LATER QUATERNARY CLIMATIC AND ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGES IN THE SOUTHEASTERN MARGIN OF INNER MONGOLIA
-
摘要:
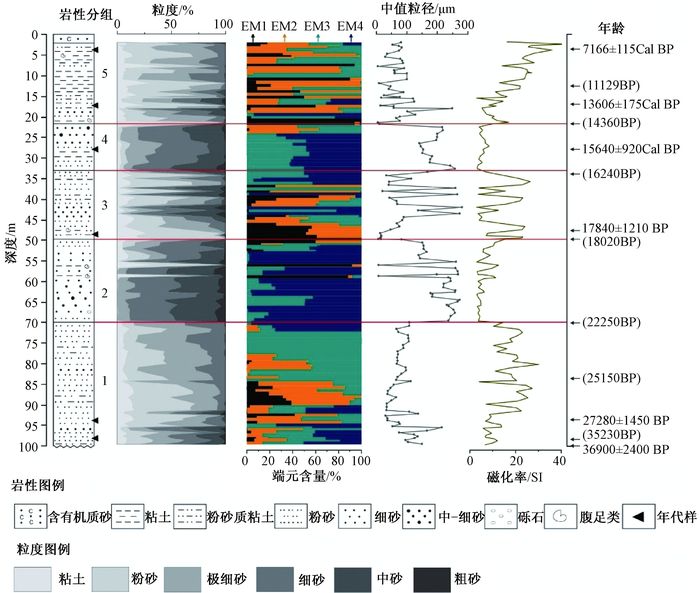
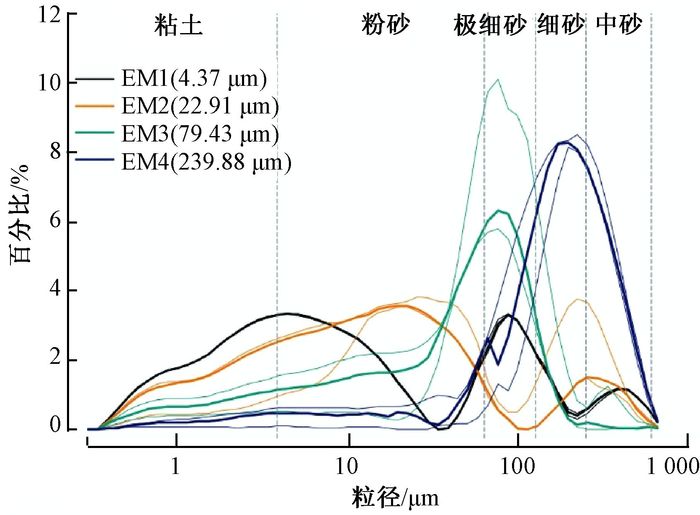
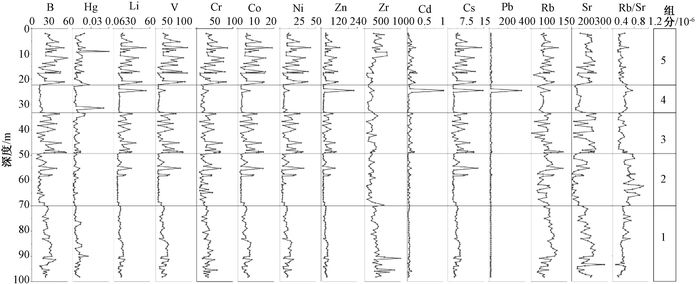
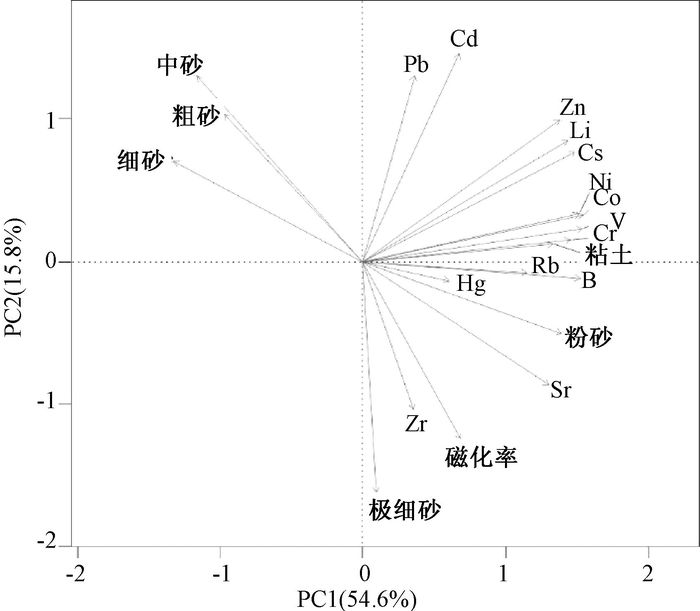
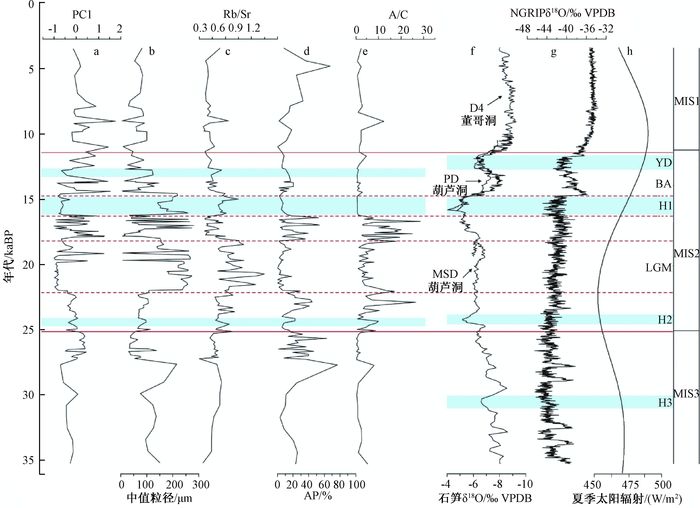
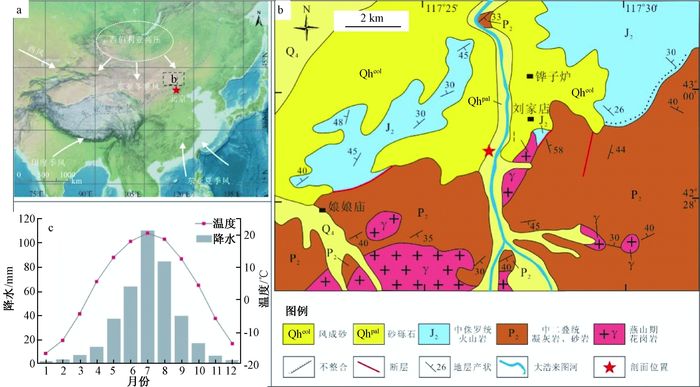
基于内蒙古东南缘西拉木伦河上游刘家店河湖相剖面的粒度、磁化率、微量元素地球化学指标,重建该区35 ka BP以来的气候演化过程。结果表明,在MIS 3晚期(35.23~25.15 ka BP)研究区气候条件总体温暖湿润,并伴有区域变干的趋势;MIS 2阶段(25.15~11.13 ka BP)气候整体寒冷干燥,但叠加有短暂回暖气候事件。剖面记录的末次盛冰期(LGM)出现于22.25~18.47 ka BP,此时气候极度干冷;MIS 2阶段叠加了两个短暂气候适宜期,分别出现于18.47~16.24 ka BP和14.72~11.13 ka BP。在11.13 ka BP前后研究区进入全新世,气候变得暖湿。刘家店剖面的气候记录与周边气候记录具有可对比性,揭示了区域上东亚夏季风进退具有一致性,并认为自MIS 3晚期以来东亚夏季风受北半球太阳辐射及冰量的共同驱动。此外,刘家店剖面记录揭示的千年尺度气候变化对典型气候事件具有一定的响应,推测这些千年尺度的季风强度变化可能与北大西洋经向翻转环流(AMOC)相关。
Abstract:A multi-proxy record including grain size, magnetic susceptibility and trace element from the fluvial-lacustrine Linjiadian section in the upper reaches of Xilamulun River, situated in the southeastern margin of Inner Mongolia, has been proposed to reconstruct the environmental and climatic changes since the last 36 ka BP. The results show that, during 35.23 to 25.15 ka BP, the late stage of Marine Isotope Stage 3 (MIS 3), warm and wet climate conditions dominated this region accompanied by the trend of regional drought climate. The following period, approximately 25.25~11.35 ka BP, corresponding to MIS 2, was characterized by frequent fluctuations in climate change. The driest and coldest interval was recognized as the last glacial maximum (LGM), ranging from 22.25 to 18.47 ka BP, and two minor climate optimums occurred in 18.47~16.24 ka BP and 14.72~11.13 ka BP. The Holocene commenced at about 11.13 ka BP with the transition to a relatively humid and warm climate. Regional comparisons suggest a roughly synchronous pattern of climate change and variation in the East Asian summer monsoon (EASM), attributing to the force of the northern hemisphere summer insolation and ice volume. In addition, the millennial-scale EASM fluctuation had some influence on the Heinrich (H), and the Younger Dryas (YD), indicating the relevance to the rapid Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) oscillations.
-

-
表 1 刘家店剖面测年结果
Table 1. Dating results of the Liujiadian Section
AMS14C测年 样品编号 深度/
m测试
材料年龄/
(a BP)校正年龄/
Cal a BPP38BF-152 4 全有机质 6269±115 7166±115 P38-128 17 全有机质 11751±175 13606±175 OSL测年 样品编号 深度/
m等效剂量
E.D/Gy环境剂量率/
(Gy/ka)年龄/
(ka BP)P38OSL-117 28 57.74±3.39 3.69 15.64±0.92 P38OSL-83 49 67.22±4.58 3.77 17.84±1.21 P38OSL-10 94 129.68±6.90 4.75 27.28±1.45 08XL-50 99 124.31±6.49 3.37 36.9±2.4 -
[1] Wang B. The Asian monsoon[M]. Chichester: Springer, 2006, 1~10.
[2] Wang W, Feng Z D. Holocene moisture evolution across the Mongolian Plateau and its surrounding areas: a synthesis of climatic records[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 122: 38~57. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.03.005
[3] Xiao J L, Xu Q H, Nakamura T, et al. Holocene vegetation variation in the Daihai Lake region of north-central China: a direct indication of the Asian monsoon climatic history[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2004, 23(14/15): 1669~1679. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ200412003011.htm
[4] Peng Y J, Xiao J L, Nakamura T, et al. Holocene East Asian monsoonal precipitation pattern revealed by grain-size distribution of core sediments of Daihai Lake in Inner Mongolia of north-central China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(3/4): 467~479. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X0500124X
[5] Xu Q H, Xiao J L, Li Y C, et al. Pollen-based quantitative reconstruction of Holocene climate changes in the Daihai Lake area, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2010, 23(11): 2856~2868. doi: 10.1175/2009JCLI3155.1
[6] Yu Z T, Liu X Q, Wang Y, et al. A 48.5-ka climate record from Wulagai Lake in Inner Mongolia, Northeast China[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 333: 13~19. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.04.006
[7] 蒋复初, 王书兵, 傅建利, 等.鄂尔多斯高原距今15 ka以来环境演化[J].地质力学学报, 2014, 20(2): 165~173. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140208&flag=1
JIANG Fuchu, WANG Shubing, FU Jianli, et al. On the environmental changes since 15 ka BP in the Ordos Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2014, 20(2): 165~173. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140208&flag=1
[8] 王燕, 叶青培, 乔彦松.内蒙古正蓝旗地区全新世古环境变迁的孢粉记录[J].地质力学学报, 2006, 12(3): 324~328. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060345&flag=1
WANG Yan, YE Qingpei, QIAO Yansong. Palynological records of the Holocene environmental changes in Zhenglan Qi, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2006, 12(3): 324~328. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060345&flag=1
[9] 中国科学院中国植被图编辑委员会.中华人民共和国植被图 1:1000000[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007.
Editorial Committee of Vegetation Map of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Vegetation map of the People's Republic of China 1:1000000[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007.
[10] 王文龙, 王友, 吕希华, 等. 中华人民共和国1: 5万地质矿产图(马架子幅)[R]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古自治区第十地质矿产勘察开发院, 2008.
WANG Wenlong, WANG You, LV Xihua, et al. 1:50000-scalegeological and mineral map of Majiazi sheet[R]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Tenth Geological Mineral Exploration Institute, 2008.
[11] 杨慧君, 王永, 迟振卿, 等.河北白洋淀老河头剖面25.5 ka BP以来气候环境变化的沉积记录[J].现代地质, 2015, 29(2): 291~298. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201502012.htm
YANG Huijun, WANG Yong, CHI Zhenqing, et al. Sedimentary record of climate change during the past 25.5 ka of Laohetou profile from Baiyangdian, Hebei Province[J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(2): 291~298. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201502012.htm
[12] Reimer P J, Bard E, Bayliss A, et al. IntCal13 and marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0~50, 000 years Cal BP[J]. Radiocarbon, 2013, 4(55): 1869~1887.
[13] The R Development Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing[M]. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2014, 1~3405.
[14] Dietze M, Dietze E. EMMAgeo: end-member modelling algorithm and supporting functions for grain-size analysis R package version 0.9.1[R]. Potsdam: GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, 2013:1~36.
[15] Dietze E, Maussion F, Ahlborn M, et al. Sediment transport processes across the Tibetan Plateau inferred from robust grain-size end members in lake sediments[J]. Climate of the Past, 2014, 10(1): 91~106. doi: 10.5194/cp-10-91-2014
[16] 曾艳, 陈敬安, 朱正杰, 等.湖泊沉积物Rb/Sr比值在古气候/古环境研究中的应用与展望[J].地球科学进展, 2011, 26(8): 805~810. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201108002.htm
ZENG Yan, CHEN Jing'an, ZHU Zhengjie, et al. Advance and prospective of Rb/Sr ratios in lake sediments as an index of paleoclimate/paleoenvironment[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2011, 26(8): 805~810. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201108002.htm
[17] Jin Z D, Cao J J, Wu J L, et al. A Rb/Sr record of catchment weathering response to Holocene climate change in Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2006, 31(3): 285~291. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9837
[18] 陈诗越, 王苏民, 金章东, 等.青藏高原中部湖泊沉积物中Zr/Rb值及其环境意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(4): 35~38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200304006.htm
CHEN Shiyue, WANG Sumin, JIN Zhangdong, et al. Variation of Zr/Rb ratios in lacustrine sediments of the central Tibetan Plateau and its environment implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(4): 35~38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200304006.htm
[19] 田庆春, 杨太保, 张述鑫, 等.青藏高原腹地湖泊沉积物磁化率及其环境意义[J].沉积学报, 2011, 29(1): 143~150. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201101017.htm
TIAN Qingchun, YANG Taibao, ZHANG Shuxin, et al. Magnetic susceptibility and its environmental significance of lake sediments in Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(1): 143~150. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201101017.htm
[20] Feng Z D, Tang L Y, Ma Y Z, et al. Vegetation variations and associated environmental changes during marine isotope stage 3 in the western part of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 246(2/4): 278~291. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10933-013-9716-8
[21] Pachur H J, Wünnemann B, Zhang H C. Lake evolution in the Tengger Desert, northwestern China, during the last 40, 000 years[J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(2): 171~180. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1061
[22] Zhang H C, Peng J L, Ma Y Z, et al. Late Quaternary palaeolake levels in Tengger Desert, NW China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2004, 211(1/2): 45~58. http://www.oalib.com/references/18733527
[23] Ma Y Z, Zhang H C, Pachur H J, et al. Late Glacial and Holocene vegetation history and paleoclimate of the Tengger Desert, northwestern China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(14): 1457~1463. doi: 10.1360/02wd0274
[24] Liu X Q, Chi Z Q, Herzschuh U, et al. A MIS 3 charcoal and pollen record and quantitative precipitation inferences from the Jingerwa section of the Nihewan Basin, north-central China[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2014, 51(2): 211~221. doi: 10.1007/s10933-013-9716-8
[25] Jiang H C, Wang P, Thompson J, et al. Last glacial climate instability documented by coarse-grained sediments within the loess sequence, at Fanjiaping, Lanzhou, China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2009, 72(1): 91~102. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.04.005
[26] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu cave, China[J]. Science, 2001, 294(5550): 2345~2348. doi: 10.1126/science.1064618
[27] Ruddiman W F. Orbital insolation, ice volume, and greenhouse gases[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003, 22(15/17): 1597~1629. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379103000878
[28] Jiang H C, Mao X, Xu H Y, et al. Last glacial pollen record from Lanzhou (northwestern China) and possible forcing mechanisms for the MIS 3 climate change in Middle to East Asia[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(5/6): 769~781. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2Fs11434-014-0611-0.pdf
[29] Yuan D X, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. Timing, duration, and transitions of the last interglacial Asian Monsoon[J]. Science, 2004, 304(5670): 575~578. doi: 10.1126/science.1091220
[30] Svensson A, Andersen K K, Bigler M, et al. A 60000 year Greenland stratigraphic ice core chronology[J]. Climate of the Past, 2008, 4(1): 47~57. doi: 10.5194/cp-4-47-2008
[31] Laskar J, Robutel P, Joutel F, et al. A long-term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth[J]. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2004, 428(1): 261~285. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20041335
[32] Lu H Y, Wu N Q, Liu K B, et al. Phytoliths as quantitative indicators for the reconstruction of past environmental conditions in China Ⅱ: palaeoenvironmental reconstruction in the Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2007, 26(5/6): 759~772. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ200801004011.htm
[33] Li Q, Wu H B, Yu Y Y, et al. Reconstructed moisture evolution of the deserts in northern China since the Last Glacial Maximum and its implications for the East Asian Summer Monsoon[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2014, 121: 101~112. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2014.07.009
[34] Herzschuh U. Palaeo-moisture evolution in monsoonal Central Asia during the last 50, 000 years[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(1/2): 163~178. http://www.nsfc.gov.cn/Portals/0/fj/fj20170118_03.xls
[35] Ding Z L, Derbyshire E, Yang S L, et al. Stepwise expansion of desert environment across northern China in the past 3.5 Ma and implications for monsoon evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 237(1/2): 45~55. http://www.academia.edu/15110723/Stepwise_expansion_of_desert_environment_across_northern_China_in_the_past_3.5_Ma_and_implications_for_monsoon_evolution
[36] Peltier W R, Fairbanks R G. Global glacial ice volume and Last Glacial Maximum duration from an extended Barbados sea level record[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(23/24): 3322~3337. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2F978-3-319-04364-7_177.pdf
[37] Sun Y B, Clemens S C, Morrill C, et al. Influence of Atlantic meridional overturning circulation on the East Asian winter monsoon[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(1): 46~49. http://doc.sciencenet.cn/DocInfo.aspx?id=6861
[38] Li Y, Song Y G, Lai Z P, et al. Rapid and cyclic dust accumulation during MIS 2 in Central Asia inferred from loess OSL dating and grain-size analysis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 32365. doi: 10.1038/srep32365
[39] Zhao Y, Yu Z C. Vegetation response to Holocene climate change in East Asian monsoon-margin region[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2012, 113(1/2): 1~10. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2012ESRv..113....1Z
[40] Wen R L, Xiao J L, Chang Z G, et al. Holocene climate changes in the mid-high-latitude-monsoon margin reflected by the pollen record from Hulun Lake, northeastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Quaternary Research, 2010, 73(2): 293~303. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.10.006
[41] Liu H Y, Xu L H, Cui H T. Holocene history of desertification along the Woodland-Steppe border in northern China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2002, 57(2): 259~270. doi: 10.1006/qres.2001.2310
[42] Jiang W Y, Guo Z T, Sun X J, et al. Reconstruction of climate and vegetation changes of Lake Bayanchagan (Inner Mongolia): Holocene variability of the East Asian monsoon[J]. Quaternary Research, 2006, 65(3): 411~420. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2005.10.007
[43] Shi P J, Song C Q. Palynological records of environmental changes in the middle part of Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(14): 1433~1438. doi: 10.1360/02wd0259
[44] 王琫瑜, 孙湘君.内蒙古察素齐泥炭剖面全新世古环境变迁的初步研究[J].科学通报, 1997, 42(5): 514~518. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199705018.htm
WANG Fengyu, SUN Xiangjun. Preliminary study of Holocene environmental change in Chasuqi[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1997, 42(5): 514~518. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199705018.htm
-



 下载:
下载: