Holocene extreme flood events in the Yangtze River Basin: Research progress and implications
-
摘要:
随着全球气候变暖和人类活动加剧,全球洪水事件的发生频率与强度正在快速变化,揭示洪水发生规律及其驱动机制是当前古洪水水文学和全球变化研究的热点问题。长江流域作为中国洪涝灾害最为严重的区域之一,其洪水活动近年来呈现快速异常变化,较短的现代器测记录已不能满足未来洪水灾害风险预测的需求,迫切需要通过各种长时间尺度记录揭示过去时期长江流域洪水事件与气候变化之间的关系。本文通过综述各种极端洪水事件的地质记录和历史记录,确定全新世以来极端洪水事件的频发期,并与区域关键气候代用指标进行对比,发现洪水事件频发期主要跟气候的急剧突变和强烈的人类活动有关。然而准确预测长江流域洪水事件未来演化趋势,需不断加强各种代用记录的综合研究,进一步探索洪水发生机制与气候变化和人类活动耦合关系,并加强有关数值模拟方面的研究,以便于为未来长江流域的洪涝灾害防御、城乡规划优化布局、资源合理开发利用提供科学依据和决策支持。
Abstract:With global warming and the intensification of human activities, the frequency and magnitude of large river flood events are increasing in recent years. To reveal the regularity of flood occurrence and its driving mechanism is a hot issue in the study of paleoflood hydrology and global change. As one of the regions with the most severe flood disasters in China, the Yangtze River Basin has shown rapid and abnormal changes in flood activities in recent years. Short modern measurement records can no longer meet the needs of future flood disaster risk prediction, and it is urgent to reveal the relationship between flood events and climate change in the Yangtze River Basin in the past through various long-term records. By summarizing the geological and historical records of various extreme flood events, the frequent periods of extreme flood events since the Holocene were determined and compared with key regional climate proxies. However, to accurately predict the future evolution trend of flood events in the Yangtze River Basin, it is necessary to strengthen continuously the comprehensive research of various proxy records, to further explore the coupling relationship of flood occurrence mechanisms to climate changes and human activities, and to strengthen research on numerical simulation. This study provided a scientific basis and decision support for future flood disaster prevention, urban and rural planning optimization layout, and rational resource development and utilization in the Yangtze River Basin.
-
Key words:
- paleoflood events /
- sedimentary record /
- global warming /
- human activities /
- the Yangtze River
-

-
表 1 长江流域极端洪水事件研究剖面位置及代用指标
Table 1. Site and proxy of research profiles of extreme flood events in Yangtze River Basin
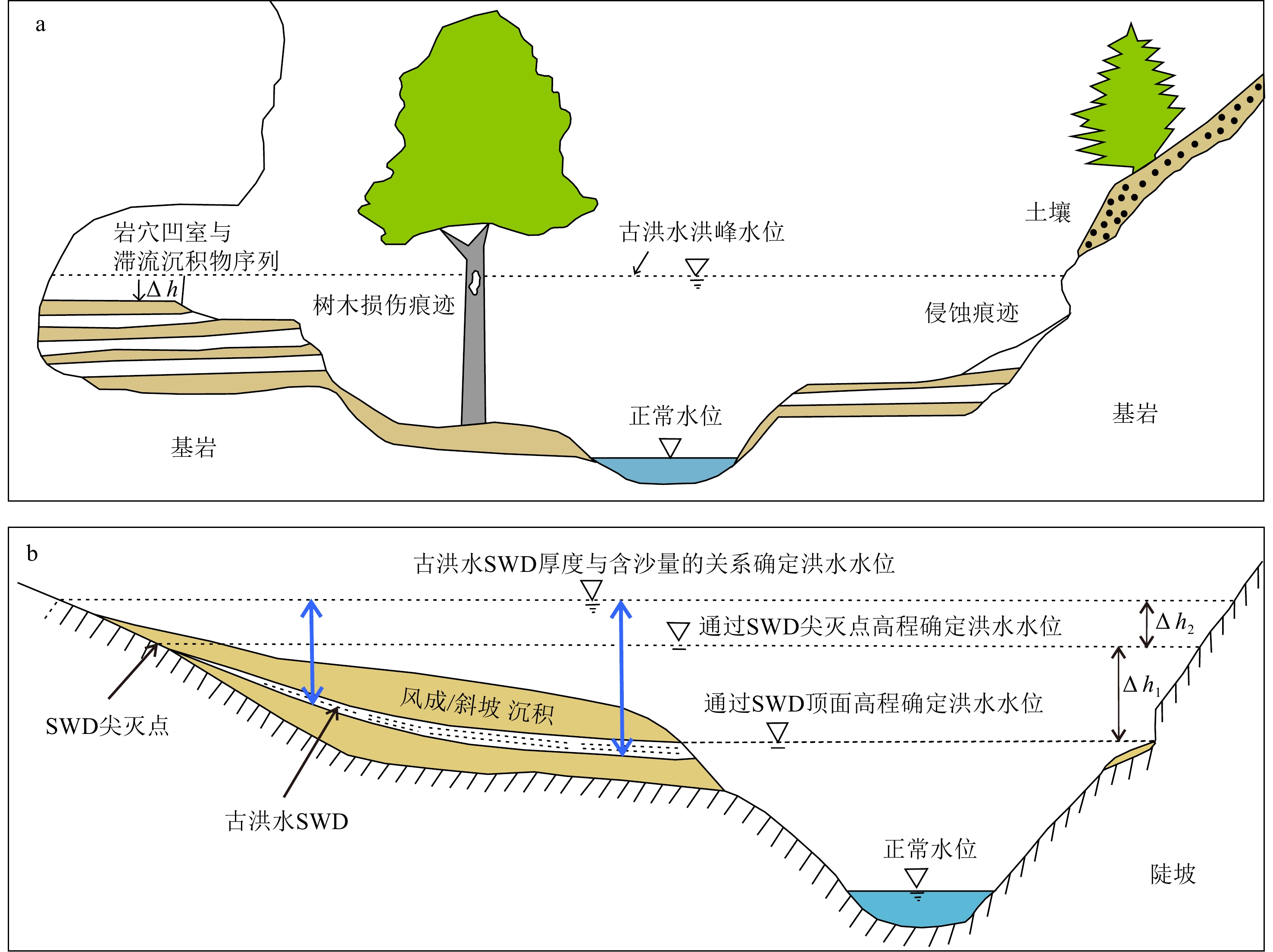
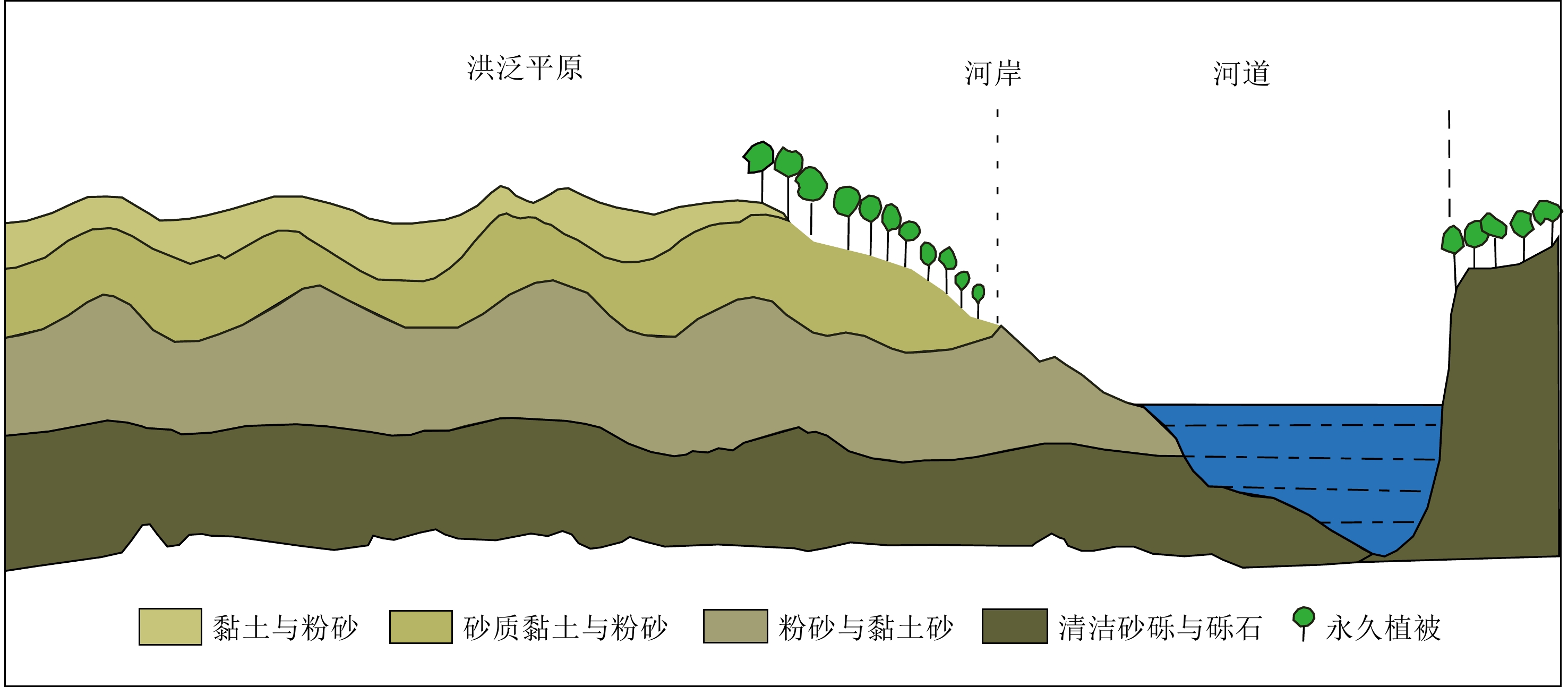
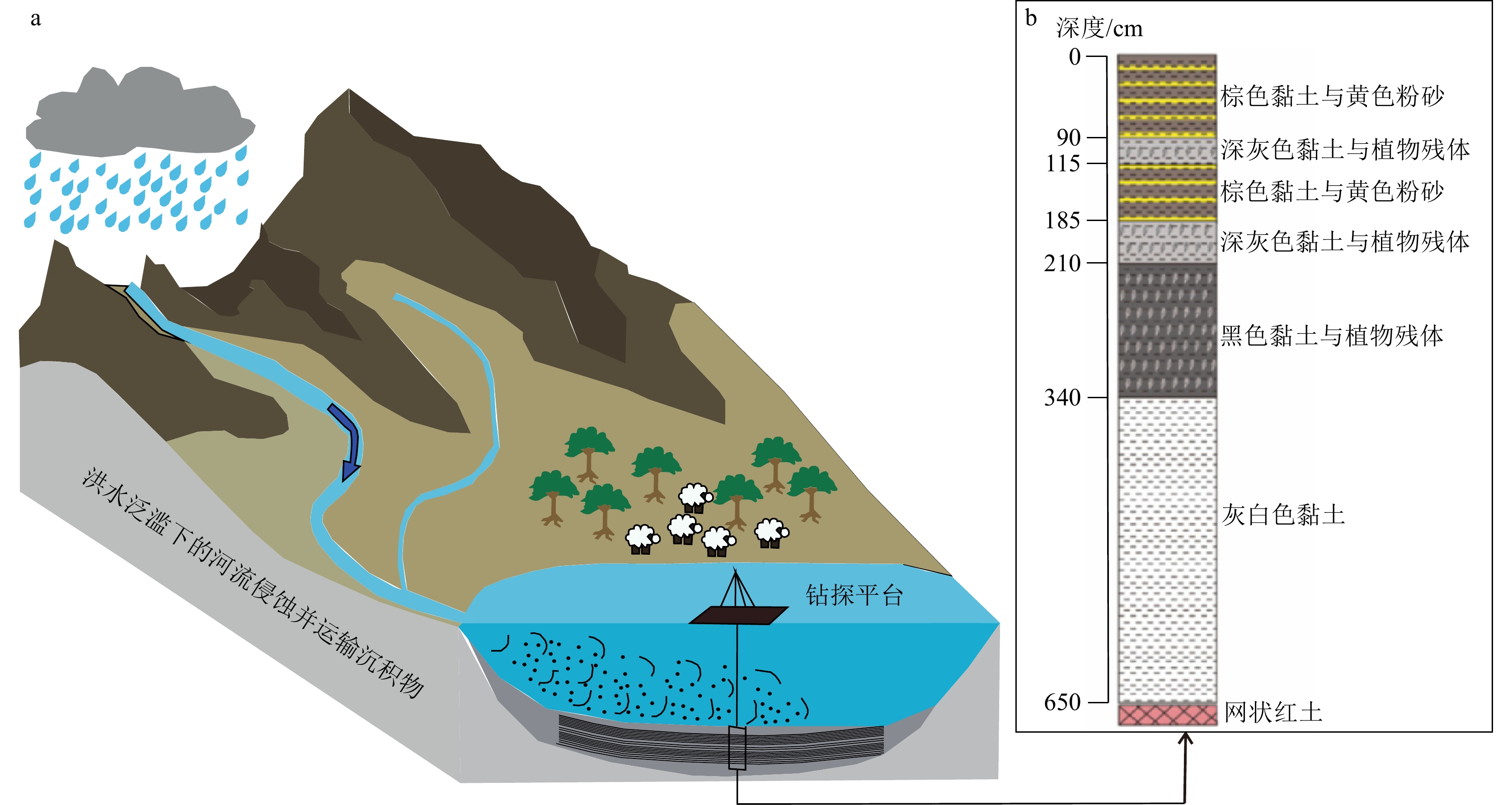
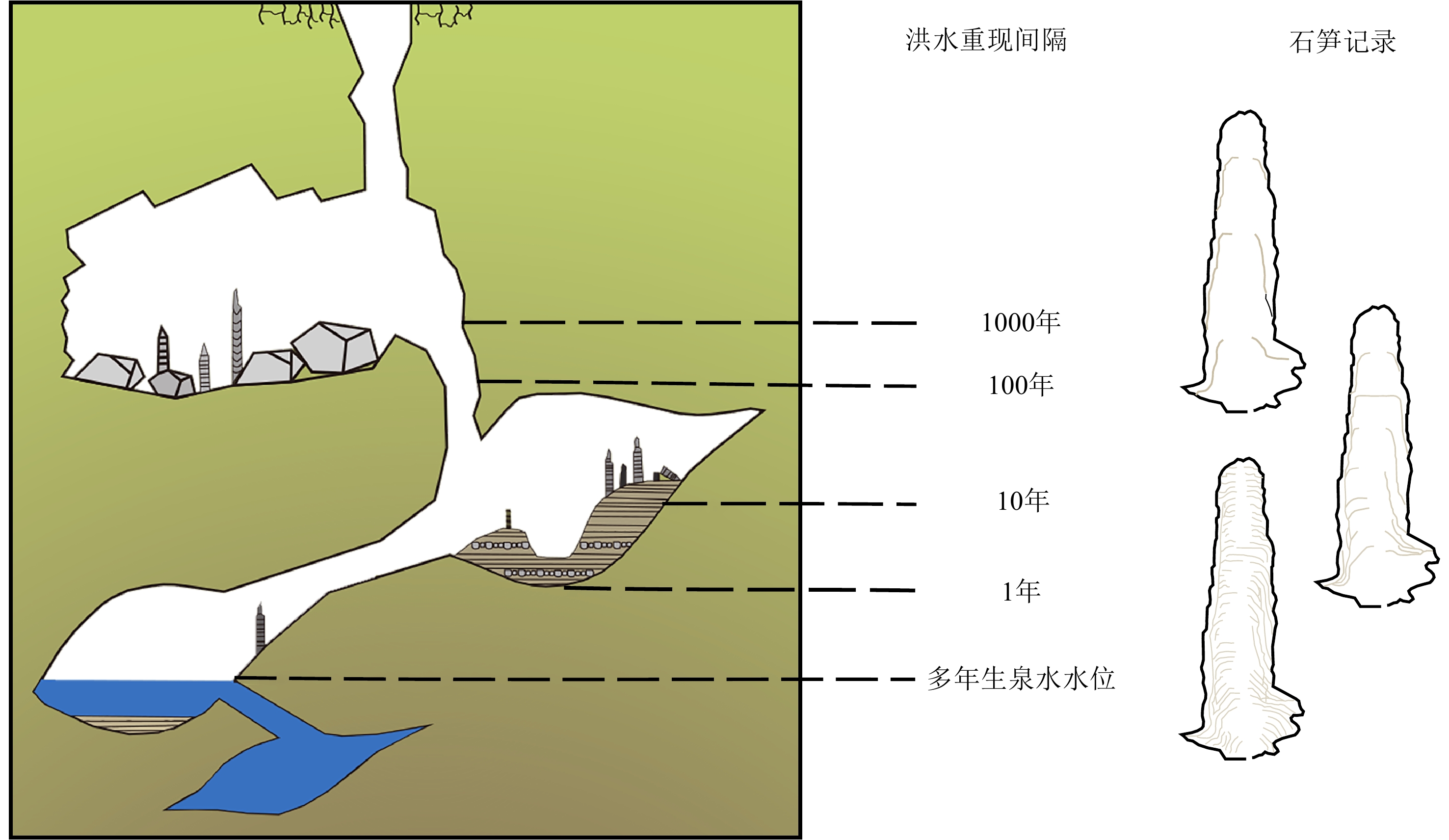
序号 河段 剖面位置 经纬度 地质记录类型 文献来源 1 上游 中坝遗址 30.34°N、108.45°E 文化遗址 [12] 2 玉溪遗址 30.03°N、107.86°E 文化遗址 [13] 3 红桥村 30.68°N、103.88°E 文化遗址 [14] 4 金沙遗址 30.68°N、104.00°E 文化遗址 [15] 5 马街遗址 30.89°N、103.92°E 文化遗址 [16] 6 张家湾遗址 31.27°N、109.77°E 文化遗址 [17] 7 汉东城遗址 29.00°N、105.84°E 文化遗址 [18] 8 涪碛口遗址 29.20°N、108.75°E 文化遗址 [19] 9 中游 曲远河 32.87°N、110.62°E 自然剖面 [20] 10 尚家河 32.84°N、110.46°E 自然剖面 [21] 11 庹家洲 32.85°N、110.39°E 自然剖面 [22] 12 庹家湾 32.86°N、110.39°E 自然剖面 [23] 13 李家咀 32.82°N、110.77°E 自然剖面 [24] 14 晏家棚 32.83°N、110.43°E 自然剖面 [25] 15 归仙河口 32.82°N、110.54°E 自然剖面 [22] 16 弥陀寺 32.82°N、110.58°E 自然剖面 [26] 17 前坊村 32.83°N、110.98°E 自然剖面 [27] 18 辽瓦店 32.82°N、110.68°E 自然剖面 [24] 19 黄坪村 32.84°N、110.74°E 自然剖面 [28] 20 万春村 33.19°N、107.69°E 自然剖面 [29] 21 祥龙洞 33.00°N、106.33°E 自然剖面 [30] 22 尾笔村 30.39°N、114.47°E 自然剖面 [31] 23 焦家台子 32.82°N、110.16°E 自然剖面 [32] 24 罗家滩 32.78°N、109.35°E 自然剖面 [33] 25 楼子滩 33.46°N、110.51°E 自然剖面 [34] 26 泥沟口 32.89°N、109.53°E 自然剖面 [35] 27 立石村 30.20°N、105.30°E 自然剖面 [36] 28 新滩村 32.76°N、109.33°E 自然剖面 [37] 29 杜家沟 33.19°N、107.67°E 自然剖面 [38] 30 三房湾 30.46°N、113.04°E 自然剖面 [39] 31 江北农场二砖厂 30.18°N、112.34°E 自然剖面 [40] 32 消泗剖面 30.32°N、113.78°E 自然剖面 [41] 33 武汉 30.64°N、114.34°E 自然剖面 [42] 34 SK10 30.60°N、114.31°E 自然剖面 [43] 35 ZK145 30.66°N、114.44°E 自然剖面 [44-45] 36 钟桥遗址 30.31°N、112.27°E 文化遗址 [46] 37 中游 JH001 30.52°N、114.39°E 自然剖面 [47] 38 扬子江剖面 30.30°N、112.12°E 自然剖面 [48] 39 网湖 29.86°N、115.33°E 自然剖面 [49] 40 中洲子 29.80°N、112.75°E 自然剖面 [50] 41 天鹅洲 29.85°N、112.57°E 自然剖面 [51] 42 下游 修河 29.05°N、115.83°E 自然剖面 [52] 43 赣江 29.10°N、116.00°E 自然剖面 [52] 44 黄茅潭 29.80°N、116.35°E 自然剖面 [52] 45 大汊湖 29.10°N、116.01°E 自然剖面 [52] 46 东门镇林峰桥 32.14°N、118.70°E 自然剖面 [53] 47 宝华山-和平冲 32.16°N、119.02°E 自然剖面 [54] 48 宝华山 32.13°N、119.09°E 自然剖面 [54] 表 2 长江流域滞流沉积物与冲积平原沉积物宏观特征对比
Table 2. Comparison of macroscopic characteristics of slack water deposits in the Yangtze River Basin and overbank flooding deposits in the floodplain
-
[1] Baker V R. Paleoflood hydrology and extraordinary flood events[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1987, 96(1-4):79-99. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(87)90145-4
[2] 顾西辉, 张强, 孔冬冬. 中国极端降水事件时空特征及其对夏季温度响应[J]. 地理学报, 2016, 71(5):718-730 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201605002
GU Xihui, ZHANG Qiang, KONG Dongdong. Spatiotemporal patterns of extreme precipitation with their responses to summer temperature[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2016, 71(5):718-730.] doi: 10.11821/dlxb201605002
[3] 王立琨, 陶祖钰, 杨阳, 等. 1998年长江洪水大暴雨的卫星云图分析[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 36(1):87-94
WANG Likun, TAO Zuyu, YANG Yang, et al. Analysis of satellite image characters of severe storm rainfall during the flood of Yangtze River in 1998[J]. Acta Scicentiarum Naturalum Universitis Pekinesis, 2000, 36(1):87-94.]
[4] 新华社. 河南郑州"7·20"特大暴雨灾害调查报告公布[EB/OL]. [2-11-26]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-01/21/content_5669723.htm.
Xinhua News Agency. Investigation Report on "7·20" Heavy Rainstorm Disaster in Zhengzhou[EB/OL]. [2022-11-26]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-01/21/content_5669723.htm.
[5] 余锡平, 单楷越. 华北平原极端暴雨洪水事件共性机制探讨及对策建议[J]. 中国水利, 2023, 58(18):24-28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2023.18.007
YU Xiping, SHAN Kaiyue. Common mechanisms and disaster prevention strategies for catastrophic rainfall and flooding events in the North China Plain[J]. China Water Resources, 2023, 58(18):24-28.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2023.18.007
[6] Yu S Y, Li W J, Zhou L, et al. Human disturbances dominated the unprecedentedly high frequency of Yellow River flood over the last millennium[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(8):eadf8576. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf8576
[7] 高启慧, 秦圆圆, 梁媚聪, 等. IPCC第六次评估报告综合报告解读及对我国的建议[J]. 环境保护, 2023, 51(Z2):82-84
GAO Qihui, QIN Yuanyuan, LIANG Meicong, et al. Interpretation of the main conclusions and suggestions of IPCC AR6 synthesis report[J]. Environmental Protection, 2023, 51(Z2):82-84.]
[8] Ely L L, Enzel Y, Baker V R, et al. A 5000-year record of extreme floods and climate change in the southwestern United States[J]. Science, 1993, 262(5132):410-412. doi: 10.1126/science.262.5132.410
[9] Ely L L. Response of extreme floods in the southwestern United States to climatic variations in the Late Holocene[J]. Geomorphology, 1997, 19(3-4):175-201. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(97)00014-7
[10] Gong D Y, Zhu J H, Wang S W. Flooding 1990s along the Yangtze River, has it concern of global warming?[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2001, 11(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/BF02837375
[11] Trenberth K E, Dai A G, Rasmussen R M, et al. The changing character of precipitation[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2003, 84(9):1205-1218. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-84-9-1205
[12] Zhu C, Zheng C G, Ma C M, et al. Identifying paleoflood deposits archived in Zhongba Site, the Three Gorges reservoir region of the Yangtze River, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(21):2493-2504. doi: 10.1007/BF03183641
[13] Zhu C, Ma C M, Xu W F, et al. Characteristics of paleoflood deposits archived in unit T0403 of Yuxi Site in the Three Gorges reservoir areas, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(S1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s11434-008-5005-8
[14] Huang M, Zhu C, Ma C M, et al. The hongqiaocun site: the earliest evidence of ancient flood sedimentation of the water conservancy facilities in the Chengdu Plain, China[J]. CATENA, 2020, 185:104296. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.104296
[15] Jia T J, Ma C M, Zhu C, et al. Depositional evidence of palaeofloods during 4.0-3.6 ka BP at the Jinsha site, Chengdu Plain, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 440:78-89. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.07.008
[16] 朱诚, 徐佳佳, 黄明, 等. 成都平原马街遗址古洪水事件遗存考古发现与研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(2):181-201
ZHU Cheng, XU Jiajia, HUANG Ming, et al. Archaeological discoveries and research on the remains of an ancient flood event at the Majie Site in the Chengdu Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(2):181-201.]
[17] 张芸, 朱诚. 长江三峡大宁河流域大昌地区环境考古[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(S1): 121-131
ZHANG Yun, ZHU Cheng. Environmental archaeology of the dachang region in the Daning Valley, the Three Gorges reservoir region of the Yangtze River, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(S1): 140-152.]
[18] 李兰, 白九江, 代玉彪. 重庆永川汉东城遗址地层记录的长江上游唐代洪水事件[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(2):556-567 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.02.24
LI Lan, BAI Jiujiang, DAI Yubiao. Flood event recorded by the layer of handongcheng site and its significance to the Upper reaches of yangtze river[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(2):556-567.] doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.02.24
[19] 李杰, 郑卓, 邹后曦, 等. 重庆阿蓬江涪碛口遗址近3000年来环境变化研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31(3):554-565 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.03.19
LI Jie, ZHENG Zhuo, ZOU Houxi, et al. Evironmental research of a 3000 year record from fuqikou archaeological sites in apeng river, chongqing[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2011, 31(3):554-565.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.03.19
[20] 郑树伟, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 汉江上游郧县曲远河河口段全新世古洪水水文状态研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2013, 22(12):1608-1613
ZHENG Shuwei, PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Palaeoflood hydrological study in the quyuanhekou reach in the Upper reaches of the hanjiang river[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2013, 22(12):1608-1613.]
[21] Zha X, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Reconstructing the palaeoflood events from slackwater deposits in the Upper reaches of Hanjiang River, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 380-381:358-367. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.06.029
[22] Mao P N, Pang J L, Huang C C, et al. A multi-index analysis of the extraordinary paleoflood events recorded by slackwater deposits in the Yunxi Reach of the Upper Hanjiang River, China[J]. CATENA, 2016, 145:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2016.05.016
[23] 查小春, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 汉江上游郧西段全新世古洪水事件研究[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(5):671-680 doi: 10.11821/xb201205009
ZHA Xiaochun, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. The Holocene palaeoflood events in the yunxi reach in the Upper reaches of Hanjiang River[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(5):671-680.] doi: 10.11821/xb201205009
[24] 查小春, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 汉江上游沉积记录的东汉时期古洪水事件考证研究[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(9):1634-1644 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201709008
ZHA Xiaochun, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. The palaeoflood events recorded by slackwater deposits in sedimentary profiles during the eastern Han Dynasty in the Upper reaches of the Hanjiang River[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(9):1634-1644.] doi: 10.11821/dlxb201709008
[25] 吉琳, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 汉江上游晏家棚段全新世古洪水研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(4):487-494
JI Lin, PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Holocene palaeoflood studies of the Yanjiapeng reach in the Upper Hanjiang River, China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(4):487-494.]
[26] 郑树伟, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 湖北弥陀寺汉江段北宋时期古洪水研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2015, 24(3):153-160
ZHENG Shuwei, PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Study on palaeoflood in northern Song Period at Mituosi segment of Hanjiang River, Hubei province[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2015, 24(3):153-160.]
[27] Huang C C, Pang J L, Zha X, et al. Extraordinary hydro-climatic events during the Period AD 200−300 recorded by slackwater deposits in the Upper Hanjiang River valley, China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 374:274-283. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.02.001
[28] 郑树伟, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 汉江上游黄坪村段古洪水滞流沉积物研究及意义[J]. 土壤通报, 2014, 45(5):1025-1031
ZHENG Shuwei, PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, et al. The significance of palaeoflood slack water deposit in Huang Ping Site in Hanjiang River[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2014, 45(5):1025-1031.]
[29] Guo Y Q, Huang C C, Zhou Y L, et al. Sedimentary record and luminescence chronology of palaeoflood events along the Gold Gorge of the Upper Hanjiang River, Middle Yangtze River Basin, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 156:96-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.12.034
[30] Tan L C, Cai Y J, Cheng H, et al. Centennial-to decadal-scale monsoon precipitation variations in the Upper Hanjiang River region, China over the past 6650 years[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 482:580-590. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.11.044
[31] Guo Y Q, Huang C C, Zhou Y L, et al. Extraordinary flood events and the response to monsoonal climatic change during the last 3000 years along the Middle Yangtze River valley, China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 462:70-84. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.09.005
[32] 李晓刚, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 汉江上游白河段万年尺度洪水水文学研究[J]. 地理科学, 2012, 32(8):971-978
LI Xiaogang, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Palaeoflood hydrological study in the baihe reach in the Upper reaches of the Hanjiang River[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2012, 32(8):971-978.]
[33] Zhang Y Z, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Holocene paleofloods related to climatic events in the Upper reaches of the Hanjiang River valley, Middle Yangtze River Basin, China[J]. Geomorphology, 2013, 195:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.03.032
[34] Li X G, Huang C C, Zhang Y Z, et al. Hydrological reconstruction of extreme palaeoflood events 9000-8500 a BP in the Danjiang River Valley, tributary of the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2020, 13:137. doi: 10.1007/s12517-020-5132-3
[35] Wang L S, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Paleofloods recorded by slackwater deposits in the Upper reaches of the Hanjiang River valley, Middle Yangtze River Basin, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 519:1249-1256. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.08.002
[36] 周亮, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 汉江上游安康东段古洪水事件光释光测年研究[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(11):1703-1714
ZHOU Liang, HUANG Chunchang, ZHOU Yali, et al. OSL dating of the palaeoflood events in the ankang east reach in the Upper Hanjiang River valley[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(11):1703-1714.]
[37] Guo Y Q, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Investigating extreme flood response to Holocene palaeoclimate in the Chinese monsoonal zone: a palaeoflood case study from the Hanjiang River[J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 238:187-197. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.03.014
[38] Mao P N, Pang J L, Huang C C, et al. Paleoflood evidence for an Upper limit of the maximum flood magnitudes along the Gold Gorge, the Upper Hanjiang River, China[J]. CATENA, 2022, 212:106111. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2022.106111
[39] Jia M, Li C, Mao X, et al. Climate–human–environment interactions in the middle Yangtze Basin (central China) during the middle Holocene, based on pollen and geochemical records from the Sanfangwan Site[J]. Catena, 2021, 204:105357. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105357
[40] 张玉芬, 李长安, 陈亮, 等. 基于磁组构特征的江汉平原全新世古洪水事件[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(6):985-992 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2009.112
ZHANG Yufen, LI Chang’an, CHEN Liang, et al. Magnetic fabric of Holocene palaeo-floods events in Jianghan plain[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009, 34(6):985-992.] doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2009.112
[41] 陈亮, 张玉芬, 李长安, 等. 江汉平原消泗剖面沉积物磁组构特征[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2007, 4(3):190-195 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2007.03.005
CHEN Liang, ZHANG Yufen, LI Chang’an, et al. Magnetic fabric characteristics of the sediments in the xiaosi profile of Jianghan Plain of Hubei province[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2007, 4(3):190-195.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2007.03.005
[42] Liu X J, Min F Y, Kettner A J. The impact of large to extreme flood events on floodplain evolution of the Middle and Lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China[J]. CATENA, 2019, 176:394-409. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.01.027
[43] 张跞颖, 李长安, 张玉芬, 等. 长江武汉段4.5~2.5 ka沉积地层与古洪水标志识别[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(4):973-982
ZHANG Luoying, LI Chang'an, ZHANG Yufen, et al. Sedimentary strata and paleoflood identification indexes of Wuhan section, Yangtze River, during 4.5~2.5 ka BP[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(4):973-982.]
[44] 熊智秋, 张玉芬, 毛欣, 等. 武汉地区ZK145钻孔沉积物磁性特征及对古洪水的记录[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(2):663-671
XIONG Zhiqiu, ZHANG Yufen, MAO Xin, et al. Magnetic characteristics of ZK145 borehole sediments in Wuhan area and its[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(2):663-671.]
[45] 朱海, 张玉芬, 李长安. 端元分析在长江武汉段古洪水识别中的应用[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(2):297-305
ZHU Hai, ZHANG Yufen, LI Chang'an. The application of end-member analysis in identification of paleo-floods in wuhan section of the Yangtze River[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(2):297-305.]
[46] 吴立, 朱诚, 李枫, 等. 江汉平原钟桥遗址地层揭示的史前洪水事件[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70(7):1149-1164 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201507011
WU Li, ZHU Cheng, LI Feng, et al. Prehistoric flood events recorded at the Zhongqiao neolithic site in the Jianghan Plain, Central China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2015, 70(7):1149-1164.] doi: 10.11821/dlxb201507011
[47] Guan S, Yang Q, Li Y N, et al. River flooding response to ENSO-related monsoon precipitation: evidence from Late Holocene core sediments in the Jianghan Plain[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2022, 589:110834. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.110834
[48] 罗淑元, 郑丽匀, 曹向明, 等. 长江中游河漫滩沉积序列对洪水事件的指示: 以荆州扬子江剖面为例[J]. 人民长江, 2021, 52(1):6-12
LUO Shuyuan, ZHENG Liyun, CAO Xiangming, et al. Indication of flood events based on floodplain sedimentary sequence in Middle reaches of Changjiang River since 19th century: case of Yangzijiang profile in Jingzhou city[J]. Yangtze River, 2021, 52(1):6-12.]
[49] 史小丽, 秦伯强. 近百年来长江中游网湖沉积物粒度特征及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(2):117-122
SHI Xiaoli, QIN Boqiang. Grain-size characteristics and their environmental significance of wanghu lake sediments in the Middle reach of yangtze river[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(2):117-122.]
[50] 袁世飞. 近百年来长江中游牛轭湖沉积记录的高分辨率环境演变研究[D]. 上海师范大学硕士学位论文, 2014
YUAN Shifei. High-resolution environmental evolution of Oxbow Lake sedimentary records in the Middle reaches of the Yangtze River in the last hundred years[D]. Master Dissertation of Shanghai Normal University, 2014.]
[51] 王峰. 近百年来长江中游牛轭湖沉积特征及其环境意义: 以长江荆江段牛轭湖群为例[D]. 上海师范大学硕士学位论文, 2015
WANG Feng. Sedimentary characteristics and environmental significance of Oxbow Lake in the Middle reaches of Yangtze River in the last hundred years[D]. Master Dissertation of Shanghai Normal University, 2015.]
[52] 曹向明. 长江中下游地区高分辨率河湖相沉积记录的洪水事件及其规律[D]. 江西师范大学硕士学位论文, 2020
CAO Xiangming. Flood events recorded by high-resolution fluvial and lacustrine deposits in the Middle and Lower reaches of the yangtze river and their properties[D]. Master Dissertation of Jiangxi Normal University, 2020.]
[53] 朱诚, 于世永, 史威, 等. 南京江北地区全新世沉积与古洪水研究[J]. 地理研究, 1997, 16(4):23-30
ZHU Cheng, YU Shiyong, SHI Wei, et al. Holocene deposits and paleo-floods on the north bank of the Yangtze River, Nanjing area[J]. Geographical Research, 1997, 16(4):23-30.]
[54] Yu S Y, Zhu C, Wang F B. Radiocarbon constraints on the Holocene flood deposits of the Ning‐Zhen Mountains, Lower Yangtze River area of China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2003, 18(6):521-525. doi: 10.1002/jqs.767
[55] Baker V R. Paleoflood hydrologic techniques for the extension of streamflow records[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1983, 4(922):18-23.
[56] Kochel R C, Baker V R. Paleoflood hydrology[J]. Science, 1982, 215(4531):353-361. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4531.353
[57] Baker V R, Kochel R C, Patton P C. Flood geomorphology[M]. Wiley, 1988.
[58] Wright M N, Bird B W, Gibson D K, et al. Fluvial responses to Late Holocene hydroclimate variability in the midcontinental United States[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2023, 301:107939. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2022.107939
[59] Macklin M G, Lewin J. River sediments, great floods and centennial‐scale Holocene climate change[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2003, 18(2):101-105. doi: 10.1002/jqs.751
[60] Wilhelm B, Arnaud F, Sabatier P, et al. Palaeoflood activity and climate change over the last 1400 years recorded by lake sediments in the north‐west European Alps[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2013, 28(2):189-199. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2609
[61] 杨劲松, 刘林敬, 赵华, 等. 黄河故道区晚全新世沉积记录及其对洪水灾害事件的响应[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(4):1004-1015 doi: 10.12029/gc20220323001
YANG Jinsong, LIU Linjing, ZHAO Hua, et al. Late Holocene sedimentary records along the abandoned channel areas of the Yellow River and their response to flood hazards[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(4):1004-1015.] doi: 10.12029/gc20220323001
[62] Huang C C, Pang J L, Zha X, et al. Holocene palaeoflood events recorded by slackwater deposits along the Lower Jinghe River valley, Middle Yellow River Basin, China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2012, 27(5):485-493. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2536
[63] Baker V R. Paleoflood hydrology: origin, progress, prospects[J]. Geomorphology, 2008, 101(1-2):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.05.016
[64] 谢悦波, 杨达源. 古洪水平流沉积基本特征[J]. 河海大学学报: 自然科学版, 1998, 26(6):5-10
XIE Yuebo, YANG Dayuan. Basic characteristics of paleoflood slack water deposits[J]. Journal of Hohai University: Natural Sciences, 1998, 26(6):5-10.]
[65] Jarrett R D. Paleohydrology and its value in analyzing floods and droughts[J]. US Geological Survey Water-Supplementary Paper, 1991, 2375:105-116.
[66] Guo Y Q, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Reconstruction palaeoflood hydrology using slackwater flow depth method in the Yanhe River valley, Middle Yellow River Basin, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2017, 544:156-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.11.017
[67] 吴帅虎, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 汉江上游河谷古洪水滞流沉积物特征[J]. 土壤通报, 2013, 44(2):271-276
WU Shuaihu, PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, et al. The palaeoflood slackwater sediments feature in the valley of the Upper reaches of the Hanjiang River[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2013, 44(2):271-276.]
[68] 李晓刚, 黄春长, 庞奖励. 丹江上游全新世早期古洪水滞流沉积物粒度特征研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2014, 37(4):646-655
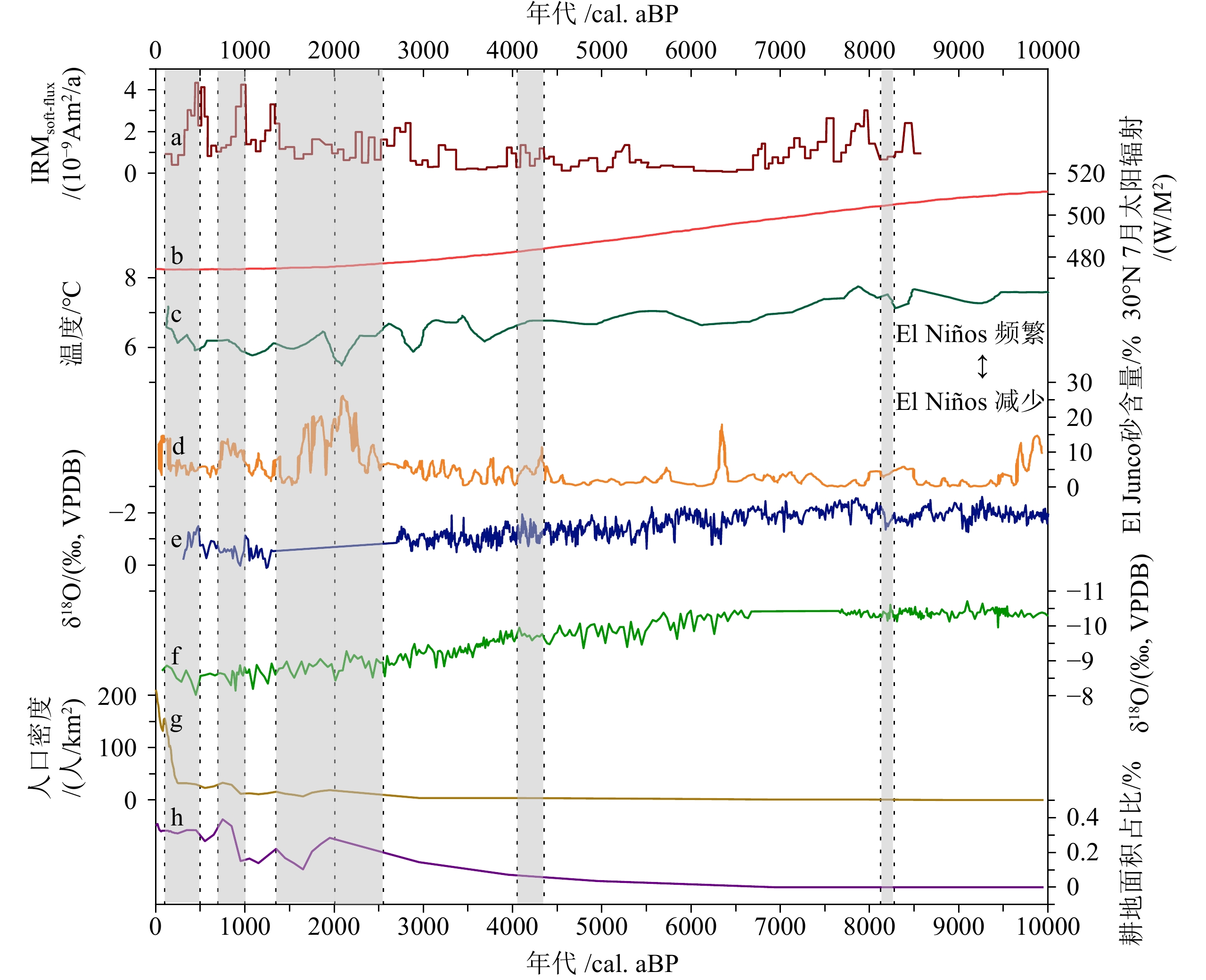
LI Xiaogang, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli. Grain-size characteristics of the early Holocene flood Slackwater deposits in the Upper reaches of Danjiang River[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2014, 37(4):646-655.]
[69] Wohl E. An integrative conceptualization of floodplain storage[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2021, 59(2):e2020RG000724. doi: 10.1029/2020RG000724
[70] Normally N R. Definition and identification of channel and overbank deposits and their respective roles in flood plain Formation[J]. The Professional Geographer, 1967, 19(1):1-4. doi: 10.1111/j.0033-0124.1967.00001.x
[71] 杨劲松, 王永, 尹金辉, 等. 我国冲积平原区洪水事件重建研究进展及展望[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(11):3944-3959
YANG Jinsong, WANG Yong, YIN Jinhui, et al. Progress and prospects in reconstruction of flood events in Chinese alluvial plains[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(11):3944-3959.]
[72] 张振克, 王苏民. 中国湖泊沉积记录的环境演变: 研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 1999, 14(4):417-422 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.04.018
ZHANG Zhenke, WANG Sumin. Advance and prospects of lake sediments and environmental changes study in China[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1999, 14(4):417-422.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.04.018
[73] 张凌华. 长江南京—镇江段现代河漫滩沉积特征与环境意义[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2015
ZHANG Linghua. Sediment characteristics and overbank sediments in the Nanjing-Zhenjiang reaches of the Yangtze River and their environmental implication[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2015.]
[74] 何报寅. 江汉平原湖泊的成因类型及其特征[J]. 华中师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2002, 36(2):241-244
HE Baoyin. The origin types and their characteristics of the lakes in Jianghan Plain[J]. Journal of Central China Normal University: Natural Science, 2002, 36(2):241-244.]
[75] 赵炳炎, 胡建芳, 刘丰豪, 等. 长江下游南漪湖沉积记录的全新世以来温度变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(4):1044-1055 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2021.04.14
ZHAO Bingyan, HU Jianfang, LIU Fenghao, et al. Variation of temperature in lake nanyi sediments from the Lower yangtze river region since the last 12.0 ka B. P.[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2021, 41(4):1044-1055.] doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2021.04.14
[76] Wu L, Zhu C, Ma C M, et al. Mid-Holocene palaeoflood events recorded at the Zhongqiao Neolithic cultural site in the Jianghan Plain, Middle Yangtze River Valley, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 173:145-160. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2017.08.018
[77] Wilhelm B, Ballesteros Cánovas J A, Macdonald N, et al. Interpreting historical, botanical, and geological evidence to aid preparations for future floods[J]. WIREs Water, 2019, 6(1):e1318. doi: 10.1002/wat2.1318
[78] 朱诚, 于世永, 卢春成. 长江三峡及江汉平原地区全新世环境考古与异常洪涝灾害研究[J]. 地理学报, 1997, 52(3):268-278 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1997.03.010
ZHU Cheng, YU Shiyong, LU Chuncheng. The study of Holocene environmental archaeology and extreme flood disaster in the three gorges of the Changjiang River and the Jianghan Plain[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1997, 52(3):268-278.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1997.03.010
[79] 吴立. 江汉平原中全新世古洪水事件环境考古研究[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2013
WU Li. Environmental Archaeology of the Mid-Holocene palaeofloods in the Jianghan Plain, Central China[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2013.]
[80] 连丽聪, 凌超豪, 李晓峰, 等. 河漫滩沉积体系对洪水事件的指示: 以修河为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(1):135-142
LIAN Licong, LING Chaohao, LI Xiaofeng, et al. Indicator of flood events based on floodplain sediments: a case study of Xiu River[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(1):135-142.]
[81] 谢悦波, 王文辉, 王平. 古洪水平流沉积粒度特征[J]. 水文, 2000, 20(4):18-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2000.04.005
XIE Yuebo, WANG Wenhui, WANG Ping. Characteristics of grain size for palaeoflood slackwater deposits[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2000, 20(4):18-20.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2000.04.005
[82] 谢远云, 李长安, 王秋良, 等. 江汉平原近3 000年来古洪水事件的沉积记录[J]. 地理科学, 2007, 27(1):81-84 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2007.01.013
XIE Yuanyun, LI Chang’an, WANG Qiuliang, et al. Sedimentary records of paleoflood events during the last 3000 years in Jianghan Plain[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2007, 27(1):81-84.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2007.01.013
[83] 李长安, 张玉芬. 长江中游洪水沉积特征与标志初步研究[J]. 水科学进展, 2004, 15(4):485-488 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2004.04.015
LI Chang'an, ZHANG Yufen. Flood sedimental characteristic and its mark on the Middle reaches of Yangtze River[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2004, 15(4):485-488.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2004.04.015
[84] 张灿, 周爱锋, 张晓楠, 等. 湖泊沉积记录的古洪水事件识别及与气候关系[J]. 地理科学进展, 2015, 34(7):898-908 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.07.011
ZHANG Can, ZHOU Aifeng, ZHANG Xiaonan, et al. Identification of Paleaoflood events by lacustrine archives and their links to climatic conditions[J]. Progress in Geography, 2015, 34(7):898-908.] doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.07.011
[85] 吴霜, 刘倩, 曹向明, 等. 赣北黄茅潭湖泊沉积记录的240年以来古洪水事件[J]. 地理科学进展, 2017, 36(11):1413-1422 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.11.010
WU Shuang, LIU Qian, CAO Xiangming, et al. A 240-year sedimentary record of paleoflood events from the Huangmaotan Lake, northern Jiangxi province[J]. Progress in Geography, 2017, 36(11):1413-1422.] doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.11.010
[86] Gilli A, Anselmetti F S, Glur L, et al. Lake sediments as archives of recurrence rates and intensities of past flood events[M]//Schneuwly-Bollschweiler M, Stoffel M, Rudolf-Miklau F. Dating Torrential Processes on Fans and Cones: Methods and Their Application for Hazard and Risk Assessment. Dordrecht: Springer, 2013: 225-242.
[87] Brown S L, Bierman P R, Lini A, et al. 10 000 yr record of extreme hydrologic events[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(4):335-338. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<335:YROEHE>2.0.CO;2
[88] Osleger D A, Heyvaert A C, Stoner J S, et al. Lacustrine turbidites as indicators of Holocene storminess and climate: Lake Tahoe, California and Nevada[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2009, 42(1):103-122. doi: 10.1007/s10933-008-9265-8
[89] Fairchild I J, Treble P C. Trace elements in speleothems as recorders of environmental change[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2009, 28(5-6):449-468. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2008.11.007
[90] Cheng H, Edwards R L, Broecker W S, et al. Ice age terminations[J]. Science, 2009, 326(5950):248-252. doi: 10.1126/science.1177840
[91] Tan L C, Cai Y J, Cheng H, et al. Climate significance of speleothem δ18O from central China on decadal timescale[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 106:150-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.008
[92] Dykoski C A, Edwards R L, Cheng H, et al. A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1-2):71-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.01.036
[93] Wang X F, Edwards R L, Auler A S, et al. Hydroclimate changes across the Amazon lowlands over the past 45, 000 years[J]. Nature, 2017, 541(7636):204-207. doi: 10.1038/nature20787
[94] Tan L C, Cai Y J, An Z S, et al. A Chinese cave links climate change, social impacts and human adaptation over the last 500 years[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1):12284. doi: 10.1038/srep12284
[95] Wang Z J, Chen S T, Wang Y J, et al. A high-resolution stalagmite record from Luoshui Cave, Central China over the past 23.5 kyr[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2022, 282:107443. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2022.107443
[96] Xie S C, Evershed R P, Huang X Y, et al. Concordant monsoon-driven postglacial hydrological changes in peat and stalagmite records and their impacts on prehistoric cultures in central China[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(8):827-830. doi: 10.1130/G34318.1
[97] Lascu I, Feinberg J M. Speleothem magnetism[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(23-24):3306-3320. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.08.004
[98] Maher B A, Thompson R. Paleorainfall reconstructions from pedogenic magnetic susceptibility variations in the Chinese loess and paleosols[J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(3):383-391. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1083
[99] Strauss B E, Strehlau J H, Lascu I, et al. The origin of magnetic remanence in stalagmites: Observations from electron microscopy and rock magnetism[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 14(12):5006-5025. doi: 10.1002/2013GC004950
[100] Bourne M D, Feinberg J M, Strauss B E, et al. Long-term changes in precipitation recorded by magnetic minerals in speleothems[J]. Geology, 2015, 43(7):595-598. doi: 10.1130/G36695.1
[101] Zhu Z M, Feinberg J M, Xie S C, et al. Holocene ENSO-related cyclic storms recorded by magnetic minerals in speleothems of central China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(5):852-857.
[102] 黄忠恕. 长江流域历史水旱灾害分析[J]. 人民长江, 2003, 34(2):1-3 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2003.02.001
HUANG Zhongshu. Analysis on historic flood and drought disasters of the Yangtze river[J]. Yangtze River, 2003, 34(2):1-3.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2003.02.001
[103] 李雨凡, 周亮, 于世永, 等. 过去两千年长江干流历史洪水事件的时空变化研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(2):241-251
LI Yufan, ZHOU Liang, YU Shiyong, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of flood events of the Yangtze River over the past 2000 years[J]. Earth and Environment, 2022, 50(2):241-251.]
[104] 温克刚. 中国气象灾害大典: (重庆卷)[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2008
WEN Kegang. The Meteorological Disaster Encyclopedia of China: Chongqing Volume[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2008.]
[105] 廖淦标, 范代读. 全球变暖是否导致台风增强: 古风暴学研究进展与启示[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(13):1489-1502 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.13.001
LIAO Ganbiao, FAN Daidu. Perspectives on the linkage between typhoon activity and global warming from recent research advances in paleotempestology[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(13):1489-1502.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.13.001
[106] Baker V R, Kochel R C, Patton P C, et al. Palaeohydrologic analysis of Holocene flood slack‐water sediments[J]. Modern and ancient fluvial systems, 1983: 229-239.
[107] Benito G, Sánchez-Moya Y, Sopeña A. Sedimentology of high-stage flood deposits of the Tagus River, Central Spain[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 157(1-2):107-132. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00196-3
[108] 杨轶文, 杨青惠. 窟野河流域水文特性分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2006, 17(1):57-60,64 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-643X.2006.01.013
YANG Yiwen, YANG Qinghui. Analysis of hydrologic characteristics in Kuye river Basin[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2006, 17(1):57-60,64.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-643X.2006.01.013
[109] Li X G, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Sedimentary and hydrological studies of the Holocene palaeofloods in the Shanxi-Shaanxi Gorge of the Middle Yellow River, China[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2015, 104(1):277-288. doi: 10.1007/s00531-014-1067-9
[110] Storozum M, Lu P, Wang S Y, et al. Geoarchaeological evidence of the AD 1642 Yellow River flood that destroyed Kaifeng, a former capital of dynastic China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1):3765. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60169-1
[111] Crookshanks S, Gilbert R. Continuous, diurnally fluctuating turbidity currents in Kluane Lake, Yukon Territory[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2008, 45(10):1123-1138. doi: 10.1139/E08-058
[112] Wilhelm B, Amann B, Corella J P, et al. Reconstructing paleoflood occurrence and magnitude from lake sediments[J]. Quaternary, 2022, 5(1):9. doi: 10.3390/quat5010009
[113] Wilhelm B, Vogel H, Crouzet C, et al. Frequency and intensity of palaeofloods at the interface of Atlantic and Mediterranean climate domains[J]. Climate of the Past, 2016, 12(2):299-316. doi: 10.5194/cp-12-299-2016
[114] 周凤琴. 荆江近5000年来洪水位变迁的初步探讨[J]. 历史地理, 1986, 6(1):46-53
ZHOU Fengqin. Preliminary study on flood level change in recent 5000 year in Jingjiang River[J]. Historical Geography, 1986, 6(1):46-53.]
[115] Knox J C. Sensitivity of modern and Holocene floods to climate change[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2000, 19(1-5):439-457. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00074-8
[116] 葛兆帅, 杨达源, 李徐生, 等. 晚更新世晚期以来的长江上游古洪水记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(5):555-560 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.05.012
GE Zhaoshuai, YANG Dayuan, LI Xusheng, et al. The paleoflooding record along the up-reaches of the Changjiang River since the Late Pleistocene Epoch[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24(5):555-560.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.05.012
[117] 王娜, 查小春, 黄春长, 等. 汉江上游晚冰期以来古洪水事件发生的气候背景分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2020, 29(10):2250-2260
WANG Na, ZHA Xiaochun, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Climate background about the palaeoflood events since Lateglacial Epoch in the Upper reaches of Hanjiang River, China[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2020, 29(10):2250-2260.]
[118] 朱诚, 于世永, 张兵, 等. 南京宝华山地区全新世沉积环境研究[J]. 地理科学, 1997, 17(3):253-258
ZHU Cheng, YU Shiyong, ZHANG Bing, et al. Study on Holocene sedimentary environment in Baohuashan area of Nanjing[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 1997, 17(3):253-258.]
[119] 王江月, 白伟明, 王照波, 等. 中国东部地区全新世气候演化及其与气候事件的对应性[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(2):167-177
WANG Jiangyue, BAI Weiming, WANG Zhaobo, et al. The Holocene climatic evolution in eastern China and its bearing on climatic events[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(2):167-177.]
[120] Berger A, Loutre M F. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1991, 10(4):297-317. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(91)90033-Q
[121] Huang X Y, Meyers P A, Jia C L, et al. Paleotemperature variability in central China during the last 13 ka recorded by a novel microbial lipid proxy in the Dajiuhu peat deposit[J]. The Holocene, 2013, 23(8):1123-1129. doi: 10.1177/0959683613483617
[122] Conroy J L, Overpeck J T, Cole J E, et al. Holocene changes in eastern tropical Pacific climate inferred from a Galápagos lake sediment record[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2008, 27(11-12):1166-1180. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2008.02.015
[123] Fleitmann D, Burns S J, Mangini A, et al. Holocene ITCZ and Indian monsoon dynamics recorded in stalagmites from Oman and Yemen (Socotra)[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2007, 26(1-2):170-188. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.04.012
[124] Dong J G, Wang Y J, Cheng H, et al. A high-resolution stalagmite record of the Holocene East Asian monsoon from Mt Shennongjia, central China[J]. The Holocene, 2010, 20(2):257-264. doi: 10.1177/0959683609350393
[125] Klein Goldewijk K, Beusen A, Doelman J, et al. Anthropogenic land use estimates for the Holocene–HYDE 3.2[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2017, 9(2):927-953. doi: 10.5194/essd-9-927-2017
[126] 施雅风, 姜彤, 苏布达, 等. 1840年以来长江大洪水演变与气候变化关系初探[J]. 湖泊科学, 2004, 16(4):289-297 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2004.04.001
SHI Yafeng, JIANG Tong, SU Buda, et al. Preliminary analysis on the relation between the evolution of heavy floods in the Yangtze River catchment and the climate changes since 1840[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2004, 16(4):289-297.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2004.04.001
[127] 葛兆帅. 长江上游全新世特大洪水对西南季风变化的响应[J]. 地理研究, 2009, 28(3):592-600 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2009.03.004
GE Zhaoshuai. The response of Holocene extreme floods in the Upper Changjiang River to changes of southwest monsoon[J]. Geographical Research, 2009, 28(3):592-600.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2009.03.004
[128] Trenberth K E. Changes in precipitation with climate change[J]. Climate Research, 2011, 47(1-2):123-138.
[129] Xie S P, Philander S G H. A coupled ocean‐atmosphere model of relevance to the ITCZ in the eastern Pacific[J]. Tellus A: Dynamic Meteorology and Oceanography, 1994, 46(4):340-350. doi: 10.3402/tellusa.v46i4.15484
[130] Bischoff T, Schneider T. Energetic constraints on the position of the intertropical convergence zone[J]. Journal of Climate, 2014, 27(13):4937-4951. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00650.1
[131] 李晓峰, 郭品文, 董丽娜, 等. 夏季索马里急流的建立及其影响机制[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 2006, 29(5):599-605
LI Xiaofeng, GUO Pinwen, DONG Lina, et al. Onset process of summer somali jet and the possible influenced mechanism[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 2006, 29(5):599-605.]
[132] Chang W Y B, King G. Centennial climate changes and their global associations in the Yangtze River (Chang Jiang) Delta, China and subtropical Asia[J]. Climate Research, 1994, 4(2):95-103.
[133] Dilley M, Heyman B N. ENSO and disaster: droughts, floods and El Niño/southern Oscillation warm events[J]. Disasters, 1995, 19(3):181-193. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7717.1995.tb00338.x
[134] 冯利华, 张强. 1998年长江巨洪与厄尔尼诺事件[J]. 东海海洋, 2001, 19(4):13-16
FENG Lihua, ZHANG Qiang. Large flood along the Changjiang River in 1998 and El Nio event[J]. Donghai Marine Science, 2001, 19(4):13-16.]
[135] Tong J, Qiang Z, Deming Z, et al. Yangtze floods and droughts (China) and teleconnections with ENSO activities (1470-2003)[J]. Quaternary International, 2006, 144(1):29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2005.05.010
-




 下载:
下载: