Petrogenesis of the early Cretaceous Jilong granodiorite porphyry in the Bangong Co-Nujiang metallogenic belt, Xizang, China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb geochronology, Hf isotopes, and whole-rock geochemistry
-
摘要:
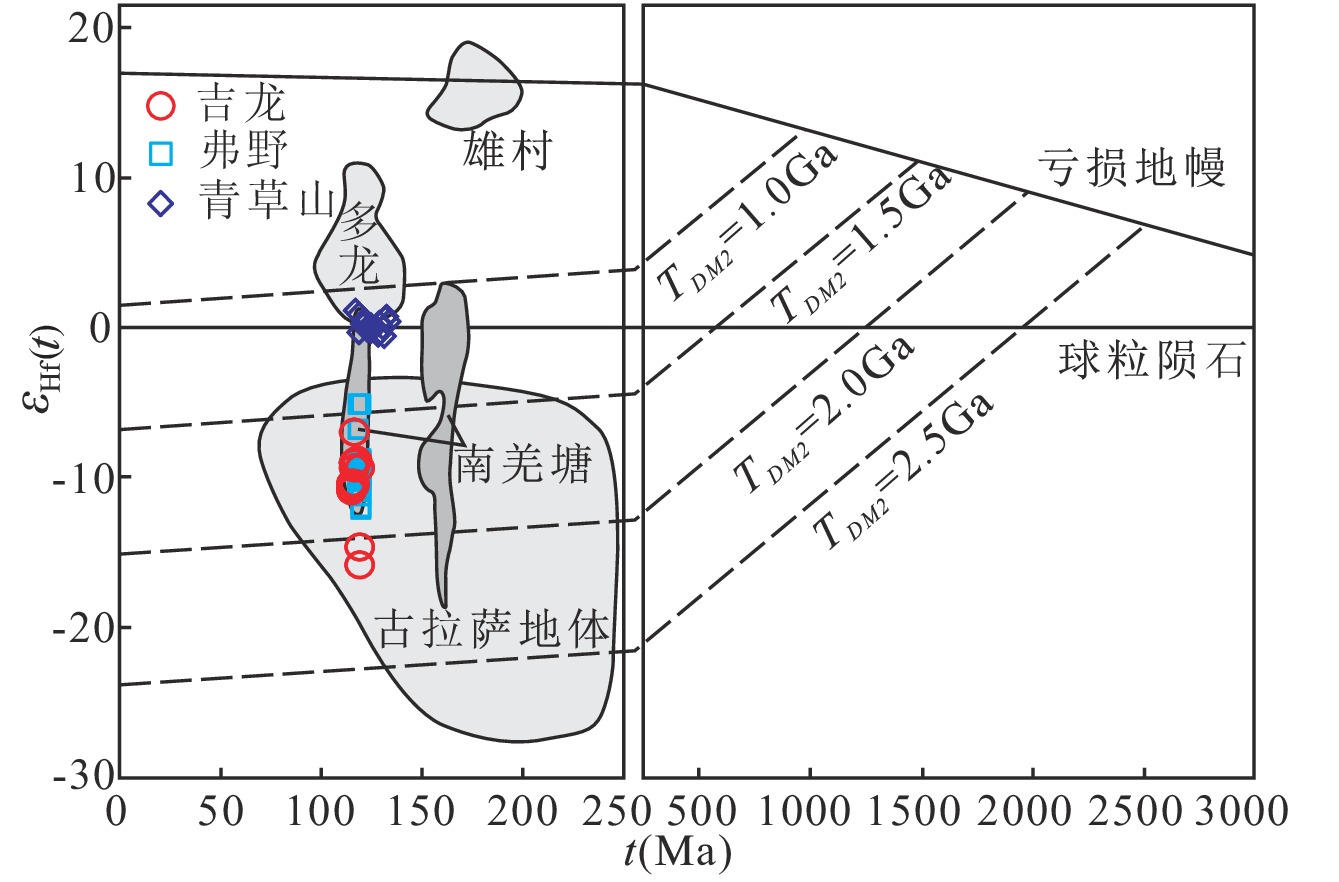
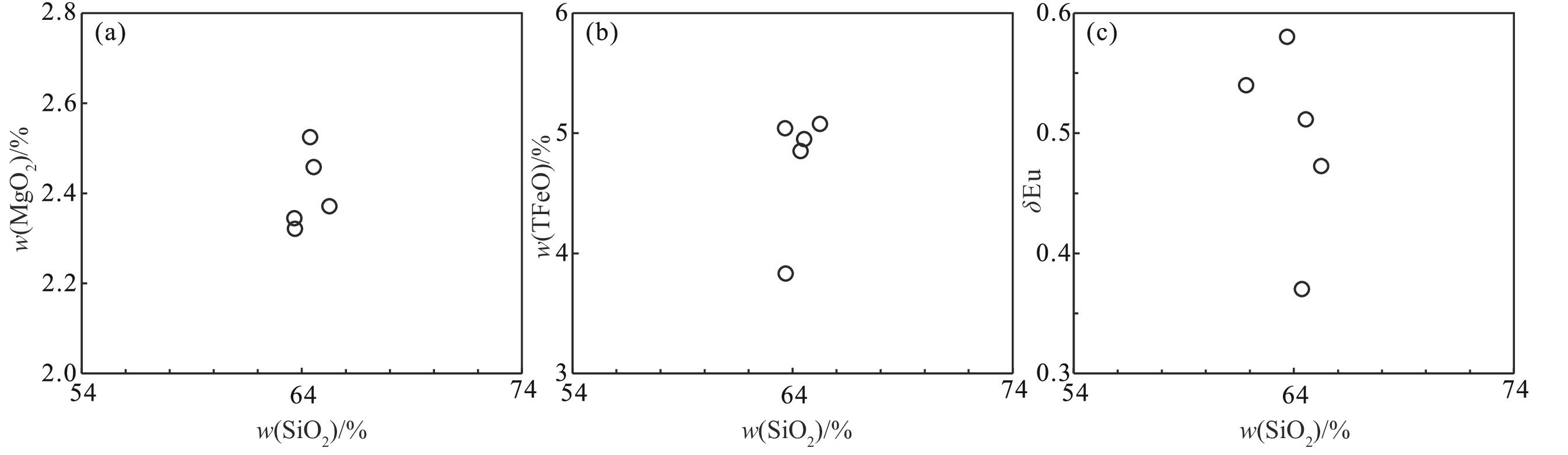
班公湖-怒江成矿带西段的龙荣地区,发育有吉龙、龙荣、双岔河等众多早白垩世成矿岩体。吉龙岩体位于龙荣地区中部,由黑云母花岗闪长斑岩和黑云母花岗闪长岩组成。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果显示,花岗闪长斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(116.4±0.7)Ma (MSWD = 1.07),表明岩体形成于早白垩世。花岗闪长斑岩全岩地球化学特征为:具有较高的SiO2(63.66%~65.24%)、Al2O3(14.23%~16.21%)、MgO(2.32%~2.53%)含量,较低的P2O5(0.24%~0.26%)、TiO2(0.53%~0.61%)含量,里特曼指数(σ43)为0.86~1.47,铝饱和指数(A/CNK)为0.98~1.12,分异系数(DI)为63~68,富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、K),亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Ti),相对于Rb和Th亏损Ba,Eu负异常(δEu = 0.37~0.58)。总体上,花岗闪长斑岩为钙碱性I型花岗岩,具有典型岛弧型岩浆岩的特征。花岗闪长斑岩具有不均一的锆石Hf同位素组成(εHf(t)= -15.7~-6.8),二阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)为2.2~1.6 Ga,具有较低的全岩锆石饱和温度(TZr = 782~790℃)和锆石Ti饱和温度(TTi = 603~772℃),Mg#值为49.38~55.96,表现出壳幔混合的特征。研究揭示,吉龙花岗闪长斑岩是古元古代地壳部分熔融形成的长英质岩浆与少量俯冲流体交代的幔源岩浆混合的产物,早白垩世晚期(120~110 Ma)向北俯冲的班公湖-怒江洋板片的折返可能是其成岩作用的主要动力学机制。
Abstract:Various Early Cretaceous metallogenic intrusions, such as Jilong, Longrong, and Shuangchahe, develop in the Longrong region, western section of the Bangong Co-Nujiang metallogenic belt. The Jilong intrusion lies in the middle of the Longrong region, consisting of biotite granodiorite porphyry and biotite granodiorite. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results show that the zircon U-Pb age of the granodiorite porphyry is (116.4±0.7) Ma (MSWD = 1.07), suggesting that the Jilong intrusion formed during the Early Cretaceous epoch. The whole-rock geochemical characteristics of the granodiorite porphyry exhibit high contents of SiO2 (63.66%~65.24%), Al2O3 (14.23%~16.21%), and MgO (2.32%~2.53%), with low contents of P2O5 (0.24%~0.26%) and TiO2 (0.53%~0.61%). The rocks have a Rittmann index (σ43) ranging from 0.86 to 1.47, an aluminum saturation index (A/CNK) from 0.98 to 1.12, and a coefficient of differentiation (DI) from 63 to 68. They are enriched in large ion lithophile elements (LILEs) such as Rb and K, depleted in high field strength elements (HFSEs) such as Nb, Ta, and Ti. They are also depleted in Ba relative to Rb and Th, with a negative Eu anomaly (δEu = 0.37~0.58). Generally, the granodiorite porphyry is a calc-alkaline arc I-type granitoid with typical island arc magmatite characteristics. It exhibits heterogeneous zircon Hf isotopic compositions (εHf(t)= -15.7~-6.8) with a two-stage Hf model age (tDM2) ranging from 2.2 Ga to 1.6 Ga. Both the whole-rock zircon saturation temperatures (TZr = 782~790℃) and the zircon Ti saturation temperatures (TTi = 603~772℃) are low, with Mg# values ranging from 49.38 to 55.96, presenting characteristics of crust-mantle mixing. It is concluded that Jilong porphyry is the product of mixing felsic magma which forms through the partial melting of the Paleoproterozoic crust, with a small amount of mantle-derived magma under the metasomatism of subduction-related fluids. The inversion of the northward subduction slabs of Bangong Co-Nujiang Tethys in the Early Cretaceous epoch (120~110 Ma) may be the primary dynamic mechanism.
-

-
图 4 吉龙花岗闪长斑岩锆石U–Th图解(a)、稀土元素配分图解(b)和锆石结晶条件判别图解(c)(底图据Grimes et al., 2007)
Figure 4.
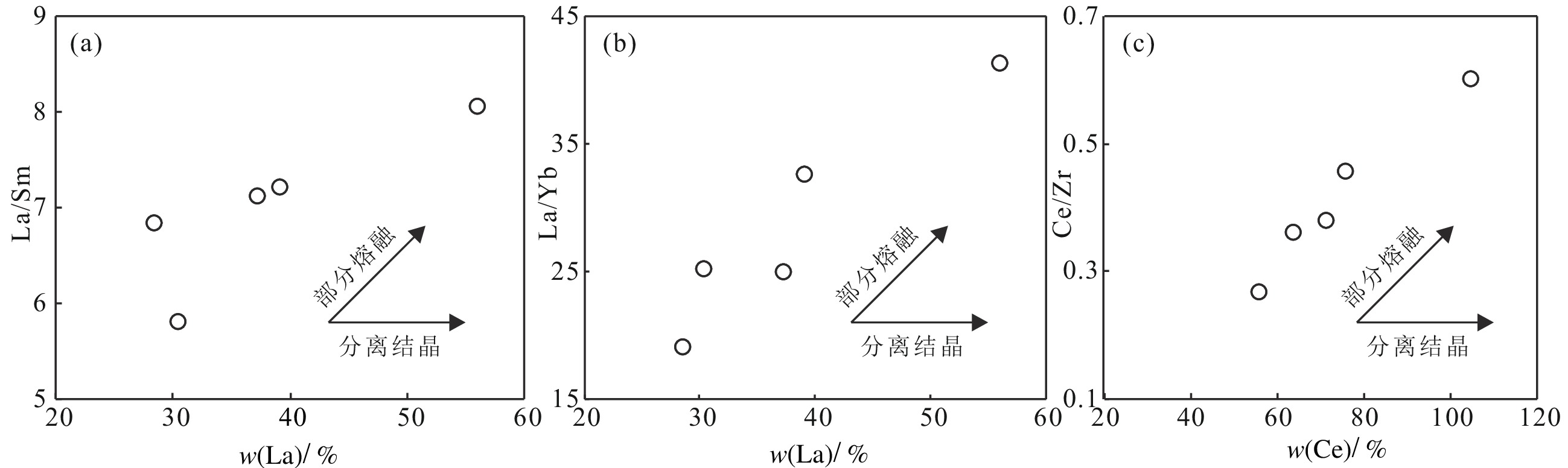
图 7 吉龙花岗闪长斑岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)图解(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Figure 7.
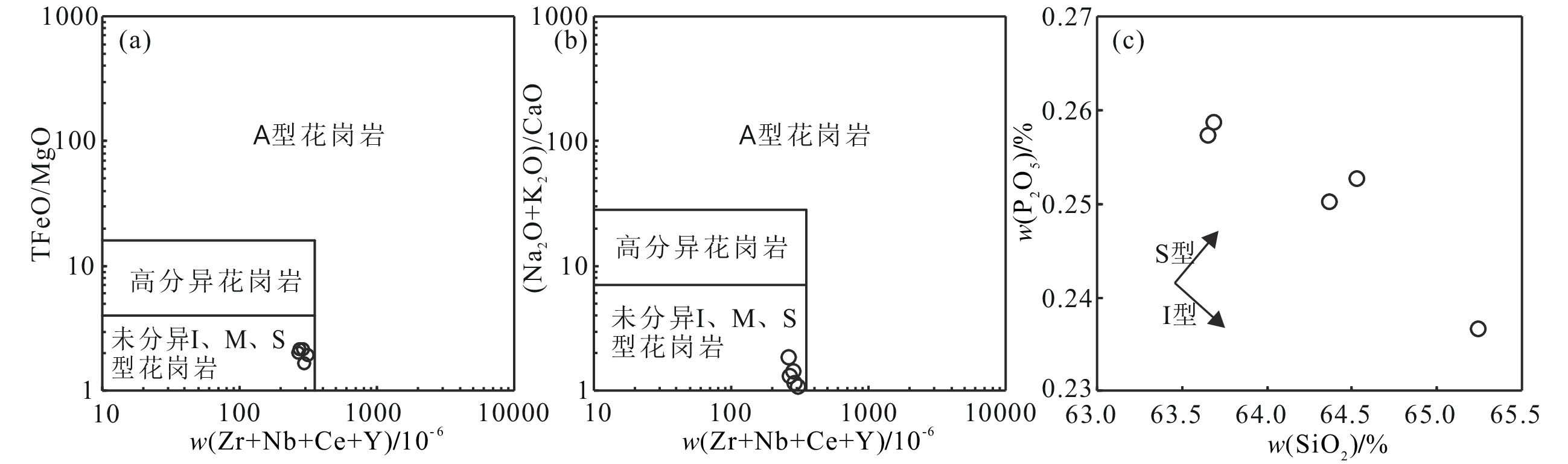
图 8 吉龙花岗闪长斑岩I–S–M–A型花岗岩判别图解(a、b,据Whalen et al., 1987;c,据Chappell, 1999)
Figure 8.
图 13 吉龙花岗闪长斑岩构造环境判别图(a,据Defant and Drummond, 1990;b,据Pearce et al., 1984)
Figure 13.
图 14 吉龙花岗闪长斑岩构造演化模式图(a,据Zhu et al., 2016; 刘洪等,2022修改;b,据Zhu et al., 2016; 林彬等,2019修改)
Figure 14.
-
[1] Ayers John, 1998. Trace element modeling of aqueous fluid-peridotite interaction in the mantle wedge of subduction zones[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 132(4): 390-404.
[2] Ballard J R. , Palin M J. , Campbell I H. , 2002. Relative oxidation states of magmas inferred from Ce(IV)/Ce(III) in zircon: application to porphyry copper deposits of northern Chile[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 144(3): 347-364.
[3] Belousova E, Griffin W, O'Reilly S Y, et al. , 2002. Igneous zircon: Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 143(5): 602-622. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
[4] Best M G, Christiansen E H, 2001. Igneous Petrology[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Science, 480.
[5] Bolhar R, Weaver S D, Whitehouse M J, et al. , 2008. Sources and evolution of arc magmas inferred from coupled O and Hf isotope systematics of plutonic zircons from the Cretaceous Separation Point Suite (New Zealand)[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 268(3): 312-324.
[6] Bonin B, 2007. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 97(1): 1-29.
[7] Cao M J, Qin K Z, Li G M, et al. , 2016. Tectono-magmatic evolution of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous granitoids in the west central Lhasa subterrane, Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 39: 386-400. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.01.006
[8] Chappell B W, 1999. Aluminium saturation in I-and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 46(3): 535-551. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3
[9] Chauvel C, Hofmann A W. , Vidal P, 1992. HIMU-EM: The French Polynesian connection[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 110(1): 99-119.
[10] Clemens J D, Vielzeuf D, 1987. Constraints on melting and magma production in the crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 86(2): 287-306.
[11] Clemens J, Watkins J, 2001. The fluid regime of high-temperature metamorphism during granitoid magma genesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 140(5): 600-606. doi: 10.1007/s004100000205
[12] Defant M J, Drummond M S, 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. nature, 347: 662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
[13] 邓晋福. 2004. 岩石成因、构造环境与成矿作用[M]. 地质出版社: 33−49.
Deng J F, 2004. Petrogenesis, tectonic environment and metallogenesis[M]. Beijing: Geology Press: 33−49.
[14] Depaolo D J, Wasserburg G J, 1979. Petrogenetic mixing models and Nd-Sr isotopic patterns[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 43(4): 615-627. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(79)90169-8
[15] 董瀚, 苟国宁, 齐玥, 等, 2016. 拉萨地块北缘早白垩世晚期地壳生长: 来自改则亚多~106Ma侵入岩的证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 40(06): 1226-1238 doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2016.06.010
Dong H, Gou G N, Qi Y, et al, 2016. Late early cretaceous crustal growth in northern Lhasa block: Evidence from ca. 106 Ma intrusive rocks in the Yaduo area, Gerze county[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(06): 1226-1238. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2016.06.010
[16] 杜德道, 曲晓明, 王根厚, 等, 2011. 西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带西段中特提斯洋盆的双向俯冲: 来自岛弧型花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和元素地球化学的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 27(07): 1993-2002
Du D D, Qu X M, Wang G H, et al. , 2011. Bidirectional subduction of the Middle Tethys oceanic basin in the west segment of Bangonghu-Nujiang suture, Tibet: Evidence from zircon U-Pb LAICPMS dating and petrogeochemistry of arc granites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7): 1993-2002.
[17] Fan J J, Li C, Xie C M, et al. , 2014. Petrology, geochemistry, and geochronology of the Zhonggang ocean island, northern Tibet: implications for the evolution of the Banggongco–Nujiang oceanic arm of the Neo-Tethys[J]. International Geology Review, 56(12): 1504-1520. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.947639
[18] Fan J J, Li C, Xie C M, et al. , 2015. The evolution of the Bangong–Nujiang Neo-Tethys ocean: Evidence from zircon U–Pb and Lu–Hf isotopic analyses of Early Cretaceous oceanic islands and ophiolites[J]. Tectonophysics, 655: 27-40. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.04.019
[19] Ferry J M, Watson E B, 2007. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 154(4): 429-437. doi: 10.1007/s00410-007-0201-0
[20] Gardien V, Thompson A B, Grujic D, et al. , 1995. Experimental melting of biotite + plagioclase + quartz ± muscovite assemblages and implications for crustal melting[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 100(B8): 15581-15591. doi: 10.1029/95JB00916
[21] 葛小月, 李献华, 陈志刚, 等, 2002. 中国东部燕山期高Sr低Y型中酸性火成岩的地球化学特征及成因: 对中国东部地壳厚度的制约[J]. 科学通报, 47(06): 474-480.
Ge X Y, Li X H, Chen Z G, et al. , 2002. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Jurassic high Sr/low Y granitoids in eastern China: Constrains on crustal thickness[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(11): 962-968.
[22] Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E, et al. , 2002. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China; in-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 61(3): 237-269.
[23] Grimes C B, John B, Kelemen P, et al. , 2007. Trace element chemistry of zircons from oceanic crust: A method for distinguishing detrital zircon provenance[J]. Geology, 35(7): 643-646. doi: 10.1130/G23603A.1
[24] Harrison T M, Watson E B, Aikman A B, 2007. Temperature spectra of zircon crystallization in plutonic rocks[J]. Geology, 35(7): 635-638. doi: 10.1130/G23505A.1
[25] Hoskin P W O, Black L P, 2000. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid‐state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 18(4): 423-439. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2000.00266.x
[26] 胡军, 王核, 慕生禄, 等, 2017. 西昆仑甜水海地块南屏雪山早古生代花岗岩地球化学、Hf同位素特征及其壳幔岩浆作用[J]. 地质学报, 91(06): 1192-1207 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.06.003
Hu J, Wang H, Mu S L, et al. , 2017. Geochemistry and Hf isotopic compositions of early Paleozoic granites in Nanpingxueshan from the Tianshuihai terrane, west Kunlun: crust-mantle magmatism[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(06): 1192-1207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.06.003
[27] Hu Z C, Gao S, Liu Y S, et al. , 2008a. Signal enhancement in laser ablation ICP-MS by addition of nitrogen in the central channel gas[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 23(8): 1093-1101. doi: 10.1039/b804760j
[28] Hu Z C, Liu YS, Gao S, et al. , 2008b. A local aerosol extraction strategy for the determination of the aerosol composition in laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 23(9): 1192-1203. doi: 10.1039/b803934h
[29] Hu Z C, Liu Y S, Gao S, et al. , 2012a. Improved in situ Hf isotope ratio analysis of zircon using newly designed X skimmer cone and jet sample cone in combination with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation multiple collector ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 27(9): 1391-1399. doi: 10.1039/c2ja30078h
[30] Hu Z C, Liu Y S, Gao S, et al. , 2012b. A “wire” signal smoothing device for laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry analysis[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B Atomic Spectroscopy, 78(78): 50-57.
[31] 黄瀚霄, 龚福志, 李光明, 等, 2016. 西藏羌塘南缘早白垩世普让岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 62(3): 569-584
Huang H X, Gong F Z, Li G M, et al. , 2016. Zircon U-Pb age and geochemical features of the early Cretaceous Purang pluton on the southern margin of Qiangtang, Xizang(Tibet), and their geological implications[J]. Geological Review, 62(3): 569-584.
[32] 黄勇, 唐菊兴, 张丽, 等, 2014. 西藏雄村斑岩铜金矿集区火山-岩浆岩锆石Hf同位素组成[J]. 地质学报, 88(8): 1528-1538
Huang Y, Tang J X, Z L, et al, 2014. Zircon Hf isotopic composition of volcanic-magmatic rocks at Xiongcun porphyry copper-gold deposit, Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(8): 1528-1538.
[33] Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Chen B, 2000. Granitoids of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and continental growth in the Phanerozoic[J]. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 91(1-2): 181-193. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300007367
[34] Kelley K A. , Cottrell E, 2009. Water and the Oxidation State of Subduction Zone Magmas[J]. Science, 325(5940): 605-607. doi: 10.1126/science.1174156
[35] Kemp A I S, Hawkesworth C J, Foster G L, et al. , 2007a. Magmatic and crustal differentiation history of granitic rocks from Hf-O isotopesin zircon. [J]. Science (New York, N. Y. ), 315(5814): 980-983.
[36] Kemp A I S, Hawkesworth C J, Foster G L. , et al. , 2007b. Magmatic and Crustal Differentiation History of Granitic Rocks from Hf-O Isotopes in Zircon[J]. Science, 315(5814): 980-983. doi: 10.1126/science.1136154
[37] Kemp A I S, Whitehouse M J, Hawkesworth C J, et al. , 2005. A zircon U-Pb study of metaluminous (I-type) granites of the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeastern Australia: implications for the high/low temperature classification and magma differentiation processes[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 150(2): 230-249. doi: 10.1007/s00410-005-0019-6
[38] King P L. , White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. , 1997. Characterization and Origin of Aluminous A-type Granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 38(3): 371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
[39] La Flèche M R, Camiré G, Jenner G A, 1998. Geochemistry of post-Acadian, Carboniferous continental intraplate basalts from the Maritimes Basin, Magdalen Islands, Québec, Canada[J]. Chemical Geology, 148(3): 115-136.
[40] Lassiter J C, DePaolo D, 1997. Plume/lithosphere interaction in the generation of continental and oceanic flood basalts: Chemical and isotopic constraints[M]//Mahoney J J and Coffin M F. Large igneous provinces: Continental, oceanic, and planetary flood volcanism, volume 100: American Geophysical Union: 335−355.
[41] Li C F, Li X H, Li Q L, et al. , 2012. Rapid and precise determination of Sr and Nd isotopic ratios in geological samples from the same filament loading by thermal ionization mass spectrometry employing a single-step separation scheme[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 727: 54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2012.03.040
[42] 李光明, 张夏楠, 秦克章, 等, 2015. 羌塘南缘多龙矿集区荣那斑岩-高硫型浅成低温热液Cu-(Au)套合成矿: 综合地质、热液蚀变及金属矿物组合证据[J]. 岩石学报, 31(08): 2307-2324
Li G M, Zhang X N, Qin K Z, et al. , 2015. The telescoped porphyry-high sulfidation epithermal Cu( -Au) mineralization of Rongna deposit in Duolong ore cluster at the southern margin of Qiangtang Terrane, Central Tibet: Integrated evidence from geology, hydrothermal alteration and sulfide assemblages[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(8): 2307-2324.
[43] Li J X, Qin K Z, Li G M, et al. , 2016. Petrogenesis of Cretaceous igneous rocks from the Duolong porphyry Cu-Au deposit, central Tibet: evidence from zircon U–Pb geochronology, petrochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotope characteristics[J]. Geological Journal, 51(2): 285-307. doi: 10.1002/gj.2631
[44] 李金祥, 李光明, 秦克章, 等, 2008. 班公湖带多不杂富金斑岩铜矿床斑岩-火山岩的地球化学特征与时代: 对成矿构造背景的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 24(03): 531-543
Li J X, Li G M, Qin K Z, et al. , 2008. Geochemistry of porphyries and volcanic rocks and ore-forming geochronology of Duobuza gold-rich porphyry copper deposit in Bangonghu belt, Tibet: Constraints on metailogenic tectonic settings[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(03): 531-543.
[45] Li W K, Cheng Y Q, Yang Z M, 2019. Geo-fO2: Integrated Software for Analysis of Magmatic Oxygen Fugacity[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 20(5): 2542-2555.
[46] 林彬, 方向, 王艺云, 等, 2019. 西藏铁格隆南超大型铜(金、银)矿含矿斑岩岩石成因及其对多龙地区早白垩世成矿动力学机制的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 35(03): 642-664 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.03.03
Lin B, Fnag F, Wang Y Y, et al. , 2019. Petrologic genesis of ore-bearing porphyries in Tiegelongnan giant Cu (Au, Ag) deposit, Tibet and its implications for the dynamic of Cretaceous mineralization, Duolong[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(03): 642-664. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.03.03
[47] Liu H, Li G M, Huang H X, et al. , 2018. Petrogenesis of Late Cretaceous Jiangla'angzong I-Type Granite in Central Lhasa Terrane, Tibet, China: Constraints from Whole-Rock Geochemistry, Zircon U-Pb Geochronology, and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf Isotopes[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 92(04): 1396-1414. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13634
[48] 刘洪, 李光明, 李文昌, 等, 2022. 西藏中拉萨地块北部早白垩世晚期控错A型花岗岩的成因及构造环境研究[J]. 岩石学报, 38(01): 230-252 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.01.15
Liu H, Li G M, Li W C, et al. , 2022. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the late Early Cretaceous Kong Co A-type granite in the northern margin of Central Lhasa Subterrane, Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 38(1): 230-252. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.01.15
[49] 刘洪, 张晖, 李光明, 等, 2016. 藏北羌塘南缘早白垩世青草山强过铝质S型花岗岩的成因: 来自地球化学和锆石U-Pb年代学的约束[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 52(5): 848-860
Liu H, Zhang H, Li G M, et al, 2016. Petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous Qingcaoshan Strongly Peraluminous S-Type Granitic Pluton, Southern Qiangtang, Northern Tibet: Constraints from Whole-Rock Geochemistry and Zircon U-Pb Geochronology[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 52(5): 848-860.
[50] Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. , 2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling−induced melt−peridotite interactions in the Trans−North China Orogen: U−Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537−571.
[51] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. , 2008a. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 257: 34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
[52] Liu Y S, Zong K Q, Kelemen P B, et al. , 2008b. Geochemistry and magmatic history of eclogites and ultramafic rocks from the Chinese continental scientific drill hole: Subduction and ultrahigh−pressure metamorphism of lower crustal cumulates[J]. Chemical Geology, 247(1–2): 133−153.
[53] Ludwig K R, 2003. ISOPLOT 3.00: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication: 1−70.
[54] 罗兰, 蒋少涌, 杨水源, 等, 2010. 江西彭山锡多金属矿集区隐伏花岗岩体的岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 26(09): 2818-2834
Luo L, Jiang S Y, Yang S Y, et al. , 2010. Petrochemistry, zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic composition of the granitic pluton in the Pengshan Sn-polymetallic orefield, Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(9): 2818-2834.
[55] 马鸿文, 1992. 花岗岩成因类型的判别分析[J]. 岩石学报, 8(4): 341−350
Ma H W. Discrimination of genetic types of granitoid rocks[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1992, 8(4): 341−350.
[56] Mcculloch M T, Bennett V C, 1994. Progressive growth of the Earth's continental crust and depleted mantle: Geochemical constraints[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 58(21): 4717-4738. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90203-8
[57] Miller C F, Mcdowell S M Mapes R W, 2003. Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 31(6): 529-532. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0529:HACGIO>2.0.CO;2
[58] 莫宣学, 潘桂棠, 2006. 从特提斯到青藏高原形成: 构造-岩浆事件的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 13(06): 43-51 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.007
Mo X X, Pan G T, 2006. From the Tethys to the formation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: constrained by tectono-magmatic events[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(6): 43-51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.007
[59] Münker Carsten, 1998. Nb/Ta fractionation in a Cambrian arc/back arc system, New Zealand: source constraints and application of refined ICPMS techniques[J]. Chemical Geology, 144(1–2): 23−45.
[60] 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等, 2006. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 22(03): 521-533 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.03.001
Pan G T, Mo X X, Hou Z Q, et al. , 2006. Spatial-temporal framework of the Gangdese Orogenic Belt and its evolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 521-533. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.03.001
[61] Patiño Douce A E, Beard J S, 1995. Dehydration-melting of Biotite Gneiss and Quartz Amphibolite from 3 to 15 kbar[J]. Journal of Petrology, 36(3): 707-738. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.3.707
[62] Patiño Douce A E, Harris N, 1998. Experimental Constraints on Himalayan Anatexis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 39(4): 689-710. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.4.689
[63] Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G, 1984. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
[64] 彭智敏, 耿全如, 王立全, 等, 2014. 青藏高原羌塘中部本松错花岗质片麻岩锆石U−Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 59(26): 2621−2629
Peng Z M, Geng Q R, Wang L Q, et al. 2014. Zircon U−Pb ages and Hf isotopic characteristics of granitic gneiss from Bunsumco, central Qiangtang, Qinghai−Tibet Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59(26): 2621–2629.
[65] Plank T, Langmuir C H, Albarede F, et al. , 1998. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 145(3–4): 325−394.
[66] 邱检生, 肖娥, 胡建, 等, 2008. 福建北东沿海高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 24(11): 2468-2484
Qiu J S, Xiao E, Hu J, et. , 2008. Petrogenesis of highly fractionated I-type granites in the coastal area of northeastern Fujian Province: Constraints from zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(11): 2468-2484.
[67] Qu X M, Hou Z Q, Li Y G, 2004. Melt components derived from a subducted slab in late orogenic ore-bearing porphyries in the Gangdese copper belt, southern Tibetan plateau[J]. Lithos, 74(3): 131-148.
[68] 曲晓明, 王瑞江, 辛洪波, 等, 2009. 西藏西部与班公湖特提斯洋盆俯冲相关的火成岩年代学和地球化学[J]. 地球化学, 38(06): 523-535 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.06.002
Qu X M, Wang R J, Qu H B, et al. , 2009. Geochronology and geochemistry of igneous rocks related to the subduction of the Tethysoceanic plate along the Bangong Lake arc zone, the western Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geochimica, 38(06): 523-535. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.06.002
[69] Rapp R P, Watson E B, 1995. Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: Implications for Continental Growth and Crust-Mantle Recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 36(4): 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
[70] Rudnick R, Gao S, 2003. Composition of the continental crust[M]. Treatise Geochem 3: 1−64.
[71] 史长义, 鄢明才, 迟清华. 2008. 中国花岗岩类化学元素丰度[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 15−20.
Shi C Y, Yan M C, Chi Q H, 2008. Abundance and characteristics of chemical elements of granites in China[M]. Beijing: Geology Press: 15−20.
[72] Shi R D, 2007. SHRIMP dating of the Bangong Lake SSZ−type ophiolite: Constraints on the closure time of ocean in the Bangong Lake−Nujiang River, northwestern Tibet[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(7): 936−941.
[73] Sisson T W, 1994. Hornblende−melt trace−element partitioning measured by ion microprobe[J]. Chemical Geology, 117(1–4): 331−344.
[74] 宋扬, 唐菊兴, 曲晓明, 等. 2014. 西藏班公湖—怒江成矿带研究进展及一些新认识[J]. 地球科学进展, 2014, 29(7): 795−809
Song Y, Tang J C, Qu X M, et al. Progress in the study of mineralization in the Bangongco−Nujiang metallogenic belt and some new recognition[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 29(7): 795−809.
[75] Sun S S, Mcdonough W F, 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[76] Tatsumi Y, Eggins S, 1995. Subduction zone magmatism[M]. Cambridge (Mass. ): Blackwell: 1−211.
[77] Wang Y J, Fan W M, Sun M, et al. , 2007. Geochronological, geochemical and geothermal constraints on petrogenesis of the Indosinian peraluminous granites in the South China Block: A case study in the Hunan Province[J]. Lithos, 96(3): 475-502.
[78] Watson E B, Harrison T M, 1983. Zircon saturation revisited: temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 64(2): 295-304.
[79] Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell Bruce W. , 1987. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 95(4): 407-419.
[80] Wu F Y, Jahn B M, Wilde S A. , et al. , 2003. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (I): geochronology and petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 66(3-4): 241-273. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00222-0
[81] Wu F Y, Yang Y H, Xie L W, et al. , 2006. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U–Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 234(1): 105-126.
[82] 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等, 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 23(02): 185-220 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.02.001
Wu F Y, Li X H, Zheng Y F, etal. , 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.02.001
[83] 吴元保, 郑永飞, 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589-1604 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002
Wu Y B, Zheng Y F, 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese science bulletin, 49(16): 1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002
[84] 西藏自治区地质调查院. 2015. 西藏龙荣地区1∶5万区域地质综合调查成果报告[R].
Tibet institute of geological survey, 2015. Report of 1∶50000 regional geological comprehensive survey results in Longrong Area, Tibet[R].
[85] 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨. 2002. 花岗岩研究思维与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1−179.
Xiao Q H, Deng J F, Ma D Q, 2002. The ways of investigation on granitoids[M]. Beijing: Geology Press: 1−179.
[86] 谢银财, 陆建军, 马东升, 等, 2013. 湘南宝山铅锌多金属矿区花岗闪长斑岩及其暗色包体成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 29(12): 4186-4214
Xie Y C, Lu J J, Ma D S, et al. , 2013. Origin of granodiorite porphyry and mafic microgranular enclave in the Baoshan Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit, southern Hunan Province: Zircon U-Pb chronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(12): 4186-4214.
[87] 熊小林, 蔡志勇, 牛贺才, 等, 2005. 东天山晚古生代埃达克岩成因及铜金成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, (03): 967-976 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2005.03.034
Xiong X L, Cai Z Y, Niu H C, et al. , 2005. The late Paleozoic adakites in eastern Tianshan area and their metallogenetic significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3): 967-976. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2005.03.034
[88] Xu W, Li C, Wang M, et al. , 2017. Subduction of a spreading ridge within the Bangong Co–Nujiang Tethys Ocean: Evidence from Early Cretaceous mafic dykes in the Duolong porphyry Cu–Au deposit, western Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 41: 128-141. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.09.010
[89] Yang JH, Wu F Y, Wilde S A. , et al. , 2007. Tracing magma mixing in granite genesis: in situ U–Pb dating and Hf-isotope analysis of zircons[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 153(2): 177-190.
[90] 于玉帅, 高原, 杨竹森, 等, 2011. 西藏措勤尼雄矿田滚纠铁矿侵入岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄与地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 27(07): 1949-1960
Yu Y S, Gao Y, Yang Z S, et al. , 2001. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and geochemistry of intrusive rocks from Gunjiu iron deposit in the Nixiong ore field, Coqen, Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7): 1949-1960.
[91] 张红, 刘洪, 刘书生, 等, 2017. 班公湖-怒江成矿带多龙矿集区北缘早白垩世究浅西I型花岗岩的成因[J]. 中国矿业, 26(11): 162-170
Zhang H, Liu H, Liu S H, et al, 2017. Petrogenesis of the early Cretaceous Jiuqianxi I-Type Granitic Pluton, Bangonghu-Nujiang metallogenic belt, northern Tibet[J]. China Mining Magazine, 26(11): 162-170.
[92] 张亮亮, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 等, 2011. 西藏申扎早白垩世花岗岩类: 板片断离的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 27(07): 1938-1948
Zhang L L, Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, et al. , 2001. Early Cretaceous granitoids in Xainza, Tibet: Evidence of slab break-off[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7): 1938-1948.
[93] 张旗, 焦守涛, 李承东, 等, 2017b. 花岗岩与大陆构造、岩浆热场与成矿[J]. 岩石学报, 33(05): 1524-1540
Zhang Q, Jiao S T, Li C D, et al. , 2017. Granite and continental tectonics, magma thermal field and metallgenesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(5): 1524-1540.
[94] 张旗, 王焰, 钱青, 等, 2001. 中国东部燕山期埃达克岩的特征及其构造-成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 17(02): 236-244 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2001.02.008
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Qian Q, et al. , 2001. The characteristics and tectonic-metallogenic significances of the adakites in Yanshan period from eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(2): 236-244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2001.02.008
[95] Zhang W, Hu Z C, Liu Y S, 2020. Iso-Compass: New freeware software for isotopic data reduction of LA-MC-ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 35.
[96] 张璋, 耿全如, 彭智敏, 等, 2015. 西藏日土地区弗野岩体的成因—锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素约束[J]. 地质通报, 34(2): 262 − 273.
Zhang Z, Geng Q R, Peng Z M, et al. , 2015. Petrogenesis of Fuye pluton in Rutog, Tibet: Zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic constraints[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(2): 262 − 273.
[97] 赵振华. 1997. 微量元素地球化学原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 56−112.
Zhao Z H, 1997. Principles of trace element geochemistry[M].Beijing: Geology Press: 56−112.
[98] 郑海涛, 郑有业, 徐净, 等, 2018. 西藏青草山斑岩铜金矿床含矿斑岩锆石U-Pb年代学及岩石成因[J]. 地球科学, 43(08): 2858-2874
Zheng H T, Zheng Y Y, Xu J, et al. , 2018. Zircon U-Pb ages and petrogenesis of ore bearing porphyry for Oingcaoshan porphyry Cu Au deposit, Tibet[J]. Earth Science, 43(08): 2858-2874.
[99] 郑有业, 许荣科, 马国桃, 等, 2006. 锆石SHRIMP测年对狮泉河蛇绿岩形成和俯冲的时间约束[J]. 岩石学报, 22(04): 895-904 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.04.013
Zheng Y Y Xu R K, Ma G T, et al. , 2006. Ages of generation and subduction of Shiquan river ophiolite: Restriction from SHRIMP zircon dating[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(4): 895-904. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.04.013
[100] Zhu D C, Li S M, Cawood P A. , et al, 2016. Assembly of the Lhasa and Qiangtang terranes in central Tibet by divergent double subduction[J]. Lithos, 245: 7-17. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.023
[101] Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. , 2011. The Lhasa Terrane: Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 301(1): 241-255.
[102] Zong K Q, Klemd R, Yuan Y, et al. , 2017. The assembly of Rodinia: The correlation of early Neoproterozoic (ca. 900Ma) high−grade metamorphism and continental arc formation in the southern Beishan Orogen, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB)[J]. Precambrian Research: 32−48.
-




 下载:
下载: