Geochemical characteristics and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of volcanic rocks in Shangqihan Formation along eastern orogenic belt in West Kunlun Mountains
-
摘要:
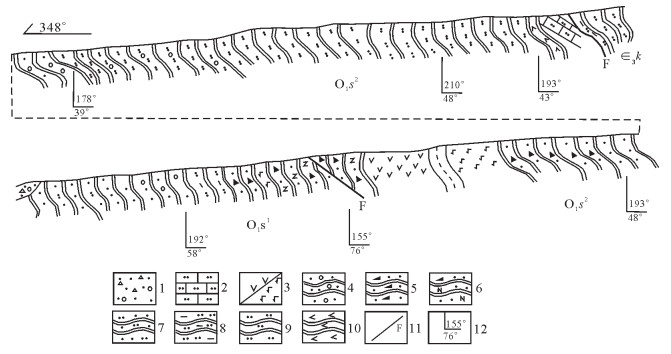
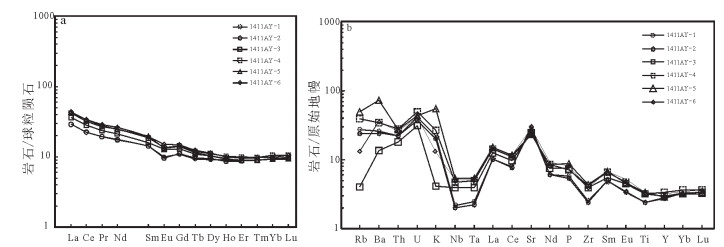
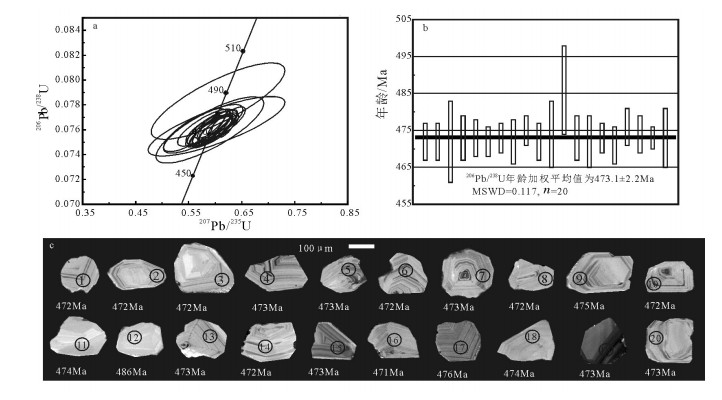
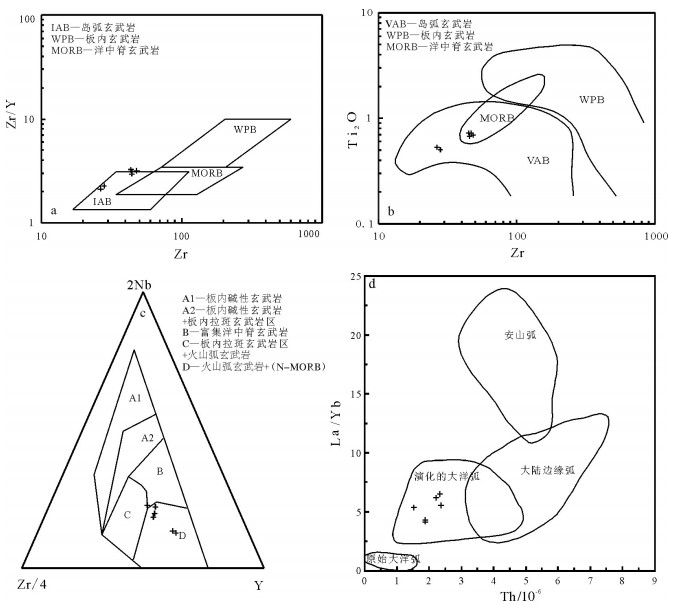
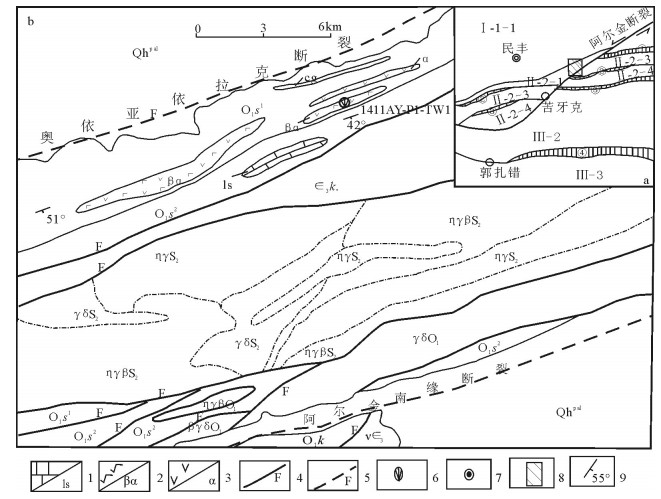
通过对西昆仑北带东段上其汗组玄武安山岩进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,获得锆石206Pb/238U年龄为473.1±2.2Ma,代表玄武安山岩的结晶年龄。研究区上其汗组火山岩富集大离子亲石元素Sr、Ba、U、Th等,亏损高场强元素Nb、Zr、Ta、Ti等,为消减带火山岩的标志性特征。不相容元素Th/Ta值为9.5~20.89,与上地壳的Th/Ta值(10)较接近。岩石具有较高的La/Nb值(2.73~4.89),明显高于大陆地壳这一比值(2.2),表明有地壳物质混染。同时,岩石中Nb含量较高,为8.14×10-6~12.3×10-6,Nb/Ta值为15.2~17.38,表明岩浆源区受到来自消减残留板片流体或熔体的交代作用。对岩石主量、微量元素特征、岩石学特征及大地构造背景综合分析认为,上其汗组火山岩形成于岛弧环境,其为库地-其曼于特洋在早古生代向北俯冲的产物。
Abstract:Through a study of LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotopes of basaltic andesite in Shangqihan Formation at the east segment in the northern belt of Western Kunlun Mountains, zircon 206Pb/238U isotopic age was obtained as 473.1±2.2Ma, which represents crystallization age of basaltic andesite. Shangqihan Formation volcanic rocks in the study area were rich in large ion lithophile elements such as Sr, Ba, U and Th, but were depleted in high field strength elements such as Nb, Zr, Ta and Ti, and these features are symbolic features of volcanic rocks in the subduction belt. Ratio of incompatible elements Th/Ta is within 9.5~20.89, relatively approximate to Th/Ta ratio (10) of the upper crust. Rocks have higher La/Nb ratios (2.73~4.89), obviously higher than the ratio (2.2) in continental crust, and this indicates hybridization of crust materials. In the meantime, Nb content in rocks is high (8.14×10-6~12.3×10-6)and Nb/Ta ratio is 15.2~17.38, which indicates magmatic source region was subjected to metasomatism from subducted residual sheet bar fluid or melt. According to comprehensive analysis of the major and trace element features, petrologic features and geotectonic background, it is believed that volcanic rocks in Shangqihan Formation were formed in an island arc environment and were products of Kudi-Qimanyute Ocean which pitched down in the northward direction in Early Paleozoic.
-
Key words:
- volcanic rocks /
- West Kunlun Mountains /
- Early Ordovician /
- Shangqihan Formation
-

-
表 1 样品主量、微量及稀土元素分析结果
Table 1. Major, trace and rare earth elements analytical results of samples
样品编号 1411AY-1 1411AY-2 1411AY-3 1411AY-4 1411AY-5 1411AY-6 岩石名称 安山岩 安山岩 安山岩 安山岩 玄武安山岩 玄武安山岩 SiO2 59.63 58.75 52.32 55.68 53.93 53.2 TiO2 0.49 0.5 0.66 0.67 0.69 0.7 Al2O3 13.04 14.03 16.35 14.85 16.46 17.13 Fe2O3 3.93 4.01 5.38 4.48 4.61 5 FeO 4.55 4.75 2.65 3.6 3.55 3.2 MnO 0.09 0.09 0.12 0.11 0.1 0.12 MgO 4.53 4.69 4.8 4.85 3.72 3.85 CaO 4.93 4.5 9.68 7.43 5.85 8.33 Na2O 3.31 3.21 3.64 3.52 3.43 3.79 K2O 0.64 0.58 0.12 0.76 1.55 0.37 P2O5 0.12 0.11 0.15 0.15 0.18 0.17 烧失量 4.05 4.11 4 3.84 5.71 3.89 总计 99.79 99.79 100.37 100.45 100.17 100.23 里特曼(σ) 0.87 0.85 1.33 1.32 1.96 1.5 碱度(A.R) 1.56 1.51 1.34 1.48 1.58 1.39 A/FM 0.57 0.59 0.72 0.64 0.81 0.83 分异指数 53.81 51.89 37.98 46.24 50.13 42.73 R1 2529 2510 2023 2137 1891 1962 R2 1059 1039 1667 1382 1206 1481 A/CNK 0.86 0.99 0.69 0.74 0.92 0.79 固结指数 26.78 27.28 29.36 28.4 22.2 24.03 K2O/Na2O 0.19 0.18 0.03 0.22 0.45 0.1 K2O+Na2O 3.95 3.79 3.76 4.28 4.98 4.16 La 6.97 6.94 8.66 9.89 10.3 10.4 Ce 13.8 13.7 17.2 19.6 20.6 20.7 Pr 1.84 1.85 2.26 2.56 2.63 2.73 Nd 8.14 8.33 9.99 11.6 11.4 12.3 Sm 2.19 2.2 2.44 2.89 3.02 2.99 Eu 0.56 0.58 0.75 0.79 0.77 0.88 Gd 2.28 2.23 2.69 2.96 2.87 3.06 Tb 0.36 0.35 0.41 0.45 0.43 0.46 Dy 2.4 2.32 2.61 2.84 2.64 2.88 Ho 0.49 0.51 0.53 0.58 0.54 0.57 Er 1.45 1.46 1.49 1.66 1.46 1.6 Tm 0.23 0.23 0.23 0.25 0.23 0.25 Yb 1.62 1.6 1.61 1.79 1.58 1.68 Lu 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.27 0.24 0.27 Y 12.5 12.7 13.5 15.1 13.2 14.5 Rb 17.4 15.2 2.57 24.8 31 8.4 K 5574.89 5054.36 1038.64 6562.31 13672.48 3202.81 Ba 183 170 94.2 242 505 245 Th 1.88 1.88 1.52 2.37 2.33 2.21 U 0.86 0.78 0.65 1.03 0.91 0.86 Nb 1.52 1.42 2.78 3.34 3.78 3.64 Sr 583 638 518 493 487 613 P 550.01 504.39 683.14 681.51 835.46 774.31 Zr 28.1 26.6 43.8 47.6 48.8 44.3 Hf 1.34 1.29 1.91 2.11 2.13 1.99 Ta 0.1 0.09 0.16 0.2 0.22 0.21 Cr 346 337 137 306 58.5 56.2 ∑REE 42.58 42.55 51.12 58.13 58.71 60.77 δEu 0.76 0.79 0.89 0.82 0.79 0.88 (La/Sm)N 2 1.98 2.23 2.15 2.37 2.15 (Ce/Yb)N 2.2 2.22 2.77 2.83 3.37 3.19 (Gd/Lu)N 1.13 1.10 1.33 1.36 1.98 1.48 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 表 2 上其汗组火山岩锆石U-Th-Pb年龄分析结果
Table 2. Zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of volcanic rocks in Shangqihan Formation
测点号 Th U Pb Th/U 同位素比值 表而年龄/Ma /10-6 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 45 214 66 0.21 0.0565 0.0023 0.5924 0.0233 0.0760 0.0008 473 69 472 15 472 5 2 36 121 38 0.30 0.0565 0.0030 0.5914 0.0310 0.0759 0.0009 472 96 472 20 472 5 3 27 86 27 0.31 0.0563 0.0065 0.5900 0.0671 0.0760 0.0018 465 213 471 43 472 11 4 165 357 116 0.46 0.0571 0.0028 0.5996 0.0283 0.0761 0.0010 496 81 477 18 473 6 5 30 201 62 0.15 0.0560 0.0026 0.5879 0.0267 0.0761 0.0009 453 80 470 17 473 5 6 63 209 66 0.30 0.0572 0.0021 0.5993 0.0211 0.0760 0.0007 499 61 477 13 472 4 7 85 235 75 0.36 0.0574 0.0021 0.6018 0.0209 0.0761 0.0007 506 59 478 13 473 4 8 34 132 42 0.26 0.0571 0.0030 0.5984 0.0304 0.0760 0.0009 497 91 476 19 472 6 9 77 232 75 0.33 0.0565 0.0022 0.5953 0.0227 0.0764 0.0007 473 68 474 14 475 4 10 119 288 94 0.41 0.0573 0.0022 0.6007 0.0219 0.0760 0.0008 504 62 478 14 472 5 11 17 44 14 0.39 0.0573 0.0082 0.6027 0.0851 0.0763 0.0016 503 280 479 54 474 9 12 27 62 22 0.43 0.0561 0.0078 0.6054 0.0832 0.0783 0.0020 456 262 481 53 486 12 13 32 131 43 0.25 0.0554 0.0034 0.5812 0.0344 0.0762 0.0010 426 110 465 22 473 6 14 44 101 34 0.43 0.0537 0.0038 0.5622 0.0391 0.0760 0.0011 357 131 453 25 472 7 15 99 420 139 0.24 0.0563 0.0017 0.5914 0.0169 0.0762 0.0007 465 48 472 11 473 4 16 31 120 40 0.25 0.0567 0.0027 0.5926 0.0271 0.0759 0.0008 478 83 473 17 471 5 17 48 265 88 0.18 0.0589 0.0023 0.6220 0.0231 0.0766 0.0008 563 62 491 14 476 5 18 68 94 33 0.72 0.0564 0.0031 0.5928 0.0316 0.0762 0.0009 469 98 473 20 474 5 19 815 2261 776 0.36 0.0593 0.0011 0.6225 0.0102 0.0762 0.0005 577 24 491 6 473 3 20 16 75 25 0.21 0.0551 0.0048 0.5774 0.0494 0.0761 0.0013 415 163 463 32 473 8 -
[1] 姜春发.中央造山带几个重要地质问题及其研究进展(代序)[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(8):453-455. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200208112&flag=1
[2] 刘彬, 马昌前, 蒋红安, 等.东昆仑早古生代洋壳俯冲与碰撞造山作用的转换:来自胡晓钦镁铁质岩石的证据[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(6):2093-2106. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201306017
[3] 贠杰.西昆仑北带晚古生代火山岩成因及构造背景研究[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2015.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1015389595.htm [4] 潘裕生, 王毅.青藏高原叶城-狮泉河路线地质特征及区域构造演化[J].地质学报, 1994, 86(4):295-307. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1994.04.007
[5] 潘裕生.西昆仑山构造特征及演化[J].地质科学, 1990, 3:224-232. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1011152758.htm
[6] 王东安, 陈瑞君.新疆库地西北一些克沟深海蛇绿质沉积岩岩石学特征及沉积环境[J].自然资源学报, 1989, 3:212-221. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1989-ZRZX198903003.htm
[7] 肖序常, 王军, 苏黎, 等.再论西昆仑库地蛇绿岩及其构造意义[J].地质通报, 2003, 22(10):745-750. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2003010145&flag=1
[8] 夏林圻, 徐学义, 夏祖春, 等.天山石炭纪碰撞后裂谷火山作用[J].地质学报, 2003, 3:358. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.03.018
[9] 杨树锋, 陈汉林, 董传万.西昆仑山库地蛇绿岩的特征及其构造意义[J].地质科学, 1999, 34(3):281-288. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199903003.htm
[10] 郑勇, 杨有生, 陈邦学, 等.东昆仑西段巴什康阔勒辉长岩地球化学特征及其构造意[J].现代地质, 2016, 30(5):1004-1013 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.05.006
[11] 计文化, 蔺新望, 王巨川, 等.西昆仑苏巴什蛇绿混杂岩带组成、特征及其地质意义[J].陕西地质, 2001, 19(2):40-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2001.02.005
[12] 李荣社, 计文化, 赵振明, 等.昆仑早古生代造山带研究进展[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(4):373-382. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070463&flag=1
[13] 刘成军.西昆仑造山带(西段)及周缘早古生代-早中生代物质组成与构造演化[D].长安大学博士学位论文, 2015: 1-170.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1015803385.htm [14] 李荣社, 计文化, 杨永成, 等.昆仑山及邻区地质图[M].北京:地质出版社, 2008.
[15] Mattem F, Schneider W. Suturing of the Proto-Paleo-Tethys oceans in the western Kunlun(Xijiang, China)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18:637-650. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00011-0
[16] 邓万明.喀喇昆仑-西昆仑地区蛇绿岩的地质特征及其大地构造意义[J].岩石学报, 1995, 11(增刊):98-111. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB5S1.007.htm
[17] 陈宁, 王炬川, 杨涛, 等.西昆仑上其汗地区火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及构造意义[J].中国地质调查, 2016, 3(3):21-18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdzdc201603004
[18] 陈邦学, 朱志新, 周能武, 等.新疆博格达东段阿克铁克协山地区辉绿岩岩石地球化学特征及其SHRIMP U-Pb测年意义[J].西北地质, 2015, 48(3):1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2015.03.001
[19] Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical geology, 2002, 192(1):59-79. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=500081c8e53f10c3181de6408e70a21d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[20] 寇贵存, 冯金炜, 罗宝荣, 等.青海阿木尼克山地区牦牛山组火山岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2017, 36(2/3):275-284. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2017020311&flag=1
[21] 王岚, 杨理勤, 王亚平, 等.锆石LA-ICP-MS原位微区U-Pb定年及微量元素的同时测定[J].地球学报, 2012, 33(5):763-772. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201205011
[22] Ludwig K R. Using isoplot/EX version2:a geolocronolgical toolkit for Microsoft excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronological Center Special Publication, 1999, 47:151-181.
[23] Sun S S, Mc Donough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implication for the mantle composition and process[C]//Saunder A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society of London Special Publication, London, 1989, 42: 313-345.
[24] Hess P C. Origins of igneous rocks[M]. London:Harvard University Press, 1989:109-275.
[25] 江庆源, 李才, 解超明, 等.藏北羌塘冈玛错地区望果山组火山岩地球化学特征及LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(13):1702-1714. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20141107&flag=1
[26] Irvine T N, Baragar W R A. A guide to the cheemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Cana. J. Earth Sci., 1971, 8:523-548 doi: 10.1139/e71-055
[27] Wilson M. Igneous Petrology[M]. London:Unwin Hyman, 1989:1-464.
[28] 李长民.锆石成因矿物学与锆石微区定年综述[J].地质调查与研究, 2009, 32(3):161-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2009.03.001
[29] 吴元保, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002
[30] 钟玉芳, 马昌前, 佘振兵.锆石地球化学特征及地质应用研究综述[J].地质科技情报, 2006, 25(1):27-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2006.01.005
[31] Weaver B L. The origin of ocean island basalt end-member composition:trace element and isotopic constraints[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1991, 104:381-397. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(91)90217-6
[32] Schmidberger S S, Hegner E. Geochemistry and isotope systematics of calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Saar-Nahe basin (SW Germany)-implications for Later Vaiscan orogenic development[J]. Contrib. Mineral. Pertrol., 1999, 135:373-385. doi: 10.1007/s004100050518
[33] Fitton J G, James D, Leeman M P. Basic magmatism associat-ed with Late Cenozoic extension in the western United States:compositional variation in space and time[J]. Geophys. Res., 1991, 96:13693-13711. doi: 10.1029/91JB00372
[34] Gill J B. Orogenic Andesites and Plate Tectonics[M]. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1981:358-360.
[35] 贾大成, 胡瑞忠, 卢焱, 等.湘东南汝城盆地火山岩的元素地球化学及源区性质讨论[J].现代地质, 2003, 17(2):131-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2003.02.003
[36] Condie K C. Chemical composition and evolution of the upper continental crust:contrasting results from surface samples and shales[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 104:1-37. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90140-E
[37] 李昌年.火成岩微量元素化学[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1992:1-195.
[38] Hollings P. Archean Nb-enriched basalts in the northern Superior Province[J]. Lithos, 2002, 64:1-14. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00154-8
[39] 邵铁全, 朱彦菲, 靳刘圆, 等.塔里木西南缘棋盘河乡玄武岩锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学研究[J].地质科学, 2015, 50(4):1120-1133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2015.04.006
[40] Pearce J A. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[C]//Andesites. 1982: 525-548.
[41] Pearce J A, Norry M J. Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb variations in volcanic rocks[J]. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1979, 69(1):33-47. doi: 10.1007/BF00375192
[42] Meschede M. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the NbZr-Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 56(3):207-218. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4f9cd6a0e41bca7a2c558b8fb8a53a5a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[43] Condie K C. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of early proterozoic supracrustal rocks in the southwestern united states[J]. Geology, 1986, 94:845-861. doi: 10.1086/629091
[44] 韩芳林, 崔建堂, 计文化, 等.西昆仑其曼于特蛇绿混杂岩的发现及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(8/9):573-578. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200208130&flag=1
[45] 黄朝阳, 王核, 刘建平, 等.西昆仑柯岗蛇绿岩地质地球化学特征及构造意义[J].地球化学, 2014, 43(6):592-601. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201406004
[46] 袁超, 孙敏, 肖文交, 等.原特提斯的消减极性:西昆仑128公里岩体的启示[J].岩石学报, 2003, 19(3):399-408. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200303003
[47] 贾群子, 李文明, 于浦生, 等.西昆仑块状硫化物矿床条件和成矿预测[M].北京:地质出版社, 1999.
① 新疆地矿局第十一地质大队.新疆西昆仑1: 5万J45E019001、J45E020001、J45E020002、J45E021001、J45E021002等5幅区调.2014.
② 河南省地质调查院.新疆1: 25万塔什库尔干塔吉克自治县幅区域地质调查报告. 2004.
-



 下载:
下载: