Early Pleistocene records of carbonate burial and terrestrial input in the Timor Sea and their paleoclimatic implications
-
摘要:
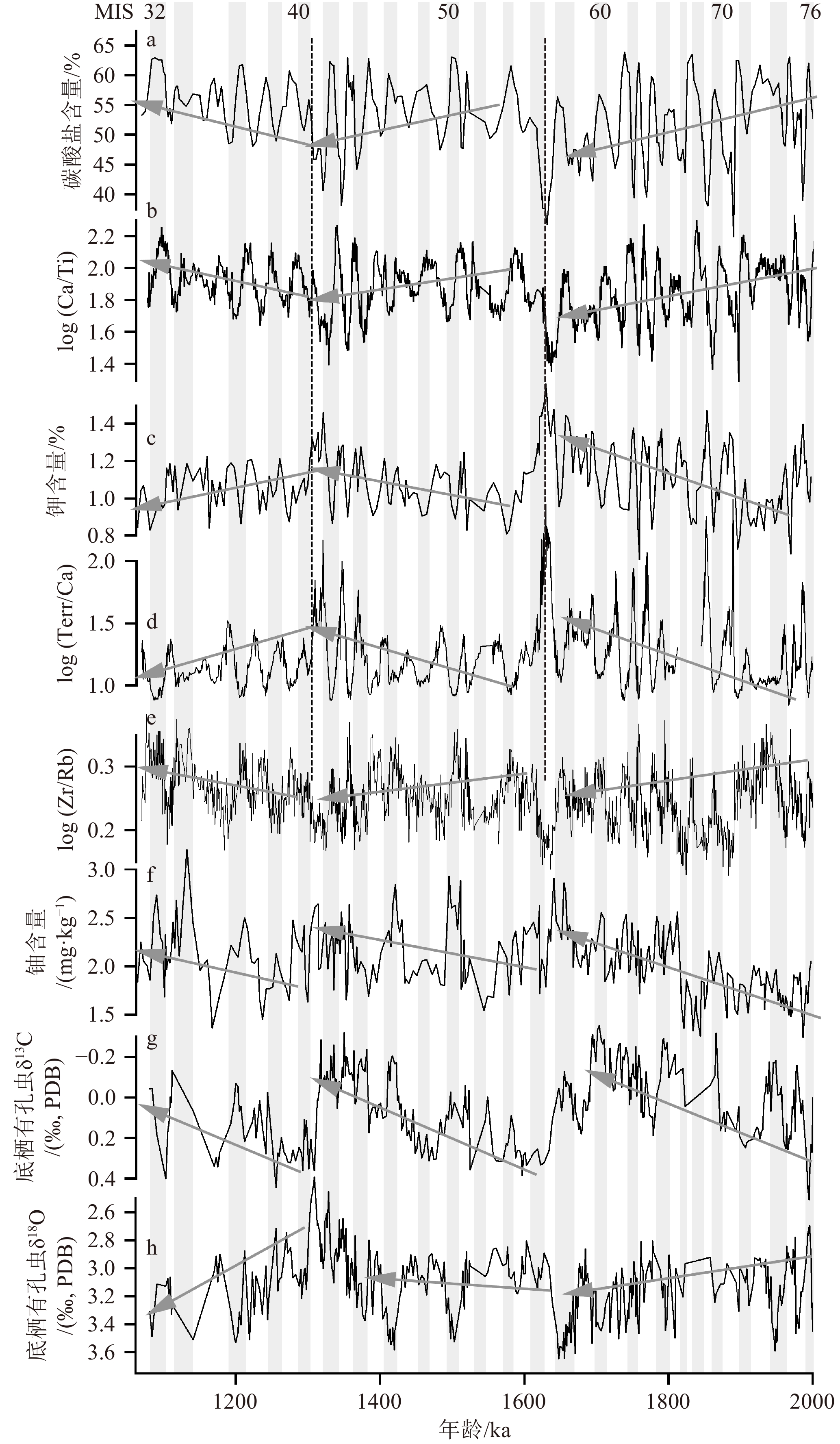
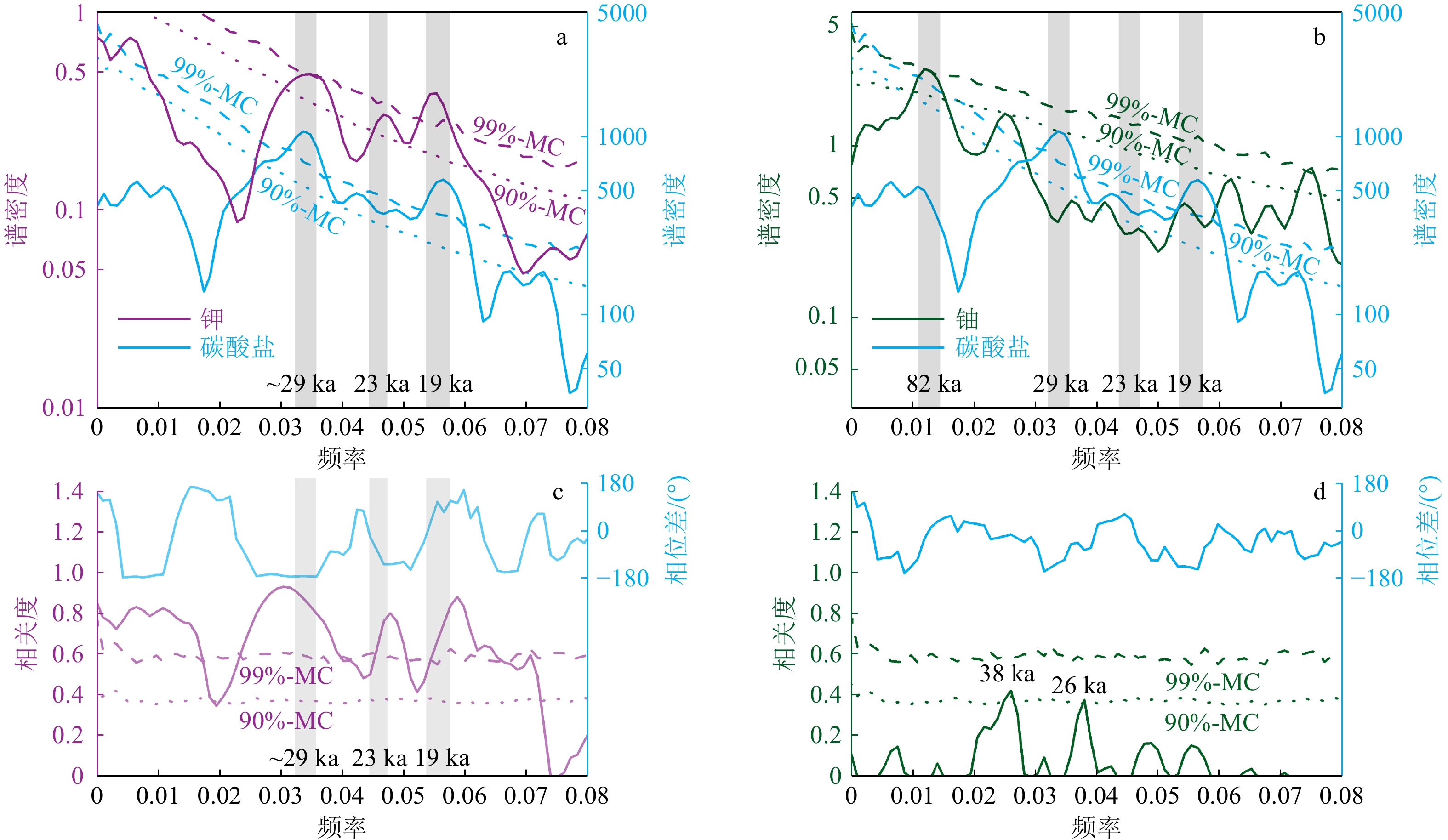
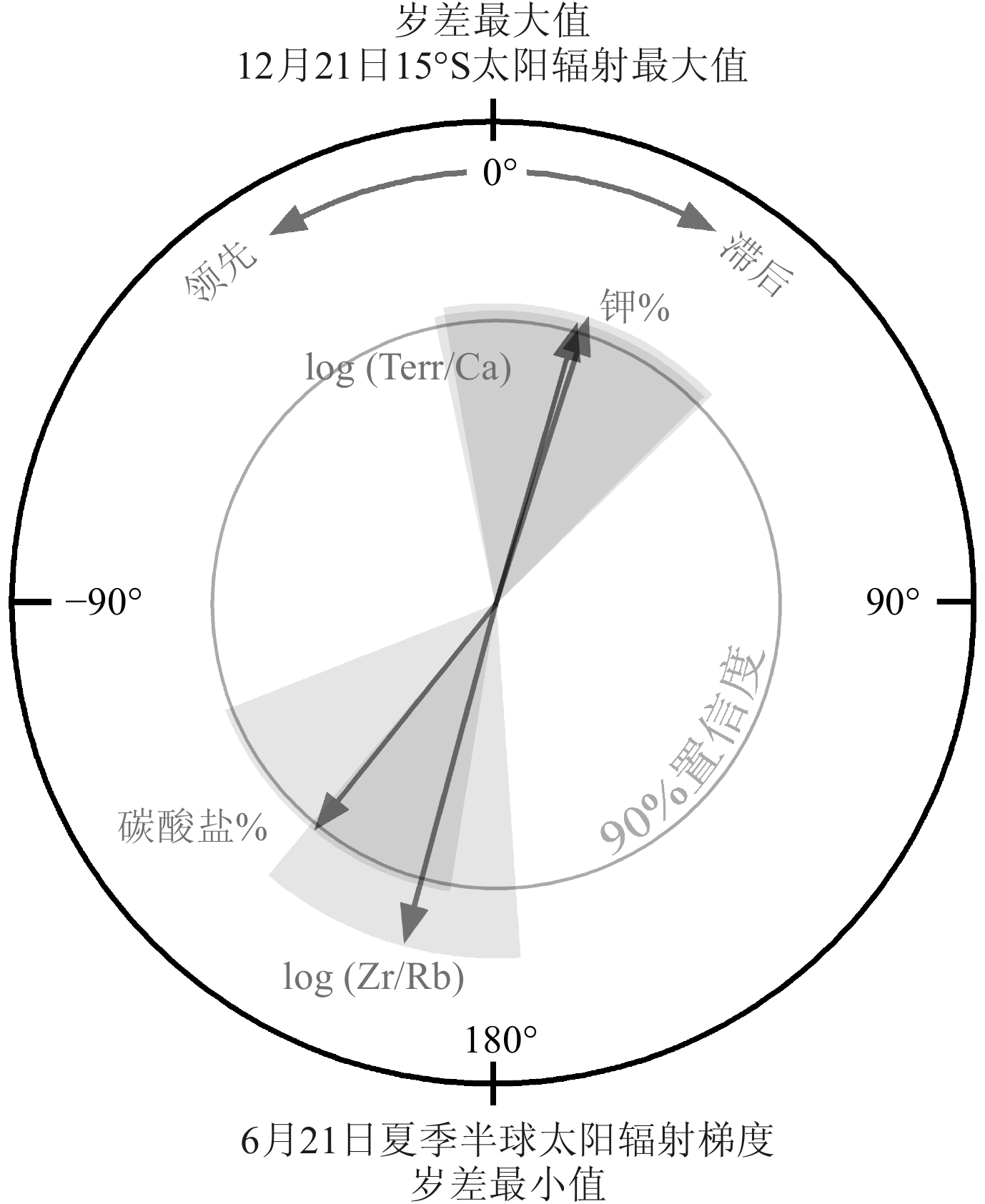
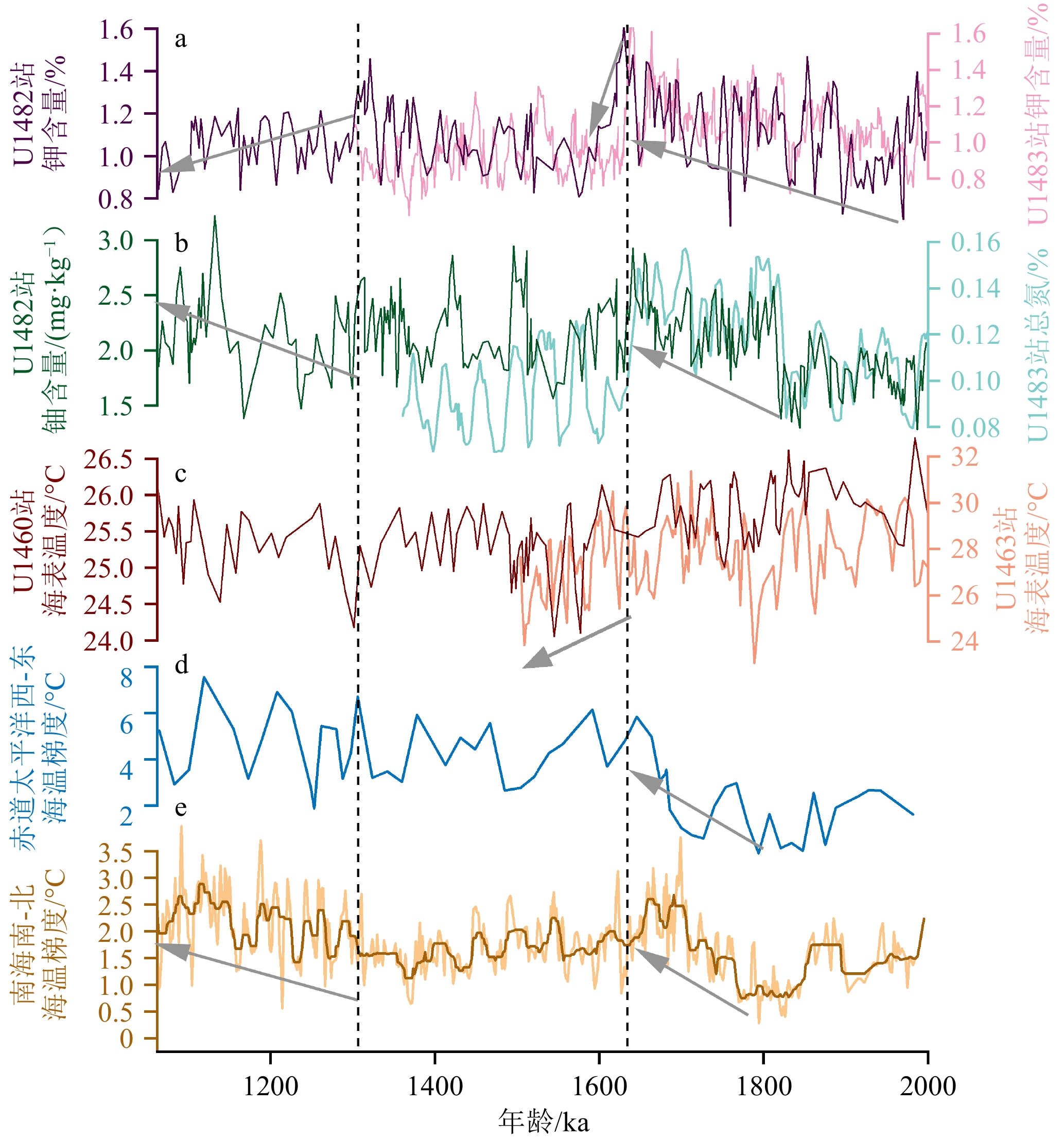
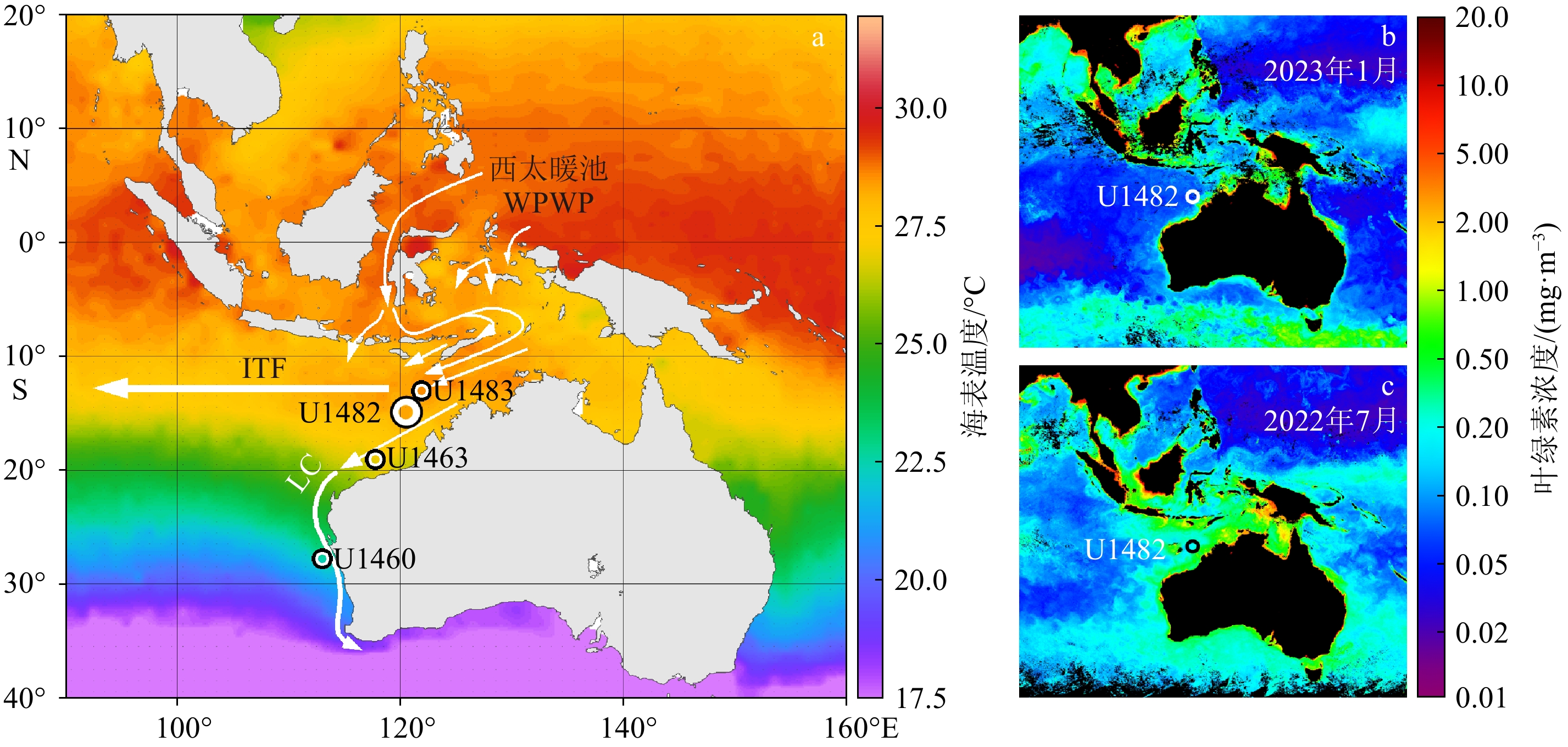
深海碳酸盐埋藏作为地球表层碳库的重要碳汇,在地质历史时期与大气二氧化碳浓度变化息息相关。古记录重建显示,大气二氧化碳浓度并不总是与全球平均气温具有较好的对应关系,其他因素可能在过去全球变化中起到了重要的作用。本文以澳大利亚西北岸外帝汶海IODP U1482站钻孔2~1.07 Ma沉积物为研究材料,测试其碳酸盐和主微量元素含量,探讨深海碳酸盐埋藏的影响因素。结果显示,碳酸盐含量与指示河流输入的钾元素含量、指示生产力的铀元素含量和底栖有孔虫δ13C以及指示风尘输入的log(Zr/Rb)等记录的长期变化趋势均可分为2~1.63 Ma、1.63~1.31 Ma和1.31~1.07 Ma等3个阶段,可能与沃克环流和哈德莱环流调控的印尼—澳洲地区的干湿条件有关。1.31 Ma之后钾元素含量的持续降低和碳酸盐含量的增加可能揭示哈德莱环流的加强导致了澳洲西北内陆的干旱化趋势。早更新世U1482站碳酸盐含量在轨道时间尺度上主要受以河流输入为主的陆源沉积物稀释的影响;频谱分析显示其具有显著的19 ka和约29 ka变化周期,可能指示该研究时段内除了岁差周期外,以斜率周期为主导的冰期-间冰期旋回对区域降水和陆源沉积物输入的调控作用。
Abstract:Deep-sea carbonate burial is an important carbon sink of the Earth’s surface carbon reservoir. Its variations are closely related to that of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Paleo-environment reconstructions show that changes in atmospheric CO2 concentration do not always correlate well with past temperature changes, implying that other factors may contribute to the past global change. We examined deep-sea sediments spanning the interval of 2~1.07 Ma retrieved from IODP Site U1482 located offshore northwestern Australia in the Timor Sea. Carbonate and elemental contents were analyzed to investigate the factors that influenced carbonate burial. The early Pleistocene records at Site U1482 indicate that all of our records including carbonate content, potassium content (a proxy of regional precipitation), log(Zr/Rb) (a proxy of aeolian dust input), benthic foraminiferal δ13C, and uranium content (proxies of paleoproductivity) show long-term changes punctuated at 1.63 Ma and 1.31 Ma, possibly related to the precipitation pattern over Indonesia-Australia modulated by Walker and Hadley circulations. The continuous decrease in carbonate content and increase in potassium content after 1.31 Ma likely implicate that the intensified aridification in the northwestern Australian hinterland was caused by strengthening of the Hadley circulation. Dilution by terrestrial sediments, mainly of riverine origin, is the predominant factor modifying carbonate content on orbital timescales. Spectral analysis shows that the carbonate record was dominated by 19 ka and 29 ka cycles, likely suggesting the effect of the obliquity-paced glacial/interglacial cyclicity on the regional precipitation and terrestrial input in addition to the precessional control.
-
Key words:
- carbonate content /
- regional precipitation /
- early Pleistocene /
- Timor Sea
-

-
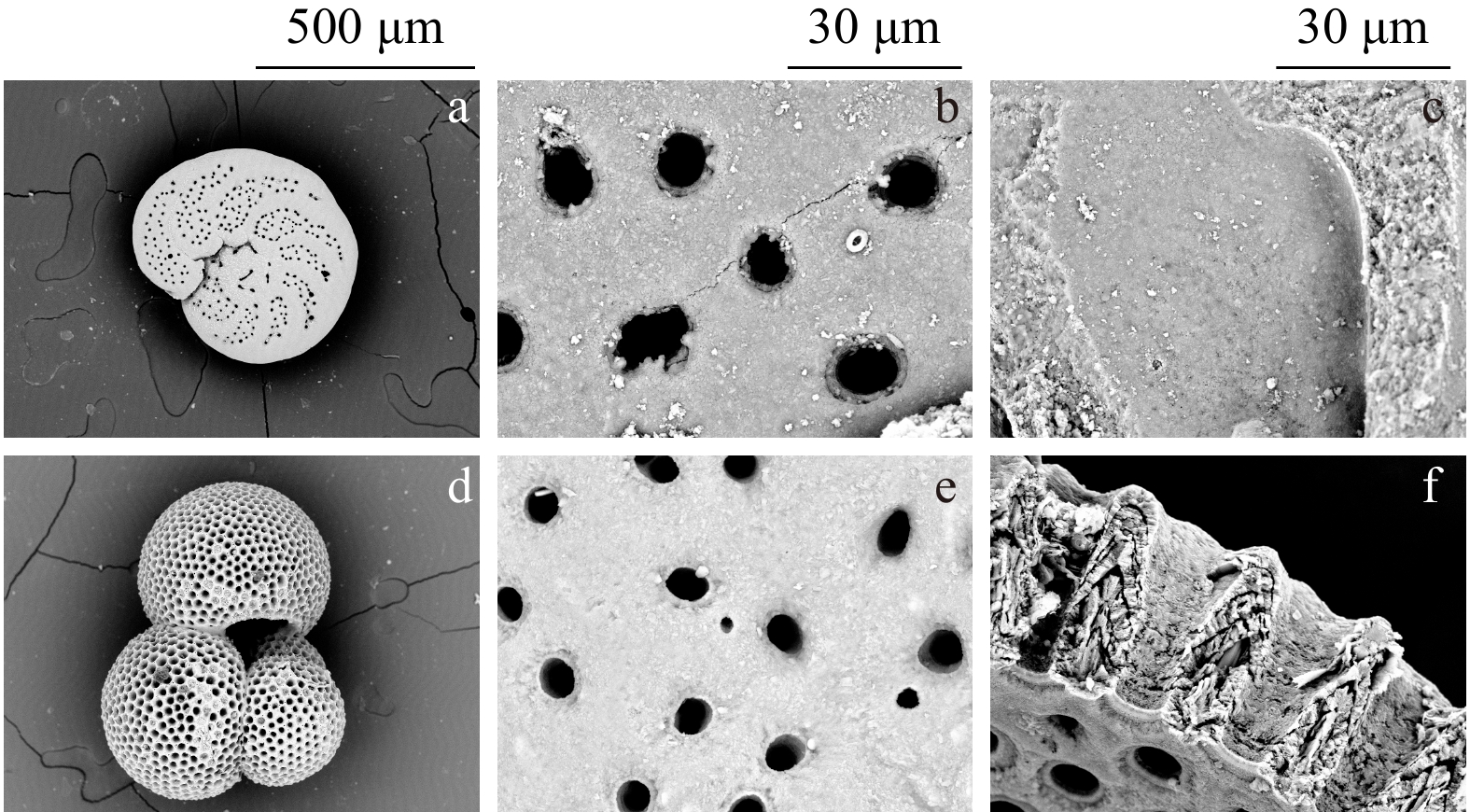
图 4 IODP U1482站有孔虫壳体和碎片扫描电镜照片[8]
Figure 4.
-
[1] Zeebe R E, Westbroek P. A simple model for the CaCO3 saturation state of the ocean: the “Strangelove, ” the “Neritan, ” and the “Cretan” Ocean[J]. Geochemistry, 2003, 4(12): 1104.
[2] Ridgwell A. A Mid Mesozoic Revolution in the regulation of ocean chemistry[J]. Marine Geology, 2005, 217(3-4):339-357. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.10.036
[3] Zhang Y G, Pagani M, Liu Z H, et al. A 40-million-year history of atmospheric CO2[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 2013, 371(2001):20130096. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2013.0096
[4] Ridgwell A, Zeebe R E. The role of the global carbonate cycle in the regulation and evolution of the earth system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 234(3-4):299-315. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.03.006
[5] Raymo M E, Ruddiman W F, Froelich P N. Influence of late Cenozoic mountain building on ocean geochemical cycles[J]. Geology, 1988, 16(7):649-653. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0649:IOLCMB>2.3.CO;2
[6] Berner R A, Lasaga A C, Garrels R M. The carbonate-silicate geochemical cycle and its effect on atmospheric carbon dioxide over the past 100 million years[J]. American Journal of Science, 1983, 283(7):641-683. doi: 10.2475/ajs.283.7.641
[7] Pagani M, Liu Z H, LaRiviere J, et al. High Earth-system climate sensitivity determined from Pliocene carbon dioxide concentrations[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2010, 3:27-30. doi: 10.1038/ngeo724
[8] Rosenthal Y, Holbourn A E, Kulhanek D K, et al. Western Pacific Warm Pool[M]. College Station: International Ocean Discovery Program, 2018.
[9] Straume E O, Nummelin A, Gaina C, et al. Climate transition at the Eocene–Oligocene influenced by bathymetric changes to the Atlantic–Arctic oceanic gateways[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022, 119(17):e2115346119.
[10] Wei J L, Liu H L, Zhao Y, et al. Simulation of the climate and ocean circulations in the middle Miocene climate optimum by a coupled model FGOALS-g3[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2023, 617:111509. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2023.111509
[11] Gordon A L. Oceanography of the Indonesian seas[J]. Oceanography, 2005, 18(4):13. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2005.18
[12] Cane M A, Molnar P. Closing of the Indonesian seaway as a precursor to east African aridification around 3-4 million years ago[J]. Nature, 2001, 411(6834):157-162. doi: 10.1038/35075500
[13] He Y X, Wang H Y, Liu Z H. Development of the Leeuwin Current on the northwest shelf of Australia through the Pliocene-Pleistocene period[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2021, 559:116767. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2021.116767
[14] Chen Y X, Xu J, Liu J, et al. Climatic and tectonic constraints on the Plio–Pleistocene evolution of the Indonesian Throughflow intermediate water recorded by benthic δ18O from IODP site U1482[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2022, 295:107666. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2022.107666
[15] Gordon A L, Susanto R D, Vranes K. Cool Indonesian throughflow as a consequence of restricted surface layer flow[J]. Nature, 2003, 425(6960):824-828. doi: 10.1038/nature02038
[16] Kuhnt W, Holbourn A, Hall R, et al. Neogene history of the Indonesian throughflow[M]//Clift P, Kuhnt W, Wang P, et al. Continent‐Ocean Interactions Within East Asian Marginal Seas. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 2004: 299-320.
[17] Talley L D, Sprintall J. Deep expression of the Indonesian Throughflow: Indonesian intermediate water in the South Equatorial Current[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2005, 110(C10):C10009.
[18] Sprintall J, Wijffels S E, Molcard R, et al. Direct estimates of the Indonesian Throughflow entering the Indian Ocean: 2004-2006[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2009, 114(C7):C07001.
[19] Rosenthal Y, Linsley B K, Oppo D W. Pacific Ocean heat content during the past 10, 000 years[J]. Science, 2013, 342(6158):617-621. doi: 10.1126/science.1240837
[20] 李铁刚, 熊志方, 贾奇. 晚中新世以来印度洋-太平洋暖池水体交换过程及其气候效应[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2020, 38(3):377-389 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2020.03.001
LI Tiegang, XIONG Zhifang, JIA Qi. Water exchange between western Pacific warm pool and Indian warm pool and its climatic effects since the late Miocene[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2020, 38(3):377-389.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2020.03.001
[21] Furnas M J, Carpenter E J. Primary production in the tropical continental shelf seas bordering northern Australia[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2016, 129:33-48. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2016.06.006
[22] Marin M, Feng M. Intra-annual variability of the North West Shelf of Australia and its impact on the Holloway Current: excitement and propagation of coastally trapped waves[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2019, 186:88-103. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2019.08.001
[23] Condie S A, Dunn J R. Seasonal characteristics of the surface mixed layer in the Australasian region: implications for primary production regimes and biogeography[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research, 2006, 57(6):569-590. doi: 10.1071/MF06009
[24] Pei R J, Kuhnt W, Holbourn A, et al. Monitoring Australian Monsoon variability over the past four glacial cycles[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 568:110280. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110280
[25] Sarim M, Xu J, Zhang P, et al. Late quaternary clay mineral and grain-size records from northwest Australia and their implications for paleoclimate, ocean currents, and paleodrainage of the Bonaparte basin[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2023, 610:111353. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.111353
[26] Hesse P P, McTainsh G H. Australian dust deposits: modern processes and the Quaternary record[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003, 22(18-19):2007-2035. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(03)00164-1
[27] Kuhnt W, Holbourn A, Schönfeld J, et al. Cruise report Sonne 257, WACHEIO - Western australian climate history from eastern Indian ocean sediment archives[R]. Darwin-Fremantle: Institut für Geowissenschaften, Christian-Albrechts-Universitat Kiel, 2017.
[28] Boyer T P, Garcia H E, Locarnini R A, et al. World Ocean Atlas 2018: sea surface temperature[DB/OL]. NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. [2022-10-24]. https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/archive/accession/NCEI-WOA18.
[29] Schlitzer R. Ocean data view[CP/DK]. [2023-10-25]. https://odv.awi.de.
[30] NASA. SeaWiFS Mission page[DB/OL]. [2023-04-07]. https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/.
[31] Murgese D S, de Deckker P. The Late Quaternary evolution of water masses in the eastern Indian Ocean between Australia and Indonesia, based on benthic foraminifera faunal and carbon isotopes analyses[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 247(3-4):382-401.
[32] de Deckker P, Barrows T T, Rogers J. Land–sea correlations in the Australian region: post-glacial onset of the monsoon in northwestern Western Australia[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 105:181-194. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.09.030
[33] Holbourn A, Kuhnt W, Kawamura H, et al. Orbitally paced paleoproductivity variations in the Timor Sea and Indonesian Throughflow variability during the last 460 kyr[J]. Paleoceanography, 2005, 20(3):PA3002.
[34] Lo Giudice Cappelli E, Holbourn A, Kuhnt W, et al. Changes in Timor Strait hydrology and thermocline structure during the past 130 ka[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 462:112-124. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.09.010
[35] Liu W, Baudin F, Moreno E, et al. Comparison of 240 ka long organic carbon and carbonate records along a depth transect in the Timor Sea: primary signals versus preservation changes[J]. Paleoceanography, 2014, 29(5):389-402. doi: 10.1002/2013PA002539
[36] de Vleeschouwer D, Dunlea A G, Auer G, et al. Quantifying K, U, and Th contents of marine sediments using shipboard natural gamma radiation spectra measured on DV JOIDES Resolution[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017, 18(3):1053-1064. doi: 10.1002/2016GC006715
[37] Ólafsdóttir K B, Schulz M, Mudelsee M. REDFIT-X: cross-spectral analysis of unevenly spaced paleoclimate time series[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2016, 91:11-18.
[38] 汪品先. 西太平洋边缘海的冰期碳酸盐旋回[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1998, 18(1):1-11
WANG Pinxian. Glacial carbonate cycles in western Pacific marginal seas[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1998, 18(1):1-11.]
[39] Feely R A, Sabine C L, Lee K, et al. In situ calcium carbonate dissolution in the Pacific Ocean[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2002, 16(4):1144.
[40] Fischer G, Wefer G. Use of Proxies in Paleoceanography: Examples from the South Atlantic[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1999: 255-284.
[41] Sulpis O, Jeansson E, Dinauer A, et al. Calcium carbonate dissolution patterns in the ocean[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2021, 14(6):423-428. doi: 10.1038/s41561-021-00743-y
[42] Kuhnt W, Holbourn A, Xu J, et al. Southern Hemisphere control on Australian monsoon variability during the late deglaciation and Holocene[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6:5916. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6916
[43] Zhang P, Xu J, Holbourn A, et al. Obliquity induced latitudinal migration of the Intertropical Convergence Zone during the past ~410 kyr[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(21):e2022GL100039. doi: 10.1029/2022GL100039
[44] Liu L W, Chen J, Chen Y, et al. Variation of Zr/Rb ratios on the Loess Plateau of Central China during the last 130000 years and its implications for winter monsoon[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(15):1298-1302. doi: 10.1360/02tb9288
[45] Schofield A. Uranium Content of Igneous Rocks of Australia 1:5000000 Maps—Explanatory Notes and Discussion[M]. Camberra: Geoscience Australia, 2009: 20.
[46] McManus J, Berelson W M, Klinkhammer G P, et al. Authigenic uranium: relationship to oxygen penetration depth and organic carbon rain[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(1):95-108. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.06.023
[47] Auer G, Hauzenberger C A, Reuter M, et al. Orbitally paced phosphogenesis in Mediterranean shallow marine carbonates during the middle Miocene Monterey event[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2016, 17(4):1492-1510. doi: 10.1002/2016GC006299
[48] Zhang Y, Andrade T, Ravelo A C, et al. Aridification of northwest Australia and nutrient decline in the Timor sea during the 40 Kyr world[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2023, 38(10):e2023PA004683. doi: 10.1029/2023PA004683
[49] Auer G, Petrick B, Yoshimura T, et al. Intensified organic carbon burial on the Australian shelf after the Middle Pleistocene transition[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2021, 262:106965. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2021.106965
[50] Lea D W, Pak D K, Spero H J. Climate impact of late quaternary equatorial pacific sea surface temperature variations[J]. Science, 2000, 289(5485):1719-1724. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5485.1719
[51] Etourneau J, Schneider R, Blanz T, et al. Intensification of the Walker and Hadley atmospheric circulations during the Pliocene-Pleistocene climate transition[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 297(1-2):103-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2010.06.010
[52] Herbert T D, Peterson L C, Lawrence K T, et al. Tropical ocean temperatures over the past 3.5 million years[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5985):1530-1534. doi: 10.1126/science.1185435
[53] Petrick B, Martínez-García A, Auer G, et al. Glacial Indonesian throughflow weakening across the mid-Pleistocene climatic transition[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1):16995. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53382-0
[54] Smith R A, Castañeda I S, Groeneveld J, et al. Retracted: Plio-Pleistocene Indonesian throughflow variability drove eastern Indian ocean sea surface temperatures[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2020, 35(10):e2020PA003872. doi: 10.1029/2020PA003872
[55] Wara M W, Ravelo A C, Delaney M L. Permanent El Niño-like conditions during the Pliocene warm period[J]. Science, 2005, 309(5735):758-761. doi: 10.1126/science.1112596
[56] Li L, Li Q Y, Tian J, et al. A 4-Ma record of thermal evolution in the tropical western Pacific and its implications on climate change[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 309(1-2):10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2011.04.016
[57] Stuut J B W, De Deckker P, Saavedra-Pellitero M, et al. A 5.3-million-year history of monsoonal precipitation in northwestern Australia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2019, 46(12):6946-6954. doi: 10.1029/2019GL083035
[58] Christensen B A, Renema W, Henderiks J, et al. Indonesian Throughflow drove Australian climate from humid Pliocene to arid Pleistocene[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(13):6914-6925. doi: 10.1002/2017GL072977
[59] Fedorov A V, Brierley C M, Lawrence K T, et al. Patterns and mechanisms of early Pliocene warmth[J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7443):43-49. doi: 10.1038/nature12003
[60] Chen H J, Xu Z K, Lim D, et al. Geochemical records of the provenance and silicate weathering/erosion from the eastern Arabian sea and their responses to the Indian summer monsoon since the mid-Pleistocene[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2020, 35(4):e2019PA003732. doi: 10.1029/2019PA003732
[61] Beaufort L, de Garidel-Thoron T, Mix A C, et al. ENSO-like forcing on oceanic primary production during the Late Pleistocene[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5539):2440-2444. doi: 10.1126/science.293.5539.2440
[62] Di Nezio P N, Timmermann A, Tierney J E, et al. The climate response of the Indo-Pacific warm pool to glacial sea level[J]. Paleoceanography, 2016, 31(6):866-894. doi: 10.1002/2015PA002890
[63] Windler G, Tierney J E, DiNezio P N, et al. Shelf exposure influence on Indo-Pacific Warm Pool climate for the last 450, 000 years[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2019, 516:66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2019.03.038
[64] Liautaud P, Huybers P. Uniformitarian prediction of early-Pleistocene atmospheric CO2[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(20):e2022GL100304. doi: 10.1029/2022GL100304
-



 下载:
下载: