Audio magnetotelluric detection of hidden karst in deep carbonate coverage area: A case study of Daguan area in Yunnan province, China
-
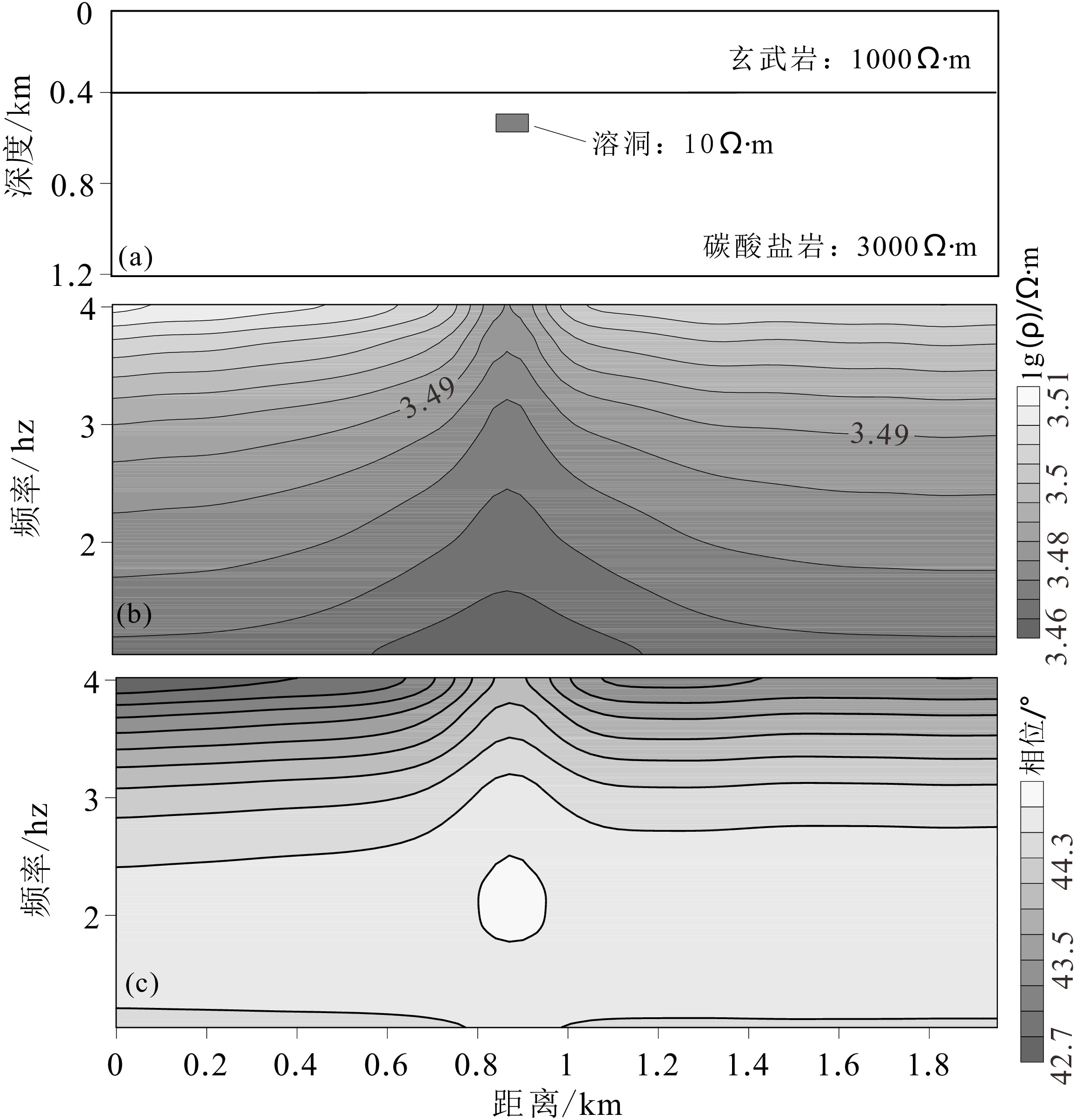
摘要:
碳酸盐岩受水溶蚀易于发育岩溶,形成溶洞、地下河等,常导致油气钻探出现掉钻、卡钻等情况。调查和研究显示,云南大关地区奥陶系五峰—志留系龙马溪组富有机质页岩具有高含气性,是勘探开发的重要领域。然而,该地区分布的二叠系茅口组和栖霞组碳酸盐地层广泛发育岩溶构造,这在很大程度上制约了页岩气的进一步勘探。同时,这两套地层的埋深可能超过1 km,对地球物理方法的探测精度也提出了挑战。本文通过理论模型试算和已有钻孔(D0)的方法试验,明确了音频大地电磁方法识别深部隐伏岩溶的可行性。在预选井位区(D1)开展音频大地电磁探测,并根据电性模型重新部署了调查井(D2),实际钻井检验了方法的可靠性,并认为不连续分布的高电阻率异常区往往指示岩溶构造的存在,井位布设的有利区可能是高电阻率异常连续分布的块状或带状异常区。因此,音频大地电磁探测不仅对岩溶覆盖区的油气钻井选址具有先导作用,同时也拓宽了该方法的应用范围。
Abstract:Karst is easy to develop in carbonate rocks through water dissolution, forming caves and underground rivers, which often causes issues like drill bit loss and sticking during oil and gas drilling. Previous research has shown that the organic-matter-rich shale of the Ordovician Wufeng to Silurian Longmaxi Formations in the Daguan area, Yunnan province, has a high gas content and is an important area for exploration and development. However, the Permian Maokou Formation and Qixia Formation carbonates in this area widely developed karst structures, which restricts the further exploration of shale gas. At the same time, the maximum burial depth of the two strata may be more than 1 km, which also poses a challenge to the detection accuracy of geophysical methods. In this paper, the feasibility of using audio magnetotelluric methods to identify deep concealed karst is confirmed by theoretical model calculation and pre-existing borehole (D0) test. Audio magnetotelluric profiles are implemented in the pre-selected borehole D1. According to the electrical model, the borehole D1 was redeployed to borehole D2. Subsequent drilling confirmed our reasoning and further suggested that the areas of discontinuous high resistivity often indicate the existence of karst structures, and favorable borehole locations may be the areas of massive or banded high resistivity. Therefore, audio magnetotelluric sounding not only plays a leading role in selecting oil and gas drilling sites in areas with karst covered, but also broadens the application scope of the method.
-
Key words:
- Carbonate /
- deep buried karst /
- AMT
-

-
图 1 四川盆地及周缘地区碳酸盐岩分布(a;据陈阵,2017修改)及研究区岩性柱状图(b)
Figure 1.
-
[1] 陈乐寿, 王天生, 1985. 几种简易有效的大地电磁一维反演方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 3: 59-72 doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.1985.03.007
Chen L S, Wang T H, 1985. Several simple and effective magnetotelluric one-dimensional inversion methods[J]. Petroleum Geophysical Prospecting, 3: 59-72 doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.1985.03.007
[2] 陈清礼, 严良俊, 胡文宝, 等, 2005. 瞬变电磁法探测水库坝基溶洞的效果[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版). 2(3): 201 − 204
Chen Q L, Yan L J, Hu W B, et al., 2005. Effect of transient electromagnetic method on detecting karst caves in dam foundation of reservoir[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural science edition). 2(3): 201 − 204
[3] 陈贻祥, 邬健强, 黄奇波, 等, 2018. 水中自然电场法探测病态水库岩溶渗漏通道——以金鸡河水库一级水电站为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 37(6): 883-891
Chen Y X, Wu J Q, Huang Q B, et al. , 2018. Detection of karst leakage passages in sick reservoirs by self-potential method on the water: An example of first-class hydropower station in Jinjihe Reservoir[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 37(6): 883-891
[4] 陈玉玲,甘伏平,卢呈杰,等,2013. 裸露岩溶区地下河管道综合地球物理方法探测研究[J].地球物理学进展,28(03):1608-1616.
Chen Y L, Gan F P, Lu C J, et al., 2013. The study of underground river course detection by integrated geophysical methods in bare karst area[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 28(3): 1608-1612.
[5] 陈宗清, 2007. 四川盆地中二叠统茅口组天然气勘探[J]. 中国石油勘探, 12(5): 1-11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2007.05.001
Chen Z Q, 2007. Natural gas exploration in the Middle Permian Maokou Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 12(5): 1-11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2007.05.001
[6] 陈阵, 2017. 西南岩溶区地下河分布图[M]. 地质出版社, 北京.
Chen Z, 2017. Distribution map of underground river in karst area of Southwest China[M]. Geological Publishing House, Beijing.
[7] Constable S C, Parker R L, Constable C G, 1987. Occam’s inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data[J]. Geophysics, 52(3): 289-300. doi: 10.1190/1.1442303
[8] D’AgostinoN, Silverii F, AmorosoO, et al., 2018. Crustal deformation and seismicity modulated by groundwater recharge of karst aquifers[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45, 12253 − 12262.
[9] 底青云, 安志国, 马凤山, 等, 2014. 高速公路隧道岩溶区地质结构电磁法精细探测研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 22(4): 692-698
Di Q Y, An Z G, Ma F S, et al. , 2014. Fine detection of geological structure in karst area of expressway tunnel by electromagnetic method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 22(4): 692-698
[10] 郭镜, 夏时斌, 2022.川东褶皱带地热系统的空间载体——相互连通的断裂系统: 以四川广安牟家镇地热井为例[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 42(4) :642-652.
Guo J, Xia S B, 2022. Spatial carrier of geothermal system in eastern Sichuan fold zone——interconnected fault system: A case study of geothermal well in Moujia Town, Guang'an, Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 42(4) :642-652.
[11] Drahor M, 2019. Identification of gypsum karstification using an electrical resistivity tomography technique: The case-study of the Sivas gypsum karst area (Turkey)[J]. Engineering Geology, 252: 78-98. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.02.019
[12] Egbert G D, 2012. Hybrid conjugate gradient-Occam algorithms for inversion of multifrequency and multitransmitter EM data[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 190: 255-266. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05523.x
[13] Festa V, Tripaldi S, Siniscalchi A, et al. , 2016. Geoelectrical resistivity variations and lithological composition in coastal gypsum rocks: A case study from the Lesina Marina area (Apulia, southern Italy) [J]. Engineering Geology, 202: 163-175. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.12.026
[14] Gan F, Han K, Lan F, et al. , 2017. Multi-geophysical approaches to detect karst channels underground — A case study in Mengzi of Yunnan Province, China[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 136: 91-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2016.10.036
[15] Giorgi L and Leucci G, 2014. Detection of Hazardous Cavities Below a Road Using Combined Geophysical Methods[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 35(4): 1003-1021.
[16] Gutiérrez F, Parise M, Waele J, et al., 2014. A review of natural and human−induced geohazards and impacts in karst. Earth Science Review 138: 61 − 88.
[17] 江青春, 胡素云, 汪则成, 等, 2012. 四川盆地茅口组风化壳岩溶古地貌及勘探选区[J]. 石油学报, 33(6): 949-960
Jiang Q C, Hu S Y, WANG Ze C, et al. , 2012. Paleokarst landform of weathering crust of Middle Permian Maokou Formation in Sichuan Basin and selection of exploration regions[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 33(6): 949-960
[18] 金民东, 李毕松, 朱祥, 等, 2020. 四川盆地东北部元坝地区及周缘震旦系灯影组四段储集层特征及主控因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 47(6): 1090-1099
Jin MD, LI B S, Zhu X, et al. , 2020. Characteristics and main controlling factors of reservoirs in the 4th member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Yuanba and its periphery area, northeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 47(6): 1090-1099
[19] Kaufmann G, Romanov D, Nielbock R, et al. , 2011. Cave detection using multiple geophysical methods: Unicorn cave, Harz Mountains, Germany[J]. Geophysics, 76(3): B71-B77. doi: 10.1190/1.3560245
[20] Kruse S, Grasmueck M, Weiss M, et al. , 2006. Sinkhole structure imaging in covered Karst terrain[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(16): 271-284.
[21] Laskow M, Gendler M, Goldberg, et al. , 2011. Deep confined karst detection, analysis and paleo-hydrology reconstruction at a basin-wide scale using new geophysical interpretation of borehole logs[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 406(3-4): 158-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.06.011
[22] 聂海宽, 包书景, 高波, 等, 2012. 四川盆地及其周缘下古生界页岩气保存条件研究[J]. 地学前缘, 19(3): 280-294
Nie H K, Bao S J, Gao B, et al. , 2012. Preservation conditions of Lower Paleozoic shale gas in Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(3): 280-294
[23] 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等, 2009. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 36(1): 1-28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.01.001
Pan G T, Xiao Q H, Lu S N, et al. , 2009. Division of geotectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 36(1): 1-28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.01.001
[24] 任纪舜, 王作勋, 陈炳蔚, 等, 1999. 从全球看中国大地构造一中国及邻区大地构造图及简要说明[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1 − 50
Ren J S, Wang Z X, Chen B W, et al., 1999. Geotectonics of China from a global perspective − Geotectonic map of China and adjacent areas and brief description[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1 − 50
[25] 万汉平, 谢迎春, 王桥, 等. 2023. 西藏谷露地热田地热资源前景及勘探方向[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 43(2):249-260.
Wan H P, Xie Y C, Wang Q, et al., 2023. The geothermal prospect and exploration direction of Gulu geothermal field in Tibetan Plateau[J ]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 43(2):249-260.
[26] Rodi W, Mackie R L, 2001. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2−D magnetotelluric inversion[J]. Geophysics, 66, 174 − 187.
[27] Siripunvaraporn W, Egbert G, Uyeshima M, et al. , 2005. Interpretation of two-dimensional magnetotelluric profile data with three-dimensional inversion: synthetic examples[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 160: 804-814.
[28] Smith J T, Booker J R, 1991. Rapid inversion of two− and three−dimensional magnetotlluric data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 96(B3): 3905 − 3922.
[29] 王桥, 唐发伟, 杨剑, 等, 2021. 激电与土壤化探方法在滇西北衙地区的勘查效果及应用前景[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,41(4): 625 − 632.
Wang Q, Tang F W, Yang J, et al., 2021. Exploration effect and application prospect of IP and soil geochemical exploration methods in Nga area of northwest Yunnan [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethys Geology, 41(4): 625 − 632.
[30] 王桥, 潘桂棠, 唐发伟, 等, 2022. 青藏高原壳幔结构构造的基本特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 42(3) : 319-329.
Wang Q, Pang G T, Tang F W, et al., 2022. Basic features of crust-mantle structure of the Tibet Plateau. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 42(3): 319-329.
[31] 汪正江, 杨菲, 刘家洪, 等, 2020. 滇东北地区五峰-龙马溪组沉积转换及其页岩气地质意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 40(3): 129-139 doi: 10.19826/j.cnki.1009-3850.2020.07006
Wang Z J, Yang F, LIU J H, et al. , 2020. Sedimentary transformation of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in northeastern Yunnan and its shale gas geological significance[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 40(3): 129-139 doi: 10.19826/j.cnki.1009-3850.2020.07006
[32] 熊小辉, 刘家洪, 邓奇, 等, 2019. 云南大关地区(云大页 1 井)龙马溪组获页岩气调查重大发现[J]. 中国地质, 46(6): 1576-1577 doi: 10.12029/gc20190622
Xiong X H, LIU J H, Deng Q, et al. , 2019. The breakthrough of shale gas survey from Longmaxi Formation of Well Yundaye-1 in Daguan area, Yunnan Province[J]. Geology of China, 46(6): 1576-1577 doi: 10.12029/gc20190622
[33] 杨剑, 王桥, 刘伟, 等, 2022. 基于宽频大地电磁法的页岩气探测实践—以川西南沐川地区须家河组为例 [J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 42(3): 444-454.
Yang J, Wang Q, Liu W., et al., 2022. Shale gas detection practice based on BMT method: A case study of the Xujiahe Formation in the Muchuan area, southwest Sichuan basin. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 42(3): 444-454.
[34] 杨平, 汪正江, 余谦, 等, 2019. 滇东北木杆向斜奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组页岩气资源潜力评价[J]. 石油实验地质,41(5):638-647.
Yang P, Wang Z J, Yu Q, et al., 2019. Evaluation of shale gas potential in Ordovician Wufeng-Silurian Longmaxi formations, Mugan syncline, northeastern Yunnan[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 41(5):638-647
[35] 杨天春, 申建平, 黎光明, 等, 2014. 天然电场选频法在充水岩溶勘查中的试验与分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 42(2): 71 − 75
Yang T C, Shen J P, Li G M, et al., 2014. Experiment and analysis of natural electric field frequency selection method in water−filled karst exploration[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration, 42(2): 71 − 75
[36] 袁道先, 2009. 新形势下我国岩溶研究面临的机遇和挑战[J]. 中国岩溶, 28(4): 329-331
Yuan D X, 2009. Opportunities and challenges in karst research under new situation[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 28(4): 329-331
[37] 张娣, 余谦, 陆俊泽, 等, 2019. 云南永善—大关地区五峰组—龙马溪组黑色页岩生物地层划分与沉积环境探讨: 以新地 2 井为例[J]. 地球科学. DOI:10.3799/dqkx.2019.028.
Zhang D, Yu Q, Lu J Z, et al., 2019. Biostratigraphic division and sedimentary environment of black shale in Wufeng−Longmaxi Formation, Yongshan−Daguan area, Yunnan Province: A case study of Xindi 2 well [J]. Earth Science. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.028.
[38] 张金川, 姜生玲, 唐玄, 等, 2009. 我国页岩气富集类型及资源特点[J]. 天然气工业, 29(12): 109-114
Zhang J C, Jiang S L, Tang X, et al. , 2009. Enrichment types and resource characteristics of shale gas in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 29(12): 109-114
[39] 张世民, 聂高众, 刘旭东, 等, 2005. 荥经−马边−盐津逆冲构造带断裂运动组合及地震分段特征[J]. 地震地质, 27(2): 221 − 233
Zhang S M, Nie G Z, Liu X D, et al., 2005. Fault movement associations and seismic subdivisions of Yingjing−Mabian−Yanjin thrust tectonic belt[J]. Seismology Geology, 27(2): 221 − 233
[40] 张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等, 2011. 中生代多向挤压构造作用与四川盆地的形成和改造[J]. 中国地质, 38(2): 233 − 250
Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Li J H, et al., 2011. Mesozoic multidirectional compressional tectonics and formation and transformation of Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology in China, 38(2): 233 − 250
[41] 钟原, 杨跃明, 文龙, 等, 2021. 四川盆地西北部中二叠统茅口组岩相古地理、古岩溶地貌恢复及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 48(1): 81 − 93
Zhong Y, Yang Y M, Wen L, et al., 2021. Lithofacies palaeogeography, paleokarst landform restoration of Middle Permian Maokou Formation in northwestern Sichuan Basin and its petroleum geological significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 48(1): 81 − 93
[42] Zou C, Zhu R, Chen Z, et al. , 2019. Organic-matter-rich shales of China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 189: 51-78. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.12.002
-




 下载:
下载: