The cycles filtered from natural gamma-ray logging curves of Lower-Middle Cambrian in the Tarim Basin and their significance in sedimentary sequence division
-
摘要:
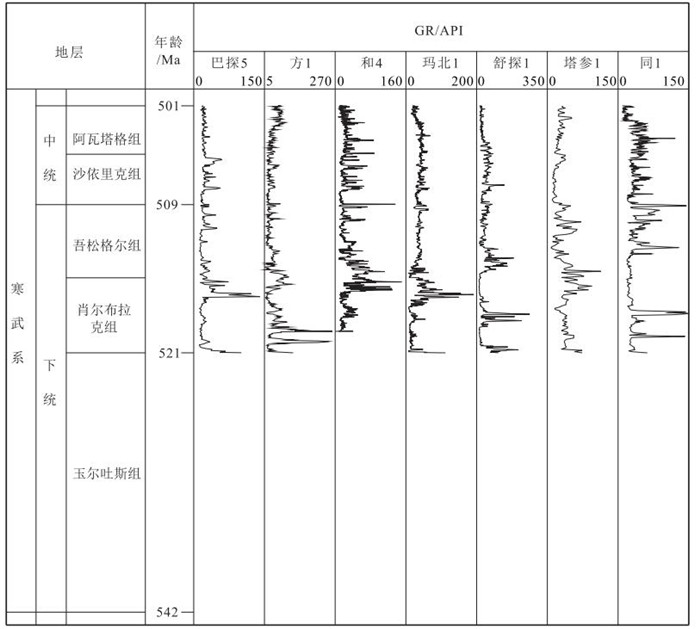
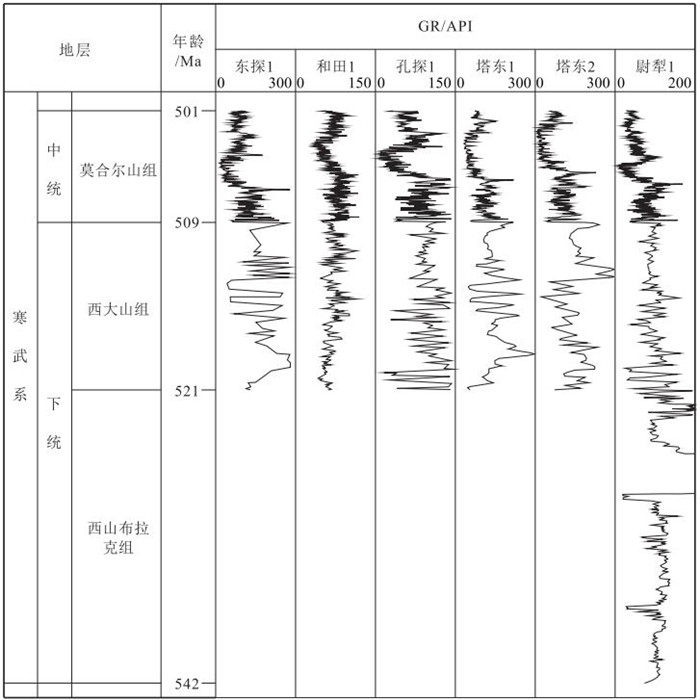
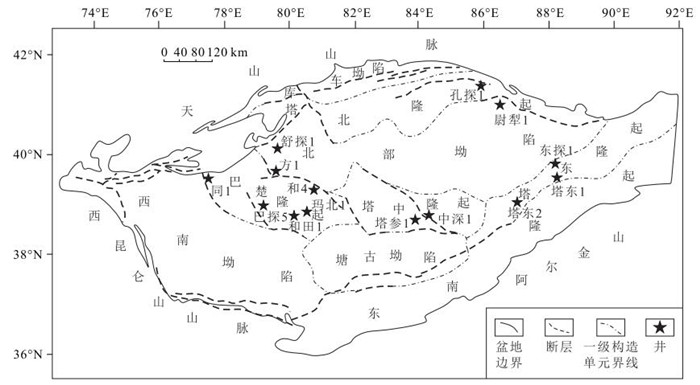
盆地的沉积充填能够反映出周期性地质过程和天文过程。塔里木盆地中下寒武统地层保存完整,有较完整的自然伽马(GR)曲线。利用环满加尔坳陷的13口钻井的自然伽马(GR)曲线,施行经验模态分解,得到0.3 Ma、2 Ma和11 Ma的周期。0.3 Ma的峰值对应地球轨道偏心率的40万年周期性变化,2 Ma周期对应冰川型海平面变化周期,11 Ma周期对应太阳能量变化周期或星际云团相遇周期。这些周期补充和校准了先前得到的地质或天文周期,并能帮助理解古气候变化周期和高频层序地层。
Abstract:The sedimentary fill of a basin always reflects periodic geological and astronomical processes.The sequence of the Lower-Middle Cambrian in the Tarim Basin has been preserved well with no erosion and has some gamma-ray (GR) well logging curves.Thirteen GR curves in the Lower-Middle Cambrian around Manjiaer depression were applied to wave analysis in terms of the empirical mode decomposition, and the time cycles of 0.3 Ma, 1~2 Ma and 10~11 Ma were obtained.The 0.3 Ma period corresponds to the change cycle of the earth's orbital eccentricity, the 1~2 Ma period to that of the glacier-type eustasy, and the 10~11 Ma period to that of the earth's rotation angular velocity or that of the solar energy.These periods have supplemented and corrected previous geological and astronomical cyclic sequence and are of significance in understanding both paleoclimate change and high frequency sedimentary sequence.
-
Key words:
- gamma-ray well logging /
- carbonate /
- Cambrian /
- wave /
- cycle
-

-
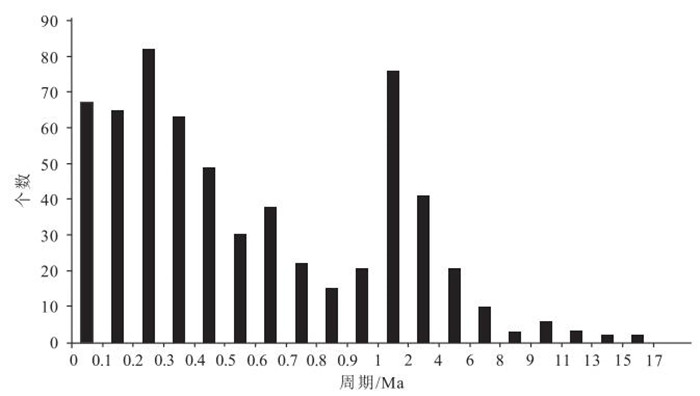
表 1 提取周期统计结果
Table 1. Cycles filtered from GR curves
序号 周期 频数 1 0.1 67 2 0.2 65 3 0.3 82 4 0.4 63 5 0.5 49 6 0.6 30 7 0.7 38 8 0.8 22 9 0.9 15 10 1 21 11 1.1 12 12 1.2 13 13 1.3 7 14 1.4 4 15 1.5 16 16 1.6 3 17 1.7 7 18 1.8 2 19 1.9 11 20 2 1 22 2.2 3 23 2.4 7 24 2.5 4 25 25 2.7 26 2.9 5 27 3.2 2 28 3.4 7 29 3.7 4 30 3.8 1 31 3.9 2 32 4.1 7 33 4.2 1 34 4.4 3 35 4.8 1 36 4.9 3 37 5 2 38 5.1 1 39 5.4 1 40 5.6 1 41 5.8 1 43 6.3 2 44 6.6 2 45 6.7 1 46 7.4 1 47 7.8 1 48 8.3 1 49 8.5 1 50 9 1 51 9.5 1 52 9.8 1 53 10.2 1 54 10.7 2 55 11 1 56 11.5 1 57 11.9 1 58 12.2 1 59 13.2 1 60 13.9 1 61 15.1 1 表 2 周期划分及原因
Table 2. Cycle divisions and their mechanisms
周期/Ma 原因 一级 220 银河年, 软流圈对流周期 120 ~ 60 陆壳下地幔热周期, 板块碰撞周期 二级 40 ~ 30 太阳系在银道面一侧的时间, 其它地内地外因素 11 ~ 10 太阳能量变化周期, 地球自转角速度变化周期, 星际云团相遇周期 三级 2 冰川型海平面变化周期, 太阳系向奥特星云靠近周期 四级 0.3 ~ 0.1 地球公转轨道偏心率变化周期 0.04 地球黄道与赤道的交角变化周期 0.02 地球的自转轴进动变化周期 -
[1] Tomschey O, Benkó F.Geological and cosmogonic cycles as reflected by the new law of universal cyclicity[M].Budapest:Akadémiai Kiadóiadd Kiadó, 1985:1-400.
[2] 王鸿祯.地球的节律与大陆动力学的思考[J].地学前缘, 1997, 4(3/4):1-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY7Z2.001.htm
[3] 张一伟, 李京昌, 金之钧, 等.中国含油气盆地波状运动特征研究[J].地学前缘, 1997, 4(3/4):305-311. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY7Z2.053.htm
[4] Jin Z J, Zhang Y W, Chen S P.Tectono-sedimentary wave processes in Tarim basin, Northwest China[J].Science in China (Series D), 2005, 35:530-539. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1360/04yd0087
[5] Chen S P, Jin Z J, Wang Y, et al.Sedimentation rate rhythms:evidence from filling of the Tarim Basin, Northwest China[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(4):1264-1275. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12527
[6] Hays J D, Imbrie J, Shackelton N J.Variations in the earth's orbit:Pacemaker of the Ice Ages[J].Science, 1976, 194(4270):1121-1132 doi: 10.1126/science.194.4270.1121
[7] Parka J, Oglesby R J.Milankovitch rhythms in the Cretaceous:A GCM modelling study[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1991, 90(4):329-355. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(12)80034-4
[8] Petit J R.Climate and atmospheric history of the past 420, 000 years from the Vostok ice core, Antarctica[J].Nature, 1999, 399(3):429-436. doi: 10.1038/20859
[9] Osmond J K, Ivanovich M.Uranium-series Mobilisation and Surface Hydrology[C]//Ivanovich M, Harmon R S.Uranium-series Disequilibrium: Applications to Earth, Marine and Enviromental Science.Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1992: 259-289.
[10] Johan H V, Postma G.Astronomically forced variations in gamma-ray intensity:Late Miocene hemipelagic successions in the eastern Mediterranean basin as a test case[J].Geology, 1996, 24(1):15-18. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1996Geo....24...15T/abstract
[11] Schnyder J, Ruffell A, Deconinck J F, et al.Conjunctive use of spectral gamma-ray logs and clay mineralogy in defining late Jurassic-early Cretaceous palaeoclimate change (Dorset, U.K.)[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 229(4):303-320. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.06.027
[12] 吴欣松, 郭娟娟, 黄永建, 等.松辽盆地晚白垩世古气候变化的测井替代指标[J].古地理学报, 2011, 13(1):103-110. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb201101010
[13] 梁文君, 肖传桃, 代城建, 等.自然伽马曲线应用于古气候、古环境研究——以柴达木盆地七个泉地区古近-新近纪地层为例[J].矿产与地质, 2015, 29(5):698-702. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2015.05.028
[14] 吴崇筠, 薛叔浩.中国含油气盆地沉积学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1993.
[15] 杨平, 陈晔, 刘泽纯.柴达木盆地自然伽马曲线在古气候及沉积环境研究中的应用[J].古地理学报, 2003, 5(1):94-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2003.01.009
[16] Herbert T D.Long climatic time series from sediment physical property measurements[J].Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1991, 61(7):1089-1108. doi: 10.1306/D4267843-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[17] 金之钧, 范国章, 刘国臣.一种地层精细定年的新方法[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 1999, 24(4):379-282. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx199904011
[18] 石巨业, 金之钧, 刘全有, 等.基于米兰科维奇理论的高精度旋回识别与划分——以南图尔盖盆地Ary301井中侏罗统为例[J].沉积学报, 2017, 35(3):436-447. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201703002
[19] 吴林, 管树巍, 任荣, 等.前寒武纪沉积盆地发育特征与深层烃源岩分布——以塔里木新元古代盆地与下寒武统烃源岩为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(6):905-915. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201606007
[20] 任荣, 管树巍, 吴林, 等.塔里木新元古代裂谷盆地南北分异及油气勘探启示[J].石油学报, 2017, 38(3):255-266. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201703002
[21] 石开波, 刘波, 姜伟民, 等.塔里木盆地南华纪-震旦纪构造-沉积格局[J].石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5):862-877. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201805002
[22] 汤良杰.略论塔里木盆地主要构造运动[J].石油实验地质, 1997, 19(2):108-114. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYSD199702001.htm
[23] Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, et al.The empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J].Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A, 1998, 454:903-995. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193
[24] 高庆华.地壳运动问题[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996:1-194
[25] Ezer D, Cameron A G W.Effects of sudden mixing in the solar core on solar neutrinos and ice ages[J].Nature, 1972, 240:180-182. http://core.ac.uk/display/10305374
[26] Napier W M.Evidence for cometary bombardment episodes[J].Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2006, 366(3):977-982. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09851.x
[27] 李前裕, 田军, 汪品先.认识偏心率周期的地层古气候意义[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2005, 30(5):519-528. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200505002
[28] 汪品先.低纬过程的轨道驱动[J].第四纪研究, 2006, 26(5):694-701. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.05.003
[29] 刘复刚, 王建, 张富, 等.地球轨道偏心率40万年和10万年周期的行星驱动[J].地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(1):25-33. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxjz201401004
[30] 史晓颖.35 Ma——地质历史上一个重要的自然周期[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 1996, 21(3):235-242. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94035X/199603/2018599.html
[31] 威尔格斯C K(编).徐怀大, 等(译).层序地层学原理[M].北京: 石油工业出版社, 1994: 1-200.
-



 下载:
下载: