Genesis of geothermal water in the Laochang area, eastern Yunnan Province: Constraints from hydrochemistry and C-H-O-S isotopes
-
摘要:
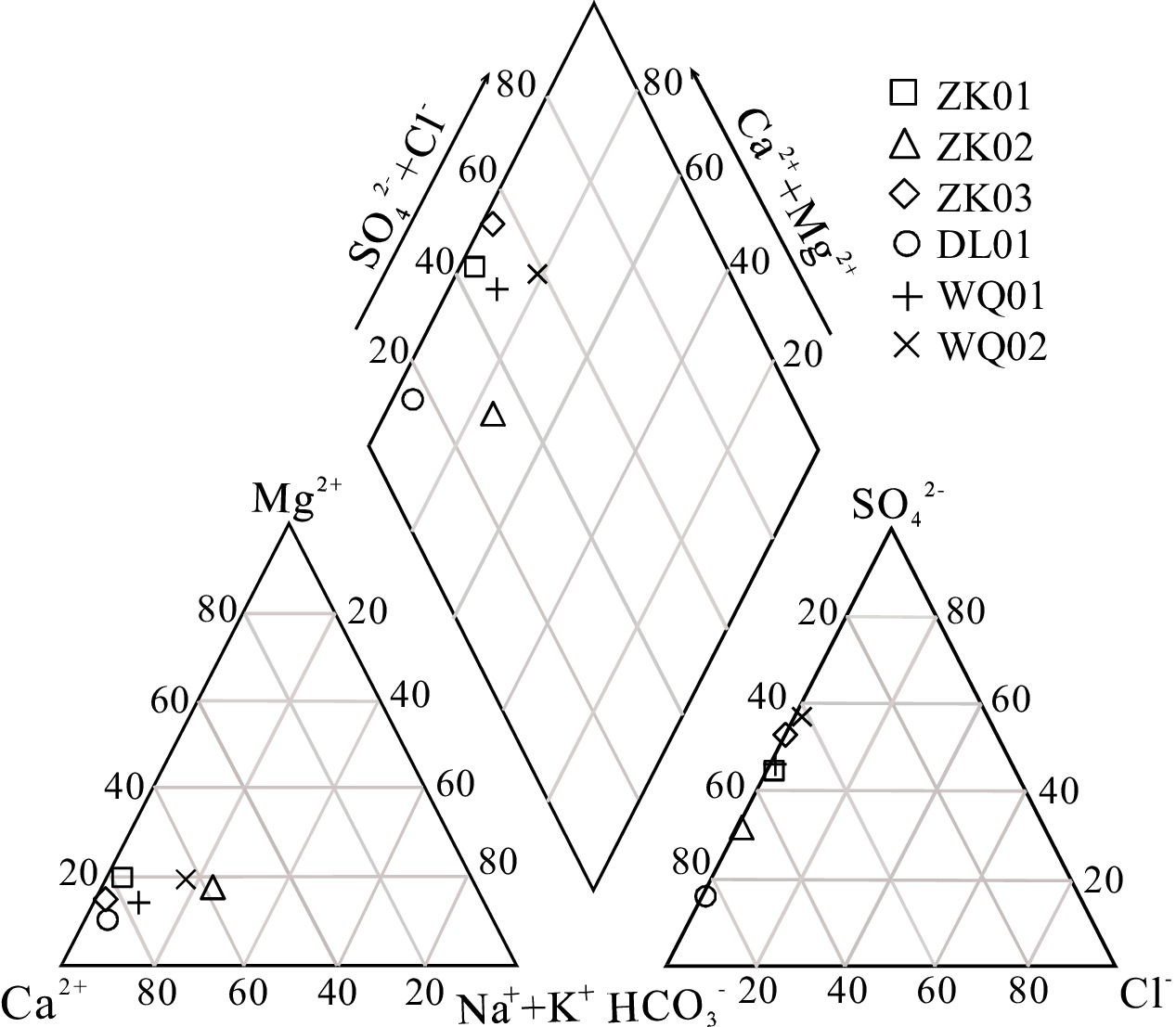
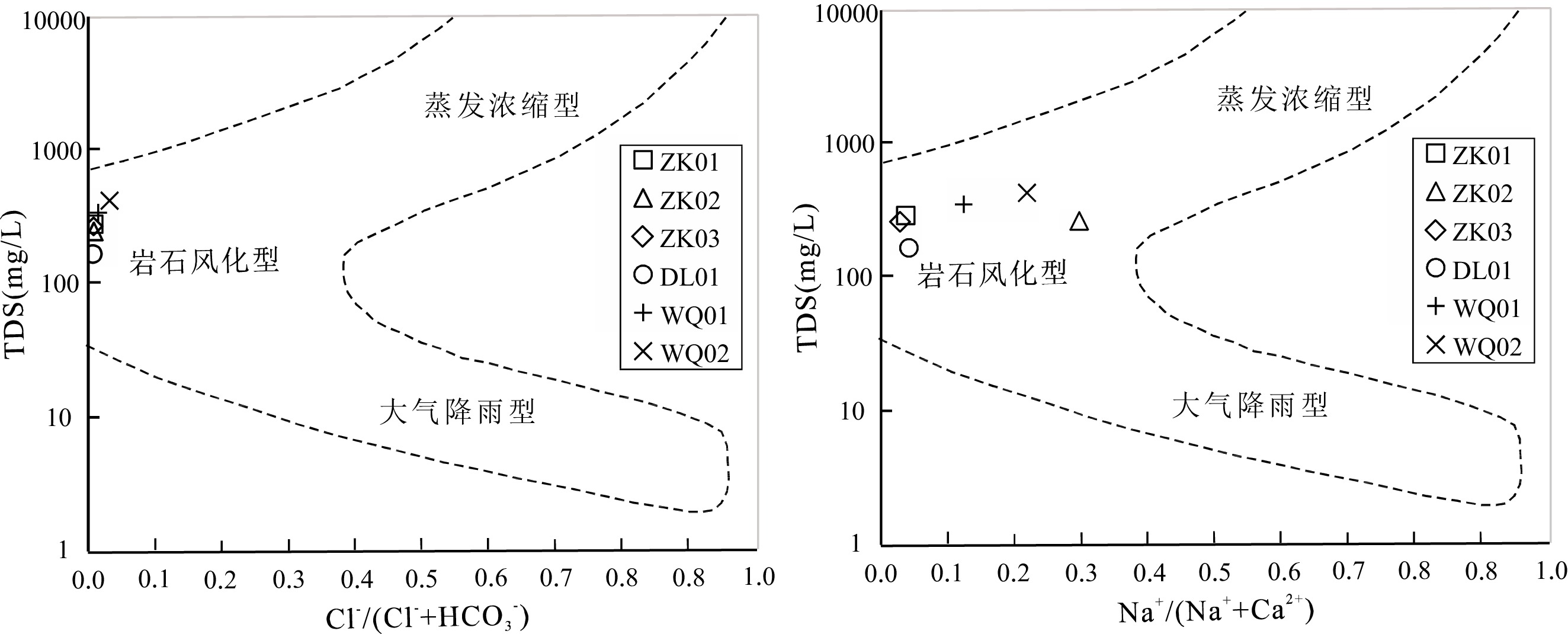
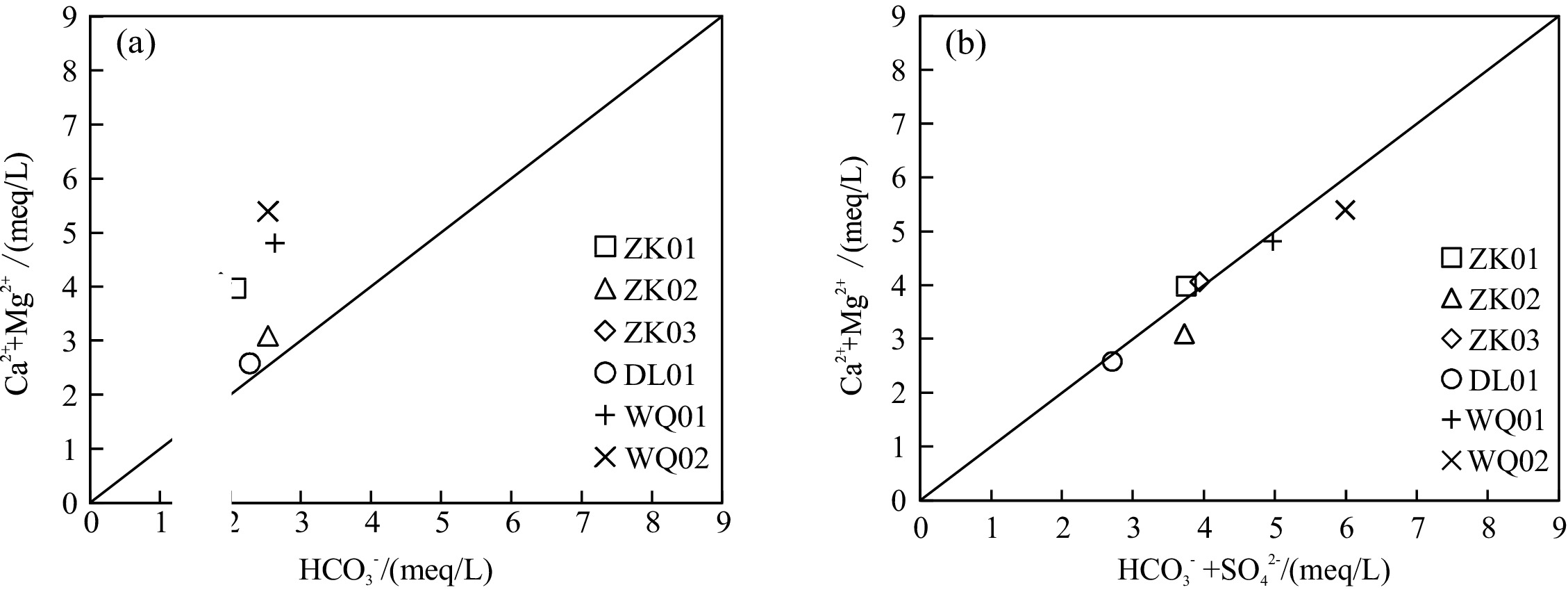
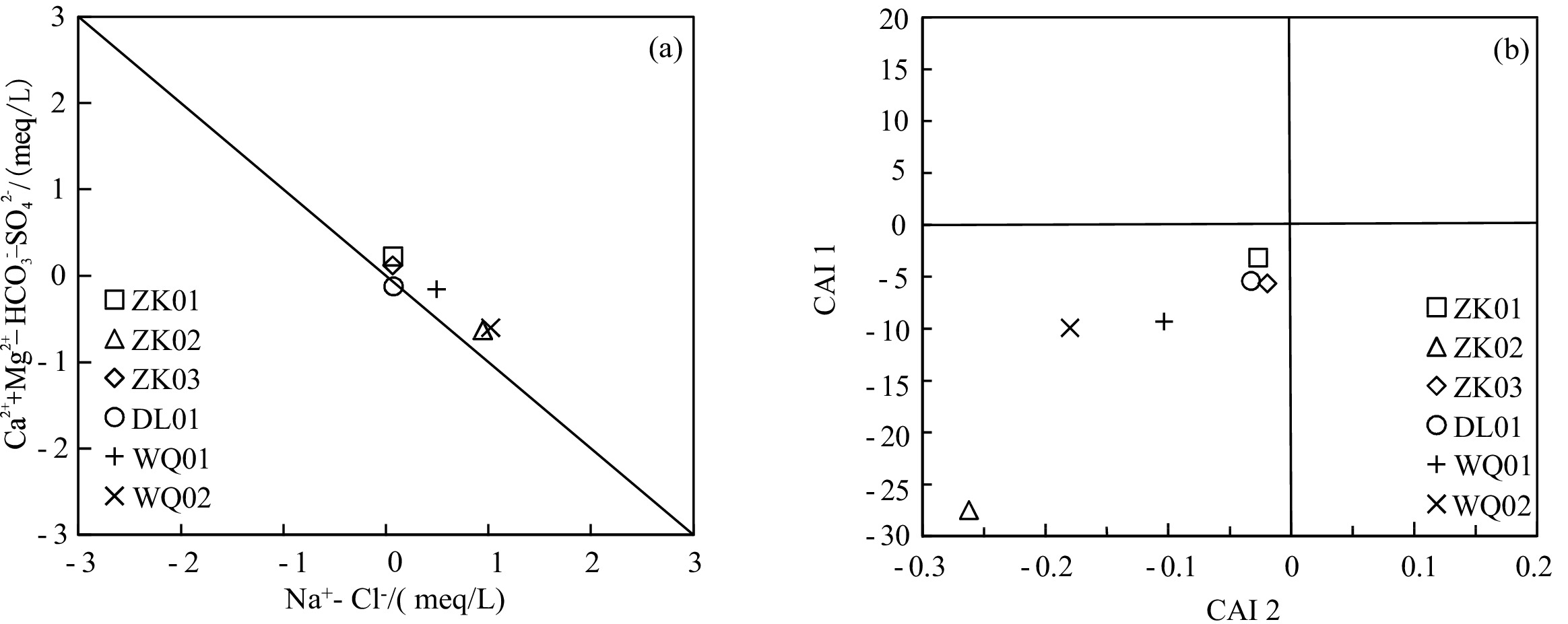
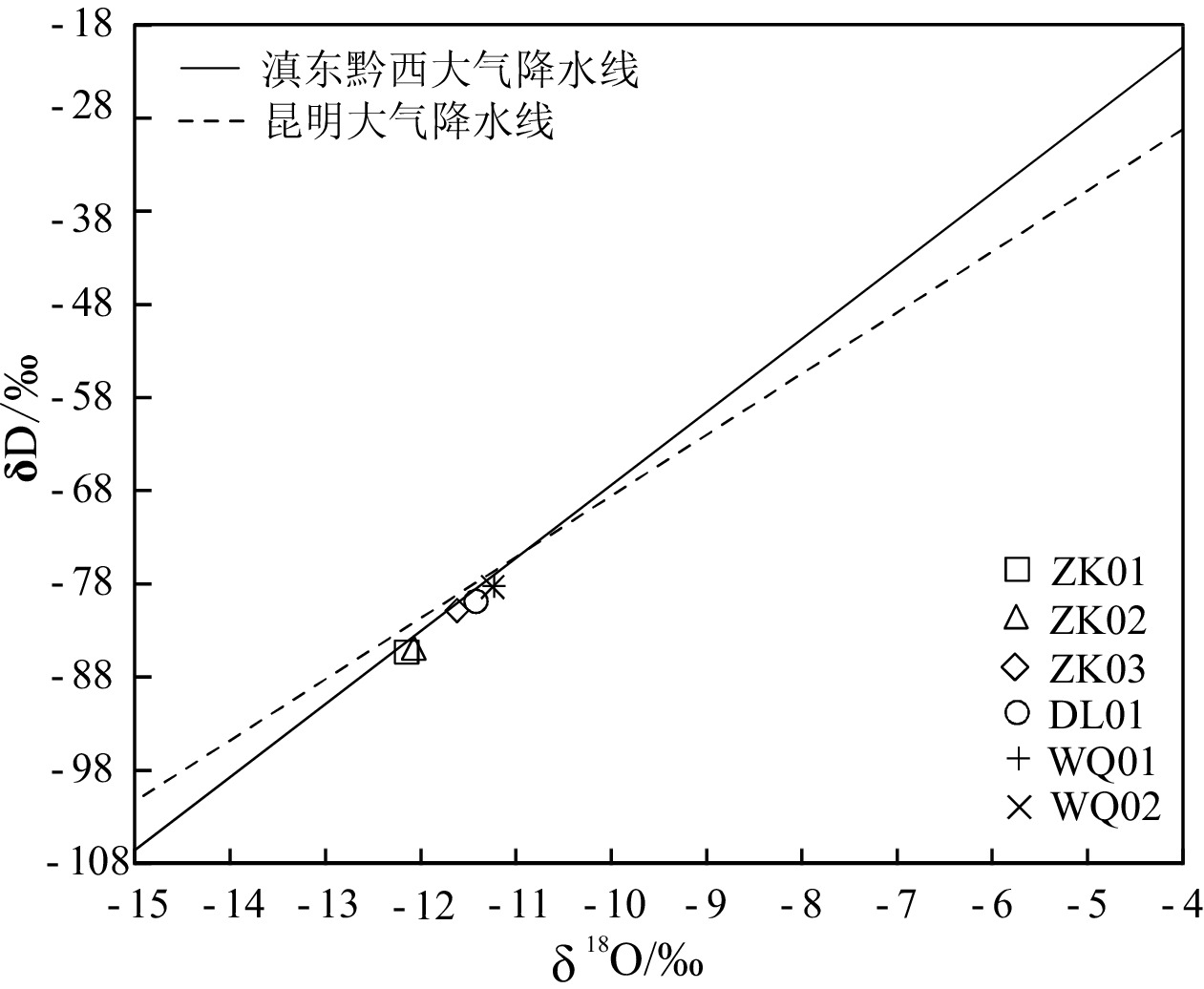
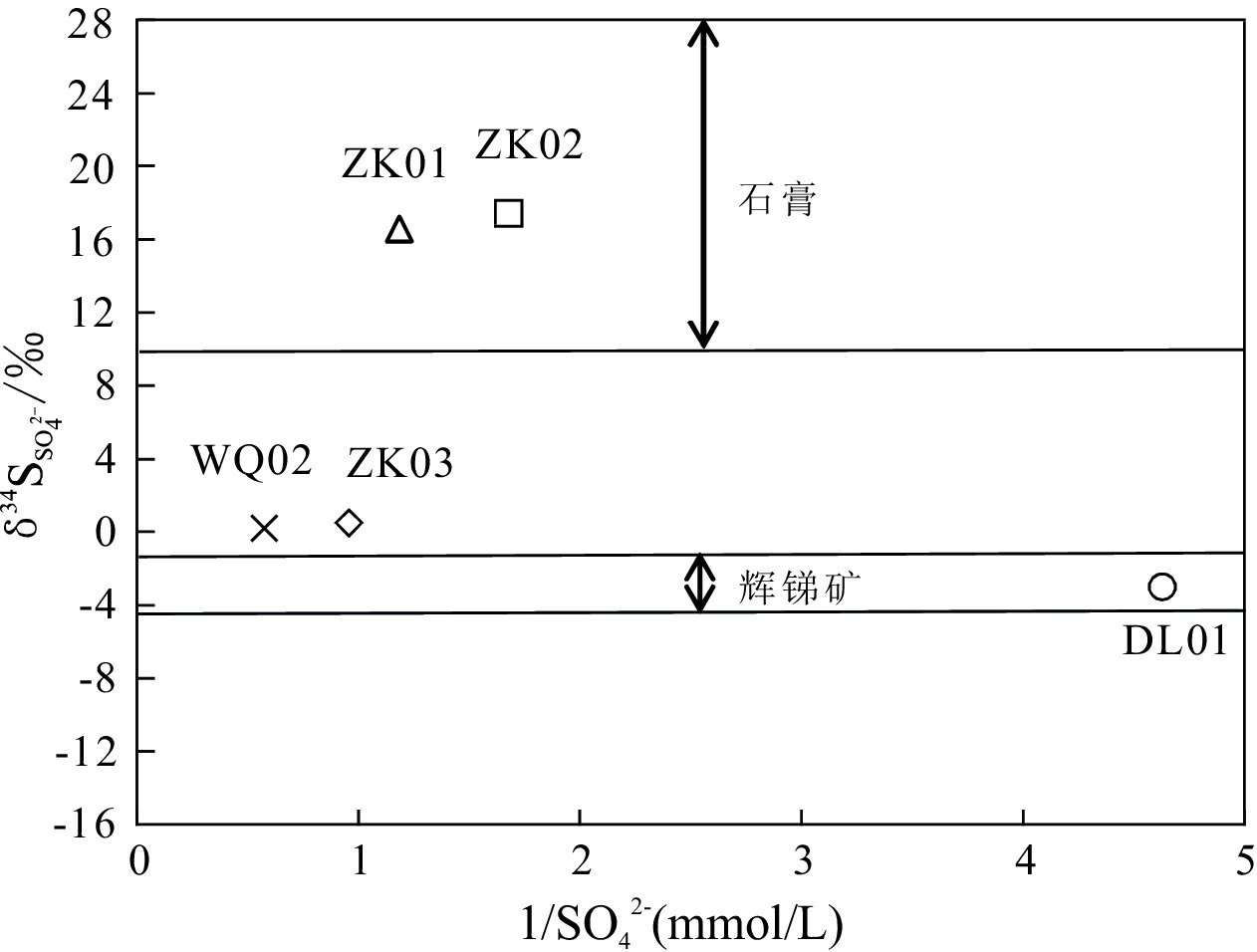
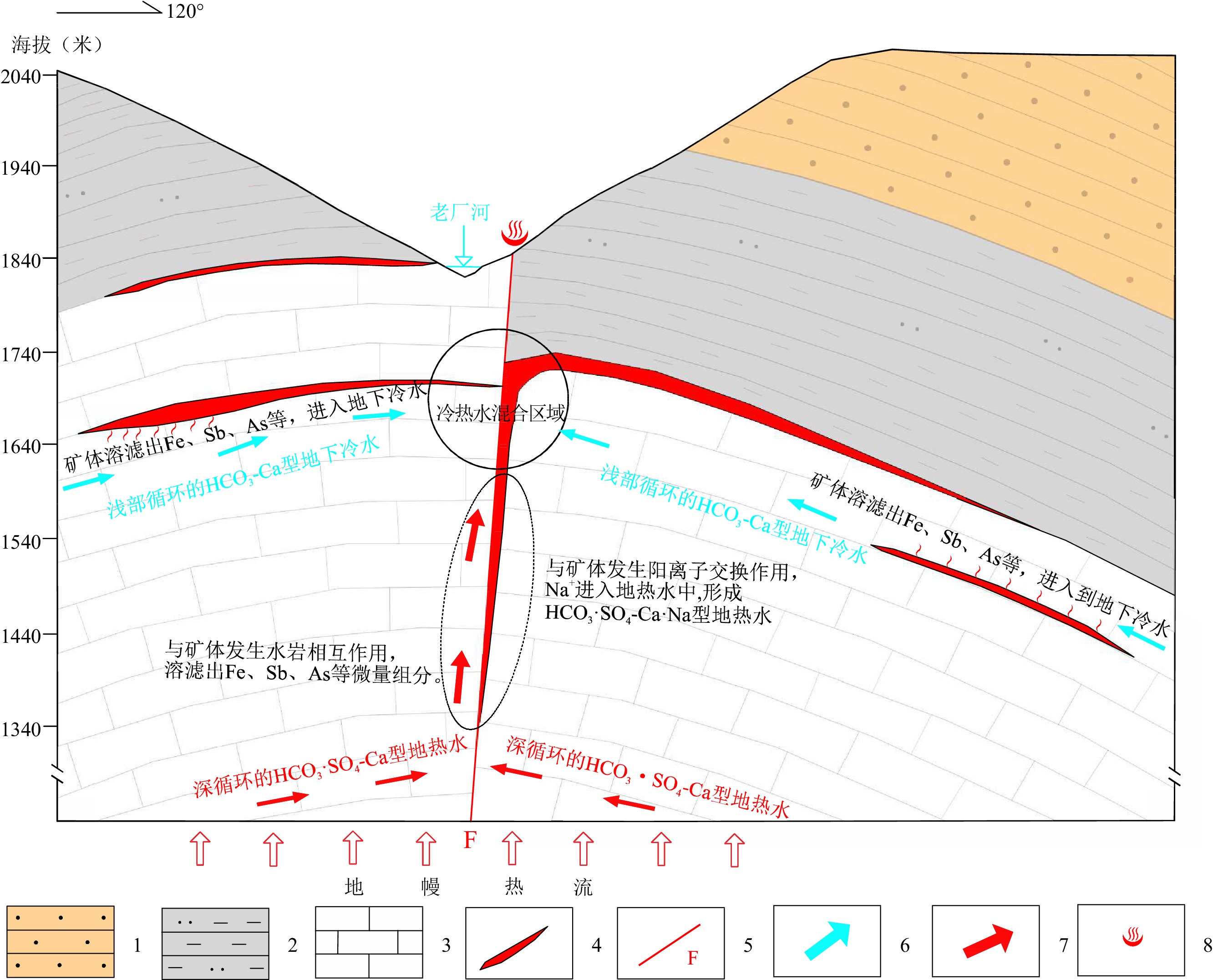
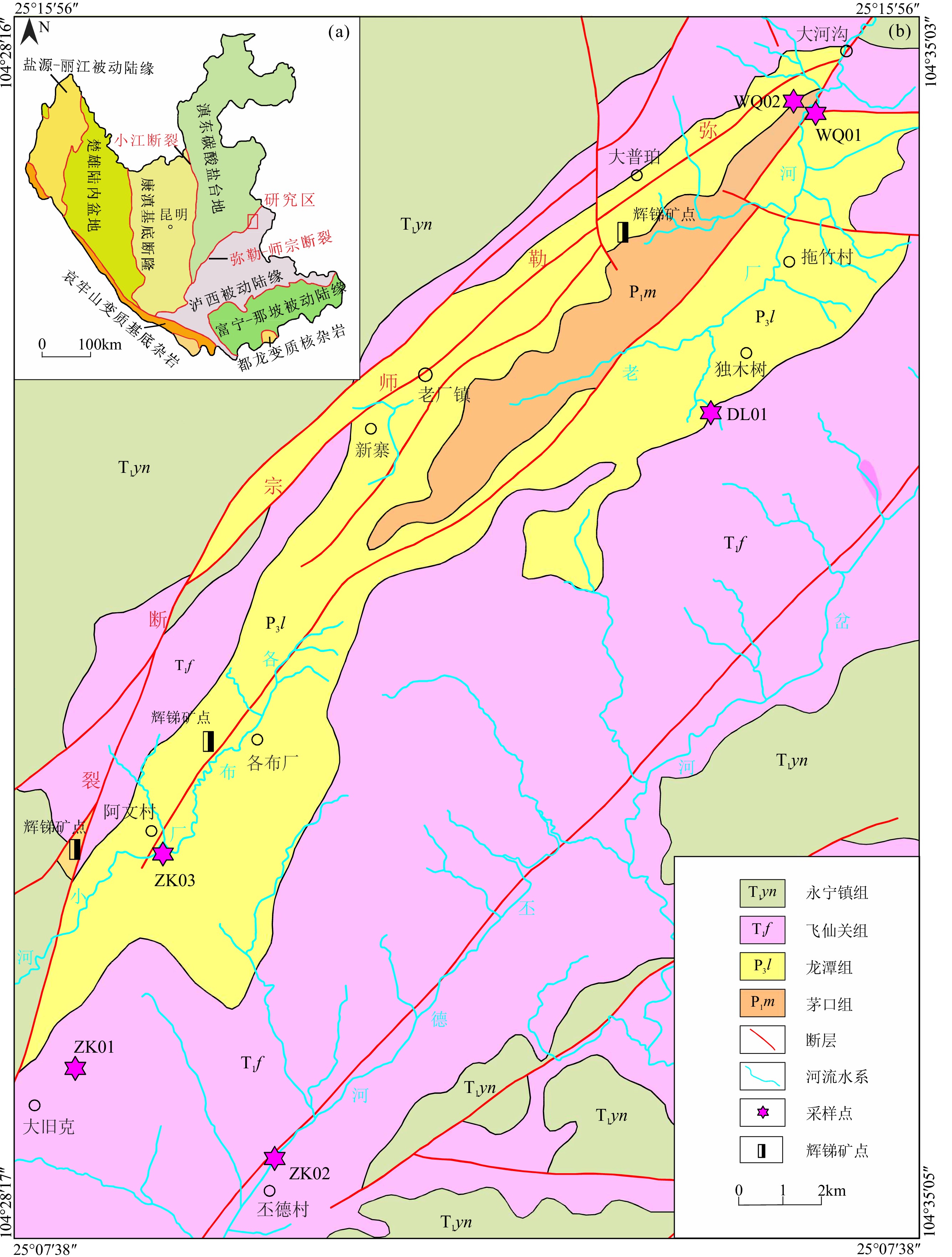
滇东弥勒-师宗断裂带地热资源丰富,但是由于研究程度较低,成因机制不明,制约了区内地热资源的可持续开发利用。本文以弥勒-师宗断裂带北段老厂地区天然温泉水和地热钻孔水为研究对象,综合应用野外调查、水文地球化学和环境同位素方法,对区内地热水的地球化学特征和成因机制进行了研究。结果显示,区内地热水pH值介于7.30~8.12之间,TDS在224~382 mg/L之间,属于弱碱性淡水。地热水水化学类型为HCO3·SO4-Ca型和HCO3·SO4-Ca·Na型,且含有较高含量的Fe、As、Sb等微量组分,不宜饮用。地热水中HCO3−的δ13C值为−3.31‰~−7.79‰,计算得出参与水岩作用的CO2的δ13C值为−9.50‰~−15.68‰,具有明显的沉积有机质来源特征。离子比值分析及硫同位素特征表明碳酸盐岩矿物和石膏的溶解是区内地热水主要离子来源的控制因素,此外赋存于浅部断裂带内的硫化物矿体氧化以及阳离子交换作用对地热水水化学组分产生了一定的影响。氢氧同位素特征及14C测年结果表明区内地热水的补给来源为晚更新世时期温度较低的大气降水,补给高程为
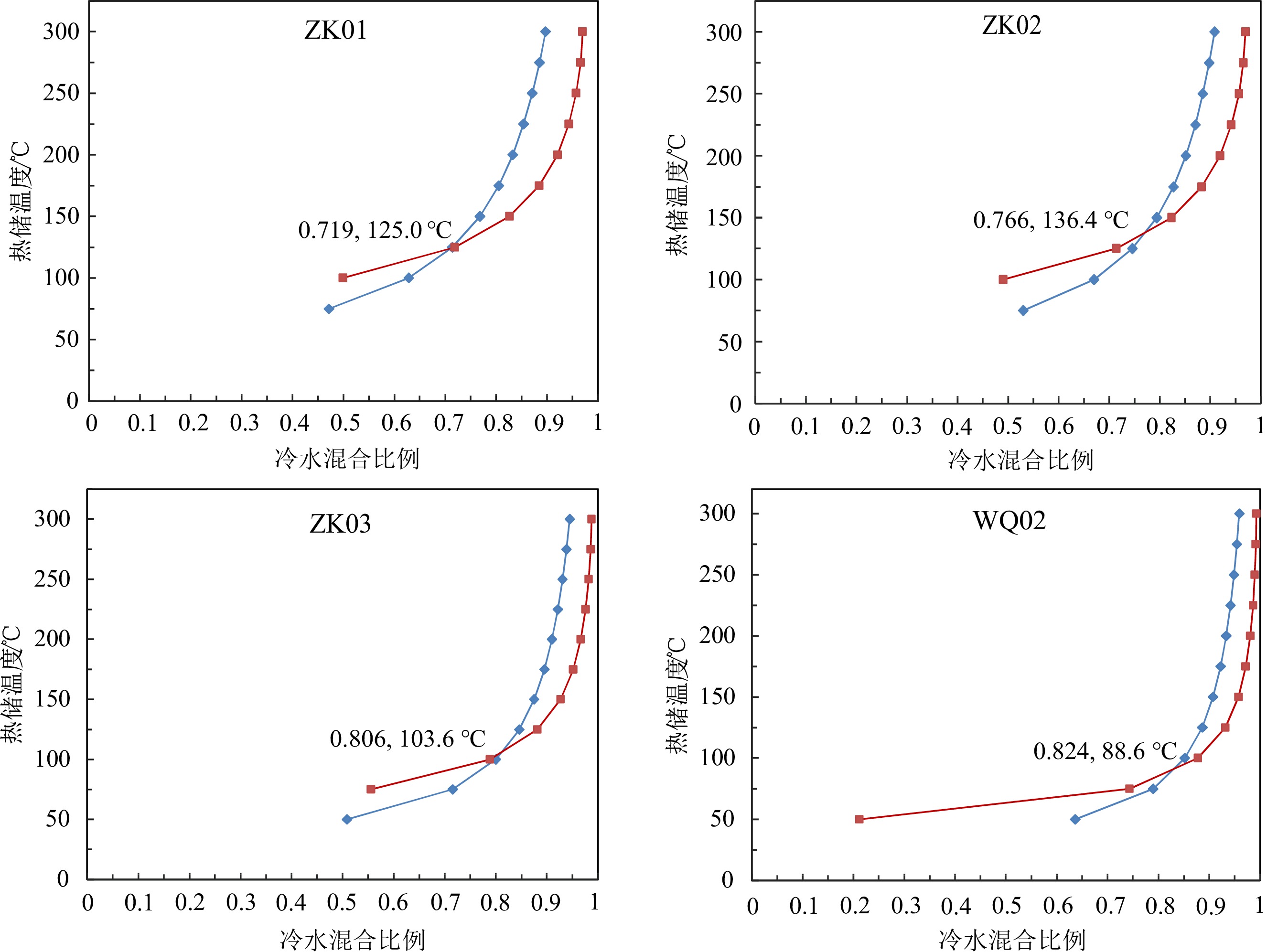
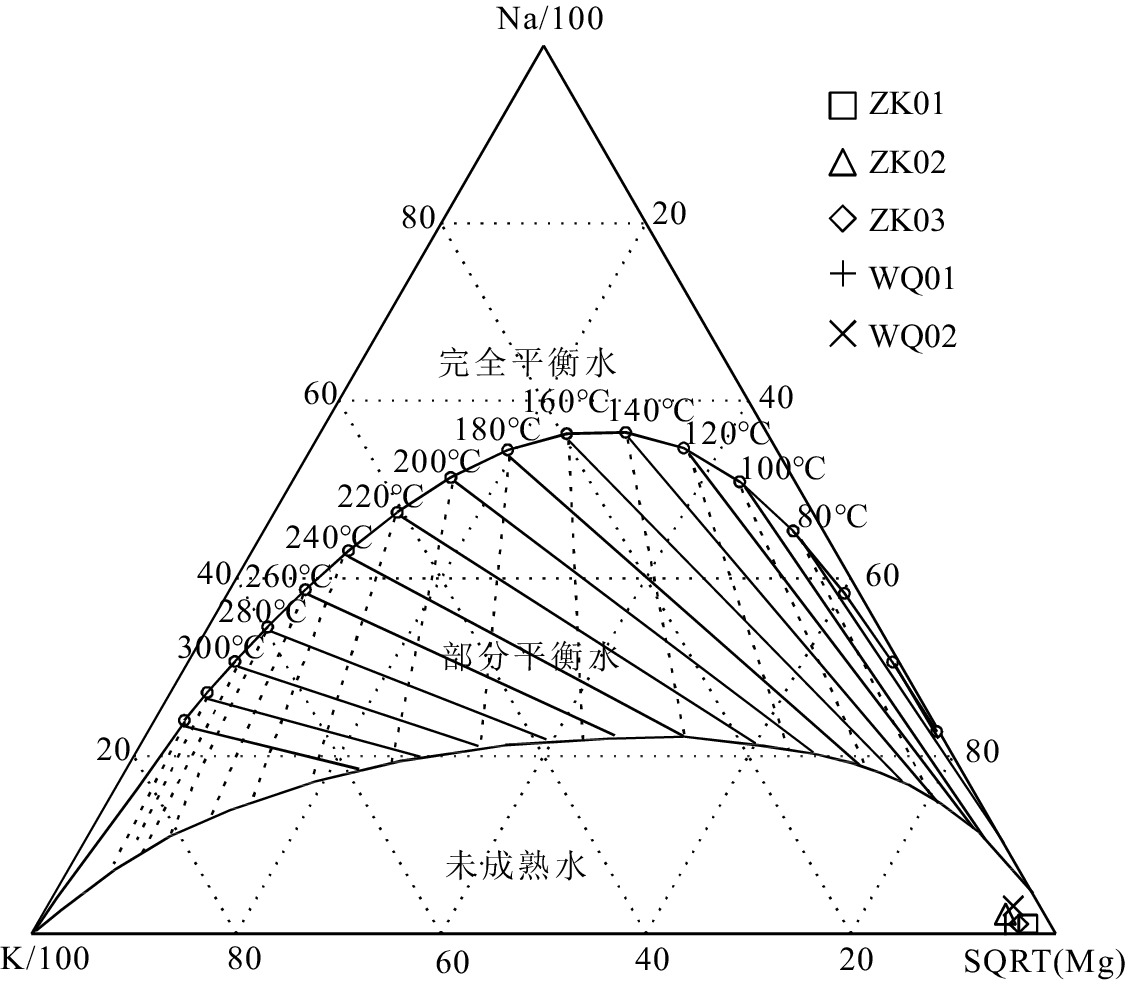
1984.9 ~2283.9 m,补给区位于研究区周边的山区。硅焓方程计算的冷水混合比例为71.9%~82.4%,综合硅焓方程计算的热储温度和校正后的石英地热温标计算的热储温度,认为区内地热水的热储温度为87.5~135.7℃,地热水循环深度为1538.0 ~2502.0 m。研究结果有助于提升滇东弥勒-师宗低温热水带地热水成因研究水平,为区内地热资源的合理开发及保护提供理论支撑。Abstract:The Mile-Shizong Fault Zone in Eastern Yunnan is rich in geothermal resources. However, due to the less research and unclear genetic mechanism, the sustainable development and utilization of geothermal resources in the region has been restricted. Taking the hot spring water and geothermal well water in Laochang area in the north section of the Mile-Shizong Fault Zone as the research object, this paper comprehensively applies the integration of field investigation, hydrogeochemistry and environmental isotope to study the characteristics and genetic mechanism of geothermal water in the study area. The pH values of the geothermal water are between 7.30~8.12 and TDS values are between 224~382 mg/L, which belongs to weakly alkaline fresh water. The hydrochemical types of geothermal water are HCO3·SO4-Ca type and HCO3·SO4-Ca·Na type. The geothermal water contains high contents of trace components such as Fe, As and Sb, and thus are not suitable for drinking. The δ13C value of HCO3− is between −3.31‰ and −7.79‰, and the calculated δ13C value of CO2 involved in water-rock reaction is between −9.50‰ and −15.68‰, which is mainly from sedimentary organic matter. Ion ratio analysis and sulfur isotope characteristics show that the dissolution of carbonate minerals and gypsum is the main factor controlling ion concentrations of geothermal water. In addition, the oxidation and cation exchange of sulfide ore bodies in the fault zone have a certain impact on the composition of geothermal water. Hydrogen and oxygen isotope characteristic and 14C dating results show that the recharge origin of the geothermal water is the atmospheric precipitation with low temperature in the late Pleistocene, and the supply elevation is between
1984.9 m and2283.9 m. The recharge area is located in the mountainous area with the elevation of1984.9 ~2283.9 m around the study area. The mixing ratio of cold water calculated by silicon enthalpy equation is between 71.9% and 82.4%. The heat reservoir temperature calculated by silicon enthalpy equation and corrected quartz geothermal temperature scale is between 87.5℃ and 135.7℃. The circulation depth of geothermal water is between1538.0 m and2502.0 m. The research results are helpful to improve the research level of geothermal water genesis in the Mile-Shizong low-temperature hot water zone in Eastern Yunnan, and provide theoretical support for the rational development and protection of geothermal resources in the area.-
Key words:
- Laochang area /
- Mile-Shizong Fault Zone /
- Geothermal water /
- Hydrochemistry /
- C-H-O-S isotope
-

-
表 1 研究区地热点出露概况
Table 1. General situation of geothermal waters in the study area
名称 编号 地貌形态 出露高程(m) 温度(℃) 构造部位 温泉出露的地层及
钻孔揭露的地层大河沟温泉 WQ01 出露于老厂河河谷右侧 1840.9 25.0 背斜扬起端的断裂带附近 二叠系茅口组(P1m)灰岩、白云质灰岩 WQ02 出露于老厂河河谷左侧 1840.9 28.1 背斜扬起端的断裂带附近 二叠系茅口组(P1m)灰岩、白云质灰岩 大旧克钻孔 ZK01 人工钻孔揭露于大旧克斜坡地带,孔深500 m。 1747.0 47.0 背斜倾伏端的断裂带附近 二叠系茅口组(P1m)灰岩、白云质灰岩 丕德村钻孔 ZK02 人工钻孔揭露于丕德河阶地,孔深600 m。 1448.0 43.5 背斜倾伏端的断裂带附近 二叠系茅口组(P1m)灰岩、白云质灰岩 阿文村钻孔 ZK03 人工钻孔揭露于各布厂小河阶地,孔深200 m。 1841.0 32.5 背斜倾伏端的断裂带附近 二叠系茅口组(P1m)灰岩、白云质灰岩 表 2 研究区水化学组成
Table 2. Chemical composition of water in the study area
样号 pH TDS Na+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ HCO3− SO42− Cl− H2SiO3 Sr F Fe As Sb 硫化物 mg/L WQ01 7.30 306 12.68 0.66 81.92 8.55 160.78 112.00 1.95 12.86 0.23 0.55 0.21 0.007 0.002 0.005 WQ02 7.58 382 26.00 2.19 82.81 14.96 154.48 166.00 3.85 15.80 0.52 0.66 3.30 0.013 0.002 0.005 ZK01 7.84 246 2.39 1.13 63.43 9.62 126.10 80.80 0.77 35.93 1.19 2.12 0.25 0.062 0.021 0.068 ZK02 8.12 224 22.51 1.26 47.57 8.55 154.48 57.10 0.58 36.38 0.91 3.03 0.61 0.082 0.011 0.136 ZK03 7.91 234 1.79 0.48 68.71 7.48 113.49 99.90 0.52 20.55 0.46 1.15 0.18 0.032 0.039 0.051 DL01 7.56 148 2.09 0.54 46.38 3.13 138.65 20.73 0.58 9.32 0.11 0.44 0.13 0.239 0.014 0.005 表 3 研究区地热水稳定同位素及相应的计算结果
Table 3. isotopic compositions of the geothermal water in the study area and its corresponding calculation results
样号 δ13C/‰ δD/‰ δ18O/‰ δ34S/‰ 补给高程/m 补给区温度/℃ 计算的δ13CCO2/‰ 式1 式2 平均值 式1 式2 平均值 WQ01 −7.79 −78.26 −11.23 / 1970.6 1999.2 1984.9 5.4 2.2 3.8 −15.68 WQ02 −6.39 −78.39 −11.25 0.19 1976.1 2004.7 1990.4 5.6 2.3 3.9 −13.72 ZK01 −3.31 −85.32 −12.15 16.55 2269.6 2298.2 2283.9 6.4 3.7 5.1 −9.50 ZK02 −4.31 −85.15 −12.07 17.44 2262.7 2291.3 2277.0 6.8 4.0 5.4 −10.74 ZK03 −6.67 −80.86 −11.62 0.50 2080.8 2109.4 2095.1 7.2 4.6 5.9 −13.91 DL01 −7.06 −79.88 −11.42 −3.00 2039.2 2067.8 2053.5 7.1 4.5 5.8 −15.72 表 4 研究区地热水主要矿物饱和指数
Table 4. Main mineral saturation index of the geothermal water in the study area
样号 硬石膏 文石 方解石 白云石 萤石 岩盐 石膏 天青石 石英 玉髓 无定型SiO2 Fe(OH)3 WQ01 −1.71 −0.22 −0.08 −0.81 −1.47 −9.18 −1.49 −2.33 0.21 −0.23 −1.07 2.12 WQ02 −1.57 0.05 0.20 0.02 −1.39 −8.59 −1.36 −1.84 0.24 −1.01 −1.01 3.16 ZK01 −1.79 0.42 0.54 0.76 −0.62 −10.35 −1.70 −1.66 0.33 −0.80 −0.80 0.99 ZK02 −2.07 0.61 0.74 1.23 −0.39 −9.49 −1.95 −1.91 0.38 −0.78 −0.78 1.53 ZK03 −1.77 0.28 0.42 0.29 −0.97 −10.62 −1.58 −2.03 0.29 −0.12 −0.93 1.66 DL01 −2.57 −0.33 −0.18 −1.31 −1.69 −10.45 −2.32 −3.25 0.20 −0.26 −1.13 2.49 表 5 研究区地热水热储温度估算结果
Table 5. Estimated temperature of the geothermal reservoir of the geothermal water in the study area
样号 SiO2含量
/mg·L−1SiO2温标热储
温度(校正前)/℃冷热水
混合比/%SiO2含量
(校正后)/mg·L−1SiO2温标热储温
度(校正后)/℃硅焓方程
热储温度/℃热储温度
平均值/℃WQ02 12.16 45.7 82.4 35.5 86.5 88.6 87.5 ZK01 27.63 76.1 71.9 80.0 125.1 125.0 125.0 ZK02 27.98 76.6 76.6 96.1 135.0 136.4 135.7 ZK03 15.81 54.8 80.6 51.7 103.4 103.6 103.5 表 6 研究区地热水3H、14C测试分析结果
Table 6. Analytical results of 3H and 14C for the geothermal water in the study area
样品 3H/TU 14C浓度/pmc 表观年龄/ka Pearson模型
校正年龄/kaZK01 <1.0 4.50 25.64 14.13 ZK02 <1.0 4.03 26.55 16.22 -
[1] Ármannsson H, 2016. The Fluid Geochemistry of Icelandic High Temperature Geothermal Areas[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 66: 14-64. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.10.008
[2] A. Baba, F. şaroğlu, I. Akkuş, et al. , 2019. Geological and hydrogeochemical properties of geothermal systems in the southeastern region of Turkey[J]. Geothermics, 78: 255-271. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.12.010
[3] 陈伟, 邓声虎, 谢方银, 2017. 云南富源县老厂萤石矿特征及成矿条件分析[J]. 云南地质, 36(4): 394-397
Chen W, Deng S H, Xie F Y, 2017. The feature and metallogenesis condition analysis of Laochang fluorite deposit in Fuyuan, Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 36(4): 394-397.
[4] 程先锋, 2008. 云南东部地热赋存规律及成因模式[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 硕士学位论文.
Cheng X F, 2008. The Geological Genetic Models and Accumulation Rule of Thermal Water in East of Yunnan Province. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, Thesis of Master’s degree.
[5] Clark I, Fritz P, 1997. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrology [M]. New York: Lewis Publishers.
[6] 党广兴, 2018. 滇东老厂矿区多煤层煤层气井产能影响因素及层间干扰分析[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 硕士学位论文.
Dang G X, 2018. Productivity Influencing Factors of Multilayer CBM Well and Interlayer Inference Analysis in Laochang Mining Area of Eastern Yunnan Province[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, Thesis of Master’s degree.
[7] 邓起东, 张裕明, 许桂林, 等, 1979. 中国构造应力场特征及其板块运动的关系[J]. 地震地质, 1(1): 11 − 22.
Deng Q D, Zhang Y M, Xu G L, et al. , 1979. On the tectonic stress field in China and its relation to plate movement[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1(1): 11 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] Denies P, Langmuir D, Harmon R S,1974. Stable carbon istopic ratios and the extence of a gas phase in the evolution of carbonate waters.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,38:1147-1164.
[9] 方丽萍, 丁建波, 1997. 云南地热资源的成因分析及开发利用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 4(17): 45-48
Fang L P, Ding J B, 1997. Analysis on the genesis and development of geothermal resources in Yunnan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 4(17): 45-48.
[10] Fournier R O, 1977. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems[J]. Geothermics, 5(4): 41-50.
[11] Gibbs R J, 1970. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 170: 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
[12] Giggenbach W F, 1988. Geothermal solute equilibria: Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca Geoindicators [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 52(12): 2749-2765. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3
[13] Guo Q H, 2012. Hydrogeochemistry of High-Temperature Geothermal Systems in China: A Review. Applied Geochemistry, 27(10): 1887−1898.
[14] 顾晓敏, 2018. 阿尔山泉群地球化学特征及成因演化机制研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 博士学位论文.
Gu X M, 2018. Geochemical Characteristics and Evolution Mechanism of Thermal and Mineral Spring in Arxan, North Eastern China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, Thesis of Doctor’s degree.
[15] Hoef, J, 2009. Stable Isotope Geochemistry (sixth edition). Springer−Verlag, doi: 10.1007/978−3−540−70708−0.
[16] 胡智丹, 2017. 贵州兴义地区活动构造及其对地貌的影响[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 硕士学位论文.
Hu Z D, 2017. Active Tectonic and Its Influence on Geomorphology in Xingyi, Guizhou[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, Thesis of Master’s degree.
[17] 蒋秀明, 吴财芳, 张二超, 等, 2020. 老厂矿区雨汪区块地温-地压系统及其展布特征[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 39(2): 32-37
Jiang X M, Wu C F, Zhang E C, et al, 2020. Geotemperature-geopressure system and its distribution characteristics of Yuwang block in Laochang mining area[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University( Natural Science), 39(2): 32-37.
[18] Krouse H R and Grinenko V A, 1991. Stable isotopes: Natural and Anthropogenic sulfur in the environment[M]. Chichester: John Wiley.
[19] 李世林, 1993. 富源老厂矿区地温场特征[J]. 云南地质, 12(2): 183-186
Li S L, 1993. Characteristics of geothermal field in Laochang mining area, Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 12(2): 183-186.
[20] 李学先, 2018. 酸性矿山废水影响下喀斯特流域水文地球化学特征及演化规律研究[D]. 贵州: 贵州大学, 博士学位论文.
Li X X, 2018. Study on Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Evolution Rules of Karst Basin under the Effects of Acid Mine Waste Water[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, Thesis of Doctor’s degree.
[21] 李晓露, 2017. 云南洱源牛街温泉的水化学[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 硕士学位论文.
Li X L, 2017. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation of the Niujie Hot Springs in Eryuan County of Yunnan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, Thesis of Master’s degree.
[22] 刘云, 2011. 云南中东部旅游温泉空间结构及其整合开发研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 硕士学位论文.
Liu Y, 2011. The Spatial Structure and Integrating Development of Tourism Hot Spring in the East Middle Section of Yunnan Province[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, Thesis of Master’s degree.
[23] Lu L, Pang Z, Kong Y, et al. , 2018. Geochemical and isotopic evidence on the recharge and circulation of geothermal water in the Tangshan Geothermal System near Nanjing, China: implications for sustainable development[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 1: 1 − 15.
[24] 罗成, 贺强, 2018. 云南蒙自坝区地热地质条件及热储特征[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 30(2): 64-67
Luo C, He Q, 2018. Geothermal geological condition and geothermal reservoir features in Mengzi Basin Area, Yunnan[J]. Coal Geology of China, 30(2): 64-67.
[25] 马燕华, 苏春利, 刘伟江, 等, 2016. 水化学和环境同位素在示踪枣庄南部地下水硫酸盐污染源中的应用[J]. 环境科学, 37(12): 4690 − 4699.
Ma Y H, Su C L, Liu W J, et al. , 2016. Identification of sulfate sources in the ground -water system of Zaozhuang: evidences from isotopic and hydrochemical characteristics[J]. Environmental Science, 37(12): 4690 − 4697. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] Moore J G, Bachelder J N and Cunningham C G, 1977. CO2-filled vesicles in mid-ocean basalt[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2: 309-327. doi: 10.1016/0377-0273(77)90018-X
[27] 倪守昌, 李润培, 1986. 富源老厂萤石矿床成矿物质来源[J]. 云南地质, 5(4): 310-314
Ni S C, Li R P, 1986. On the sources of the ore-forming materials of Laochang fluorite deposit in Fuyuan County[J]. Yunnan Geology, 5(4): 310-314.
[28] 倪守昌, 孙林元, 1984. 老厂萤石矿床地质特征及成因的探讨[J]. 地质论评, 30(5): 496-300
Ni S C, Sun L Y, 1984. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Laochang fluorite deposit, Yunnan[J]. Geological Review, 30(5): 496-300.
[29] Pearson F J, 1965. Use of 13C/12C ration to correct radiocarbon ages of material initially diluted by limestone [C]. In: Proceeding of the 6th International Conference on Radiocarbon and Tritium Dating, Pulman, Washington: 357.
[30] 彭冰霞,王岳军,范蔚茗,等,2006.贵州乐康剖面茅口阶—吴家坪阶碳同位素组成变化及峨眉山大火山岩省的响应[J].地球化学,35(2):126-132.
Peng B X, Wang Y J,Fan W M, et al.,2006.Carbon isotope composition changes of Maokouian-Wuchiapingian and the environmental effect of Emeishan large igneous province at Lekang section, Guizhou Province[J]. Geochimica, 35(2):126-132.
[31] Piper A M, 1944. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation of Water−Analyses [J]. Trans. AGU, 25 (6): 914−928.
[32] 秦勇, 费安玮, 金奎励, 等, 1992. 云南腾冲盆地晚更新世孢粉组合及古植被、古气候和古环境演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 12(1): 109-118
Qin Y, Fei A W, Jin K L, et al. , 1992. Late Pleistocene sporopollen assemblages and evolution of palaeovegetation, palaeoclimate and palaeoenvironments in Tengchong Basin, Western Yunnan[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 12(1): 109-118.
[33] Saibi H, Batir J F, Pocasangre C, 2021. Hydrochemistry and geothermometry of thermal waters from UAE and their energetic potential assessment[J]. Geothermics, http://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102061.
[34] Schoeller H, 1967. Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resource: Methods and groundwater investigation and development[J]. Water Research, 33: 44-52.
[35] B. Y. C. Sunan Sakti Syah Alam, Ryuichi Itoi, Sachihiro Taguchi, et al. , 2019. Hydrogeochemical and isotope characterization of geothermal waters from the Cidanau geothermal field, West Java, Indonesia[J]. Geothermics, 78: 62-69. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.11.003
[36] 陶时雨, 张世涛, 张东泽, 等, 2015. 滇东南薄竹山地区温泉地质特征及其成因分析[J]. 云南师范大学学报, 35(6): 65-69
Tao S Y, Zhang S T, Zhang D Z, et al. , 2015. Analysis of Geological characteristics and genesis of hot springs in Bozhushan Area in Southeast of Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Yunnan Normal University, 35(6): 65-69.
[37] Veizer, J. , Hoefs, J. , 1976. The nature of O18/O16 and C13/C12 secular trends in sedimentary carbonate rocks [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta , 40 (11), 1387–1395.
[38] 汪集暘, 2016. 地热学及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
Wang J Y, 2016. Geothermics and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press.
[39] 汪新伟, 王婷灏, 张瑄, 等, 2019. 太原盆地西温庄地热田的成因机制 [J]. 地球科学, 44(3): 1042−1056
Wang X W, Wang T H, Zhang X, et al. , 2019. Genetic mechanism of Xiwenzhuang geothermal field in Taiyuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 44(3): 1042−1056. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[40] 汪缉安, 徐青, 张文仁, 1990. 云南大地热流及地热地质问题[J]. 地震地质, 12(4): 367-377
Wang J A, Xu Q, Zhang W R, 1990. Heat flow data and some geologic-geothermal problems in Yunnan Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 12(4): 367-377.
[41] 王伶俐, 王青华, 张勇, 等, 2016. 基于GPS的云南地区主要断裂带现今运动特征分析[J]. 防灾科技学院学报, 18(1): 1-8
Wang L L, Wang Q H, Zhang Y, et al. , 2016. Analysis of current activity of main faults in Yunnan Region based on GPS[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention, 18(1): 1-8.
[42] 王云, 赵慈平, 李其林, 等, 2018. 滇东南楔形构造区典型地热流体地球化学特征研究[J]. 地震研究, 41(4): 534-543
Wang Y, Zhao C P, Li Q L, et al. , 2018. Study on geochemical characteristics of geothermal fluid in the wedge-shaped tectonics, Southeast Yunnan[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 41 (4): 534-543.
[43] 王云, 赵慈平, 刘峰, 等, 2014. 小江断裂带及邻近地区温泉地球化学特征与地震活动关系研究[J]. 地震研究, 37(2): 228-243
Wang Y, Zhao C P, Liu F, et al. , 2014. Research on relationship between geochemical characteristics of thermal springs and seismic activity in Xiaojiang Fault Zone and its adjacent area[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 37(2): 228-243.
[44] 王云, 2021. 滇东南地热流体地球化学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所, 博士学位论文.
Wang Y, 2021. A Research on Geochemical Characteristics of Geothermal Fluids in Southeast Yunnan Province, China[J]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, Thesis of Doctor’ s degree.
[45] 王砚耕,王立亭,张明发,等,1995. 南盘江地区浅层地壳结构与金矿分布模式[J]. 贵州地质, 12(2):91-183.
Wang Y G, Wang L T, Zhang M F,et al., 1995.Texture of the upper crust and pattern of the disseminated gold deposits distributed in Nanpanjiang Area[J].Guizhou Geology,12(2):91-183.
[46] 吴胜光, 韩辉友, 余锦标, 1995. 贵州晴隆碧痕营晚第四系及古环境研究[J]. 地理研究, 14(2): 49-55
Wu S G, Han H Y, Yu J B, 1995. Analysis of the Late Quaternary sediments and paleoenvironment in Bihenying in Qinglong, Guizhou Province[J]. Geographical Research, 14(2): 49-55.
[47] 肖琼, 沈立成, 杨雷, 等, 2013. 重庆北温泉地热水碳硫同位素特征研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 40(4): 127-133
Xiao Q, Shen L C, Yang L, et al. , 2013. Environmental significance of carbon and sulfur isotopes of the North hot spring in Chongqing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 40 (4): 127-133.
[48] 谢富仁, 祝景忠, 粱海庆, 等, 1993. 中国西南地区现代构造应力场基本特征[J]. 地震学报, 15(4): 407-417
Xie F R, Zhu J Z, Liang H Q, et al. , 1993. Basic characteristics of modern tectonic stress field in Southwest China[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 15(4): 407-417.
[49] 谢韬, 张启跃, 刘伟, 等, 2010. 罗平地区断裂构造的遥感研究[J]. 中国地质, 37(5): 1405-1409
Xie T, Zhang Q Y, Liu W, et al. , 2010. A study of faults in Luoping area based on remote sensing technique[J]. Geology in China, 37(5): 1405-1409.
[50] 杨雷, 肖琼, 沈立成, 等, 2011. 不同地质背景地热系统水岩作用下温泉水的地球化学特征—以重庆温塘峡背斜温泉、滇东小江断裂带温泉为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 30(2): 209-215
Yang L, Xiao Q, Shen L C, et al. , 2011. Hydrogeochemical features of hot spring under water-rock processes of different geologic conditions—A case in the Wentangxia hot spring of Chongqing and the hot spring at Xiaojiang fault zone of the East Yunnan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 30(2): 209-215.
[51] 姚六三, 李庆仁, 马文华, 1983. 云南地热地质特征[J]. 云南地质, 2(1): 48-56
Yao L S, Li Q R, Ma W H, 1983. Geothermal geological characteristics of Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 2(1): 48-56.
[52] 袁建飞, 邓国仕, 徐芬, 等, 2017. 川西南喜德热田地下水水文地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 31(1): 200-208 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.01.019
Yuan J F, Deng G S, Xu F, et al. , 2017. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in the Xide geothermal field, Southwest Sichuan, China[J]. Geoscience, 31(1): 200-208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.01.019
[53] 袁利娟, 张进平, 何云成, 等, 2021. 北京市通州区地热流体水化学和同位素特征及其地热学意义[J]. 地质论评, 67(5): 1545-1555
Yuan L J, Zhang J P, He Y C, et al. , 2021. Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of geothermal fluids in Tongzhou District, Beijing, and their geothermal significance[J]. Geological Review, 67(5): 1545-1555.
[54] 云南省地质矿产局, 1990. 云南省区域地质志[M]. 北京, 地质出版社.
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Yunnan Province, 1990. Regional Geological Records of Yunnan Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House.
[55] Yurtsever Y, 1975. Worldwide survey of stable isotopes in precipitation[R]. Vienna: isotope Hydrology International Atomic Energy Agency.
[56] 张云辉, 李晓, 许模, 等, 2021. 鲜水河地热带道孚地区地热水水文地球化学特征研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 28(3): 42 − 50.
Zhang Y H, Li X, Xu M, et al. , 2021. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of geothermal waters in the Daofu area of the Xianshuihe Geothermal Belt[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 28(3): 42 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[57] 张明亮, 2019. 滇东黔西地下水氢氧同位素特征[J]. 四川地质学报, 39(3): 508-511
Zhang M L, 2019. The δ18O and δD value of groundwater in East Yunnan and West Guizhou[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 39(3): 508-511.
[58] 赵珂, 姜光辉, 杨琰, 等, 2005. 滇东主要断裂带温泉CO2成因浅析[J]. 地球与环境, 33(2): 11-15
Zhao K, Jiang G H, Yang Y, et al. , 2005. Brief analysis of the reasons of CO2 degassing from hot spring on main faults within the east of Yunnan[J]. Earth and Environment, 33(2): 11-15.
[59] 周训, 金晓媚, 梁四海, 2017. 地下水科学专论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
Zhou X, Jin X M, Liang S H, 2017. Special Topics on Groundwater Science[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House.
[60] 朱秀勤, 范弢, 官威, 2013. 昆明大气降水稳定同位素分析[J]. 云南地理环境研究, 25(5): 91-95
Zhu X Q, Fan T, Guan W, 2013. The analysis of stable isotopes of precipitation in Kunming[J]. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 25(5): 91-95.
-



 下载:
下载: