Risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in wetland sediments in the northern Yellow River Delta
-
摘要:
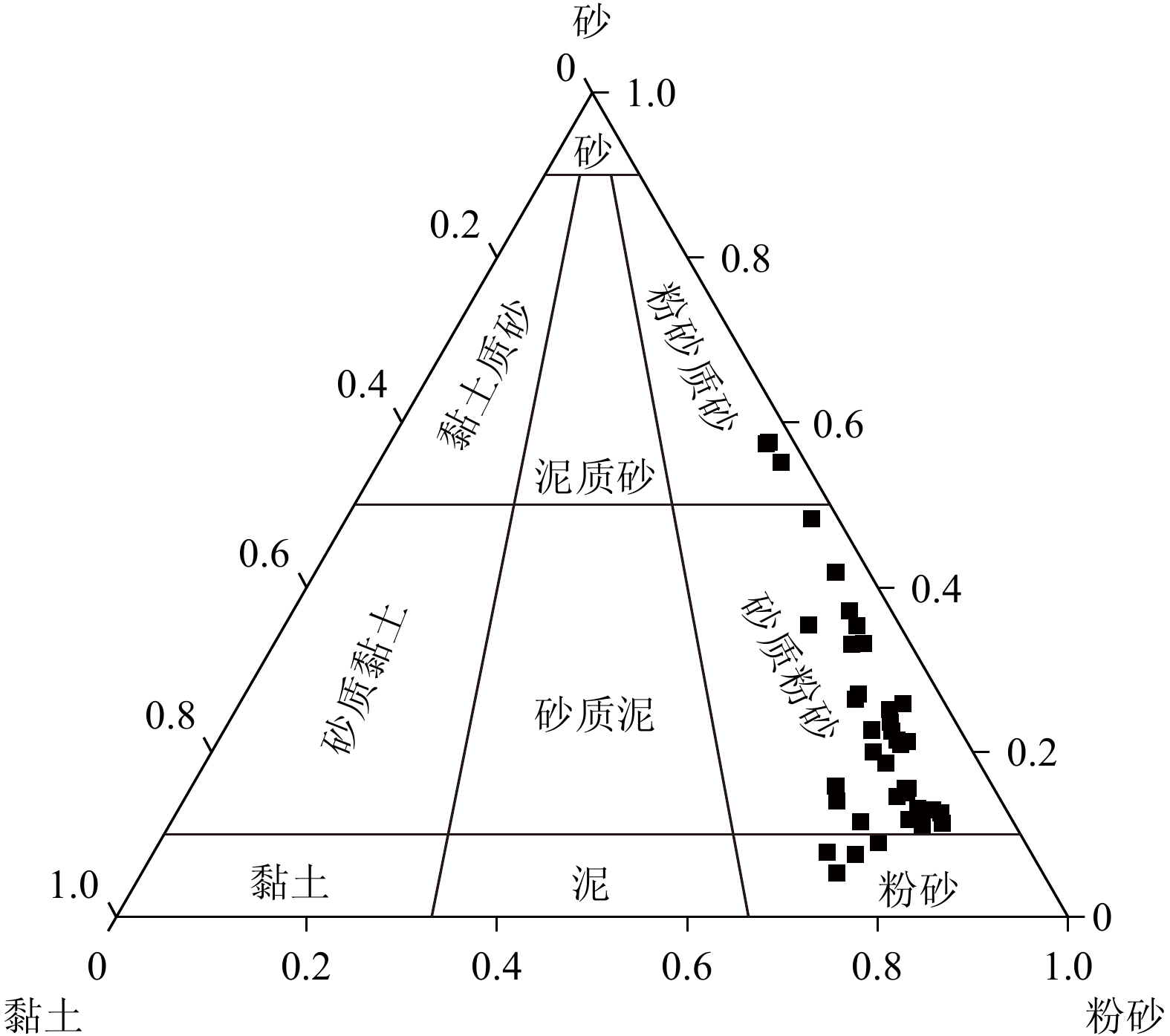
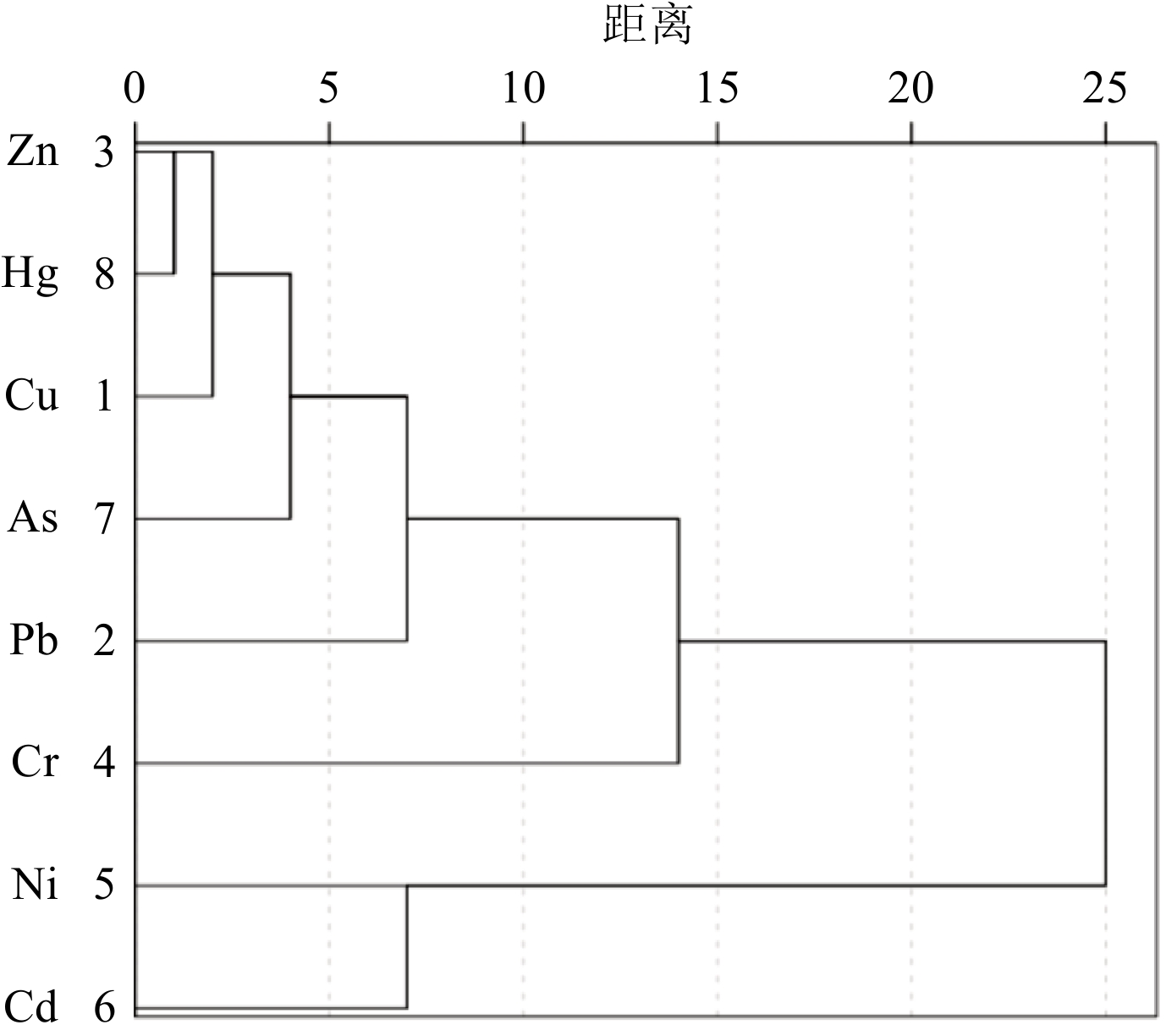
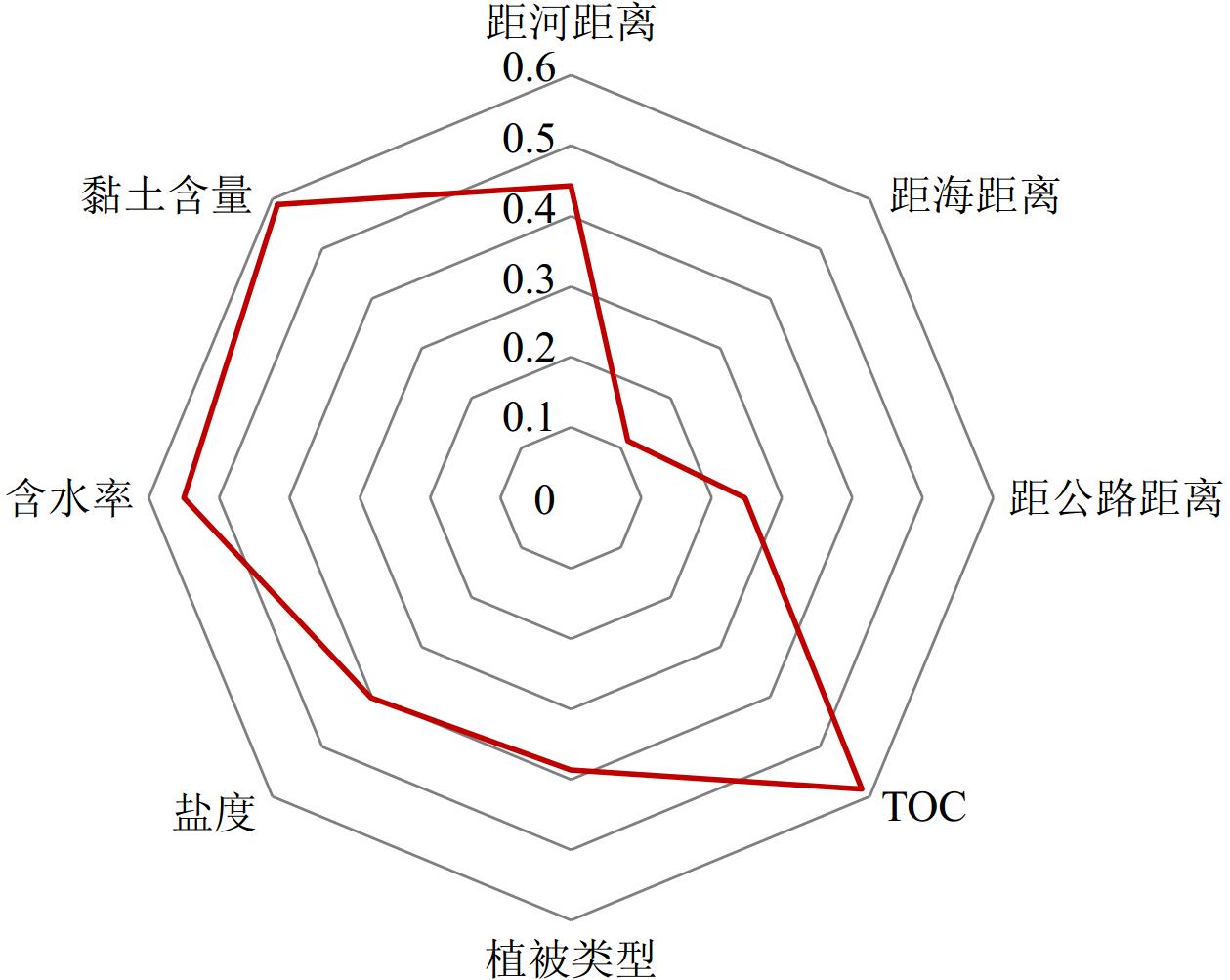
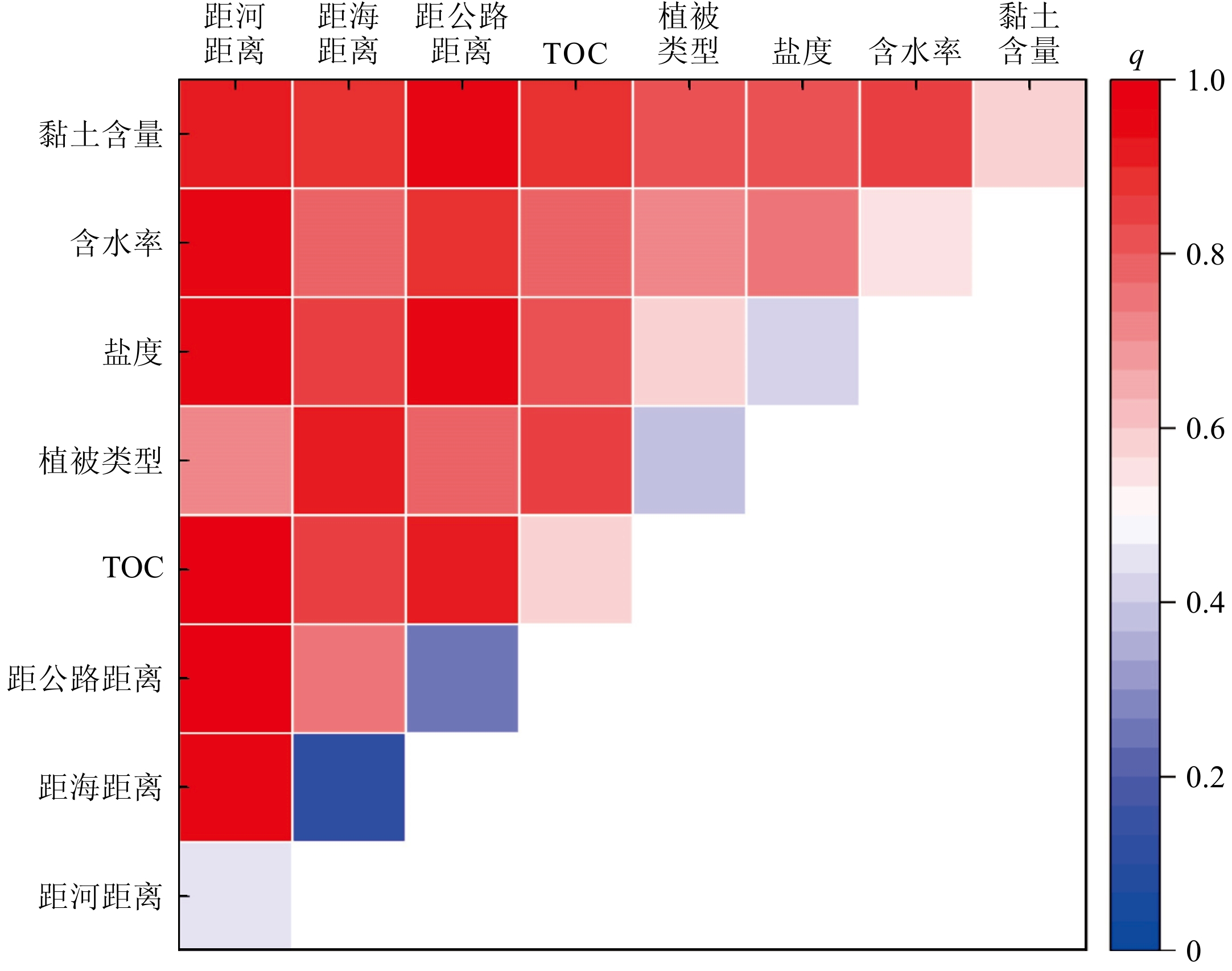
以黄河三角洲北部湿地39个表层沉积物样品为研究对象,测定Cu、Pb、Zn、Cr、Ni、Cd、As、Hg的含量,对其进行重金属污染风险评价及来源分析。结果表明:8种重金属元素在表层沉积物中平均含量由高到低顺序为:Cr>Zn>Ni>Pb>Cu>As>Cd>Hg, 除As外其含量均低于山东省土壤背景值;沉积物以砂质粉砂为主,重金属元素的空间分布特征相似,可能受到“粒度效应”的影响;基于地累积指数法和潜在生态危害指数法,揭示了Cd、Hg为研究区主要污染物和重要的潜在生态危害因子;相关分析和因子分析表明,Cu、Pb、Zn、Cr、As、Hg可能来源于成土母质、工业活动以及油田开采, Ni、Cd可能来源于农业活动、水产养殖以及油田开采;聚类分析表明,可进一步把Cr单独分为一类;通过因子探测分析发现,黏土含量、TOC和含水率对潜在生态危害指数(RI值)解释力较大,表明其对RI值的影响较大;通过交互作用探测分析可知,任意两个影响因子交互作用后结果为双因子增强或非线性增强,表明复杂的环境加剧了湿地的潜在生态危害。
Abstract:The contents of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Ni, Cd, As and Hg in 39 surface sediment samples collected in June 2021 from the northern wetland of the Yellow River Delta were determined, and the risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in the sediments of the northern wetland of the Yellow River Delta were carried out. Results show that the average contents of eight heavy metal elements in the surface sediments of the wetland in the northern Yellow River Delta were in the order of Cr>Zn>Ni>Pb>Cu>As>Cd>Hg, which were lower than the soil background values of Shandong Province except for As. The sediments were mainly sandy silt, and the spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metal elements are similar, which may be affected by the “grain size effect”. The cumulative index and potential ecological hazard index (RI) revealed that Cd and Hg were the main pollutants and important potential ecological risk factors in the study area. Correlation analysis and factor analysis showed that the sources of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, As, and Hg might be soil parent materials, industrial activities, and oilfield exploitation, and the sources of Ni and Cd might be from agricultural activities, aquaculture and oilfield exploitation. Cluster analysis showed that Cr could be placed into separate category. Through factor detection analysis, it was found that clay content, TOC and water content had a greater explanatory power on the RI, indicating that they had a greater impact on the RI value. The interaction detection analysis showed that the interaction of any two influencing factors resulted in two-factor enhancement or nonlinear enhancement, indicating that the complex environment aggravated the potential ecological hazards of wetlands. This study provided a scientific support for the control of heavy metal pollution in wetlands in the northern Yellow River Delta.
-

-
表 1 地累积指数法(Igeo)分级标准
Table 1. Scaling of the land accumulation index (Igeo)
地累积指数Igeo 等级 污染程度 Igeo<0 0 无污染 0≤Igeo<1 1 轻度—中度污染 1≤Igeo<2 2 中度污染 2≤Igeo<3 3 中度—重度污染 3≤Igeo<4 4 重度污染 4≤Igeo<5 5 重度—极度污染 5≤Igeo 6 极严重污染 表 2 潜在生态危害指数法分级标准
Table 2. Scaling of the potential ecological hazard index
潜在生态危害单项系数Eir 单个污染物潜在生态风险程度 潜在生态危害指数RI 综合潜在生态风险程度 Eir<40 轻微生态危害 RI<150 轻微生态危害 40≤Eir<80 中等生态危害 150≤RI<300 中等生态危害 80≤Eir<160 强生态危害 300≤RI<600 强生态危害 160≤Eir<320 很强生态危害 600≤RI< 1200 很强生态危害 Eir≥320 极强生态危害 RI≥ 1200 极强生态危害 表 3 黄河三角洲北部湿地沉积物重金属含量
Table 3. Contents of heavy metals in surface sediments of wetlands in northern Yellow River Delta
项目 Cu Pb Zn Cr Ni Cd As Hg 最小值 7.70 13.20 43.50 45.50 18.00 0.06 5.66 0.01 最大值 28.60 26.80 81.80 75.70 35.00 0.20 14.70 0.03 平均值 17.60 17.70 58.20 59.00 23.40 0.09 9.07 0.02 中值 17.10 18.09 58.17 60.32 24.04 0.11 9.09 0.02 变异系数/% 0.29 0.16 0.15 0.10 0.15 0.31 0.21 0.28 国家一级标准值[23] 35.00 35.00 100.00 90.00 40.00 0.20 15.00 0.15 珠江流域[24] 48.72 63.97 186.60 67.44 – 2.76 49.29 – 长江三角洲[25] 29.94 31.95 86.17 75.39 30.85 0.18 8.30 0.15 莱州湾[26] 19.06 20.30 55.98 60.10 – 0.11 11.72 0.04 山东省背景值[27] 22.60 23.60 63.30 62.00 27.10 0.13 8.60 0.03 东营市背景值[28] 21.00 19.40 62.20 65.50 27.50 0.13 10.30 0.02 注:表中除变异系数外,其他单位均为mg/kg。 表 4 黄河三角洲北部湿地沉积物中8种重金属含量及其与粒径相关性
Table 4. The contents of 8 heavy metals in wetland sediments in the northern Yellow River Delta and their correlation with particle size
Cu Pb Zn Cr Ni Cd As Hg 砂 粉砂 黏土 Cu 1 Pb 0.74** 1 Zn 0.93** 0.83** 1 Cr 0.50** 0.70** 0.68** 1 Ni 0.42** 0.39* 0.45** 0.26 1 Cd 0.36* 0.52** 0.47** 0.28 0.79** 1 As 0.86** 0.73** 0.88** 0.69** 0.36* 0.28 1 Hg 0.87** 0.85** 0.93** 0.66** 0.50** 0.58** 0.81** 1 砂 –0.67** –0.46** –0.67** –0.29 –0.19 –0.15 –0.62** –0.58** 1 粉砂 0.50** 0.24 0.49** 0.09 0.08 0.02 0.43** 0.40* –0.95** 1 黏土 0.79** 0.76** 0.82** 0.60** 0.37* 0.37* 0.80** 0.77** –0.74** 0.50** 1 注:**表示在p<0.01水平,相关性显著;*表示在p<0.05水平,相关性显著。 表 5 黄河三角洲北部湿地沉积物重金属地累积指数评价结果
Table 5. Evaluation results of heavy metal land accumulation index in wetland sediments in northern Yellow River Delta
Cu Pb Zn Cr Ni Cd As Hg 最小值 –2.03 –1.14 –1.10 –1.11 –1.20 –1.63 –1.45 –1.72 最大值 –0.14 –0.12 –0.19 –0.38 –0.24 0.04 –0.07 0.00 平均值 –0.94 –0.70 –0.70 –0.71 –0.79 –0.95 –0.80 –0.84 标准偏差 0.44 0.22 0.21 0.15 0.21 0.41 0.30 0.39 无污染比例/% 100 100 100 100 100 97 100 97 轻度—中度污染比例/% 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 3 表 6 黄河三角洲北部湿地沉积物重金属潜在生态危害指数评价结果
Table 6. Evaluation results of potential ecological risk index of heavy metals in surface sediments of wetlands in northern Yellow River Delta
Eir RI Cu Pb Zn Cr Ni Cd As Hg 最小值 1.70 2.80 0.69 1.47 3.32 14.54 6.58 12.13 47.15 最大值 6.33 5.68 1.29 2.44 6.46 46.15 17.09 40.00 119.36 平均值 3.78 3.83 0.92 1.95 4.44 24.26 10.57 23.11 72.86 轻微生态危害比例/% 100 100 100 100 100 95 100 97 100 中等生态危害比例/% – – – – – 5 – 3 – 表 7 黄河三角洲北部湿地沉积物中重金属元素因子分析
Table 7. Factor analysis of heavy metal elements in wetland sediments in the northern Yellow River Delta
元素 因子1 因子2 As 0.921 0.117 Zn 0.918 0.305 Cu 0.874 0.248 Hg 0.850 0.431 Pb 0.829 0.364 Cr 0.763 0.094 Cd 0.197 0.940 Ni 0.184 0.879 黏土 0.859 0.208 TOC 0.521 0.447 特征值 5.529 2.394 方差百分比/% 55.293 23.937 累积方差百分比/% 55.293 79.230 注:旋转方法采用凯撒正态化最大方差法。 -
[1] 王辉, 赵悦铭, 刘春跃, 等. 辽河干流沉积物重金属污染特征及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(11):65-69
WANG Hui, ZHAO Yueming, LIU Chunyue, et al. Characterization of heavy metal contamination and evaluation of potential ecological risk of sediments in the main stream of Liaohe River[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(11):65-69.]
[2] 柴元武, 宫静. 重金属对人类健康的影响[J]. 固原师专学报, 2002, 23(6):19-20
CHAI Yuanwu, GONG Jing. Effects of heavy metals on human health[J]. Journal of Guyuan Teachers College, 2002, 23(6):19-20.]
[3] 陈雪娟, 高放, 王青, 等. 黄河三角洲湿地淡水修复区重金属分布特征及潜在风险[J]. 环境工程, 2023, 41(1):232-239
CHEN Xuejuan, GAO Fang, WANG Qing, et al. Distribution characteristics and potential risks of heavy metals in freshwater restored wetlands in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2023, 41(1):232-239.]
[4] Ding Z, Wu J, You A, et al. Effects of heavy metals on soil microbial community structure and diversity in the rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp. japonica, Food Crops Institute of Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences) rhizosphere[J]. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 2017, 63(1): 75-83.
[5] 宋颖, 李华栋, 时文博, 等. 黄河三角洲湿地重金属污染生态风险评价[J]. 环境保护科学, 2018, 44(5):118-122
SONG Ying, LI Huadong, SHI Wenbo, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in wetlands of the Yellow River Delta[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2018, 44(5):118-122.]
[6] 贾少宁, 申发, 颜宁, 等. 黄河三角洲不同土地利用方式下土壤重金属分析评价[J]. 鲁东大学学报:自然科学版, 2023, 39(3):193-202
JIA Shaoning, SHEN Fa, YAN Ning, et al. Analysis and evaluation of soil heavy metals under different land use in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Journal of Ludong University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 39(3):193-202.]
[7] 吴志勇, 黄川友. 湿地构成变化与湿地保护[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2001(S2):32-34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2001.z2.014
WU Zhiyong, HUANG Chuanyou. Changes in wetland composition and wetland conservation[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2001(S2):32-34.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2001.z2.014
[8] 杨清香, 李小庆, 于淼成, 等. 黄河三角洲实验区表层沉积物重金属污染特征及防控策略[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(7):2424-2432 doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202212135
YANG Qingxiang, LI Xiaoqing, YU Miaocheng, et al. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of the Yellow River Delta Experimental Area and strategies for prevention and control[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2023, 17(7):2424-2432.] doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202212135
[9] Yang H, Sun J, Xia J, et al. Distribution and Assessment of Cr, Pb, Ni and Cd in Topsoil of the Modern Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Wetlands, 2021, 41(2): 26.
[10] 别君, 黄海军, 樊辉, 等. 现代黄河三角洲地面沉降及其原因分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(4):29-35
BIE Jun, HUANG Navy, FAN Hui, et al. Ground subsidence in the modern Yellow River Delta and its causes[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(4):29-35.]
[11] 薛春汀, 叶思源, 高茂生, 等. 现代黄河三角洲沉积物沉积年代的确定[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(1):117-124
XUE Chunting, YE Siyuan, GAO Maosheng, et al. Determination of sedimentary age of modern Yellow River Delta sediments[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2009, 31(1):117-124.]
[12] 王奎峰, 李念春, 王薇. 黄河三角洲多年海岸线动态变迁特征及演化规律[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2018, 37(3):330-338 doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.03.004
WANG Kueifeng, LI Nianchun, WANG Wei. Characteristics of multi–year coastline dynamics change and evolution law in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2018, 37(3):330-338.] doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.03.004
[13] 陈柯欣, 丛丕福, 曲丽梅, 等. 黄河三角洲湿地水文连通及驱动力分析[J]. 水文, 2023, 43(3):112-117
CHEN Kexin, CONG Pifu, QU Limei, et al. Hydrological connectivity and driving force analysis of wetlands in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Hydrology, 2023, 43(3):112-117.]
[14] 熊燕. 土壤质量和土壤重金属污染评价方法综述[J]. 贵阳学院学报:自然科学版, 2021, 16(3):92-95
XIONG Yan. Review of soil quality and soil heavy metal pollution evaluation methods[J]. Journal of Guiyang College (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 16(3):92-95.]
[15] 刘晶, 滕彦国, 崔艳芳, 等. 土壤重金属污染生态风险评价方法综述[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2007, 19(3):6-11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2007.03.003
LIU Jing, TENG Yanguo, CUI Yanfang, et al. A review of ecological risk assessment methods for soil heavy metal pollution[J]. Environmental Monitoring Management and Technology, 2007, 19(3):6-11.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2007.03.003
[16] 刘德成, 李玉倩, 郑纯静, 等. 土壤重金属污染风险评价方法对比研究[J]. 河北农业科学, 2020, 24(4):89-95
LIU Decheng, LI Yuqian, ZHENG Chunjing, et al. Comparative study of risk assessment methods for soil heavy metal pollution[J]. Hebei Agricultural Science, 2020, 24(4):89-95.]
[17] 田文, 顾延生, 丁俊傑. 江汉平原仙桃地区湿地沉积物重金属污染风险评价[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2023, 30(4):243-252
TIAN Wen, GU Yansheng, DING Junjie. Risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in wetland sediments in Xiantao, Jianghan Plain[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2023, 30(4):243-252.]
[18] 滕彦国, 庹先国, 倪师军, 等. 应用地质累积指数评价沉积物中重金属污染: 选择地球化学背景的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2002, 25(2):7-9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2002.02.003
TENG Yanguo, TOU Xiangguo, NI Shijun, et al. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination in sediments using the geoaccumulation index: Influence of selecting the geochemical background[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2002, 25(2):7-9.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2002.02.003
[19] 李逸平, 王香莲, 金如意, 等. 鄱阳湖南矶山湿地沉积物重金属污染特征及潜在生态风险[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2022, 44(11):1491-1496, 1502
LI Yiping, WANG Xianglian, JIN Ruyi, et al. Characteristics of heavy metal contamination and potential ecological risk in the sediments of Nanjishan Wetland, Poyang Lake[J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 2022, 44(11):1491-1496, 1502.]
[20] 陈晨, 王兵, 王寒冰, 等. 山东东营市三角洲地区土壤重金属污染及生态风险评价[J]. 自然保护地, 2023, 3(3):94-102 doi: 10.12335/2096-8981.2022091901
CHEN Chen, WANG Bing, WANG Hanbing, et al. Evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in the delta area of Dongying City, Shandong Province[J]. Nature Reserve, 2023, 3(3):94-102.] doi: 10.12335/2096-8981.2022091901
[21] 王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器: 原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1):116-134 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201701010
WANG Jinfeng, XU Chengdong. Geoprobes: principles and perspectives[J]. Journal of Geography, 2017, 72(1):116-134.] doi: 10.11821/dlxb201701010
[22] Cheng Q, Lou G, Huang W, et al. Assessment and potential sources of metals in the surface sediments of the Yellow River Delta, Eastern China[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2017, 24(21): 17446-17454.
[23] 国家环境保护局. GB15618–1995土壤环境质量标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1995
National Environmental Protection Bureau. GB15618–1995 Quality Standard for Soil Environment [S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 1995.]
[24] 涂春霖, 和成忠, 马一奇, 等. 珠江流域沉积物重金属污染特征、生态风险及来源解析[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(3):410-419
TU Chunlin, HE Chengzhong, MA Yiqi, et al. Characterization, ecological risk and source analysis of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Pearl River Basin[J]. Geological Frontiers, 2024, 31(3):410-419.]
[25] 张明, 陈国光, 刘红樱, 等. 长江三角洲地区土壤重金属含量及其分异特征[J]. 土壤通报, 2012, 43(5):1098-1103
ZHANG Ming, CHEN Guoguang, LIU Hongzhu, et al. Heavy metal contents of soils and their differentiation characteristics in the Yangtze River Delta region[J]. Soil Bulletin, 2012, 43(5):1098-1103.]
[26] 段云莹, 裴绍峰, 廖名稳, 等. 莱州湾表层沉积物重金属分布特征、污染评价与来源分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(6):67-81
DUAN Yunying, PEI Shaofeng, LIAO Mingjian, et al. Distribution characteristics, pollution assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments of Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(6):67-81.]
[27] 庞绪贵, 代杰瑞, 胡雪平, 等. 山东省土壤地球化学背景值[J]. 山东国土资源, 2018, 34(1):39-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2018.01.005
PANG Xugui, DAI Jieri, HU Xueping, et al. Soil geochemical background values in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land Resources, 2018, 34(1):39-43.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2018.01.005
[28] 庞绪贵, 代杰瑞, 陈磊, 等. 山东省17市土壤地球化学背景值[J]. 山东国土资源, 2019, 35(1):46-56 doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2019.01.008
PANG Xugui, DAI Jieri, CHEN Lei, et al. Soil geochemical background values of 17 cities in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land Resources, 2019, 35(1):46-56.] doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2019.01.008
[29] Wilding L P. Spatial variability: its documentation, accommodation and implication to soil surveys[C]. Soil spatial variability, 1985: 166-194.
[30] 韦彩嫩, 牛红义, 吴群河, 等. 珠江(广州河段)表层沉积物中重金属的粒度效应[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2011, 36(10):53-56, 46 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2011.10.014
WEI Caineng, NIU Hongyi, WU Qunhe, et al. Particle size effects of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Pearl River (Guangzhou River Section)[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2011, 36(10):53-56, 46.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2011.10.014
[31] 赵玉庭, 孙珊, 由丽萍, 等. 莱州湾沉积物粒度与重金属分布特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(3):43-50
ZHAO Yuting, SUN Shan, YU Liping, et al. Characteristics of sediment particle size and heavy metal distribution in Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Science, 2021, 45(3):43-50.]
[32] 李伟迪, 崔云霞, 曾撑撑, 等. 太滆运河流域农田土壤重金属污染特征与来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(11):5073-5081
LI Weidi, CUI Yunxia, ZENG Zandao, et al. Characteristics and sources of heavy metal pollution in farmland soils in the Taige Canal Basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(11):5073-5081.]
[33] Shan C Q, Zhang Z W, Zhao D Y, et al. Heavy Metal Contamination in soils from a major planting base of winter Jujube in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Processes, 2022, 10(9): 1777.
[34] 郑美洁, 郑冬梅, 辛愿, 等. 互花米草入侵对黄河三角洲湿地表层沉积物金属元素分布格局的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42(10):2368-2375
ZHENG Meijie, ZHENG Dongmei, XIN Wang, et al. Impacts of M. alterniflora invasion on the distribution pattern of metal elements in surface sediments of the Yellow River Delta wetland[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2023, 42(10):2368-2375.]
[35] 张娜, 熊健, 李伟, 等. 巴嘎雪湿地土壤理化性质及其重金属风险评价[J]. 高原科学研究, 2023, 7(2):38-50
ZHANG Na, XIONG Jian, LI Wei, et al. Physicochemical properties of soil and heavy metal risk assessment in Bagaxue wetland[J]. Plateau Science Research, 2023, 7(2):38-50.]
[36] Förstner U, Wittmann G T W. Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1979.
[37] El Azzi D, Probst J L, Teisserenc R, et al. Trace element and pesticide dynamics during a flood event in the save agricultural watershed: soil-river transfer pathways and controlling factors[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2016, 227(12): 1-19.
[38] 马泉来, 万小强, 杨崇科, 等. 南太行典型区小流域土壤铅含量空间分异及影响因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(18):226-233 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202306206
MA Quanlai, WAN Xiaoqiang, YANG Chongke, et al. Spatial differentiation of soil lead content in small watersheds in the South Taihang Typical Area and analysis of influencing factors[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(18):226-233.] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202306206
-




 下载:
下载: