Study on Water Wettability Mechanism of Pyrite and Coal Surfaces Based on Density Functional Theory
-
摘要:
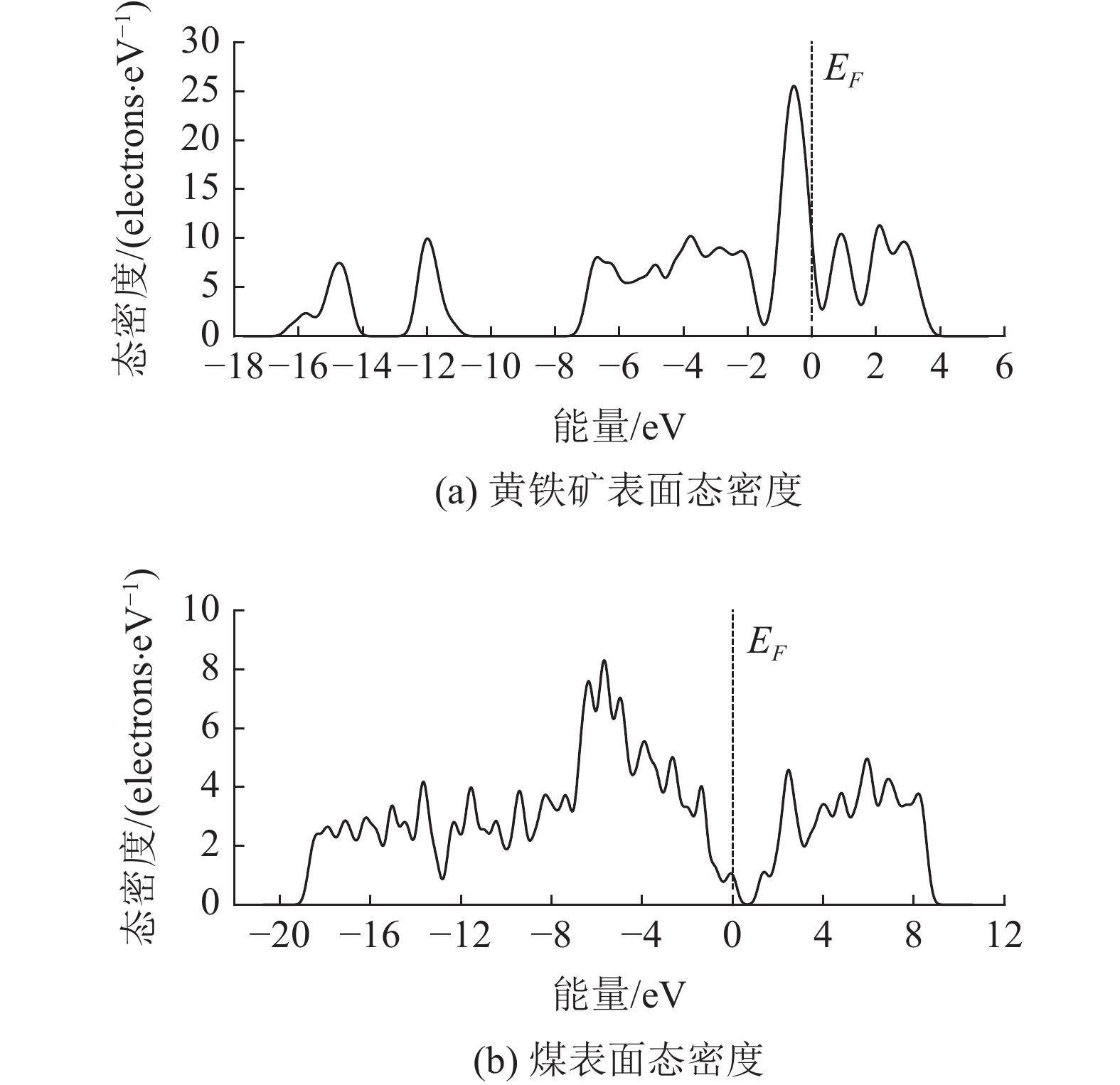
浮选建立在矿物表面润湿性差异之上,为了研究水对黄铁矿和煤表面的润湿机理,构建了黄铁矿和理想化的煤表面模型,并采用密度泛函理论(DFT)分析了水分子和氧分子在黄铁矿和理想化的煤表面上的吸附。结果表明:黄铁矿表面的电子性质活跃,表面Fe与S原子均有未成键的悬挂键,使得黄铁矿表面对水具有较强的吸附活性;水分子在黄铁矿表面各吸附位的吸附能均为负值,底部对硫穴位为水分子吸附的最稳定构型(吸附能为−87.42 kJ/mol);氧分子在黄铁矿表面吸附时会发生解离,但其对已吸附的水分子影响较小。理想化的煤表面原子的配位数与体相相同,且表面对电子的束缚较强,使得理想化的煤表面吸附活性较弱;水分子在各吸附位的吸附能均为正值,说明水分子难以吸附在理想化的煤表面上;氧分子在理想化的煤表面上吸附时未发生解离,且将已吸附的水分子排离表面。因此,黄铁矿表面具有较强的亲水性,而理想化的煤表面具有较强的疏水性。
Abstract:Flotation is based on the difference of wettability of mineral surfaces. In order to study the water wettability mechanism of pyrite and coal surfaces, pyrite and perfect coal surface models were constructed. The adsorptions of water and oxygen molecules on pyrite and perfect coal surface were analyzed by density functional theory (DFT). The results show that the electrons of pyrite surface are more active. There are hanging bonds on the Fe and S atoms which make the pyrite surface have strong adsorption activity. The adsorption energy of water molecules on the pyrite surface is negative value. The adsorption configuration of water molecules on the sulfur acupoint (adsorption energy is −87.42 kJ/mol) is the most stable. Oxygen molecules adsorbed on the pyrite surface can dissociate, but it has little effect on the adsorbed water molecules. The coordination number of atoms on the perfect coal surface is the same as the bulk phase. The binding of electrons on the surface is strong, which makes the adsorption activity on the perfect coal surface weak. The adsorption energy of water molecules on each adsorption site is positive value, which indicates that water molecules are difficult to adsorb on the surface. Oxygen molecules cannot dissociate when adsorbing on the perfect coal surface, and the adsorbed water molecules are discharged from the surface. Therefore, pyrite surface has strong hydrophilicity, while perfect coal surface has strong hydrophobicity.
-
Key words:
- Pyrite /
- Coal /
- Wettability /
- Density functional theory /
- Adsorption /
- Electron density
-

-
表 1 黄铁矿和煤表面原子位移和配位数
Table 1. Atomic displacement and coordination on the surface of pyrite and coal
矿物 原子 配位数 原子位移/Å Δx △y △Z 黄铁矿 Fe1 5 −0.362 −0.005 −0.122 Fe2 5 0.036 −0.004 −0.121 S1 4 −0.003 0.024 0.007 S2 4 0.003 0.024 0.007 S3 3 0.029 0.089 −0.044 S4 3 −0.03 0.089 −0.045 煤 C1 3 −0.015 0.008 0.062 C2 3 −0.015 0.007 0.063 C3 3 −0.015 0.008 0.062 C4 3 −0.014 0.007 0.063 C5 3 −0.015 0.008 0.062 C6 3 −0.014 0.007 0.063 表 2 水分子在黄铁矿和煤表面上的吸附能
Table 2. Adsorption energy of water molecule on pyrite and coal
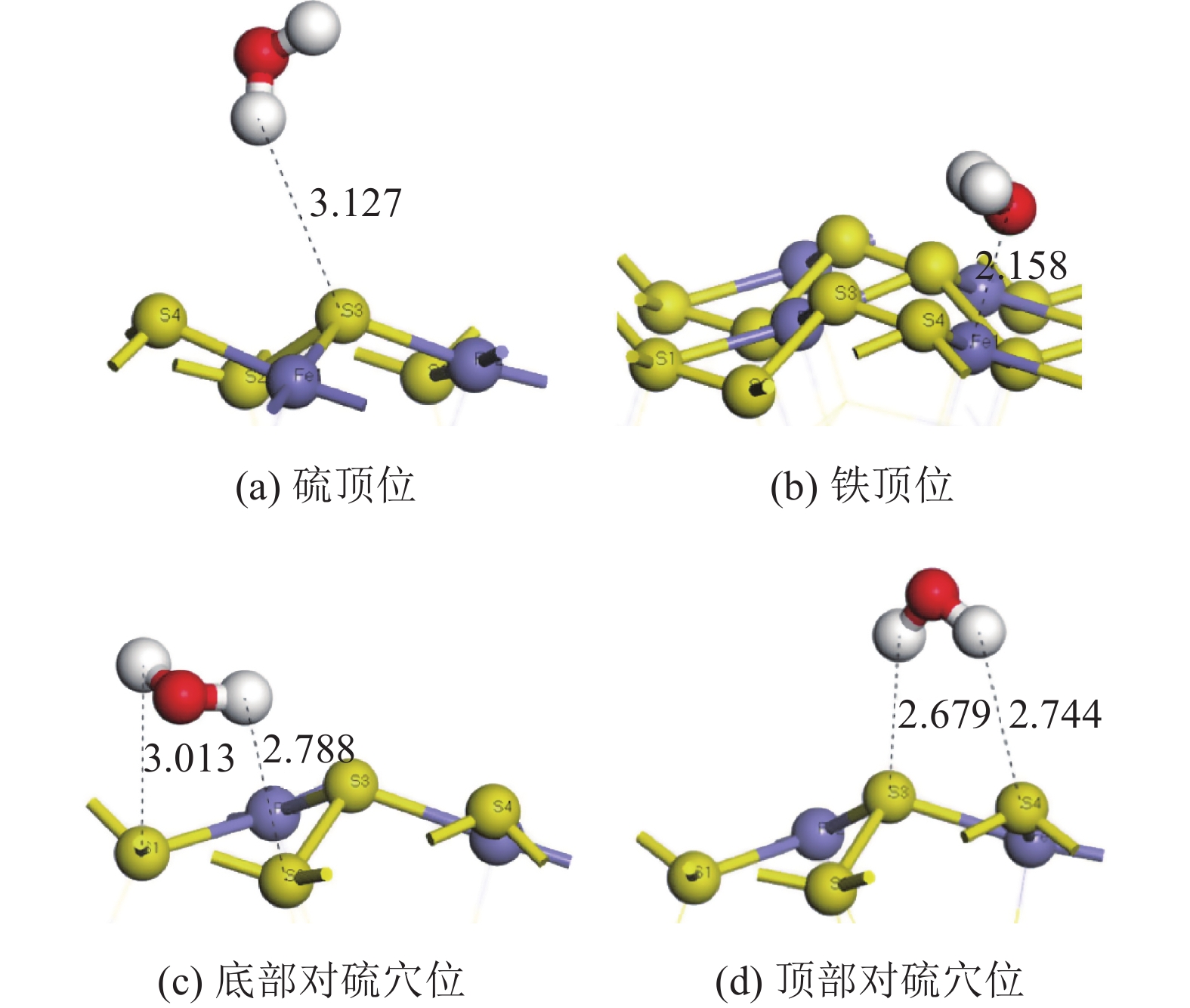
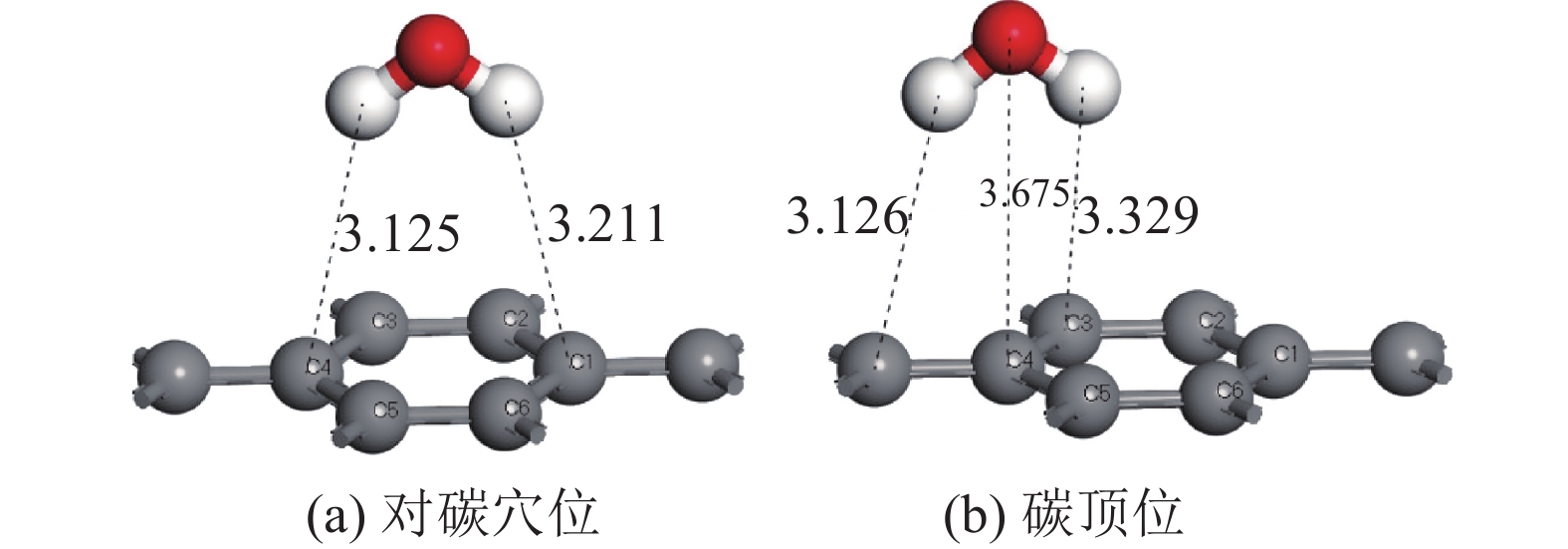
矿物 吸附位 吸附能/(kJ·mol−1) 黄铁矿 硫顶位 −9.17 铁顶位 −38.79 底部对硫穴位 −87.42 顶部对硫穴位 −6.95 煤 对碳穴位 26.85 碳顶位 27.44 表 3 氧分子在已吸附水分子的矿物表面上的吸附能
Table 3. Adsorption energy of oxygen molecule on the mineral surface adsorbed by water molecule
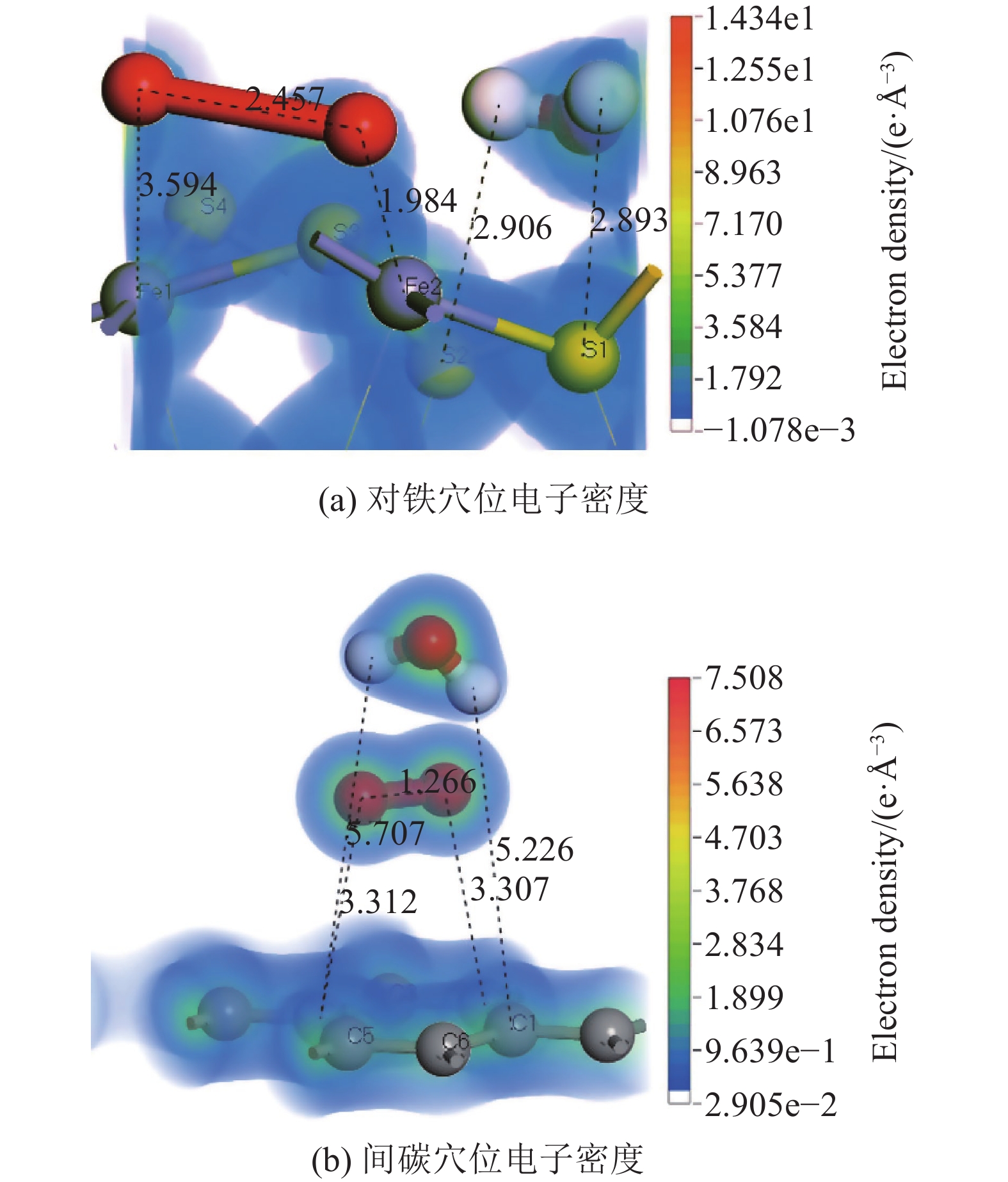
矿物 吸附位 吸附能/(kJ·mol−1) 黄铁矿 底部对硫穴位 −224.71 平行硫铁键 −187.47 对铁穴位 −499.31 煤 邻碳位 87.24 间碳穴位 −26.75 对碳穴位 −24.69 -
[1] 朱一民. 2019年浮选药剂的进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(5):1-17.
ZHU Y M. Development of flotation reagent in 2019[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(5):1-17.
[2] 商林萍, 石磊, 王艳. 青海某银矿浮选试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(1):62-64.
SHANG L P, SHI L, WANG Y. Experimental study on flotation of a silver ore in Qinghai[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):62-64.
[3] Stirling A, Bernasconi M, Parrinello M. Abinitio simulation of water interaction with the (100) surface of pyrite[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2003, 118(19):8917. doi: 10.1063/1.1566936
[4] 陈建华, 朱阳戈. 硫化矿物表面水化层结构及其对药剂作用的影响[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2018(3):1-8.
CHEN J H, ZHU Y G. Structure of hydration layer on sulfide mineral surface and its effect on reagent action[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(3):1-8.
[5] 高正阳, 杨维结. 不同煤阶煤分子表面吸附水分子的机理[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(3):753-759.
GAO Z Y, YANG W J. Mechanism of adsorption of water molecules on the surface of coal molecules of different coal rank[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(3):753-759.
[6] 王丽, 张蓬洲. 煤的XRD的结构分析[J]. 煤炭转化, 1997, 20(1):50-53.
WANG L, ZHANG P Z. XRD structure analysis of coal[J]. Coal Conversion, 1997, 20(1):50-53.
[7] Hung A, Muscat J, Yarovsdy I, et al. Density-functional theory studies of pyrite FeS2 (100) and (110) surfaces[J]. Surface Science, 2002, 513(3):511-524. doi: 10.1016/S0039-6028(02)01849-6
[8] Pfrommer B, Côté M, Louie S, et al. Relaxation of crystals with the Quasi-Newton method[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1997, 131:133-140.
[9] Kusalik P, Svishchev I. The Spatial structure in liquid water[J]. Science, 1994; 265(5176): 1219-1221.
[10] 李玉琼, 陈建华, 蓝丽红, 等. 氧分子在黄铁矿和方铅矿表面的吸附[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(4):1184-1194.
LI Y Q, CHEN J H, LAN L H, et al. Adsorption of oxygen molecules on the surface of pyrite and galena[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(4):1184-1194.
[11] 李焕龙, 金晶, 侯封校, 等. Fe元素及点缺陷对焦炭表面NH3异相吸附的影响: 密度泛函理论研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2018, 46(12):1505-1512.
LI H L, JIN J, HOU F X, et al. Effect of Fe element and point defect on heterogeneous adsorption of NH3 on coke surface: a density functional theory study[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2018, 46(12):1505-1512.
[12] Zhao C, Chen J, Long X, et al. Study of H2O adsorption on sulfides surfaces and thermokinetic analysis[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2014, 20(2):605-609. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2013.05.021
[13] 相建华, 曾凡桂, 梁虎珍, 等. CH4/CO2/H2O在煤分子结构中吸附的分子模拟[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2014, 44(7):1418-1428.
XIANG J H, ZENG F G, LIANG H Z, et al. Molecular simulation of adsorption of CH4/CO2/H2O in coal molecular structure[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2014, 44(7):1418-1428.
-




 下载:
下载: