Remote Sensing Alteration Anomaly Information Extraction and Metallogenic Prediction Based on MPT Method-- A Case Study of Dagelegou Area in Qinghai Province
-
摘要:
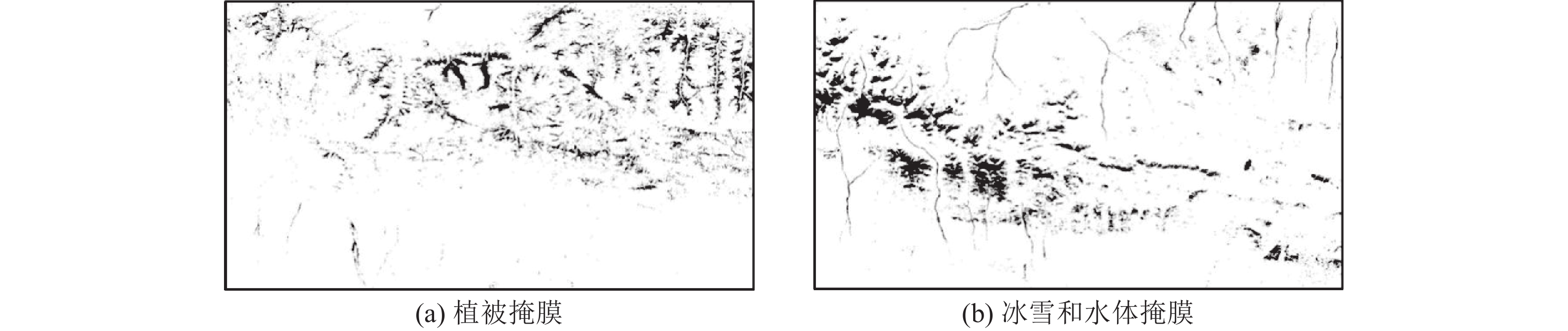
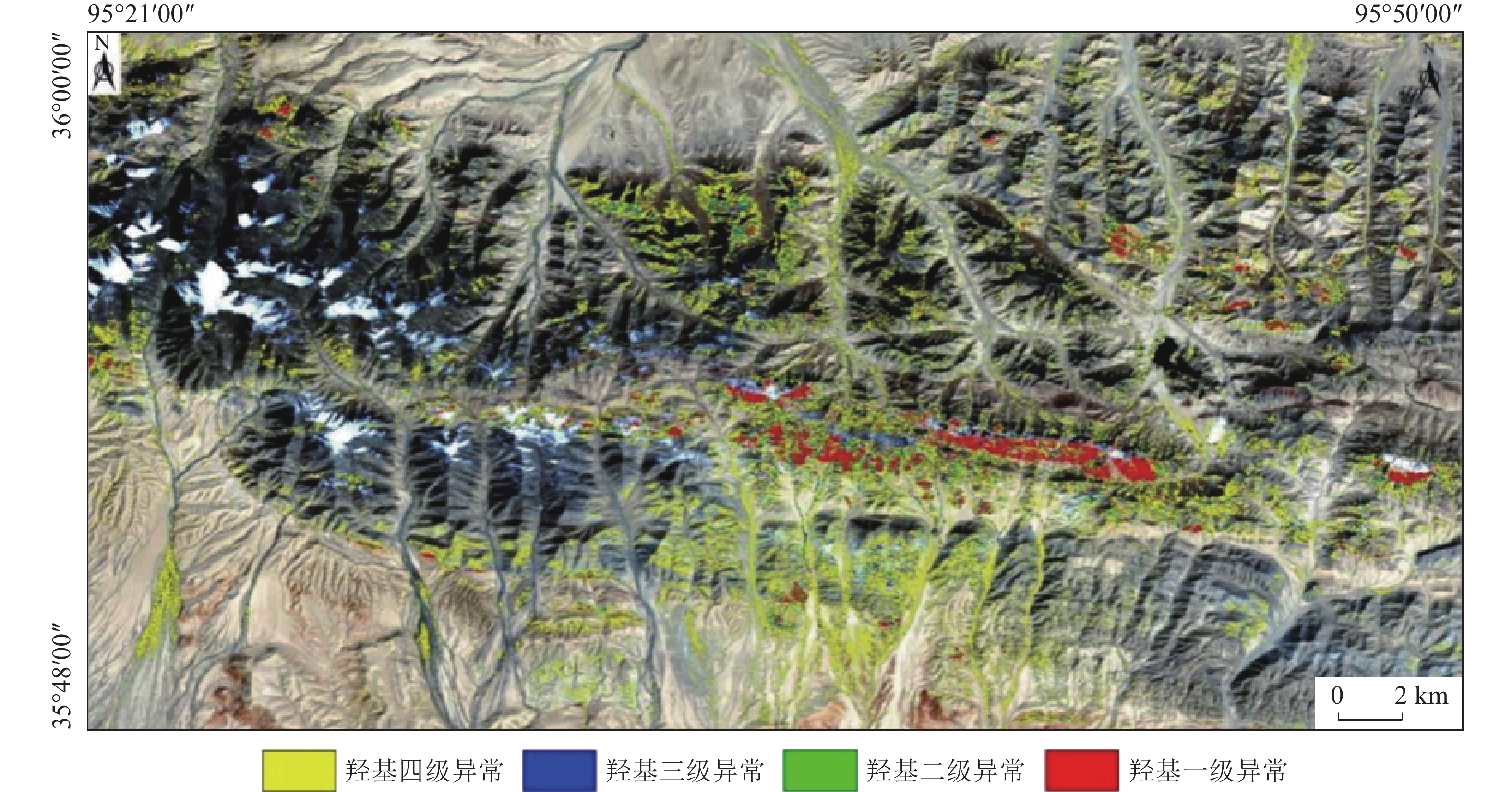
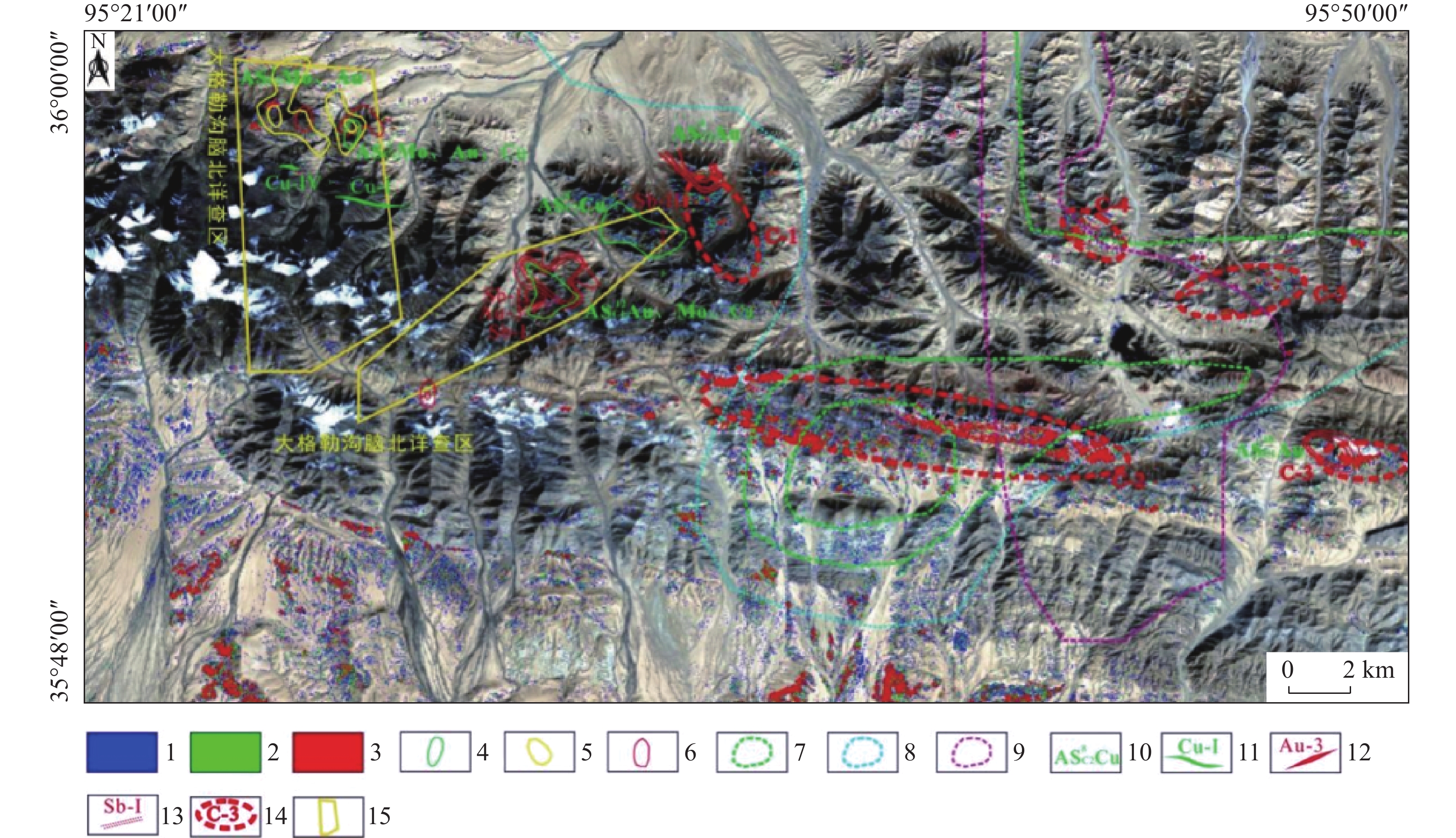
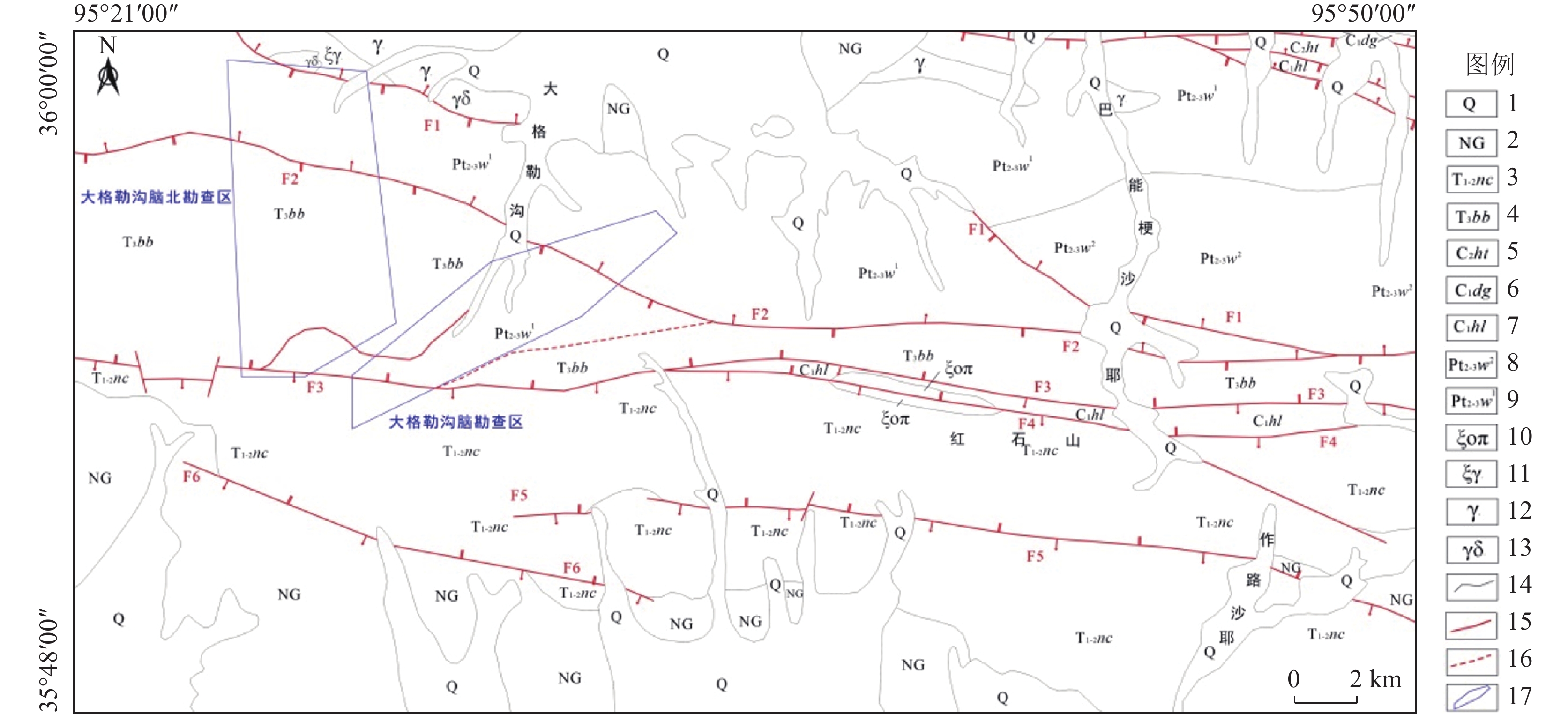
MPT方法是基于“掩膜技术+主成分分析+门限化分级”数据处理流程的蚀变信息提取方法,其能够在有效排除植被、冰雪、水体等干扰信息基础上,定量提取主成分中弱蚀变信息并进行等级划分。本文以landsat8 OLI数据为基础,基于MPT方法提取了大格勒沟地区的铁染和羟基蚀变信息,并与已知地质背景进行了分析比较。结果表明,区内现有金多金属矿详查区内铁染和羟基综合蚀变异常信息与水系沉积物Au、Cu和Mo元素异常、铜金矿体以及断裂破碎蚀变带分布吻合程度高,遥感蚀变异常信息能够有效指示矿化部位。基于综合蚀变异常信息、异常验证分析结果和区域地质背景,圈定了5个成矿远景区,为该区下一步找矿工作提供了参考。
Abstract:MPT method is an alteration information extraction method based on the data processing process of "mask technology + principal component analysis + threshold classification". It can quantitatively extract the weak alteration information in principal components and classify them based on the effective exclusion of vegetation, ice, snow and water. In this paper, based on Landsat8 OLI data and MPT method, iron staining and hydroxyl alteration information in Dagelegou area were extracted and compared with the known geological background. The results showed that the comprehensive alteration anomaly information of iron staining and hydroxyl in the existing gold polymetallic ore detailed survey area were highly consistent with the distribution of Au, Cu and Mo anomalies in river sediments, copper and gold orebodies and fracture alteration zones, and the remote sensing alteration anomaly information could effectively indicate the mineralization location. Based on the comprehensive alteration anomaly information, anomaly verification analysis results and regional geological background, five metallogenic prospects were delineated, which provided reference for further prospecting work in this area.
-

-
表 1 或然率与误差的关系
Table 1. Relationship between probability and error
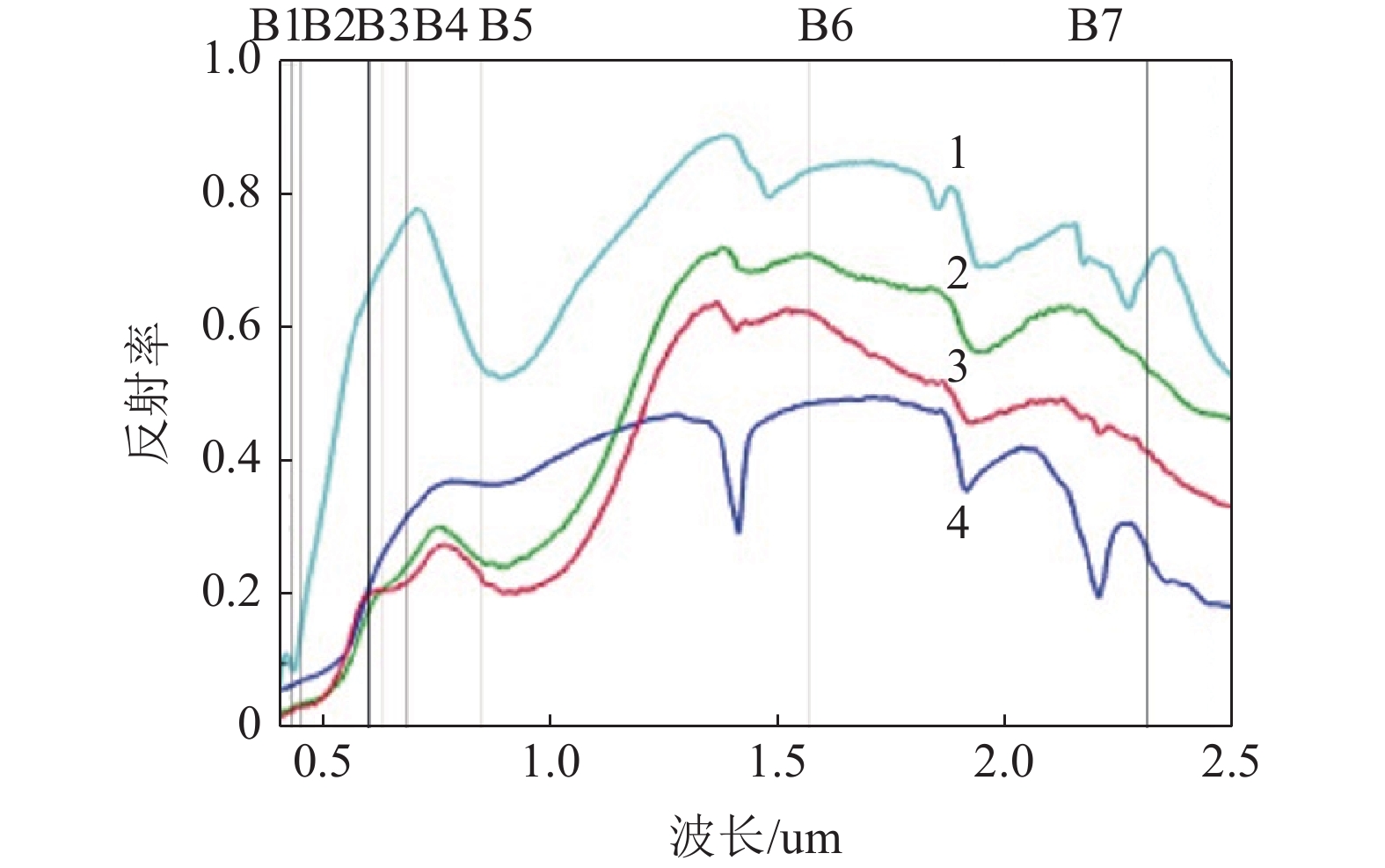
k 0.000 0.320 0.670 1.000 1.150 1.960 2.000 2.580 3.000 p 0.000 0.250 0.500 0.680 0.750 0.950 0.955 0.990 0.997 表 2 OLI数据主成分分析特征向量矩阵
Table 2. Eigenvectors covariance of PCA for OLI data
主成分 OLI2波段 OLI4波段 OLI5波段 OLI6波段 PC1 -0.254805 -0.387241 -0.583034 -0.667226 PC2 -0.572355 -0.624299 0.060279 0.528229 PC3 0.166713 0.210446 -0.809742 0.521764 PC4 0.761374 -0.644986 0.027497 0.059547 表 3 铁染蚀变异常分级
Table 3. Thresholds of the iron stain alteration anomaly
序号 蚀变异常
级别异常值
范围具体
参数值异常
颜色1 铁染一级 >2.5 
>0.0111725 红 2 铁染二级 2  ~2.5
~2.5
0.0089380~0.0111725 绿 3 铁染三级 1.5 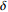 ~2
~2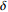
0.0067035~0.008938 蓝 4 铁染四级 1 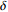 ~1.5
~1.5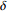
0.004469~0.0067035 黄 表 4 OLI数据主成分分析特征向量矩阵
Table 4. Eigenvectors covariance of PCA for OLI data
主成分 OLI2波段 OLI5波段 OLI6波段 OLI7波段 PC1 0.230627 0.53156 0.612224 0.537994 PC2 -0.403923 -0.653003 0.178428 0.615301 PC3 0.783076 -0.238183 -0.426465 0.384953 PC4 -0.412855 0.484045 -0.641462 0.428694 表 5 羟基蚀变异常分级
Table 5. Thresholds of the hydroxyl alteration anomaly
序号 蚀变异常
级别异常值
范围具体
参数值异常
颜色1 羟基一级 >3 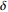
>0.023481 红 2 羟基二级 2.5 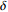 ~3
~3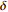
0.0195675~0.023481 绿 3 羟基三级 2 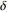 ~2.5
~2.5
0.015654~0.0195675 蓝 4 羟基四级 1  ~2
~2
0.007827~0.015654 黄 -
[1] 赵泽霖, 李俊建, 张鹏鹏. 蒙古东部道尔脑德矿集区成矿作用及找矿标志[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2021, 36(3):355-365. ZHAO Z L, LI J J, ZHANG P P. Metallogenesis and ore prospecting marks in the Dornod ore deposit-cluster area, the east Mongolia[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2021, 36(3):355-365. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2021.03.012
[2] 付淳. 滇西北香格里拉春都斑岩铜矿成矿模式及找矿标志[J]. 现代矿业, 2021, 37(4):20-24. FU C. Metallogenic model and prospecting criteria of Chundu porphyry copper deposit in Shangri-La, Northwest Yunnan[J]. Modern Mining, 2021, 37(4):20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2021.04.005
[3] 陈华慧. 遥感地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1984, 18-19.
CHEN H H. Remote sensing geology [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1984, 18-19.
[4] Crosta A P, Mc M Moore J. Enhancement of landsat thematic mapper imagery for residual soil mapping in S W Minais Gerrain[A]. In: Proceedings of the7th (ERIM) thematic conference: remote sensing for exploration geology[C]. Calgary, 1989, 1173 -1187.
[5] Di Tommaso, N. Rubinstein. Hydrothermal alteration mapping using ASTER Data in the infernillo porphyry deposit, Argentina[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 32(1-2):275-290. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2006.05.004
[6] Pour AB, Hashim M, Makoundi C, et al. Structural mapping of the Bentong-Raub Suture Zone using PALSAR remote sensing data, Peninsular Malaysia: implications for sediment-hosted/orogenic gold mineral systems exploration[J]. Resource Geology, 2016, 66(4):368-385. doi: 10.1111/rge.12105
[7] 吴志春, 郭福生, 李华亮, 等. 主成分分析法在相山火山盆地蚀变分带解译中的应用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(3):385-403. WU Z C, GUO F S, LI H L, et al. Application of principal component analysis in interpretation of alteration zone in the Xiangshan Volcanic Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2020, 44(3):385-403. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2020.03.005
[8] 马建文. 利用TM数据快速提取含矿蚀变带方法研究[J]. 遥感学报, 1997, 1(3):208-213. MA J W. Methodology study of quickly identifying mineral bearing alterations from TM Data[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 1997, 1(3):208-213. doi: 10.11834/jrs.19970308
[9] 塔娜, 鲍甜甜, 冯一鸣等. 湖南长城岭-凤凰山地区遥感蚀变信息提取与成矿预测[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2021, 36(3):328-341. TA N, BAO T T, FENG Y M, et al. Remote sensing alteration information extraction from Changchengling-Fenghuangshan area, Hunan province and the metallogenic prediction[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2021, 36(3):328-341. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2021.03.010
[10] 赵忠海, 陈俊, 乔锴等. 基于分形理论的遥感蚀变信息和构造分析研究: 以黑龙江多宝山地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(3):1-16. ZHAO Z H, CHEN J, QIAO K, et al. Remote sensing alteration information and structure analysis based on fractal theory: a Case Study of Duobaoshan Area of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(3):1-16.
[11] 吴志春, 叶发旺, 郭福生等. 主成分分析技术在遥感蚀变信息提取中的应用研究综述[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2018, 20(11):1644-1656. WU Z C, YE F W, GUO F S, et al. A review on application of techniques of principle component analysis on extracting alteration information of remote sensing[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2018, 20(11):1644-1656. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2018.180195
[12] 郭学飞. 基于分形理论的遥感蚀变异常提取方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016, 28-35.
GUO X F. Research on alteration anomaly extraction from remote sensing imagery based on fractal theory[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) , 2016, 28-35.
[13] 张晓东, 张永庭, 艾宁, 等. 北山地区遥感找矿地质异常信息提取及分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2012, 26(4):344-349. ZHANG X D, ZHANG Y T, AI N, et al. The extraction and analysis of remote sensing geological anomaly informations in Weining north mountain[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2012, 26(4):344-349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2012.04.014
[14] 张海霞, 卞正富. 遥感影像植被信息提取方法研究及思考[J]. 地理空间信息, 2007, 5(6):65-67. ZHANG H X, BIAN Z F. Method for vegetation information extraction from remote sensing images[J]. Geospatial Information, 2007, 5(6):65-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4623.2007.06.022
[15] 陈三明, 赵袁磊, 涂媛, 等. 桂北平乐地区锰矿的遥感胁迫植被指示指数异常的提取[J]. 矿产与地质, 2019, 33(5): 885-890.
CHEN S M, ZHAO Y L, TU Y, et al. Vegetation indicator index anomaly extraction of manganese mineralization under remote sensing stress in Pingle Area of North Guangxi[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 33(5): 885-890.
[16] 徐涵秋. 利用改进的归一化差异水体指数(MNDWI)提取水体信息的研究[J]. 遥感学报, 2005, 9(5):589-595. XU H Q. A study on information extraction of water body with the modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI)[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2005, 9(5):589-595. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20050586
[17] 李丹, 吴保生, 陈博伟, 等. 基于卫星遥感的水体信息提取研究进展与展望[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 60(2): 147-161.
LI D, WU B S, CHEN B W, et al. Review of water body information extraction based on satellite remote sensing[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology) , 60(2): 147-161.
[18] 任小玉. 基于遥感数据的地表地球化学成分反演模型研究[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学, 2021, 20-25.
REN X Y. Study on inversion model of surface geochemical composition based on remote sensing data [D]. Jilin: Jilin University, 2021, 20-25.
[19] 张玉君, 曾朝铭, 陈薇. ETM+(TM)蚀变遥感异常提取方法研究与应用-方法选择与技术流程[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2003, 56(2): 44-49.
ZHANG Y J, ZENG C M, CHEN W. A study of the method for extraction of alteration anomalies from the ETM+(TM) date and its application: on the basis of geologic evidence and spectral [J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, (4): 30-36.
[20] 王大钊, 田宁, 魏俊浩, 等. 人工重砂在蚀变岩金矿勘查中的应用——以宁夏树龙沟金矿为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(3):491-501. WANG D Z, TIAN N, WEI J H, et al. Application of placer in exploration of altered rock type ore deposit-A case study of the Shulonggou gold deposit[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2017, 41(3):491-501. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2017.03.006
-



 下载:
下载: