APPLICATION OF HIGH RESOLUTION AIRBORNE LIDAR IN XIAOJIANG ACTIVE TECTONICS AND GEOLOGICAL DISASTER STUDY
-
摘要:
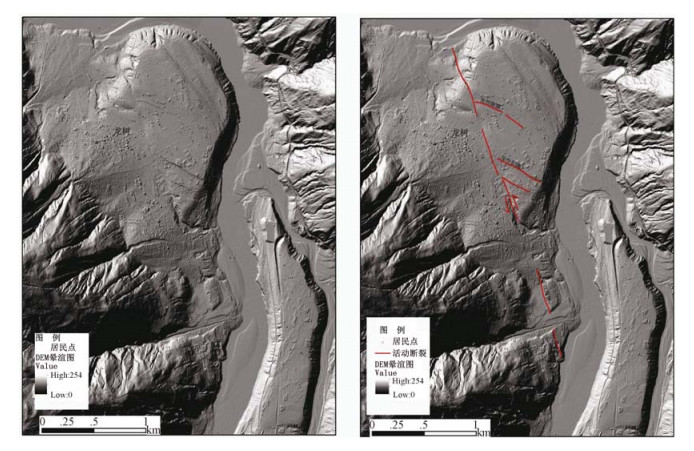
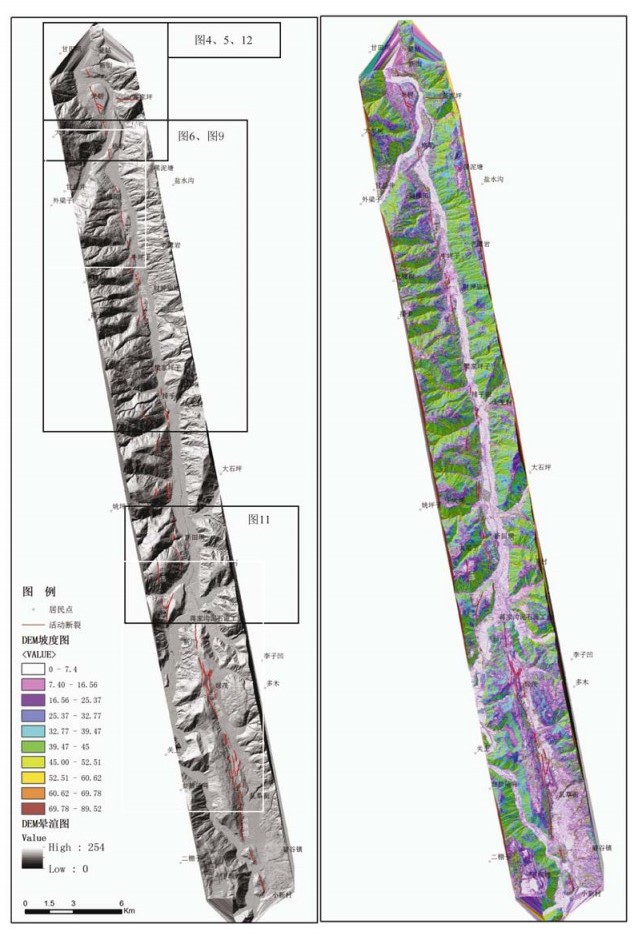
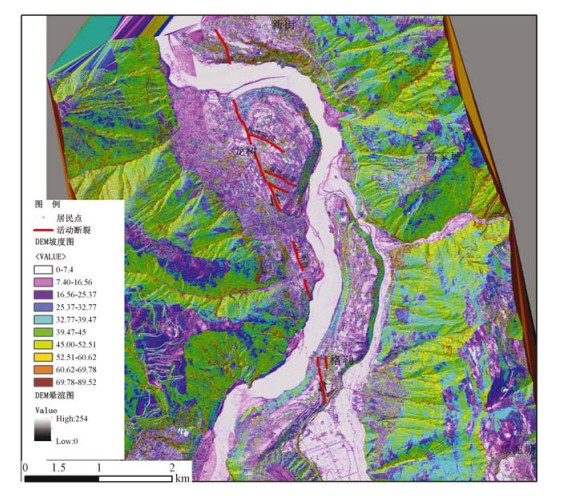
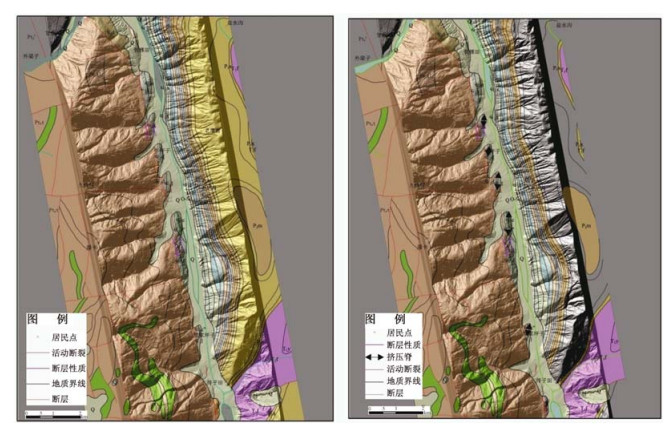
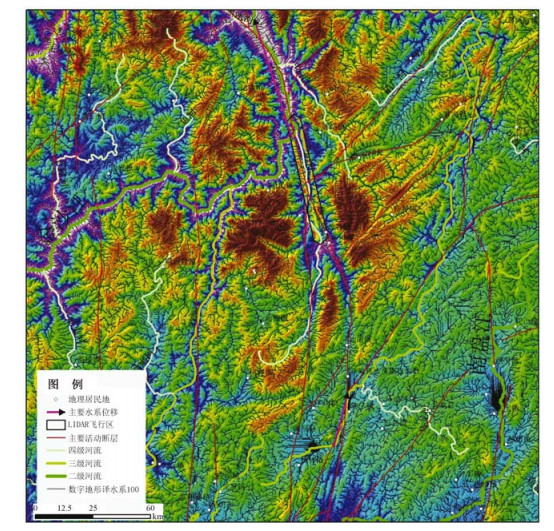
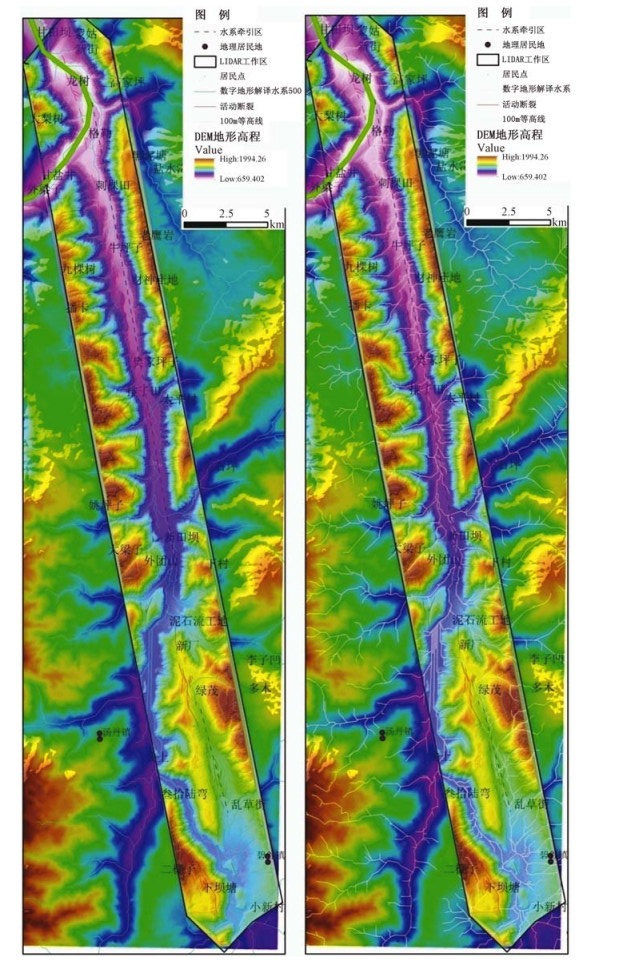
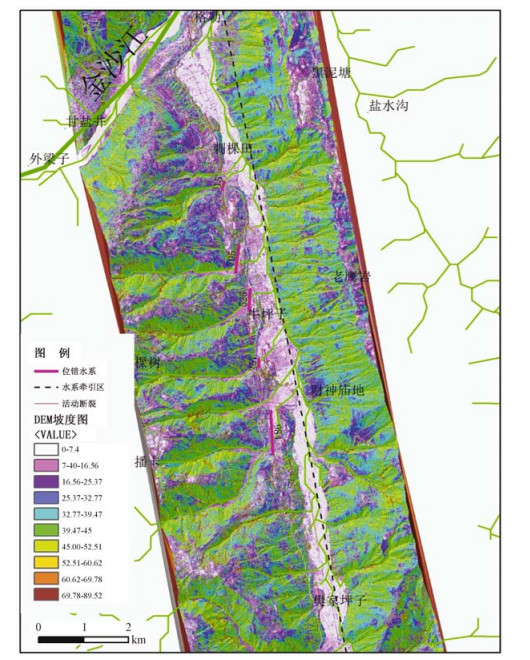
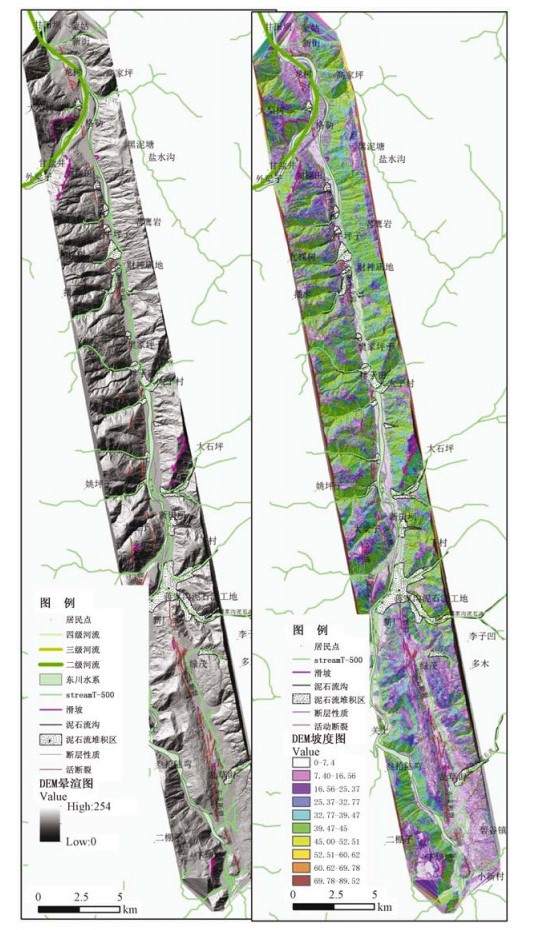
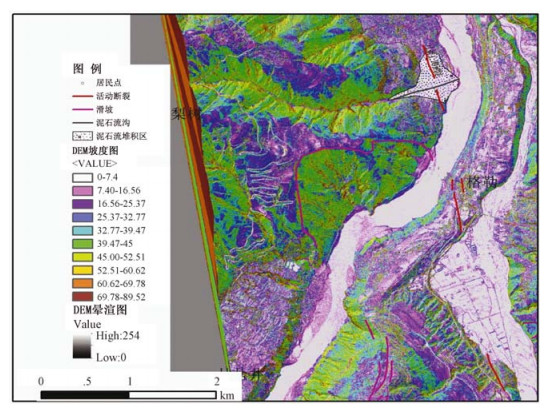
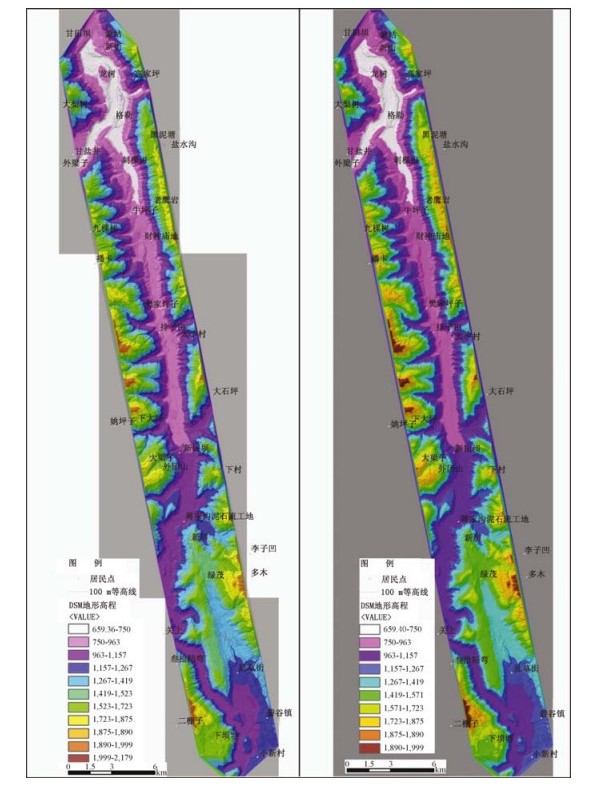
通过机载LiDAR飞行数据处理,获得飞行区内高精度的数字高程模型(DEM)和数字地表模型(DSM)等数字地形成果,应用数字地形进行地质构造解译,确定小江活动断裂展布及构造地貌特征,圈定飞行区内金沙江、小江的滑坡及泥石流的分布范围,估算其面积及体积,为此类地质灾害的预警提供可靠信息。
Abstract:By processing airborne LiDAR flight data of Jinsha River and Xiaojiang, we obtained high precision Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and Digital Surface Model (DSM). Using the digital terrain in geological structure interpretation, we may determine the distribution of active faults and the characteristics of tectonic geomorphology, delineating the range of the landslide and debris flow in Jinsha River and Xiaojiang, also estimating the area and volume of the landslide and debris flow. High precision airborne LiDAR data provides reliable information for such geological disaster warning.
-
Key words:
- LiDAR /
- DEM /
- Xiaojiang fracture /
- active faults /
- debris flow
-

-
[1] Arrowsmith J R, Zielke O. Tectonic geomorphology of the San Andreas fault zone from high resolution topography: An example from the Cholame segment[J]. Geomorphology, 2009, 113(1/2): 70~81. https://asu.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/tectonic-geomorphology-of-the-san-andreas-fault-zone-from-high-re
[2] 马洪超.激光雷达测量技术在地学中的若干应用[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(2): 347~354. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201102022.htm
MA Hong-chao. Review on applications of LiDAR mapping technology to geoscience[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geoscience, 2011, 36(2): 347~354. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201102022.htm
[3] 刘静, 陈涛, 张培震, 等.机载激光雷达扫描揭示海原断裂带微地貌的精细结构[J].科学通报, 2013, 58(1): 41~45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201301003.htm
LIU Jing, CHEN Tao, ZHANG Pei-zhen, et al. Illuminating the active Haiyuan fault, China by Airborne Light Detection and Ranging[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(1): 41~45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201301003.htm
[4] 任治坤, 陈涛, 张会平, 等.LiDAR技术在活动构造研究中的应用[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(6): 1196~1207. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201406019.htm
REN Zhi-kun, CHEN Tao, ZHANG Hui-ping, et al. LiDAR survey in active tectonics studies: An introduction and overview[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(6): 1196~1207. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201406019.htm
[5] 魏占玉, 何宏林, 高伟, 等.基于LiDAR数据开展活动断层填图的实验研究——以新疆独山子背斜-逆冲断裂带为例[J].地震地质, 2014, 36(3): 794~813. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201403020.htm
WEI Zhan-yu, HE Hong-lin, GAO Wei, et al. Experimental study on geologic mapping of active tectonics based on LiDAR data: A case of Dushanzi anticline-reverse fault zone in XinJiang[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2014, 36(3): 794~813. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201403020.htm
[6] 郑文俊, 雷启云, 杜鹏, 等.激光雷达(LiDAR):获取高精度古地震探槽信息的一种新技术[J].地震地质, 2015, 37(1): 232~241. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201501018.htm
ZHENG Wen-jun, LEI Qi-yun, DU Peng, et al. 3-D laser scanner (LiDAR): A new technology for acquiring high precision palaeoearthquake trench information[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2015, 37(1): 232~241. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201501018.htm
[7] 肖春蕾, 郭兆成, 郑雄伟, 等.机载LiDAR技术在地质调查领域中的几个典型应用[J].国土资源遥感, 2016, 28(1): 136~143. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2017.01.21
XIAO C Lhun-lei, GUO Zhao-cheng, ZHENG Xiong-wei, et al. Typical applications of airborne LiDAR technique in geological investigation[J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 2016, 28(1): 136~143. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2017.01.21
[8] 李占飞, 刘静, 邵延秀, 等.基于LiDAR的海原断裂松山段断错地貌分析与古地震探槽选址实例[J].地质通报, 2016, 35(1): 104~116. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201601009.htm
LI Zhan-fei, LIU Jing, SHAO Yan-xiu, et al. Tecto-geomorphic analysis and selection of trench sites along Haiyuan fault in Songshan site based on high-resolution airbone LiDAR data[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(1): 104~116. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201601009.htm
[9] 马晓雪, 吴中海, 李家存.LiDAR技术在地质环境中的主要应用与展望[J].地质力学学报, 2016, 22(1): 93~103. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160110&journal_id=dzlxxb
MA Xiao-xue, WU Zhong-hai, LI Jia-cun. LiDAR Technology and its application and prospect in geological environment[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(1): 93~103. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160110&journal_id=dzlxxb
[10] Arrowsmith J R, Zielke O.通过高分辨率地形数据解析圣安德烈斯断层带的构造地貌:以乔莱姆段为例[J].世界地震译丛, 2011, (5): 64~80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYC201105007.htm
Arrowsmith J R, Zielke O. Tectonic geomorphology of the San Andreas Fault zone from high resolution topography: An example from the Cholame segment[J]. Transland World Seismology, 2011, (5): 64~80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYC201105007.htm
[11] 朱成男, 膝德贞, 段加乐, 等.云南巧家段金沙江断错河谷[J].科学通报, 1984, 24: 1520~1523. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198424012.htm
ZHU Cheng-nan, QI De-zhen, DUAN Jia-le, et al. Qiaojia section of Jinsha River in Yunnan dislocation river valley[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1984, 24: 1520~1523. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198424012.htm
[12] Wang E, Burchiel B C, Royden L H, et al. Late Cenozoic Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang, Red River, and Dali fault system of southwestern Sichuan and central Yunnan, China[C]//Special Paper of Geological Society of American 327. 1998: 1~108.
[13] 李显巨. 基于LiDAR技术的复杂地质环境区滑坡识别研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2012.
LI Xian-ju. Research of the landslide recognition based on LiDAR technology in the complex geological environmental area[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2012.
-



 下载:
下载: