Basic Characteristics of Concrete Prepared with Activated Coal Powder instead of Cement
-
摘要:
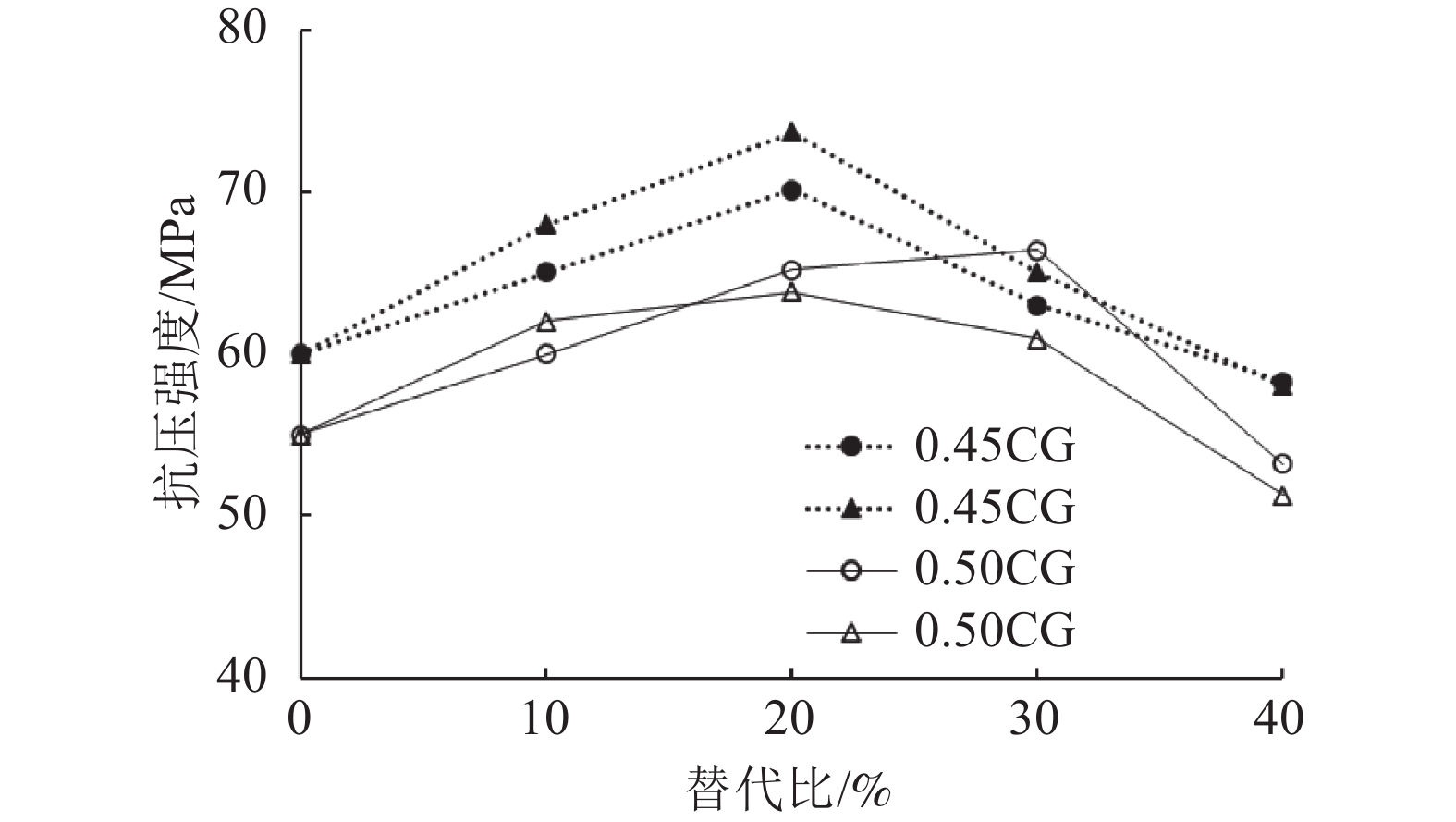
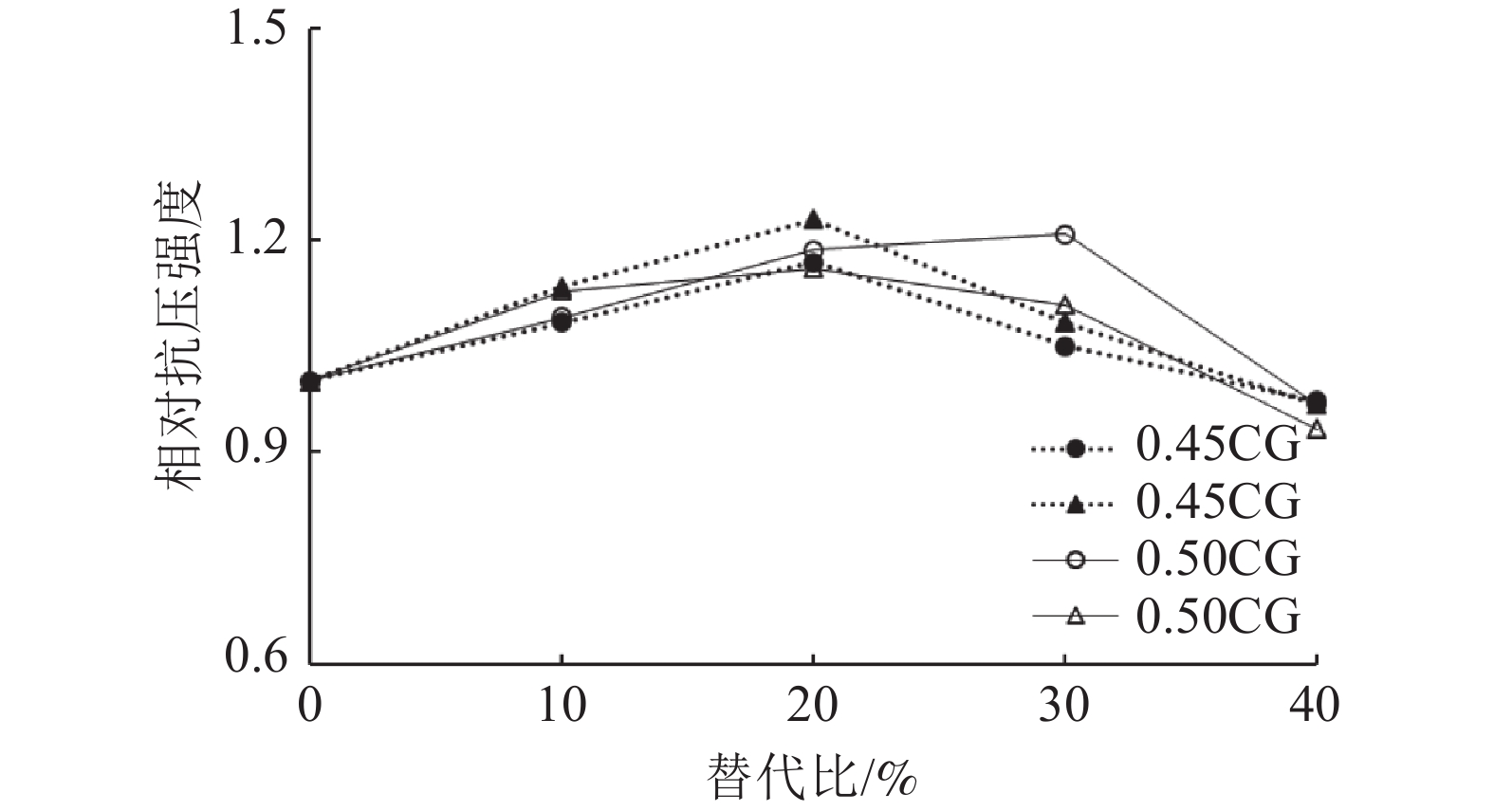
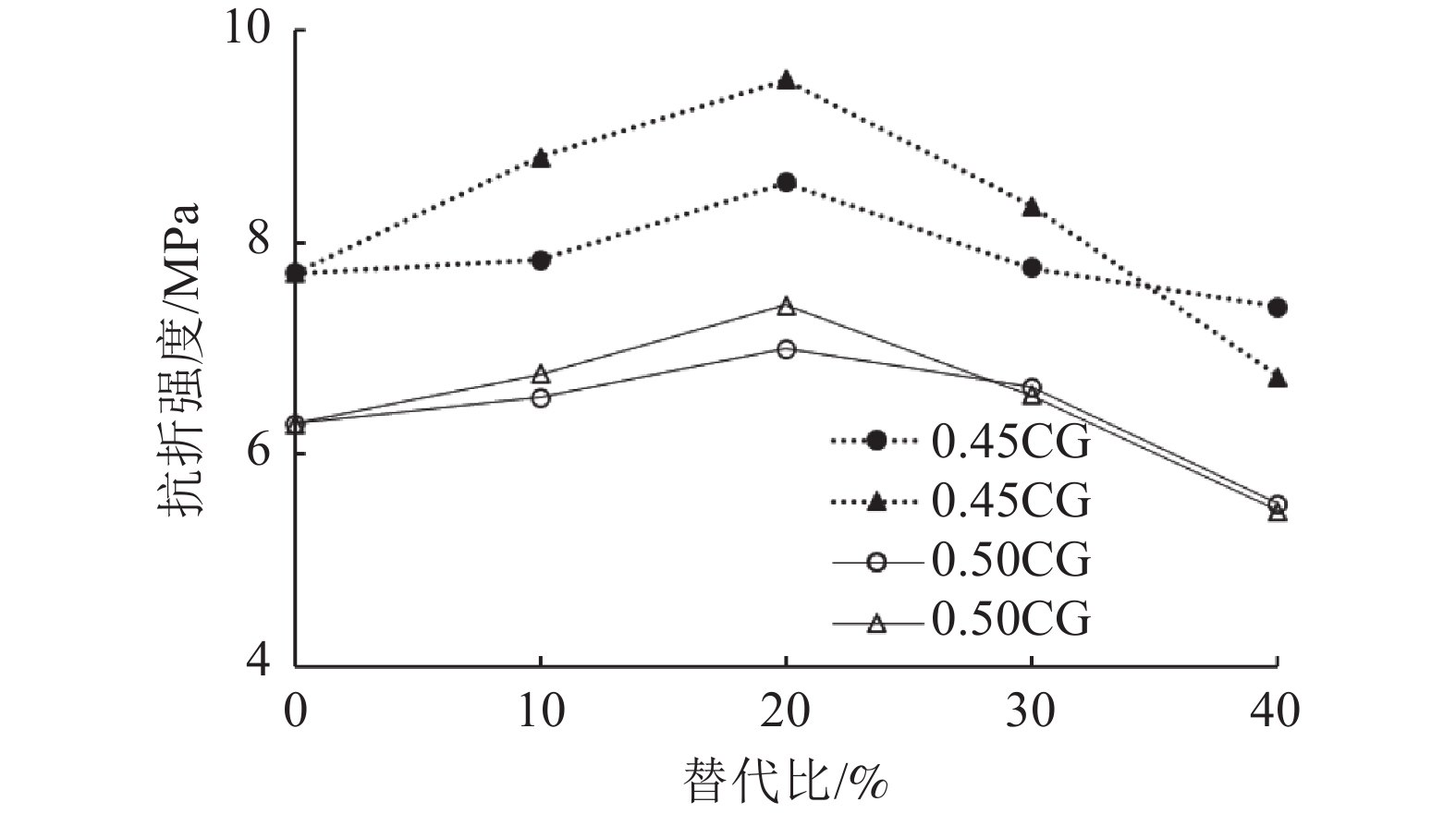
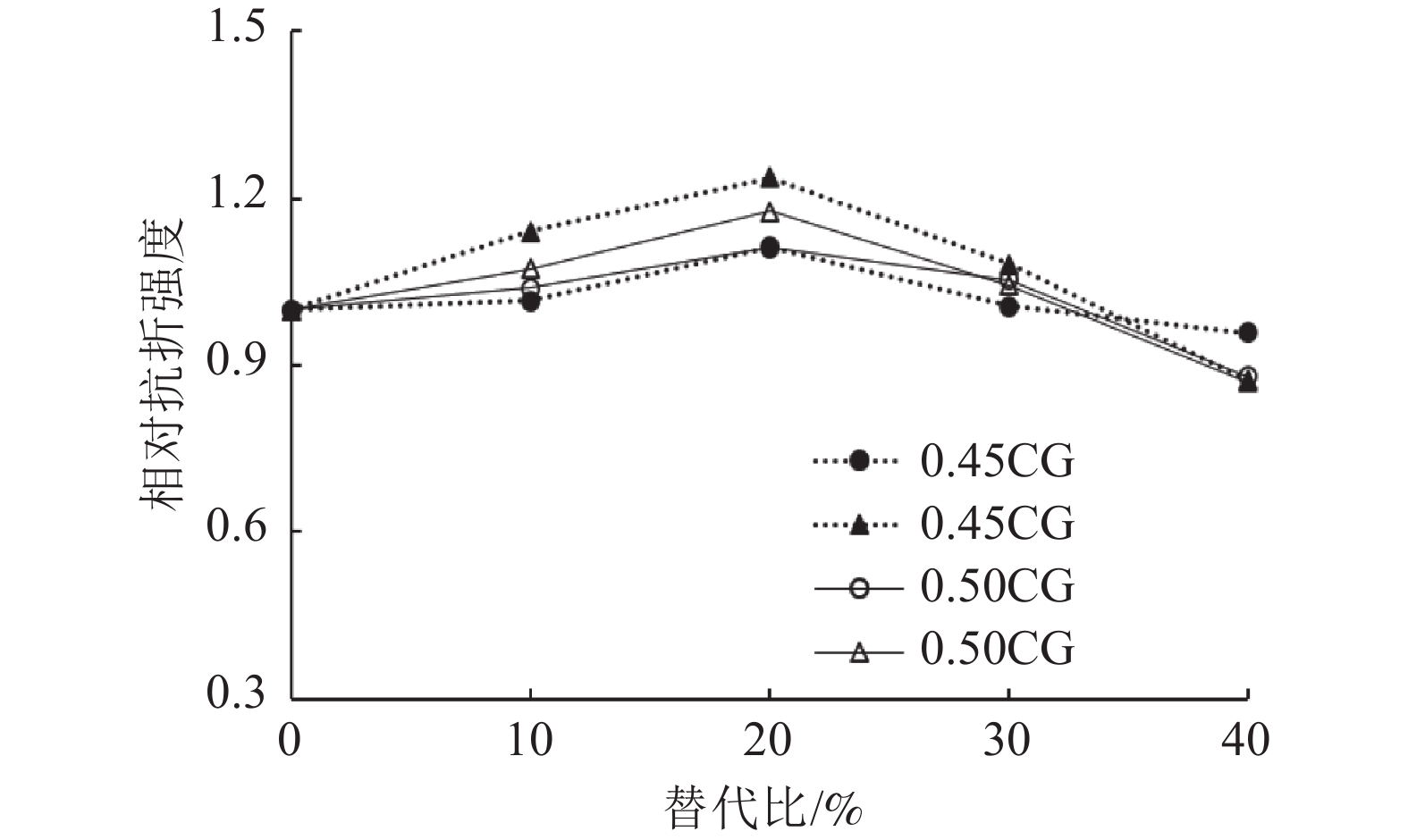
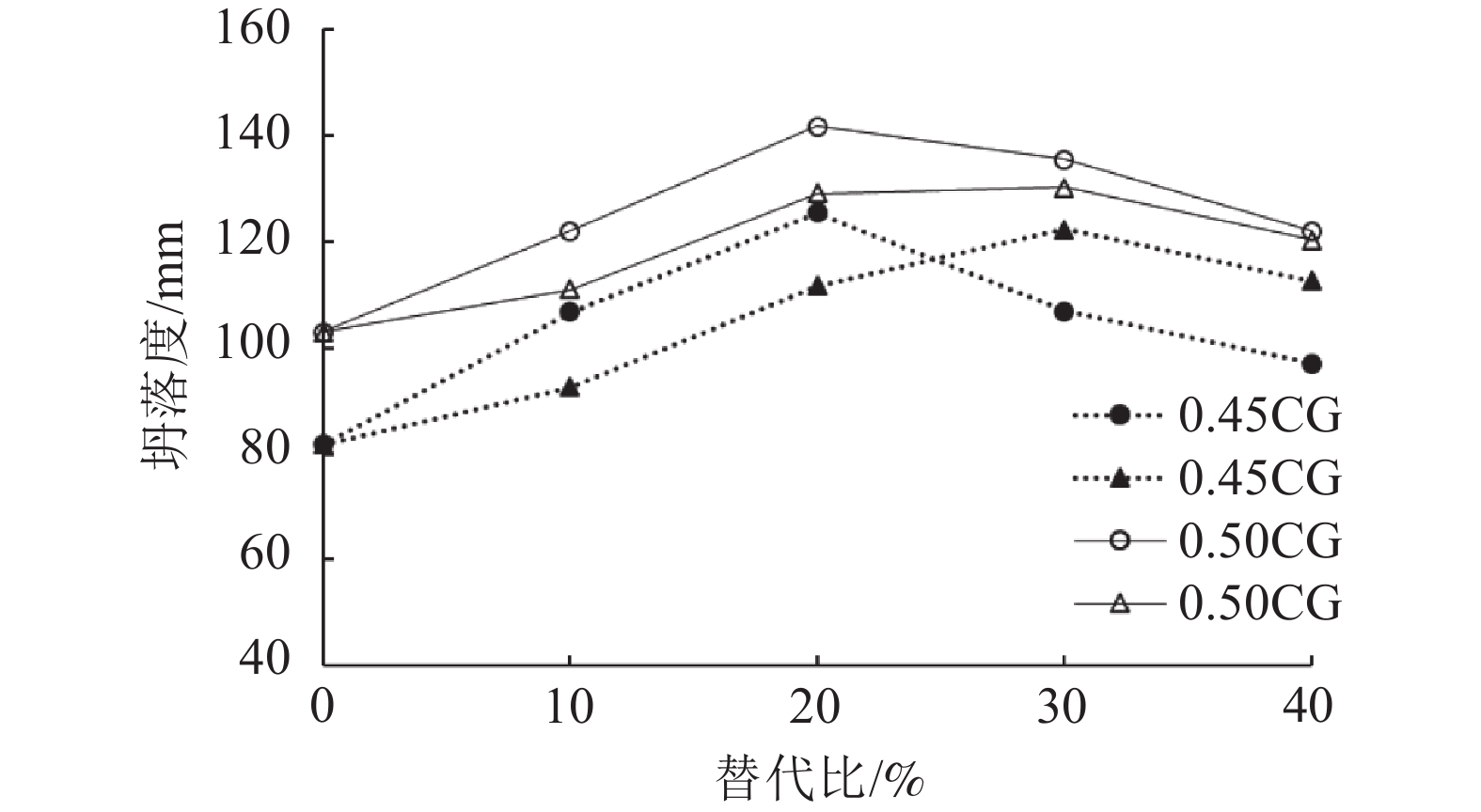
这是一篇陶瓷及复合材料领域的论文。为探索煤废料替代水泥进行混凝土制备的可行性,利用活性化处理的煤渣粉和煤矸石粉按照0、10%、20%、30%和40%的比例替代水泥进行混凝土试样的制备并对混凝土试样的坍落度、抗压和抗折强度进行测试,同时耐高温性能实验,结果证明:随着替代比的增加,坍落度、抗压强度和抗折强度均先增后减;煤废料的较优替代比为20%~30%。活化煤渣粉试样的早期强度增长率大;而活化煤矸石粉试样的长期强度增长率较大。当水灰比=0.45时,试样的抗压强度随着温度的升高先增后减,在100 ℃时达到极大值;当水灰比=0.5时,混凝土试样的抗压强度均随着温度的升高逐渐降低;活性煤渣粉试样界面区域的水合胶结构较最多,对照组次之,活化煤矸石粉试样较少。随着温度升高,试样表面的孔隙和裂缝明显增多且破坏面的破碎程度逐渐加剧。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of ceramics and composites.To explore the feasibility of using coal waste to replace cement for concrete preparation, the activated coal slag powder and coal gangue powder were used to replace cement at a ratio of 0%, 10%, 20%, 30%, and 40% to prepare concrete samples and prepare concrete samples. The slump, compressive strength, flexural strength and high-temperature performance were tested, and the results show that: as the substitution ratio increases, the slump, compressive strength and flexural strength all increase first and then decrease; The optimal substitution ratio is 20%~30%. The early strength growth rate of the activated coal slag powder sample is large; while the long-term strength growth rate of the activated coal gangue powder sample is large. When the water-cement ratio=0.45, the compressive strength of the sample increases first and then decreases with the increase of temperature, and reaches the maximum at 100 ℃; when the water-cement ratio=0.5, the compressive strength of the concrete sample increases with the temperature; the hydration cement structure in the interface area of the activated coal slag powder sample is the most, followed by the control group, and the activated coal gangue powder sample is the least. With the increase in temperature, the pores and cracks on the surface of the sample increased significantly and the degree of fracture of the damaged surface gradually increased.
-
Key words:
- Ceramics and composites /
- Concrete /
- Coal waste /
- Slump /
- Strength /
- High temperature resistance
-

-
表 1 混凝土和煤废料的化学成分/%
Table 1. Chemical composition of concrete and coal waste
名称 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O SO3 TiO2 烧失量 水泥 22.13 7.7 3.2 57.9 1.7 1.6 4.3 0.15 1.32 活化煤矸石粉 49.79 22.77 4.07 14.84 0.64 2.74 0.27 1.07 3.81 活化煤渣粉 52.63 25.29 4.64 10.2 0.77 3.09 0.27 1.17 1.94 表 2 试样分组及材料含量/(kg/m3)
Table 2. Sample grouping and material content
编号 混凝土 水灰比(W/C) 砂 碎石 活化煤矸石粉 活化煤渣粉 高效减水剂 0.4C 515 0.45 1275 720 0 0 9 0.45CG10 463.5 0.45 1275 720 51.5 0 9 0.45CG20 412 0.45 1275 720 103 0 9 0.45CG30 360.5 0.45 1275 720 154.5 0 9 0.45CG40 309 0.45 1275 720 206 0 9 0.45CC10 463.5 0.45 1275 720 0 51.5 9 0.45CC20 412 0.45 1275 720 0 103 9 0.45CC30 360.5 0.45 1275 720 0 154.5 9 0.45CC40 309 0.45 1275 720 0 206 9 0.5C 515 0.45 1275 720 0 0 9 0.5CG10 463.5 0.50 1275 720 51.5 0 9 0.5CG20 412 0.50 1275 720 103 0 9 0.5CG30 360.5 0.50 1275 720 154.5 0 9 0.5CG40 309 0.50 1275 720 206 0 9 0.5CC10 463.5 0.50 1275 720 0 51.5 9 0.5CC20 412 0.50 1275 720 0 103 9 0.5CC30 360.5 0.50 1275 720 0 154.5 9 0.5CC40 309 0.50 1275 720 0 206 9 -
[1] 施惠生, 娄邦. 利用煤渣替代砂研制混凝土小型空心砌块[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2005(1):9-11.SHI H S, LOU B. Development of concrete small hollow blocks using cinder as a substitute for sand[J]. New Building Materials, 2005(1):9-11.
SHI H S, LOU B. Development of concrete small hollow blocks using cinder as a substitute for sand[J]. New Building Materials, 2005(1):9-11.
[2] 赵世冉, 张凯峰, 米钰, 等. 煤渣-陶粒混凝土挤压内墙板的实验研究[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2014, 41(12):20-22.ZHAO S R, ZHANG K F, MI Y, et al. Experimental study of cinder-ceramic concrete extruded interior wall panels[J]. New Building Materials, 2014, 41(12):20-22.
ZHAO S R, ZHANG K F, MI Y, et al. Experimental study of cinder-ceramic concrete extruded interior wall panels[J]. New Building Materials, 2014, 41(12):20-22.
[3] 夏群, 易磊, 朱平华, 等. 掺煤渣的再生混凝土保温空心砌块力学行为与热工性能研究[J]. 混凝土, 2016(9):106-110.XIA Q, YI L, ZHU P H, et al. Research on mechanical behavior and thermal properties of recycled concrete insulated hollow core blocks with cinder doping[J]. Concrete, 2016(9):106-110.
XIA Q, YI L, ZHU P H, et al. Research on mechanical behavior and thermal properties of recycled concrete insulated hollow core blocks with cinder doping[J]. Concrete, 2016(9):106-110.
[4] 张立明, 李佳, 刘福明. 掺活化煤渣粉混凝土表面氯离子浓度的时变规律[J]. 混凝土, 2017(8):96-98+110.ZHANG L M, LI J, LIU F M. Time-varying pattern of chloride ion concentration on the surface of concrete with activated cinder powder[J]. Concrete, 2017(8):96-98+110.
ZHANG L M, LI J, LIU F M. Time-varying pattern of chloride ion concentration on the surface of concrete with activated cinder powder[J]. Concrete, 2017(8):96-98+110.
[5] 张立明, 余红发. 煤渣粉掺量对再生混凝土氯离子扩散系数的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2017, 36(7):2332-2336+2342.ZHANG L M, YU H F. Effect of cinder powder admixture on chloride ion diffusion coefficient of recycled concrete[J]. Silicate Bulletin, 2017, 36(7):2332-2336+2342.
ZHANG L M, YU H F. Effect of cinder powder admixture on chloride ion diffusion coefficient of recycled concrete[J]. Silicate Bulletin, 2017, 36(7):2332-2336+2342.
[6] 王庆贺, 李喆, 周梅, 等. 自燃煤矸石骨料取代率对煤矸石混凝土梁受弯性能的影响[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2020, 41(12):64-74.WANG Q H, LI Z, ZHOU M, et al. Effect of self-combustion gangue aggregate substitution rate on the bending performance of gangue concrete beams[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2020, 41(12):64-74.
WANG Q H, LI Z, ZHOU M, et al. Effect of self-combustion gangue aggregate substitution rate on the bending performance of gangue concrete beams[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2020, 41(12):64-74.
[7] 白国良, 朱超, 王建文, 等. 煤矸石混凝土梁受剪性能实验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2020, 41(12):49-55.BAI G L, ZHU C, WANG J W, et al. Experimental study on shear performance of gangue concrete beams[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2020, 41(12):49-55.
BAI G L, ZHU C, WANG J W, et al. Experimental study on shear performance of gangue concrete beams[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2020, 41(12):49-55.
[8] Yao Z, Fang Y, Kong W, et al. Experimental study on dynamic mechanical properties of coal gangue concrete[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 2020(13):1-16.
[9] Ma H, Zhu H, Wu C, et al. Effect of shrinkage reducing admixture on drying shrinkage and durability of alkali-activated coal gangue-slag material[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 270(3):121372.
[10] Ni K, Shi Y, Hu Z, et al. Effect of coal gangue grain size on strength of foam concrete[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1635(1): 012080 (8pp).
-



 下载:
下载: