Bedding structure types, combinations and reservoir significances of fine-grained rocks of the Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin
-
摘要:
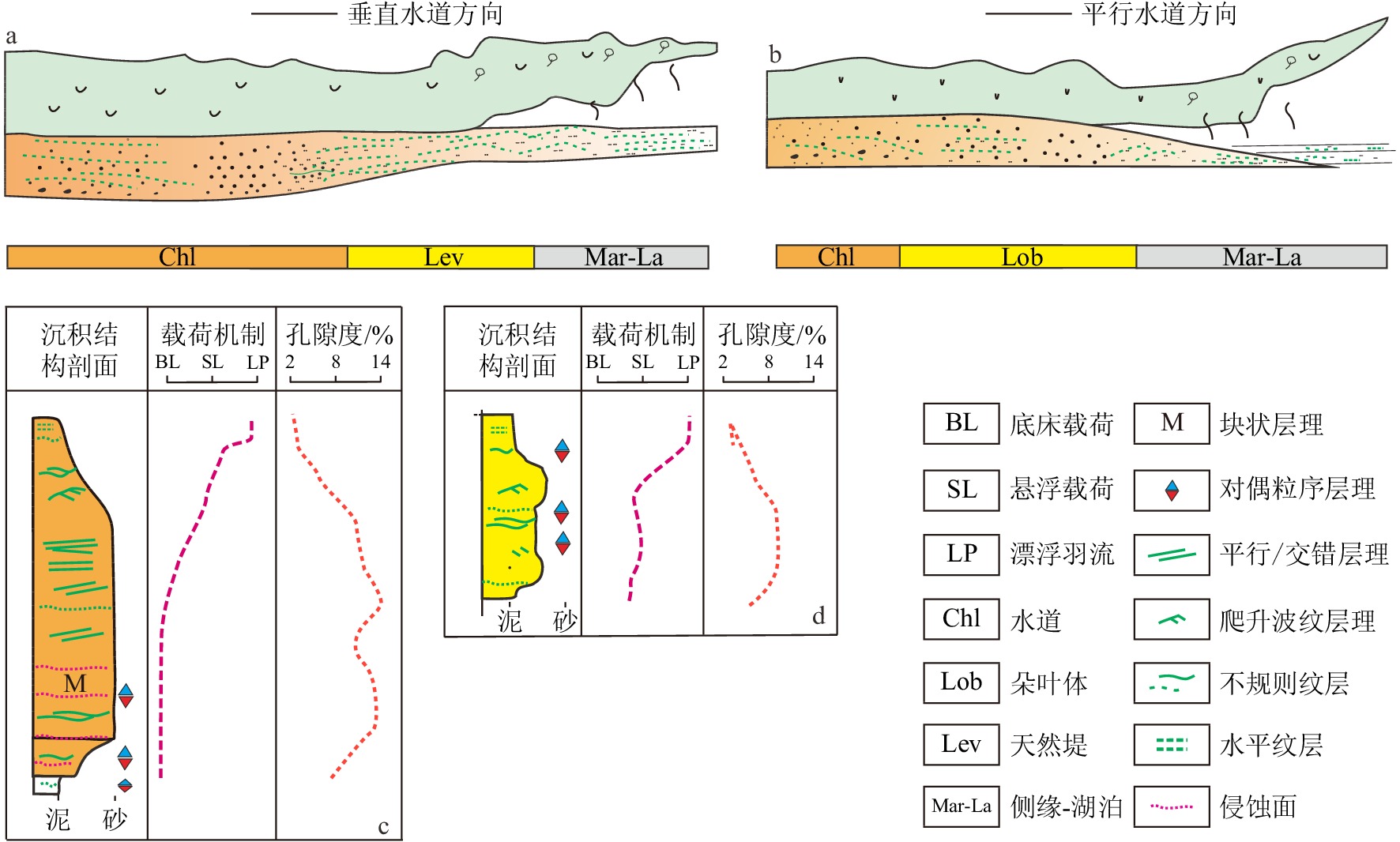
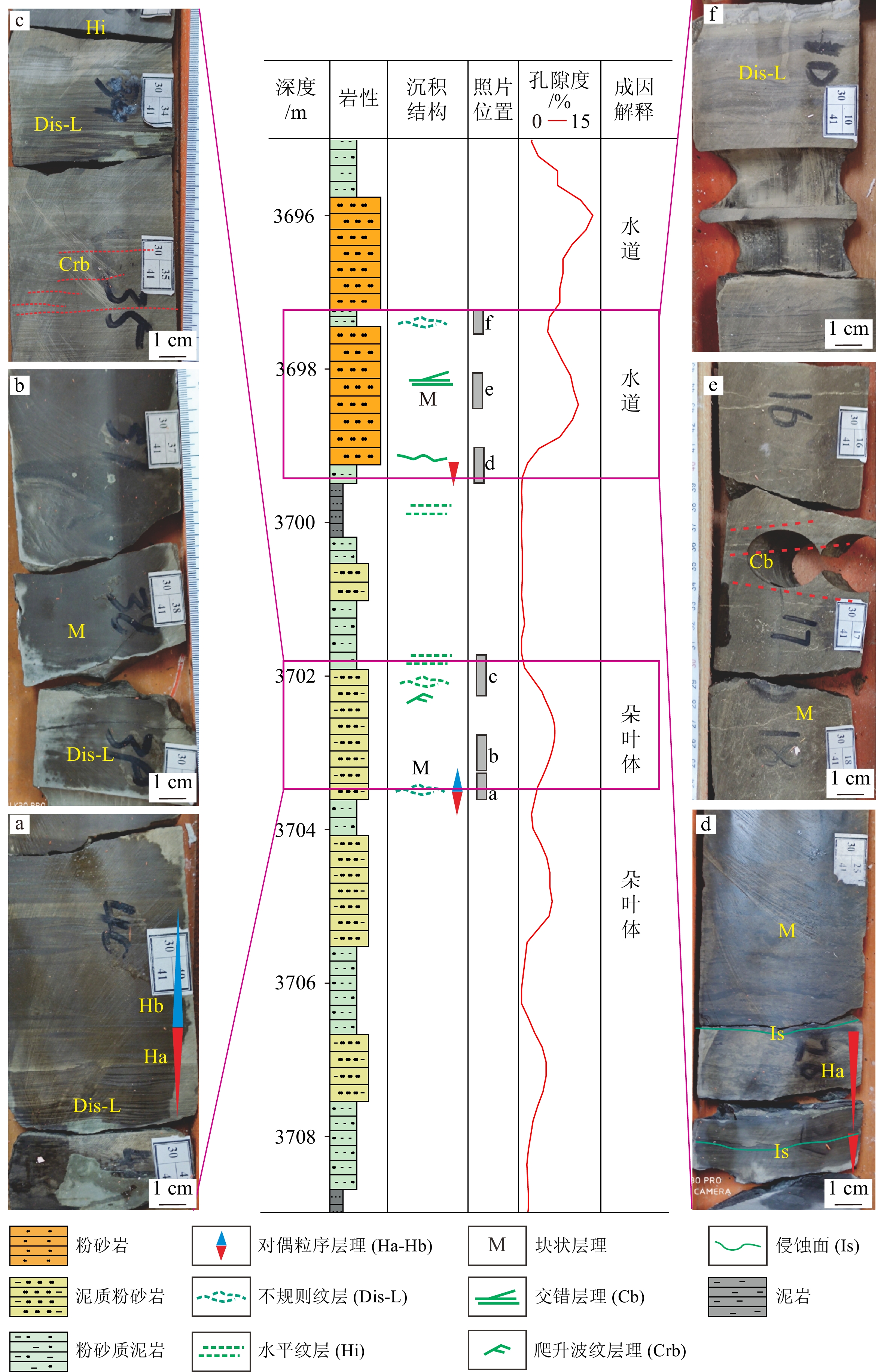
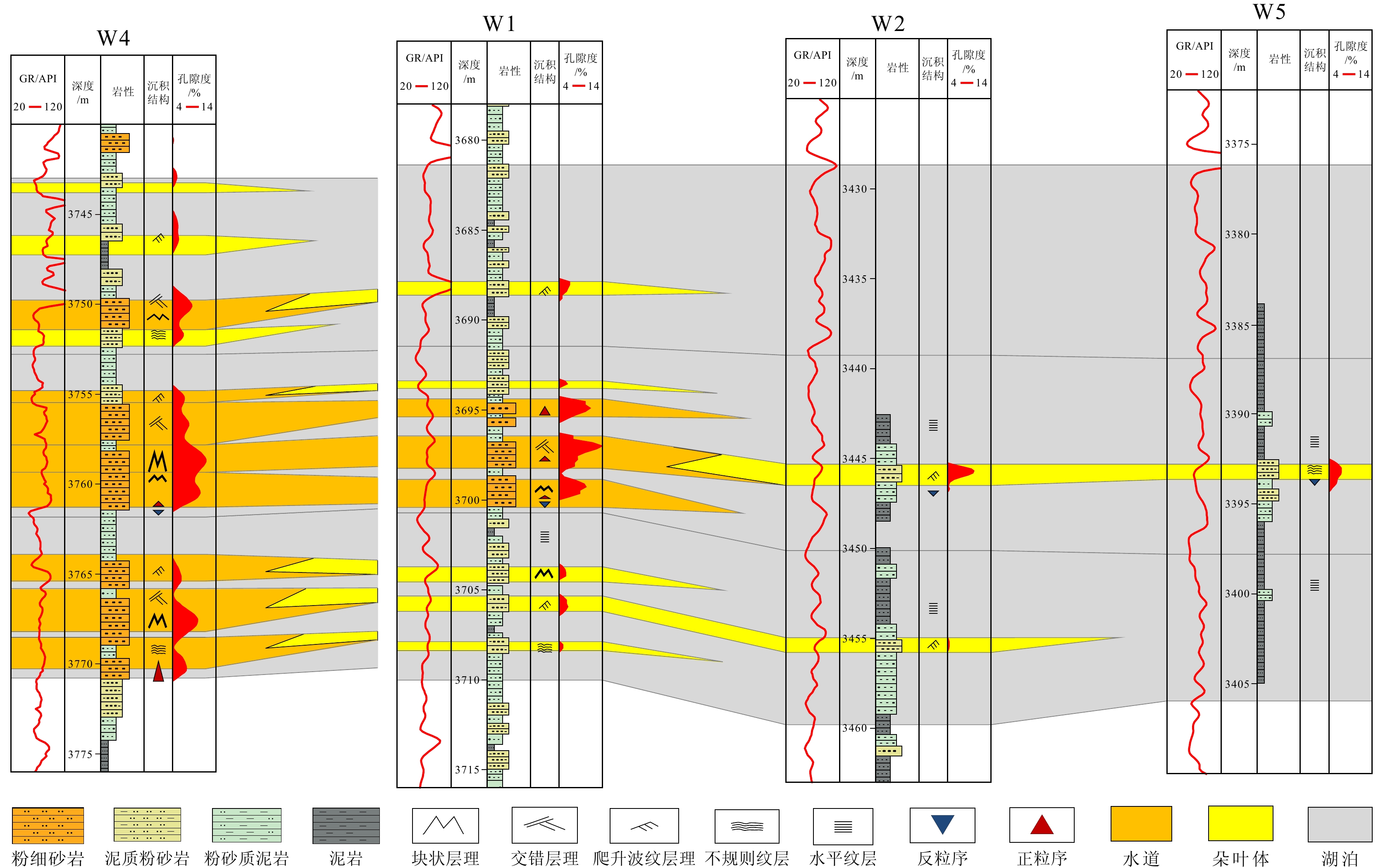
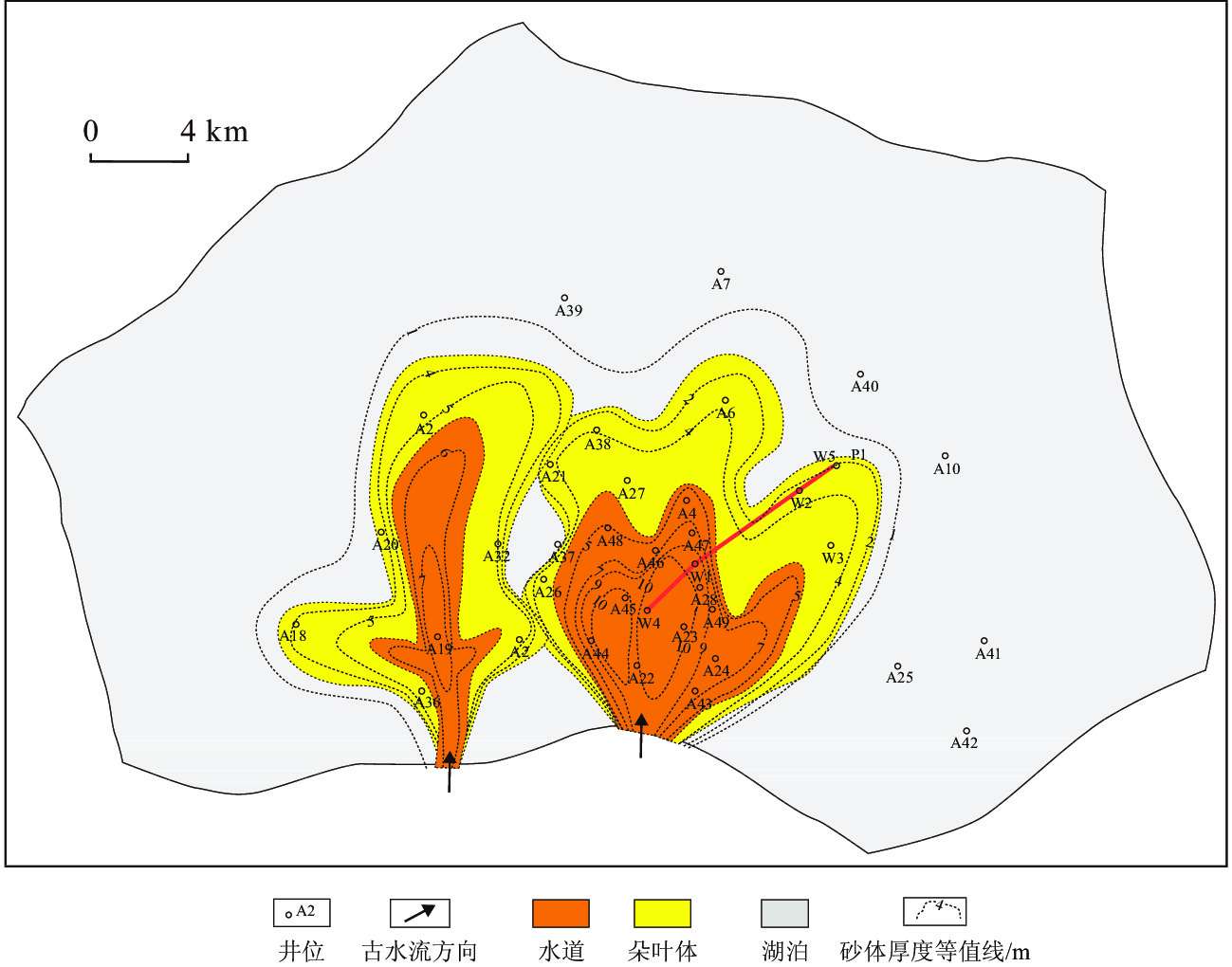
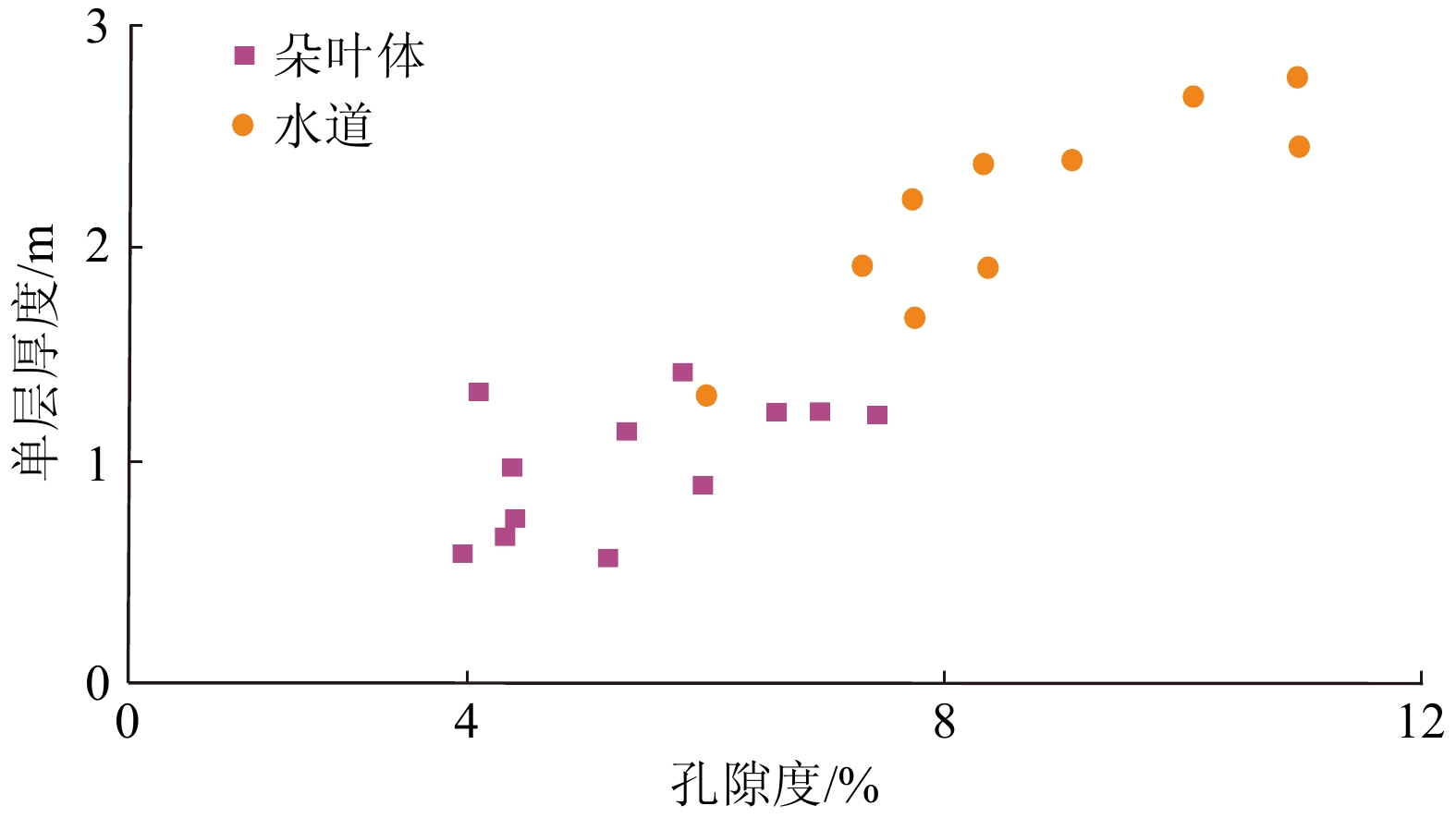
细粒沉积岩中的层理是影响页岩储层物性的关键因素。吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组发育丰富的层理构造。基于工区内钻井、岩芯、薄片及物性资料,开展了层理构造特征、成因及储集意义分析。本文将1 cm厚度作为界限,小于1 cm的沉积层称为纹层,大于1 cm沉积层称为层理。研究表明:纹层与层理在形成沉积水动力条件及厚度规模上存在差异,识别出两类层理组合,第一类为厚层的层理-纹层组合,主要见于粉细砂岩中,垂向上依次发育对偶粒序层理、块状层理、交错层理、爬升波纹层理及不规则纹层,反映异重流水道成因;第二类为薄纹层为主的组合,通常见于泥质粉砂岩,垂向上为对偶粒序层理与不规则纹层,反映出异重流朵叶体成因特征。第一类组合指示了强水动力条件,如异重流水道,其单层厚度及累计厚度大,储集性好;第二类组合指示较弱水动力条件,如异重流朵叶体,其单层厚度及累计厚度较小,储集性相对较差。该研究可以为细粒沉积学及页岩油勘探开发实践提供有价值的参考。
Abstract:Abstracts: The lamination and bedding structures in fine-grained rocks are key factors affecting the quality of shale oil reservoir. The Permian Lucaogou Formation in the Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China was studied for this. Based on drilling wells, cores, thin sections, and physical property data of the area, the characteristics, genesis, and reservoir significance of bedding structures were analyzed. Thickness of 1cm was defined as the boundary: less than 1cm referred to a lamina, and greater than 1 cm referred to a bedding. Results show that, both laminae and beddings are in sedimentary origin, showing differences in hydrodynamic condition and thickness. Two types were identified. The first one is thick-bedded bedding-lamination type, often shown in fine-grained sandstone, with vertical development of upward-coarsening/finning bedding, massive bedding, cross bedding, climbing ripple bedding, and irregular lamination, indicating the strong hydrodynamic origin such as hyperpycnal channels. The second type is laminae-dominated one usually seen in muddy siltstone, consisting of vertical upward-coarsening/finning bedding and irregular lamination, which is formed in hyperpycnal lobe indicative of week hydrodynamic origin. The first type generated large single-layer thickness and cumulative thickness, and good reservoir properties, the second type resulted in smaller single-layer thickness and cumulative thickness, and relatively poor reservoir properties. This understanding provides valuable references for study in sedimentology of fine-grained rocks, and for shale oil exploration and development practices.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary structures /
- bedding /
- lamination /
- hyperpycnal flow /
- shale oil /
- Lucaogou Formation
-

-
表 1 芦草沟组纹层、纹层组及层理特征
Table 1. Characteristics of lamination, lamina set, and bedding of the core data of Lucaogou Formation
基本单元 特征 厚度范围/mm 纹层 水平纹层 微米级泥纹层与砂纹层水平互层,无明显层界面 0.2~2 不规则纹层 微米-毫米级泥纹层与砂纹层水平互层,无明显层界面 0.5~8 纹层组 砂泥纹层组 砂泥互层,呈现平行、不规则几何形态,有明显层界面 0.5~40 层理 块状层理 长英质颗粒片均匀分布,内部无明显界面,顶底侵蚀面 100~800 平行层理 长英质颗粒为主,顶底突变面,呈现平行特征 10~50 交错层理 长英质颗粒为主,顶底突变面,呈现斜交特征 20~10 -
[1] Folk R L. Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks[M]. Austin: Hemphill Publishing Company, 1980.
[2] Schieber J. Possible indicators of microbial mat deposits in shales and sandstones: examples from the Mid-Proterozoic Belt Supergroup, Montana, USA.[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1998, 120(1-4):105-124. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(98)00029-3
[3] Macquaker J H S, Bentley S J, Bohacs K M. Wave-enhanced sediment-gravity flows and mud dispersal across continental shelves: reappraising sediment transport processes operating in ancient mudstone successions[J]. Geology, 2010, 38(10):947-950. doi: 10.1130/G31093.1
[4] Lazar O R, Bohacs K M, Macquaker J H S, et al. Capturing key attributes of fine-grained sedimentary rocks in outcrops, cores, and thin sections: nomenclature and description guidelines[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2015, 85(3):230-246. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2015.11
[5] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望: 以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2):173-187 doi: 10.7623/syxb201202001
ZOU Caineng, ZHU Rukai, WU Songtao, et al. Types, characteristics, genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations: taking tight oil and tight gas in China as an instance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2):173-187.] doi: 10.7623/syxb201202001
[6] 赵文智, 朱如凯, 胡素云, 等. 陆相富有机质页岩与泥岩的成藏差异及其在页岩油评价中的意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(6):1079-1089 doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.06.02
ZHAO Wenzhi, ZHU Rukai, HU Suyun, et al. Accumulation contribution differences between lacustrine organic-rich shales and mudstones and their significance in shale oil evaluation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6):1079-1089.] doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.06.02
[7] 刘庆, 曾翔, 王学军, 等. 东营凹陷沙河街组沙三下-沙四上亚段泥页岩岩相与沉积环境的响应关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3):147-156
LIU Qing, ZENG Xiang, WANG Xuejun, et al. Lithofacies of mudstone and shale deposits of the Es3-Es4 formation in Dongying sag and their depositional environment[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(3):147-156.]
[8] Lamont A. First use of current-bedding to determine orientation of strata[J]. Nature, 1940, 145(3687):1016-1017. doi: 10.1038/1451016a0
[9] Campbell C V. Lamina, laminaset, bed and bedset[J]. Sedimentology, 1967, 8(1):7-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1967.tb01301.x
[10] Hooson W. The miners discovery[M]. Likley: Scholar Press for the Institution of Mining and Metallury, 1947.
[11] Potter P E, Maynard J B, Depetris P J. Mud and Mudstones: Introduction and Overview[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2005:75-126.
[12] 施振生, 董大忠, 王红岩, 等. 含气页岩不同纹层及组合储集层特征差异性及其成因: 以四川盆地下志留统龙马溪组一段典型井为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(4):829-840 doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.04.20
SHI Zhensheng, DONG Dazhong, WANG Hongyan, et al. Reservoir characteristics and genetic mechanisms of gas-bearing shales with different laminae and laminae combinations: a case study of member 1 of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi shale in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(4):829-840.] doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.04.20
[13] 李婷婷, 朱如凯, 白斌, 等. 酒泉盆地青西凹陷下沟组湖相细粒沉积岩纹层特征及研究意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2015, 20(1):38-47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2015.01.004
LI Tingting, ZHU Rukai, BAI Bin, et al. Characteristics and research significance of fine lacustrine sedimentary rock laminations of Xiagou Formation in Qingxi Depression of Jiuquan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2015, 20(1):38-47.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2015.01.004
[14] 熊敏, 陈雷, 陈鑫, 等. 海相页岩纹层特征、成因机理及其页岩气意义[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 53(9):3490-3508
XIONG Min, CHEN Lei, CHEN Xin, et al. Characteristics, genetic mechanism of marine shale laminae and its significance of shale gas accumulation[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2022, 53(9):3490-3508.]
[15] 武瑾, 李海, 杨学锋, 等. 深层海相页岩纹层类型、组合及其对储层品质的影响: 以四川盆地南部泸州区块龙马溪组一段一亚段为例[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(9):1517-1531 doi: 10.7623/syxb202309009
WU Jin, LI Hai, YANG Xuefeng, et al. Types and combinations of deep marine shale laminae and their effects on reservoir quality: a case study of the first submember of Member 1 of Longmaxi Formation in Luzhou block, south Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(9):1517-1531.] doi: 10.7623/syxb202309009
[16] 柳波, 吕延防, 孟元林, 等. 湖相纹层状细粒岩特征、成因模式及其页岩油意义: 以三塘湖盆地马朗凹陷二叠系芦草沟组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(5):598-607
LIU Bo, LV Yanfang, MENG Yuanlin, et al. Petrologic characteristics and genetic model of lacustrine lamellar fine-grained rock and its significance for shale oil exploration: a case study of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Malang sag, Santanghu Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(5):598-607.]
[17] 勇朋林. 不同构造背景下细粒纹层多尺度划分与细粒岩相成因模式[D]. 山东科技大学硕士学位论文, 2018
YONG Penglin. Multi-scale fine grained lithosphere division and patterns of fine-grained facies in different tectonic setting[D]. Master Dissertation of Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2018.]
[18] Mulder T, Syvitski J P M, Migeon S, et al. Marine hyperpycnal flows: initiation, behavior and related deposits. A review[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2003, 20(6-8):861-882. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2003.01.003
[19] Zavala C, Carvajal J, Marcano J, et al. Sedimentological indexes: a new tool for regional studies of hyperpycnal systems[C]//AAPG Hedberg Conference “Sediment Transfer from Shelf to Deep Water-Revisiting the Delivery Mechanisms”. Ushuaia-Pa-tagonia: AAPG, 2008.
[20] Zavala C, Pan S X. Hyperpycnal flows and hyperpycnites: Origin and distinctive characteristics[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(1):1-27.
[21] 杨志浩, 李胜利, 于兴河, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘中二叠统芦草沟组富砂型湖泊深水扇沉积特征及其相模式[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(6):989-1000 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2018.06.072
YANG Zhihao, LI Shengli, YU Xinghe, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and facies model of deep-water fan in sand-rich lake of the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation in southern Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2018, 20(6):989-1000.] doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2018.06.072
[22] 李书琴, 印森林, 高阳, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组混合细粒岩沉积微相[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(2):235-249
LI Shuqin, YIN Senlin, GAO Yang, et al. Study on sedimentary microfacies of mixed fine-grained rocks in Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(2):235-249.]
[23] 张奎华, 曹忠祥, 王越, 等. 博格达地区中二叠统芦草沟组沉积相及沉积演化[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(4):1-12
ZHANG Kuihua, CAO Zhongxiang, WANG Yue, et al. Sedimentary facies and evolution of Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation in Bogda area[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(4):1-12.]
[24] Schieber J, Southard J, Thaisen K. Accretion of mudstone beds from migrating floccule ripples[J]. Science, 2007, 318(5857):1760-1763. doi: 10.1126/science.1147001
[25] 李映艳, 陈轩, 高阳, 等. 井震结合分析页岩油“甜点”沉积特征及分布——以吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组“下甜点”为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(2): 186-195
LI Yingyan, CHEN Xuan, GAO Yang, et al. Sedimentary morphology and distributions of shale oil “sweet spot” by the data of well to seismic analysis: a case study of the lower sweet pot in Lucaogou Formation of Jimsar Sag. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2023, 30(2): 186-195.
[26] 邓远, 陈轩, 覃建华, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组一段沉积期古地貌特征及有利储层分布[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(1):136-144 doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240113
DENG Yuan, CHEN Xuan, QIN Jianhua, et al. Paleogeomorphology and favorable reservoir distribution of the first member of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2024, 36(1):136-144.] doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240113
[27] 何起祥. 沉积动力学若干问题的讨论[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(4):1-10
HE Qixiang. A discussion on sediment dynamics[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(4):1-10.]
[28] 蔡毅, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 泥岩与页岩特征辨析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3):96-107
CAI Yi, ZHU Rukai, WU Songtao, et al. Discussion on characteristics of mudstone and shale[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3):96-107.]
-




 下载:
下载: