Research on Geological and Environmental Factors Related to the Sunk Ship Incident in the Laoyemiao Water Area, Poyang Lake-Yangtze River Channel
-
摘要:
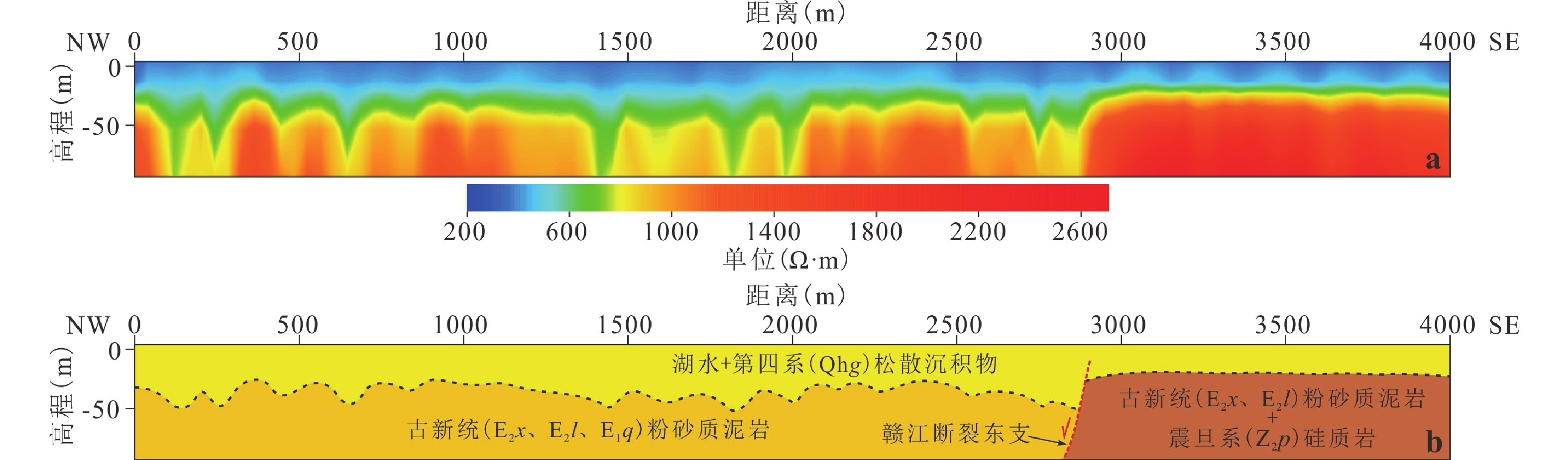
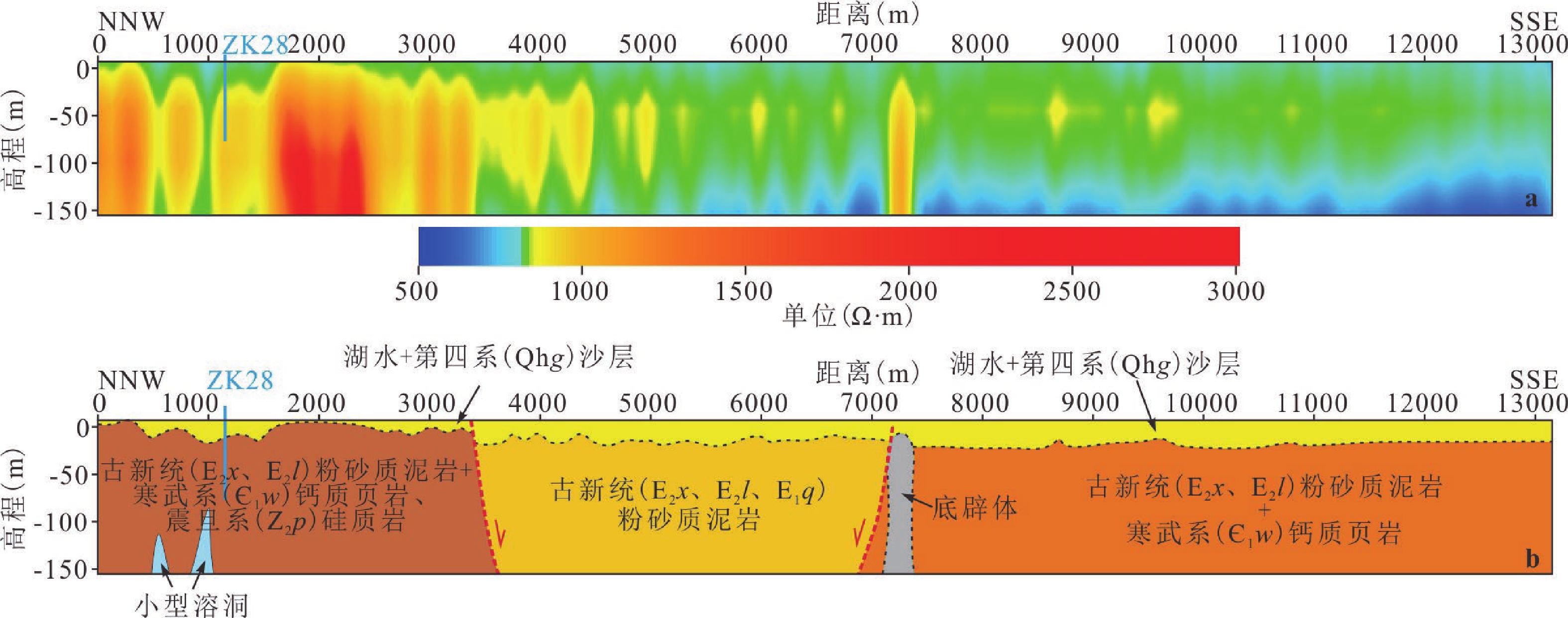
鄱阳湖是我国最大的淡水湖泊,其与长江连通的航道老爷庙水域常年可通航千吨级船舶,该水域历史上沉船事件多发,造成了巨大的生命财产损失,被称为“东方百慕大”。目前对该地区沉船原因的相关研究极少,本研究通过水下地层结构探测、湖底地形探测、水动力数值模拟等多方法手段,探索了导致沉船的相关地质环境因素。在老爷庙水域之下的碳酸盐岩中发现了很多不同尺度的溶洞。此外,发现老爷庙除航道位置外,水深很浅,每年3、4月份水流在水域不同部位出现急流和旋涡。结合探测和模拟结果,本研究认为导致老爷庙水域沉船的因素除大风外,还有以下几种:水下溶蚀洞穴、急流和旋涡。此外,“五河”来水携泥沙可能使老爷庙区域水体浑浊及老爷庙水域湖底地形复杂、水流紊乱,也可能是沉船原因。其中,溶蚀洞穴导致沉船概率相对较小,大风及水流湍急、紊乱是导致沉船的主要原因。
Abstract:Poyang Lake is the largest freshwater lake in China. Laoyemiao waters, the only waterway of Poyang Lake connected to the Yangtze River, are navigable for ships of thousand-ton level. The Laoyemiao waters are known as the "Eastern Bermuda" as shipwrecks occur frequently in this area that results in life and property lost. Rare researches are applied in exploring the reasons, so multi-methods including geophysical prospecting, topography detection and hydrodynamic numerical simulation fill the void of evidence on study of shipwreck. Many karst caves in different scale are revealed. It is shallow except the channel in Laoyemiao waters. Torrents and vortexs are easy to show up in March and April. The result of geophysical prospecting and hydrodynamic numerical suggest that shipwreck in the Laoyemiao waters was mainly caused by the followings in addition to strong wind: underwater karst caves, torrents and vortexs. Besides, muddy water from five rivers makes the waters turbid as well as the underwater terrain and flow intricate. Among these causes, strong wind, torrents and vortexs dominate the shipwrecks and karst caves rarely result in shipwrecking.
-

-
表 1 鄱阳湖老爷庙段历史沉船事件统计
Table 1. Statistics of shipwrecks in the Laoyemiao waters of the the Poyang Lake in history
时间 事故及损失概况 信息来源 明清时期 运送瓷器船只沉没 江西日报(2011年8月4日),鄱阳湖岸考古发现
大量明代中晚期瓷器碎片1985年8月3日 13条船只沉没 九江海事局档案资料,CCTV-10节目采访 1990年7月4日 船只沉没 九江海事局档案资料,CCTV-10节目采访 2009年 湖南船只沉没 九江海事局,CCTV-10节目采访 2011年 安徽省怀远县01571号运沙船沉没 九江日报,2011年12月22日 2013年3月18日 老爷庙水域发现首艘长28米、宽7米的铁沉船 新华网,2013年3月18日 2021年8月 沉没民船1艘 表 2 老爷庙水域水动力数值模拟主要参数
Table 2. Main parameters in hydrodynamic model of the Laoyemiao waters
参数名称 参数值 参数名称 参数值 时间步数 17280 时间步长 100 s 模拟时段 2010/3/5-3/25 最小时间步长 0.01 s 最大时间步长 5 s CFL数 0.8 曼宁数 32 m1/3/s 干水深 0.005 m 淹没水深 0.05 m 湿水深 0.1 m 涡流模型 Smagorinsky 涡粘系数 0.28 科氏力 参照29°N 风速 定常风15 m/s 风向 315° 风力软启动 1200 s“源”的个数 3 “堰”的个数 1 桥墩的个数 33 初始水位 9.25 m 初始“u”、“v” 均为0 开边界数 3 -
[1] 曹渐华,刘熙明,李国平,邹海波.2015.鄱阳湖地区湖陆风特征及成因分析[J]. 高原气象,34(2):426-435.
[2] 崔焕玉,沈金松,冉 尚,周杰民.2022.基于有限体积法的煤矿巷道瞬变电磁响应二维反演与富水区探测应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),52(4):1314-1327.
[3] 付 超,于兴河,李胜利,李顺利,高明轩,彭子霄,赵海权.2022.差异可容纳空间背景下湖相层序样式与三角洲形态响应:鄱阳湖与岱海湖对比研究[J]. 古地理学报,24(6):1084-1098.
[4] 郝林南,杨小宸.2016.辽河口三维水动力数值模拟[J]. 东北水利水电,(12):44-45+53.
[5] 黄波林,王世昌,殷跃平,刘广宁,陈小婷.2013.崩塌落石产生涌浪的流固耦合运动分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),43(6):1936-1942.
[6] 黄 秀,刘可禹,邹才能,桂丽黎,袁选俊,秦雁群.2013.鄱阳湖浅水三角洲沉积体系三维定量正演模拟[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报,38(5):1005-1013.
[7] 李晨阳,王新春,何春珍,吴 轩,孔昭煜,李晓蕾.2019.全国1∶200 000数字地质图(公开版)空间数据库[J]. 中国地质,46(S1):1-10.
[8] 李琦炜,龚志军,罗 明,彭花明,王 瀚,王 威.2023.鄱阳湖沙山两处具有平行层理砂层的粒度分析及其对沉积环境的指示意义[J]. 中国沙漠,(3):1-8.
[9] 李 燕,金振奎,高白水,石 良,李桂仔.2021.汊口滩沉积特征及沉积模式——以鄱阳湖赣江三角洲汊口滩为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),51(6):1678-1688.
[10] 李云良,姚 静,张 奇.2017.长江倒灌对鄱阳湖水文水动力影响的数值模拟[J]. 湖泊科学,29(5):11.
[11] 李云良,张 奇,姚 静,李梦凡.2015.湖泊流域系统水文水动力联合模拟研究进展综述[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,24(2):263-270.
[12] 李云良,张 奇,姚 静,李相虎.2013.鄱阳湖湖泊流域系统水文水动力联合模拟[J]. 湖泊科学,25(2):227-235.
[13] 刘怀山. 2005. 百慕大三角之谜新解[A]. //刘代志. 陕西地球物理文集(五)国家安全与军事地球物理研究. 西安:西安地图出版社.
[14] 刘江波.2023.内河船舶事故次生污染风险防控对策研究[J]. 管理研讨,6:30-32.
[15] 刘 宇,徐凤雷,朱峻言.2022.物探法在大连湾海底隧道地质勘察中的应用研究[J]. 中国港湾建设,42(12):7-12.
[16] 赖格英,潘瑞鑫,黄小红.2011.鄱阳湖水动力形态结构模式的模拟系统设计与应用[J]. 地球信息科学学报,13(4):447-454.
[17] 赖格英,王 鹏,黄小兰,熊家庆,刘 影,曾峰海.2015.鄱阳湖水利枢纽工程对鄱阳湖水文水动力影响的模拟[J]. 湖泊科学,27(1):13.
[18] 赖锡军,黄 群,张英豪,万荣荣,姜加虎.2014.鄱阳湖泄流能力分析[J]. 湖泊科学,26(4):529-534.
[19] 裴肖明,冯国瑞,戚庭野.2021.瞬变电磁法探测复杂状态下煤矿充水采空区物理模拟实验[J]. 物探与化探,45(4):1055-1063.
[20] 齐述华,熊梦雅,廖富强,刘贵花,郑海金.2016.人类活动对鄱阳湖泥沙收支平衡的影响[J]. 地理科学,36(6):888-894.
[21] 宋 伟,邓刘洋.2020.复杂地形条件下瞬变电磁法中心回线装置发射线框大小选取研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报,17(6):768-774.
[22] 苏彦龙.2021.矿井瞬变电磁法在超前探测采空积水区中的应用研究[J]. 世界有色金属,(16):119-120.
[23] 唐昌新,熊 雄,邬年华,张晓航,邹文楠.2015.长江倒灌对鄱阳湖水动力特征影响的数值模拟[J]. 湖泊科学,27(4):700-711.
[24] 王 敬,齐向生,刘慧卿,杨 敏,李小波,刘洪光,张拓峥.2022.缝洞型油藏水驱剩余油形成机制及换向注水增油机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发,49(5):1-12.
[25] 王旻昊,王启福,庄延峰.2023.船舶污染事故中的应急傍靠/傍离( STS) 引航操纵[J]. 航海技术,2:8-12.
[26] 魏 伟,骆蓓菁,丁 玲.2021.近三十年长江口横沙岛潮滩湿地地貌演变对河口工程的响应[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),51(4):1193-1203.
[27] 吴桂平,刘元波,范兴旺.2015.近30年来鄱阳湖湖盆地形演变特征与原因探析[J]. 湖泊科学,27(6):1168-1176.
[28] 吴景勤.1998.鄱阳湖上令人惊叹的三角[J]. 中国物资再生,2:38-40.
[29] 吴 琼,张超美,许 彬,谢佳杏.2020.鄱阳湖区域关键气候要素变化特征[J]. 干旱气象,38(3):371-379.
[30] 席海燕,王圣瑞,郑丙辉,刘志刚,杨常青,冯明雷,张 莉.2014.流域人类活动对鄱阳湖生态安全演变的驱动[J]. 环境科学研究,27(4):398-405.
[31] 谢小国,魏良帅,王绪本,陶俊利,张赛民,张振雄,田银川,李 维,罗 兵,陈彩玲.2021.半航空瞬变电磁法在古河道结构探测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展,36(4):1734-1742.
[32] 谢昭晖,陈 清,吴牧阳,徐正玉.2021.FCTEM小回线瞬变电磁法在铁路桥梁基础勘查中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报,18(5):568-572.
[33] 徐正玉,付能翼,周 洁,付志红.2022.瞬变电磁法非线性优化反演算法对比[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),52(3):744-753.
[34] 薛国强,潘冬明,于景邨.2018.煤矿采空区地球物理探测应用综述[J]. 地球物理学进展,2018,33(5):2187-2192.
[35] 杨 罡,刘树华,朱 蓉,周荣卫.2011.鄱阳湖地区大气边界层特征的数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报,54(4):896-908.
[36] 杨中华,朱政涛,槐文信,白凤朋.2018.鄱阳湖水利调控对湖区典型丰枯水年水动力水质影响研究[J]. 水利学报,49(2):156-167.
[37] 闫海军,何东博,贾爱林,李治平,郭建林,彭 先,孟凡坤,李新豫,朱占美,邓 惠,夏钦禹,郑国强,杨 山,石晓敏.2022.川中震旦系灯四段岩溶储集层特征与发育模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发,49(4):704-715.
[38] 姚 静,张 奇,李云良,李梦凡.2016.定常风对鄱阳湖水动力的影响[J]. 湖泊科学,28(1):225-236.
[39] 杨晓东,吴中海,张海军.2016.鄱阳湖盆地的地质演化、新构造运动及其成因机制探讨[J]. 地质力学学报,22(3):667-684.
[40] 尹宗贤,张俊才.1987.鄱阳湖水文特征(Ⅱ)[J]. 海洋与湖沼,18(2):208-214.
[41] 张保祥,刘春华.2004.瞬变电磁法在地下水勘查中的应用综述[J]. 地球物理学进展,(3):537-542.
[42] 章飞亮,田占峰.2021.综合物探技术在空铁岩溶探测中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报,18(5):730-737.
[43] 张银松,李 斌,张家刘.2016.瞬变电磁法在水域地质勘察中的应用[J]. 物探与化探,40(1):160-162.
[44] 张莹莹.2021.多辐射场源半航空瞬变电磁法多分量响应特征分析[J]. 物探与化探,45(1):102-113.
[45] 赵 鲁,刘建国,桂爱刚,王丽华.2007.都昌老爷庙风电场风能资源研究[J]. 能源研究与管理,3:24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7676.2007.01.011
[46] 朱 诚,张 奇,陈 星,徐长青,水 涛,蔡天赦.2021.江西鄱阳湖老爷庙水域环境特征与沉船事件的成因研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,30(6):198-208.
[47] 朱玲玲,陈剑池,袁 晶,董炳江.2014.洞庭湖和鄱阳湖泥沙冲淤特征及三峡水库对其影响[J]. 水科学进展,25(3):348-357.
[48] 褚庆忠,徐阳可.2007.百慕大魔鬼三角区可能蕴含着丰富的天然气水合物[J]. 科学技术与工程,7(6):1157-1160.
[49] 朱秀涛.2009.鄱阳湖特大桥溶洞区钻孔桩施工[J]. 科技风,(8):5-7+14.
[50] Jiang C Y, Constantinescu G, Yuan S Y, Tang H W. 2023. Flow hydrodynamics, density contrast effects and mixing at the confluence between the Yangtze River and the Poyang Lake channel[J]. Environmental fluid mechanics, 23(2): 229-257. doi: 10.1007/s10652-022-09848-3
[51] Gan C S, Wang Y J, Barry T L, Zhang Y Z, Qian X. 2020. Spatial and temporal influence of Pacific subduction on South China: geochemical migration of Cretaceous mafic–intermediate rocks[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 177(5): 1013-1024. doi: 10.1144/jgs2019-208
[52] Guo H, Hu Q, Zhang Q, Feng S. 2012. Effects of the Three Gorges Dam on Yangtze River Flow and River Interaction With Poyang Lake, China: 2003-2008[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 416-417: 19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.11.027
[53] Li J W, Zhou M F, Li X F, Fu Z R, Li Z J. 2001. The Hunan-Jiangxi strike-slip fault system in southern China: southern termination of the Tan-Lu fault[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 32: 333-354. doi: 10.1016/S0264-3707(01)00033-3
[54] Li Y L, Zhang Q, Yao J, Werner A D, Li X H. 2014. Hydrodynamic and Hydrological Modeling of the Poyang Lake Catchment System in China[J]. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 19(3): 607-616. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000835
[55] Mei X F, Dai Z J, Du J Z, Chen J Y. 2015. Linkage between Three Gorges Dam impacts and the dramatic recessions in China’s largest freshwater lake, Poyang Lake[J]. Scientific Reports, 5: 18197. doi: 10.1038/srep18197
[56] Mollidor L, Tezkan B, Bergers R, LὅHken Jὅrn. 2013. Float-transient electromagnetic method: in-loop transient electromagnetic measurements on Lake Holzmaar, Germany[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 61(5): 1056-1064. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12025
[57] Pritam Y, Mira K, Tezkan, B, Volker R. 2020. Innovative Boat-Towed Transient Electromagnetics - Investigation of the Furnas Volcanic Lake Hydrothermal System, Azores[J]. Geophysics, 85(2): 41-56. doi: 10.1190/geo2019-0292.1
[58] Tezkan B, Mollidor L, Bergers R, Löhken J. 2008. Float TEM-Inloop Transient Electromagnetic Measurements on a Lake[J]. Physical Review E Statistical Physics Plasmas Fluids & Related Interdisciplinary Topics, 54(2): 1749-1762.
[59] Thiery W, Edouard L D, Panitz H J, Matthias D, Stef Lhermitte, Nicole van Lipzig. 2015. The impact of the African Great Lakes on the regional climate[J]. Journal of Climate, 28(10): 4061-4085. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00565.1
[60] Song P H, Zhang X M, Liu Y S, Teng J W. 2017. Moho imaging based on receiver function analysis with teleseismic wavefield reconstruction: Application to South China[J]. Tectonophysics, 718: 118-131. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.05.031
[61] Vignoli G, Fiandaca G, Christiansen A V, Kirkegaard C, Auken E. 2015. Sharp spatially constrained inversion with applications to transient electromagnetic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 63(1): 243-255. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12185
[62] Wang Y, Ji Y J, Li S Y, Lin J, Zhou F D, Yang G H. 2013. A wavelet-based baseline drift correction method for grounded electrical source airborne transient electromagnetic signals[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 44(4): 229-237. doi: 10.1071/EG12078
[63] Yuan S Y, Tang H W, Li K, Xu L, Xiao Y, Gualtieri C, Rennie C, Melville B. 2021. Hydrodynamics, Sediment Transport and Morphological Features at the Confluence Between the Yangtze River and the Poyang Lake[J]. Water Resources Research, 57(3): e2020WR028284. doi: 10.1029/2020WR028284
[64] Zhang S J, Chen L S, Li Y. 2012. Statistical analysis and numerical simulation of Poyang Lake’s influence on tropical cyclones[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 18(2): 249-262.
[65] Zhang X L, Zhang Q, Werner A D, Tan Z Q. 2017. Characteristics and causal factors of hysteresis in the hydrodynamics of a large floodplain system: Poyang Lake (China)[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 553: 574-583. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.08.027
-




 下载:
下载: