Geochemistry of the Zhanbeicun Formation volcanic rocks in Xinlin area of northern Great Xing'an Range and its tectonic environment
-
摘要:
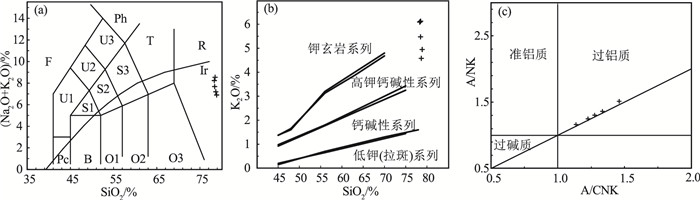
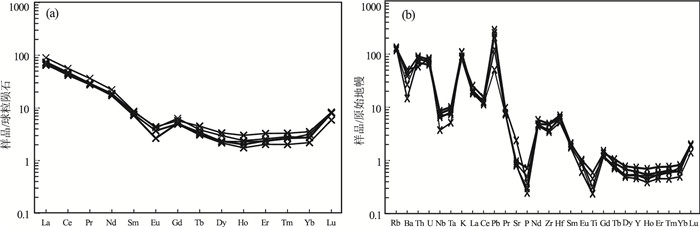
大兴安岭北段新林地区下侏罗统战备村组火山岩岩石组合主要为流纹岩、流纹质火山碎屑岩。岩石地球化学研究显示,流纹岩具有高硅、富碱、贫钙镁的特征,属于高钾钙碱性系列。火山岩稀土元素总量较低(ΣREE=81.84×10-6~110.32×10-6),轻、重稀土元素分馏明显,(La/Yb)N值为21.57~40.21,中等负Eu异常,δEu值为0.42~0.62。岩石富集大离子亲石元素Rb、K、Th、U,亏损高场强元素Nb、Ta、P、Ti,基性相容元素Cr、Co、Ni和Mg#值均较低,具有壳源岩浆的特点。流纹岩Sr、Yb值较低,具有喜马拉雅型花岗岩的特征。结合区域早侏罗世火山岩的构造特征,认为战备村组火山岩形成于蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋SE向俯冲的构造环境。
Abstract:The Lower Jurassic volcanic rocks of the Zhanbeicun Formation in Xinlin area of the northern Great Xing'an Range are petrographically composed of rhyolite and rhyolitic pyroclastic rocks.Chemically, these rhyolites belong to high-K calc-alkaline series characterized by high contents of silica, alkalis, low abundances of calcium and magnesium.The volcanic rocks have the characteristics of low ΣREE content(ΣREE=81.84×10-6~110.32×10-6), obvious differentiation between light rare earth and heavy rare earth elements[(La/Yb)N=21.57~40.21], with moderate negative Eu anomaly(δEu=0.42~0.62).These rocks also have characteristics of crust-derived magma with enrichment of large ion lithophile elements(LILEs, such as Rb, K, Th and U), depletion of high field strength elements(HFSEs, such as Nb, Ta, Ti and P)and lower content of basic compatible elements(such as Cr, Co and Ni)and Mg#.The low Sr and Yb content of rhyolites indicates that it is similar to Himalayan type.Combined with tectonic characteristics of the regional Early Jurassic volcanic rocks, it is suggested that the Zhanbeicun Formation volcanic rocks were formed in the tectonic background of the southeastward subduction of the Mongolia-Okhotsk ocean.
-
Key words:
- Lower Jurassic /
- Zhanbeicun Formation /
- tectonic setting /
- Great Xing'an Range
-

-
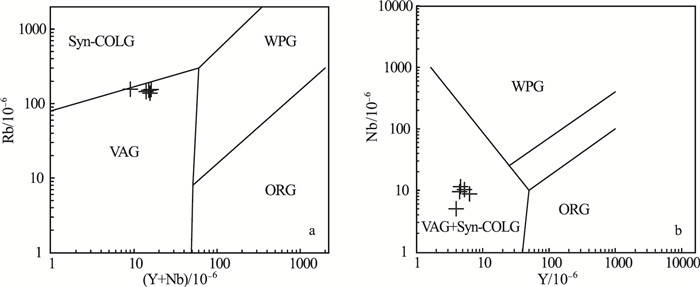
图 5 战备村组火山岩构造环境判别图[49]
Figure 5.
表 1 战备村组火山岩岩石化学测试分析数据
Table 1. Major, trace element and REE of Zhanbeicun Formation volcanic rocks
样品编号 P4T60 P4T74 P4T84 P4T96 P4T32 样品编号 P4T60 P4T74 P4T84 P4T96 P4T32 名称 流纹岩 流纹岩 流纹质晶屑凝灰岩 流纹岩 流纹质晶屑凝灰岩 名称 流纹岩 流纹岩 流纹质晶屑凝灰岩 流纹岩 流纹质晶屑凝灰岩 SiO2 77.49 77.72 77.65 77.73 77.62 Er 0.42 0.49 0.69 0.54 0.48 Al2O3 12.47 12.08 12.32 12.77 12.43 Tm 0.06 0.09 0.11 0.09 0.08 TiO2 0.1 0.1 0.25 0.13 0.19 Yb 0.47 0.59 0.77 0.58 0.69 Fe2O3 0.47 0.25 0.75 0.46 0.45 Lu 0.2 0.27 0.28 0.27 0.27 FeO 0.05 0.12 0.08 0.07 0.08 Li 8.57 18.5 14.42 8.44 16.4 CaO 0.07 0.09 0.08 0.17 0.09 Be 1.17 2.66 2.05 2.88 2.13 MgO 0.1 0.21 0.42 0.38 0.34 Nb 5 11.44 8.7 10.27 9.46 K2O 6.03 6.06 4.52 4.88 5.39 Sc 2.64 2.71 3.94 3.04 3.21 Na2O 2.12 2.37 2.54 1.92 2.27 Ga 14.52 17.43 18.25 17.65 16.45 MnO 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.02 Zr 72.3 77.7 99.8 104 78.5 P2O5 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.03 Th 9.14 12.51 10.84 14.13 13.4 灼失量 0.95 0.91 1.25 1.35 0.98 U 3.24 2.88 2.45 3.1 2.63 总计 99.89 99.95 99.91 99.89 99.89 Sr 32.2 33.3 38.9 95.5 35.4 Mg# 30.9 56.03 53.58 62.55 59.95 V 22.3 5.7 36.2 6.4 15.6 TFeO 0.48 0.34 0.76 0.48 0.48 Cr 6.13 5.86 6.96 6.07 6.9 σ 1.93 2.05 1.44 1.33 1.69 Ba 666.2 192 507.6 580.4 346 A/CNK 1.23 1.14 1.34 1.46 1.28 Rb 155.8 154.5 150.9 137.4 144.5 A/NK 1.25 1.16 1.36 1.51 1.3 Pb 6.66 37.23 15.99 32.49 26.63 Y 4.01 4.66 6.38 5.33 4.52 Co 0.21 0.13 0.41 0.08 0.25 La 23.93 26.68 23.2 32.54 25.58 Ni 0.85 0.72 1.24 0.63 0.8 Ce 37.6 42.66 40.36 51.41 41.56 Hf 3.01 3.69 3.66 4.09 3.46 Pr 3.76 4 4.03 5.05 3.9 Ta 0.39 0.78 0.61 0.71 0.57 Nd 11.3 11.21 12.36 14.7 12.01 ΣREE 81.84 90.07 86.92 110.3 99.89 Sm 1.56 1.47 1.71 1.79 1.52 (La/Yb)N 36.88 32.56 21.57 40.21 32.55 Eu 0.27 0.19 0.33 0.31 0.28 (La/Sm)N 8.28 9.92 11.72 8.74 10.46 Gd 1.32 1.38 1.55 1.72 1.35 (Gd/Yb)N 2.34 1.94 1.66 2.45 2.11 Tb 0.15 0.15 0.22 0.19 0.17 δEu 0.59 0.42 0.62 0.55 0.59 Dy 0.69 0.74 1.09 0.96 0.73 Zr/Hf 24.04 21.04 27.25 25.45 27.06 Ho 0.12 0.14 0.22 0.17 0.16 Nb/Ta 12.67 14.71 14.19 14.55 15.31 注:σ=(Na2O+K2O)2/(SiO2-43), TFeO=FeO+0.8998Fe2O3;Mg#=100×n(Mg2+)/[(n(Mg2+)+n(Fe2+)];主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
[1] 孙德有, 苟军, 任云生, 等. 满洲里南部玛尼吐组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄与地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(10): 3083-3094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201110024.htm
[2] 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等. 中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景: 来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(2): 339-353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201302002.htm
[3] 唐杰, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 张广才岭帽儿山组双峰式火岩成因: 年代学与地球化学证据[J]. 世界地质, 2011, 30(4): 508-513. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2011.04.002
[4] 郑吉林, 王文东, 杨华本, 等. 大兴安岭北部下侏罗统战备村组的建立及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(7): 1106-1114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.07.006 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160707&flag=1
[5] 王泉, 表尚虎, 李喜明, 等. 黑龙江省孙吴地区早侏罗世火山岩的识别及其地质意义[J]. 矿产与地质, 2017, 31(2): 378-388. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2017.02.026
[6] 李研, 王建, 韩志滨, 等. 大兴安岭北段八大关地区早侏罗世流纹岩锆石U-Pb定年与岩石成因[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(2): 346-357. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201702011.htm
[7] 赵胜金, 于海洋, 申亮, 等. 大兴安岭北段下侏罗统柴河组的厘定及地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(7): 1302-1313. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180714&flag=1
[8] 赵国龙, 杨桂林, 王忠, 等. 大兴安岭中南部中生代火山岩[M]. 北京: 科学技术出版社, 1989: 1-260.
[9] 马家骏, 方大赫. 黑龙江省中生代火山岩初步研究[J]. 黑龙江地质, 1991, 2(2): 1-6. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97312A/199102/516379.html
[10] 孙德有, 许文良, 周燕, 等. 大兴安岭中生代火山岩的形成机制[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通讯, 1994, 3: 162-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH403.015.htm
[11] Zhang J H, Ge W C, Wu F Y, et al. Large-scale Early Cretaceous volcanic events in the northern Great Xing'an Range, Northeastern China[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102: 138-157. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.08.011
[12] Zhang J H, Gao S, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China: Implications for subduction-induced delamination[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 27(6): 144-165. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254110001774
[13] 张宏, 马俊孝, 权恒, 等. 大兴安岭北段中生代火山岩形成的动力学环境[J]. 贵金属地质, 1999, 8(1): 56-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD901.012.htm
[14] 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟堡垒, 等. 大兴安岭中生代伸展造山过程中的岩浆作用[J]地学前缘, 1996, (4): 339-346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY199904025.htm
[15] 林强, 葛文春, 孙德有, 等. 东北地区中生代火山岩的大地构造意义[J]. 地质科学, 1998, 3(32): 129-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX802.000.htm
[16] 葛文春, 林强, 孙德有, 等. 大兴安岭中生代玄武岩的地球化学特征: 壳慢相互作用的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 1999, 15(3): 396-407. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199903007.htm
[17] 吴福元, 曹林. 东北地区的若干重要基础地质问题[J]. 世界地质, 1999, 18(2): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ902.001.htm
[18] Meng Q R. What drove Late Mesozoic extension of the northern China-Mongolia tract[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 36(9): 155-174. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/article/cpfdtotal-dzdq200312005012.htm
[19] Wang P J, Chen F K, Shen S M, et al. Geochemical and Nd-Sr-Pb isotopic composition of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Songliao basin, NE China[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2006, 40: 149-159. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.40.149
[20] 陈志广, 张连昌, 周新华, 等. 满洲里新右旗火山岩剖面年代学和地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(12): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200612013.htm
[21] 张玉涛, 张连昌, 英基丰, 等. 大兴安岭北段塔河地区早白垩世火山岩地球化学及源区特征[J]. 岩石学报2007, 23(11): 2811-2822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.012
[22] Ying J F, Zhou X H, Zhang L C, et al. Geochronological framework of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, NE China, and their geodynamic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 39(6): 786-793. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.04.035
[23] 徐美君, 许文良, 孟恩, 等. 内蒙古东北部额尔古纳地区上护林-向阳盆地中生代火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(9): 1321-1338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.001 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110901&flag=1
[24] Yu J J, Wang F, Xu W L, et al. Early Jurassic mafic magmatism in the Lesser Xing'an-Zhangguangcai Range, NE China and its tectonic implications: Constrains from zircon U-Pb chronology and geochemistry[J]. Lithos, 2012, 142/143: 256-266. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.03.016
[25] Wu F F, Sun D Y, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1): 1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
[26] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(s1/2): 34-43. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254108003501
[27] Winchester J A, Floyd P A. Geochemical magma type discrimination: application to altered and metamorphosed basic igneous rocks[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1976, 28(3): 459-469. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X76902077
[28] Le Maitre R W, Bakteman P, Dudek A, et al. A Classification of Igneous Rocks and Glossary of Terms Oxford: Blackwell[M]. Scientific Publications, 1989: 1-193.
[29] Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Elsevier, 1984: 63-114.
[30] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of ocean basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in Oceanic Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42: 313-345.
[31] Hirose K. Melting experiments on lherzolite KLB-1 under hydrous conditions and generation of high-magnesian andesitic melts[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(1): 42-44. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0042:MEOLKU>2.3.CO;2
[32] Tischendorf G, Paelchen W. Zur Klassifikation von Granitoiden. Classification of granitoids[J]. Zeitschrift fuer Geologische Wissenschaften, 1985, 13(5): 615-627. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/294693677_Zur_Klassifikation_von_Granitoiden
[33] Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[C]//Rudnick R L. Treatiseo Geochemisty. Elsevier, 2003, 3: 1-64.
[34] Hofmann A W. Chemical differentiation of the Earth: the relationship between mantle, continental, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Scientific Letters, 1988, 90(3): 297-314. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(88)90132-X
[35] Wedepohl K H. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(7): 1217-1232. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2
[36] 张遵忠, 顾连兴, 吴昌志, 等. 东天山印支早期尾亚石英正正长岩: 成岩作用及成岩意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(5): 1135-1149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605007.htm
[37] Xu M J, Xu W L, Wang F, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Early Jurassic granitoids in then orthwestern Lesser Xing an Range, NE Chaina and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologina Sinica, 2013, 29(2): 34-368. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/282283160_Geochronology_and_geochemistry_of_the_Early_Jurassic_granitoids_in_the_central_Lesser_Xing'an_Range_NE_China_and_its_tectonic_implications/download
[38] 王召林, 金浚, 李占龙, 等. 大兴安岭中北段莫尔道嘎地区含矿斑岩的U-Pb锆石年龄Hf同位素特征及成矿意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 796-810. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.06.015
[39] Chen Z G, Zhang L C, Wan B, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Wunugetushan porphyry Cu-Mo deposit in NE China, and their geological significance[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 43(1): 92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.08.007
[40] Li N, Chen Y J, Ulrich T, et al. Fluid inclusion study of the Wunugtu Cu-Mo deposit, InnerMongolia, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(5): 467-482. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0384-1
[41] 李宇, 丁磊磊, 许文良, 等. 孙吴地区中侏罗世白云母花岗岩的年代学与地球化学: 对蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合时间的限定[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(1): 56-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201501004.htm
[42] 徐美君, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 小兴安岭中部早侏罗世花岗质岩石的年代学与地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(2): 354-368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201302003.htm
[43] 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22: 2249-2269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200609000.htm
[44] 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩按照压力的分类[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25: 1274-1278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.11.004 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2006011236&flag=1
[45] 张旗, 王焰, 熊小林, 等. 埃达克岩和花岗岩: 挑战与机遇[M]. 北京: 中国大地出版社, 2008: 1-344.
[46] 杨华本, 王文东, 闫永生, 等. 大兴安岭北段新林区塔木兰沟组火山岩成因及地幔富集作用[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(6): 1471-1486. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201606010.htm
[47] Kravchinsky V A, Cogne J P, Harbrt W P, et al. Evolution of the Mongol-Ocean as constrained by newpalaeomagnetic data from the Mongol-Okhotsk suture zone, Sliberia[J]. GeophysicalJourmal International, 2002, 148(1): 34-57. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.2002.01557.x
[48] Sorokin A A, Sorokin A P, Ponomarchuk VA, et al. The age and geochemistry of volcaic rocks on the eastern flank of the Umlekan-Ogodzha volcanoplutonic belt(Amurregion)[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2010, 51(4): 369-379. doi: 10.1016/j.rgg.2010.03.004
[49] Pearce J A, Lippard S J, Roberts S. Charactesitcs and tectonic significance of supra-subducion zone ophiolites. Geological Society[M]. London, Special Publications, 1984: 77-94.
① 黑龙江省地质调查院. 黑龙江1: 25万漠河县、漠河、兴安幅区调(修测)报告. 2016.
② 中国人民武装警察部队黄金第三支队. 1: 5万战备村、二中队幅区域地质矿产调查报告. 2014.
-



 下载:
下载: