Practice of the mapping method in continental volcanic rocks outcrop area:A case study of Cenozoic basalt in Shengzhou, Zhejiang Province
-
摘要:
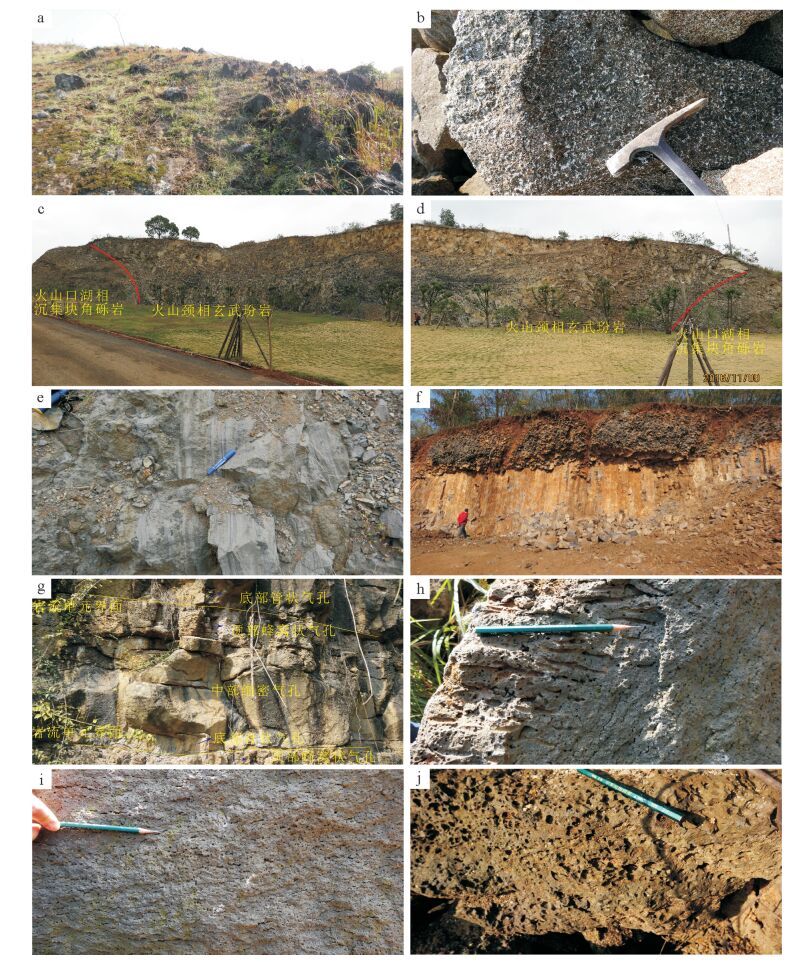
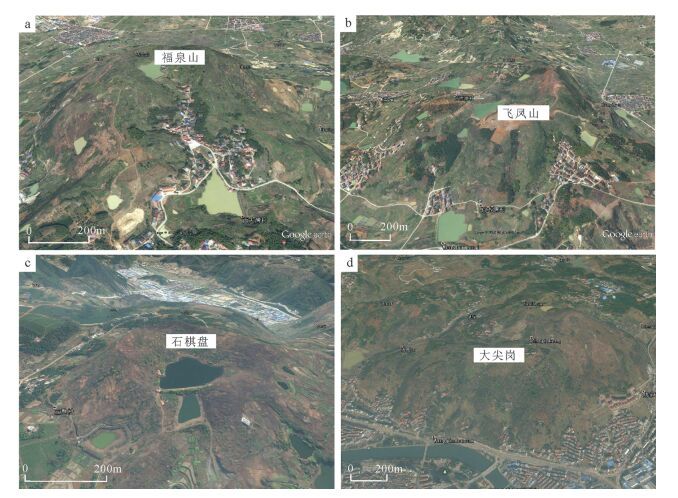
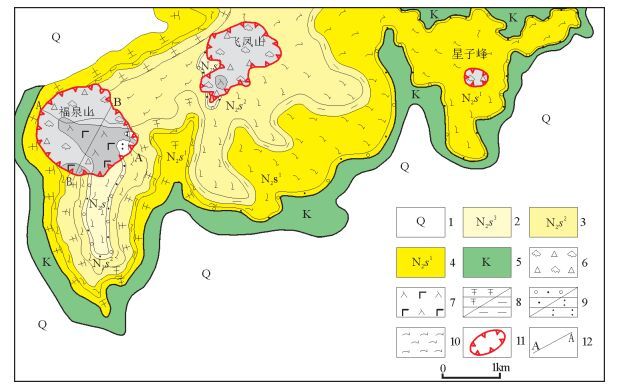
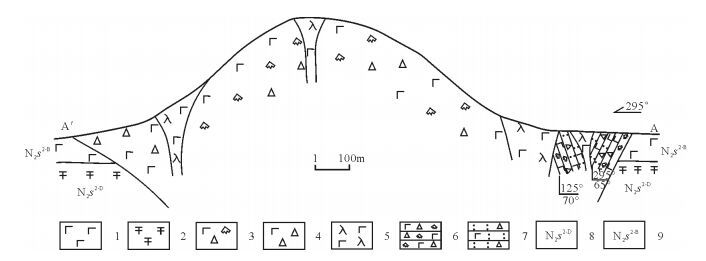
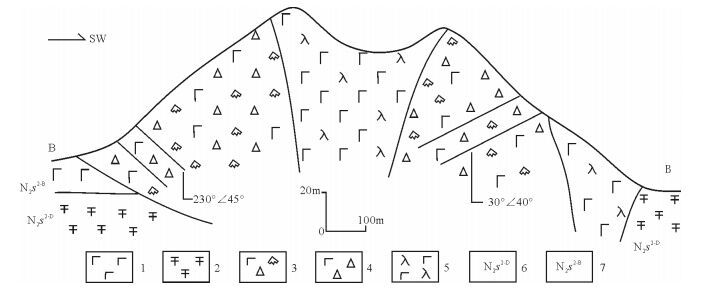
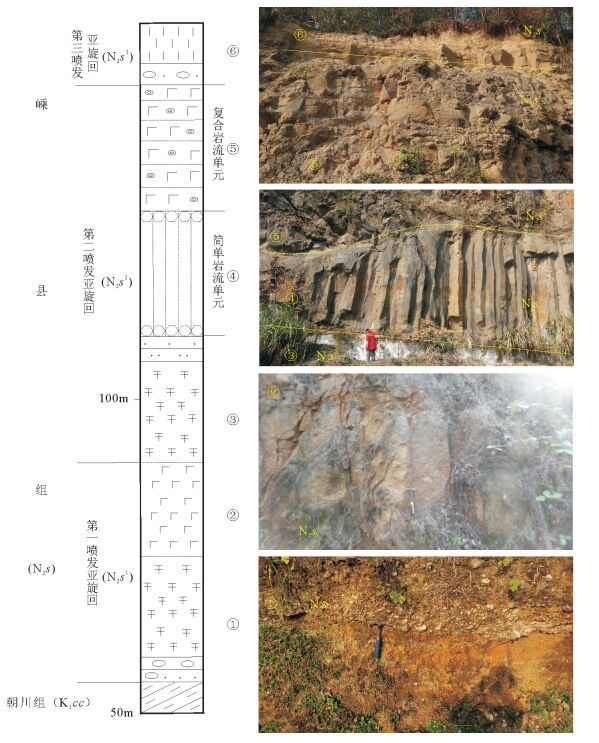
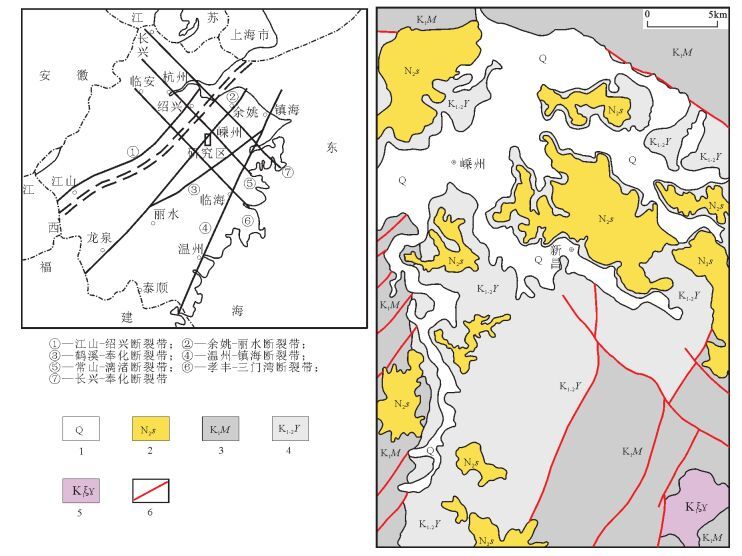
从20世纪90年代以来,中国陆相火山岩区调查工作普遍采用"火山构造-火山岩相-火山岩性"三位一体的思路与工作方法。以浙江嵊州地区1:5万区域地质调查工作为例,探讨了该方法在大面积新生代玄武岩区中的应用。系统的野外调查及研究显示,在新生代玄武岩区,遥感技术及新的影像图是火山岩区填图的关键,图像解译-野外验证的反复实践,是提高填图效果和质量的有效方法。在野外,特殊的地貌、爆发相的集块角砾岩及火山颈相的玄武玢岩往往指示了火山机构的中心;火山岩相、喷发间断是划分火山旋回的关键。火山机构、火山岩相、火山岩性的时间-空间变化是恢复古火山喷发历史的关键手段。
Abstract:The "volcanic structure-volcanic lithofacies-volcanic lithology" trinity mapping method has been wildly used in the continental volcanic rock outcrop area of China since the 1990s. This paper discussed the applicability of this mapping method in the 1:50000 Shengzhou geological mapping program for large outcrop area of Cenozoic basalts. According to field investigation and research work in the Cenozoic basalt area, the remote sensing technology and the new remote sensing images are the key factors of the volcanic rock area mapping. Image interpretation combined with field verification is one of the effective methods to improve the quality and effectiveness of the mapping. In the field, the special landscape and outcrops of eruption facies of breccias and volcanic neck facies of basalt porphyrite often indicate the central position of the volcano. Volcanic rock facies and eruption gaps are the key factors for the division of volcanic cycle. Volcanic edifice, volcanic lithofacies, volcanic lithology-space-time change are the key factors for restoration of ancient volcanic eruption histories.
-
Key words:
- continental volcanic rocks /
- mapping methods /
- Cenozoic basalt
-

-
[1] 地质矿产部区域地质矿产地质司.火山岩地区区域地质调查方法指南[M].北京:地质出版社, 1987.
[2] 陶奎元, 吴岩, 黄光召, 等.娘娘山古火山口的构造和岩相特征[J].地质学报, 1978, (1):40-53. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4877175
[3] 谢家莹, 蓝善先, 张德宝, 等, 运用火山地质学理论研究竹田头火山机构[J].火山地质与矿产, 2000, 21(2):87-95. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2000.02.002
[4] 陶奎元.火山岩相构造学[M].南京:江苏科学技术出版社, 1994.
[5] 傅树超, 卢清地.陆相火山岩区填图方法研究新进展——"火山构造-岩性岩相-火山地层"填图方法[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(11):1640-1648. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20101106&journal_id=gbc
[6] 马金清, 李进堂, 冯宗帜.火山构造组合研究和地质填图方法[J].中国区域地质, 2000, 19(2):198-204. http://www.docin.com/p-700890329.html
[7] 王美星, 王占宇, 陶奎元, 等.桐庐碎斑熔岩岩穹地质、岩石特征及其成因机理探讨[J].中国地质科学院南京地质矿产研究所所刊, 1985, 6(4):32-49. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ198510002004.htm
[8] 冯宗帜.福建省中新生代古火山构造基本特征[J].中国区域地质, 1984, 10:1-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD198403000.htm
[9] 李相传, 孙柏年, 肖良, 等.浙江新近纪嵊县组地层特征及其化石研究进展[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 50(2):145-153.
[10] Ho K S, Chen J C, Lo C H, et al. 40Ar-39Ar dating and geochemical characteristics of late Cenozoic basaltic rocks from the ZhejiangFujian Region, SE China:eruption ages, magma evolution and petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 197(1/4):287-318. https://es.scribd.com/.../Mechanism-of-Sedimentary-Basin-Formation-pdf
[11] 刘若新, 陈文寄, 孙建中, 等.中国新生代火山岩的K-Ar年代与构造环境[M].北京:地震出版社, 1992:1-43.
[12] 王人镜, 杨淑荣.浙江嵊县-新昌新生代玄武岩及包体的研究[J].地球科学, 1987, 12(3):241-248.
[13] 胡雅琴. 浙江嵊州早上新世植物群的重建和古气候定量研究[D]. 中国科学院植物研究所博士学位论文, 2007.
[14] Li J F, Hu Y Q, Ferguson D, et al. An early Pliocene lake and its surrounding vegetation in Zhejiang, East China[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2010, 43(4):751-769. doi: 10.1007/s10933-009-9366-z
[15] 王开发, 蒋辉, 郑卓, 等.浙江天台、新昌、嵊县地区玄武岩沉积夹层的孢粉、硅藻组合[J].地层学杂志, 1985, 9(1):28-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1985-DCXZ198501003.htm
[16] 黄成彦, 蔡祖仁.浙江中新世嵊县组的硅藻植物群[J].古生物学报, 1984, 23(3):358-372.
[17] Wang W M. Correlation of pollen sequencesin the Neogene palyno floristic regions of China[J]. Palaeoworld, 2006, 15(1):77-99. doi: 10.1016/j.palwor.2006.03.002
① 浙江省地质局区域地质调查大队. 中华人民共和国区域地质调查报告(1: 20万)诸暨幅(地质部分). 1975.
② 浙江省地质局区域地质调查大队. 中华人民共和国区域地质调查报告(1: 20万)仙居幅(地质部分). 1978.
-



 下载:
下载: