GEOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SELENIUM IN THE SOIL OF HORQIN DISTRICT, INNER MONGOLIA
-
摘要:
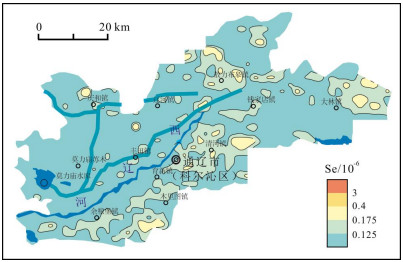
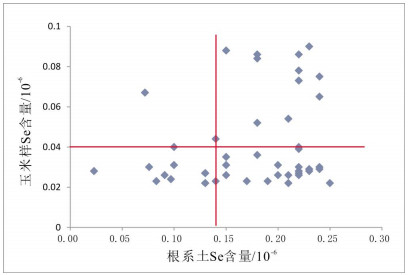
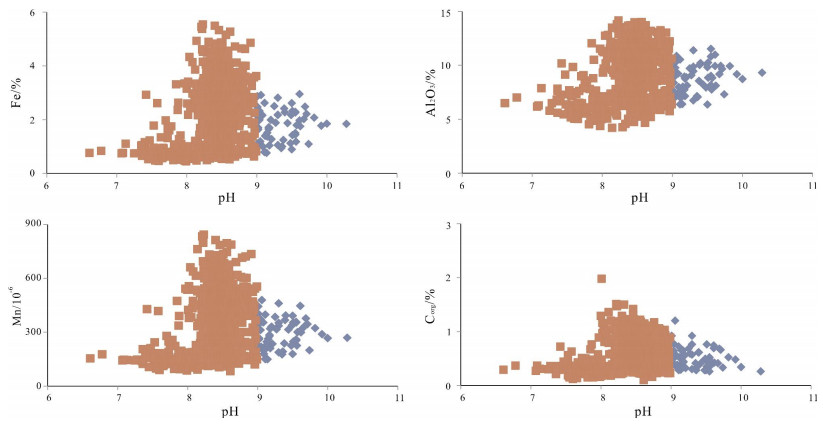
对通辽市科尔沁区土壤与农作物中硒元素地球化学特征及影响因素的系统研究显示,研究区土壤硒含量水平普遍较低,且空间分布不均,仅局部达到足硒水平.硒元素主要富集在表层土壤中,且与有机碳、Al2O3、TFe2O3、Mn、P等呈正相关关系,表明土壤中有机碳、黏土矿物、铁锰氧化物对硒元素地球化学行为有重要影响.研究区土壤呈碱性至强碱性,富硒农作物并不严格产出在富硒土壤中.因此,开发富硒农产品要综合考虑土壤硒含量、土壤有效态硒含量、农作物硒含量、土壤理化性质及地理景观等因素.
Abstract:A systematic study on the geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium (Se) in soil and crops of Horqin district, Tongliao City, shows that the Se content in the soil is generally low with uneven spatial distribution and only partially reaching the Se-sufficient level. Se is mainly concentrated in surface soil and positively correlated with organic carbon, Al2O3, TFe2O3, Mn and P, showing that the organic carbon, clay minerals and Fe-Mn oxides significantly affect the geochemical behavior of Se. The soil in the study area is alkaline to strongly alkaline. However the Se-rich crops are not strictly produced in Se-rich soil. Therefore, the development of Se-rich agricultural products should comprehensively consider such factors as Se content, available Se content in soil, Se content in crops, soil physicochemical property and geographical landscape.
-

-
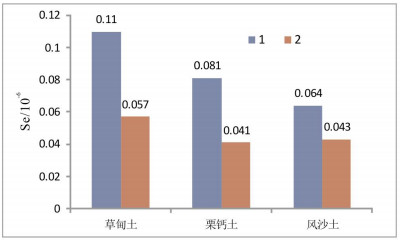
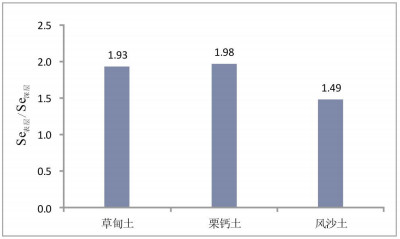
表 1 主要土壤类型Se含量特征值对比
Table 1. Comparison of Se content eigenvalues in major soil types
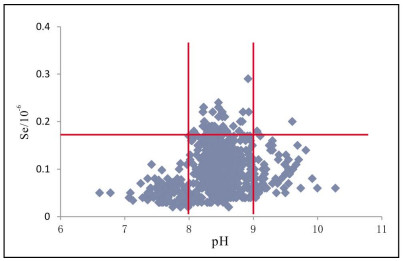
分布区 样品数 平均值 中位数 标准离差 变化系数 范围 表层 研究区 889 0.098 0.09 0.043 0.436 0.02~0.29 草甸土 614 0.11 0.11 0.04 0.362 0.02~0.29 栗钙土 143 0.081 0.07 0.04 0.494 0.02~0.19 风沙土 107 0.064 0.05 0.036 0.57 0.02~0.24 深层 研究区 221 0.052 0.045 0.024 0.466 0.02~0.21 草甸土 146 0.057 0.052 0.022 0.394 0.02~0.13 栗钙土 43 0.041 0.036 0.029 0.699 0.02~0.21 风沙土 25 0.043 0.039 0.016 0.38 0.02~0.08 含量单位:10-6(质量分数). 表 2 土壤硒丰缺划分界限表
Table 2. Abundance and deficiency demarcation values of Se content in soil
含量分级 表土总硒/10-6 硒效应 研究区占比 缺乏 ≤0.125 硒不足 73.45% 边缘 0.125~0.175 潜在硒不足 21.71% 适量 0.175~0.4 足硒 4.84% 高 0.4~3 富硒 0 过剩 >3 硒中毒 0 表 3 足硒区土壤Se含量参数统计表
Table 3. Parameters of Se content in Se-sufficient soil area
平均含量 标准差 变异系数 中位数 变化范围 0.192 0.0203 0.106 0.189 0.164~0.238 含量单位:10-6(质量分数). 表 4 不同土壤成因类型Se含量特征值
Table 4. Eigenvalues of Se content in different genetic types of soil
土壤成因类型 平均值 标准差 变化范围 东北地区硒平均含量 全国硒背景值 冲积物 0.115 0.038 0.04~0.29 0.184 0.29 风积物 0.064 0.029 0.02~0.24 含量单位:10-6(质量分数). 表 5 主要土壤类型中Fe2O3、Mn、Al、Ca、P、Se含量平均值
Table 5. Average contents of Fe2O3, Mn, Al, Ca, P and Se in major soil types
土壤类型 TFe2O3/% Al2O3/% CaO/% Mn/10-6 P/10-6 Se/10-6 草甸土 2.59 10.2 2.07 413 461 0.11 栗钙土 1.48 8.1 1.09 253 282 0.081 风沙土 1.19 7.1 0.95 208 236 0.064 -
[1] Kolachi N F, Kazi T G, Wadhwa S K, et al. Evaluation of selenium in biological sample of arsenic exposed female skin lesions and skin cancer patients with related to non-exposed skin cancer patients[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2011, 409(17):3092-3097. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.05.008
[2] Ben A I, Troudi A, Garoui E, et al. Protective effects of selenium on methimazole nephrotoxicity in adult rats and their offspring[J]. Exp Toxicol Pathol, 2011, 63(6):553-561. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2010.04.007
[3] Jarzynska G, Falandysz J. Selenium and 17 other largely essential and toxic metals in muscle and organ meats of Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) -Consequences to human health[J]. Environ Int, 2011, 37(5):882-888. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.02.017
[4] 谭见安, 朱文郁, 李日邦, 等.克山病与环境硒等生命元素的关系[J].中国地方病学杂志, 1991, 10(5):269-274. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1991-ZDFB199105004.htm
[5] 何锦, 安永会, 贾小丰, 等.阿坝州饮水中硒和氟元素与大骨节病关系研究[J].地下水, 2012, 34(2):9-10. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dixs201202004t
[6] 刘晓庆, 王斌, 雷艳霞.硒、碘、氟与大骨节病关系的研究进展[J].国外医学:医学地理分册, 2012, 33(2):83-85. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gwyx-yxdlfc201202004
[7] 杨志强, 李杰, 郑国东, 等.广西北部湾沿海经济区富硒土壤地球化学特征[J].物探与化探, 2014, 38(6):1260-1264, 1269. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201406030
[8] 马强, 姬丙艳, 张亚峰, 等.青海东部土壤及生物体中硒的地球化学特征[J].地球科学进展, 2012, 27(10):1149-1152. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7955967
[9] 高宗军, 崔浩浩, 庞绪贵, 等.山东省泰莱盆地及章丘市土壤中硒的成因[J].安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(31):19133-19135, 19138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.31.040
[10] 文帮勇, 张涛亮, 李西周, 等.江西龙南地区富硒土壤资源开发可行性研究[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(1):256-263. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.021
[11] 张弛, 吴永尧, 彭振坤, 等.植物硒的研究进展[J].湖北民族学院学报:自然科学版, 2002, 20(3):58-62. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbmzxyxb-zrkx200203019
[12] 廖启林, 华明, 冯金顺, 等.苏南局部富硒土壤及其天然富硒茶叶初步研究[J].中国地质, 2007, 34(2):347-353. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.02.018
[13] 戴慧敏, 宫传东, 董北, 等.东北平原土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J].土壤学报, 2015, 52(6):1356-1364. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trxb201506015
[14] 王美珠, 章明奎.我国部分高硒低硒土壤的成因探讨[J].浙江农业大学学报, 1996, 22(1):89-93. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZJNY601.020.htm
[15] 王金达, 于君宝, 张学林.黄土高原土壤中硒等元素的地球化学特征[J].地理科学, 2000, 20(5):469-473. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2000.05.014
[16] 龚河阳, 李月芬, 汤洁, 等.吉林省西部土壤硒含量、形态分布及影响因素[J].吉林农业大学学报, 2015, 37(2):177-184, 190. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jlnydxxb201502009
[17] 付强, 王冬艳, 李月芬, 等.吉林中部黑土区土壤硒元素土壤地球化学研究[J].世界地质, 2014, 33(1):102-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2014.01.010
[18] 魏振山, 涂其军, 唐蜀虹, 等.天山北坡乌鲁木齐至沙湾地区富硒土壤地球化学特征及成因探讨[J].物探与化探, 2016, 40(5):893-898. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201605008
[19] 杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等.海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J].现代地质, 2012, 26(5):837-849. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.001
[20] 张丽珊, 朱岩, 可夫, 等.东北大骨节病病区主要土壤腐植酸硒与大骨节病关系的研究[J].应用生态学报, 1990, 1(4):333-337. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YYSB199004007.htm
[21] 迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊, 等.黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J].土壤学报, 2016, 53(5):1262-1274. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201605017
[22] 胡艳华, 王加恩, 蔡子华, 等.浙北嘉善地区土壤硒的含量、分布及其影响因素初探[J].地质科技情报, 2010, 29(6):84-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2010.06.014
[23] 内蒙古自治区土壤普查办公室, 内蒙古自治区土壤肥料工作站.内蒙古土壤[M].北京:科学出版社, 1994:420-421.
-



 下载:
下载: