OIL AND GAS EXPLORATION IN THE MESOZOIC OF EAST CHINA SEA SHELF BASIN: PROGRESS AND CHALLENGES
-
摘要:
东海陆架盆地是我国海域的一个大型中—新生代复合型含油气盆地,中生代盆地是我国海域油气勘探战略接替区之一。2005年之前主要以新生界为目的层,2005年之后,随着地震采集和处理技术的提高以及勘探思路的转变,针对中生界开展了富有成效的调查研究,取得了一系列成果与进展:①初步建立了一套深层二维地震采集技术和处理技术;②通过海陆对比和地震地层学分析,东海中生界分布广,具有“东海西陆”的古地理格局;③中生代盆地具有北东分带结构特征和3期演化;④中生界发育2套烃源岩和2套生储盖组合。在此基础上分析了东海陆架中生代盆地油气调查所面临的问题与挑战。
Abstract:The East China Sea Shelf Basin is a large-scale Cenozoic complex petroliferous basin in China's sea area. The Mesozoic basins there are regarded as the strategic successor for oil and gas exploration in China. In the period prior to 2005, the Cenozoic was the major exploration target in the country. After 2005, however, with the improvement of seismic acquisition and processing technology and the change of exploration ideas, a series of progress has been achieved in exploration in the Mesozoic, such as, 1) the rapid development of deep 2D seismic acquisition and processing technology; 2) the distribution pattern of the Mesozoic in East China, i.e. "the terrestrial Mesozoic in the west and the marine in the east " was established through stratigraphic correlation between the sea and the land; 3) the NE zonation of the Mesozoic basins is confirmed and the basins have passed through three evolutionary stages. 4) Two sets of source rocks are discovered in the Mesozoic. On the above basic facts, the problems and challenges of oil and gas exploration in Mesozoic basins in the East China Sea Shelf Basin are analyzed and discussed.
-
Key words:
- oil and gas exploration /
- progress /
- challenge /
- Mesozoic /
- East China Sea Shelf Basin
-

-
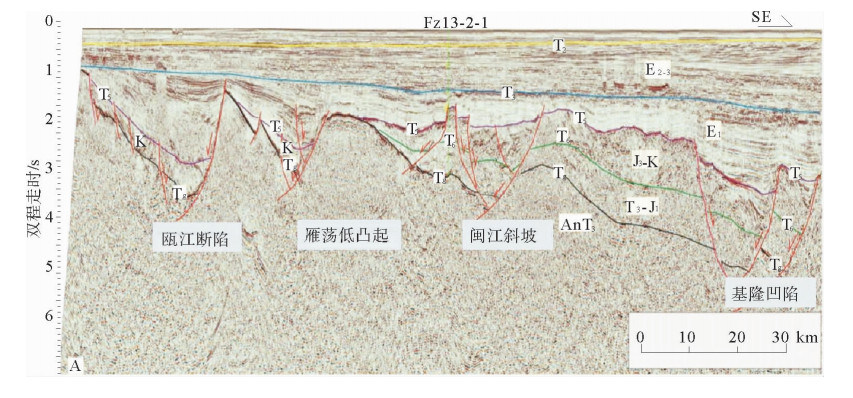
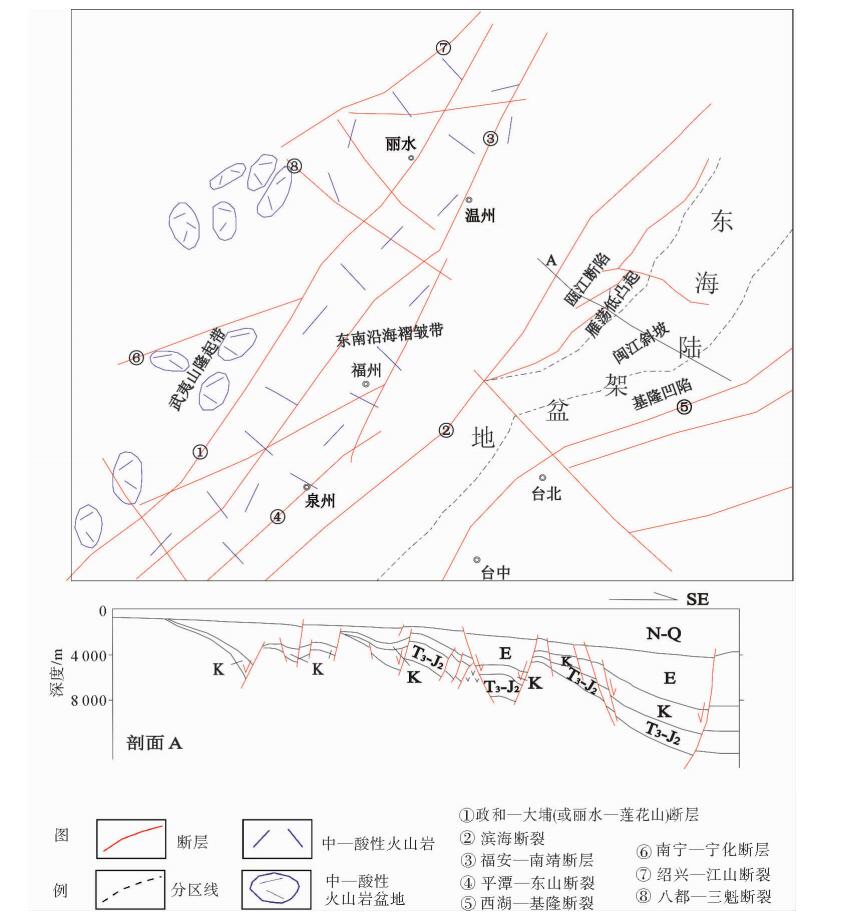
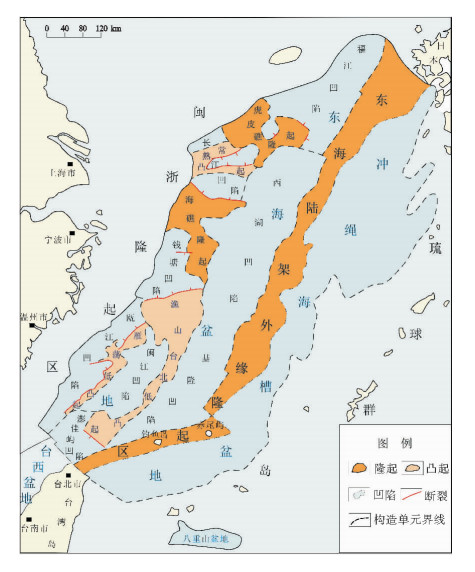
图 5 东海陆架盆地与邻域构造格架(据文献[12])
Figure 5.
表 1 东海陆架针对中生界地震采集参数
Table 1. Seismic acquisition parameters for the Mesozoic in the East China Sea Shelf Basin
参数名称 参数值 道间距/m 12.5 炮间距/m 37.5 震源容量/in3 6 060 电缆工作段总长/m 8 100 道数/道 648 覆盖次数/次 108 采样率/ms 2 记录长度/ s 12 最小偏移距/m <250 震源沉放深度/m 10 电缆沉放深度/m 16 记录格式 SEG-D,8058 滤波档位 低截止3 Hz/陡度12 dB/oct,
高截止206 Hz/陡度276 dB/oct表 2 东海陆架盆地与邻近陆域中生代地层对比
Table 2. Correlation of Mesozoic in the East China Sea Shelf Basin and adjacent land areas

-
[1] MaruyamaS, SantoshM, ZhaoD.Superplume, supercontinent, and post-perovskite:mantle dynamics and anti-plate tectonics on the Core-Mantle Boundary[J].GondwanaResearch.2007, 11(1):7-37. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3e86c718a9bf74a51eceb4d8ba18b0ad&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] 李家彪.东海区域地质[M].北京:海洋出版社, 2008: 1-4.
[3] 张敏强, 钟志洪, 夏斌, 等, 东海西湖凹陷中南部晚中新世构造反转与油气运聚[J].中国海上油气, 2005, 17(2):73-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2005.02.001
[4] 杨长清, 杨传胜, 李刚, 等.东海陆架盆地南部中生代构造演化与原型盆地性质[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3): 105-111. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201203013
[5] 冯晓杰, 蔡东升, 王春修, 等.东海陆架盆地中新生代构造演化特征[J].中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1): 33-37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-dz200301007
[6] Zhou X M, Li W X.Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in Southeastern China:implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J].Tectonophysics2000, 326(3):269-287. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100001207
[7] Cukur D, Horozal S, Lee G H, et al.Structural evolution of the northern East China Sea Shelf Basin interpreted from cross-section restoration[J].Marine Geophysical Research, 2011, 32(3): 363-381. doi: 10.1007/s11001-011-9114-4
[8] 刘金水, 廖宗廷, 贾健谊, 等.东海陆架盆地地质结构及构造演化[J].上海地质, 2003(3): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2003.03.001
[9] 李上卿, 彭伟欣.东海地球物理勘探历史回顾[M]//刘申叔, 李上卿.东海油气地球物理勘探.北京: 地质出版社, 2001: 5-13.
[10] 姜亮.东海陆架盆地油气资源勘探现状及含油气远景[J].中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2003.01.001
[11] 金春爽, 乔德武, 须雪豪, 等.东海陆架盆地南部油气资源前景与选区[J].中国地质, 2015, 42(5): 1601-1609. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.05.027
[12] 杨艳秋, 李刚, 戴春山.东海陆架盆地西部坳陷带中生界分布特征极其有利区探讨[J].世界地质, 2011, 30(3): 396-403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2011.03.011
[13] Yang C Q, Yang Y Q, Li G, et al.The Mesozoic basin-mountain Coupling process of the Southern East China SeaShelf Basin and its adjacent land area[J].ACTA GEOLOGICA SINICA (English Edition), 2016, 90(3):1051-1052. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12748
[14] 冯晓杰, 张川燕, 王春修, 等.东海陆架和台西南盆地中生界及其油气勘探潜力[J].中国海上油气(地质), 2001, 15(5): 306-310, 316. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-dz200105002
[15] 高乐.东海陆架中生代残余盆地特征及勘探方向探讨[J].中国海上油气, 2005, 17(3): 148-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2005.03.002
[16] 须雪豪, 陈琳琳, 汪企浩.东海陆架盆地中生界地质特征与油气资源潜力浅析[J].海洋石油, 2004, 24(3):1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2004.03.001
[17] 杨长清, 李刚, 龚建明, 等.中国东南海域中生界油气地质条件与勘探前景[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2015, 45(1):1-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201501001
[18] 蔡东升, 冯晓杰, 高乐, 等.中国近海前第三纪残余盆地及其勘探潜力与方向[J].中国海上油气, 2004, 16(1): 1-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2004.01.001
-



 下载:
下载: