Spatial Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Rare Earth in a Tin Ore Area of Hunan Province
-
摘要:
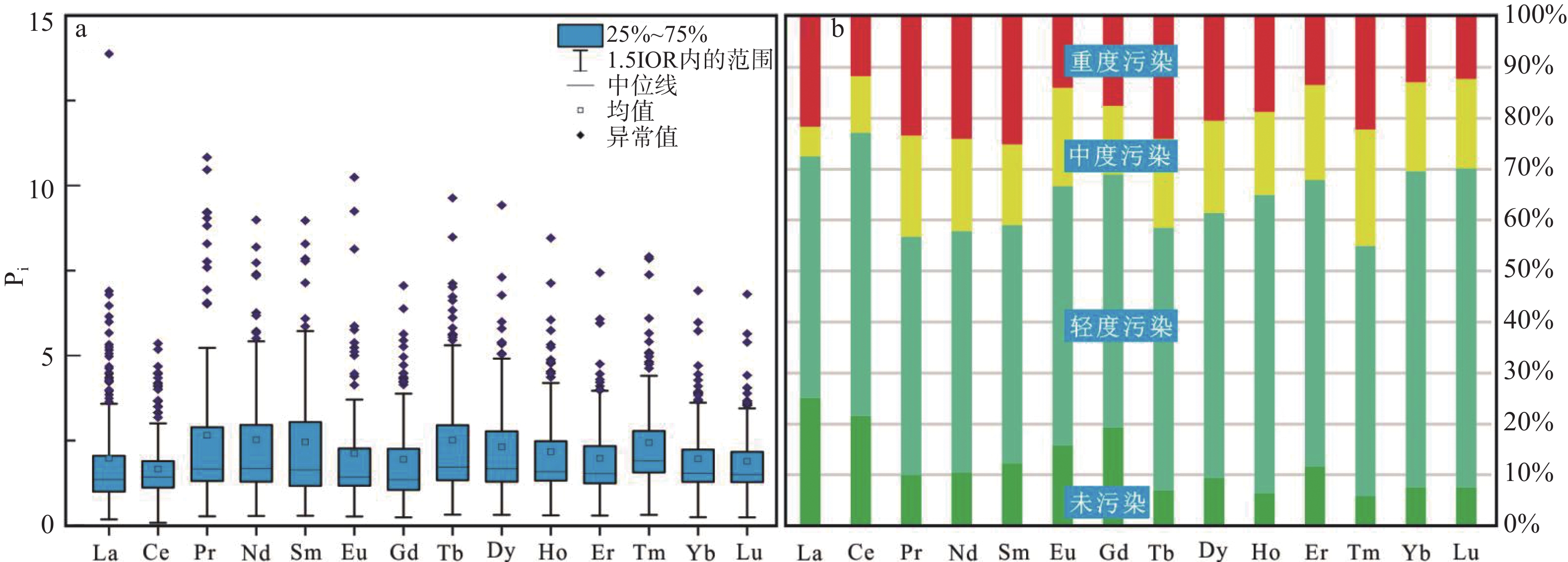
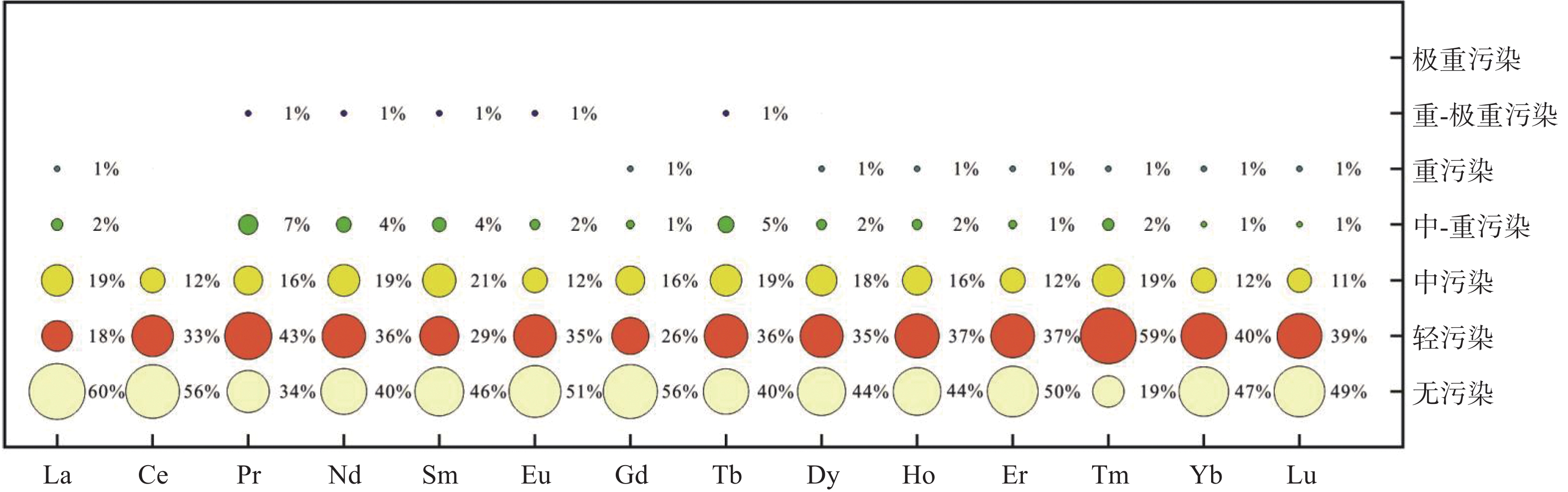
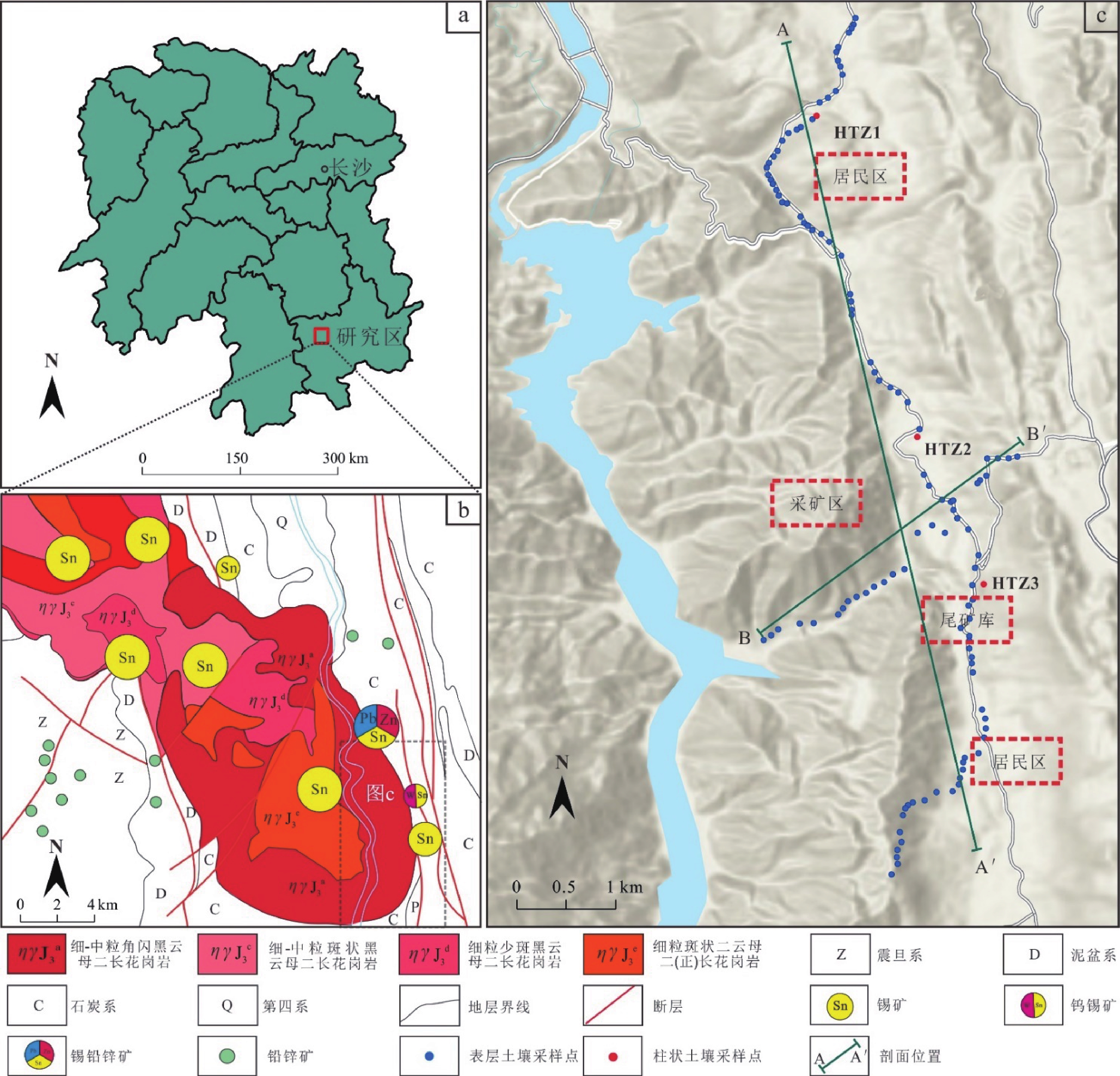
为科学评价矿区土壤稀土空间分布与风险,本文采集某锡矿区表层土壤样品141件、柱状土壤样品3组30件,分析测定14种稀土元素含量;采用单项污染指数、地累积指数、内梅罗综合污染指数、潜在生态风险指数等方法对其进行系统研究。结果表明:(1) 全部样品14种稀土元素均值全部超出湖南省土壤背景值;其地累积指数(Igeo)从大到小依次为:Tm(0.468)>Pr(0.420)>Tb(0.403)>Nd(0.377)>Dy(0.320)>Sm(0.317)>Ho(0.267)>Yb(0.157)>Er(0.150)>Eu(0.117)>Lu(0.112)> Gd(0.051) >La(0.021)>Ce(−0.159),均属无污染范畴;内梅罗综合污染指数(PN)显示全部样品综合污染指数集中于0.29~8.96,平均2.48,以轻度污染为主;(2) 潜在生态风险因子($ {\mathrm{E}}_{\mathrm{r}}^{\mathrm{i}} $)占比表明,La、Ce、Yb,Pr、Nd、Sm、Eu、Gd、Dy、Er,Tb、Ho、Tm样本轻微生态风险占比分别为100%、>90%和>84.8%;潜在生态风险指数(RI)为25.43~1904,平均199.44;处于中度生态风险水平;(3) ΣREE、LREE、PN及RI的空间变化规律一致,证实区内表层土壤稀土富集主要受花岗岩风化作用和水文条件控制,而矿业开发对其影响有限。总之,区内土壤稀土污染和生态风险均很低,处于安全可控状态。
Abstract:To evaluate the spatial distribution and risk of rare earth in mining soil, in this paper, 141 pieces of surface soil and three sets of 30 pieces of columnar soil were collected from a tin mining area, and then 14 kinds of rare earth elements content of these samples were analyzed and determined. It was systematically studied by single pollution index, the geo-accumulation index , Nemerow comprehensive pollution index and potential ecological risk index. The results showed that: (1) the average values of 14 rare earth elements in all the samples exceeded the soil background values in Hunan Province; The geo-accumulation index (Igeo) in descending order is: Tm (0.468)>Pr (0.420)>Tb (0.403)>Nd (0.377)>Dy (0.320)>Sm (0.317)>Ho (0.267)>Yb (0.157)>Er (0.150)>Eu (0.117)>Lu (0.112)>the Gd (0.051)>La (0.02)>Ce (−0.159), indicating they are pollution-free; The Nemerow comprehensive pollution index (PN) showed that the comprehensive pollution index of all samples was concentrated in 0.29~8.96, with an average of 2.48, suggesting they are mainly light polluted; (2) As for the proportion of potential ecological risk factors ($ {\mathrm{E}}_{\mathrm{r}}^{\mathrm{i}} $), the proportion of minor ecological risk of three groups of La-Ce-Yb, Pr-Nd-Sm-Eu-Gd-Dy-Er and Tb-Ho-Tm in samples were 100%, >90% and >84.8%, respectively. Potential ecological risk index (RI) ranges from 25.43 to 1904, with an average of 199.44, which means the soil is in a moderate ecological risk; (3) ΣREE, LREE, PN and RI have the same spatial variation law. It is confirmed that the accumulation of rare earth in the surface soil is mainly controlled by granite weathering and hydrological conditions, and the mining development has limited influence on it. In short, the light soil rare earth pollution and little ecological risk in the area are safe and controllable.
-
Key words:
- soil rare earth /
- spatial distribution /
- risk assessment /
- environmental geology /
- tin ore /
- Hunan
-

-
表 1 研究区土壤稀土含量(×10−6)与指标统计
Table 1. Soil rare earth content(×10−6) and index statistics in the study area
元素 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 含量 最大值 519 396 192 776 128 26.5 95.9 15.4 88.7 13 36.7 5.72 35.3 5.21 最小值 6.86 5.99 1.7 6.63 1.27 0.22 1.29 0.19 1.25 0.23 0.71 0.1 0.58 0.087 平均值 73.99 122.50 16.61 60.03 10.75 1.74 10.42 1.51 9.18 1.67 4.77 0.78 4.63 0.68 标准偏差 64.22 77.15 18.29 67.29 11.62 2.24 9.37 1.45 8.33 1.32 3.63 0.57 3.41 0.50 变异系数 0.87 0.63 1.10 1.12 1.08 1.29 0.90 0.96 0.91 0.79 0.76 0.73 0.74 0.73 湖南省土壤背景值 37.4 73.9 6.26 23.8 4.37 0.82 5.36 0.6 3.97 0.77 2.42 0.32 2.36 0.36 中国土壤背景值 39.7 68.4 7.17 24.4 5.22 1.03 4.6 0.63 4.13 0.87 2.5 0.37 2.44 0.36 Pi 最大值 13.88 5.36 30.67 32.61 29.29 32.32 17.89 25.67 22.34 16.88 15.17 17.88 14.96 14.47 最小值 0.18 0.08 0.27 0.28 0.29 0.27 0.24 0.32 0.31 0.30 0.29 0.31 0.25 0.24 平均值 1.98 1.66 2.65 2.52 2.46 2.12 1.94 2.51 2.31 2.17 1.97 2.44 1.96 1.89 标准偏差 1.72 1.04 2.92 2.83 2.66 2.73 1.75 2.42 2.10 1.72 1.50 1.77 1.44 1.38 变异系数 0.87 0.63 1.10 1.12 1.08 1.29 0.90 0.96 0.91 0.79 0.76 0.73 0.74 0.73 Igeo 最大值 3.21 1.84 4.35 4.44 4.29 4.43 3.58 4.10 3.90 3.49 3.34 3.57 3.32 3.27 最小值 −3.03 −4.21 −2.47 −2.43 −2.37 −2.48 −2.64 −2.24 −2.25 −2.33 −2.35 −2.26 −2.61 −2.63 平均值 0.02 −0.16 0.42 0.38 0.32 0.12 0.05 0.40 0.32 0.27 0.15 0.47 0.16 0.11 标准偏差 1.01 1.03 0.99 0.96 1.00 0.92 0.91 0.93 0.88 0.83 0.80 0.79 0.79 0.77 变异系数 47.39 −6.45 2.36 2.54 3.14 7.90 17.77 2.30 2.74 3.11 5.34 1.69 5.01 6.92 $ {\mathrm{E}}_{\mathrm{r}}^{\mathrm{i}} $ 最大值 13.88 5.36 153.4 65.21 146.5 323.2 89.46 256.7 111.7 168.8 75.83 178.8 29.92 289.4 最小值 0.18 0.08 1.36 0.56 1.45 2.68 1.20 3.17 1.57 2.99 1.47 3.13 0.49 4.83 平均值 1.98 1.66 13.27 5.04 12.30 21.16 9.72 25.11 11.56 21.70 9.86 24.37 3.92 37.80 标准偏差 1.72 1.04 14.61 5.65 13.30 27.33 8.74 24.20 10.49 17.19 7.50 17.73 2.89 27.51 变异系数 0.87 0.63 1.10 1.12 1.08 1.29 0.90 0.96 0.91 0.79 0.76 0.73 0.74 0.73 表 2 研究区土壤稀土地球化学参数
Table 2. Rare earth geochemical parameters of soil in the study area
地化指标 ΣREE(×10−6) LREE(×10−6) HREE(×10−6) LREE/HREE LaN/YbN δEu δCe 最大值 2062 1767 295.9 12.40 21.72 0.73 2.42 最小值 29.33 24.89 4.44 4.51 6.34 0.16 0.10 平均数 319.3 285.6 33.64 8.61 10.75 0.52 1.01 标准偏差 237.7 211.3 28.44 1.88 3.16 0.14 0.40 变异系数 0.74 0.74 0.85 0.22 0.29 0.26 0.40 湖南省土壤背景值 181.10 144.55 38.04 中国土壤背景值 184.72 145.92 38.80 -
[1] 程 胜,林龙勇,李俊春,韩存亮,李晓源,李朝晖,邓一荣.2024.离子吸附型稀土矿区生态环境问题与土壤修复技术研究进展[J]. 地球化学,53(1):17-29.
[2] 范宏瑞,牛贺才,李晓春,杨奎锋,杨占峰,王其伟.2020.中国内生稀土矿床类型、成矿规律与资源展望[J]. 科学通报,65:3778-3793.
[3] 高娟琴,于 扬,李以科,李瑞萍,柯昌辉,王登红,于 讽,张 塞,王雪磊.2021.内蒙白云鄂博稀土矿土壤一植物稀土元素及重金属分布特征田[J]. 岩矿测试,40(6):871-882. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2021.6.ykcs202106007
[4] 高瑞忠,张阿龙,张 生,贾德彬,杜丹丹,秦子元,王喜喜.2019.西北内陆盐湖盆地土壤重金属Cr、Hg、As空间分布特征及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 生态学报,39(7):2532-2544.
[5] 何东明,王晓飞,陈丽君,苏 荣.2014.基于地积累指数法和潜在生态风险指数法评价广西某蔗田土壤重金属污染[J]. 农业资源与环境学报,31(2):126-131.
[6] 何宏平,杨武斌.2022.我国稀土资源现状和评价[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,46(5):829-841.
[7] 李剑锋,冯李霄.2023.湖南某锡矿区土壤重金属污染及健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质,50(3):897-910. doi: 10.12029/gc20220825003
[8] 李剑锋,卢友月,张遵遵,付建明,秦拯纬.2023a.南岭大义山岩体研究与找矿进展[J]. 地球科学,48(10):3707-3724.
[9] 李剑锋,冯李霄,陈希清,付建明,卢友月,马可蒙,谢昊霖.2023b.大义山东南部土壤重金属分布特征及其风险评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报,13(1):287-294.
[10] 刘永林,雒昆利,袁余洋.2020.重庆市江津区表层土壤中稀土元素含量与分布特征[J]. 中国稀土学报,38(2):215-224.
[11] 王园园,傅浩洋,朱建喜,何宏平,梁晓亮.2024.稀土元素的生物毒害性研究进展[J]. 地球化学,53(1):3-16.
[12] 赵莹晨. 2021. 白云鄂博矿区周边土壤稀土污染特征及稳定化修复研究[D]. 内蒙古科技大学硕士学位论文.
[13] 中国环境监测总站. 1990. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京:中国环境科学出版社.
[14] Adeel M, Lee J Y, Zain M, Rizwan M, Nawab A, Ahmad M A, Shafiq M, Yi Hao, Jilani G, Javed R, Horton R, Rui Y K, Tsang D C W, Xing B S. 2019. Cryptic footprints of rare earth elements on natural resources and living organisms[J]. Environment International, 127: 785-800. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.022
[15] Balaram V. 2019. Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 10(4): 1285-1303. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2018.12.005
[16] Chen H B, Chen Z B, Chen Z Q, Ou X L, Chen J J. 2020. Calculation of Toxicity Coefficient of Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Rare Earth Elements[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 104(5): 582-587. doi: 10.1007/s00128-020-02840-x
[17] Forstner U, Ahlf W, Calmano W. 1993. Sediment quality objectives and criteria development in Germany[J]. Water Science and Technology, 28(8): 307-314.
[18] García A, Espinosa R, Delgado L. 2011. Acute toxicity of cerium oxide, titanium oxide and iron oxide nanoparticles using standardized tests[J]. Desalination, 269(1-3): 136-141. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.10.052
[19] Gwenzi W, Mangori L, Danha C, Chaukura N, Dunjana N, Sanganyado E. 2018. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 636: 299-313. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.235
[20] Hakanson L. 1980. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[21] Hao Z, Li Y H, Li H R, Wei B G, Liao X Y, Liang T, Yu J P. 2015. Levels of rare earth elements, heavy metals and uranium in a population living in Baiyun Obo, Inner Mongolia, China: A pilot study[J]. Chemosphere, 128: 161-170. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.057
[22] Khan A M, Bakar N K A, Bakar A F A, Ashraf M A. 2017. Chemical speciation and bioavailability of rare earth elements (REEs) in the ecosystem: A review[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(29): 22764-22789. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7427-1
[23] Li J X, Hong M, Yin X Q, Liu J L. 2010. Effects of the accumulation of the rare earth elements on soil macrofauna community[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 28(6): 957-964. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(09)60233-7
[24] Li X, Yang H, Zhang C, Zeng G M, Liu Y G, Xu W H, Wu Y, Lan S M. 2017. Spatial distribution and transport characteristics of heavy metals around an antimony mine area in central China[J]. Chemosphere, 170: 17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.011
[25] Lu X X, Gu Y G, Wang Z H, Liang R Z, Han Y J, Li H S. 2022. Risk on assessment of 15 REEs and mixtures by DGT in Songhua River system sediments of China’s largest old industrial base[J]. Environmental Research, 212: 113368. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113368
[26] Ma Y H, Kuang L L, He X, Bai W, Ding Y Y, Zhang Z Y, Zhao Y L, Chai Z F. 2010. Effects of rare earth oxide nanoparticles on root elongation of plants[J]. Chemosphere, 78(3): 273-279. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.10.050
[27] Meite F, Alvarez-Zaldívar P, Crochet A, Wiegert C, Payraudeau S, Imfeld G. 2018. Impact of rainfall patterns and frequency on the export of pesticides and heavy-metals from agricultural soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 616: 500-509.
[28] Pagano G, Guida M, Tommasi F, Oral R. 2015. Health effects and toxicity mechanisms of rare earth elements-Knowledge gaps and research prospects[J]. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 115: 40-48.
[29] Wang L, Li J F, Liu X W, Feng L X. 2024. Heavy metal pollution in water and soil and associated health risks in a tin mining region of Hunan Province[J]. China Geology, 7: 1-11.
[30] Wang L Q, Liang T. 2014. Accumulation and fractionation of rare earth elements in atmospheric; partic;ulates around a mine tailing in Baotou, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 23(6): 747-751.
[31] Wei B G, Li Y H, Li H R, Yu J P, Ye B X, Liang T. 2013. Rare earth elements in human hair from a mining area of China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 96: 118-123. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.05.031
[32] Wu J, Lu J, Zhang C, Zhang Z H, Min X Y. 2019. Distribution, pollution, and ecological risks of rare earth elements in soil of the northeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau[J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 25(7): 1816-1831. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2018.1475215
[33] Xia P H, Ma L, Sun R G, Yang Y, Tang X C, Yan D B, Lin T, Zhang Y T, Yi Y. 2020. Evaluation of potential ecological risk, possible sources and controlling factors of heavy metals in surface sediment of Caohai Wetland, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 740: 140231. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140231
[34] Zhang Z Z, Lu Y Y, Li J F, Quan H Y, Dai L Q, Fu J M, Yu Y S, Lin D Y, Dai P Y. 2024. Tin-polymetallic mineralization and granitic rocks in the Nanling daping mining area: Geochemical and geochronological constraints[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 170: 106144. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2024.106144
-



 下载:
下载: