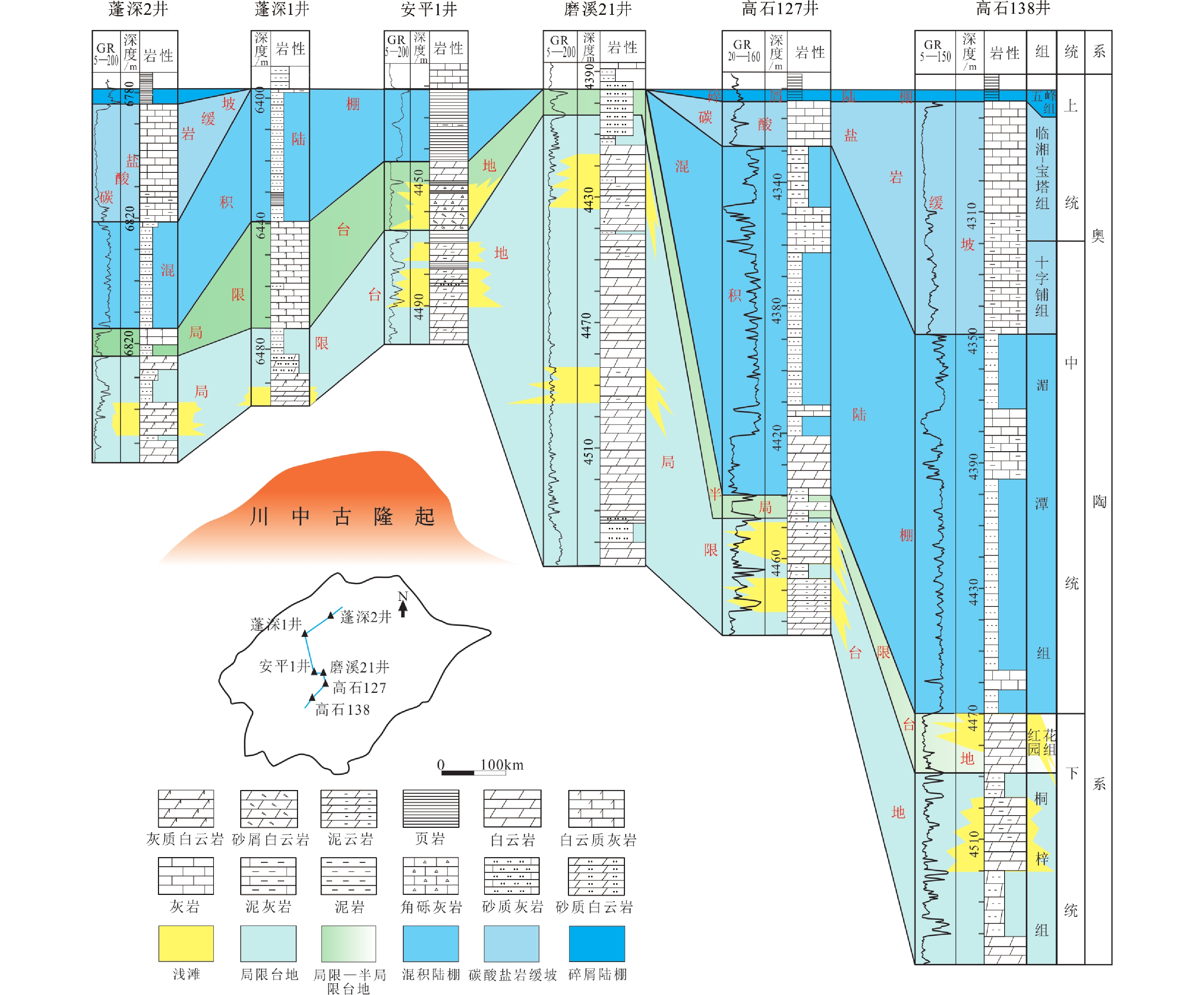
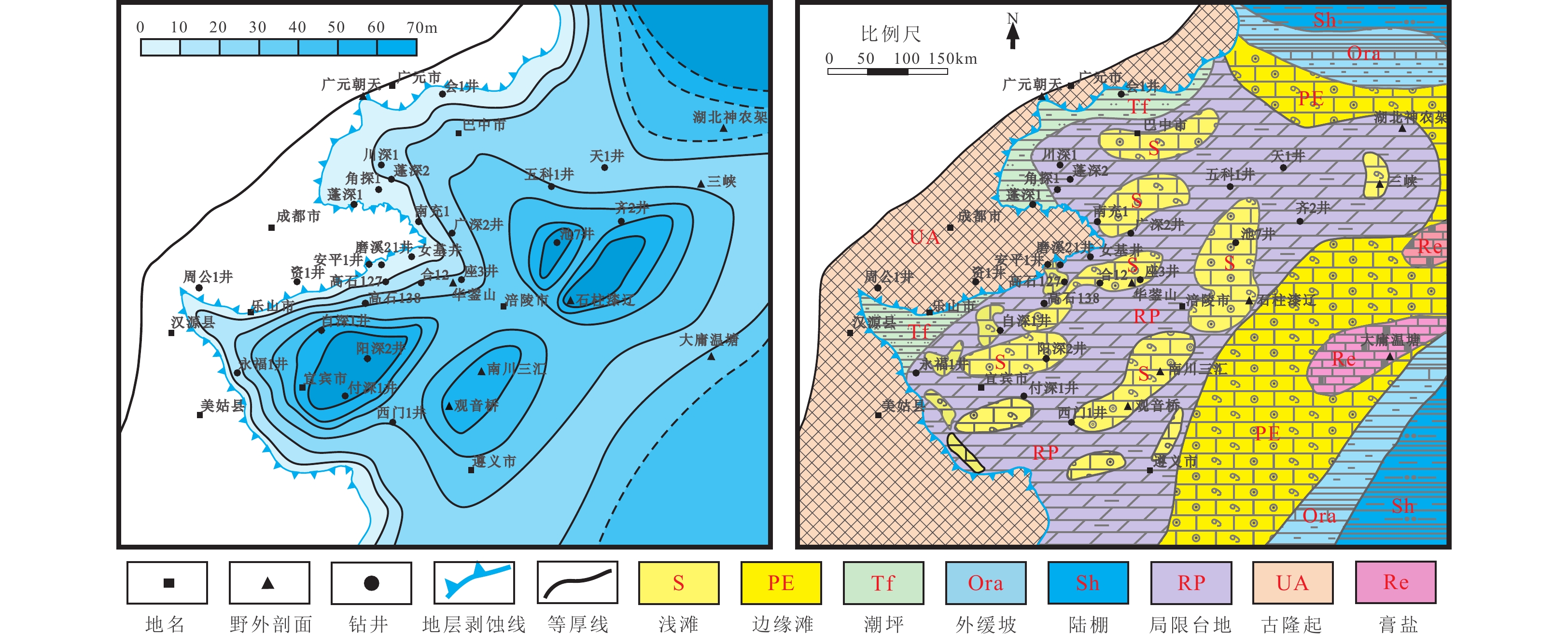
Evolution of the Ordovician sedimentary system and paleogeographic reconstruction in the Sichuan Basin, China
-
摘要:
我国塔里木、鄂尔多斯盆地的奥陶系海相碳酸盐岩中发现了多个大型油气田,但四川盆地奥陶系油气发现方面至今未取得实质性突破。此前的勘探着重于岩溶储层和裂缝型储层,只有少量井获得天然气流发现,四川盆地奥陶系是否发育更具规模勘探潜力的滩相储层是当前亟需回答的问题。由于奥陶系岩性变化快,关于其沉积体系,仍存在争议,这一定程度上限制了对潜在储集相带的认识。本文根据测井、地震及露头剖面资料,分析了四川盆地奥陶系沉积相特征,重建了各沉积期的岩相古地理格局。结果表明:桐梓组—红花园组沉积期,四川盆地所在的扬子板块受泛非运动影响,上扬子构造较为稳定,发育以碳酸盐岩台地为主的沉积相,沉积模式为陆表海浅水台地,滩相白云岩围绕乐山-龙女寺古隆起的周缘分布;湄潭组沉积期,由于全球海平面上升,构造环境转变为加里东运动主控的强挤压背景,隆-坳格局加剧,沉积环境主要为混积陆棚;十字铺—宝塔—临湘组沉积期,重新发育以灰岩为主的碳酸盐岩,为陆表海碳酸盐岩缓坡环境;五峰组沉积期,加里东运动导致在川东南形成局限的深水海湾环境,沉积了一套富有机质页岩。总体上,四川盆地奥陶纪沉积演化经历了由陆表海浅水台地到混积陆棚、再演变为陆表海缓坡、最后演变为滞留深水陆棚的过程。
Abstract:With many large oil and gas fields having been discovered in the Ordovician marine carbonate rocks in the Tarim and Ordos basins, however, no substantial breakthrough has been made in the oil and gas discoveries in the Ordovician of the Sichuan Basin. Previous exploration focused on karst and fractured reservoirs, and only a few wells were found to have natural flow. Whether there is grater potential of large-scale exploration potential beach reservoirs in the Ordovician of the Sichuan Basin is an urgent question to be answered. Due to the rapid change of lithology, the sedimentary system of the Ordovician is still controversial, which limits the understanding of potential reservoir facies belts to some extent. Based on logging, seismic, and outcrop profile data, the characteristics of Ordovician sedimentary facies in the Sichuan Basin are analyzed, and the lithofacies paleogeographic pattern of each sedimentary period is reconstructed. The results show that during the sedimentary period of the Tongzi–Honghuayuan formations, the Yangtze plate, where the Sichuan Basin is located, was influenced by the Pan-African movement, and the upper Yangtze structure was relatively stable. The dominant sedimentary facies was a carbonate platform, and the sedimentary model was an epigenetic shallow platform. Beach facies dolomite distributed around the periphery of the Leshan-Longnüsi palaeouplift. During the sedimentary period of the Meitan Formation, due to the rise in global sea level, the tectonic environment changed into a strong compressive background dominated by the Caledonian movement, the uplift and depression pattern was intensified, and the sedimentary environment was mainly mixed shelf. In the sedimentary period of the Shizipu–Baota–Linxiang formations, carbonate deposits dominated by limestone redeveloped, representing an epigenetic carbonate gentle slope environment. During the sedimentary period of the Wufeng Formation, the Caledonian movement led to the formation of a limited deep-water bay environment in the southeast Sichuan Basin, where a set of organic-rich shales were deposited. In general, the Ordovician sedimentary evolution in the Sichuan Basin has undergone a process from epicontinental shallow platform to mixed shelf, then to epicontinental gentle slope, and finally to lingering deep shelf.
-
Key words:
- paleogeography /
- Paleo-uplift /
- Ordovician /
- sedimentary evolution /
- epeiric carbonate platform
-

-
[1] Borchert H, 1977. On the Formation of Lower Cretaceous Potassium Salts and Tachhydrite in the Sergipe Basin (Brazil) with Some Remarks on Similar Occurrences in West Africa(Gabon, Angola etc.)[J]. Time-and Strata-Bound Ore Deposits: 94 − 111
[2] 陈安清, 杨帅, 陈洪德, 等, 2017. 陆表海台地沉积充填模式及内克拉通碳酸盐岩勘探新启示[J]. 岩石学报, 33(4): 1243-1256
Chen A Q, Yang S, Chen H D, et al. , 2017. The sedimentary filling model of epeiric platform and new inspiration of innercratonic carbonate for oil & gas exploration[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(4): 1243-1256 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] 郭彤楼, 2014. 四川盆地奥陶系储层发育特征与勘探潜力[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 35(3): 372-378
Guo T L, 2014. Charateristics and exploration potential of Ordovician reservoirs in Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 35(3): 372-378 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] 郭旭升, 赵永强, 申宝剑, 等, 2022. 中国南方海相页岩气勘探理论: 回顾与展望[J]. 地质学报, 96(1): 172-182
Guo X S, Zhao Y Q, Shen B J, et al. , 2022. Marine shale gas exploration theory in southern China: review and prospects[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(1): 172-182 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] 何登发, 李德生, 张国伟, 等, 2011. 四川多旋回叠合盆地的形成与演化[J]. 地质科学, 46(3): 589-606
He D F, Li D S, Zhang G W, et al. , 2011. Formation and evolution of multi-cycle superposed Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 46(3): 589-606 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] 胡东风, 王良军, 黄仁春, 等, 2021. 四川盆地中国石化探区油气勘探历程与启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 42(3): 283-290
Hu D F, Wang L J, Huang R C, et al. , 2021. Petroleum Exploration History and Enlightenment in Sichuan Basin: A Case Study on Sinopec Exploration Areas[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 42(3): 283-290 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] 胡华蕊, 邢凤存, 侯明才, 等, 2019. 上扬子奥陶纪层序岩相古地理重建及油气勘探启示[J]. 地球科学, 44(3): 798-809
Hu H R, Xing F C, Hou M C, et al. , 2019. Ordovician Sequence and Lithofacies Paleogeography Reconstruction in Upper Yangtze Region and Its Implications for Oil and Gas Exploration[J]. Earth Science, 44(3): 798-809 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Huang B C, Yan Y G, Piper J D A, et al. , 2018. Paleomagnetic constraints on the paleogeography of the East Asian blocks during Late Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic times[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 186(1): 8-36.
[9] 黄福喜, 陈洪德, 侯明才, 等, 2011. 中上扬子克拉通加里东期(寒武—志留纪)沉积层序充填过程与演化模式[J]. 岩石学报, 27(8): 2299-2317
Huang F X, Chen H D, Hou M C, et al. , 2011. Filling process and evolutionary model of sedimentary sequence of Middle-Upper Yangtze craton in Caledonian (Cambrian-Silurian)[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(8): 2299-2317 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] 黄文明, 刘树根, 马文辛, 等, 2011. 四川盆地奥陶系油气勘探前景[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 32(3): 461-473
Huang G M, Liu S G, Ma W X, et al. , 2011. Petroleum exploration potential of the Ordovician in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 32(3): 461-473 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Irwin M L, 1965. General theory of epeiric clear water sedimentation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 49(4): 445-459.
[12] 李皎, 何登发, 梅庆华, 2015. 四川盆地及邻区奥陶纪构造-沉积环境与原型盆地演化[J]. 石油学报, 36(4): 427-445
Li J, He D F, Mei Q H, 2015. Tectonic-depositional environment and prototype basins evolution of the Ordovician in Sichuan Basin and adjacent areas[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(4): 427-445 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] 李伟, 易海永, 胡望水, 等, 2014. 四川盆地加里东古隆起构造演化与油气聚集的关系[J]. 天然气工业, 34(3): 8-15
Li W, Yi H Y, Hu W S, et al. , 2014. Tectonic evolution of Caledonian paleohigh in the Sichuan Basin and its relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 34(3): 8-15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] 梁狄刚, 张水昌, 张宝民, 等, 2000. 从塔里木盆地看中国海相生油问题[J]. 地学前缘, (4): 534-547
Liang D G, Zhang S C, Zhang B M, et al. , 2000. Understanding On Marine Oil Generation In China Based On Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, (4): 534-547 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] 刘宝珺, 许效松, 1994. 中国南方岩相古地理图集 震旦纪—三叠纪[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 61− 73.
Liu B J, Xu X S, 1994. Paleogeographic atlas of Sinian Triassic in South China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 61 − 73.
[16] 刘树根, 李智武, 孙玮, 等, 2011. 四川含油气叠合盆地基本特征[J]. 地质科学, 46(1): 233-257
Liu S G, Li Z W, Sun W, et al. , 2011. Basic geological features of superimposed basin and hydrocarbon accumulation in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 46(01): 233-257 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] 刘伟, 洪海涛, 徐安娜, 等, 2017. 四川盆地奥陶系岩相古地理与勘探潜力[J]. 海相油气地质, 22(4): 1-10
Liu W, Hong H T, Xu A N, et al. , 2017. Lithofacies Paleogeography and Exploration Potential of Ordovician in Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 22(4): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] 马永生, 陈洪德, 王国力, 等, 2009. 中国南方层序地层与古地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
Ma Y S, Chen H D, Wang G L, et al., 2009. Sequence Stratigraphy and Palaeogeography in South China[M]. Science Press, Beijing.
[19] 牟传龙, 许效松, 2010. 华南地区早古生代沉积演化与油气地质条件[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 30(3): 24-29
Mou C L, Xu X S, 2010. Sedimentary evolution and petroleum geology in South China during the Early Palaeozoi[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 30(3): 24-29 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] 牟传龙, 许效松, 林明, 1992. 层序地层与岩相古地理编图-以中国南方泥盆纪地层为例[J]. 岩相古地理, 4: 1-9
Mou C L, Xu X S, Lin M, 1992. Sequence stratigraphy and compilation of lithofacies and palaeogeographic maps: an example from the devonian strata in southern China. [J]. Lithofacies Palaeogeography, 4: 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Nie H K, Jin Z J, Li P, et al. , 2023. Deep shale gas in the Ordovician-Silurian Wufeng–Longmaxi formations of the Sichuan Basin, SW China: Insights from reservoir characteristics, preservation conditions and development strategies[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 244: 105521. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105521
[22] Wang Y J, Fan W M, Zhang, G W, et al. , 2013. Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China Block: Key observations and controversies[J]. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1273-1305. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.019
[23] 汪泽成, 赵文智, 张林, 等, 2002. 四川盆地构造层序与天然气勘探[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
Wang Z C, Zhao W Z, Zhang L, et al., 2002. Tectonic sequences and natural gas exploration of Sichuan Basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 76 − 100.
[24] 汪正江, 王启宇, 杨菲, 等, 2022. 扬子西缘泛非造山与绵阳—长宁克拉通裂陷的沉积充填过程研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 42(3): 350-367
Wang Z J, Wang Q Y, Yang F, 2022. Stutly on the dleposition and filing process of the Mianyang-Clanging craonie rit: Implicaion for the pan-Alfican orogeny on the western margin of Yangte Bock[J]. Sedlimentary Ceology and Tethyan Geology, 42(3): 350-367 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] 汪正江, 谢渊, 杨平, 等, 2012. 雪峰山西侧震旦纪—早古生代海相盆地演化与油气地质条件[J]. 地质通报. 31(11): 1795 − 1811
Wang Z J, Xie Y, Yang P, et al., 2012. Marine basin evolution and oil and gas geology of Sinian-early Paleozoic period on the western side of the Xuefeng Mountain[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(11): 1795 − 1811 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Wardlaw N C, 1972. Unusual Marine Evaporites with Salts of Calcium and Magnesium Chloride in Cretaceous basins of Sergipe, Brazil[J]. Economic Geology, 67(2): 156-168. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.67.2.156
[27] 夏日元, 唐健生, 关碧珠, 等, 1999. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系古岩溶地貌及天然气富集特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 20(2): 37 − 40
Xia R Y, Tang J S, Guan B Z, et al., 1999. Ordovician palaeokarst landform in Ordos basin and gas enrichment characteristics[J]. Oil & Gas Geology. 20(2): 37 − 40 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] 许效松, 万方, 尹福光, 等, 2001. 奥陶系宝塔组灰岩的环境相、生态相与成岩相[J]. 矿物岩石, (3): 64-69
Xu X S, Wan F, Yin F G, et al. , 2001. Environment facies, ecological facies and diagenetic facies of Baota Formation, of Late Ordovician [J]. Mineral Petrol, (3): 64-69 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] 薛平, 1986. 陆表海台地型蒸发岩的成因探讨[J]. 地质论评, 32(1): 59-66
Xue P, 1986. Origin of evaporites in a vast epicontinental platform sea[J]. Geological Review, 32(1): 59-66 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Yan C N, Jin Z J, Zhao J H, et al. , 2018. Influence of sedimentary environment on organic matter enrichment in shale: A case study of the Wufeng and Longmaxi Formations of the Sichuan Basin, China. [J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 92: 880-894.
[31] 严德天, 王清晨, 陈代钊, 等, 2008. 扬子及周缘地区上奥陶统—下志留统烃源岩发育环境及其控制因素[J]. 地质学报, 82(3): 321-327
Yan D T, Wang Q C, Chen D Z, et al. , 2008. Sedimentary Environment and Development Controls of the Hydrocarbon Sources Beds: the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation and the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Yangtze Area[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 82(3): 321-327 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] 杨威, 谢武仁, 魏国齐, 等, 2012. 四川盆地寒武纪—奥陶纪层序岩相古地理、有利储层展布与勘探区带[J]. 石油学报, 33(202): 21-34
Yang W, Xie W R, Wei G Q, et al. , 2012. Sequence lithofacies paleogeography, favorable reservoir distribution and exploration zones of the Cambrian and Ordovician in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 33(202): 21-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] 张国伟, 郭安林, 王岳军, 等, 2013. 中国华南大陆构造与问题[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 43(10): 1553 − 1582.
Zhang G W, Guo A L, Wang Y J, et al. 2013. Tectonics of South China continent and its implications[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 43(10): 1553 − 1582 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] 朱东亚, 张殿伟, 李双建, 等, 2015. 四川盆地下组合碳酸盐岩多成因岩溶储层发育特征及机制[J]. 海相油气地质, 20(1): 33-44
Zhu D Y, Zhang D W, Li S J, et al. , 2015. Development Genesis and Characteristics of Karst Reservoirs in Lower Assemblage in Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 20(1): 33-44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
-




 下载:
下载: