Analysis of Soil Geochemical Characteristics and Metallogenic Potential in Huolongmengou Area of Heilongjiang
-
摘要:
黑龙江霍龙门沟地区位于东乌珠穆沁旗-嫩江多金属成矿带的南段,具有较好的找矿前景。本文以1∶10000土壤地球化学测量成果为依据,利用元素变异系数、浓集系数及分形特征等方法对黑龙江霍龙门沟地10种元素地球化学特征进行了统计,运用聚类分析、因子分析法及分形方法对元素的共生组合关系进行了分析,结果表明:区内Au、Ag、Cu、As、Mo等元素具有较高的找矿潜力,Au元素可能是研究区主要的成矿矿种。根据元素异常组合分布规律及成矿地质条件,共圈定综合异常7处,并与区域典型的永新浅成低温热液型金矿床和多宝山斑岩型铜-钼-(金)矿床的成矿地质背景及地球化学特征进行对比研究,划分出大狼沟Au-Ag成矿远景区和霍龙门沟Cu-Au成矿远景区,为研究区下一步找矿勘查部署提供科学依据。
Abstract:Heilongjiang Huolongmengou area is located in the southern section of the DongwuzhuMuqi-Nenjiang polymetallic mineralization belt, and has a good prospect for exploration prospecting. Based on the results of 1∶10000 soil geochemical measurements, this paper uses the methods of element variation coefficient, thick set coefficient and fractal characteristics to count the geochemical characteristics of 10 elements in Heilongjiang Huolongmengou area. Cluster analysis, factor analysis and fractal method were used to analyze the symbiotic association of elements. The results show that Au, Ag, Cu, As and Mo have high prospecting potential in the study area, and Au may be the main ore-forming minerals in the study area. According to the distribution law of elemental abnormal combination and the geological conditions of mineralization, a total of 7 comprehensive anomalies were circled, and compared with the mineralization geological background and geochemical characteristics of the typical Yongxin shallow into low temperature hydrothermal gold deposit and Duobaoshan spot rock Copper-Molybdenum-(Gold) deposit in the region, and the prospect area of Au-Ag mineralization and the Cu-Au mineralization prospect area of Huolongmengou were divided to provide scientific basis for the next step of prospecting and deployment of the research area.
-
Key words:
- Soil geochemistry /
- Comprehensive anomaly /
- Minerogenic prospect /
- Huolongmengou area /
- Heilongjiang
-

-
表 1 霍龙门地区土壤地球化学测量数据统计
Table 1. Statistics of soil geochemical measurements in Huolongmengou area
元素 平均值
X背景值 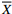
最小值
Xmin最大值
Xmax标准离差
S剔除前变
异系数Cv1剔除后变
异系数Cv2区域1∶20万地球
化学元素背景值K富集系数
C异常下限
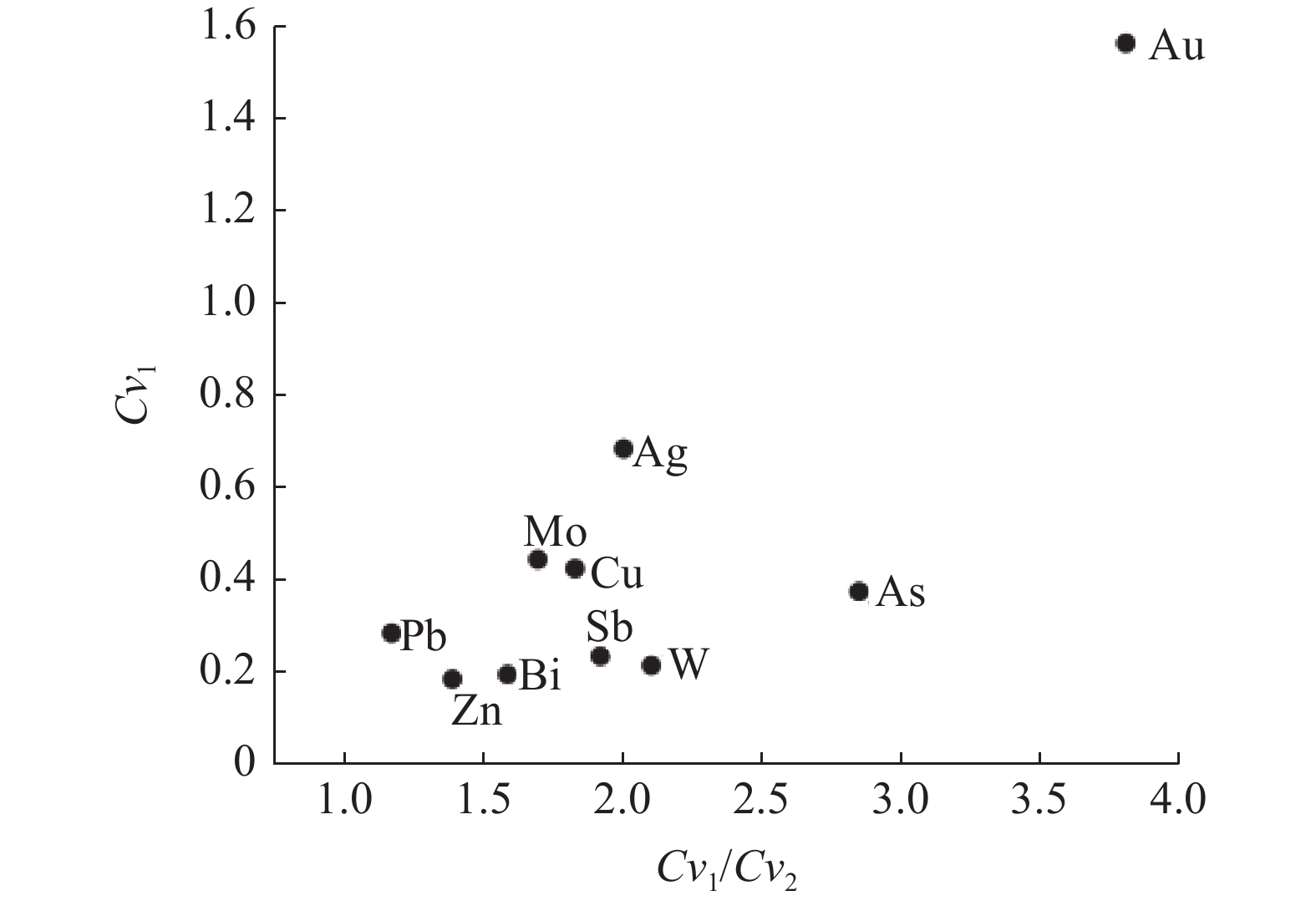
TAu 1.00 0.8 0.10 100.80 1.60 1.56 0.41 0.48 1.67 5.60 Ag 0.11 0.10 0.01 1.26 0.08 0.68 0.34 0.04 2.23 0.32 As 9.56 8.89 2.38 122.86 3.57 0.37 0.13 7.29 1.22 13.50 Sb 0.57 0.55 0.09 7.93 0.13 0.23 0.12 0.32 1.71 0.82 Bi 0.36 0.36 0.04 2.89 0.07 0.19 0.12 0.11 3.39 0.44 Cu 21.50 19.9 8.99 201.66 9.00 0.42 0.23 17.18 1.16 35.90 Pb 21.40 21.00 4.42 83.77 5.90 0.28 0.24 17.70 1.18 32.70 Zn 69.30 67.6 32.30 244.36 12.30 0.18 0.13 24.20 2.78 91.80 W 2.25 2.21 0.84 36.60 0.46 0.21 0.10 0.615 3.59 2.83 Mo 1.15 1.10 0.26 24.05 0.51 0.44 0.26 0.78 1.41 1.68 注:Au元素含量为×10-9,其他元素为×10-6;数据来源于黑龙江省地质调查研究总院 表 2 霍龙门沟地区不同地质子区土壤元素参数特征
Table 2. Characteristics of soil element parameters in different geological regions of Huolongmengou areas
地质子区 参数 Ag As Au Bi Cu Mo Pb Sb W Zn 多宝山组 X 92.7 9.5 1.2 0.34 29.6 1.12 22.7 0.6 1.96 83.4 S 25.3 1.7 0.5 0.06 7.5 0.28 2.3 0.1 0.28 14.5 CV 0.3 0.2 0.5 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.2 0.1 0.2 裸河组、泥鳅河组、腰桑南组 X 92.6 9.8 1.2 0.34 27.2 1.00 23.8 0.6 1.96 82.3 S 27.7 2.3 0.5 0.06 6.5 0.25 3.9 0.2 0.31 13.8 CV 0.3 0.2 0.5 0.2 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.2 龙江组、光华组、九峰山组 X 78.9 9.7 0.9 0.32 20.6 1.09 24.9 0.6 1.85 74.8 S 17.8 2.6 0.4 0.06 5.3 0.32 3.6 0.1 0.26 16.0 CV 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.2 0.3 0.3 0.1 0.2 0.1 0.2 甘河组、西山玄武岩、大熊山玄武岩 X 73.6 11.5 1.1 0.34 22.8 0.93 27.2 0.6 2.01 66.7 S 12.3 2.7 0.4 0.05 3.7 0.22 3.5 0.1 0.32 11.5 CV 0.2 0.2 0.4 0.1 0.2 0.2 0.1 0.2 0.2 0.2 早世炭世花岗质糜棱岩-奥陶纪侵入岩 X 91.9 8.9 1.0 0.35 20.4 1.11 25.0 0.5 1.93 75.9 S 29.1 2.0 0.5 0.08 5.8 0.36 3.3 0.1 0.43 16.2 CV 0.3 0.2 0.5 0.2 0.3 0.3 0.1 0.2 0.2 0.2 早世炭世正长花岗岩-中石炭世花岗岩 X 88.3 9.3 0.9 0.33 17.9 1.13 24.5 0.5 1.91 70.9 S 28.3 2.6 0.4 0.08 5.3 0.37 4.5 0.1 0.45 17.7 CV 0.3 0.3 0.5 0.2 0.3 0.3 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.3 早白垩世、中侏罗世侵入岩 X 79.7 9.0 0.9 0.36 18.0 1.03 26.1 0.5 1.91 66.9 S 19.6 2.4 0.3 0.09 5.1 0.30 3.7 0.1 0.40 15.5 CV 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.1 0.2 0.2 0.2 全区 X 95.2 10.7 1.73 0.37 23.3 1.1 26.3 0.62 2.06 75.2 S 82.6 5.35 17.6 0.36 8.57 1.5 5.93 0.30 1.11 18.8 CV 0.85 0.50 10.2 0.97 0.37 1.36 0.23 0.49 0.54 0.25 注:X为均值,S为标准离差,Cv为变异系数,Au元素含量为×10-9,其他元素为×10-6;数据来源于黑龙江省地质调查研究总院(据曲晖等[36],修改) 表 3 正交旋转因子载荷矩阵
Table 3. Orthogonal rotating factor score matrix
元素 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 Au 0.028 -0.027 0.08 0.007 0.011 0.994 Ag 0.027 0.326 0.804 0.122 -0.071 0.059 Pb 0.051 0.799 -0.062 0.108 -0.060 0.006 Mo -0.021 0.102 -0.007 0.934 0.039 -0.019 W 0.001 0.112 -0.018 0.092 0.937 0.002 Cu 0.124 -0.444 0.704 -0.057 0.096 0.054 Zn 0.066 0.727 0.117 -0.023 0.225 -0.035 As 0.860 -0.038 0.058 0.106 0.001 -0.020 Sb 0.851 0.146 0.06 -0.049 0.034 0.053 Bi 0.303 -0.037 0.354 0.509 0.374 0.091 λ 1.580 1.518 1.298 1.185 1.090 1.007 △ 15.804 30.985 43.970 55.820 66.715 76.788 注:λ-特征值;△-旋转后累计方差贡献/% 表 4 元素异常下限、浓度分带及单元素异常数统计
Table 4. 10 elements anomaly threshold, concentration zoning and single element anomaly number
元素 异常下限使用值 浓度分带 单元素异常数 外带 中带 内带 Au 5.60 ≥5.6~11.2 ≥11.2~22.4 ≥44.8 24 Ag 0.32 ≥0.32~0.64 ≥0.64~1.28 ≥1.28 38 As 13.50 ≥13.5~27 ≥27~54 ≥54 17 Sb 0.82 ≥0.82~1.64 ≥1.64~3.28 ≥3.28 30 Bi 0.44 ≥0.44~0.88 ≥0.88~1.76 ≥1.76 49 Cu 35.90 ≥35.9~71.8 ≥71.8~143.6 ≥143.6 24 Pb 32.70 ≥32.7~65.4 ≥65.4~130.8 ≥130.8 25 Zn 91.80 ≥91.8~183.6 ≥183.6~367.2 ≥367.2 22 W 2.83 ≥2.83~5.66 ≥5.66~11.32 ≥11.32 14 Mo 1.68 ≥1.68~3.36 ≥3.36~6.72 ≥6.72 31 注:Au元素含量为×10-9,其他元素为×10-6。 -
[1] GE W C, WU F Y, ZHOU C Y, et al. Mineralization ages and geodynamic implications of porphyry Cu-Mo deposits in the east of Xingmeng–orogenicbelt[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(20):2407-2417. doi: 10.1360/csb2007-52-20-2407
[2] LIU J, WU G, LI Y, et al. Re–Os sulfide (chalcopyrite, pyrite and molybdenite) systematics and fluid inclusion study of the Duobaoshan porphyry Cu (Mo) deposit, Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 49(3):300-312.
[3] ZENG Q D, LIU J M, CHU S X, et al. Re–Os and U–Pb geochronology of the Duobaoshan porphyry Cu–Mo–(Au) deposit, northeast China, and its geological significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79(2):895-909.
[4] HAO Y J, REN Y S, DUAN M X, et al. Metallogenic events and tectonic setting of the Duobaoshan ore field in Heilongjiang Province, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97:442-458. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.08.007
[5] 王乐, 秦克章, 庞绪勇, 等. 多宝山矿田铜山斑岩铜矿床地质特征与蚀变分带: 对热液—矿化中心及深部勘查的启示[J]. 矿床地质, 2017, 36(5):1143-1168. WANG L, QIN K Z, PANG X Y, et al. Geological characteristics and alteration zonation of Tongshanporphyry copper deposit within Duobaoshanorefield, Heilongjiang: Implications for hydrothermal-mineralization center and further exploration[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2017, 36(5):1143-1168.
[6] YUAN M W, LI L, LI S R, et al. Mineralogy, fluidinclusions and S-Pb-H-O isotopes of the Erdaokan Ag-Pb-Zn deposit, Duobaoshan metallogenic belt, NE China: implications for ore genesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 113:103074. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103074
[7] GAO R Z, XUE C J, LV X B, et al. Genesis of the Zhengguang gold deposit in the Duobaoshan ore field, Heilongjiang Province, NE China: Constraints from geology, geochronology and S-Pb isotopic compositions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 84:202-217. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.12.031
[8] 张志华, 孙丰月, 舒旭. 黑龙江三道湾子金矿Au-Ag-Te系列矿物特征及其成矿阶段分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018, 54(S1):1416-1424. ZHANG Z H, SUN F Y, SHU X. Characteristics of the Au–Ag–Te minerals from the Sandaowanzi gold deposit, Heilongjiang Province and the metallogenic stage[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2018, 54(S1):1416-1424.
[9] YU R T, LI B L, SUN F Y, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry and Hf isotopes of andesites in the Sandaowanzi gold deposit (Great Xing'an Range, NE China): implications for petrogenesis, tectonic setting, and mineralization[J]. Acta Geochimica, 2021, 40(2):251-270. doi: 10.1007/s11631-020-00448-w
[10] 李成禄, 李胜荣, 袁茂, 等. 黑龙江省嫩江—黑河构造混杂岩带科洛金矿床成因: 来自黄铁矿化学成分及He-Ar、S、Pb同位素证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(5):099-115. LI C L, LI S S, YUAN M, et al. Genesis of the Keluo Au deposit in the Nenjiang-Heihe tectonic melange belt, Heilongjiang Province: evidence from chemical composition and pyrite He-Ar, S, Pb isotopes[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(5):099-115.
[11] ZHAO Z H, SUN J G, LI G H, et al. Early Cretaceous gold mineralization in the Lesser Xing'an Range of NE China: the Yongxin example[J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(12):1522-1549. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2018.1522521
[12] ZHAO Z H, SUN J G, LI G H, et al. Age of the Yongxin Au deposit in the Lesser Xing'an Range: Implications for an Early Cretaceous geodynamic setting for gold mineralization in NE China[J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 54(4):2525-2544. doi: 10.1002/gj.3310
[13] ZHAO Z H, SUN J G, LI G H, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic constraints on the timing and origin of the Early Cretaceous igneous rocks in the Yongxin gold deposit in the Lesser Xing'an Range, NE China[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55(4):2684-2703. doi: 10.1002/gj.3545
[14] 杨笑笑, 罗先熔, 郑超杰, 等. 衡阳盆地北缘国庆矿区土壤地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018, 54(4):762-771. YANG X X, LUO X R, ZHENG C J, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil and prospecting direction in the Guoqing area, northern margin of the Hengyang Basin[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2018, 54(4):762-771.
[15] 黄文斌, 罗先熔, 贾飞, 等. 陕西汉南碑坝地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿预测[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(6):1110-1117. HUANG W B, LUO X R, JIA F, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soils in the Beiba area, Southern Hanzhong City, Shaanxi Province and their application for mineral prospecting prediction[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2019, 38(6):1110-1117.
[16] 蒋艳明, 曹微, 燕振之. 2015. 印度尼西亚Buti铜矿的土壤地球化学特征与成矿预测[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 30(3): 422-428.
JIANG Y M, CAO W, YAN Z Z. The soil geochemical characteristics of the Buti Cu deposit in Indonesia and the oreprediction[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2015, 30(3): 422-428.
[17] 董一博, 焦建刚, 刘凯, 等. 土壤地球化学测量在南秦岭夏家店金矿刘家峡测区的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(5):1202-1213. DONG Y B, JIAO J G, LIU K, et al. Application of soil geochemical measurement to the Liujiaxia area of the Xiajiadian gold mine in the South Qinling[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2019, 55(5):1202-1213.
[18] 王仔章, 刘铭. 青海省都兰县丘吉东沟金矿地球化学特征及找矿潜力分析[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2020, 35(3):332-338. WANG Z Z, LIU M. Geochemical characteristics and prospecting potential analysis of Qiujidonggou gold deposit, Dulan county, Qinghai province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2020, 35(3):332-338. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2020.03.009
[19] ZHENG C J, LUO X R, WEN M L, et al. Axial primary halo characterization and deep orebody prediction in the Ashele copper-zinc deposit, Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 213:1-16.
[20] AN W T, CHEN J P, LI Y C, et al. The superposition characteristics of primary halo in the Daping gold deposit, Yunnan Province, China and its significance for exploration[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 228:1-12.
[21] WANG Q, WANG X Q, LIU H L, et al. Targeting deep-seated gold deposits: A study from the Qujia Gold Deposit, Shandong Province, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2021, 130:1-13.
[22] 赵忠海. 小兴安岭西北部永新大型金矿成因、成矿地质模式与深部三维成矿预测[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 2019, 21-52.
ZHAO Z H. Ore genesis, metallogenic geological mode and deep metallogenic prediction of the Yongxin large Au deposit based on 3D digital model in the northwestern Lesser Xing’an Range[D]. Changchun: Jilin University: 2019, 21-52.
[23] 张璟, 邵军, 杨宏智, 等. 东北扎兰屯奥陶纪碱性辉长岩锆石U-Pb 年代学证据[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(3):616-617. ZHANG J, SHAO J, YANG H Z, et al. U-Pb chronological evidence from zircons of Ordovician essexite in Zhalantun area, Northeast China[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(3):616-617.
[24] 叶琴, 于洋, 高曦, 等. 内蒙古阿拉坦合力苏木汗贝布敦昭奥陶纪裸河组的重新厘定及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(10):1548-1557. YE Q, YU Y, GAO X, et al. Revision of the Ordovician Luohe Formation in Hanbeibudunzhao area of AltanHil, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(10):1548-1557. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.10.006
[25] GAO S, XU H, ZANG Y Q, et al. Late Mesozoic magmatism and metallogeny in NE China: The Sandaowanzi–Beidagou example[J]. International Geology Review, 2016, 59(11):1413-1438.
[26] 王苏珊, 刘佳宜, 季洪伟, 等. 黑龙江三道湾子金矿区龙江组安山岩的年代学与地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(8):2604-2618. WANG S S, LIU J Y, JI H W, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the andesites of Longjiang Formation in the Sandaowanzi gold deposit, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Acta PetrologicaSinica, 2017, 33(8):2604-2618.
[27] 张超, 吴新伟, 张渝金, 等. 大兴安岭北段龙江盆地光华组碱流岩LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(9):1531-1541. ZHANG C, WU X W, ZHANG Y J, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and geochemical characteristics of the pantellerite of Guanghua Formation from Longjiang basin in northern Da Hinggan Mountains and their geological implications[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2017, 36(9):1531-1541.
[28] SUN J G, HAN S J, ZHANG Y, et al. Diagenesis and metallogenetic mechanisms of the Tuanjiegou gold deposit from the Lesser Xing’an Range, NE China: Zircon U–Pb geochronology and Lu–Hfisotopic constraints[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 62:373-388. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.10.021
[29] 胡二红, 张善明, 贺中银, 等. 内蒙古额济纳旗微波山地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿潜力[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(6):1303-1317. HU E H, ZHANG S M, HE Z Y, et al. Soil Geochemical Characteristics and Metallogenic Potential in Weibo Mountain Area of EjinaBanner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(6):1303-1317.
[30] 张永三, 胡兆国, 刘静, 等. 水系沉积物测量在云南临沧地区离子吸附型稀土矿找矿中的应用[J]. 矿物学报, 2021, 41(2):171-180. ZHANG Y S, HU Z G, LIU J, et al. Application of stream sediment survey for prospecting the ion adsorption type REE deposit in the Lincang area, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta MineralogicaSinica, 2021, 41(2):171-180.
[31] 陈炳锦, 郑崔勇, 赵亮亮, 等. 土壤地球化学测量在陕西勉县瓦子坪铅锌多金属矿勘查中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2):455-465. CHEN B J, ZHENG C Y, ZHAO L L, et al. Application of soil geochemical survey in the exploration of lead–zinc polymetallic ore in Waziping, Mianxian County, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(2):455-465.
[32] 黄永高, 冯佐海, 罗改, 等. 三江特提斯兰坪盆地通甸地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿靶区优选[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 56(4):732-744. HUANG Y G, FENG Z H, LUO G, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting target optimization in Tongdian area of Lanping Basin, Sanjiang Tethys[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(4):732-744.
[33] 张勤山, 马楠, 郝亚青, 等. 综合化探方法在青海夏日哈木超大型铜镍矿床中的找矿应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(3):429-437. ZHANG Q S, MA N, HAO Y Q, et al. A study of integrated geochemical exploration method and its application to Xiarihamu superlarge Cu-Ni deposit, Qinghai Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(3):429-437.
[34] 丁吉顺, 陈伟, 周恒, 等. 西藏雄梅地区1: 5万水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(1):48-63. DING J S, CHEN W, ZHOU H, et al. Geochemical characteristics from 1: 50000 survey data of stream sediments and ore–search prospects in the Xiongmei Area, Tibet[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2019, 55(1):48-63.
[35] 胡兆国, 张永三, 王战华, 等. 云南省者太地区金锑矿找矿预测—来自水系沉积物测量的证据[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(3):753-764. HU Z G, ZHANG Y S, WANG Z H, et al. Prospecting of gold-antimony deposits in the Zhetai area of Yunnan Province: Evidence from stream sediment survey[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2019, 55(3):753-764.
[36] 曲晖, 王佰义, 王建民, 等. 土壤地球化学测量在永新金矿勘查中的应用及找矿效果研究[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2018, 26(2):143-152. QU H, WANG B Y, WANG J M, et al. Application of soil geochemical survey in the exploration of Yongxin gold deposit and its prospecting effect[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2018, 26(2):143-152.
[37] 孙雨, 神元, 鲁正清, 等. 河南卢氏三官庙钼多金属矿区土壤地球化学特征及成矿预测[J]. 金属矿山, 2018(1):128-136. SUN Y, SHEN Y, LU Z Q, et al. Soil geochemical characteristics and metallogenic prediction of Sanguanmiao Mo-polymetallid mining area in Lushi County, Henan Province[J]. Metal Mine, 2018(1):128-136. doi: 10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.201801026
[38] 王永开. 内蒙古额济纳旗沙河北幅土壤地球化学特征与异常评价[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2021, 36(2):195-201. WANG Y K. Characteristics and anomly evaluation of soil geochemistry of Shahebei sheet of Ejinaqi in Inner Mongolia[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2021, 36(2):195-201.
[39] 薛盈杉, 张军军, 曾小波. 基于AHP-熵权法的金属矿山开发利用水平综合评价研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(4):66-72+58. XUE Y S, ZHANG J J, ZENG X B. Multipurpose evaluation of exploitation and utilization level of metal mines based on AHP and entropy weight method[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(4):66-72+58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.04.010
[40] 姚玉玲. 聚焦耦合微波萃取沉积物中甲基汞前处理条件的研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2013(4):48-51. YAO Y L. Study on pretreatment condition of extracting of methylmercury in sediments by focusing coupling microwave-assisted[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2013(4):48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2013.04.013
[41] 辛存林, 王磊, 路阔, 等. 甘肃天水火鸡山地区土壤地球化学异常信息提取与评价[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(2):169-179. XIN C L, WANG L, LU K, et al. Extraction and evaluation of soil geochemical anomaly information in the Huojishan Area of Tianshui, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Sciences), 2020, 56(2):169-179. doi: 10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2020.002.004
[42] 成秋明. 多维分形理论和地球化学元素分布规律[J]. 地球科学, 2000(3):311-318. CHENG Q M. Multifractal theory and geochemical element distribution pattern[J]. Earth Science, 2000(3):311-318. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2000.03.017
[43] 成秋明, 张生元, 左仁广, 等. 2009. 多重分形滤波方法和地球化学信息提取技术研究与进展[J]. 地学前缘, 16(2): 185-198.
CHENG Q M, ZHANG S Y, ZUO R G, et al. Progress of multifractal filtering techniques and their applications in geochemical information extraction[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 6(2): 185-198.
[44] 申维. 分形求和法及其在地球化学数据分组中的应用[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2007(2):134-137. SHEN W. Fractal summation method and its application in geochemical data grouping[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2007(2):134-137.
[45] 蒙勇, 文件生, 吕宇明, 等. 广西贵港银山岭铅锌矿土壤地球化学找矿研究[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(5):1013-1020. MENG Y, WEN J S, LV Y M, et al. Study on soil geochemical prospection of lead-zinc deposit in Yinshanling, Guigang, Guangxi[J]. Geoscience, 2011, 25(5):1013-1020.
[46] 鄢旭久, 薛林福, 刘正宏. 分形模型在黑龙江漠河地区金矿成矿预测中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(2):384-392. YAN X J, XUE L F, LIU Z H. Application of fractal model in gold prospecting in Mohe Area, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(2):384-392. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2012.02.013
[47] 袁和, 许云鹏, 邵华, 等. 藏南邦卓玛地区金多金属矿土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 金属矿山, 2019(3):147-155. YUAN H, XU Y P, SHAO H, et al. Soil geochemical characteristics and prospecting potential of Au-polymetallic deposit in Bangzhuoma area, South Tibet[J]. Metal Mine, 2019(3):147-155. doi: 10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.201903023
[48] 赵忠海, 孙景贵, 郭艳. 黑龙江永新金矿床原生晕轴向分带特征及深部矿体预测[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(S1):157-158. ZHAO Z H, SUN J G, GUO Y. Axial zoning characteristics of primary halos and deep orebody prediction in Yongxin gold deposit, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geological Review, 2017, 63(S1):157-158. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2017.s1.074
[49] 梁科伟, 赵忠海, 郭艳. 原生晕在深部成矿预测中的应用——以黑河地区永新金矿为例[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(6):512-518. LIANG K W, ZHAO Z H, GUO Y. Application of primary halo in deep metallogenic prediction: A case study of yongxin gold deposit in heihe area[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(6):512-518. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2019.06.002
[50] 蔡文艳. 黑龙江省多宝山矿集区铜—钼—金多金属成矿作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020, 39-83.
CAI W Y. Metallogenesis of copper–molybdenum–gold polymetallic in the Duobaoshan orefield, Heilongjiang Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020, 39-83.
[51] 徐东海, 万太平, 石国明. 黑龙江多宝山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及成矿远景区划分[J]. 黄金, 2019, 40(6):18-22. XU D H, WAN T P, SHI G M. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and division of metallogenic prospective regions in Duobaoshan area, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Gold, 2019, 40(6):18-22. doi: 10.11792/hj20190605
-




 下载:
下载: