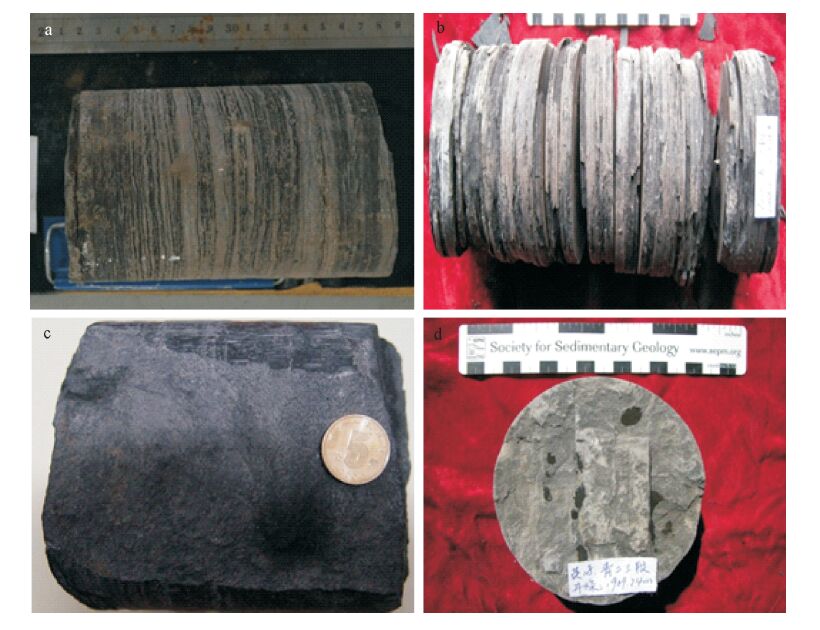
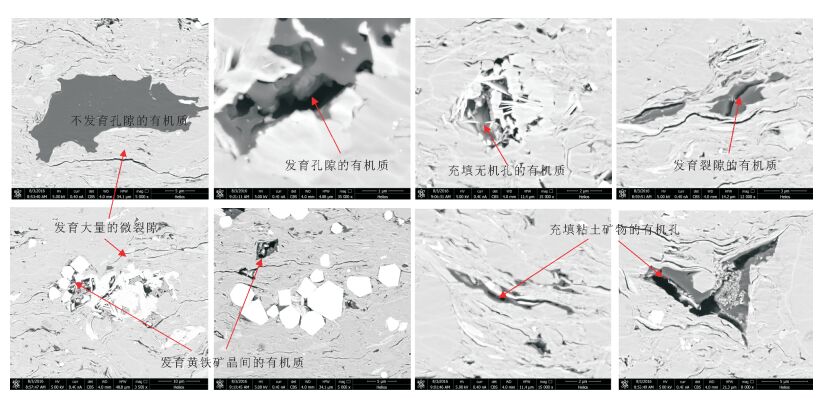
The characteristics of mudstones of Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation and favorable area optimization of shale oil in the north of Songliao Basin
-
摘要:
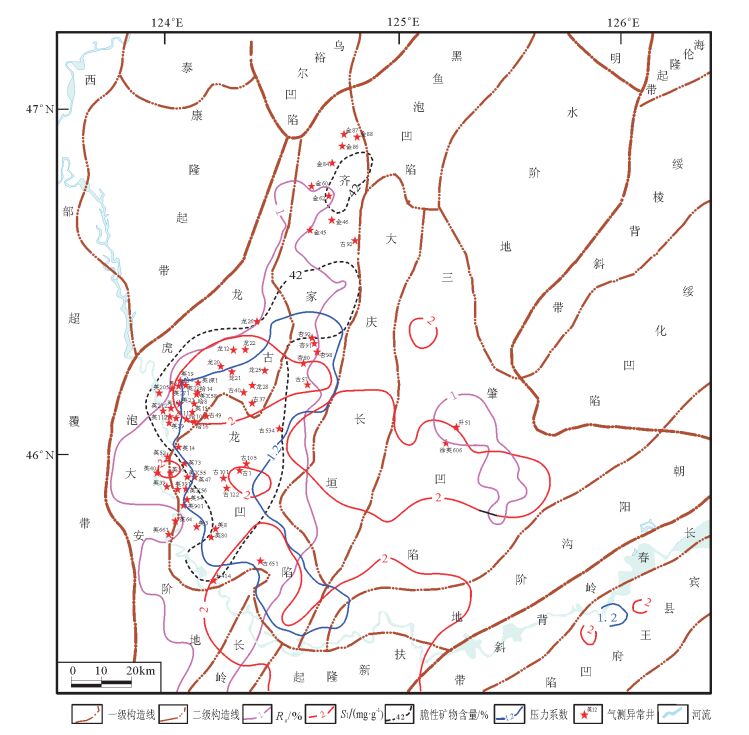
以松辽盆地北部为研究区域,以上白垩统青山口组一、二段泥岩为研究对象,通过国内外页岩油研究资料收集整理分析、典型井岩心观察、样品测试数据分析等,对研究区青山口组一、二段泥岩的岩性、物性、电性、含油气性、烃源岩、脆性及地应力特征七方面页岩油评价参数进行了研究,结果表明,松辽盆地北部上白垩统青山口组一、二段具有页岩油发育的有利石油地质条件,其中古龙凹陷为页岩油的有利区,具有良好的勘探前景。
Abstract:This study mainly focuses on the north of Songliao Basin with the purpose of investigating mudstone in the first and second member of Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation. Through the collection and analysis of the data available in China and abroad, core description of topical wells and sample test data analysis, the authors studied the lithology, physical property, electric property, oil-gas possibility, hydrocarbon, brittleness and ground stress of mudstone in the first and second member of Qingshankou Formation. The results show that the first and second member of Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in the north of Songliao Basin has favorable petroleum geological conditions for the development of shale oil, and Gulong sag seems to be a favorable area of shale oil with good exploration prospects.
-

-
表 1 齐平1井泥岩岩心物性分析数据
Table 1. Physical property analysis data of mudstone core of Qiping 1 well
样品编号 顶深/m 底深/m 原样体积密
度/(g· cm-3)原样颗粒密
度/(g· cm-3)原样充气
孔隙度/%干燥体积密
度/(g· cm-3)干燥颗粒密
度/(g· cm-3)干燥氦孔
隙度/%原样压降
渗透率/mD1-4 1929.20 1929.24 2.47 2.62 5.8 2.42 2.72 11 2.4×10-3 1-12 1937.18 1937.23 2.45 2.53 3.4 2.38 2.67 11.1 2.1×10-3 1-16 1940.98 1941.03 2.49 2.59 3.7 2.44 2.7 9.9 2.6×10-3 1-20 1945.17 1945.23 2.48 2.61 4.8 2.43 2.71 10.4 2.2×10-3 1-31 1956.66 1956.74 2.5 2.63 4.8 2.47 2.69 8.4 0.8×10-3 1-35 1959.97 1960.03 2.51 2.61 4.1 2.45 2.73 10.3 2.1×10-3 1-39 1964.7 1964.73 2.52 2.66 5.1 2.5 2.72 8.2 0.9×10-3 1-62 1987.67 1987.74 2.51 2.63 4.5 2.47 2.71 9.1 1.4×10-3 1-71 1996.16 1996.24 2.44 2.53 3.5 2.38 2.66 10.8 2.4×10-3 2-3 2002.17 2002.23 2.5 2.6 3.7 2.44 2.71 10 1.9×10-3 2-7 2006.48 2006.51 2.44 2.58 5.7 2.39 2.68 10.9 2.9×10-3 2-13 2012.48 2012.51 2.49 2.63 5.2 2.46 2.69 8.7 2.0×10-3 2-30 2028.98 2029.02 2.44 2.58 5.6 2.39 2.69 11 3.4×10-3 平均值 2.48 2.6 4.6 2.43 2.7 10 2.1×10-3 注:数据来源于大庆油田有限责任公司勘探开发研究院 表 2 松辽盆地北部青山口组一、二段烃源岩特征数据
Table 2. The characteristics of hydrocarbon in the first and second member of Qingshankou Formation in the north of Songliao Basin
凹陷名称 层段 泥岩厚度
/m有机质丰度 有机质成熟度 TOC/% TOC>2%的面积/km2 Ro/% Ro>1%的面积/km2 齐家凹陷 青一段 35~105 1.5~3.0 1788.4 0.6~2.0 864 青二段 50~200 1.0~1.6 0 0.6~1.1 91.49 古龙凹陷 青一段 40~85 1.5~2.4 1322.2 0.75~2.0 4107 青二段 110~230 1.0~2.3 147.5 0.6~1.4 1492.27 三肇凹陷 青一段 40~75 2.0~-3.5 5462 0.6~1.2 514 青二段 70~200 1.0~2.6 793.5 0.6~0.8 0 表 3 松辽盆地北部页岩油有利区优选参考标准及优选结果
Table 3. The standard and optimization result of favorable area for shale oil in the north of Songliao Basin
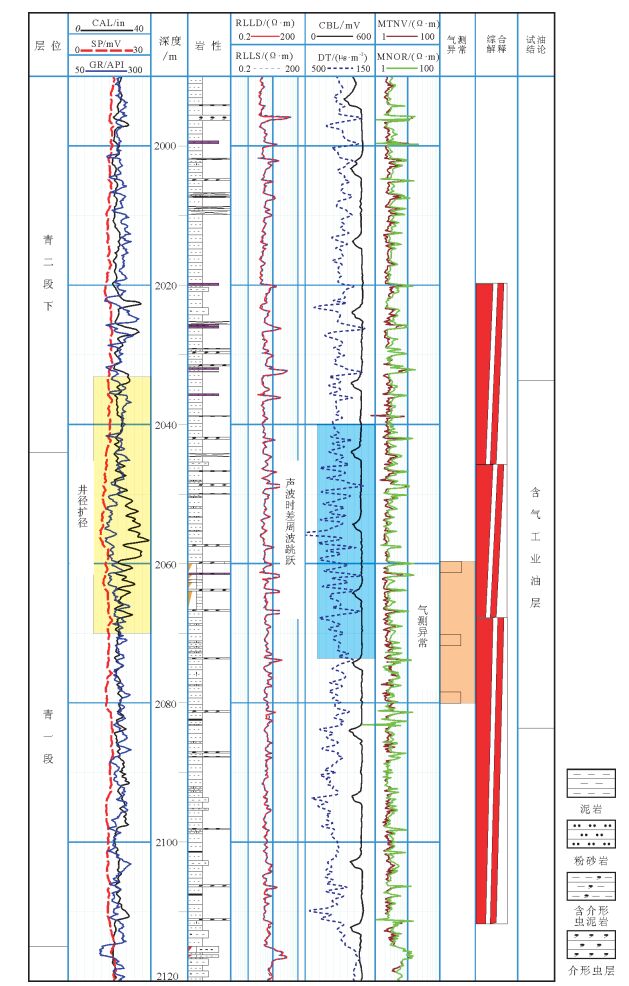
主要参数 参考标准 有利区 岩性 泥岩夹砂条或介形虫层 古龙 电性 扩径、声波周波跳跃 古龙 含
油
性气测 异常活跃 齐家、古龙 S1 >2.0mg/g 古龙、长垣、三肇 TI >80mg· HC/(g· C-1) 古龙、长垣、三肇 烃
源
岩泥页岩厚度 >30m 齐家、古龙、三肇 TOC >2.0% 齐家、古龙、三肇 Ro >1.0% 齐家、古龙、三肇 地层压力系数 >1.2 古龙 脆性特征 >42% 齐家、古龙 地应力 压差较小 齐家、古龙、三肇 表 4 古龙凹陷青山口组页岩油藏与美国鹰滩页岩油气藏特征对比
Table 4. A comparison of oil and gas reservoir characteristics between shale oil in Qingshankou Formation of Guolong depression and that in Eagle Ford of the USA
参数 美国鹰滩(Eagle Ford)
页岩油气藏古龙凹陷青山
口组页岩油藏对比结论 沉积相 半封闭的浅海 半深湖-深湖 不同 埋深/m 1500~3900 1800~2500 稍浅 岩性 泥灰岩与钙质 泥岩夹砂质、介形 相似 页岩薄互层 虫条带或薄层 厚度/m 42~122 130~300 较大 孔隙度/% 3.4~14.6 8.2~11.1 相近 渗透率/mD 0.3×10-3~3.0×10-3 0.8×10-3~3.4×10-3 相近 烃源岩 TOC/% 2~8 1~2.4 较小 Ro/% 0.88~1.10 0.6~2.0 相近 脆性矿物含量/% 80 42~51 较小 -
[1] 陈详, 王敏, 严永新, 等.陆相页岩油勘探[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2015.
[2] 舒树良, 慕玉福, 王伯长.松辽盆地含油气地层及其构造特征[J].地层学杂志, 2003, 23(4):340-347. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200304013.htm
[3] 张静平, 唐书恒, 吕建伟, 等.松辽盆地青山口组一段油页岩成矿条件及有利目标区分析[J].地学前缘, 2012, 19(1):156-162. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201201018.htm
[4] 高瑞祺, 蔡希源.松辽盆地油气田形成条件与分布规律[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1997.
[5] 辛仁臣, 蔡希源, 王英民.松辽坳陷深水湖盆层序界面特征及低位域沉积模式[J].沉积学报, 2004, 22(3):387-391. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200403003.htm
[6] 赵澄林, 朱筱敏.沉积岩石学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2001.
[7] 邹才能等.非常规油气地质[M].北京:地质出版社, 2013.
[8] 邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等.页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策[J].石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(1):14-26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201301003.htm
[9] 邹才能, 张国生, 杨智, 等.非常规油气油气概念、特征、潜力及技术——兼论非常规油气地质学[J].石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(4):385-397. doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.04.01
[10] 姜在兴.沉积学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2003.
[11] 张爱云, 武大茂, 郭丽娜, 等.海相黑色页岩建造地球化学与成矿意义[M].北京:科学出版社, 1987.
[12] 翟光明, 王志武.中国石油地质志 (卷2)[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1993.
[13] 高有峰, 王璞珺, 程日辉, 等.松科1井南孔白垩系青山口组一段沉积序列精细描述:岩石地层、沉积相与旋回地层[J].地学前缘, 2009, 16(2):314-323. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200902029.htm
[14] 王璞珺, 高有峰, 程日辉, 等.松科1井南孔白垩系青山口组二、三段沉积序列精细描述:岩石地层、沉积相与旋回地层[J].地学前缘, 2009, 16(2):288-313. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200902028.htm
[15] 刘成林, 李冰, 吴林强, 等.松辽盆地上白垩统页岩油地质条件评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2016:200-203.
[16] 张善文, 王永诗, 张林晔, 等.济阳坳陷渤南洼陷页岩油气形成条件研究[J].中国工程科学, 2012, 14(4):49-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKX201206006.htm
[17] 陈祥, 王敏, 严永新, 等.泌阳凹陷陆相页岩油气成藏条件[J].石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(2):568-577. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201104013.htm
[18] 梁世君, 黄志龙, 柳波, 等.马朗凹陷芦草沟组页岩油形成机理与富集条件[J].石油学报, 2012, 33(4):588-594. doi: 10.7623/syxb201204007
[19] 姜在兴, 张文昭, 梁超, 等.页岩油储层基本特征及评价要素[J].石油学报, 2014, 35(1):184-195. doi: 10.7623/syxb201401024
[20] 王丽静.松辽盆地下白垩统青山口组油气成藏与分布特征研究[J].石油天然气学报, 2014, 36(9):8-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201409002.htm
[21] 董清源, 刘小平, 李洪香, 等.黄骅坳陷孔南地区孔二段页岩油藏形成条件分析[J].天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(1):189-198. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201301029.htm
[22] 吴世强, 唐小山, 杜小娟, 等.江汉盆地潜江凹陷陆相页岩油成藏特征[J].江汉石油科技, 2012, 22(4):1-4. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSK201204004.htm
[23] Lucas W B, Larkin S D, Lattibeaudiere M G. Improving produc-tion in the Eagle Ford Shale with fracture modeling, increased con-ductivity and optimized stage and cluster spacing along the horizon-tal wellbore[C]//Tight Gas Completions Conference:San Anto-nio, Texas, USA, 2010.
[24] 秦长文, 秦璇.美国鹰滩和尼奥泊拉拉页岩油富集主控因素[J].特种油气藏, 2015, 22(4):34-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201503008.htm
[25] Mullen J, Lowry J C, Nwabuoku K C. Lessons learned developing the Eagle Ford Shale[C]//Tight Gas Completions Conference:San Antonio, Texas, USA, 2010.
[26] EIA U.S. Technically recoverable shale oil and shale gas resources:An assessment of 137 shale formations in 41 countries outside the United States[M]. Washington DC:US Department of Energy/EIA, 2013.
-



 下载:
下载: