CALCULATION MODEL FOR CRITICAL VELOCITY OF SAND MOVEMENT IN DECOMPOSED HYDRATE CEMENTED SEDIMENT
-
摘要:
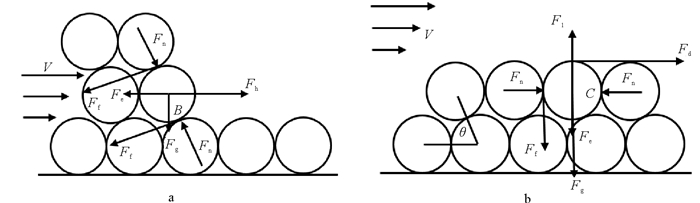
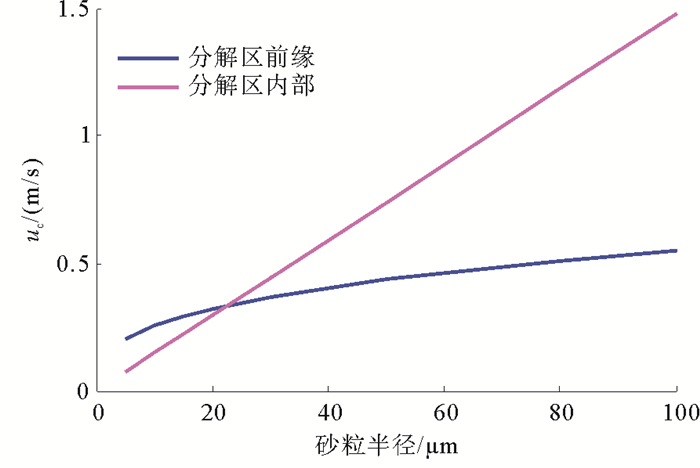
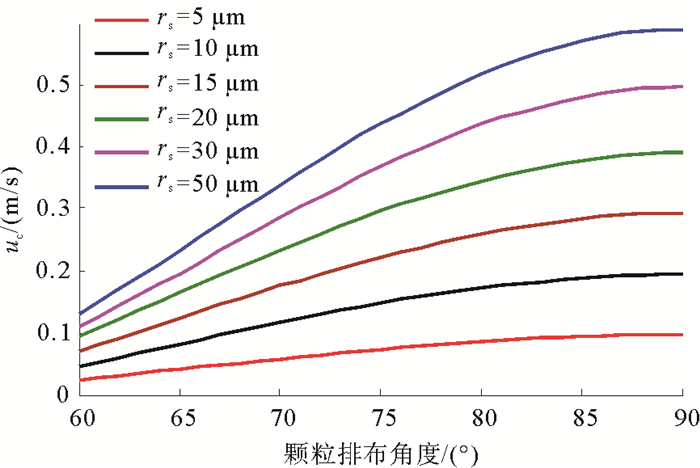
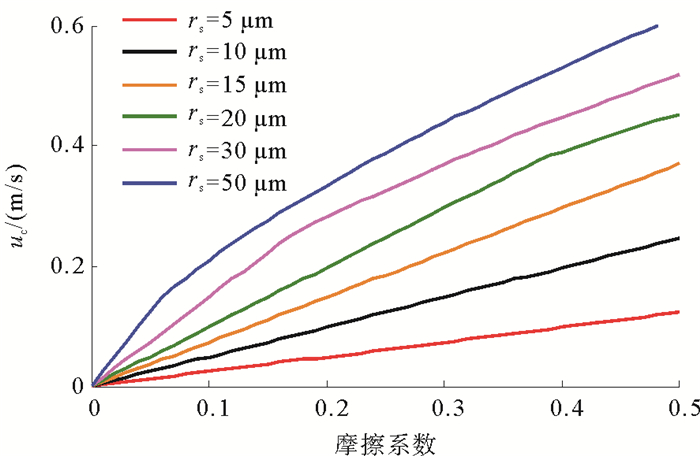
出砂是制约当前天然气水合物长效开发的关键因素之一。基于水合物分解区地层松散沉积物球形颗粒堆积假设,分析了水合物分解前缘和分解区内部地层砂微粒的受力情况,基于力矩平衡条件建立了松散沉积物中地层砂颗粒启动运移临界流速的计算模型,并进行模型敏感性分析。结果表明,水合物分解前缘和分解区内部微粒的临界流速均随着粒径、排布角度、颗粒摩擦系数的增加而增加,胶结物性质、流体中的电解质类型以及浓度等参数均对临界出砂流速产生一定的影响。本文建立的砂粒启动运移临界流速模型能够为水合物开采储层出砂评价提供支撑。
Abstract:In the mining process of natural gas from a hydrate reservoir, sanding is one of the major factors restricting the development of natural gas hydrate. In this paper, based on the assumption that hydrate cemented sediment is composed of tightly squeezed balls in equal size, we analyzed the stress conditions of such sand particles on the leading edge and in the decomposed zone. A critical velocity model for sand migration in decomposed hydrate-cemented sediment is built then on account of torque balance conditions. The results indicate that critical velocity of particles on the leading edge and in the decomposed zone increases with the increase in particle diameter, arrangement angle and coefficient of friction, and the properties of cement and the type and concentration of electrolyte in the fluid also influence the critical velocity of sand migration. The model proposed in this paper can provide a theoretical basis for evaluation of hydrate sanding.
-

-
[1] Wu N Y, Zhang H Q, Yang S X, et al. Gas hydrate system of Shenhu area, northern South China Sea: geochemical results[J]. Journal of Geological Research, 2011, 2011: Article ID 370298.
[2] Zhang G X, Liang J Q, Lu J A, et al. Geological features, controlling factors and potential prospects of the gas hydrate occurrence in the east part of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 67: 356-367. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.05.021
[3] 李彦龙, 刘乐乐, 刘昌岭, 等.天然气水合物开采过程中的出砂与防砂问题[J].海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(7): 36-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201607005
LI Yanlong, LIU Lele, LIU Changling, et al. Sanding prediction and sand-control technology in hydrate exploitation: a review and discuss[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(7): 36-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201607005
[4] Terao Y, Duncan M, Hay B, et al. Deepwater methane hydrate gravel packing completion results and challenges[C]//Offshore Technology Conference. Houston, Texas: Offshore Technology Conference, 2014.
[5] Chong Z R, Yang S H B, Babu P, et al. Review of natural gas hydrates as an energy resource: Prospects and challenges[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 162: 1633-1652. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030626191401318X
[6] Kjorholt H, Joranson H, Markestad P, et al. Advanced sand prediction in a user friendly wrapping[C]//SPE/ISRM Rock Mechanics in Petroleum Engineering. Trondheim, Norway: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 1998.
[7] 董长银, 张清华, 崔明月, 等.复杂条件下疏松砂岩油藏动态出砂预测研究[J].石油钻探技术, 2015, 43(6): 81-86. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syztjs201506015
DONG Changyin, ZHANG Qinghua, CUI Mingyue, et al. A dynamic sanding prediction model for unconsolidated sandstone reservoirs with complicated production conditions[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2015, 43(6): 81-86. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syztjs201506015
[8] Muller A L, do AmaralVargas Jr E, Vaz L E, et al. Numerical analysis of sand/solids production in boreholes considering fluid-mechanical coupling in a Cosserat continuum[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2011, 48(8): 1303-1312. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.09.012
[9] Talaghat M R, Esmaeilzadeh F, Mowla D. Sand production control by chemical consolidation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2009, 67(1-2): 34-40. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2009.02.005
[10] Papamichos E, Tronvoll J, Skjærstein A, et al. Hole stability of Red Wildmoor sandstone under anisotropic stresses and sand production criterion[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2010, 72(1-2): 78-92. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2010.03.006
[11] 王静丽, 梁金强, 宗欣, 等.南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物差异性分布的控制因素[J].海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(1): 24-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201501004
WANG Jingli, LIANG Jinqiang, ZONG Xin, et al. Differentiated distribution of methane hydrate in the Shenhu Area of the northern South China Sea and controlling factors[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(1): 24-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201501004
[12] 李彦龙, 刘昌岭, 刘乐乐.含水合物沉积物损伤统计本构模型及其参数确定方法[J].石油学报, 2016, 37(10): 1273-1279. doi: 10.7623/syxb201610007
LI Yanlong, LIU Changling, LIU Lele. Damage statistic constitutive model of hydrate-bearing sediments and the determination method of parameters[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(10): 1273-1279. doi: 10.7623/syxb201610007
[13] 张光学, 黄永样, 祝有海, 等.南海天然气水合物的成矿远景[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(1): 75-81. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200201012
ZHANG Guangxue, HUANG Yongyang, ZHU Youhai, et al. Prospect of gas hydrate resources in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(1): 75-81. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200201012
[14] Liu C L, Meng Q G, Hu G W, et al. Characterization of hydrate-bearing sediments recovered from the Shenhu area of the South China Sea[J]. Interpretation, 2017, 5(3): 1-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=77d2f5c137cf262216acf0faf8f923c0
[15] 张卫东, 王瑞和, 任韶然, 等.天然气水合物储层物理模型[J].石油学报, 2011, 32(5): 866-871. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201105020
ZHANG Weidong, WANG Ruihe, REN Shaoran, et al. A study on physical models of gas hydrate reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(5): 866-871. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201105020
[16] 董刚, 龚建明, 王家生.从天然气水合物赋存状态和成藏类型探讨天然气水合物的开采方法[J].海洋地质前沿, 2011, 27(6): 59-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201106010
DONG Gang, GONG Jianming, WANG Jiasheng. Gas hydrate exploitation methods upon types and occurrence of gas hydrate accumulations[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2011, 27(6): 59-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201106010
[17] 吴剑, 常毓文, 穆歌, 等.水驱黏土微粒迁移理论及作用[J].油田化学, 2015, 32(1): 57-61. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ythx201501013
WU Jian, CHANG Yuwen, MU Ge, et al. Theory and function for clay fines migration in water flooding[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2015, 32(1): 57-61. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ythx201501013
[18] Altmann J, Ripperger S. Particle deposition and layer formation at the crossflow microfiltration[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 1997, 124(1): 119-128. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0376-7388(96)00235-9/
[19] Gregory J. Approximate expressions for retarded van der Waals interaction[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1981, 83(1): 138-145. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(81)90018-7
[20] Gregory J. Interaction of unequal double layers at constant charge[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1975, 51(1): 44-51. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(75)90081-8
[21] Bedrikovetsky P G, Siqueira F D, Furtado C J A, et al. Quantitative theory for fines migration and formation damage[C]//SPE International Symposium and Exhibiton on Formation Damage Control. Lafayette, Louisiana, USA: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2010.
-



 下载:
下载: