Late spring thermocline and chemoclines in the area off the Rizhao–Lianyungang coast, western South Yellow Sea
-
摘要:
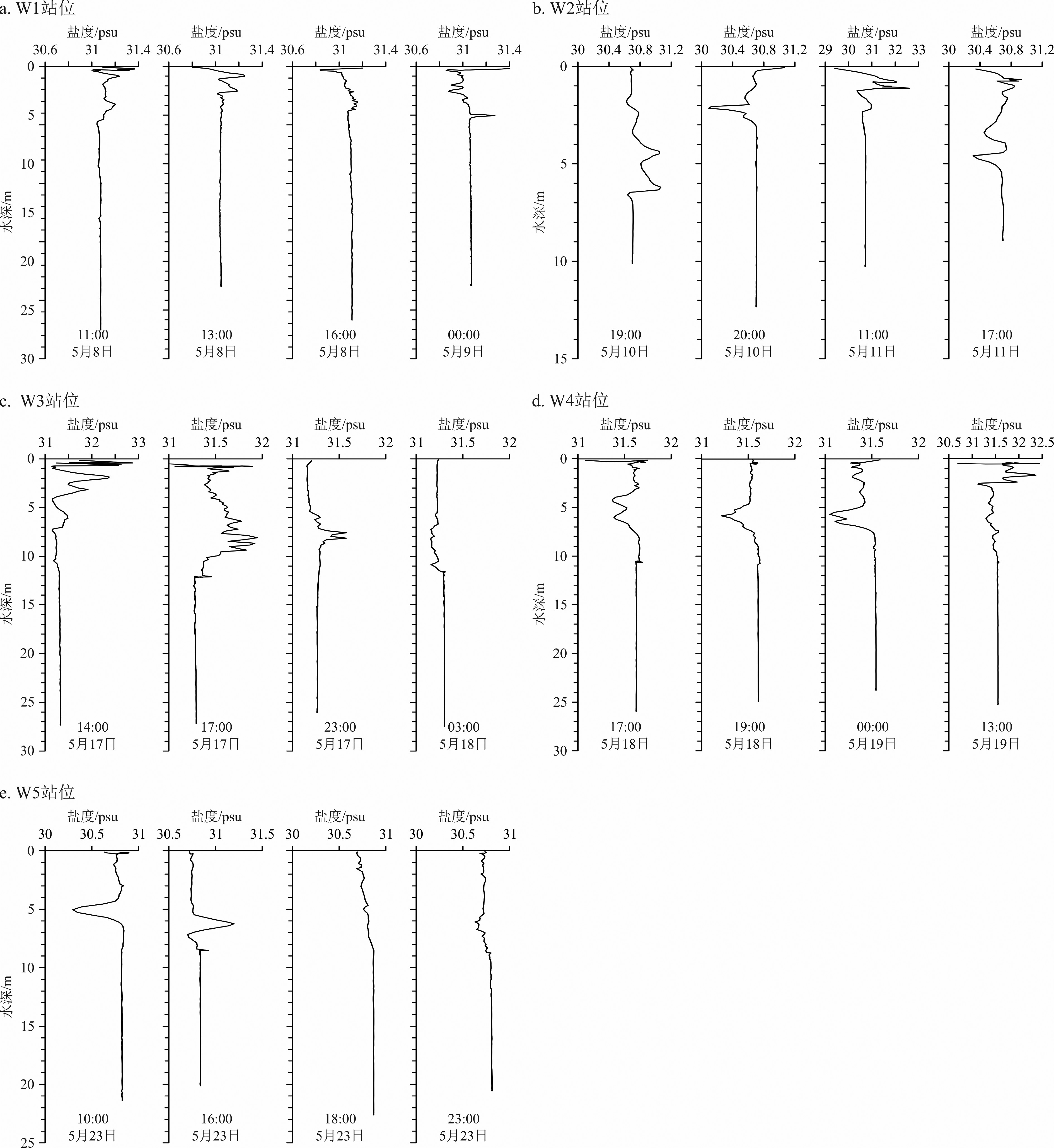
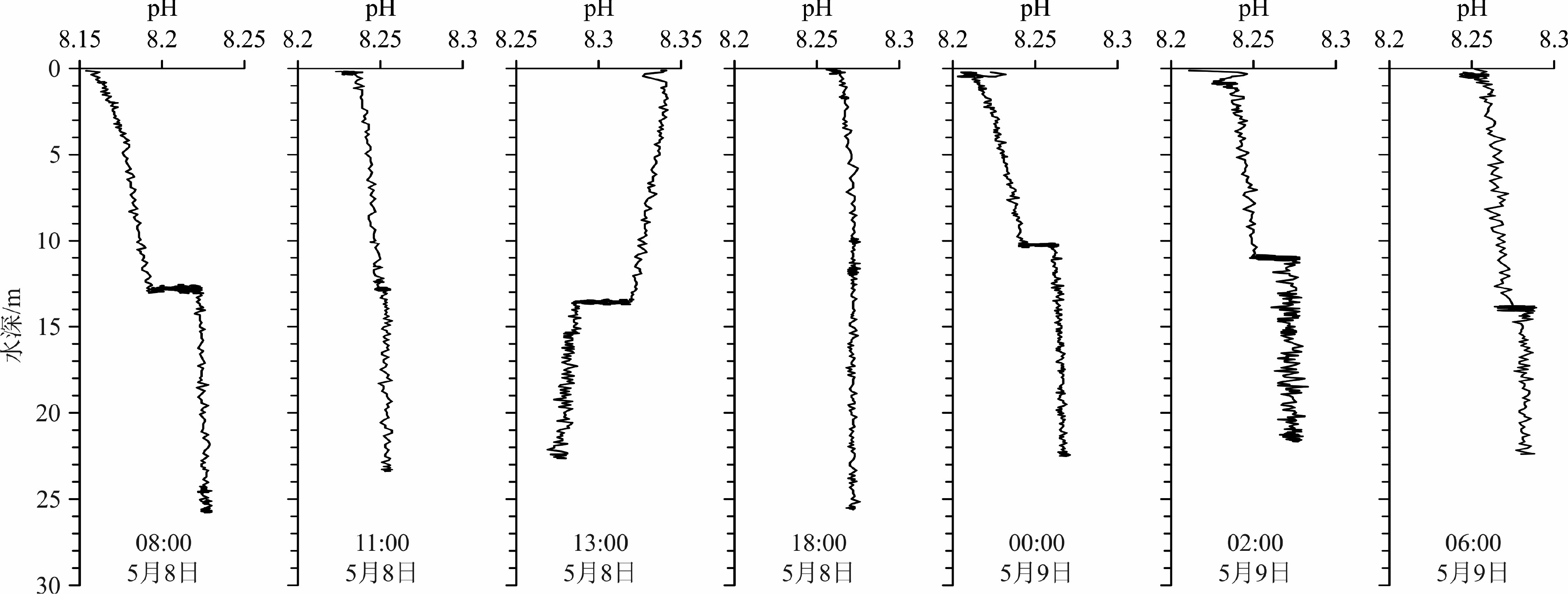
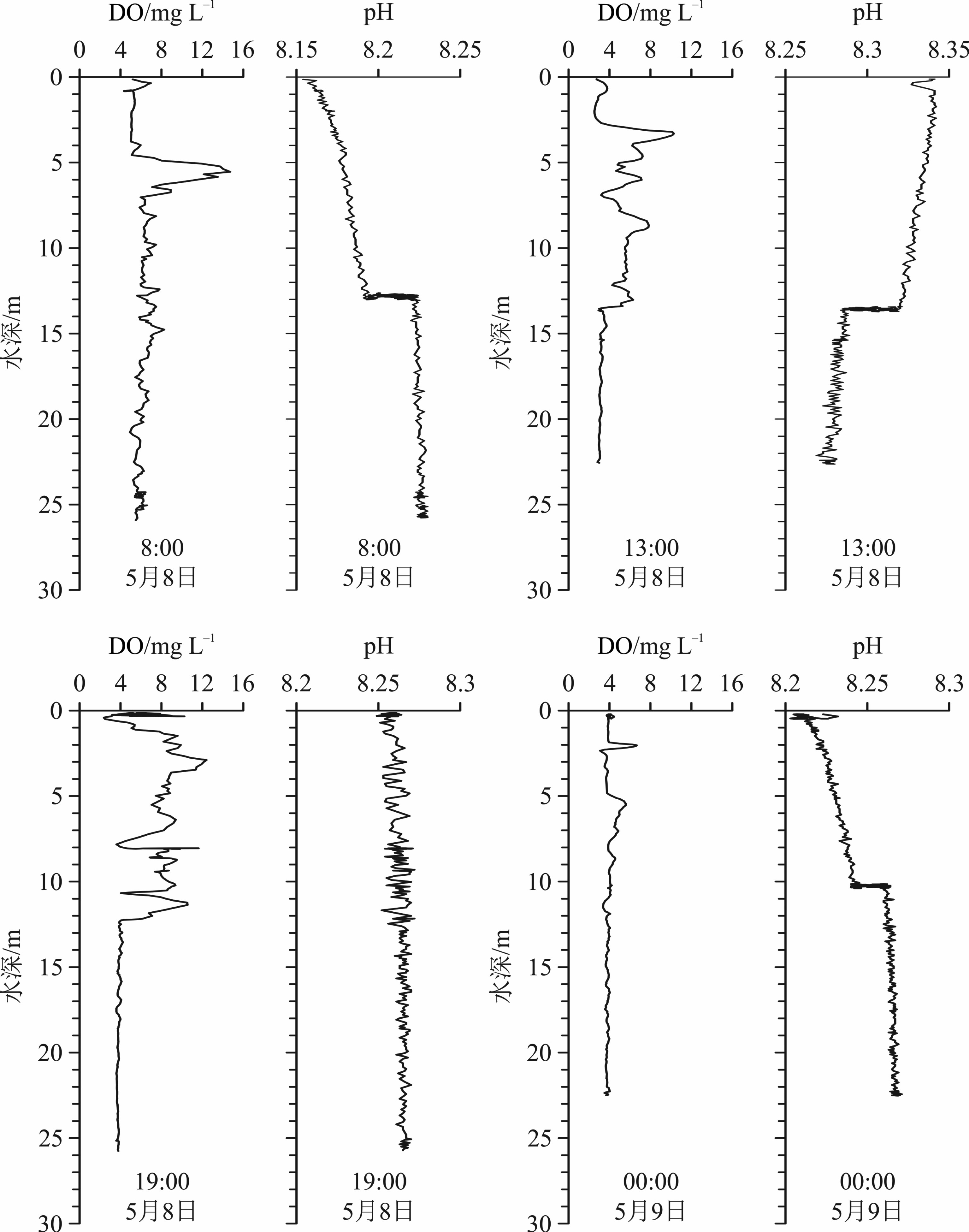
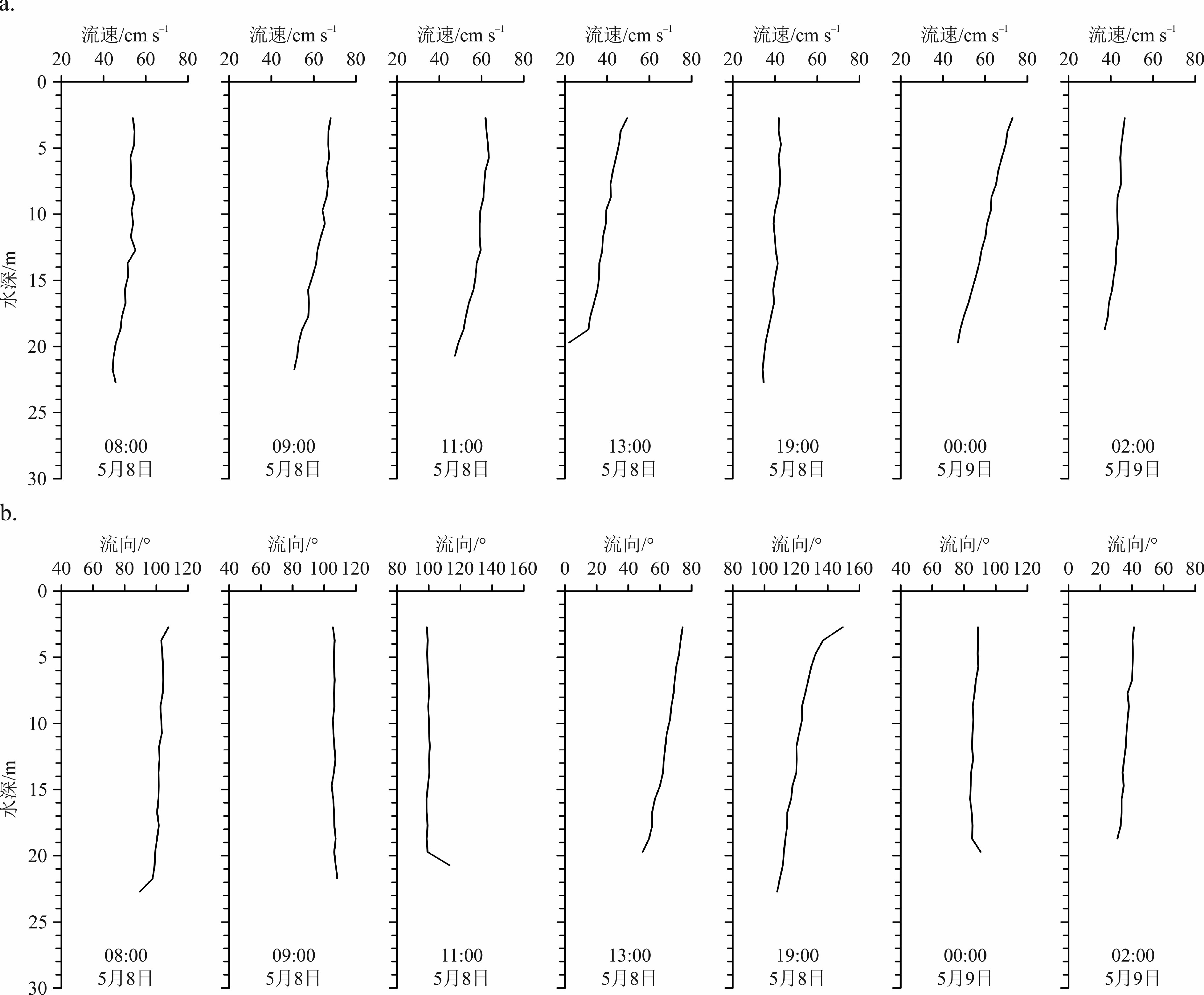
利用2016年5月5个站位的温盐深(CTD)和海流(ADCP)同步测量资料,分析南黄海西部日照至连云港海域温跃层和化学跃层的日内生消过程及强度变化,探讨深层水温度、盐度的周期性变化及其与潮流的关系。结果表明:南黄海西部海域在5月已存在日内生消的温跃层和溶解氧(DO)、pH跃层。温跃层厚度为2~4 m,层位水深为4~7 m至7~10 m之间波动,跃层强度最大可达0.80 ℃/m。DO跃层和pH跃层位于温跃层之下,水深为10~14 m,两者的形成在时间上和深度上具有一定的同步性,且不受温跃层控制。在DO跃层之上,氧浓度在白天都保持在相当高的水平,甚至处于过饱和状态,但存在显著波动,其峰值并不出现在表层(0~2 m),而是位于次表层(2~14 m)。在DO跃层之下,氧浓度低且稳定,约为4 mg·L−1,向下呈缓慢降低的趋势。pH跃层表现为垂向上的快速跳变,包括向下的正跳变和负跳变,强度最大值可达0.03~0.04个pH单位。小潮期间,温跃层稳定,强度较大;大潮期间,温跃层强度明显减弱,稳定性变差;这表明潮流的增强对温跃层有明显的抑制和破坏作用。深层水的温度、盐度等参数存在日内周期性变化,与潮位变化同步,是潮流驱动下水体水平对流的结果。
Abstract:Conductivity–temperature–depth (CTD) measurement and continuous current observation with an Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP) were synchronously conducted in May, 2016, at five hydrographic stations off the Rizhao–Lianyungang coast, western South Yellow Sea. The intraday evolution of thermocline and chemoclines is analyzed and the relation of the periodical changes in temperature and salinity of the deep water with tidal currents is discussed. Results show that the thermocline and chemoclines of dissolved oxygen (DO) and pH have formed as early as in May. The thickness of thermocline usually varies between 2~4 m. It mostly dwells in the depth range from 4~7 m to 7~10 m. The maximum gradient reaches 0.80 °C/m. DO and pH chemoclines dwell at the depths of 10~14 m, which are deeper than the thermocline. To some degree, the chemoclines of DO and pH occur synchronously at the same depths and have no relations to the thermocline. Above the chemocline DO fluctuates markedly and maintains at a high level or even oversaturated in daytime. Its peak concentrations do not occur in the surface layer (0~2 m) but in the sub-surface layer (2~14 m). Below the chemocline it invariably remains about 4 mg·L−1 and slowly drops downward. The pH chemocline is characterized by vertical rapid jump, including downward positive and negative jumps with a maximum strength of 0.03~0.04 pH units. In the neap tides thermocline is stable with a large gradient, whereas in the spring tides the gradient and sustainability is reduced apparently. These results suggest that the enhancement of tidal currents undermines the sustainability of thermocline. The periodical changes in temperature and salinity of deep waters are consistent with that of the tidal level, indicating the consequence of advection driven by tidal currents.
-
Key words:
- thermocline /
- chemoclines /
- pH profile /
- DO profile /
- tidal current /
- South Yellow Sea
-

-
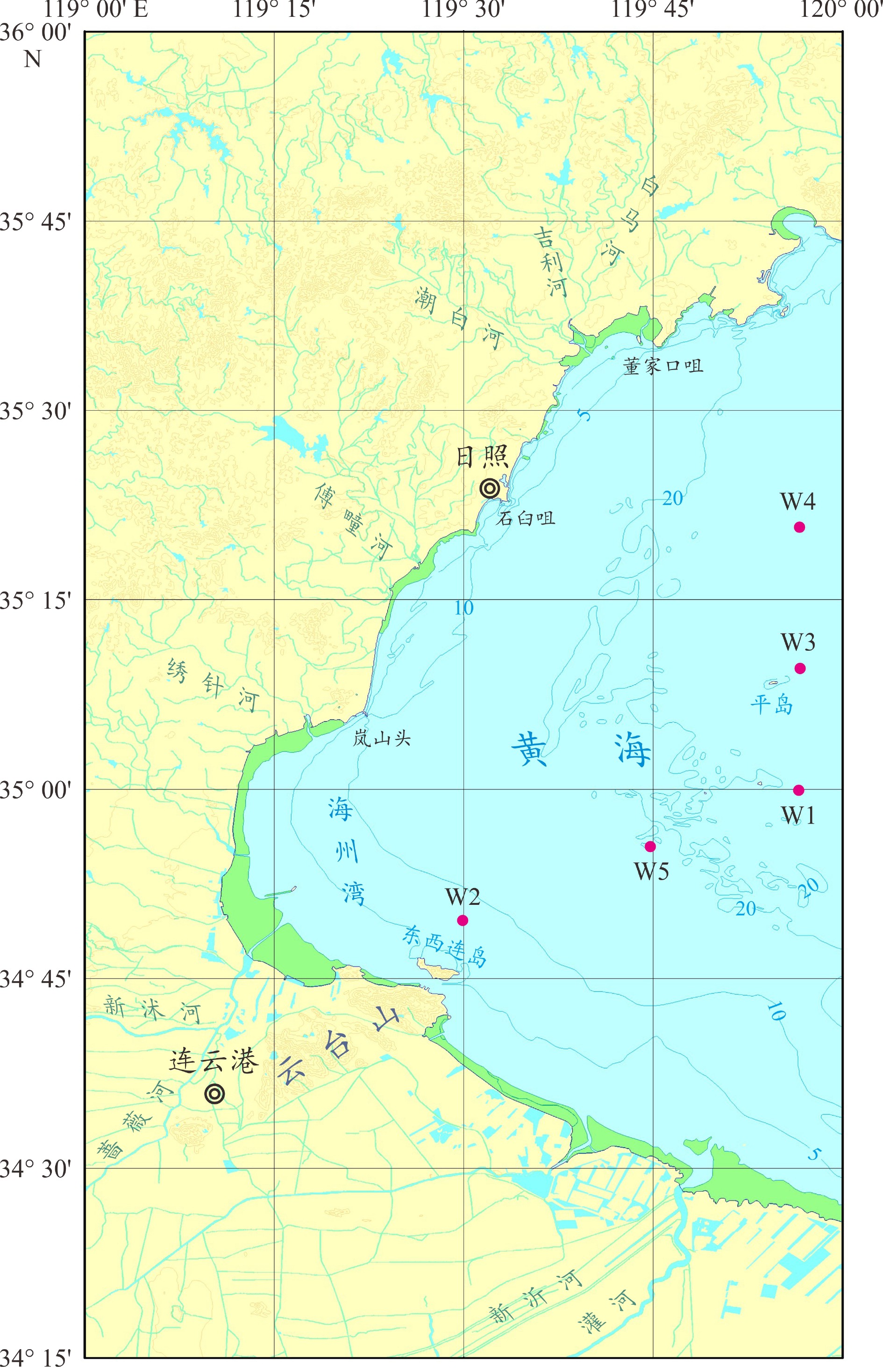
表 1 观测站位信息一览表
Table 1. The detailed information from the observation stations off the Rizhao-Lianyungang coast, western South Yellow Sea
站位 北纬 东经 观测周期 阴历日期 潮周期 平均水深/m W1 34° 59′ 56.688" 119° 56′ 32.064" 5/08 07:00 – 5/09 07:00 初二、初三 大潮 23.2 W2 34° 49′ 37.164" 119° 29′ 56.508" 5/10 17:00 – 5/11 17:00 初四、初五 中潮 10.3 W3 35° 09′ 33.840" 119° 56′ 40.200" 5/17 14:00 – 5/18 14:00 十一、十二 小潮 26.7 W4 35° 20′ 46.968" 119° 56′ 36.924" 5/18 16:00 – 5/19 16:00 十二、十三 中潮 25.2 W5 34° 55′ 27.624" 119° 44′ 46.824" 5/23 10:00 – 5/24 11:00 十七、十八 大潮 21.2 -
[1] 苏纪兰, 袁业立. 中国近海水文[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005: 14-23.
SU Jilan, YUAN Yeli. Offshore Hydrology in China[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2005: 14-23.
[2] Park S, Chu P C, Lee J H. Interannual-to-interdecadal variability of the Yellow Sea Cold Water Mass in 1967-2008: characteristics and seasonal forcings [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2011, 87(3-4): 177-193. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2011.03.012
[3] Zhang S W, Wang Q Y, Lü Y, et al. Observation of the seasonal evolution of the Yellow Sea Cold Water Mass in 1996-1998 [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2008, 28(3): 442-457. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2007.10.002
[4] 孙湘平. 中国近海区域海洋[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2006: 201-228, 276-280.
SUN Xiangping. Regional Oceanography of China Seas[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2006: 201-228, 276-280.
[5] 万邦君, 郭炳火, 陈则实. 黄海热结构的三层模式[J]. 海洋学报, 1990, 12(2):137-148
WAN Bangjun, GUO Binghuo, CHEN Zeshi. A three-layer model of the thermal structure in the Yellow Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1990, 12(2): 137-148.
[6] 杨殿荣, 匡国瑞, 张玉琳, 等. 黄、东海夏季温跃层的诊断研究[J]. 海洋学报, 1990, 12(1):14-23
YANG Dianrong, KUANG Guorui, ZHANG Yulin, et al. Diagnosis of the summer thermocline in the Yellow and East China Seas [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1990, 12(1): 14-23.
[7] 赵保仁. 渤、黄海及东海北部强温跃层的基本特征及形成机制的研究[J]. 海洋学报, 1989, 11(4):401-410
ZHAO Baoren. Basic characteristics and formation mechanism of the strong thermocline in the Bohai, Yellow, and northern East China Seas [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1989, 11(4): 401-410.
[8] Yuan Y L, Li H Q. On the circulation structure and formation mechanism of the Cold Water Mass of the Yellow Sea (I): zero-order solution and circulation structure [J]. Science in China (Series B), 1993, 36(12): 1518-1528.
[9] 乔方利, 马建, 夏长水, 等. 波浪和潮流混合对黄海、东海夏季温度垂直结构的影响研究[J]. 自然科学进展, 2004, 14(12):1434-1441 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2004.12.010
QIAO Fangli, MA Jian, XIA Changshui, et al. The impacts of tidal and wave mixing on the vertical structure of summer temperature in the Yellow and East China Seas [J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2004, 14(12): 1434-1441. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2004.12.010
[10] Ma J, Qiao F L, Xia C S, et al. Tidal effects on temperature front in the Yellow Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2004, 22(3): 314-321. doi: 10.1007/BF02842565
[11] Yang Y Z, Qiao F L, Xia C S, et al. Wave-induced mixing in the Yellow Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2004, 22(3): 322-326. doi: 10.1007/BF02842566
[12] Xie L P, Wang B D, Pu X M, et al. Hydrochemical properties and chemocline of the Sansha Yongle Blue Hole in the South China Sea [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 649: 1281-1292. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.333
[13] Hendriks I E, Olsen Y S, Ramajo L, et al. Photosynthetic activity buffers ocean acidification in seagrass meadows [J]. Biogeosciences, 2014, 11(2): 333-346. doi: 10.5194/bg-11-333-2014
[14] Frieder C A, Nam S H, Martz T R, et al. High temporal and spatial variability of dissolved oxygen and pH in a nearshore California kelp forest [J]. Biogeosciences, 2012, 9(3): 3917-3930. doi: 10.5194/bgd-9-3917-2012
[15] Saba G K, Wright-Fairbanks E, Miles T N, et al. Developing a profiling glider pH sensor for high resolution coastal ocean acidification monitoring[C]//OCEANS 2018 MTS/IEEE Charleston. Charleston, SC, USA: IEEE, 1-8.
[16] 张志欣, 郭景松, 乔方利, 等. 苏北沿岸水的去向与淡水来源估算[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(3):527-532
ZHANG Zhixin, GUO Jingsong, QIAO Fangli, et al. Whereabouts and freshwater origination of the Subei coastal water [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2016, 47(3): 527-532.
[17] 秦亚超. 南黄海西部日照至连云港海域表层沉积物粒度特征及其指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(6):1412-1428 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2017.06.23
QIN Yachao. Grain-size characteristics of bottom sediments and its implications offshore between Rizhao and Lianyungang in the western South Yellow Sea [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2017, 37(6): 1412-1428. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2017.06.23
[18] Sorkin A, Sorkin V, Leizerson I. Salt fingers in double-diffusive systems [J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2002, 303(1-2): 13-26. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4371(01)00396-X
[19] USGS. DOTABLES[EB/OL]. (2019-12-19). https://www.usgs.gov/software/dotables.2019.
[20] Meng Q J, Li P L, Zhai F G, et al. The vertical mixing induced by winds and tides over the Yellow Sea in summer: a numerical study in 2012 [J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2020, 70(7): 847-861. doi: 10.1007/s10236-020-01368-2
-



 下载:
下载: