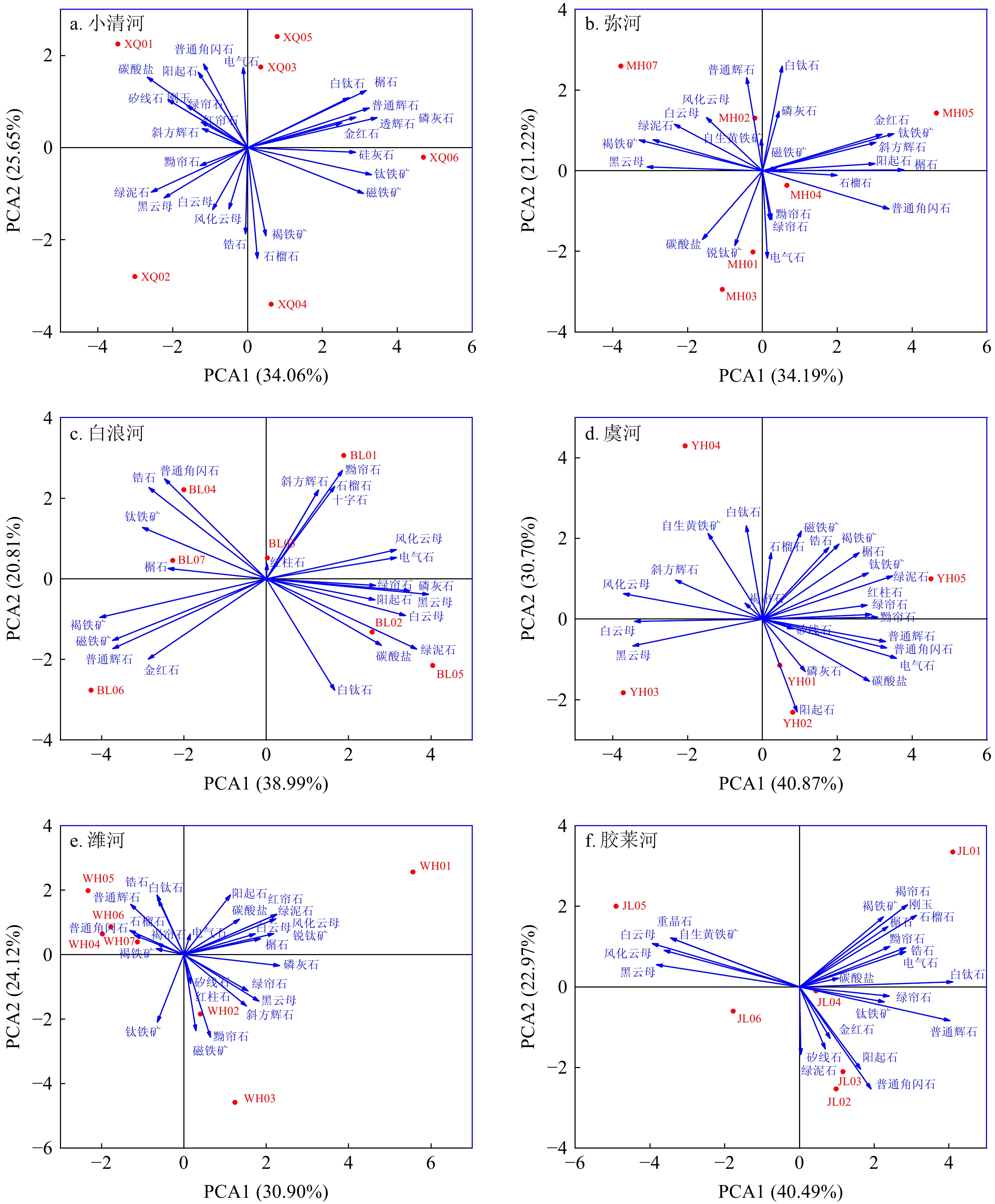
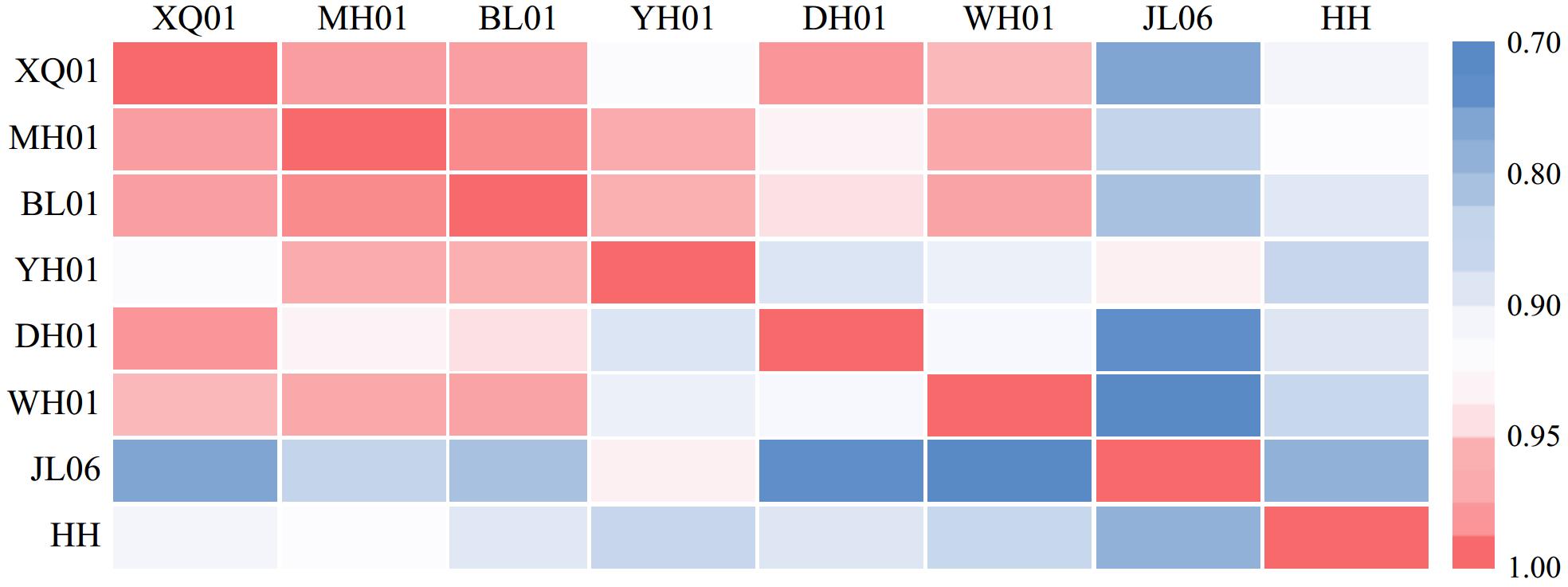
Characteristics of heavy minerals in rivers entering the sea from the south bank of Laizhou Bay and their provenance significance
-
摘要:
在关注大河物源辨别和示踪的同时,“短源河流-瞬时大通量-快速物质转换”的源-汇体系值得重视。莱州湾南岸入海的中小河流沉积物来源明确,母岩、气候及水动力条件等复杂程度低,易于进行有限边界条件下的物质端元特征分析。本文对莱州湾南岸的小清河、弥河、白浪河、虞河、堤河、潍河、胶莱河等中小河流进行碎屑重矿物特征差异研究,判别分析不同河源物质来源。结果显示,莱州湾南岸中小河流沉积物中共鉴定出31种重矿物,以角闪石和绿帘石为主。重矿物含量较高(>5.5%)的小清河和潍河沉积物中褐铁矿含量高,而重矿物含量低(<1.5%)的其他河流沉积物中黑云母含量较高。石榴石-榍石-磷灰石组成的特征矿物组合以及标型矿物(硅灰石、矽线石、刚玉、十字石和红柱石等)反映物源区出露的酸性花岗岩、区域变质岩以及接触变质岩等不同岩性,它们是产生不同河流矿物特征组合差异的主控因素。另外,双标图和热力图显示来自黄河与莱州湾南部近岸海域重矿物特征差异较为显著。莱州湾南岸近海海区沉积物主要来自附近河流物质,而黄河来源物质的影响程度自西向东减弱。因此,对短源河流碎屑重矿物特征分析,可为山东半岛近海碎屑沉积物的物源辨识探究提供依据,对深入认识大陆边缘物质供应过程具有重要意义。
Abstract:While focusing on identifying and tracing the sources of large rivers, the source-sink system of "short-source river flow – instantaneous large flux – rapid material transformation" deserves attention. The sediment sources of small- and medium-sized rivers entering the sea on the south bank of Laizhou Bay have clear sources, and low complexity in parent rocks, climate, and hydrodynamic conditions, which makes it easy to analyze the characteristics of material end-members under limited boundary conditions. We studied the differences in the characteristics of detrital heavy minerals from small- and medium-sized rivers, including Xiaoqing River, Mihe River, Bailang River, Yuhe River, Dihe River, Weihe River, and Jiaolai River on the south bank of Laizhou Bay, by which the sources of different river sources were analyzed and discriminated. Results show that a total of 31 heavy minerals were identified, mainly amphibole and epidote. The sediments of Xiaoqing River and Weihe River had a high heavy mineral content (>5.5%) typical of abundant limonite, while those of other rivers had a low heavy mineral content (<1.5%) typical of ample biotite. The characteristic mineral assemblages composed of garnet-sphene-apatite and standard minerals (wollastonite, sillimanite, corundum, staurolite, and andalusite, and so on) reflect different rock types such as acidic granites, regional metamorphic rocks, and contact metamorphic rocks exposed in the source area, which are the main controlling factors for the differences in the characteristic assemblages of different riverine minerals. In addition, the biplot and heatmap show that the spectra of heavy minerals from Huanghe River and the southern coastal waters of Laizhou Bay are quite different. The sediments in the offshore area of the southern coast of Laizhou Bay mainly come from nearby river materials, and the impact of Huanghe River materials weakens from west to east. Therefore, analyzing the characteristics of heavy minerals in short-source river sediments can provide a basis for identifying the sources of detrital sediments in the Shandong Peninsula, which is of great significance for a deeper understanding of the material supply process at the continental margin.
-

-
表 1 莱州湾南岸近海河流水系概况
Table 1. Hydrology in the nearshore rivers of the southern coast of Laizhou Bay
河流 源头 全长/km 流域面积/km2 小清河 济南市趵突泉 237 10 276 弥河 临朐县沂山西麓 177 3 863 白浪河 昌乐县唐吾大鼓山 127 1 237 虞河 安丘市许营 75 890 潍河 沂山北麓官庄乡 246 6 367 胶莱河 平度市南部姚家 146 5 400 表 2 莱州湾南岸近海河流主要重矿物族类平均含量
Table 2. Average content of major heavy minerals in the coastal rivers on the south bank of Laizhou Bay
% 河流 闪石族 帘石族 云母族 稳定矿物类 辉石族 铁质金属类 HMC XQ 40.36 23.44 5.89 4.87 6.88 14.55 5.56 MH 36.11 17.55 18.98 5.16 1.77 9.89 1.33 BL 37.63 26.97 7.90 5.53 3.60 12.27 1.51 YH 26.81 21.04 31.46 3.64 1.28 8.33 0.26 DH 49.06 5.97 20.44 4.09 5.03 5.03 0.41 WH 44.58 27.86 2.13 4.82 3.52 12.96 6.08 JL 39.51 28.33 13.67 6.99 0.95 8.05 1.43 注:矿物族类为体积含量,HMC为重矿物质量含量。 -
[1] 高抒. 全球变化中的浅海沉积作用与物理环境演化: 以渤、黄、东海区域为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2002, 9(2):329-335
GAO Shu. Shallow marine sedimentation and physical environment evolution as a part of global change: an example from the Bohai, Yellow and East China Sea regions[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2002, 9(2):329-335.]
[2] Kremer H H. River catchment-coastal sea interaction and human dimensions[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2004, 4(1):1-4. doi: 10.1007/s10113-003-0066-3
[3] Yang H F, Yang S L, Xu K H, et al. Human impacts on sediment in the Yangtze River: a review and new perspectives[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2018, 162:8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.01.001
[4] Peng J, Chen S L. Response of delta sedimentary system to variation of water and sediment in the Yellow River over past six decades[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2010, 20(4):613-627. doi: 10.1007/s11442-010-0613-z
[5] Ma Q, Li H L, Wang X J, et al. Estimation of seawater–groundwater exchange rate: case study in a tidal flat with a large-scale seepage face (Laizhou Bay, China)[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2015, 23(2):265-275. doi: 10.1007/s10040-014-1196-z
[6] Gao M S, Guo F, Huang X Y, et al. Sediment distribution and provenance since Late Pleistocene in Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China[J]. China Geology, 2019, 2(1):16-25. doi: 10.31035/cg2018062
[7] 黄学勇, 高茂生, 侯国华, 等. 莱州湾海洋沉积物粒度特征及其环境响应分析[J]. 华东地质, 2023, 44(4):402-414
HUANG Xueyong, GAO Maosheng, HOU Guohua, et al. Grain size characteristics and environmental response of marine sediments in Laizhou Bay[J]. East China Geology, 2023, 44(4):402-414.]
[8] 杨作升, 孙宝喜, 沈渭铨. 黄河口毗邻海域细粒级沉积物特征及沉积物入海后的运移[J]. 山东海洋学院学报, 1985, 15(2):121-129
YANG Zuosheng, SUN Baoxi, SHENG Weiquan. Characteristics of fine-grained sediment of the shelf area adjacent to the mouth of the Huanghe River and sediment dispersion in that region[J]. Journal of Shandong College of Oceanology, 1985, 15(2):121-129.]
[9] 秦蕴珊. 黄海地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989
QIN Yunshan. Geology of Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1989.]
[10] Milliman J D, Lee T Y, Huang J C, et al. Impact of catastrophic events on small mountainous rivers: temporal and spatial variations in suspended- and dissolved-solid fluxes along the Choshui River, central western Taiwan, during typhoon Mindulle, July 2-6, 2004[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 205:272-294. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.02.015
[11] Simpson G, Castelltort S. Model shows that rivers transmit high-frequency climate cycles to the sedimentary record[J]. Geology, 2012, 40(12):1131-1134. doi: 10.1130/G33451.1
[12] 杨守业, 印萍. 自然环境变化与人类活动影响下的中小河流沉积物源汇过程[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(1):1-10
YANG Shouye, YIN Ping. Sediment source-to-sink processes of small mountainous rivers under the impacts of natural environmental changes and human activities[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(1):1-10.]
[13] 金秉福, 宫立新, 宋键. 大沽河泥沙来源的重矿物分析及其环境意义[J]. 海洋科学, 2010, 34(10):71-76
JIN Bingfu, GONG Lixin, SONG Jian. Heavy mineral analysis in the sediment originated from the Daguhe River and its environmental significance[J]. Marine Sciences, 2010, 34(10):71-76.]
[14] 邓凯, 杨守业, 王中波, 等. 台湾山溪性小河流碎屑重矿物组成及其示踪意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(3):531-542
DENG Kai, YANG Shouye, WANG Zhongbo, et al. Detrital heavy mineral assemblages in the river sediments from Taiwan and its implications for sediment provenance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(3):531-542.]
[15] 宁泽, 韩宗珠, 林学辉, 等. 山东半岛南部近岸海域碎屑矿物对中小河流的物源响应[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(4):57-68
NING Ze, HAN Zongzhu, LIN Xuehui, et al. Provenance response of detrital minerals from medium and small rivers in offshore southern Shandong Peninsula[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(4):57-68.]
[16] 于健, 金秉福, 王孟瑶, 等. 短源河流碎屑矿物在河道、河口和海滩的组分变化及其控制因素: 以山东半岛辛安河为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2023, 45(7):168-182
YU Jian, JIN Bingfu, WANG Mengyao, et al. Component changes and control factors of detrital minerals in riverbed, estuary and beach of short source rivers: taking the Xin’an River in Shandong Peninsula as an example[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2023, 45(7):168-182.]
[17] 马丽芳. 中国地质图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002
MA Lifang. Geological Atlas of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2002.]
[18] Garzanti E, Andò S, Vezzoli G. Settling equivalence of detrital minerals and grain-size dependence of sediment composition[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 273(1-2):138-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2008.06.020
[19] Garzanti E, Andò S, France-Lanord C, et al. Mineralogical and chemical variability of fluvial sediments: 1. Bedload sand (Ganga-Brahmaputra, Bangladesh)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 299(3-4):368-381. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2010.09.017
[20] 陈丽蓉. 中国海沉积矿物学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008
CHEN Lirong. Sedimentary Mineralogy of the China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2008.]
[21] 孔祥淮, 叶思源, 王松涛, 等. 莱州湾海岸带海陆统筹综合地质调查(试点)成果报告[R]. 青岛: 中国地质调查局青岛海洋地质研究所, 2017
KONG Xianghuai, YE Siyuan, WANG Songtao, et al. Report on the results of marine and land integrated geological survey (pilot) in Laizhou Bay coastal zone[R]. Qingdao: Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, China Geological Survey, 2017.]
[22] 于永海, 张盼, 王鹏, 等. 莱州湾现代沉积特征及中全新世以来沉积环境演变研究[M]. 南京: 河海大学出版社, 2017
YU Yonghai, ZHANG Pan, WANG Peng, et al. Study on the Modern Sedimentary Characteristics and Sedimentary Environment Evolution since the Mid-Holocene in Laizhou Bay[M]. Nanjing: Hohai University Press, 2017.]
[23] 山东省地质矿产局. 山东省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Shandong Province. Regional Geology of Shandong Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991.]
[24] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 12763.8-2007 海洋调查规范 第8部分: 海洋地质地球物理调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 12763.8-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey: part 8: marine geology and geophysics survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008.]
[25] Mange M A, Maurer H F W. Heavy Minerals in Colour[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 1992: 11-22.
[26] Marcinkowski B, Mycielska-Dowgiałło E. Heavy-mineral analysis in Polish investigations of Quaternary deposits: a review[J]. Geologos, 2013, 19(1-2):5-23. doi: 10.2478/logos-2013-0002
[27] Montero-Serrano J C, Palarea-Albaladejo J, Martín-Fernandez J A, et al. Sedimentary chemofacies characterization by means of multivariate analysis[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2010, 228(3-4):218-228. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2010.04.013
[28] 匡荟芬, 胡春华, 吴根林, 等. 结合主成分分析法(PCA)和正定矩阵因子分解法(PMF)的鄱阳湖丰水期表层沉积物重金属源解析[J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(4):964-976 doi: 10.18307/2020.0406
KUANG Huifen, HU Chunhua, WU Genlin, et al. Combination of PCA and PMF to apportion the sources of heavy metals in surface sediments from Lake Poyang during the wet season[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(4):964-976.] doi: 10.18307/2020.0406
[29] Martens H, Næs T. Multivariate Calibration[M]. New York: John Wiley &Sons, 1992.
[30] Lee H J, Jeong K S, Han S J, et al. Heavy minerals indicative of Holocene transgression in the southeastern Yellow Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1988, 8(3):255-266. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(88)90032-5
[31] Morton A C, Hallsworth C R. Processes controlling the composition of heavy mineral assemblages in sandstones[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1999, 124(1-4):3-29. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(98)00118-3
[32] Sevastjanova I, Hall R, Alderton D. A detrital heavy mineral viewpoint on sediment provenance and tropical weathering in SE Asia[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2012, 280:179-194. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.03.007
[33] 陆凯, 秦亚超, 王中波, 等. 东海中南部海域表层沉积物碎屑重矿物组合分区及其物源分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(8):20-26
LU Kai, QIN Yachao, WANG Zhongbo, et al. Heavy mineral provinces of the surface sediments in central-southern East China Sea and implications for provenance[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(8):20-26.]
[34] 王濮, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝. 系统矿物学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1982
WANG Pu, PAN Zhaolu, WENG Lingbao. Systematic Mineralogy[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1982.]
[35] 陈光远, 孙岱生, 殷辉安. 成因矿物学与找矿矿物学[M]. 2版. 重庆: 重庆出版社, 1988
CHEN Guangyuan, SUN Daisheng, YIN Huian. Genetic and Prospecting Mineralogy[M]. 2nd ed. Chongqing: Chongqing Press, 1988.]
[36] 常丽华, 陈曼云, 金巍, 等. 透明矿物薄片鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006
CHANG Lihua, CHEN Manyun, JIN Wei, et al. Manual for the Identification of Thin Sections of Transparent Minerals[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2006.]
[37] 薛君治, 白学让, 陈武. 成因矿物学[M]. 2版. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1991
XUE Junzhi, BAI Xuerang, CHEN Wu. Genetic Mineralogy and Prospecting Mineralogy[M]. 2nd ed. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1991.]
[38] Hawthorne F C, Oberti R, Harlow G E, et al. Nomenclature of the amphibole supergroup[J]. American Mineralogist, 2012, 97(11-12):2031-2048. doi: 10.2138/am.2012.4276
[39] 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985
LIU Dongsheng. Loess and Environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.]
[40] Jin B F, Wang M Y, Yue W. Comparative analysis of heavy mineral characteristics of sediments from the Huanghe River and the Changjiang River based on the multiple-window grain size strategy[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2021, 216:104326. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2020.104326
-




 下载:
下载: