Petrology, geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age characteristics and significance of Dengfuxian pluton in Hu'nan Province
-
摘要:
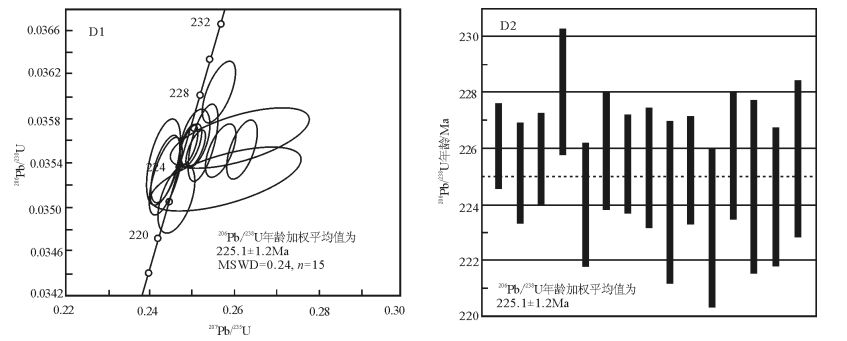
对湖南中生代邓阜仙岩体进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年和岩石学、岩石地球化学分析。获得斑状黑云母花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为225.1±1.2Ma,表明其形成于晚三叠世,结合已发表的岩体年龄资料,邓阜仙岩体是侵位于印支期(222.9~225.7Ma)和燕山期(151.1~159Ma)的复式岩体。邓阜仙岩体印支期、燕山期花岗岩均具有高的SiO2含量、高的A/CNK值,含过铝质白云母、堇青石等矿物。富集大离子亲石元素Rb、Th、U,明显亏损Nb、Ba、Sr、Ti,稀土元素配分模式为右倾,轻稀土元素富集,Eu亏损相对明显。邓阜仙岩体具低的εNd(t)值,176Hf/177Hf值小于球粒陨石的值。综上认为,邓阜仙岩体印支期、燕山期为S型花岗岩,源区分别为古元古代地壳贫粘土质岩石、富粘土质岩石部分熔融。研究区印支期、燕山期花岗岩均形成于伸展构造体制下,印支期花岗岩形成于印支运动碰撞后的伸展环境,燕山期花岗岩则在太平洋板块俯冲消减作用下形成。
-
关键词:
- 湖南 /
- 邓阜仙岩体 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄 /
- S型花岗岩
Abstract:In this paper, the authors analyzed LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating, petrology and petro-geochemistry of Mesozoic Dengfuxian pluton in Hu'nan Province. The zircon U-Pb age is 225.1±1.2Ma for granodiorite, which suggests that it was formed in Late Triassic. Combined with the age data available, the authors hold that Defuxian pluton is complex rock which intruded in Indo-sinian(222.9~225.7Ma)and Yanshanian(151.1~159Ma). Granites in Indosinian and Yanshanian Dengfuxian pluton all have high content of SiO2 and high ratios of A/CNK and contain para-aluminous muscovite and cordierite mineral. In terms of trace elements, large ion element Rb, Th, U are rich, whereas Nb, Ba, Sr, Ti are poor obviously. The REE distribution patterns exhibit right devia-tion, with rich light rare earth elements and relatively poor Eu. As for isotopes, Dengfuxian pluton has low values of εNd(t), and the ratios of 176Hf/177Hf are lower than the ratio of chondrite (0.282772). In combination with the above-mentioned characteristics and by means of (87sr/86Sr)i-εNd(t) discrimination, the authors consider that the granites in Indosinian and Yanshanian Dengfuxian pluton are of S-type granites, and the source area was formed by partial melting of crustal argillaceous-poor pluton in the region in Paleo-proterozoic and argillaceous-rich pluton. It is considered that the granites in Indosinian and Yanshanian Dengfuxian pluton were formed under the extended tectonic regime, and the granites in Indosinian intruded in the extension setting after the collision of Indo-sinian movement, whereas the granites in Yanshanian period were formed by the subduction of Pacific plate.
-
Key words:
- Hu'nan /
- Dengfuxian pluton /
- LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age /
- S-type granite
-

-
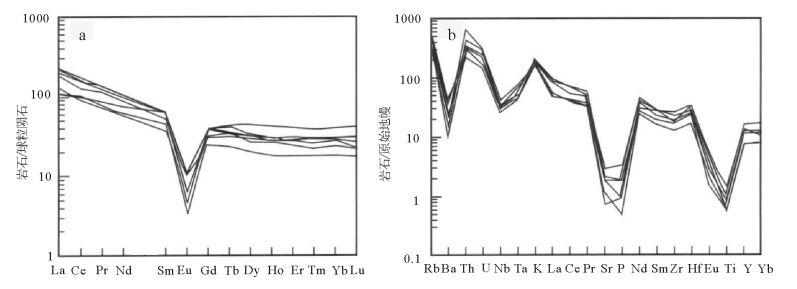
图 5 邓阜仙岩体花岗岩微量元素原始地幔蛛网图(标准化数据据参考文献[15])
Figure 5.
图 6 邓阜仙岩体花岗岩稀土元素球粒陨石配分模式图(标准化数据据参考文献[15])
Figure 6.
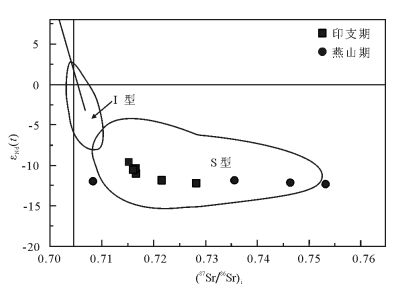
图 7 邓阜仙岩体Ⅰ型、S型花岗岩(87sr/86Sr)i-εNd(t)图解[16]
Figure 7.
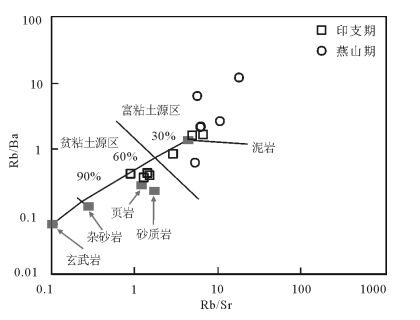
图 8 邓阜仙岩体的Rb/Sr-Rb/Ba图解[18]
Figure 8.
图 9 典型A型花岗岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图(a)及微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)[23]
Figure 9.
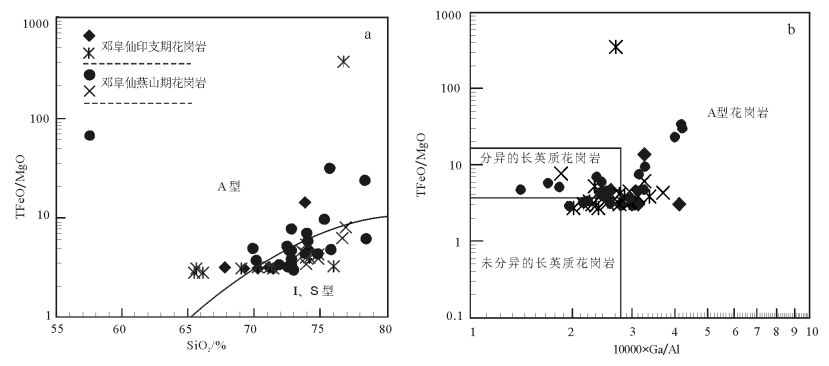
图 10 邓阜仙花岗岩岩石类型判别图解(底图据参考文献[24])
Figure 10.
图 11 邓阜仙岩体构造环境判别图解(底图据参考文献[14])
Figure 11.
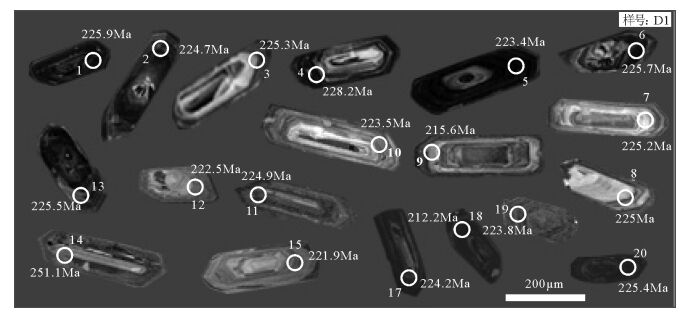
表 1 邓阜仙岩体斑状黑云母花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1. Isotopic analytical results of zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb for biotite granites from Dengfuxian pluton
测点
号含量/10-6 比值 年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 206Pb/
238U1σ 208Pb/
232Th1σ 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 206Pb/
238U1σ 208Pb
232Th1σ D1-1 140.1 253.4 783.7 0.05126 0.00020 0.25199 0.00122 0.03567 0.00012 0.00223 0.00024 253.8 9.3 228.2 1.0 225.9 0.8 45.1 4.9 D1-2 96.8 189.4 582.0 0.05136 0.00021 0.25114 0.00138 0.03548 0.00015 0.00210 0.00023 257.5 4.6 227.5 1.1 224.7 0.9 42.4 4.6 D1-3 74.7 126.5 476.3 0.05069 0.00024 0.24860 0.00151 0.03557 0.00014 0.00268 0.00029 227.8 11.1 225.4 1.2 225.3 0.8 54.1 5.8 D1-4 122.2 192.6 1090.9 0.05159 0.00037 0.25635 0.00236 0.03603 0.00018 0.00293 0.00059 333.4 16.7 231.7 1.9 228.2 1.2 59.2 11.9 D1-5 140.0 217.9 484.2 0.05303 0.00231 0.25814 0.01191 0.03526 0.00018 0.00208 0.00028 331.5 102.8 233.2 9.6 223.4 1.1 41.9 5.7 D1-6 46.5 73.3 270.5 0.05313 0.00211 0.26137 0.01086 0.03563 0.00017 0.00392 0.00087 344.5 88.9 235.8 8.7 225.7 1.1 79.1 17.5 D1-7 200.1 353.4 829.5 0.05088 0.00019 0.24930 0.00133 0.03554 0.00014 0.00149 0.00017 235.3 4.6 226.0 1.1 225.2 0.9 30.1 3.4 D1-8 75.5 114.6 415.4 0.05343 0.00035 0.26176 0.00232 0.03552 0.00017 0.00221 0.00032 346.4 14.8 236.1 1.9 225.0 1.1 44.6 6.5 D1-9 338.3 488.4 1818.7 0.06525 0.00031 0.30599 0.00210 0.03401 0.00016 0.00149 0.00021 783.3 10.0 271.1 1.6 215.6 1.0 30.2 4.2 D1-10 86.8 137.0 596.8 0.05007 0.00039 0.24355 0.00240 0.03528 0.00024 0.00210 0.00045 198.2 13.9 221.3 2.0 223.5 1.5 42.4 9.0 D1-11 152.1 247.2 854.5 0.05247 0.00041 0.25682 0.00231 0.03550 0.00016 0.00138 0.00024 305.6 18.5 232.1 1.9 224.9 1.0 27.9 4.8 D1-12 72.8 139.2 339.2 0.05097 0.00057 0.24660 0.00284 0.03512 0.00024 0.00138 0.00028 239.0 25.9 223.8 2.3 222.5 1.5 27.9 5.7 D1-13 121.0 223.2 513.9 0.05101 0.00039 0.25040 0.00236 0.03560 0.00019 0.00105 0.00022 242.7 12.0 226.9 1.9 225.5 1.2 21.3 4.5 D1-14 148.6 210.4 655.9 0.05449 0.00027 0.29840 0.00224 0.03972 0.00021 0.00145 0.00032 390.8 38.9 265.1 1.8 251.1 1.3 29.3 6.4 D1-15 121.6 196.1 381.8 0.05805 0.00031 0.28018 0.00187 0.03502 0.00015 0.00131 0.00032 531.5 11.1 250.8 1.5 221.9 0.9 26.5 6.5 D1-17 120.5 176.5 563.3 0.04979 0.00037 0.24299 0.00261 0.03540 0.00026 0.00155 0.00043 183.4 21.3 220.9 2.1 224.2 1.6 31.3 8.7 D1-18 85.6 164.4 185.8 0.05161 0.00040 0.23800 0.00207 0.03347 0.00016 0.00130 0.00040 333.4 18.5 216.8 1.7 212.2 1.0 26.2 8.0 D1-19 48.6 113.3 258.1 0.05017 0.00048 0.24423 0.00249 0.03533 0.00020 0.00171 0.00062 211.2 22.2 221.9 2.0 223.8 1.3 34.5 12.5 D1-20 170.6 244.9 477.3 0.05146 0.00042 0.25234 0.00241 0.03558 0.00023 0.00136 0.00052 261.2 18.5 228.5 2.0 225.4 1.4 27.5 10.4 表 2 邓阜仙花岗岩体主量、微量和稀土元素组成
Table 2. The composition of major, trace and rare earth elements for Dengfuxian pluton
样号 Z7 D1 DF54 DF55 DF56 DF57 D2 D3 36 37 Z8 20 DF58 印支期花岗岩 燕山期花岗岩 SiO2 69.2 67.7 71.4 71.1 73.7 70.2 74.1 76.8 76.5 73.5 74.8 73.8 73.8 TiO2 0.72 0.66 0.39 0.42 0.21 0.38 0.18 0.05 0.27 0.18 0.14 0.11 0.16 Al2O3 14.5 15.8 13.7 13.7 13.6 13.8 14.6 13.5 12.5 14.6 14.5 14.7 13.8 FeO 3.71 3.62 1.97 2.28 1.92 2.16 1.47 0.61 0.91 0.61 1.14 0.71 1.05 Fe2O3 0.21 0.71 0.35 0.27 0.36 0.28 0.36 0.38 0.92 1.14 0.1 0.64 0.43 MnO 0.08 0.11 0.07 0.05 0.04 0.06 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.14 0.07 MgO 1.28 1.37 0.75 0.81 0.16 0.79 0.38 0.12 0.28 0.36 0.32 0.38 0.33 CaO 2.37 2.76 1.36 1.39 0.71 1.52 0.82 0.36 0.62 0.95 0.65 0.73 0.81 Na2O 2.65 2.36 2.48 2.72 3.12 2.66 3.12 3.59 2.82 3.32 3.17 3.68 3.71 K2O 5.02 4.64 5.63 5.89 5.43 5.73 4.83 4.52 5.01 5.12 4.95 4.95 4.25 P2O5 0.27 0.25 0.18 0.23 0.06 0.24 0.21 0.07 0.11 0.18 0.21 0.15 0.23 烧失量 0.11 0.09 1.12 0.54 0.32 1.32 0.17 0.12 0.13 0.21 0.14 0.21 1.08 总计 100 100 99.3 99.3 99.6 99.1 100 100 100 100 100 100 99.7 TFeO 3.89 4.26 2.29 2.52 2.24 2.41 1.79 0.94 1.73 1.64 1.23 1.28 1.44 ASI 1.03 1.13 1.08 1.02 1.10 1.04 1.25 1.18 1.12 1.14 1.23 1.15 1.13 A/NK 1.48 1.77 1.34 1.26 1.23 1.31 1.44 1.25 1.25 1.32 1.37 1.29 1.29 ALK 7.67 7.01 8.11 8.61 8.55 8.39 7.83 8.11 7.82 8.44 8.12 8.63 7.96 Rb 295 342 272 280 309 454 372 335 349 362 487 372 621 Zr 368 298 193 249 142 193 78.2 31.8 63.2 81.1 68.2 71.3 71.5 Nb 15.5 17.7 14.5 19.3 20.4 15.2 14.7 9.75 15.4 14 11.5 14.1 42.1 Hf 9.74 3.24 5.35 7.01 4.71 4.82 4.72 1.91 2.17 2.32 2.32 1.41 2.51 Th 45.1 37.2 43.7 57.5 63.9 40.3 13.5 3.71 11.4 11.7 11.5 12.3 11.2 U 7.53 5.25 6.91 7.53 9.49 9.85 7.74 8.98 9.67 4.23 13.6 10.4 27.6 Ba 802 900 850 801 210 608 258 57 178 660 203 189 54.6 Sr 337 246 214 188 48.2 159 78.1 60.2 58.1 70.2 46.8 60.4 35.8 Rb/Sr 0.88 1.39 1.27 1.49 6.42 2.86 4.76 5.56 6.01 5.17 10.4 6.16 17.35 La/Nb 8.97 6.67 5.81 4.95 2.96 4.88 1.53 0.81 1.23 1.86 1.33 0.08 0.29 Ba/Nb 51.7 50.9 58.6 41.5 10.3 40.1 17.6 5.85 11.5 47.1 17.7 13.5 1.29 Nb★ 0.12 0.15 0.13 0.16 0.21 0.14 0.21 0.17 0.22 0.19 0.17 0.24 0.74 Y 23.3 22.3 17.6 19.8 61.8 20.7 8.77 27.7 9.71 13.1 8.66 1.59 9.57 La 139 118 84.2 95.5 60.42 74.2 22.5 7.88 18.9 26.1 15.3 1.18 12.3 Ce 303 213 149 173 119 136 47.1 16.9 35.2 53.6 28.7 2.51 24.1 Pr 25.4 23.8 17.5 20.3 14.1 16.2 5.28 2.12 4.31 6.69 3.78 0.32 3.12 Nd 83.5 76.1 54.3 64.6 49.6 51.7 18.2 7.15 15.4 23.9 13.6 1.02 9.81 Sm 11.6 10.9 9.12 10.3 10.6 9.56 3.92 2.09 4.31 4.99 3.14 0.36 2.41 Eu 1.88 1.88 1.46 1.28 0.64 1.26 0.45 0.161 0.53 0.57 0.36 0.04 0.13 Gd 7.15 7.09 6.01 7.51 9.28 6.32 3.29 2.41 3.07 3.75 2.64 0.28 1.83 Tb 1.01 0.92 0.81 0.98 1.59 0.96 0.42 0.51 0.51 0.54 0.37 0.07 0.42 Dy 4.56 4.62 3.62 4.26 10.3 4.17 2.02 3.85 2.25 2.53 1.85 0.31 1.8 Ho 0.8 0.81 0.71 0.75 2.14 0.81 0.31 0.85 0.34 0.36 0.27 0.07 0.37 Er 2.43 2.02 1.92 2.12 6.11 2.18 0.69 2.78 0.85 1.01 0.75 0.12 1.01 Tm 0.29 0.31 0.23 0.26 0.91 0.29 0.11 0.53 0.12 0.13 0.08 0.04 0.15 Yb 1.86 1.94 1.79 1.65 5.93 1.97 0.66 3.86 0.72 0.87 0.54 0.17 0.95 Lu 0.28 0.29 0.28 0.26 0.86 0.27 0.09 0.63 0.11 0.12 0.08 0.03 0.16 ∑REE 606 484 349 403 353 326 114 79.4 96.3 138 80.1 8.1 68.1 (La/Yb)N 53.6 43.6 33.7 41.5 7.31 27.1 24.6 1.46 18.8 21.4 20.3 4.98 9.29 δEu 0.59 0.61 0.57 0.42 0.19 0.47 0.37 0.22 0.42 0.39 0.37 0.39 0.18 LREE 564 443.7 316 366 254 289 97.4 36.3 78.6 116 64.9 5.43 51.8 HREE 41.7 40.3 32.9 37.6 98.9 37.7 16.36 43.1 17.7 22.3 15.2 2.67 16.3 LREE/HREE 13.5 11.1 9.57 9.7 2.57 7.66 5.96 0.84 4.45 5.19 4.26 2.03 3.19 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量为10-6 表 3 邓阜仙岩体花岗岩全岩Sr-Nd同位素组成
Table 3. The Sr-Nd isotopic data of granites from Dengfuxian pluton
样品号 年龄/Ma 87Rb/86Sr 147Sm/144Nd 87Sr/86Sr(2σ) (87Sr/86Sr)i 143Nd/144Nd(2σ) (143Nd/144Nd)i εNd(t) 数据来源 邓阜仙
印支期227 2.641 0.082 0.723602(15) 0.7151 0.512016(5) 0.511894 -8.82 227 0.1321 0.511967(4) 0.511771 -11.24 本文 227 0.1267 0.511951(6) 0.511763 -11.87 225.7 2.27 0.099 0.723783(9) 0.716493 0.511958(2) 0.511812 -10.4 [7] 225.7 2.83 0.092 0.725229(7) 0.716155 0.511959(4) 0.511823 -10.2 225.7 1.95 0.092 0.722598(6) 0.716339 0.511988(13) 0.511853 -9.7 225.7 3.24 0.081 0.726328(8) 0.715923 0.511958(9) 0.511839 -9.9 222.9 20.2 0.13 0.785388(4) 0.721407 0.511961(20) 0.511772 -11.3 222.9 13.2 0.128 0.769876(5) 0.728078 0.511940(14) 0.511754 -11.7 160 0.1267 0.511951(5) 0.51182 -11.87 本文 154.4 44.8 0.133 0.806505(8) 0.708145 0.511988(4) 0.511854 -11.4 邓阜仙 154.4 69 0.137 0.830597(13) 0.679049 0.512010(6) 0.511871 -11.1 燕山期 154.4 18.9 0.161 0.787593(8) 0.746210 0.512007(22) 0.511845 -11.6 [7] 154.4 23.7 0.146 0.790698(135)0.735473 0.511980(23) 0.511859 -11.3 154.4 17.2 0.146 0.776834(7)0.752989 0.511944(4) 0.511832 -11.8 表 4 邓阜仙岩体成岩成矿年龄对比统计
Table 4. The statistical table for the comparison of diagenetic and metallogenic ages for Dengfuxian pluton
岩体期次 样品特征 测试对象 测试方法 测试结果/Ma 文献 邓阜仙岩体
印支期花岗闪长岩 锆石 LA-ICP-MS 225.1±1.2 本文 黑云母花岗岩 锆石 LA-ICP-MS 225.7±1.6 [19] 黑云母花岗岩 锆石 LA-ICP-MS 225.3±1.2 二云母花岗岩 锆石 LA-ICP-MS 224.3±2.4 二云母花岗岩 锆石 LA-ICP-MS 222.9±1.6 黑云母花岗岩 锆石 LA-ICP-MS 230±1.6 [8] 黑云母花岗岩 锆石 LA-ICP-MS 218.03±0.85 邓阜仙岩体
燕山期二云母花岗岩 锆石 LA-ICP-MS 154.4±2.2 [7] 斑状二云母花岗岩 锆石 LA-ICP-MS 151.1±2.3 [7] 二云母花岗岩 锆石 LA-ICP-MS 159±0.8 [30] 邓阜仙岩体
成矿年龄石英脉型黑钨矿 辉钼矿 Re-Os等时线 150.5±5.2 [31] -
[1] 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1217-1238. http://youxian.cnki.com.cn/yxdetail.aspx?filename=DGYK20160520000&dbname=CAPJ2015
[2] Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimina-tion diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Jour-nal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
[3] Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:petroge-netic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7):641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
[4] Eby G N. The A-type granitoids:A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculation on their petrogenesis[J]. Lith-os, 1990, 26(1/2):115-126. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/002449379090043Z
[5] Barbarin B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46:605-626. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00085-1
[6] 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大栓, 等.花岗岩研究思维与方法[M].北京:地质出版社, 2002:1-305.
[7] 蔡杨, 陆建军, 马东升, 等.湖南邓阜仙印支晚期二云母花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其意义[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(12):4215-42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201312011.htm
[8] 黄卉, 马东升, 陆建军, 等.湖南邓阜仙复式花岗岩体的锆石U-Pb年代学研究[J].矿物学报, 2011, (Sup):590-591. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2011S1303.htm
[9] 杨毅. 湖南邓阜仙钨矿花岗岩浆演化与成矿作用研究[D]. 昆明理工大学硕士学位论文, 2014: 1-97.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10674-1014356273.htm [10] 郑明泓, 邵拥军, 隗含涛, 等.湘东八团岩体的成因:地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学以及Hf同位素的制约[J].中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(11):3171-3181. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201511028.htm
[11] 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(10):2595-2604. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.025
[12] Cox K G. Bell J D, Pankhurst R J. The Interpretation of Igneoue Rock[M]. London:George Allen and Unwin, 1979:1-450.
[13] Wilson M B. Igneous Petrogenesis:A Golbal Tectonic Approach[M]. London:Springer, 1989:1-466.
[14] Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tcetonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
[15] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins[J]. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., 1989, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[16] Ling H F, Shen W Z, Wang R C, et al.Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Neoproterozoic granitiods in the Northwestern mar-gin of the Yangtze Block[J].Phys. Chem. Earth, 2001, 26:805-819. doi: 10.1016/S1464-1895(01)00129-6
[17] Zheng W, Chen M H, Zhao H J, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochrono-logical and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of Yingwuling tungsten polymetallic deposit in Guangdong Province and its geo-logical significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(12):4121-4135.
[18] Sylvester P J. Post-collisional peraluminous granites[J].Lithos, 1998, 45:29-44. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00024-3
[19] 蔡杨. 湖南邓阜仙岩体及其成矿作用研究[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2013: 1-153.
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GTDK201410022.htm [20] 蒋少涌, 赵葵东, 姜耀辉, 等.十杭带湘南-桂北段中生代A型花岗岩带成岩成矿特征及成因讨论[J].高校地质学报, 2008, 14(4):496-509. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200804006.htm
[21] 朱金初, 陈骏, 王汝成, 等.南岭中西段燕山早期北东向含锡钨A型花岗岩带[J].高校地质学报, 2008, 14(4):474-484. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200804004.htm
[22] 陈迪, 邵拥军, 刘伟, 等.湖南锡田复式花岗岩体岩石学、岩石地球化学特征[J].华南地质与矿产, 2015, 35(1):11-25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC201501002.htm
[23] 张旗, 冉白皋, 李承东.A型花岗岩的实质是什么?[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(4):621-626. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201302014.htm
[24] Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites:Geochem-ical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4):407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
[25] Chappell B W, White A J R. Two contrasting granite types[J].Pa-cific Geology, 1974, 8:173-174. http://geoscienceworld.org/georef/1975-030452
[26] Chen L, Ma C Q, She Z B, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic implica-tions of A-type granites in the Dabie orogenic belt, China:geo-chronological and geochemical constraints[J]. Geological Magazine, 2009, 146(5):638-651. doi: 10.1017/S0016756808005918
[27] 周新民, 陈培荣, 徐夕生.南岭地区晚中生代花岗岩成因与岩石圈动力学演化[M].北京:科学出版社, 2007:1-691.
[28] Carter A, Roques D, Bristow C, et al. understanding Mesozoic ac-cretion in Southeast Asia:significance of Triassic thermotectonnism (Indosinian orogeny)in Vietnam[J]. Geology, 2001, 29(3):211-214. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0211:UMAISA>2.0.CO;2
[29] Zhang L J. North and South CHina collision along the eastern and south China margins[J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 270(1/2):145-156. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/ExternalResource-gxdzxb200603008%5e63.aspx
[30] 黄鸿新. 湖南邓埠仙钨锡多金属矿床地球化学和成矿机制研究[D]. 长江大学硕士学位论文, 2013: 1-103.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10489-1014349755.htm [31] 蔡杨, 马东升, 陆建军, 等.湖南邓阜仙钨矿辉钼矿铼-锇同位素定年及硫同位素地球化学研究[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(12):3798-3808. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201212002.htm
[32] 邢光福, 卢清地, 陈荣, 等.华南晚中生代构造体制转折结束时限研究兼与华北燕山地区对比[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(4):451-463. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200804003.htm
[33] 陈培荣, 华仁民, 章邦桐, 等.南岭燕山早期后造山花岗岩类:岩石学制约和地球动力学背景[J].中国科学(D辑), 2002, 32(4):279-289. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200204002.htm
[34] 范蔚茗, 王岳军, 郭锋, 彭头平, 湘赣地区中生代镁铁质岩浆作用与岩石圈伸展[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10(3):159-169. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200303022.htm
[35] 王岳军, 廖超林, 范蔚茗, 等.赣中地区早中生代OIB碱性玄武岩的厘定及构造意义[J].地球化学, 2004, 33(2):109-117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200402000.htm
[36] Jiang Y H, Jiang S Y, Dai B Z, et al. Middle to late Jurassic felsic and mafic magmatism in southern Hunan Province, southeast Chi-na:Implications for a continental arc to rifting[J]. Lithos, 2008, 107(3/4):185-204. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11430-016-9044-5
[37] Zhao K D, Jiang S Y, Yang S Y, et al. Mineral chemistry, trace ele-ments and Sr-Nd-Hf isotope geochemistry and petrogenesis of Cailing and Furong granites and mafic enclaves from the Qitianling batholith in the Shi-Hang zone, South China[J]. Gondwana Re-search, 2011. 22(1):310-324. http://www.academia.edu/9477611/The_giant_Dexing_porphyry_Cu_Mo_Au_deposit_in_east_China_product_of_melting_of_juvenile_lower_crust_in_an_intracontinental_setting
[38] Li Z X, Li X H, Formation of the 1300km wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:a flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology, 2007, 35:179-182. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1
-




 下载:
下载: