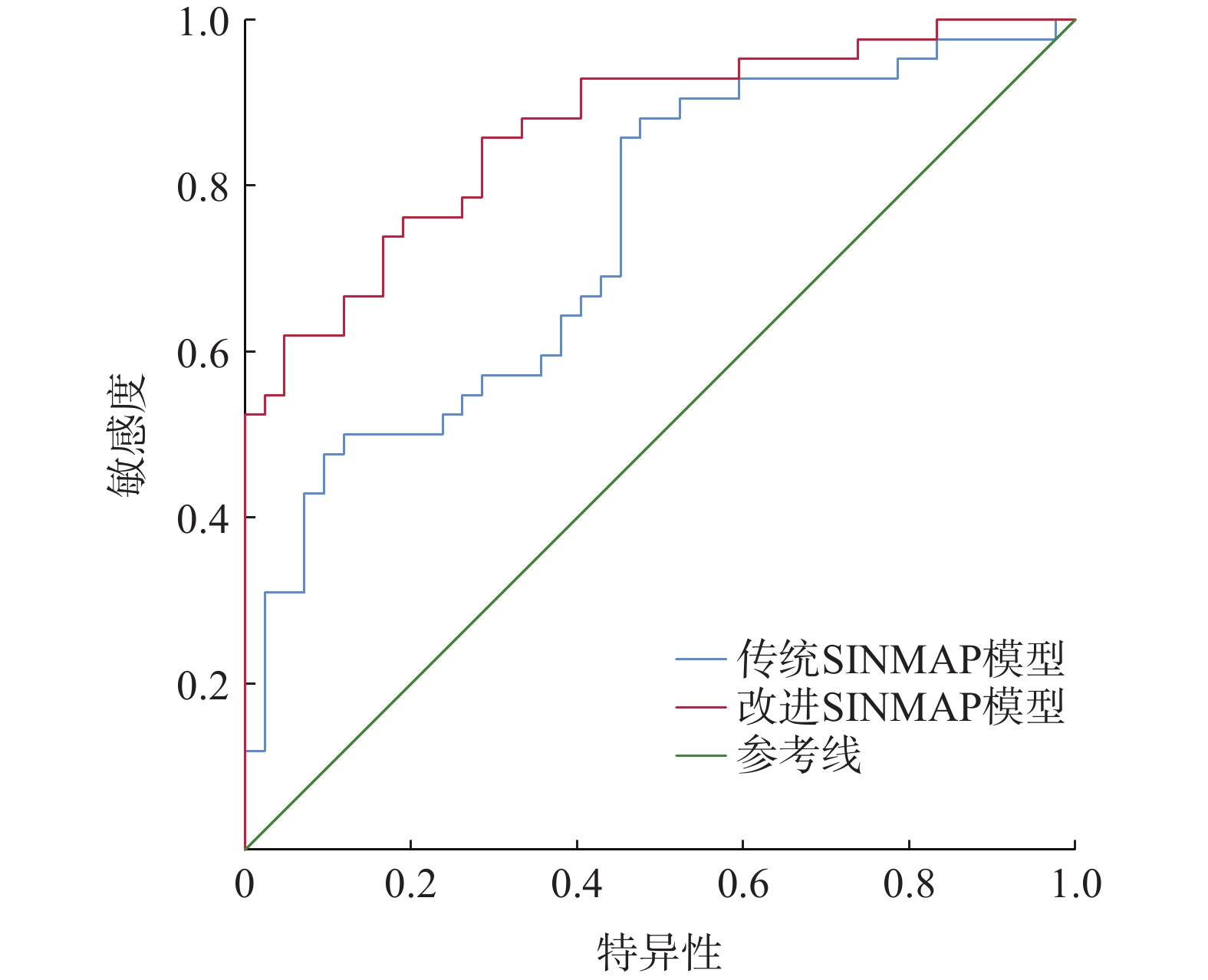
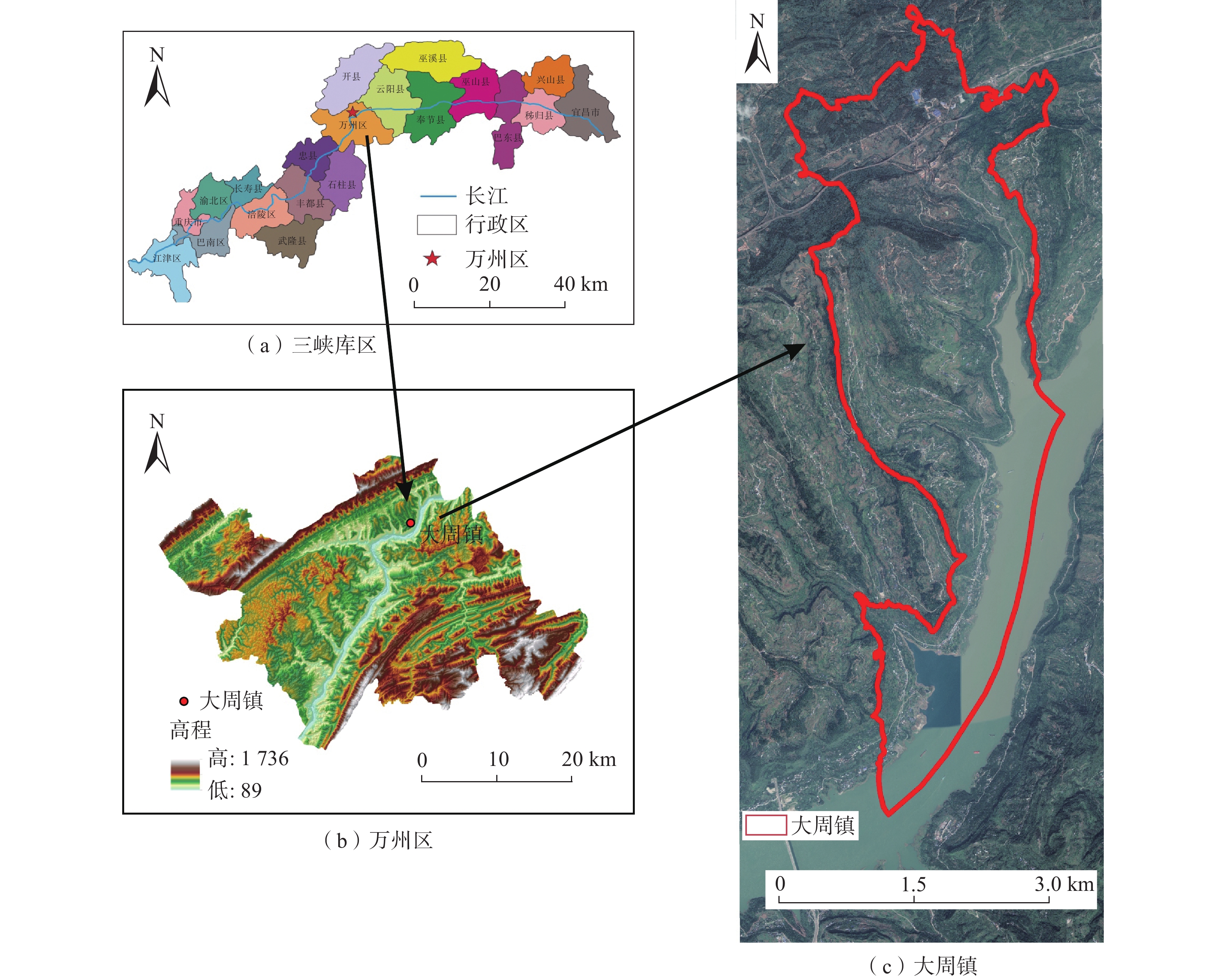
滑坡危险性评价是区域滑坡灾害风险预警与管控的关键环节之一。分布式斜坡稳定性定量评估模型(stability index mapping,SINMAP)因能有效反映边坡稳定性的物理力学机制,广泛用于滑坡危险性评价中。但传统SINMAP模型忽略了岩土体特征随地质环境变化而产生的空间差异性,导致评价结果精确度偏低。针对上述不足,文章开展了基于不同空间校准区域的改进SINMAP模型研究。以重庆市万州区大周镇为例,经频率比和敏感性指数分析,从反映滑坡成因的8个指标因子中确定岩土体类型、植被覆盖度和距道路距离作为关键指标因子。根据关键指标因子的空间分布差异,将研究区划分为6个不同空间校准区域,赋予对应岩土体物理力学参数,开展传统SINMAP及其改进模型的滑坡危险性评价对比研究。结果表明:(1)总体上,两种模型预测的高和极高滑坡危险区主要分布在研究区库岸、河流两侧以及工程活动强烈的区域;(2)最危险工况下,改进SINMAP模型的AUC值为86.8%,高于传统SINMAP模型的AUC值(73.9%),识别准确度提高了12.9%;(3)在滑坡灾害局部计算结果上,最危险工况下有81.82%的真实滑坡点落入中危险等级以上的区域,大于传统SINMAP模型的72.73%。因而,改进SINMAP模型具备识别效果更佳,识别结果空间分布较连续,计算结果更符合真实滑坡实际发育特征的优势。
Abstract:Landslide hazard assessment is a crucial component of regional landslide disaster risk warning and control. The distributed slope stability quantitative evaluation model SINMAP (stability index mapping) is widely used in landslide hazard assessment because it effectively mirrors the physical and mechanical mechanisms underlying slope stability. However, traditional SINMAP models overlook the spatial differences in rock and soil characteristics due to geological environmental changes, resulting in low accuracy in assessment results. To address these deficiencies, this paper explored an enhanced SINMAP model tailored to various spatial calibration zones.Using Dazhou Town, Wanzhou District, Chongqing as a case study and employing frequency ratio and sensitivity index analysis, the key indicator factors are determined as rock and soil type, vegetation coverage, and proximity to roads from the eight indicator factors reflecting the cause of landslides. Based on the spatial distribution differences of key indicators, the study area was segmented into 6 different spatial calibration zones, and each assigned corresponding physical and mechanical parameters of the rock and soil. A comparative study of landslide hazard assessment using both traditional SINMAP and its improved models was conducted. The results indicate that: (1) Overall, the high and extremely high-risk landslide zones predicted by the two models are mainly distributed along the reservoir bank, adjacent to the river, and areas with strong engineering activities in the study area. (2) Under the most dangerous working conditions, the improved SINMAP model achieved an AUC value of 86.8%, surpassing the traditional model’s AUC of 73.9%, and enhancing the accuracy of landslide recognition by 12.9%. (3) In the local calculation results of landslide disasters, 81.82% of the actual landslide points were in areas above the medium risk level under the most dangerous working conditions, compared to 72.73% in the traditional SINMAP model. Therefore, the improved SINMAP model offers superior detection capabilities, a more continuous spatial distribution of detection results, and more accurate alignment with the real-world characteristics of landslide development.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- hazard assessment /
- frequency ratio /
- SINMAP model /
- geo-harzard
-

-
表 1 滑坡危险性分区表
Table 1. Landslide hazard zoning table
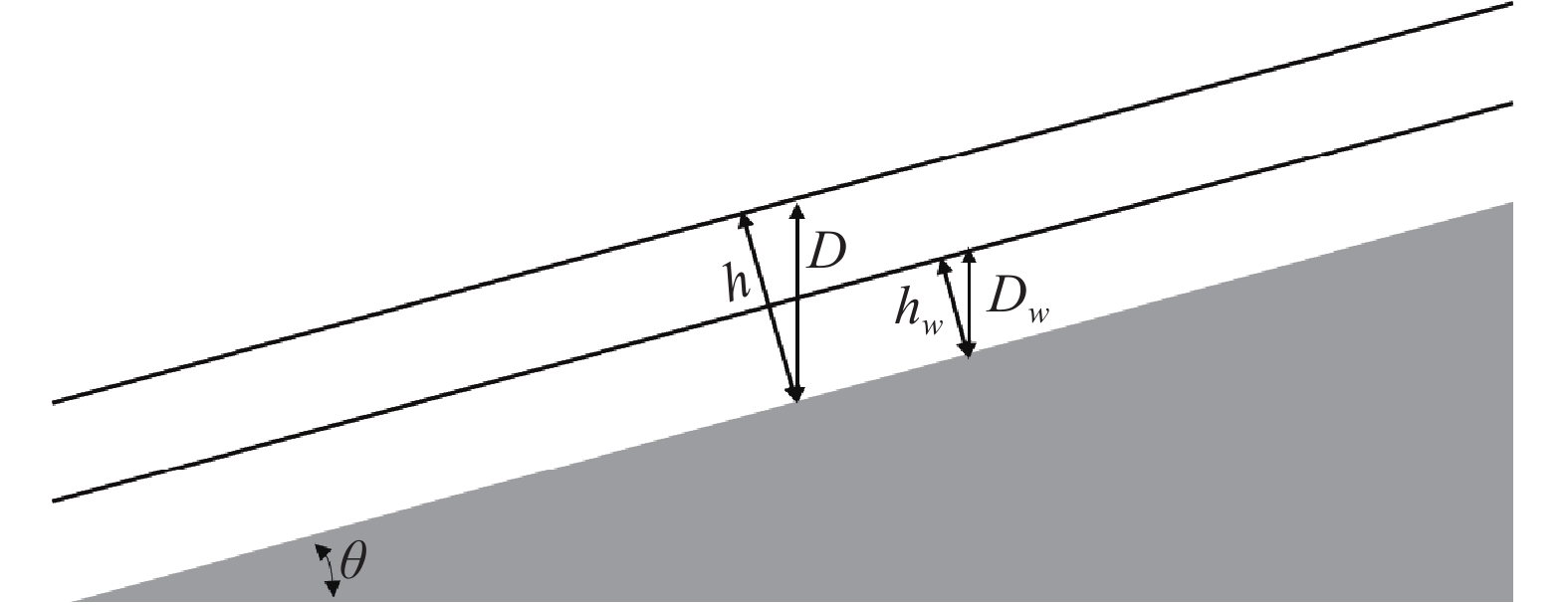
条件 类别 预测状态 SI≥1.5 1 极稳定区 1.5>SI≥1.25 2 稳定区 1.25>SI≥1.0 3 基本稳定区 1.0>SI≥0.5 4 潜在不稳定区 0.5>SI≥0 5 不稳定区 表 2 4种降雨工况下的降雨量值和T/R的上下限
Table 2. Rainfall values and upper and lower limits of T/R under four rainfall conditions
类别 降雨工况 降雨量值
/mm模型参数T/R 下限 上限 1 多年平均单日最大降雨量 91 1836 3000 2 20年一遇单日最大降雨量 161 1038 3000 3 50年一遇单日最大降雨量 188 889 3000 4 100年一遇单日最大降雨量 208 803 3000 表 3 传统SINMAP模型计算参数
Table 3. Calculation parameters of traditional SINMAP model
g
/(m·s−2)湿度/% 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 岩土体密度
/(kg·m−3)下限 上限 下限 上限 9.8 10 5 25 10 25 1900 表 4 传统SINMAP模型4种工况下滑坡灾害危险分区统计表
Table 4. Traditional SINMAP model landslide hazard zoning statistical table under four working conditions
工况 危险性分级 滑坡数
/个各危险等级
面积/m2占总滑坡
比例/%占总面积
比例/%工况一 低危险区 25 15 235 400 56.82 62.57 高危险区 3 1 145 600 6.82 4.70 中危险区 16 7 671 880 36.36 31.51 极高危险区 0 297 200 0.00 1.22 工况二 低危险区 16 9 764 400 36.36 40.10 中危险区 22 12 463 400 50.00 51.18 高危险区 6 1 825 100 13.64 7.50 极高危险区 0 297 200 0.00 1.22 工况三 低危险区 11 7 047 230 25.00 28.94 中危险区 17 9 985 030 38.64 41.00 高危险区 13 5 878 900 29.55 24.14 极高危险区 3 1 438 930 6.82 5.91 工况四 低危险区 9 7 047 230 20.45 28.94 中危险区 16 9 724 080 36.36 39.93 高危险区 13 4 685 400 29.55 19.24 极高危险区 6 2 893 380 13.64 11.88 表 5 各因子频率比及敏感性指数值
Table 5. Frequency ratios and sensitivity index values of each factor
指标因子 $ {{E}}_{{i}} $ 分级 滑坡数/个 FR 坡度/(°) 1.503 245 0~10 9 − 0.139740 10~15 11 0.503245 15~20 6 0.157018 20~25 7 0.407057 25~30 4 − 0.118700 30~35 5 0.145126 35~50 2 − 0.768240 50~75 0 −1 高程/m 1.211 059 115~215 19 0.501409 215~315 12 0.293254 315~415 6 − 0.441150 415~515 5 − 0.345820 515~660 2 − 0.709650 斜坡形态 0.471677 凹形坡 24 0.255 287 直线形 4 − 0.091880 凸形坡 16 − 0.216390 地形湿度指数 2.034 442 0~3.38 2 − 0.829100 3.38~4.62 8 − 0.244240 4.62~5.77 12 0.011489 5.77~7.00 12 0.887885 7.00~8.42 7 1.034442 8.42~10.18 1 −1 10.18~12.92 0 −1 12.92~23.08 1 0.198803 距水系距离/m 1.467 326 >200 19 −0.132430 <100 12 1.234746 100~200 14 − 0.232580 植被覆盖度 3.026 948 0~0.05 0 −1 0.05~0.1 1 − 0.263940 0.1~0.15 2 − 0.165240 0.15~0.2 2 − 0.307280 0.2~0.25 5 0.341520 0.25~0.3 13 2.026948 0.3~0.35 1 − 0.812460 0.35~0.4 5 − 0.240920 0.4~0.45 8 0.624582 0.45~0.54 1 − 0.419160 岩土体类型 3.151 116 第四系堆积层 32 2.366056 硬岩岩组 5 − 0.510910 软岩岩组 3 − 0.748480 软硬互层 4 − 0.785060 斜坡结构 1.191 694 顺向坡 9 0.988524 逆向坡 4 − 0.095070 斜交坡 25 − 0.203170 水平坡 6 0.743289 距道路距离/m 2.492 95 0~50 22 0.727403 50~100 9 1.631703 100~150 2 − 0.640560 150~200 7 0.437250 200~250 3 − 0.091470 表 6 改进SINMAP模型计算参数
Table 6. Improved SINMAP model calculation parameters
校准区域 g/(m·s−2) 含水率
/%c/kPa $ \varphi $ /(°)ρ/(kg·m−3) 下限 上限 下限 上限 ①第四系堆积层-
高植被覆盖度-
路网分布密集9.79 10 10 20 16 28 1990 ②泥岩-高植被
覆盖度-路网
分布中等9.79 10 14 22 22 30 2190 ③泥砂互层-
中等植被覆盖度-
路网分布密集9.79 10 15 24 15 30 2280 ④泥砂互层-
低植被覆盖度-
路网分布稀疏9.79 10 15 26 15 40 2280 ⑤砂岩-中等
植被覆盖度-
路网分布密集9.79 10 18 30 26 30 2460 ⑥砂岩-中等
植被覆盖度-
路网分布稀疏9.79 10 18 35 26 35 2460 表 7 改进SINMAP模型4种工况下滑坡灾害危险分区统计表
Table 7. Improved SINMAP model landslide hazard zoning statistical table under four working conditions
工况 危险性分级 滑坡数
/个各危险等级
面积/m2占总滑坡
比例/%占总面积
比例/%工况一 低危险区 14 13 078 258 31.82 53.71 高危险区 21 10 039 697 47.73 41.23 中危险区 3 1 142 031 6.82 4.69 极高危险区 1 90 843 2.27 0.37 工况二 低危险区 11 8 676 595 25.00 35.63 中危险区 23 13 428 910 52.27 55.15 高危险区 9 1 940 453 20.45 7.97 极高危险区 1 304 871 2.27 1.25 工况三 低危险区 6 6 139 994 13.64 25.21 中危险区 22 11 401 591 50.00 46.82 高危险区 12 5 628 730 27.27 23.12 极高危险区 4 1 180 514 9.09 4.85 工况四 低危险区 4 5 579 180 9.09 22.91 中危险区 21 9 941 706 47.73 40.83 高危险区 10 6 363 600 22.73 26.13 极高危险区 9 2 466 343 20.45 10.13 -
[1] 阳清青,余秋兵,张廷斌,等. 基于GDIV模型的大渡河中游地区滑坡危险性评价与区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(5):130 − 140. [YANG Qingqing,YU Qiubing,ZHANG Tingbin,et al. Landslide hazard assessment in the middle reach area of the Dadu River based on the GDIV model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(5):130 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Qingqing, YU Qiubing, ZHANG Tingbin, et al. Landslide hazard assessment in the middle reach area of the Dadu River based on the GDIV model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(5): 130 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] HUANG Ziyan,PENG Li,LI Sainan,et al. GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping in the Longmen Mountain area (China) using three different machine learning algorithms and their comparison[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2023,30(38):88612 − 88626. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-28730-3
[3] 曲雪妍,李媛,房浩,等. 基于时空维度耦合的地质灾害发育程度评价研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(1):137 − 145. [QU Xueyan,LI Yuan,FANG Hao,et al. A study of the evaluation of geo-hazards development degree based on time-space coupling[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(1):137 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
QU Xueyan, LI Yuan, FANG Hao, et al. A study of the evaluation of geo-hazards development degree based on time-space coupling[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(1): 137 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 周苏华,付宇航,邢静康,等. 基于不同统计模型的肯尼亚滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(4):114 − 124. [ZHOU Suhua,FU Yuhang,XING Jingkang,et al. Assessment of landslide hazard risk in Kenya based on different statistical models[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(4):114 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHOU Suhua, FU Yuhang, XING Jingkang, et al. Assessment of landslide hazard risk in Kenya based on different statistical models[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(4): 114 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] GAUTAM P,KUBOTA T,SAPKOTA L M,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping with GIS in high mountain area of Nepal:A comparison of four methods[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2021,80(9):359. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09650-2
[6] 李星,杨赛,李远耀,等. 面向区域滑坡易发性精细化评价的改进斜坡单元法[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(3):81 − 92. [LI Xing,YANG Sai,LI Yuanyao,et al. An improved slope element method for fine-grained evaluation of regional landslide susceptibility[J] Geological Science and Technology Bulletin,2023,42 (3):81 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Xing, YANG Sai, LI Yuanyao, et al. An improved slope element method for fine-grained evaluation of regional landslide susceptibility[J] Geological Science and Technology Bulletin, 2023, 42 (3): 81 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 谢家龙,李远耀,王宁涛,等. 考虑库水位及降雨联合作用的云阳县区域滑坡危险性评价[J]. 长江科学院院报,2021,38(12):72 − 81. [XIE Jialong,LI Yuanyao,WANG Ningtao,et al. Assessment of regional landslide hazard in Yunyang County consi-dering the combined effect of reservoir water level and rainfall[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2021,38(12):72 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200815
XIE Jialong, LI Yuanyao, WANG Ningtao, et al. Assessment of regional landslide hazard in Yunyang County consi-dering the combined effect of reservoir water level and rainfall[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2021, 38(12): 72 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200815
[8] TIEN BUI D,TUAN T A,KLEMPE H,et al. Spatial prediction models for shallow landslide hazards:A comparative assessment of the efficacy of support vector machines,artificial neural networks,kernel logistic regression,and logistic model tree[J]. Landslides,2016,13(2):361 − 378. doi: 10.1007/s10346-015-0557-6
[9] 石爱红,李国庆,丁德民,等. 考虑非饱和土基质吸力的丁家坡滑坡变形机制及稳定性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):141 − 151. [SHI Aihong,LI Guoqing,DING Demin,et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Dingjiapo landslide considering the matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):141 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHI Aihong, LI Guoqing, DING Demin, et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Dingjiapo landslide considering the matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 141 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 高波,王晓勇. 基于SINMAP模型的延安市滑坡危险性区划[J]. 水土保持通报,2019,39(3):211 − 216. [GAO Bo,WANG Xiaoyong. Risk zoning of landslide based on SINMAP model in Yan’an City[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,39(3):211 − 216. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GAO Bo, WANG Xiaoyong. Risk zoning of landslide based on SINMAP model in Yan’an City[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(3): 211 − 216. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李艳杰,唐亚明,邓亚虹,等. 降雨型浅层黄土滑坡危险性评价与区划——以山西柳林县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):105 − 114. [LI Yanjie,TANG Yaming,DENG Yahong,et al. Hazard assessment of shallow loess landslides induced by rainfall:A case study of Liulin County of Shanxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):105 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Yanjie, TANG Yaming, DENG Yahong, et al. Hazard assessment of shallow loess landslides induced by rainfall: A case study of Liulin County of Shanxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 105 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] HE Jianyin,QIU Haijun,QU Feihang,et al. Prediction of spatiotemporal stability and rainfall threshold of shallow landslides using the TRIGRS and Scoops3D models[J]. Catena,2021,197:104999. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104999
[13] 郭子正,何俊,黄达,等. 降雨诱发浅层滑坡危险性的快速评估模型及应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(5):1188 − 1201. [GUO Zizheng,HE Jun,HUANG Da,et al. Fast assessment model for rainfall-induced shallow landslide hazard and application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023,42(5):1188 − 1201. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Zizheng, HE Jun, HUANG Da, et al. Fast assessment model for rainfall-induced shallow landslide hazard and application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(5): 1188 − 1201. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李婧,卢玲,唐泽. 基于TRIGRS模型的区域降雨型浅层滑坡危险性评价[J]. 甘肃水利水电技术,2022,58(1):24 − 27. [LI Jing,LU Ling,TANG Ze. Risk assessment of regional rainfall induced shallow landslides based on TRIGRS model[J] Gansu Water Resources and Hydropower Technology,2022,58 (1):24 − 27 (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Jing, LU Ling, TANG Ze. Risk assessment of regional rainfall induced shallow landslides based on TRIGRS model[J] Gansu Water Resources and Hydropower Technology, 2022, 58 (1): 24 − 27 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] TAYLOR D W. Fundamentals of soil mechanics[J]. Soil Science,66(2):161.
[16] MONTGOMERY D R,DIETRICH W E. A physically based model for the topographic control on shallow landsliding[J]. Water Resources Research,1994,30(4):1153 − 1171. doi: 10.1029/93WR02979
[17] PACK R T, TARBOTON D G, GOODWIN C N. The SINMAP approach to terrain stability mapping[J]. Congress of the International Association of Engineering Geology, 1998: 21 − 25.
[18] NERY T D,VIEIRA B C. Susceptibility to shallow landslides in a drainage basin in the Serra do Mar,São Paulo,Brazil,predicted using the SINMAP mathematical model[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2015,74(2):369 − 378. doi: 10.1007/s10064-014-0622-8
[19] LIN Wei,YIN Kunlong,WANG Ningtao,et al. Landslide hazard assessment of rainfall-induced landslide based on the CF-SINMAP model:A case study from Wuling Mountain in Hunan Province,China[J]. Natural Hazards,2021,106(1):679 − 700. doi: 10.1007/s11069-020-04483-x
[20] 武利. 基于SINMAP模型的区域滑坡危险性定量评估及模型验证[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2012,28(2):35 − 39. [WU Li. A SINMAP-based quantitative assessment and model verification of regional landslide hazard[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science,2012,28(2):35 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WU Li. A SINMAP-based quantitative assessment and model verification of regional landslide hazard[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2012, 28(2): 35 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 刘凡,邓亚虹,慕焕东,等. 基于最大熵-无限边坡模型的降雨诱发浅层黄土滑坡稳定性评价方法研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023:1 − 13. [LIU Fan,DENG Yahong,MU Huandong,et al. Research on the stability evaluation method of shallow loess landslides induced by rainfall based on the maximum entropy infinite slope model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023:1 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Fan, DENG Yahong, MU Huandong, et al. Research on the stability evaluation method of shallow loess landslides induced by rainfall based on the maximum entropy infinite slope model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023: 1 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 汪莹. 不同模型的滑坡易发性评价精度讨论[J]. 贵州地质,2022,39(2):144 − 151. [WANG Ying. Discussion on the accuracy of landslide susceptibility evaluation of different models[J]. Guizhou Geology,2022,39(2):144 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2022.02.007
WANG Ying. Discussion on the accuracy of landslide susceptibility evaluation of different models[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2022, 39(2): 144 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2022.02.007
[23] 郭子正,殷坤龙,黄发明,等. 基于滑坡分类和加权频率比模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(2):287 − 300. [GUO Zizheng,YIN Kunlong,HUANG Faming,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(2):287 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Zizheng, YIN Kunlong, HUANG Faming, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(2): 287 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 王志恒,胡卓玮,赵文吉,等. 基于确定性系数概率模型的降雨型滑坡孕灾环境因子敏感性分析——以四川省低山丘陵区为例[J]. 灾害学,2014,29(2):109 − 115. [WANG Zhiheng,HU Zhuowei,ZHAO Wenji,et al. Susceptibility analysis of precipitation-induced landslide disaster-pregnant environmental factors based on the certainty factor probability model:Taking the hilly area in Sichuan as example[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2014,29(2):109 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Zhiheng, HU Zhuowei, ZHAO Wenji, et al. Susceptibility analysis of precipitation-induced landslide disaster-pregnant environmental factors based on the certainty factor probability model: Taking the hilly area in Sichuan as example[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2014, 29(2): 109 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 邵山,汤明高,聂兵其,等. 宣汉地区降雨型滑坡空间发育规律及敏感性分析[J]. 长江科学院院报,2018,35(5):41 − 46. [SHAO Shan,TANG Minggao,NIE Bingqi,et al. Spatial development law and sensitivity analysis of rainfall-induced landslide in Xuanhan County[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2018,35(5):41 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20170418
SHAO Shan, TANG Minggao, NIE Bingqi, et al. Spatial development law and sensitivity analysis of rainfall-induced landslide in Xuanhan County[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2018, 35(5): 41 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20170418
[26] 刘文,余天彬,王猛,等. 四川宜宾市地质灾害隐患与地层岩性-地质构造关系分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(3):118 − 126. [LIU Wen,YU Tianbin,WANG Meng,et al. Analysis on the relationship between geological hazard and lithology,geological structure in Yibin City of Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(3):118 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Wen, YU Tianbin, WANG Meng, et al. Analysis on the relationship between geological hazard and lithology, geological structure in Yibin City of Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(3): 118 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 豆红强,简文彬,王浩,等. 高植被覆盖区台风暴雨型滑坡成灾机制及预警模型研究综述[J]. 自然灾害学报,2023,32(2):1 − 15. [DOU Hongqiang,JIAN Wenbin,WANG Hao,et al Summary of research on disaster mechanism and early warning model of typhoon rain landslide in high vegetation coverage area[J] Journal of Natural Disasters,2023,32 (2):1 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DOU Hongqiang, JIAN Wenbin, WANG Hao, et al Summary of research on disaster mechanism and early warning model of typhoon rain landslide in high vegetation coverage area[J] Journal of Natural Disasters, 2023, 32 (2): 1 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: