Environmental evolution and its driving mechanisms of southeastern Beibu Gulf since the Last glacial period
-
摘要:
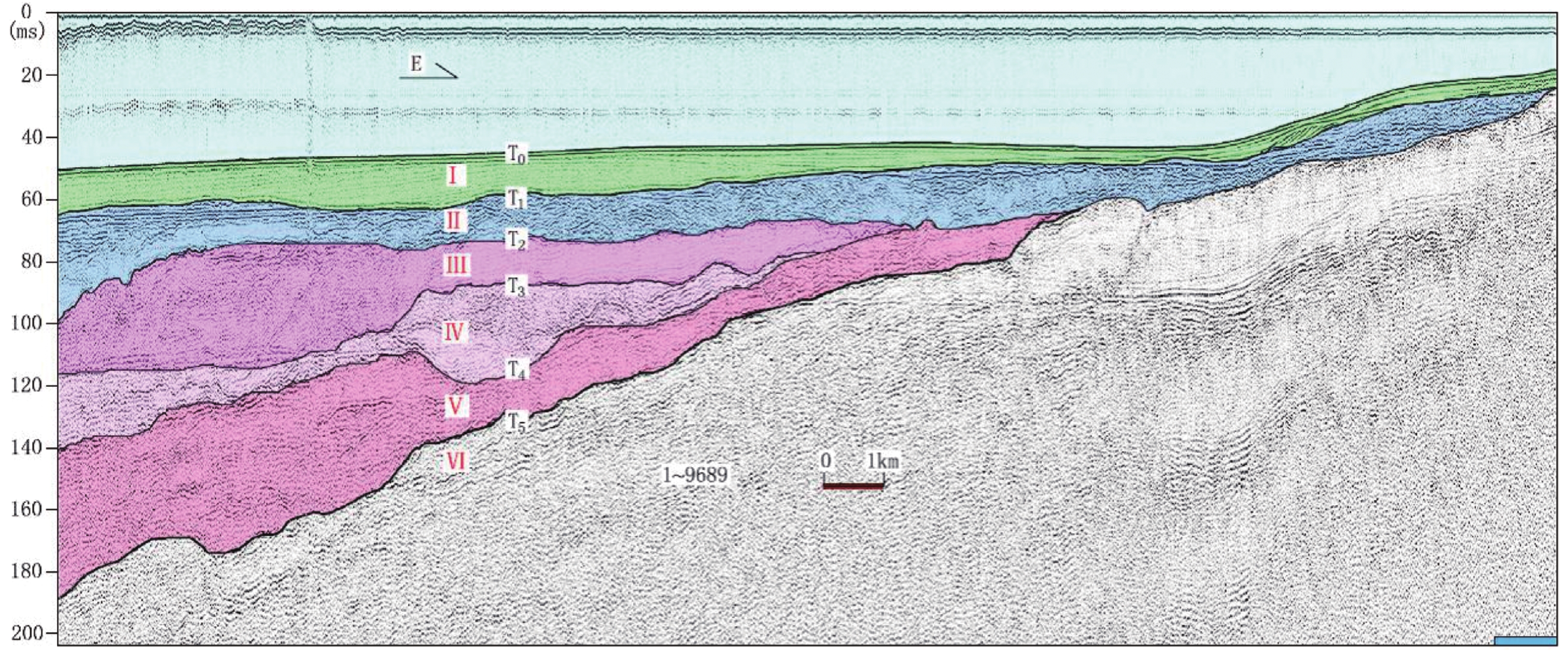
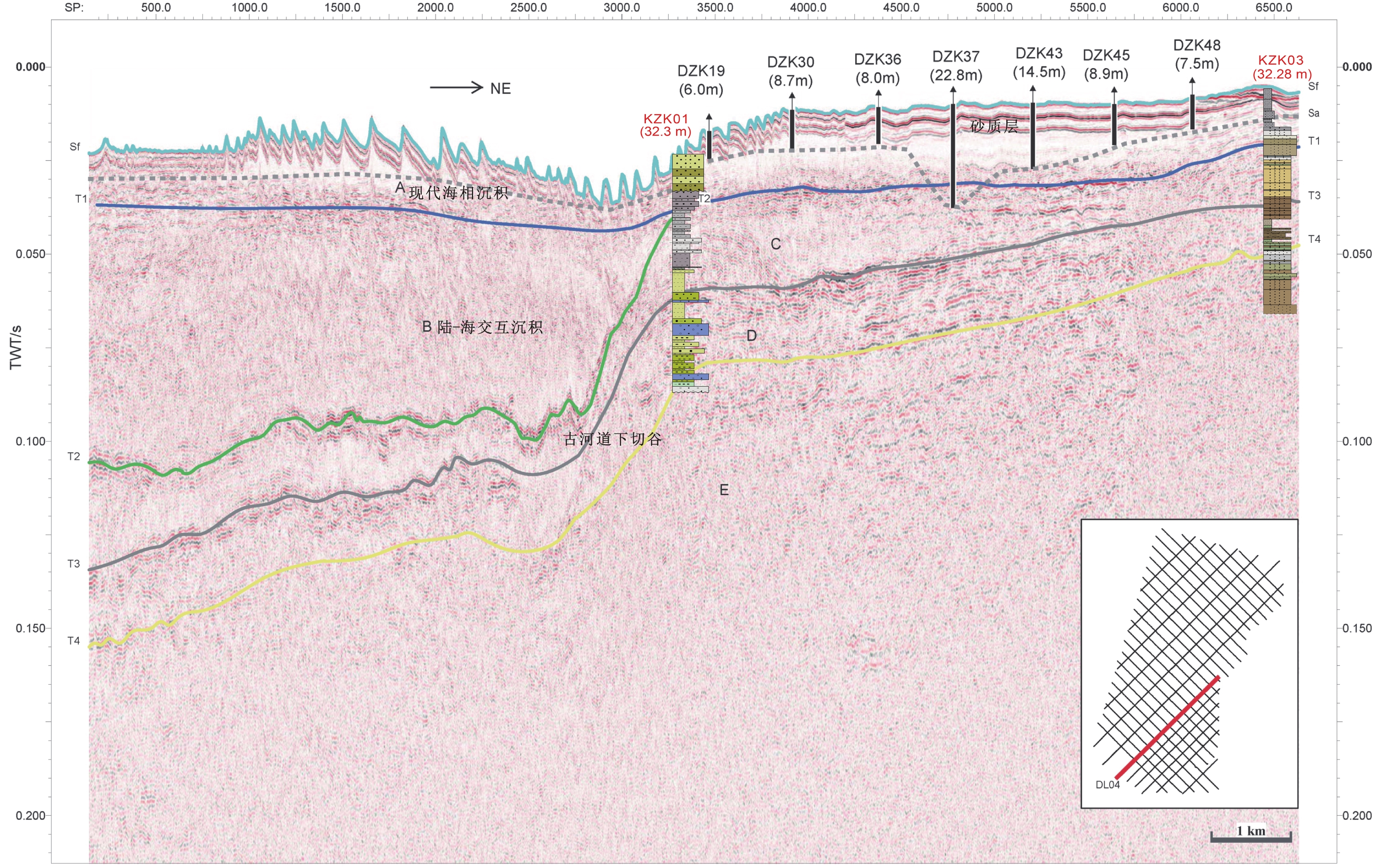
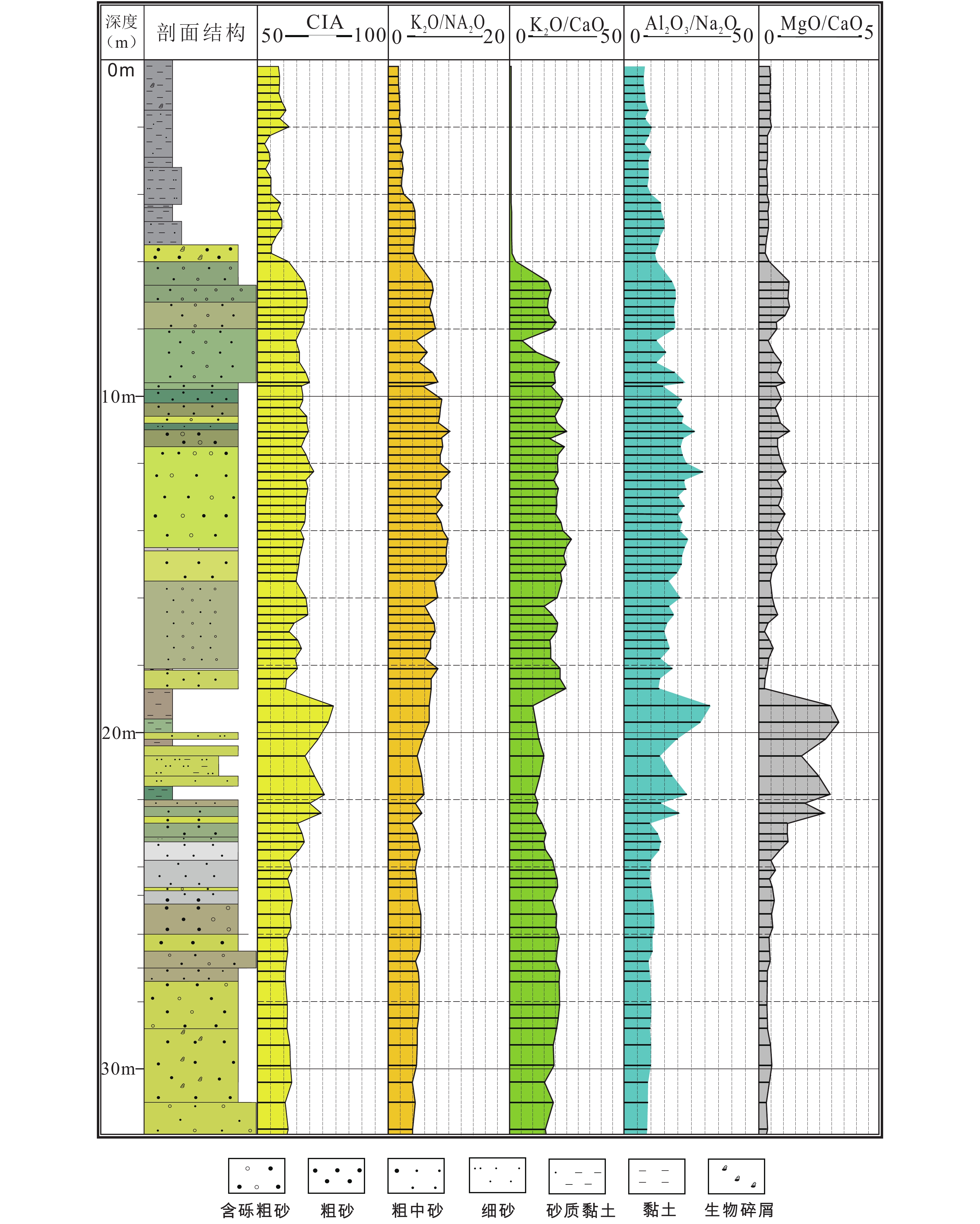
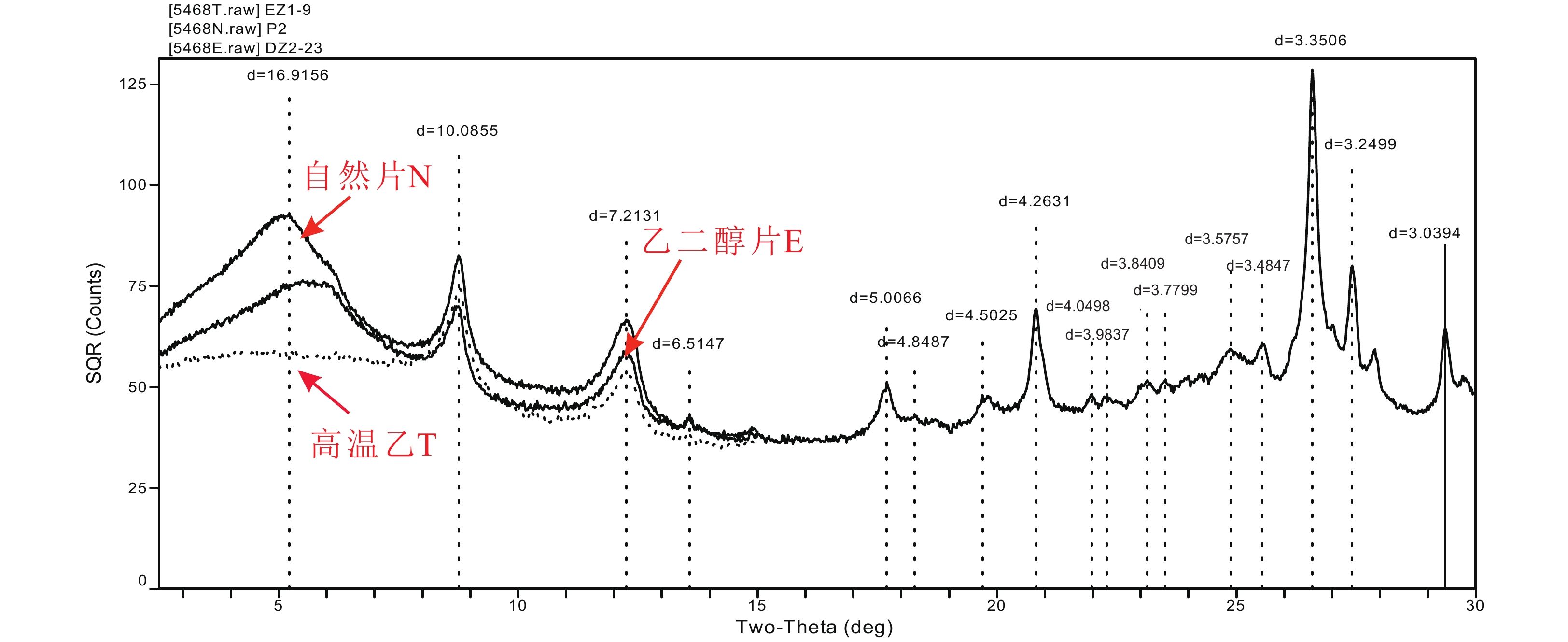
应用单道浅层地震、等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)和X射线衍射(XRD)等测试技术对地层结构及主微量元素地球化学、黏土矿物组成和结晶学特征等气候代用指标进行分析,高精度刻画了北部湾东南部末次间冰期以来的气候演化及驱动机制。指标变化显示南海西北部75千年(75 ka)以来物源供给受气候及海平面变化的协同控制。晚更新世受海因里希(Heinrich)全球气候变冷事件及青藏高原巨大高度和纬度效应的调控导致56 ka、41 ka和28 ka东亚季风的冬季风较夏季风阶段性增强,步入全新世以来,北部湾东南部历经多次干湿交替性升温过程,逐步演化到现今气候阶段。
Abstract:The stratigraphic structure, the geochemistry of major and trace elements, and the composition of clay minerals and the crystallographic characteristics have been analyzed by single-channel shallow seismic, ICP-MS, EDS, and XRD. The climate evolution and its driving mechanisms since the last interglacial period in the southeastern Beibu Gulf have been accurately characterized. The variation of indices shows that the provenance supply of the northwest South China Sea has been controlled by climate and sea level changes since 75 thousand years (75 ka) ago. In the late Pleistocene, the Heinrich event and the differential uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau caused the East Asian monsoon, especially the winter monsoon, to gradually increase at 56 ka, 41 ka, and 28 ka. Since the Holocene (11.5 ka ago), the southeastern part of the Beibu Gulf has experienced several drying-humid warming processes, which gradually evolved into the current climate stage.
-
Key words:
- clay mineral /
- East Asian monsoon /
- Pleistocene /
- South China Sea
-

-
表 1 宝桥水文站流量泥沙资料统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of flow and sediment data in Baoqiao Hydrological Station
统计年份 1957—1994 1995—2014 年平均流量(m3/s) 116.6 134.2 年径流量(亿m3) 37.55 41.75 年最大流量(m3/s) 20000 14800 平均含沙量(kg/m3) 0.173 0.089 多年平均输沙量(104t) 82.0 40.9 -
[1] Broecker W, Bond G, Klas M, et al. , 1992. Origin of the northern Atlantic's Heinrich events [J]. Climate Dynamics, 6(3): 265-273.
[2] Bond G, Broecker W, Johnsen S, et al. , 1993. Correlations between climate records from North Atlantic sediments and Greenlandice [J]. Nature, 365(6442): 143-147. doi: 10.1038/365143a0
[3] Gibbs R J, 1997. Clay mineral segregation in the marine environment [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 47(1) : 237-243.
[4] Hilton R G and West A J, 2020. Mountains, erosion and the carbon cycle [J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 1(6): 284-99.
[5] Heinrich H, 1988. Origin and consequences of cyclic ice rafting in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean during the past130, 000years [J]. Quaternary Research, 29: 142-152. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(88)90057-9
[6] Liu Z F, Trentesaux A, Clemens S C et al, 2003. Clay mineral assemblages in the northern South China Sea: Implications for EastAsian monsoon evolution over the past 2 million years. Marine Geology, 201( 1): 133~146.
[7] Nesbitt H W and Young G M, 1982. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites [J]. Nature, 299(5885): 715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
[8] Raymo M E, Ruddiman W, Froelich P N, 1988. Influence of late Cenozoic mountain building on ocean geochemical cycles [J]. Geology, 16(7): 649-653. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0649:IOLCMB>2.3.CO;2
[9] 陈仕涛, 汪永进, 吴江滢, 等, 2006. 东亚季风气候对Heinrich2事件的响应: 来自石笋的高分辨率记录[J]. 地球化学, 35(6): 586-92. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2006.06.002
[10] Chen S T, WANG Y J, WU J Y, et al, 2006. An event of the East Asian monsoon responding to Heinrich Event 2: Evidence from high-resolution stalagmite record[J]. Geochica, 35(6): 586-92
[11] 程捷, 唐德翔, 张绪教, 等, 2003. 粘土矿物在黄河源区古气候研究中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 17(1): 47-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2003.01.008
[12] Cheng J, Tang D X, Zhang X J, et al, 2003. Reseach on the holocene climate in source area of the Yellow Rive by clay minerals[J]. Geoscience, 17(1): 47-51.
[13] 何海军, 甘华阳, 石要红, 等. 2016. 北部湾沉积物粘土矿物分布特征及其环境意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 52(3): 584-593.
[14] He H J, G H Y, Shi Y B, et al, 2016. Distribution features of clay minerals in sediments of the Beibu Gulf and their environmental significance [J]. Geology and Exploration, 52(3): 0584-0593.
[15] 黄向青, 梁开, 夏真, 等. 2018. 北部湾北部上更新统的沉积特征及其记录的古环境[J]. 第四纪研究38(2): 454-471.
[16] Huang X Q, Liang K, Xia Z, et al, 2018. The sedimentary characterstics of Upper Pleistocene and its palaeo-environmental records in northern Beibu Gulf [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 38(2): 454-471.
[17] Kump, L R. Chemical Weathering, Atmospheric CO2, and Climate [J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28:611-667.
[18] 刘景昱和方念乔, 2019. 海因里希事件与类海因里希事件[J]. 地球科学进展, 34(6): 618-628. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.06.0618
[19] Liu J Y, Fang N Q, 2019. Heinrich events and Heinrich(-like ) events [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 34(6): 618-628.
[20] 刘志飞, 李夏晶, Christophe C, 等, 2010. 南海北部末次冰盛期以来高分辨率黏土矿物记录及其时间序列物源区分析[J]. 科学通报, 55(29): 72-82.
[21] Liu Z F, Li X J, Colin C, et al., 2010. A High-resolution clay mineralogical record in the northern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum and its time series provenance analysis. Chinese Sci Bull, 2010, 55(35): 4058 − 4068.
[22] 密蓓蓓, 张勇, 梅西, 等, 2020. 中国东部海域表层沉积物稀土元素赋存特征及物源探讨[J]. 中国地质, 47(5): 1530-1541.
[23] Mi B B, Zhang Y, Mei X, et al, 2020. The rare earth element content in surface sediments of coastal areas in eastern China`s sea areas and an analysis of material sources[J]. Geology in China, 47(5): 1530-1541
[24] 孙卫东, 林秋婷, 张丽鹏, 等, 2018. 跳出南海看南海-新特提斯洋闭合与南海的形成演化[J]. 岩石学报, 34(12): 3467-3478.
[25] Sun W D, Lin C T, Zhang L P, et al, 2018. The formation of the South China Sea resulted from the closure of the Neo-Tethys: A perspective from regional geology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34( 12): 3467-3478.
[26] 邵菁清和杨守业, 2012. 化学蚀变指数(CIA)反映长江流域的硅酸盐岩化学风化与季风气候?[J]. 科学通报, 57(11): 933.
[27] Sbao J Q, Yang S Y, 2012. Does cbeniical index of alteration (CIA) reflect silicate weathering and monsoonal climate in the Changjiang River basin?. China Sci Bull, 57: 1178-1187.
[28] 史兴民, 李有利, 杨景春, 2007. 新疆玛纳斯河蘑菇湖沉积物中粘土矿物及其环境意义[J]. 干旱区地理, 30(1): 84-88. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6060.2007.01.014
[29] Shi X M, Li Y L, Yang J C. 2007. Environmental significance and clay mineral characteristice of Mogu lake sediment of manas river[J]. Early Dry Zone Geography, 30(1): 84-88.
[30] Tapponnier P, Lacassin R, LeloupP P H, et al. The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt: Tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China[J]. Nature, 1990, 343(6257): 431-437.
[31] 吴江滢, 汪永进, 邵晓华, 等, 2002. 晚更新世东亚季风气候不稳定性的洞穴石笋同位素证据[J]. 地质学, C
[32] Wu J Y, Wang Y J, Shao X H, et al., Instability of the Late Pleistocene East Asian Monsoon Climate-Evidence from the Variation of the Stable Isotope Composition of a Cave Stalagmite[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2002,76(3): 413-419 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] 夏真, 林进清, 郑志昌, 等. 2015. 珠江三角洲近岸海洋地质环境综合研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 106-155.
[34] Xia Z, Lin J Q, Zheng Z C, et al., 2015. Comprehensive study on offshore marine geological environment in Pearl River Delta[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 106-155 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] 杨希冰, 傅恒, 何小胡, 等, 2019. 琼东南盆地南部隆起带新生界沉积体系及其构造-沉积演化[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 39(3): 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2019.03.001
[36] Yang X B, Fu H, H X H, et al , 2019. Cenozoic sedimentary systems and their tectonic-sedimentary evolution in southern uplift zone of the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 39(3): 1-10.
[37] 周世文, 刘志飞, 赵玉龙, 等, 2014. 北部湾东北部2000年以来高分辨率粘土矿物记录及古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2014(3): 160-170.
[38] Zhou S W, Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, et al, 2014. A High-resolution clay mineralogical record and its paleoenvironmetal significance in the Northeastern gulf of tonkin over the past 2000 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014(3): 160-170.
-



 下载:
下载: