Geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes of the Early Permian volcanic rocks in Hangwula of northern Alxa area and their tectonic significance
-
摘要:
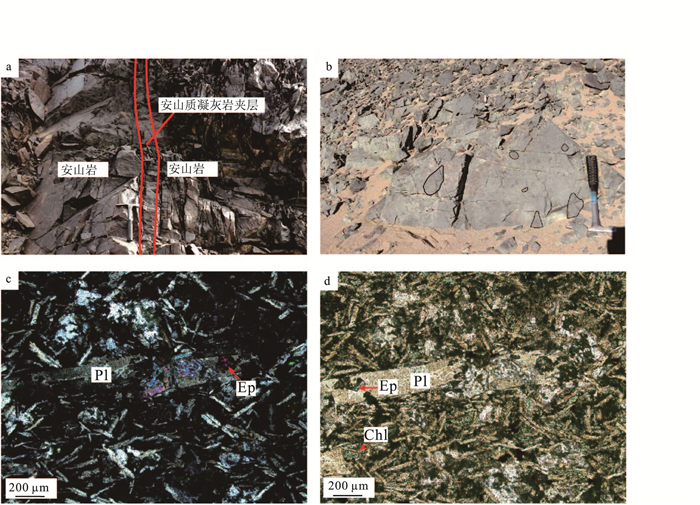
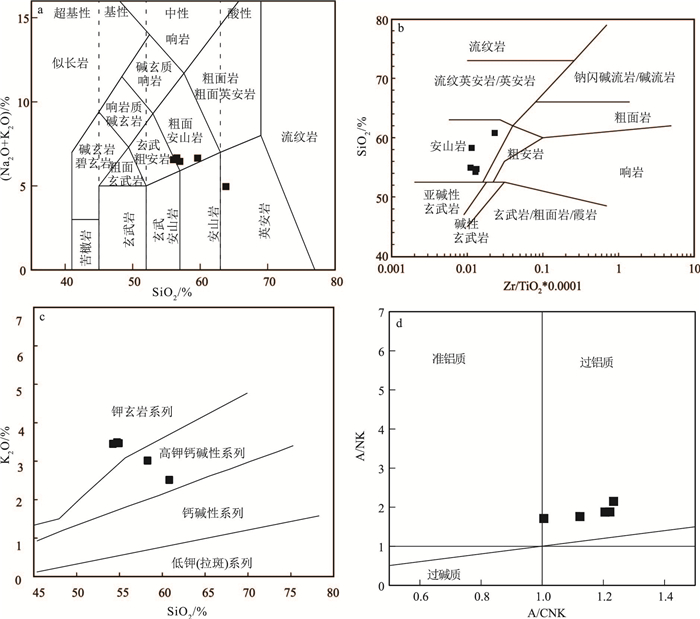
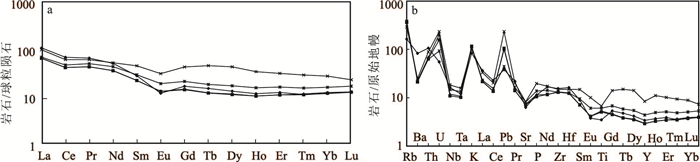
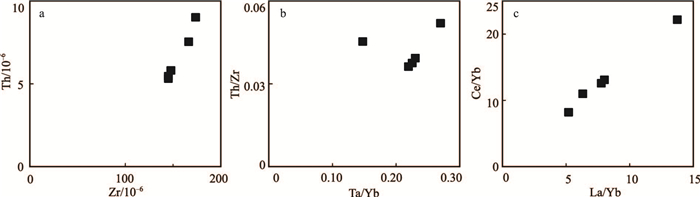
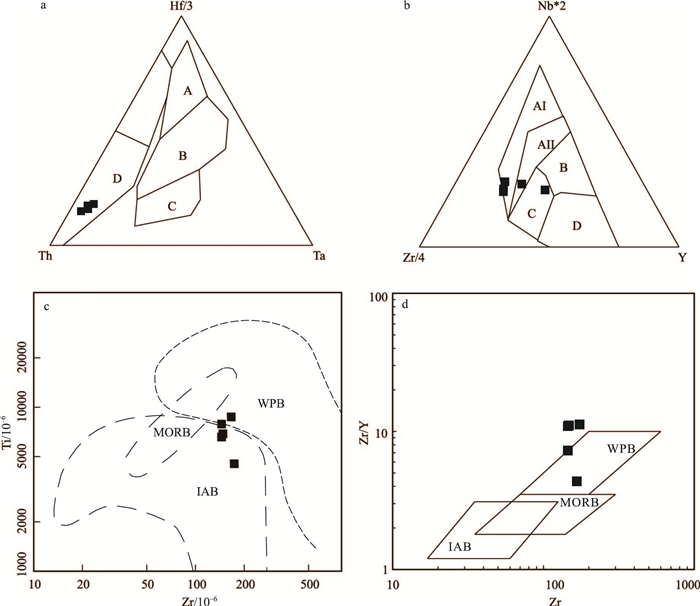
位于阿拉善恩格尔乌苏蛇绿岩带北侧的珠斯楞-杭乌拉构造带,分布较完整的早二叠世方山口组火山岩,对解析阿拉善地块晚古生代晚期的构造演化具有重要意义。方山口组以灰绿色安山岩、安山质角砾熔岩为主,局部含集块。安山岩SiO2含量为54.23%~60.81%,Al2O3为13.67%~15.96%,MgO为4.26%~5.76%,Mg#值为42~50;Na2O含量(2.21%~3.48%)与K2O(2.51%~3.49%)相当,具较高的TFe2O3(7.98%~11.24%),低的CaO(2.52%~3.36%)和TiO2(0.75%~1.32%),为过铝质钙碱性安山岩;安山岩在稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图上,轻稀土元素略富集,(La/Yb)N=3.73~9.86,具负Eu异常(δEu=0.52~0.75);在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图上,富集Rb、K,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等;变化范围非常大的εNd(t)(-4.3~-14.2)、εHf(t)(-19.8~+1.4)。上述特征表明,安山岩属于壳幔物质混合的产物,形成于板内裂谷环境。结合区域地质背景研究资料,进一步指出,恩格尔乌苏蛇绿岩带所代表的大洋在晚石炭世之前已经闭合;晚石炭世-早二叠世北山-阿拉善-内蒙古中部地区已进入板内构造岩浆-沉积阶段。
Abstract:Volcanic rocks of Fangshankou Formation are widely distributed in Hangwula area on the northern side of Engger Us ophiolitic belt in the Alxa area.These rocks are very essential for interpreting tectonic evolution of the southern part of Central Asian orogenic belt.Early Permian rocks in this stratum mainly consist of grayish green andesite and andesitic breccia lava, partly with agglomerate.The andesite has SiO2 content of 54.23%~60.81%, Al2O3 content of 13.67%~15.96%, MgO content of 4.26%~5.76%, and Mg# of 42~50 with the content of Na2O(2.21%~3.48%)less than that of K2O(2.51%~3.49%).These rocks also have high TFe2O3(7.98%~11.24%)and low CaO(2.52%~3.36%)as well as TiO2(0.75%~1.32%).They should be peraluminous calc-alkaline rocks.Andesite samples are enriched in light rare earth elements(LREE)and depleted in heavy rare earth elements(HREE).The differentiation between LREE and HREE is not obvious with(La/Yb)N equal to 3.73~9.86.Samples show negative Eu anomalies with δEu being 0.52~0.75.The chondrite-normalized REE patterns are similar to E-MORB.The samples of andesite are enriched in such elements as Rb and K and depleted in such elements as Nb, Ta and Ti.What's more, they have εNd(t)=-4.3~-14.2 and εHf(t)=-19.8~+1.4.These characteristics suggest that andesites were sourced from mixing of the mantle and the crust and formed in intraplate rift.Considering a lot of geological materials related to this area, the authors conclude that the branch of the PAO(Paleo-Asian Ocean)represented by Engger Us ophiolitic belt had been closed before Late Carboniferous, and that, during Late Carboniferous to Early Permian, magmatic activities in the study area occurred in an intraplate extensional setting.
-
Key words:
- Fangshankou Formation /
- volcanic rocks /
- Early Permian /
- Alxa area /
- Paleo-Asian Ocean
-

-
图 5 方山口组安山岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b) (标准化值据参考文献[41])
Figure 5.
表 1 方山口组安山岩主量、微量及稀土元素分析结果
Table 1. Major, trace and rare earth elements analytical results of andesites from Fangshankou Formation
样品号 16YG-80 16YG-81 16YG-82 16YG-83 16YG-84 SiO2 60.81 54.72 54.23 58.28 54.94 TiO2 0.75 1.10 1.15 1.46 1.32 Al2O3 13.67 15.46 15.96 15.85 14.88 TFe2O3 7.98 10.11 10.49 8.12 11.24 MnO 0.08 0.06 0.07 0.05 0.06 MgO 4.42 5.64 5.76 4.26 4.62 CaO 2.60 2.52 2.52 2.81 3.36 Na2O 2.21 2.71 2.89 3.48 3.00 K2O 2.51 3.49 3.45 3.02 3.47 P2O5 0.25 0.23 0.25 0.43 0.30 烧失量 4.85 2.93 3.03 1.77 3.00 总计 100.13 98.96 99.80 99.51 100.18 Mg# 49.70 49.86 49.46 48.31 42.27 Ba 579 148 156 175 159 Rb 104 231 230 184 242 Cs 1.41 17.68 17.88 14.24 23.33 Th 9.01 5.44 5.81 7.54 5.32 U 1.16 3.29 4.25 4.87 1.94 Nb 11.57 7.78 8.42 13.06 10.51 Ta 0.49 0.42 0.44 0.65 0.55 K 20872 28988 28666 25055 28802 Pb 2.70 7.43 7.08 16.56 3.12 Sr 133 149 155 174 170 Zr 174 145 148 166 145 Hf 4.99 3.79 3.89 4.60 3.88 P 1077 996 1095 1868 1305 Ti 4523 6580 6891 8724 7891 Cr 60.11 170 175 38.16 154 Ni 30.04 54.04 54.20 39.94 53.24 Co 32.81 34.72 25.88 36.00 53.07 V 76.43 129 135 127 135 Sc 13.71 22.40 23.29 21.42 23.45 Ga 22.49 20.30 21.19 20.58 21.95 La 25.01 14.82 14.89 22.72 15.75 Ce 40.38 24.22 24.11 35.86 27.44 Pr 6.02 3.90 3.89 5.55 4.55 Nd 22.69 15.81 15.74 23.41 19.26 Sm 3.98 3.15 3.15 6.57 4.19 Eu 0.63 0.69 0.70 1.69 1.02 Gd 3.17 2.67 2.74 8.36 4.04 Tb 0.52 0.41 0.42 1.62 0.63 Dy 3.07 2.58 2.66 10.37 4.01 Ho 0.60 0.54 0.54 1.81 0.81 Er 1.87 1.66 1.66 4.87 2.45 Tm 0.26 0.26 0.27 0.69 0.36 Yb 1.82 1.85 1.92 4.37 2.50 Lu 0.29 0.29 0.30 0.54 0.39 Y 15.46 13.28 13.37 38.26 19.96 ΣREE 110.32 72.85 72.97 128.44 87.40 LREE/HREE 8.51 6.10 5.96 2.93 4.75 δEu 0.52 0.71 0.71 0.70 0.75 δCe 0.78 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.78 (La/Yb)N 9.86 5.75 5.57 3.73 4.53 (Gd/Yb)N 1.44 1.19 1.18 1.58 1.34 (La/Sm)N 4.06 3.03 3.05 2.23 2.43 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 方山口组安山岩Nd-Hf同位素分析结果
Table 2. Whole-rock Lu-Hf isotope compositions of andesites from Fangshankou Formation
样品号 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd(2σ) fSm/Nd εNd(t) TDM(Nd)/Ma 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf(2σ) fLu/Hf εHf(t) TDM(Hf)/Ma YG-80 0.106034 0.511742± 3 -0.46 -14.21 1990 0.008306 0.282079± 5 -0.75 -19.83 2044 YG-81 0.120526 0.512279 ± 3 -0.39 -4.25 1426 0.011053 0.282713 ± 4 -0.67 2.09 1041 YG-82 0.121058 0.512278 ± 3 -0.38 -4.28 1436 0.010897 0.282694 ± 6 -0.67 1.43 1072 YG-83 0.169614 0.512041 ± 3 -0.14 -10.66 3809 0.016918 0.282386 ± 5 -0.49 -10.58 2111 -
[1] Wan B, Li S H, Xiao W J, et al.Where and when did the Paleo-Asian ocean form?[J].Precambrian Research, 2018, 317:241-252. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2018.09.003
[2] Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W J, et al.Tectonic models for accretion of the central asian orogenic belt[J].Geol.Soc.London, 2007, 164:31-47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
[3] Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Chen B.Granitoids of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and continental growth in the Phanerozoic[J].Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh:Earth Sciences, 2000, 91:181-193. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300007367
[4] Sengör A M C, Natalin B A, Burtman V S.Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J].Nature, 1993, 364:299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
[5] Badarch G, Dickson C W, Windley B F.A new terrane subdivision for Mongolia:implications for the Phanerozoic crustal growth of Central Asia[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 21:87-110. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00017-2
[6] Lehmann J, Schulmann K, Lexa O, et al.Structural constraints on the evolution of the Central Asian orogenic belt in SW mongolia[J].American Journal of Science, 2010, 310:575-628. doi: 10.2475/07.2010.02
[7] Xiao W J, Windley B F, Sun S, et al.A tale of amalgamation of three Permo-Triassic collage systems in central Asia:oroclines, sutures, and terminal accretion[J].Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2015, 43:477-507. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060614-105254
[8] Xiao W J, Windley B F, Han C M, et al.Late Paleozoic to early Triassic multiple roll-back and oroclinal bending of the Mongolia collage in Central Asia[J].Earth Science Reviews, 2017, 186:94-128. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=01d8c0dd8b7005c62e7be74b90a2311d
[9] 左国朝, 张淑玲, 何国琦, 等.北山地区早古生代板块构造特征[J].地质科学, 1990, 4:305-314, 411. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000368852
[10] 吴泰然, 何国琦.阿拉善地块北缘的蛇绿混杂岩带及其大地构造意义[J].现代地质, 1992, 6(3):286-296. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDDZ199203005.htm
[11] 吴泰然, 何国琦.内蒙古阿拉善地块北缘的构造单元划分及各单元的基本特征[J].地质学报, 1993, (2):97-108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE199302000.htm
[12] 王廷印, 王金荣, 王士政.阿拉善北部恩格尔乌苏蛇绿混杂岩带的发现及其构造意义[J].兰州大学学报, 1992, (2):194-196. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0455-2059.1992.02.037
[13] 王廷印, 刘金坤, 王士政, 等.阿拉善北部中蒙边界地区晚古生代拉伸作用及构造岩浆演化[J].中国区域地质, 1993, (4):317-327. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000004039358
[14] 王廷印.阿拉善地区古生代陆壳的形成和演化[M].兰州:兰州大学出版社, 1994.
[15] Han B F, Wang S G, Jahn B M, et al.Depleted-mantle source for the Ulungur River A-type granites from North Xinjiang, China:geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic evidence, and implications for Phanerozoic crustal growth[J].Chemical Geology, 1997, 138:135-159. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00003-X
[16] Charvet J, Shu L S, Laurent-Charvet S, et al.Palaeozoic tectonic evolution of the Tianshan belt, NW China[J].Science in China, 2011, 54:166-184. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1039-c1cc14396d/
[17] Han B F, He G Q, Wang X C, et al.Late Carboniferous collision between the Tarim and Kazakhstan-Yili terranes in the western segment of the South Tian Shan Orogen, Central Asia, and implications for the Northern Xinjiang, western China[J].Earth Science Reviews, 2011, 109:74-93. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.09.001
[18] 张文, 吴泰然, 冯继承, 等.阿拉善地块北缘古大洋闭合的时间制约:来自乌力吉花岗岩体的证据[J].地球科学, 2013, 43(8):1299-1311. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK201308006.htm
[19] Feng J Y, Xiao W J, Windley B F, et al.Field geology, geochronology and geochemistry of mafc-ultramafc rocks from Alxa, China:implications for Late Permian accretionary tectonics in the southern Altaids[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 78:114-142. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.01.020
[20] Zheng R G, Wu T R, Zhang W, et al.Late Paleozoic subduction system in the northern margin of the Alxa block, Altaids:Geochronological and geochemical evidences from ophiolites[J].Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(2):842-858. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.011
[21] Liu Q, Zhao G C, Han Y G, et al.Timing of the final closure of the PaleoAsian Ocean in the Alxa Terrane:constraints from geochronology and geochemistry of Late Carboniferous to Permian gabbros and diorites[J].Lithosphere, 2017, 274/275:19-30. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493716304649
[22] Song D F, Xiao W J, Collins A S, et al.Final subduction processes of the Paleo-Asian Ocean in the Alxa Tectonic Belt(NW China):Constraints from field and chronological data of Permian arc-related volcano-sedimentary rocks[J].Tectonics, 2018, 37:1658-1687. doi: 10.1029/2017TC004919
[23] Cleven N, Lin S, Guilmette C, et al.Petrogenesis and implications for tectonic setting of Cambrian suprasubduction-zone ophiolitic rocks in the central Beishan orogenic collage, Northwest China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113:369-390. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.038
[24] 姜亭, 李玉宏, 陈高潮, 等.内蒙古西部额济纳旗及邻区上石炭统-下二叠统阿木山组火山岩的地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(6):932-942. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.06.015 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110615&flag=1
[25] 党犇, 赵虹, 林广春, 等.内蒙古西部银根-额济纳旗盆地及邻区二叠纪火山岩的地球化学特征和构造环境[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(6):923-931. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.06.014 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110614&flag=1
[26] 曾勇.内蒙古阿拉善哈日敖日布格气象一带晚古生代花岗岩地球化学特征及构造意义[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1014233970.htm [27] 尹海权.内蒙古阿拉善地区北部古生代沉积及其大地构造演化特征[D].中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2016.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1016067686.htm [28] 宋嘉佳.阿拉善地块北部雅干断裂带周缘晚古生代花岗岩体特征[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2017.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1017129926.htm [29] Liu Q, Zhao G C, Han Y G, et al.Geochronology and Geochemistry of Paleozoic to Mesozoic Granitoids in Western Inner Mongolia, China:Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of the Southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].The Journal of Geology, 2018, 126(4):451-471. doi: 10.1086/697690
[30] Fei M M, Pan M, Xie C L, et al.Timing and tectonic settings of the Late Paleozoic intrusions in the Zhusileng, northern Alxa:implication for the metallogeny[J].Geosciences Journal, 2019, 23(1):37-57. doi: 10.1007/s12303-018-0018-z
[31] 郑亚东, 张青.内蒙古亚干变质核杂岩与伸展拆离断层[J].地质学报, 1993, 67(4):301-309. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400844711
[32] Webb L E, Graham S A, Johnson C L, et al.Occurrence, age, and implications of the Yagan-Onch Hayrhan metamorphic core complex, southern Mongolia[J].Geology.1999, 27(2):143-146. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0143:OAAIOT>2.3.CO;2
[33] 王涛, 郑亚东, 李天斌, 等.中蒙边界区亚干变质核杂岩的组成与结构[J].地质科学, 2002, 37(1):79-85. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2002.01.009
[34] 杨立业.内蒙古阿拉善北部二叠系地质特征与构造演化[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1014233806.htm [35] Wu T R, He G Q, Zhang C.On Palaeozoic Tectonics in the Alxa Region, Inner Mongolia, China[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 1998, 72(3):256-263. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1111/j.1755-6724.1998.tb00402.x
[36] Bao Z A, Zong C L, Fang L R, et al.Determination of Hf-Sr-Nd isotopic ratios by MC-ICP-MS using rapid acid digestion after flux-free fusion in geological materials[J].Acta Geochimica, 2018, 37(2):244-256. doi: 10.1007/s11631-017-0207-x
[37] Lebas M J, Lemaitre R W, Strekeisen A, et al.A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkalisilica diagram[J].Journal of Petroloy, 1986, 27(3):745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745
[38] Winchester J A, Floyd P A.Geochemical discrimination of different magma series their differentiation products using immobile elements[J].Chem.Geol., 1977, 20:325-345. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2
[39] Rickwood P C.Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J].Lithos, 1989, 22(4):247-263. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5
[40] Maniar P D, Piccolip M.Tectonic discrimination of granitoids.The Geological Society of America of Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
[41] Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J].Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[42] 唐功建, 王强, 赵振华, 等.西天山东塔尔别克金矿区安山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、元素地球化学与岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(6):1341-1352. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200906006
[43] Chen L, Zhao Z F.Origin of continental arc andesites:The composition of source rocks is the key[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 145:217-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.04.012
[44] Petford N, Atherton M.Na-rich Partial Melts from Newly Underplated Basaltic Crust:the Cordillera Blanca Batholith, Peru[J].Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37(6):1491-1521. doi: 10.1093/petrology/37.6.1491
[45] Jung S, Hoernes S, Mezger K.Synorogenic melting of mafic lower crust:constraints from geochronology, petrology and Sr, Nd, Pb and O isotope geochemistry of quartz diorites(Damara orogen, Namibia)[J].Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 2002, 143(5):551-566. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=714e6c4bc044998f37a64f037d3b4d15&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[46] Bonin B.Do coeval mafic and felsic magmas in post-collisional to within-plate regimes necessarily imply two contrasting, mantle and crustal, sources? A review[J].Lithos, 2004, 78(1/2):1-24. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b99d4ef7dc8a447aa6716bfd5156ebf3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[47] Lee C T A, Lee T C, Wu C T.Modeling the compositional evolution of recharging, evacuating, and fractionating(REFC)magma chambers:Implications for differentiation of arc magmas[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 143:8-22. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.08.009
[48] Guo F, Nakamuru E, Fan W M, et al.Generation of Palaeocene Adakitic Andesites by Magma Mixing; Yanji Area, NE China[J].Journal of Petrology, 2007, 48(4):661-692. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egl077
[49] 卿敏, 唐明国, 葛良胜, 等.内蒙古苏右旗毕力赫金矿区安山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、元素地球化学特征及其形成的构造环境[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):514-524. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201202013
[50] 贺健, 李龙明, 任升莲, 等.福建政和粗面安山岩的年代学、地球化学特征:对中国东南沿海晚中生代挤压-伸展构造的指示[J].地质科学, 2017, 52(2):592-615. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkx201702018
[51] Kelemen P B.Genesis of high Mg# andesites and the continental crust[J].Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1995, 120(1):1-19. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=fb3622d384b7fe45eacfb9e96557cbc3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[52] 林木森, 彭松柏, 乔卫涛.滇西腾冲更新世粗面安山岩Ar-Ar年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2017, 33(10):3137-3146. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201710011
[53] 纪政, 葛文春, 杨浩, 等.大兴安岭中段晚三叠世安第斯型安山岩:蒙古-鄂霍茨克大洋板片南向俯冲作用的产物[J].岩石学报, 2018, 34(10):2917-2930. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201810007
[54] Atherton M P, Petford N.Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust[J].Nature, 1993, 362(6416):144-146. doi: 10.1038/362144a0
[55] Rudnick R L, Gao S.Composition of the Continental Crust[J].Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 3:1-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-0016-7037(95)00038-2/
[56] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义, 等.利用地球化学方法判别大陆玄武岩和岛弧玄武岩[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, (1):77-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2007.01.011
[57] Wang X C, Wilde S A, Xu B, et al.Origin of arc-like continental basalts:Implications for deep-Earth fluid cycling and tectonic discrimination[J].Lithos, 2016, 261:5-45. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.12.014
[58] Taylor S R, McLennan S M.The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[J].The Journal of Geology, 1986, 94(4):632-633. doi: 10.1086/629067
[59] Fitton J G, Saunders A D, Norry M J, et al.Thermal and chemical structure of the Iceland plume[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 153:197-208. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00170-2
[60] Baker J A, Menzies M A, Thirlwall M F, et al.Petrogenesis of Quaternary Intraplate Volcanism, Sana'a, Yemen:Implications for Plume-Lithosphere Interaction and Polybaric Melt Hybridization[J].Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(10):1359-1390. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.10.1359
[61] Mecdonald R.Plume-Lithosphere Interactions in the Generation of the Basalts of the Kenya Rift, East Africa[J].Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(5):877-900. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.5.877
[62] Campbell I H, Griffiths R W.The Changing Nature of Mantle Hotspots through Time:Implications for the Chemical Evolution of the Mantle[J].Journal of Geology, 1992, 100(5):497-523. doi: 10.1086/629605
[63] Campbell I H, Griffiths R W.The evolution of the mantle's chemical structure[J].Lithos, 1993, 30(3/4):389-399. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-0024-4937(93)90047-G/
[64] 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等.Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, (2):185-220. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200702001
[65] 刘欣雨, 张旗, 张成立.全球新生代安山岩构造环境有关问题探讨[J].地质科学, 2017, 52(3):649-667. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkx201703002
[66] Wood D A.The application of a Th, Hf, Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary Volcanic Province[J].Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 50(1):11-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-0012-821X(80)90116-8/
[67] Meschede M.A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram[J].Chem.Geol., 1986, 56(3):207-218. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cc2424abfa7883b09b4e22b86032a617&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[68] Pearce J A.Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[J].Orogenic Andesites and Related Rocks, 1982:525-548. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=07172bff16d4303c212691c016029b47&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[69] 吴元伟.北山与银额地区晚古生代构造-沉积背景对比研究[D].长安大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1014071000.htm [70] 李永军, 李甘雨, 佟丽莉, 等.玄武岩类形成的大地构造环境Ta、Hf、Th、La、Zr、Nb比值对比判别[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2015, 37(3):14-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2015.03.004
[71] 党犇, 赵虹, 林广春, 等.阿拉善北部地区石炭纪火山岩岩石成因及构造意义[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2013, 38(5):963-974. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201305006
[72] 郑荣国, 李锦轶, 刘建峰.阿拉善地块北缘地区阿木山组火山岩时代:锆石U-Pb定年证据[J].中国地质, 2017, 44(3):612-613. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201703019
[73] 安屹.甘肃北山东部地区双峰式火山岩地球化学特征及构造意义研究[D].兰州大学硕士学位论文, 2018.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10730-1018979667.htm [74] Su B X, Qin K Z, Sakyi P A, et al.Geochemistry and geochronology of acidic rocks in the Beishan region, NW China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1):1-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
[75] Li S, Wilde S A, Wang T.Early Permian post-collisional high-K granitoids from Liuyuan area in southern Beishan orogen, NW China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].Lithos, 2013, 179:99-119. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.08.002
[76] Pang C J, Wang X C, Xu B, et al.Late Carboniferous N-MORB-type basalts in central Inner Mongolia, China:Products of hydrous melting in an intraplate setting?[J].Lithos, 2016, 261:55-71. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.05.005
-



 下载:
下载: