Early-Middle Holocene paleoenvironmental evolution revealed by a la-custrine sediment sequence in Leizhou Peninsula
-
摘要:
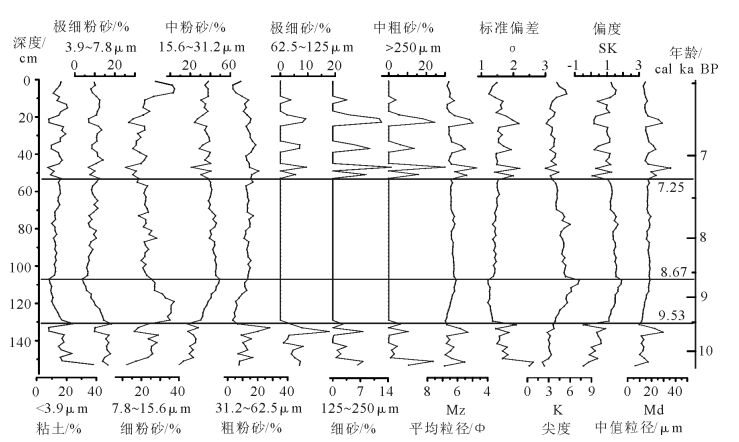
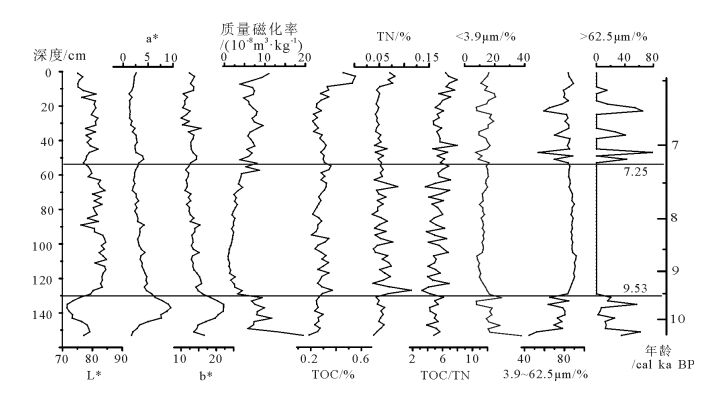
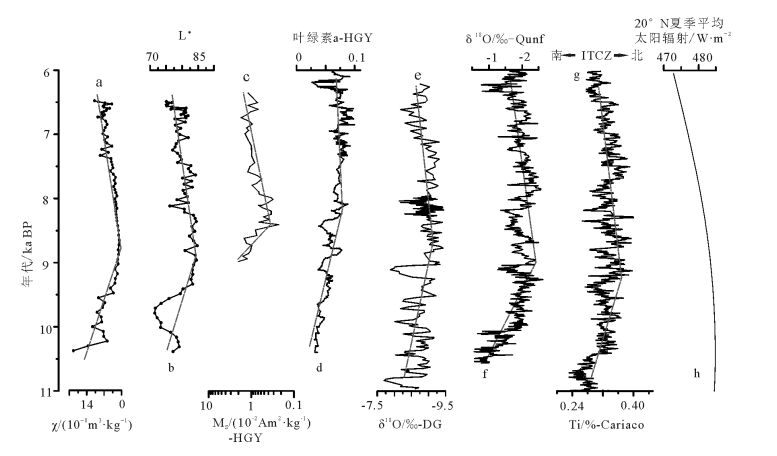
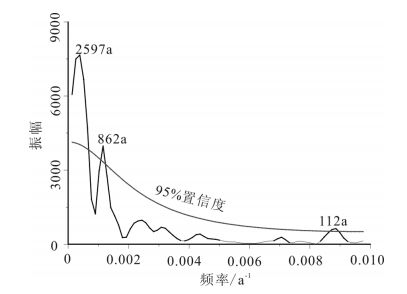
对雷州半岛南部徐闻县九亩村一段1.54m厚的湖相沉积剖面进行粒度、磁化率、色度及有机碳氮分析,结合AMS14C测年结果,重建了该地区10.5~6.5cal ka BP的气候环境变化。共分为3个阶段:①10.5~9.5cal ka BP,湖泊水体较浅,气候较干燥;②9.5~7.2cal ka BP,湖泊水位较高,环境稳定,气候较湿润;③7.2~6.5cal ka BP,湖水相对变浅,气候相对阶段②干燥。雷州半岛地区降水变化与印度季风演变模式一致,可与北半球夏季平均太阳辐射及其影响下热带辐合带(ITCZ)的移动进行对比,指标时间序列的红外噪声谱分析结果表明,存在千年-百年的准周期,反映了研究区气候环境变化对太阳活动的响应。
Abstract:This study presents the record of paleoenvironmental evolution results from a radiocarbon-dated 1.54m-long lacustrine sediment sequence in south Leizhou Peninsula. Measurement of grain size, magnetic susceptibility (MS), total nitrogen (TN), total or-ganic carbon (TOC), atomic TOC/TN (C/N) and color reflectance values was carried out in order to reconstruct the climate span-ning the interval 10.5~6.5cal ka BP. Three distinct stages can be identified as follows:①10.5~6.5 cal ka BP, a shallow lake level and relatively dry climate dominated this area. ②The interval from 9.5~7.2cal ka BP was characterized by a relatively high lake level and humid climate. ③During 7.2~6.5cal ka BP, lake level was relatively shallow with a relatively dry climate. Indian monsoon was more responsible for precipitation variability in this area, which was interconnected with average monthly solar radiation in summer and ITCZ migration. Red noise spectrum analysis of proxies shows centennial to millennia time scale cycles, which suggests that the envi-ronmental evolution was probably sensitive to the secular solar activity.
-
Key words:
- Leizhou Peninsula /
- Early-Middle Holocene /
- paleoenvironmental evolution
-

-
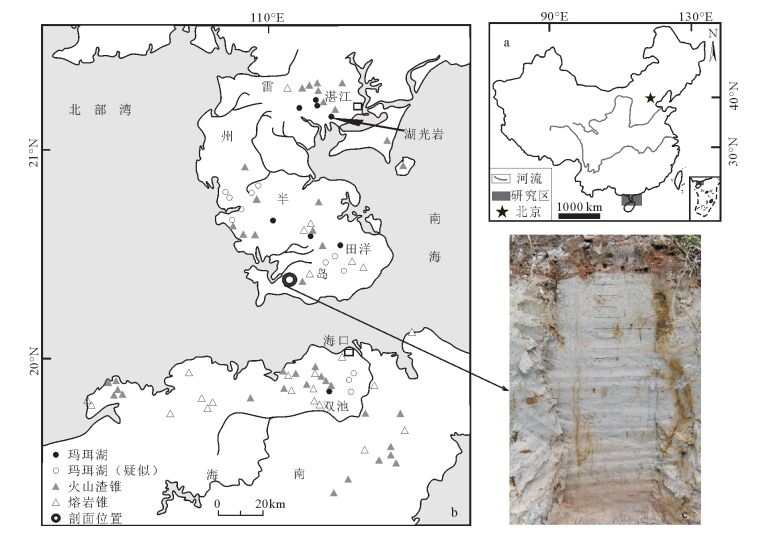
图 1 研究区位置(a)、剖面位置(b, 据参考文献[26]修改)和剖面照片(c)
Figure 1.
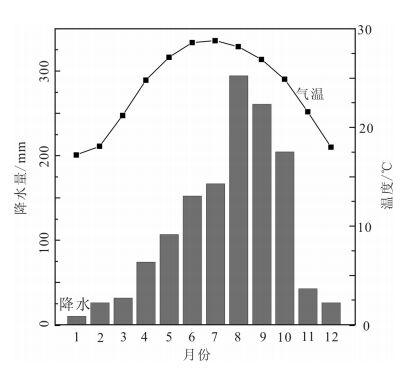
图 2 徐闻月平均气温与降水图(1981—2010年)[32]
Figure 2.
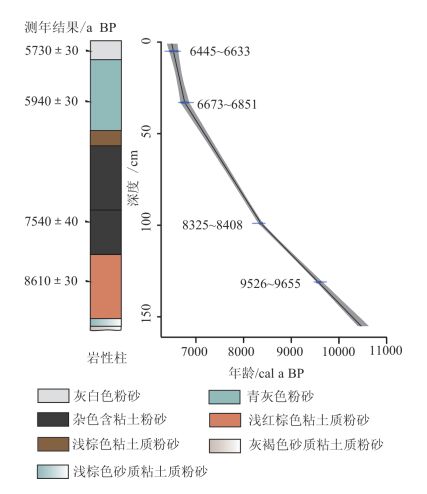
表 1 JM剖面沉积物14C测年结果
Table 1. AMS radiocarbon dates for JM section
样品编号 实验室编号 深度/cm 测年材料 14C年龄/a BP 校正年龄/cal a BP 13jm-3 Beta-416459 5~6 沉积物 5730±30 6445~6633 13jm-27 Beta-434636 53~54 沉积物 5940±30 6673~6851 13jm-50 Beta-434638 99~100 沉积物 7540±40 8325~8408 13jm-66 Beta-416461 131~132 沉积物 8610±30 9526~9655 -
[1] Bond G, Showers W, Cheseby M, et al. A Pervasive MillennialScale Cycle in North Atlantic Holocene and Glacial Climates[J]. In-organic Chemistry, 1997, 278:1257-1266. http://www.docin.com/p-505547048.html
[2] Bond G, Bonani G. Persistent solar influence on North Atlantic cli-mate during the Holocene[J]. Science, 2001, 294:2130-2136. doi: 10.1126/science.1065680
[3] Wang Y, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. The Holocene Asian mon-soon:links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate[J]. Science, 2005, 308:854-857. doi: 10.1126/science.1106296
[4] Judson W. Partin et al, Millennial-scale trends in west Pacific warm pool hydrology since the Last Glacial Maximum[J].Nature, 2007, 449:452-456. doi: 10.1038/nature06164
[5] Kerr R A. The tropics return to the climate system[J]. Science, 2001, 292:660-661. doi: 10.1126/science.292.5517.660
[6] Hong Y T, Hong B, Lin Q H, et al. Inverse phase oscillations be-tween the East Asian and Indian Ocean summer monsoons during the last 12000 years and paleo-El Niño[J]. Earth & Planetary Sci-ence Letters, 2005, 231(3):337-346. http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/130176
[7] Moy C M, Seltzer G O, Rodbell D T, et al. Variability of El Niño/Southern Oscillation activity at millennial timescales during the Ho-locene epoch.[J]. Nature, 2002, 420:162-165. doi: 10.1038/nature01194
[8] Chen S, Hoffmann S S, Lund D C, et al, A high-resolution speleo-them record of western equatorial Pacific rainfall:Implications for Holocene ENSO evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, (442):61-71. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379108000589
[9] Rodbell D T, Newman J H. An~15, 000-Year Record of El NiñoDriven Alluviation in Southwestern Ecuador[J]. Science, 1999, 283:516-520. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5401.516
[10] 闻新宇, 王绍武, 朱锦红.古ENSO的研究进展[J].地球物理学报, 2007, 50(2):387-396. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200702007.htm
[11] 郑卓, 王建华, 王斌, 等.海南岛双池玛珥湖全新世高分辨率环境纪录[J].科学通报, 2003, 48(3):282-286. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200303016.htm
[12] 白雁, 刘春莲, 郑卓, 等.海南岛双池玛珥湖沉积中的碳、氮地球化学记录及其环境意义[J].古地理学报, 2003, 5(1):87-93. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200301007.htm
[13] 罗攀, 郑卓, 杨小强.海南岛双池玛珥湖全新世磁化率及其环境意义[J].热带地理, 2006, 26(3):211-217. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDDD200603003.htm
[14] 张华, 郑卓, 王建华, 等.海南岛近2500a来盘星藻记录的周期性气候变化[J].热带地理, 2004, 24(2):109-112. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDDD200402003.htm
[15] Yang X, Wei G, Yang J, et al. Paleoenvironmental shifts and pre-cipitation variations recorded in tropical maar lake sediments during the Holocene in Southern China[J]. Holocene, 2014, 24(10):1216-1225. doi: 10.1177/0959683614540962
[16] 王淑云, 吕厚远, 刘嘉麒, 等.湖光岩玛珥湖高分辨率孢粉记录揭示的早全新世适宜期环境特征[J].科学通报, 2007, 52(11):1285-1291. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.11.012
[17] Yancheva G, Nowaczyk N R, Mingram J, et al. Influence of the in-tertropical convergence zone on the East Asian monsoon.[J]. Na-ture, 2007, 445(7123):74-77. https://miami.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/influence-of-the-intertropical-convergence-zone-on-the-east-asian
[18] Wu X, Zhang Z, Xu X, et al. Asian summer monsoonal variations during the Holocene revealed by Huguangyan maar lake sediment record[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2012, 323(1):13-21. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S003101821200034X
[19] Duan Z, Liu Q, Yang X, et al. Magnetism of the Huguangyan Maar Lake sediments, Southeast China and its paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2013, 395(1):158-167. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ201501001006.htm
[20] Jia G, Bai Y, Yang X, et al. Biogeochemical evidence of Holocene East Asian summer and winter monsoon variability from a tropical maar lake in southern China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2015, 111:51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.01.002
[21] 刘嘉麒, 吕厚远, Negendank J, 等.湖光岩玛珥湖全新世气候波动的周期性[J].科学通报, 2000, 45(11):1190-1195. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.11.015
[22] 吴旭东, 沈吉, 汪勇.湖光岩玛珥湖沉积物反映的全新世以来古环境演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, (4):155-162. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201104025.htm
[23] 吴旭东, 沈吉, 汪勇.广东湛江湖光岩玛珥湖全新世磁化率变化特征及其环境意义[J].热带地理, 2011, 31(4):346-352. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDDD201104004.htm
[24] 巩伟明, 张朝晖.湖光岩玛珥湖全新世时期沉积物碳氮同位素组成的环境指示意义[J].高校地质学报, 2014, (4):582-589. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201404010.htm
[25] 匡欢传, 周浩达, 胡建芳, 等.末次盛冰期和全新世大暖期湖光岩玛珥湖沉积记录的正构烷烃和单体稳定碳同位素分布特征及其古植被意义[J].第四纪研究, 2013, 33(6):1222-1233. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201306018.htm
[26] Fuhrmanna A, Mingram J, Lücke A, et al. Variations in organic matter composition in sediments from Lake Huguang Maar(Hu-guangyan), south China during the last 68 ka:implications for envi-ronmental and climatic change[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2003, 34(11):1497-1515. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(03)00158-X
[27] 余克服, 钟晋梁, 赵建新, 等.雷州半岛珊瑚礁生物地貌带与全新世多期相对高海平面[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(2):27-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200202005.htm
[28] 时小军, 余克服, 陈特固, 等.中-晚全新世高海平面的琼海珊瑚礁记录[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(5):1-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200805002.htm
[29] Huang J, Li A, Wan S. Sensitive grain-size records of Holocene East Asian summer monsoon in sediments of northern South China Sea slope[J]. Quaternary Research, 2011, 75(3):734-744. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2011.03.002
[30] Yan H, Sun L, Shao D, et al. Seawater temperature seasonality in the South China Sea during the late Holocene derived from highresolution Sr/Ca ratios of Tridacna gigas[J]. Quaternary Research, 2015, 83(2):298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2014.12.001
[31] 沈吉.湖泊沉积研究的历史进展与展望[J].湖泊科学, 2009, 21(3):307-313. doi: 10.18307/2009.0301
[32] 中国地面累年值月值数据集(1981-2010年)[EB/OL](2012-08-28)[2016-05-26]中国气象数据网. http://data.cma.cn.
[33] Zheng Z, Lei Z Q. A 400000 year record of vegetational and cli-matic changes from a volcanic basin, Leizhou Peninsula, southern China[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 1999, 145(4):339-362. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(98)00107-2
[34] 陈俊仁, 姚伯初, 吴能友.湛江田洋玛珥湖的形成与演化[J].广东地质, 2002, 17(1):12-18. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gddz200201002
[35] Peng Y, Xiao J, Nakamura T, et al. Holocene East Asian monsoonal precipitation pattern revealed by grain-size distribution of core sedi-ments of Daihai Lake in Inner Mongolia of north-central China[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(3/4):467-479. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-007-7817-7_3/fulltext.html
[36] Reimer P J, Bard E, Bayliss A, et al. Selection and Treatment of Data for Radiocarbon Calibration:An Update to the International Calibration (IntCal) Criteria[J]. Radiocarbon, 2013, 55(4):1923-1945. doi: 10.2458/azu_js_rc.55.16955
[37] Blaauw M, Christen J A. Flexible paleoclimate age-depth models using an autoregressive gamma process[J]. Bayesian Analysis, 2011, 3(6):457-474. http://www.academia.edu/2826503/Flexible_paleoclimate_age-depth_models_using_an_autoregressive_gamma_process
[38] Wentworth C K. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sedi-ments[J]. Journal of Geology, 1922, 30(5):377-392. doi: 10.1086/622910
[39] 黄思静.用EXCEL计算沉积物粒度分布参数[J].成都理工学院学报, 1999, 26(2):98-100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG902.019.htm
[40] Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos River bar[Texas]:a study in the sig-nificance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Re-search, 1957, 27(1):3-26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[41] Xiao J, Fan J, Zhou L, et al. A model for linking grain-size compo-nent to lake level status of a modern clastic lake[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 355(12):149-158. http://www.cge.ac.cn/kyxx/fblw/201507/W020150724617346516205.pdf
[42] Xiao J L, Fan J W, Zhai D Y, et al.Testing the model for linking-grain-size component to lake level status of modern clastic lakes[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 355:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.04.023
[43] Vandenberghe J. Grain size of fine-grained windblown sediment:A powerful proxy for process identification[J]. Earth-Science Re-views, 2013, 121(6):18-30. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013ESRv..121...18V
[44] 孙千里, 周杰, 肖举乐.岱海沉积物粒度特征及其古环境意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(1):93-95. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200101018.htm
[45] Chen J A, Wan G J, Tang D G. Recent climate changes recorded by sediment grain sizes and isotopes in Erhai Lake[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2000, 10(1):54-61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJY200001009.htm
[46] Xu H, Zhou X, Lan J, et al. Late Holocene Indian summer mon-soon variations recorded at Lake Erhai, Southwestern China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2015, 83(2):307-314. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2014.12.004
[47] 陈敬安, 万国江, 张峰, 等.不同时间尺度下的湖泊沉积物环境记录——以沉积物粒度为例[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(6):563-568. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200306009.htm
[48] 王心源, 吴立, 张广胜, 等.安徽巢湖全新世湖泊沉积物磁化率与粒度组合的变化特征及其环境意义[J].地理科学, 2008, 28(4):548-553. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200804015.htm
[49] 田庆春, 杨太保, 石培宏, 等.可可西里BDQ0608钻孔沉积物色度环境意义及其影响因素[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(1):133-140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201201024.htm
[50] 吴艳宏, 李世杰.湖泊沉积物色度在短尺度古气候研究中的应用[J].地球科学进展, 2004, 19(5):789-792. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200405016.htm
[51] 吴健, 沈吉.兴凯湖沉积物磁化率和色度反映的28ka BP以来区域古气候环境演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, (3):123-131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200903022.htm
[52] 王永, 姚培毅, 迟振卿, 等. 内蒙古浩来呼热湖泊沉积物色度记录的末次冰消期以来的环境演变[C]//全国古地理学及沉积学学术会议. 2012.
[53] Ji J, Shen J, Balsam W, et al. Asian monsoon oscillations in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since the late glacial as inter-preted from visible reflectance of Qinghai Lake sediments[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1):61-70.
[54] Meyers P A, Lallier-Vergès E. Lacustrine sedimentary organicmat-ter records of late Quaternary paleoclimates[J]. Journal of Paleolim-nology, 1999, 21:345-372. doi: 10.1023/A:1008073732192
[55] 李军. 藏北高原湖泊表层沉积物有机碳、碳氮比以及有机碳同位素特征及其环境意义[D]. 兰州大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10730-1014302379.htm [56] Xue J, Zhong W, Xie L, et al. Vegetation responses to the last gla-cial and early Holocene environmental changes in the northern Lei-zhou Peninsula, south China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2015, 84(2):223-231. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2015.08.001
[57] Yue Y, Zheng Z, Rolett B V, et al. Holocene vegetation, environ-ment and anthropogenic influence in the Fuzhou Basin, southeast China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 99:85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.12.004
[58] 韩艳, 肖霞云, 羊向东, 等.全新世以来滇西北地区天才湖粒度特征及古降水[J].第四纪研究, 2011, 31(6):999-1010. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201106008.htm
[59] Fleitmann D, Matter A. Holocene Forcing of the Indian Monsoon Recorded in a Stalagmite from Southern Oman[J]. Science, 2003, 300(5626):1737-1739. doi: 10.1126/science.1083130
[60] Dykoski C A, Edwards R L, Cheng H, et al. A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(s1-2):71-86. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X05000865
[61] Zhang J, Chen F, Holmes J A, et al. Holocene monsoon climate documented by oxygen and carbon isotopes from lake sediments and peat bogs in China:a review and synthesis[J]. Quaternary Sci-ence Reviews, 2011, 30(15/16):1973-1987. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0277379111001259
[62] Chen F, Chen X, Chen J, et al. Holocene vegetation history, pre-cipitation changes and Indian Summer Monsoon evolution docu-mented from sediments of Xingyun Lake, south-west China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2014, 29(7):661-674. doi: 10.1002/jqs.v29.7
[63] Liu J, Chen J, Zhang X, et al. Holocene East Asian summer mon-soon records in northern China and their inconsistency with Chi-nese stalagmite δ18O records[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2015, 148:194-208. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.06.004
[64] 覃嘉铭, 袁道先, 程海, 等.新仙女木及全新世早中期气候突变事件:贵州茂兰石笋氧同位素记录术[J].中国科学, 2004, 34(1):69-74. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200401007.htm
[65] 王宁练, 姚檀栋, Thompson L G, 等.全新世早期强降温事件的古里雅冰芯记录证据[J].科学通报, 2002, 47(11):818-823. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.11.004
[66] 余克服, 陈特固, 钟晋梁, 等.雷州半岛全新世高温期珊瑚生长所揭示的环境突变事件[J].中国科学, 2002, 32(2):149-156. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200202008.htm
[67] Members C. Climatic Changes of the Last 18000 Years:Observa-tions and Model Simulations[J]. Science, 1988, 241(4869):1043-1052. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4869.1043
[68] Laskar J, Robutel P, Joutel F, et al. A long-term numerical solu-tion for the insolation quantities of the Earth[J]. Photographic Sci-ence & Photochemistry, 2004, 428(1):101-106. https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/abs/2004/46/aa1335/aa1335.html
[69] Haug G H, Hughen K A, Sigman D M, et al. Southward migration of the intertropical convergence zone through the Holocene.[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5533):1304-1308. doi: 10.1126/science.1059725
[70] Schulz M, Mudelsee M. REDFIT:estimating red-noise spectra di-rectly from unevenly spaced paleoclimatic time series[J]. Computer & Geoscience, 2002, 28:421-426.
[71] 薛积彬, 钟巍, 彭晓莹, 等.南岭东部大湖泥炭沉积记录的古气候[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(5):105-113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200705018.htm
[72] Wang L, Sarnthein M, Erlenkeuser H, et al. East Asian monsoon climate during the Late Pleistocene:high-resolution sediment re-cords from the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 156(1/4):245-284. http://www.academia.edu/3439008/East_Asian_monsoon_climate_during_the_Late_Pleistocene_high-resolution_sediment_records_from_the_South_China_Sea
-



 下载:
下载: