Automatic monitoring of natural resource in Anqing City of Anhui Province based on statistical learning methods-a case study of mountains
-
摘要:
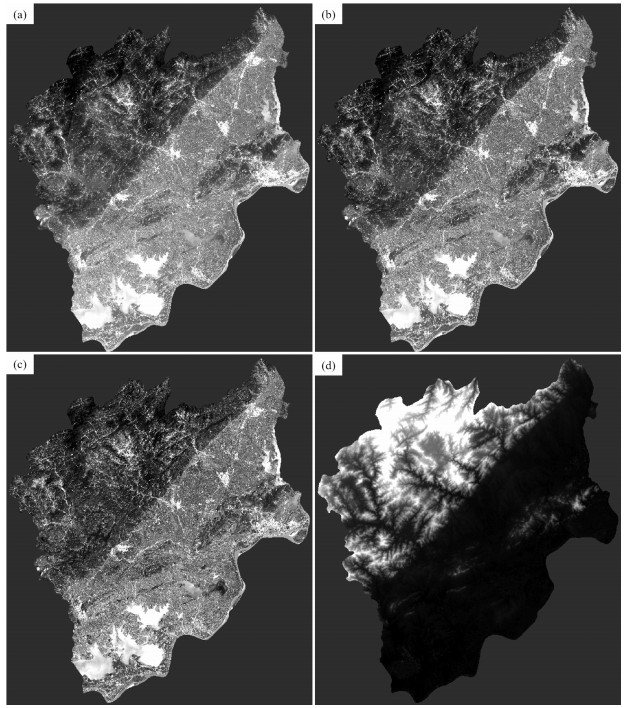
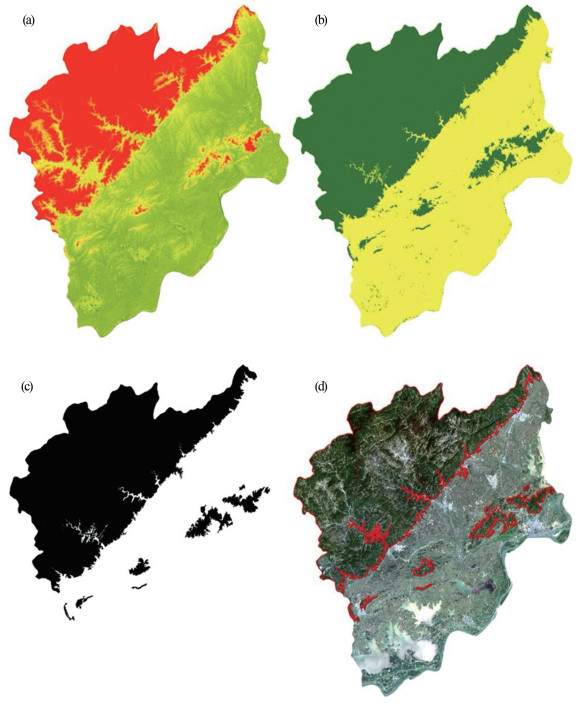
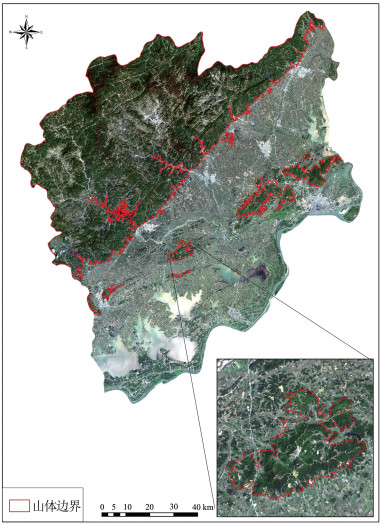
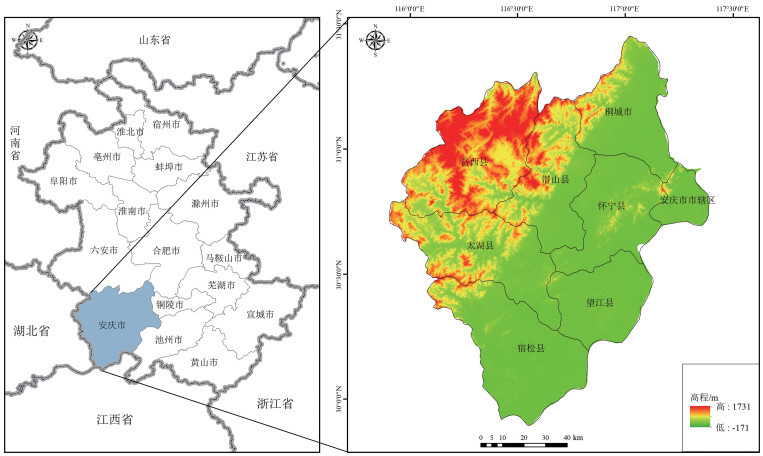
遥感作为一种可以快速、大范围获取地表覆盖信息的技术手段,为复杂的自然资源调查任务提供了可靠的数据来源。针对山体确界问题,以遥感卫星影像为数据支撑,采用非监督的统计学习方法,为山体特征建模。然后,采用DBSCAN算法和边缘检测思想,识别山体区域,并提取山体边界。该方法不依赖于人工标记真值,实现了山体边界的全自动识别。实验采用安庆市Landsat 8遥感卫星影像数据,有效识别了安庆市境内的山体,并提取山体边界。通过定性和定量化分析,验证了方法的可靠性,证明了遥感技术和统计学习理论在自然资源调查领域的应用潜力。该研究方法和结果能够为安庆市明确山体范围,界定山体的完整性与山体保护规划工作提供理论支撑。
Abstract:Remote sensing, a technology used for quickly and extensively acquisition of land cover information, provides a reliable data source for complex natural resource survey.Aiming at the problem of mountain boundary recognition, an unsupervised statistical learning method was proposed to extract mountain features using remote sensing satellite images for modeling of mountain features.Specifically, DBSCAN algorithm and edge detection ideas were used to identify the mountain area and extract the mountain boundary.This approach recognizes the mountain boundary automatically, which does not rely on marking the ground truth manually.In the experiment, the Landsat 8 remote sensing satellite image data of Anqing City were used to effectively identify the mountainous area and extract the boundaries of the mountains.Through qualitative and quantitative analysis, the reliability of the proposed method was verified.Moreover, it proved the application potential of remote sensing technology and statistical learning theory in the field of natural resource survey.
-
Key words:
- natural resources /
- mountain /
- remote sensing /
- statistical learning /
- recognition /
- Anhui Province
-

-
表 1 定量化结果分析
Table 1. Analysis result of the quantitative results
评价指标 准确率(pc) 误判率(pe) 漏检率(pm) 精度/误差 88.61% 5.53% 10.76% -
[1] 李瑞敏, 殷志强, 李小磊, 等. 资源环境承载协调理论与评价方法[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(1): 80-87. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200108&flag=1
[2] 王薇, 张太平, 王强, 等. 黄河下游地区浅层地下水资源特征及保护建议[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(s1): 93-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE2019S1012.htm
[3] 杨鹏, 袁杰, 秦鹏. 日照市地下水动态特征及演化规律[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(s1): 100-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE2019S1013.htm
[4] 代晶晶, 王登红, 等. 我国三稀矿产资源遥感调查综述[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(6): 1270-1278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.008
[5] 黄国成, 程海艳, 李翔, 等. 浙江矿产时空分布规律综述[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(1): 102-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202001009.htm
[6] Cao R, Chen Y, Shen M, et al. A simple method to improve the quality of NDVI time-series data by integrating spatiotemporal information with theSavitzky-Golay filter[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 217: 244-257. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.08.022
[7] Watson C S, King O S, Miles E, et al. Optimising NDWI supraglacial pond classification on Himalayan debris-covered glaciers[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 217: 414-425. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.08.020
[8] 韩芳, 张百平, 李西灿, 等. 青藏高原山体效应的遥感估算及其生态效应分析[J]. 山地学报, 2016, 34(6): 788-798. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201606014.htm
[9] 李勇, 孙晓鹏, 李海亮. InSAR技术在西部山区某高速公路山体变形机理分析研究中的应用[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2020, 31(3): 88-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB202003016.htm
[10] 陈兴芳, 张福存, 王晓东, 等. 基于时序InSAR技术的山体滑坡灾害监测研究[J]. 测绘工程, 2020, 29(5): 45-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHGC202005008.htm
[11] 杨燕, 杜甘霖, 曹起铜. 无人机航测技术在地质灾害应急测绘中的研究与应用——以9·28丽水山体滑坡应急测绘为例[J]. 测绘通报, 2017, 增刊: 110-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHTB2017S1032.htm
[12] 王琳, 陈楚, 吴正鹏. 无人机遥感在山体创面三维模型制作中的应用研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2020, 43(4): 361-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ202004013.htm
[13] 李超. 三维激光扫描技术在山体形变监测中的应用[J]. 测绘通报, 2012, 11: 98-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHTB201211032.htm
[14] 杨奇勇, 马祖陆, 蒋忠诚. 峰丛洼地遥感图像山体阴影缺失的克里格修复[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2012, 95(4): 112-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG201204020.htm
[15] 岳照溪, 张永军, 段延松, 等. DEM辅助的卫星光学遥感影像山地阴影检测与地形辐射校正[J]. 测绘学报, 2018, 47(1): 113-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201801015.htm
[16] 都伟冰, 李均力, 包安明, 等. 高山冰川多时相多角度遥感信息提取方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2015, 44(1): 59-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201501012.htm
[17] 林俊强, 龚岳, 李贵才. 精明增长视角下的生态控制线研究——以珠海生态控制线规划为例[J]. 规划师, 2018, 34(2): 67-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHSI201802013.htm
[18] 冯泉霖, 李洪涛, 赵振华, 等. 济南城市建设区外山体保护线划定探索及实践[J]. 山东国土资源, 2020, 36(10): 58-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI202010010.htm
[19] Ju Z, Liu H. Fuzzy gaussian mixture models[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2012, 45(3): 1146-1158.
[20] Shen J, Hao X, Liang Z, et al. Real-timesuperpixel segmentation by DBSCAN clustering algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(12): 5933-5942.
[21] McIlhagga W. The Canny Edge Detector Revisited[J]. Int Journal of Computer Vision, 2011, 91: 251-261.
[22] LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521: 436-444.
[23] Lake B M, Salakhutdinov R, Tenenbaum J B. Human-level concept learning through probabilistic program induction[J]. Science, 2015, 350(6266): 1332-1338.
-



 下载:
下载: