Tracing infiltration and recharge of thick silt by using D and 18O isotopes of soil moisture in Xiaogan, Hubei and its ecological efffects
-
摘要:
黏性土的渗透系数极低,水分及溶质在黏性土中运移速率慢、耗时长,本次研究通过分析大别山区-江汉平原三水转换野外科学试验场(下文简称"试验场")ZK1、ZK2钻孔剖面土壤水、大气降雨D、18O同位素测试数据与孝感站(站号57482)多年年降雨量数据,确定了厚层黏性土土壤水入渗补给年份与深度的对应关系。结果表明:试验场区黏性土垂向岩性差异较小,无明显分层现象,土壤水分以"活塞流"的方式向下运移,夏、秋季的大气降雨为土壤水的主要补给来源;ZK1(取样间隔0.5~2.7 m,深度15 m)的土壤水δD、δ18O值随着埋深的增大出现周期性的波动,ZK2(取样间隔0.1 m,深度6.2 m)的土壤水δD、δ18O值随着埋深的增大出现分层波动现象;确定了黏性土层0~6.2 m深度对应的降雨入渗补给年份,并通过18O的峰值位移法计算得出降雨入渗补给在黏性土层的垂向运移速度为10.8~15.0 cm/a,年均入渗补给量为43.1~58.1 mm,占多年年均降雨量的4.01%,推算出降雨入渗补给需要近130年的时间才能穿透试验场厚层黏性土补给至地下水含水层,表明该厚层黏性土的防污性能良好。本研究所揭示大气-土壤界面下黏性土土壤水分入渗迁移历史演化特征及补给年际对应关系,对江汉平原区地下水环境保护、生态环境改善、旱涝灾害防治等具有重要意义。
Abstract:As well known, the permeability coefficient of cohesive soil is extremely low, and the transport rate of water and solute in the cohesive soil is slow and time-consuming. Stable isotopes δD and δ18O data of soil moisture and rainfall of two boreholes (ZK1, ZK2) in Dabie Mountain Area-Jianghan Plain rainfall-soil moisture-groundwater transformation scientific field test site were studied to trace the characteristics of historical infiltration and recharge of cohesive soil. The results show that there's no obvious layer boundary but just a little difference among the 15 m deep cohesive soil, and soil water moves in the way of "piston flow" vertically. The closer relation of rainfalls in summer and autumn to soil moisture in δD and δ18O value indicates that the main recharge of soil moisture comes from rainfall infiltration in summer and autumn. The δD and δ18O values of soil water in ZK1 (sampling interval 0.5-2.7 m, depth 15 m) fluctuate periodically with the increase of buried depth, while the δD and δ18O values of soil water in ZK2 (sampling interval 0.1m, depth 6.2 m) fluctuate stratified with the increase of buried depth. On the basis of determining the rainfall infiltration recharge years corresponding to the 0-6.2 m depth in the cohesive soil layer, based on 18O isotopes peak displacement method, it is calculated that the vertical migration velocity of rainfall infiltration recharge in the cohesive soil layer is 10.8-15.0 cm/a, and the annual infiltration recharge is 43.1-58.1 mm, accounting for 4.01% of the annual average rainfall. It takes about 130 years for rainfall infiltration to penetrate the thick cohesive soil for groundwater recharge, which means the thick cohesive soil has good antifouling properties. The historical evolution characteristics of soil water infiltration and migration at the air-soil interface and the inter-annual correspondence of soil water recharge are of great significance for groundwater environmental protection, ecological environment improvement, drought and flood disaster prevention and control in Jianghan Plain.
-

-
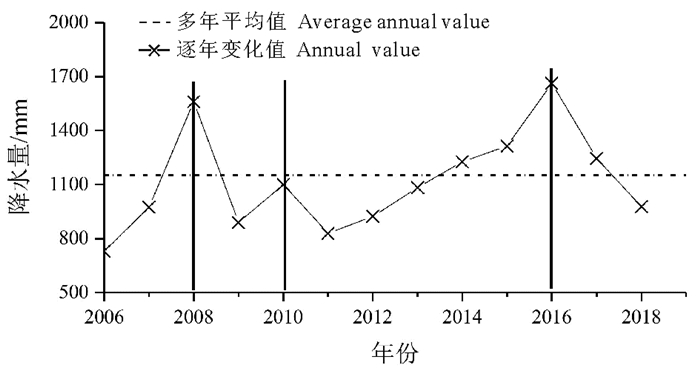
图 2 1957-2006年孝感市年降水量变化图(张涛等,2010)
Figure 2.
表 1 试验场区地质结构信息表
Table 1. Geological structure information of test site
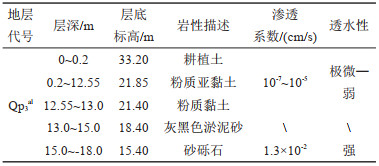
表 2 试验场区土壤岩性命名及垂向渗透系数
Table 2. Soil texture and vertical hydraulic conductivity of the test site
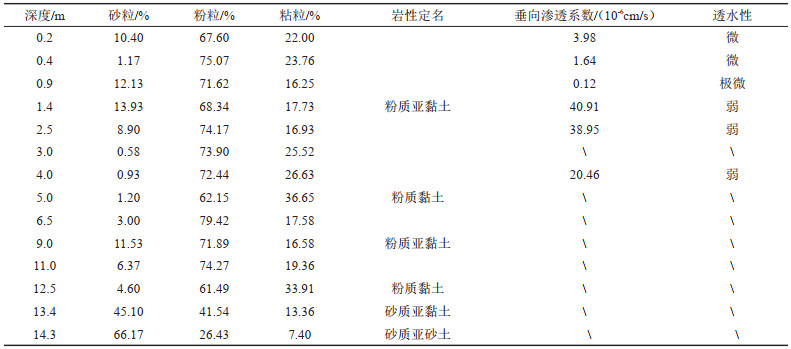
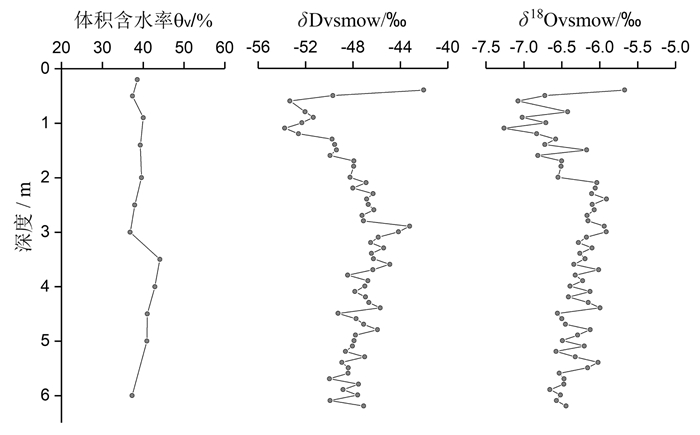
表 3 试验场区土壤体积含水率
Table 3. Soil volumetric moisture content (VWC) of test site

表 4 ZK1土壤水及地下水的δD、δ18O值表(2019/4/12)
Table 4. δD、δ18O of soil water in ZK1 and groundwater
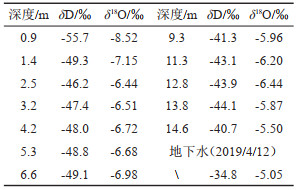
表 5 ZK2土壤水及地下水的δD、δ18O值(2019/7/25)
Table 5. δD、δ18O of soil water in ZK2 and groundwater
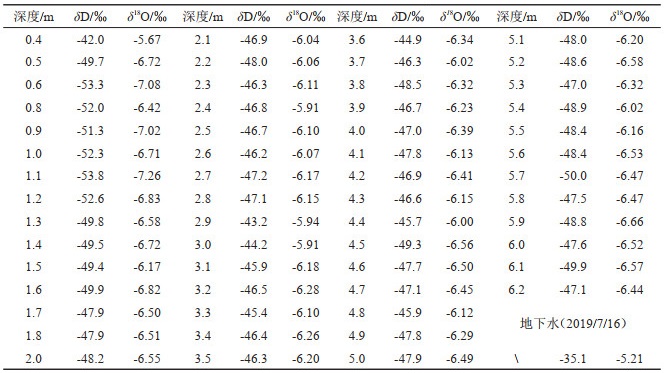
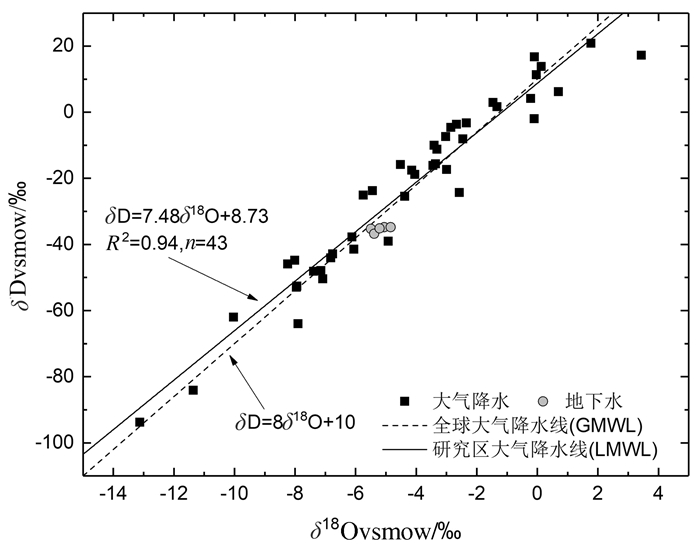
表 6 大气降雨、土壤水及地下水的氢氧稳定同位素组成特征表
Table 6. Hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes of soil moisture, precipitation and groundwater
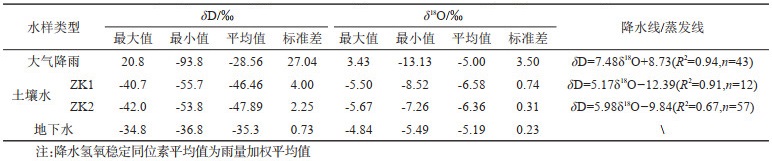
表 7 孝感市1957-2018年丰水年、枯水年一览
Table 7. Low flow year and high flow year in Xiaogan from 1957 to 2018
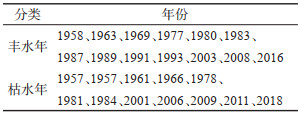
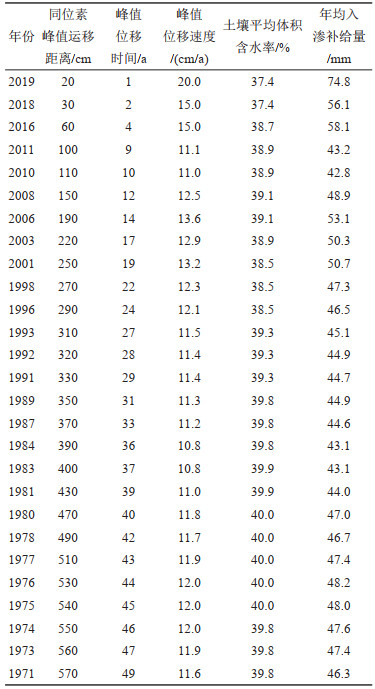
表 8 年均入渗补给量
Table 8. Yearly average annual recharge
-
Cao Jianwen, Xia Riyuan, Fang Shangwu, Zhao Liangjie, Wang Zhe, Wang Ruofan, Yi Rui. 2019. Model and mechanism of "water exploration by cross layer" for high sulfate area in slope region of Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau[J]. Geology in China, 46(2): 235-243(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201902003.htm
Craig H. 1961. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters[J]. Science, 133(3465): 1702-1703. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
Dai Junjie, Zhang Xinping, Luo Zidong, Wang Yue, Liu Fuji, He Xinguang. 2019. Characteristics of stable isotope in soil water and indication to soil water movement in a grove dominated by Cinnamomun camphora in Changsha[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 32(6): 974-983(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_research-environmental-sciences_thesis/0201272816983.html
Deng Zhimin, Zhang Xiang, Pan Guoyan. 2016. Variations of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in Meteoric precipitation in Wuhan, China[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 33(7): 12-17, 22(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB201607003.htm
Dong Xiaofang, Deng Huangyue, Zheng Xiangmin, Zhou Limin. 2017. Analysis of stable isotope characteristics and water vapor origins in atmospheric precipitation in the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(4): 78-84(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201704013.htm
Ministry of Water Resources of the People's Repulic of China. 2008. Code for Engineering Geological Investigation of Water Resources and Hydropower (GB 50487-2008)[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press(in Chinese).
He Jun, Tan Ting, Qi Zhichong, Hao Yiguo, Ma Teng. 2015. Study on contamination sources of the nitrate in groundwater by nitrogen and oxygen isotopes in Ramotswa, Botswana[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 31(4): 421-427(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC201504012.htm
Hsieh J C, Chadwick O A, Kelly E F, Savin S M. 1998. Oxygen isotopic composition of soil water: Quantifying evaporation and transpiration[J]. Geoderma, 82(1/2/3): 269-293. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Oliver_Chadwick/publication/229406618_Oxygen_isotope_composition_of_soil_water_Quantifying_evaporation_and_transpiration/links/00b49538df37c86d51000000.pdf
Hu Haiying, Bao Weimin, Wang Tao. 2008. Simulation and experiment on variations of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in soil water[J]. Water Resources and Power, (4): 149-152(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000037231458410_f4de.html
Lei Zhidong, Yang Shixiu, Xie Senchuan. 1988. Soil Water Dynamics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 5-7(in Chinese).
Ji Wangjia, Huang Yanan, Li Bingbing, Li Zhi. 2019. Oxygen and hydrogen stable isotope compositions of soil water in deep loess profile under different land use types of northern Shaanxi, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(12): 4143-4149(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31840459
Liu Beilin, Phillips F, Hoines S, Andrew. R, Pankaj S. 1995. Water movement in desert soil traced by hydrogen and oxygen isotopes, chloride, and chloride-36, southern Arizona[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 168: 91-110. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(94)02646-S
Liu Jun, Nie Zhenlong, Duan Baoqian, Liu Fuliang, Zhang Lin. 2016. Characteristics of stable isotope (δ2H、δ18O) in soil water in Hohhot area[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 30(10): 145-150(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GHZH201610025.htm
Liu Jun, Wei Wen, Zhang Lin, Wang Ying, Duan Baoqian, Liu Fuliang. 2012. Application on isotopes D and 18O of soil water in water movement of unsaturated zone[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology, (5): 38-43(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCKX201205011.htm
Ma Bin, Liang Xing, Lin Dan, Liu Shaohua, Xu Min. 2014. Tracing infiltration and recharge of the unsaturated zone using 2H, 18O Isotopes in Shijiazhuang, North China Plain[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 33(3): 163-168, 174(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201403021
Ma Yingbin, Zhang Biebei, Xu Qing, Gao Deqiang, Wang Ting, Sui Mingzhen, Huang Yaru. 2018. Response of deuterium isotope in soil water to rainfall in freshwater wetland forests of Shaoxing, Zhejiang Province[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 54(10): 11-19(in Chinese with English abstract).
Prudhomme Edmunds W M, Ma Jinzhu, Li Ding, Zhang Jiawu. 2003. Groundwater recharge and climatic change during the last 1000 years from unsaturated zone of SE Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(14): 1469-1474. doi: 10.1360/02wd0262
Song Xianfang, Wang Shiqin, Xiao Guoqiang, Wang Zhimin, Liu Xin, Wang Peng. 2009. A study of soil water movement combining soil water potential with stable isotopes at two sites of shallow groundwater areas in the North China Plain[J]. Hydrological Process, 23(9): 1376-1388. doi: 10.1002/hyp.7267
Sun Fangqiang, Yin Lihe, Wang Xiaoyong, Ma Hongyun, Zhang Jun, Dong Jiaqiu, He Shuaijun. 2017. Determination of vertical infiltration recharge of groundwater in the thick unsaturated zone of Sangong River Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Geology in China, 44(5): 913-923(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Fugang, Liao Zisheng. 2007. Study of the precipitation infiltration recharge with the D、18O isotopes peak displacement Method[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), (2): 284-287, 334(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200702013.htm
Wu Qianqian, Ren Jiaguo, Xu Mo. 2008. Isotope features and supply sources of groundwater in the Yarkant River drainage area, Xinjiang[J]. Geology in China, (2): 331-336(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xia Pingying, Zhang Feng. 2014. Study on flood control and disaster reduction in Xiaogan City[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 11(15): 21-22(in Chinese).
Xu Yingde, Wang Jingkuan, Gao Xiaodan, Zhang Yulong. 2018. Application of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope techniques on soil water research: A review[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 32(3): 1-9, 15(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/325965897_Application_of_Hydrogen_and_Oxygen_Stable_Isotope_Techniques_on_Soil_Water_Reaearch_A_Review
Yu Hongyang, 2016. Xiaogan 2016: Super historical flood attacks[J]. Insight China, (19): 18-23(in Chinese).
Zhang Tao, Duan Chunfang, Fang Fang, Wang Li. 2010. Precipitation variation characteristics of Xiaogan city for last 50 years[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 29(1): 81-84(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HBQX201001015.htm
Zhang Xiang, Deng Zhimin, Pan Guoyan, Wu Shaofei, Zhu Yang, Zhu Cairong. 2015. Variation in stable composition in soil water in Poyang Lake Wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(22): 7580-7588(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-STXB201522032.htm
Zhang Xiaojuan, Song Weifeng, Wu Jinkui, Wang Zhuojuan. 2015. Characteristics of Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes of Soil Water in the Water Source Area of Yuanyang Terrace[J]. Environmental Science, 36(6): 2102-2108(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201506029.htm
Zimmermann U, Munnich K O, Roether W. 1967. Dowanward movement of soil moisture traced by means of hydrogen isotopes[J]. Isotope Techniques in the Hydrologic Cycle, 11: 28-36.
曹建文, 夏日元, 方尚武, 赵良杰, 王喆, 王若凡, 易瑞. 2019. 云贵高原斜坡地带典型地下水富硫酸盐地区"越层找水"模式及其机理研究[J]. 中国地质, 46(2): 235-243. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190202&flag=1
戴军杰, 章新平, 罗紫东, 王锐, 刘福基, 贺新光. 2019. 长沙地区樟树林土壤水稳定同位素特征及其对土壤水分运动的指示[J]. 环境科学研究, 32(6): 974-983. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201906007.htm
邓志民, 张翔, 潘国艳. 2016. 武汉市大气降雨的氢氧同位素变化特征[J]. 长江科学院院报, 33(7): 12-17, 22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB201607003.htm
董小芳, 邓黄月, 郑祥民, 周立旻. 2017. 长江流域降水中氢氧同位素特征及水汽来源[J]. 环境科学与技术, 40(4): 78-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201704013.htm
中华人民共和国水利部. 2009. 水利水电工程地质勘察规范(GB 50487-2008)[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社.
何军, 谭婷, 祁志冲, 郝义国, 马腾. 2015. 利用15N和18O识别地下水硝酸盐污染源-以博茨瓦纳东南部拉莫茨瓦为例[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 31(4): 421-427. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2015.04.011
胡海英, 包为民, 王涛, 瞿思敏. 2008. 土壤水中氢氧同位素变化模拟及实验[J]. 水电能源科学, (4): 149-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7709.2008.04.046
姬王佳, 黄亚楠, 李冰冰, 李志. 2019. 陕北黄土区深剖面不同土地利用方式下土壤水氢氧稳定同位素特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(12): 4143-4149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201912017.htm
雷志栋, 杨诗秀, 谢森传. 1988. 土壤水动力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 5-7.
刘君, 聂振龙, 段宝谦, 田言亮, 刘福亮, 张琳. 2016. 氢氧稳定同位素指示的呼和浩特地区土壤水的补给特征[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 30(10): 145-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201610025.htm
刘君, 卫文, 张琳, 王莹, 段宝谦, 刘福亮. 2012. 土壤水D和18O同位素在揭示包气带水分运移中的应用[J]. 勘察科学技术, (5): 38-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2012.05.010
马斌, 梁杏, 林丹, 刘绍华, 徐敏. 2014. 应用2H、18O同位素示踪华北平原石家庄包气带土壤水入渗补给及年补给量确定[J]. 地质科技情报, 33(3): 163-168, 174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201403023.htm
马迎宾, 张蓓蓓, 徐庆, 高德强, 王婷, 隋明浈, 黄雅茹. 2018. 绍兴淡水湿地森林土壤水氘同位素对降水的响应[J]. 林业科学, 54(10): 11-19. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20181002
孙芳强, 尹立河, 王晓勇, 马洪云, 张俊, 董佳秋, 贺帅军. 2017. 新疆三工河流域厚层包气带区地下水垂向补给量的厘定[J]. 中国地质, 44(5): 913-923. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170506&flag=1
王福刚, 廖资生. 2007. 应用D、18O同位素峰值位移法求解大气降雨入渗补给量[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), (2): 284-287+334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200702013.htm
武倩倩, 任加国, 许模. 2008. 新疆叶尔羌河流域地下水同位素特征及其补给来源分析[J]. 中国地质, (2): 331-336 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.02.018 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080218&flag=1
夏苹应, 张峰. 2014. 孝感城市防洪与减灾对策研究[J]. 科技创新导报, 11(15): 21-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-098X.2014.15.023
徐英德, 汪景宽, 高晓丹, 张玉龙. 2018. 氢氧稳定同位素技术在土壤水研究上的应用进展[J]. 水土保持学报, 32(3): 1-9, 15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS201803001.htm
余弘阳. 2016. 孝感2016: 超历史洪水来袭[J]. 小康, (19): 18-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXK201619007.htm
张涛, 段春锋, 方芳, 王俐. 2010. 近50年孝感市降水变化特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 29(1): 81-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9045.2010.01.014
张翔, 邓志民, 潘国艳, 吴绍飞, 肖洋, 朱才荣. 2015. 鄱阳湖湿地土壤水稳定同位素变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 35(22): 7580-7588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201522032.htm
张小娟, 宋维峰, 吴锦奎, 王卓娟. 2015. 元阳梯田水源区土壤水氢氧同位素特征[J]. 环境科学, 36(6): 2102-2108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201506029.htm
-




 下载:
下载: