The development of in situ detection technology and device for dissolved methane and carbon dioxide in deep sea
-
摘要:
甲烷、二氧化碳的地质和生物地球化学循环对海洋环境和全球气候变化有着重要影响,其在深海环境中通常以气泡或流体的形式向四周扩散,甲烷还是探测海底天然气水合物资源的重要指标之一。目前,国内外研究团队提出了各种背景下原位探测海洋溶解甲烷、二氧化碳的新技术、新方法,以促进对海洋碳循环的研究。简述了基于电化学技术、光学技术、质谱技术和生物传感技术等对海洋溶解甲烷、二氧化碳进行原位探测的最新进展,系统介绍了各传感器的工作原理和性能,分析其应用价值和前景,并在此基础上对未来的研究方向提出一些建议。
Abstract:The geological and biogeochemical cycle of methane and carbon dioxide in the ocean has an important impact on the marine environment and global climate change. In many deep-sea environments, methane and carbon dioxide usually diffuse in the form of bubbles or fluids, Methane is also one of the important indicators to detect the resources of natural gas hydrates. At present, in order to promote the study of marine carbon cycle and flux, research groups at home and abroad have proposed new technologies and methods for in-situ detection of dissolved methane and carbon dioxide in the ocean under various backgrounds. In this paper, the latest progress of in situ detection of dissolved methane and carbon dioxide in the ocean based on electrochemical, optical, mass spectrometry and biosensor technologies is reviewed, the working principle and performance of each sensor are introduced systematically, the application value and prospect of it are analyzed, and some suggestions for future research are put forward.
-

-
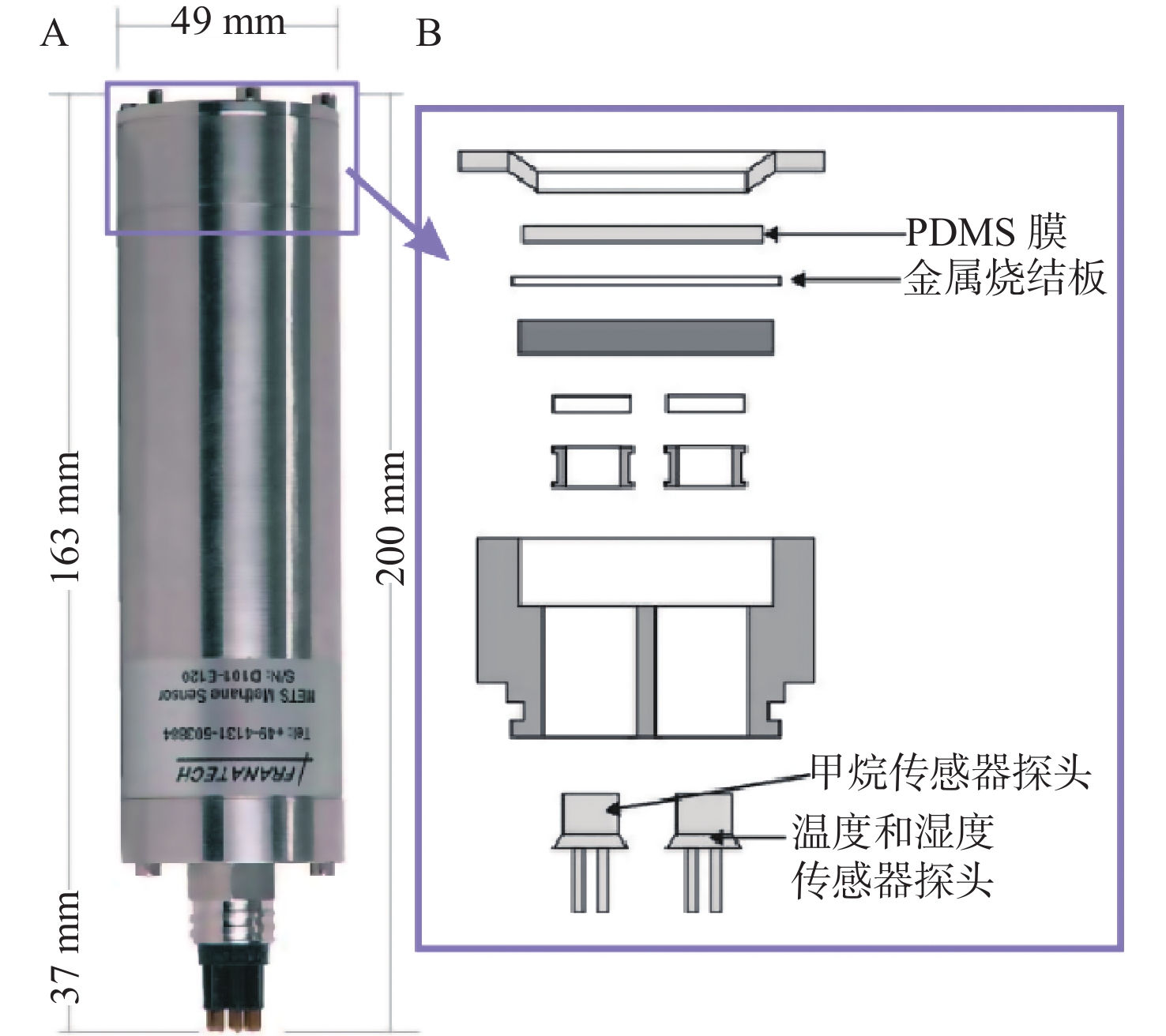
图 1 METS传感器结构图[12]
Figure 1.
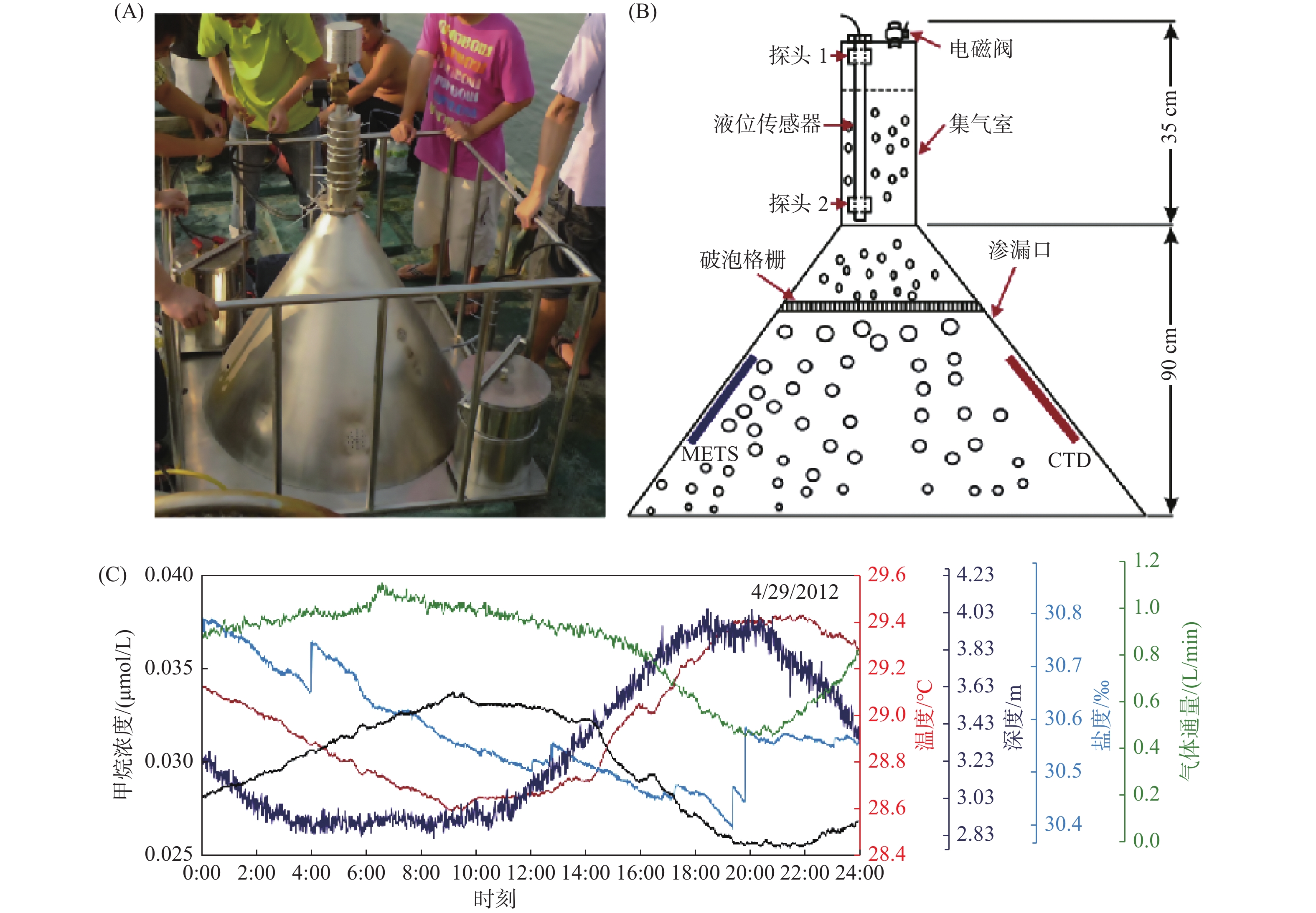
图 2 原位在线测量装置及应用[13]
Figure 2.
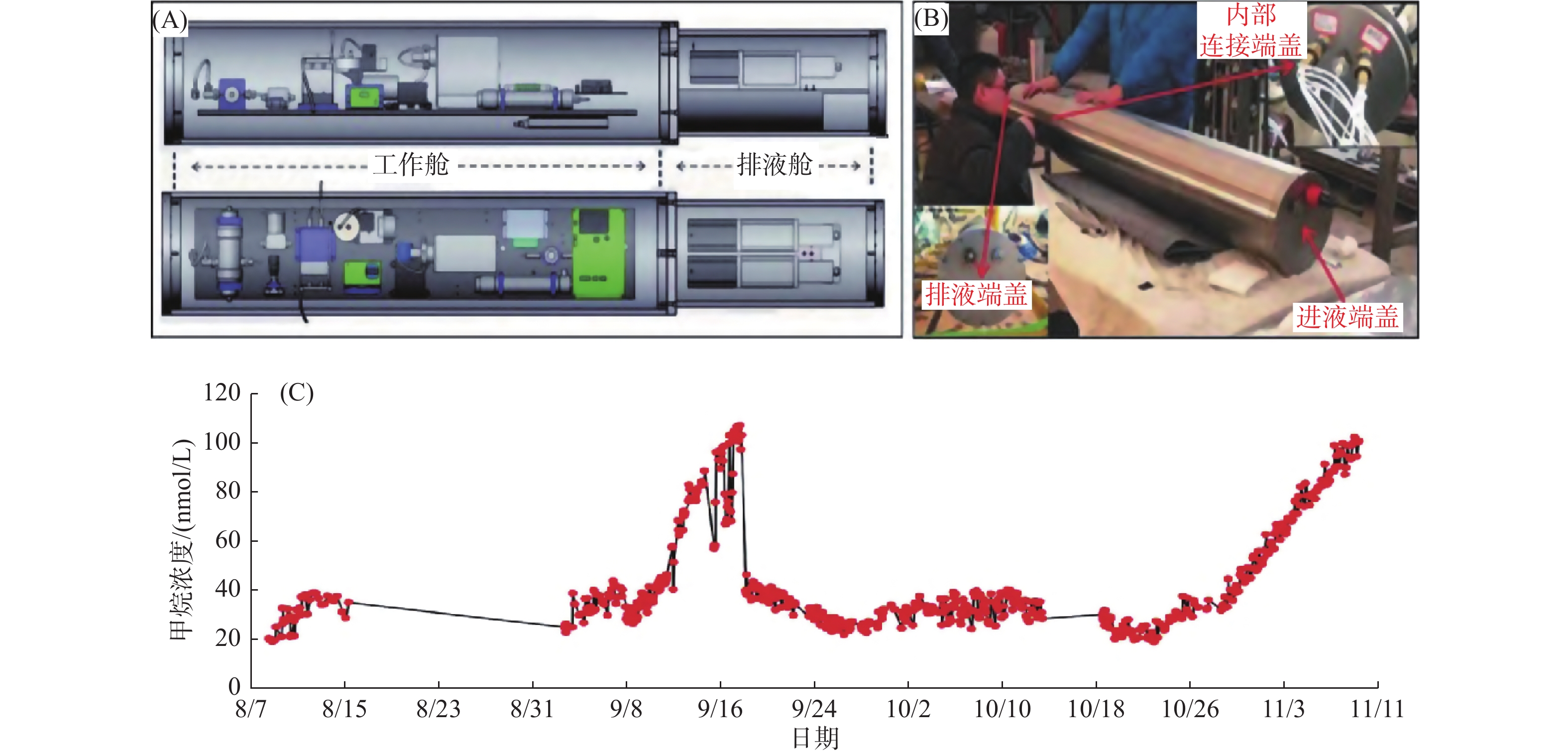
图 3 深海溶解CH4原位长期监测仪器及应用 [18]
Figure 3.
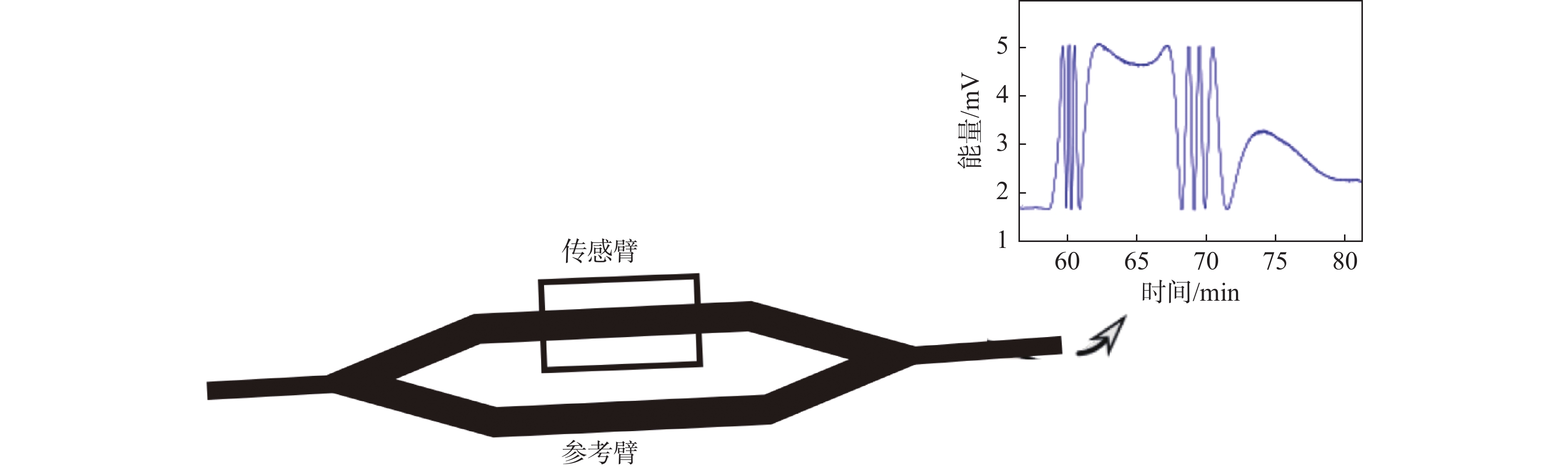
图 4 电位传感器布局及原位观测数据[19]
Figure 4.
图 6 ICOS分析仪及其原位观测数据[22]
Figure 6.
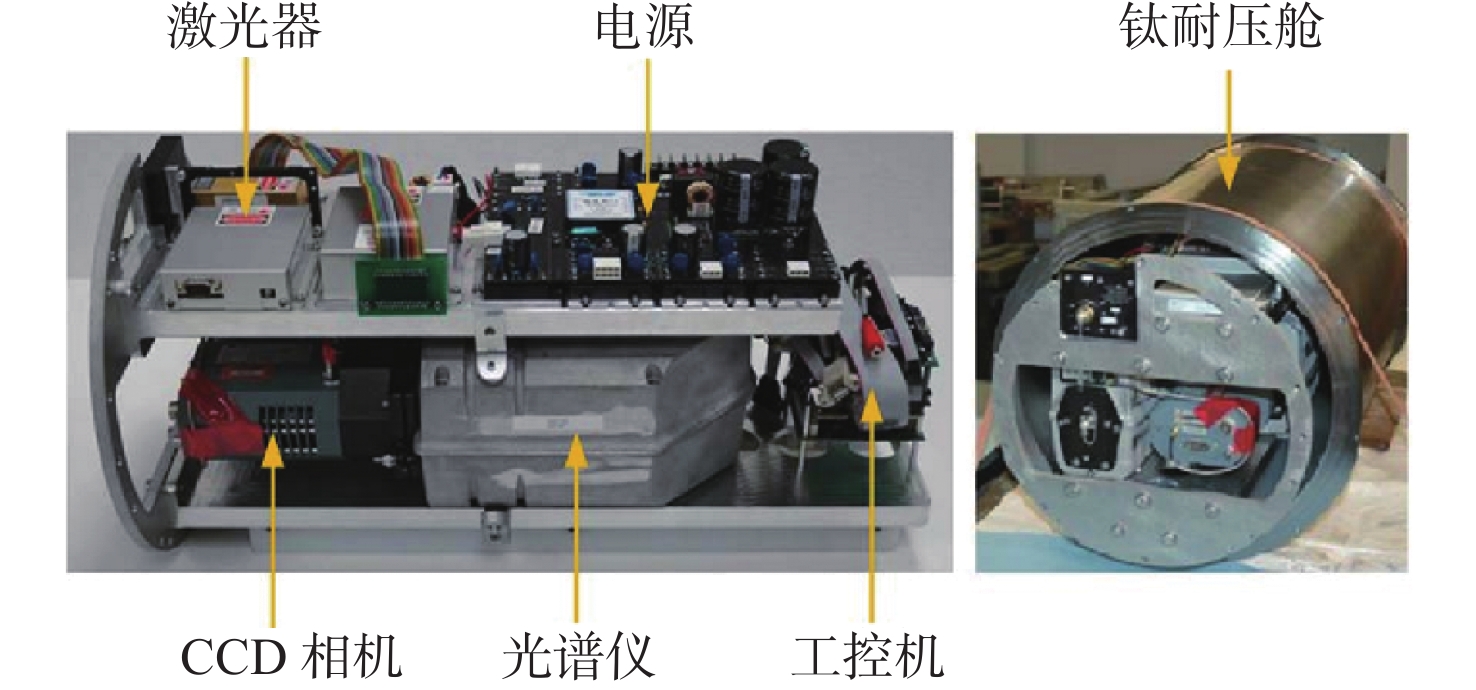
图 7 第2代ICOS光谱仪及其原位观测数据[31]
Figure 7.
图 8 Sub Ocean传感器及其应用[33]
Figure 8.
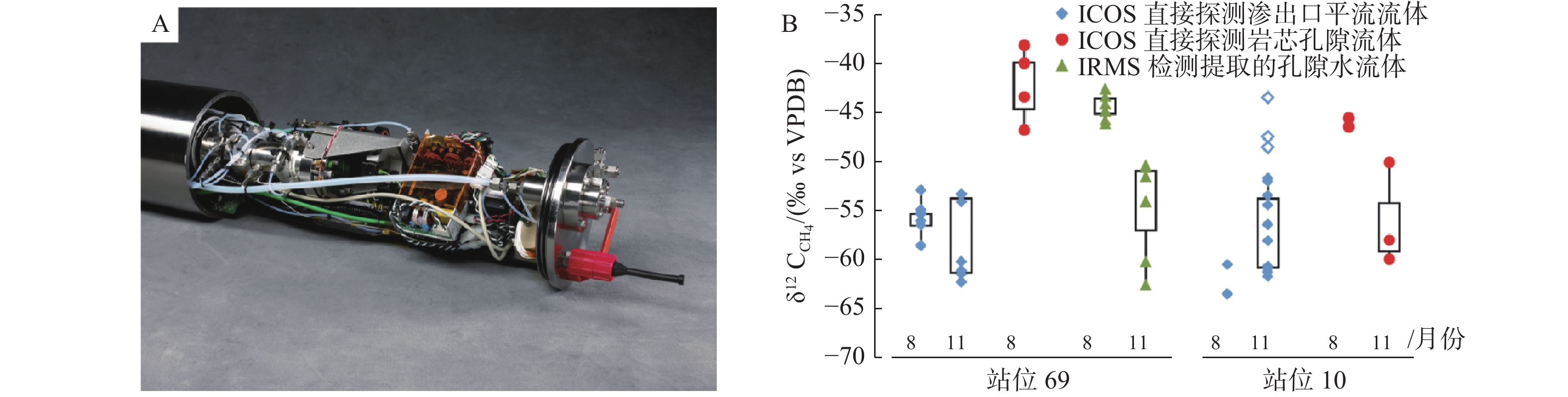
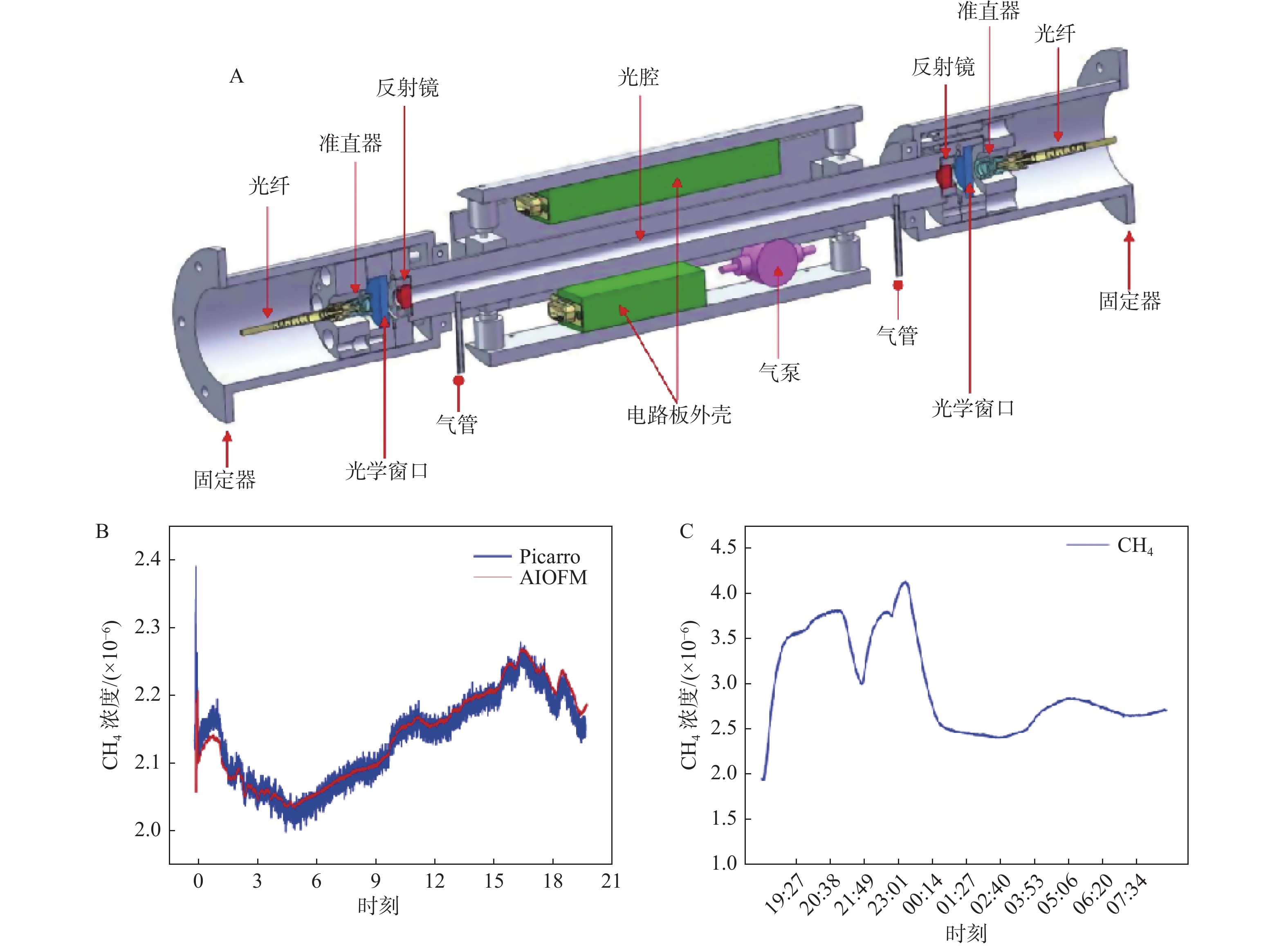
图 9 AIOFM装置结构图和测试结果[35]
Figure 9.
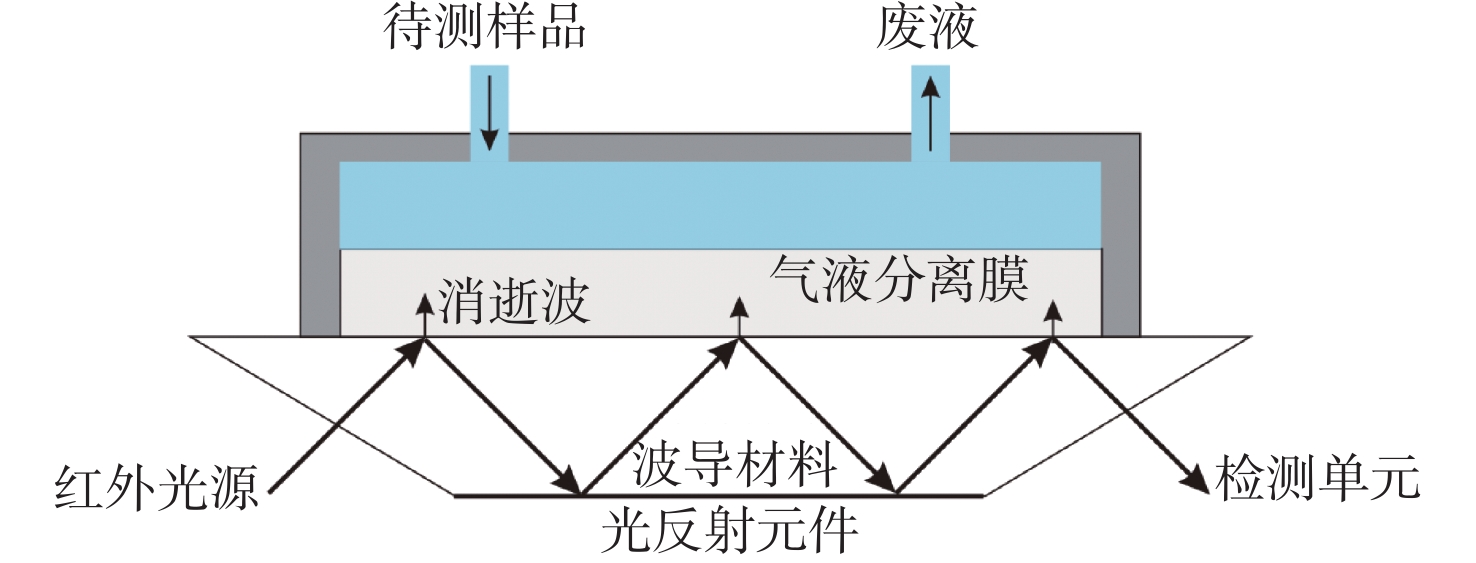
图 10 基于衰减全反射技术的红外传感器原理图[38]
Figure 10.
图 11 便携式红外传感器系统示意图[40]
Figure 11.
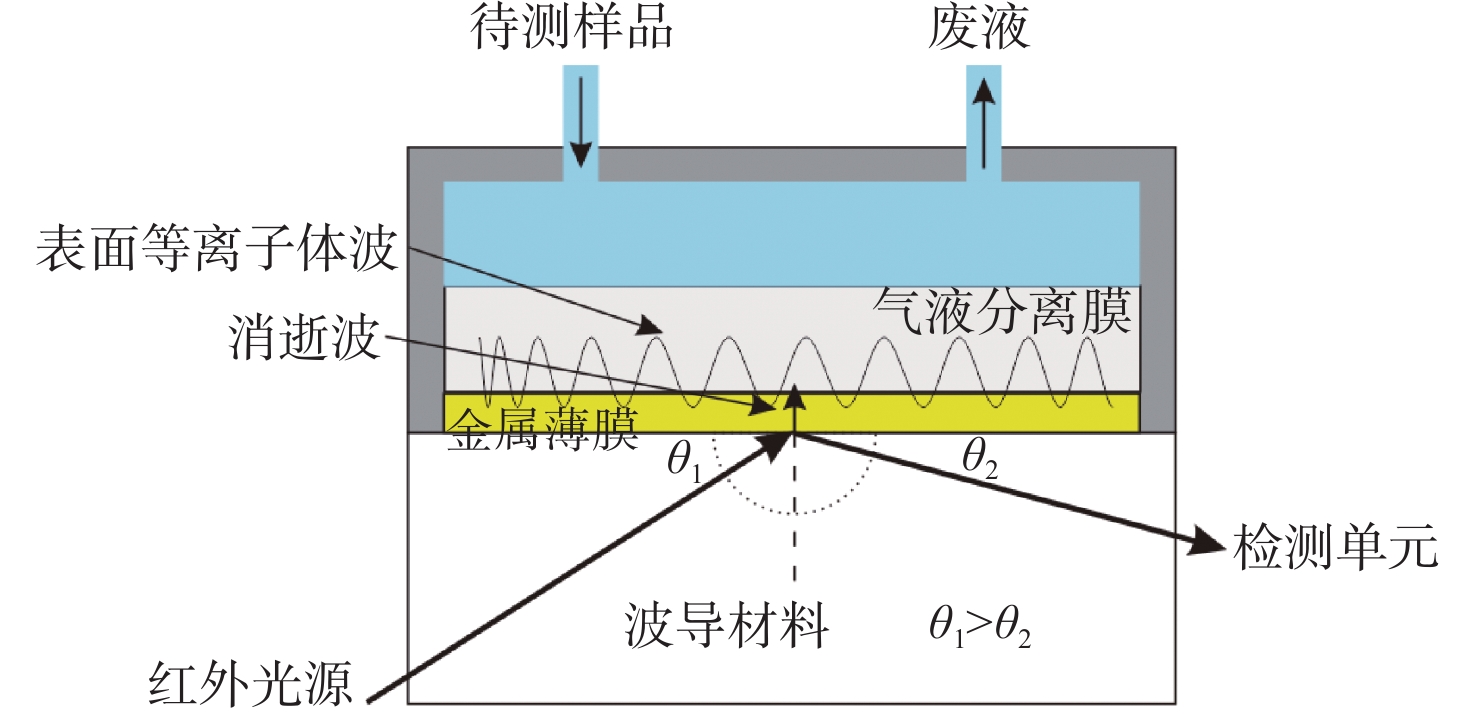
图 12 表面等离子体共振检测原理[41]
Figure 12.
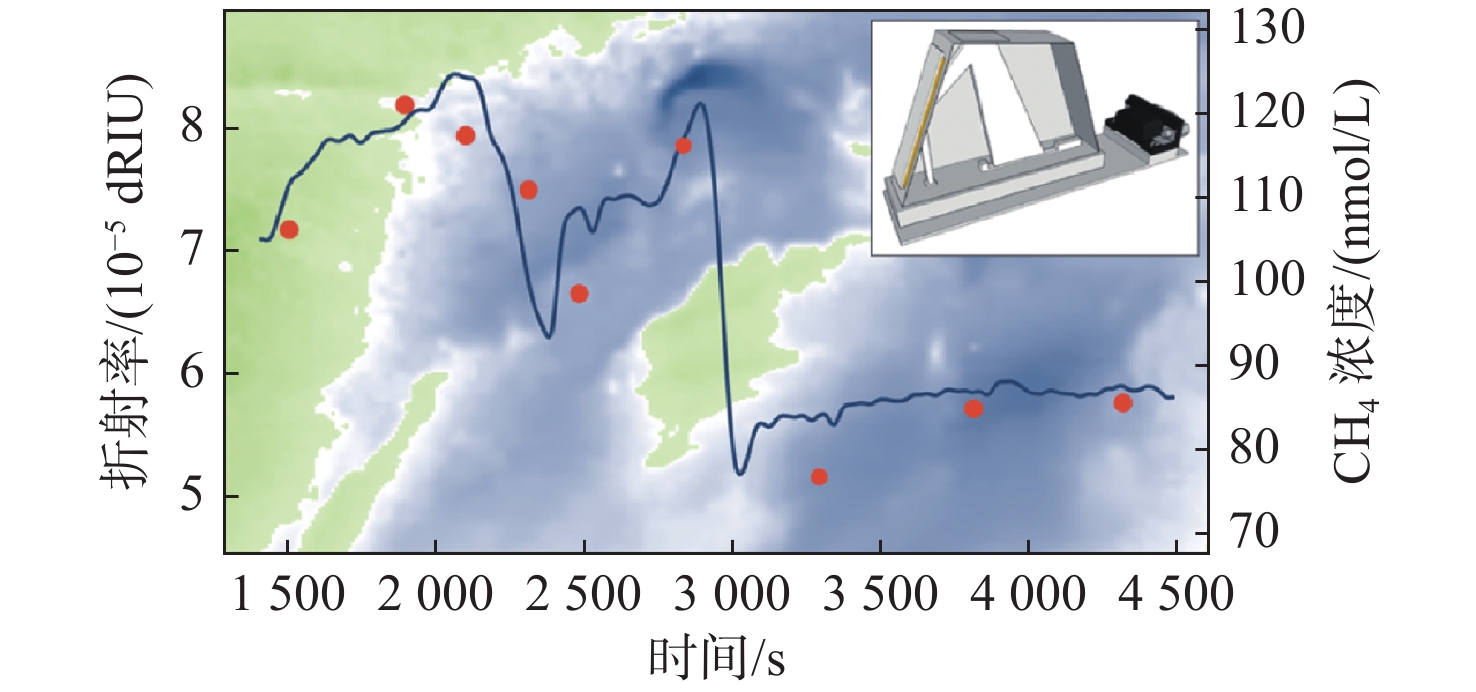
图 13 传感器示意图及通过折射率获得的CH4浓度数据[44]
Figure 13.
图 14 马赫曾德尔干涉仪结构图[41]
Figure 14.
图 15 深海拉曼原位光谱仪实物图[52]
Figure 15.
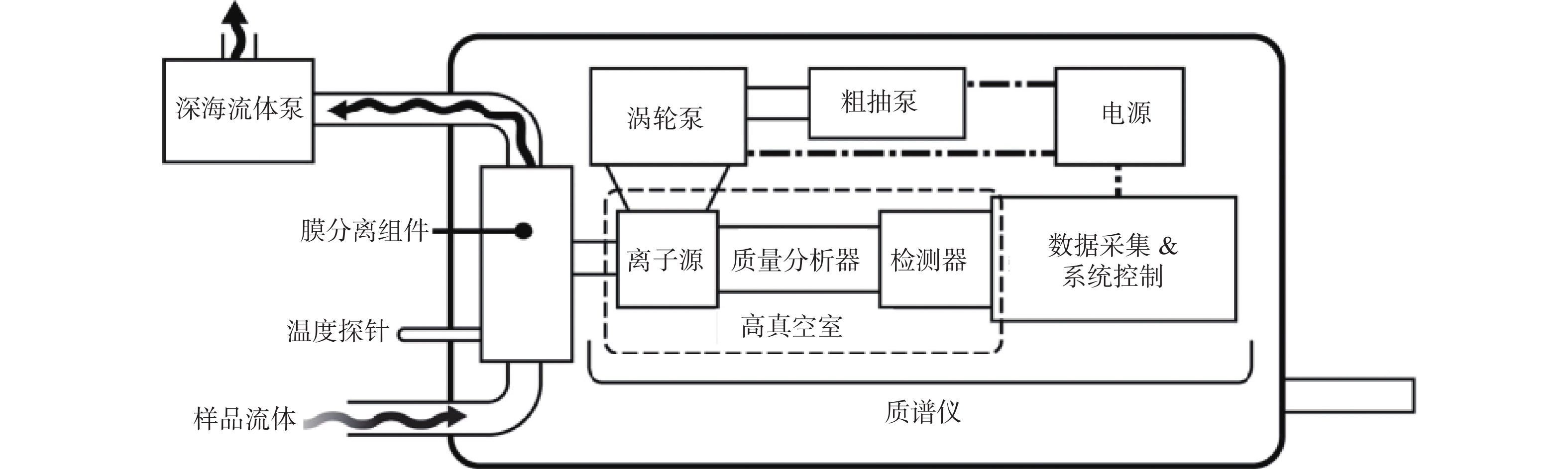
图 18 通用水下质谱系统的总体布局[68]
Figure 18.
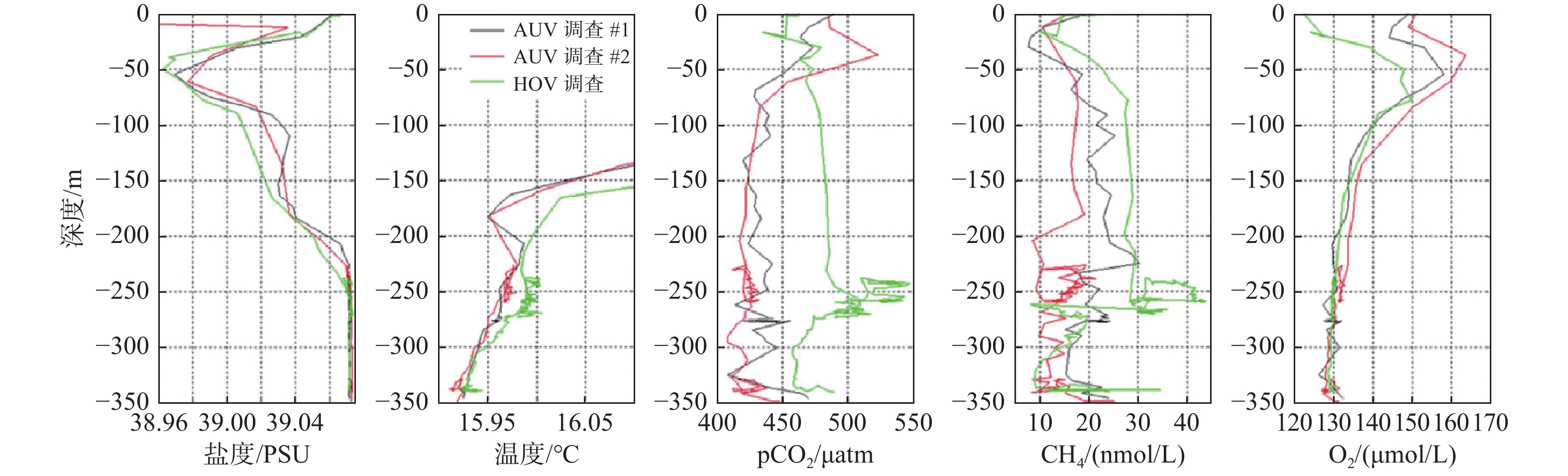
图 19 TETHYS质谱仪在2次AUV调查和1次HOV调查期间记录的盐度、温度、CO2分压、溶解CH4和溶解氧分布的剖面图[72]
Figure 19.
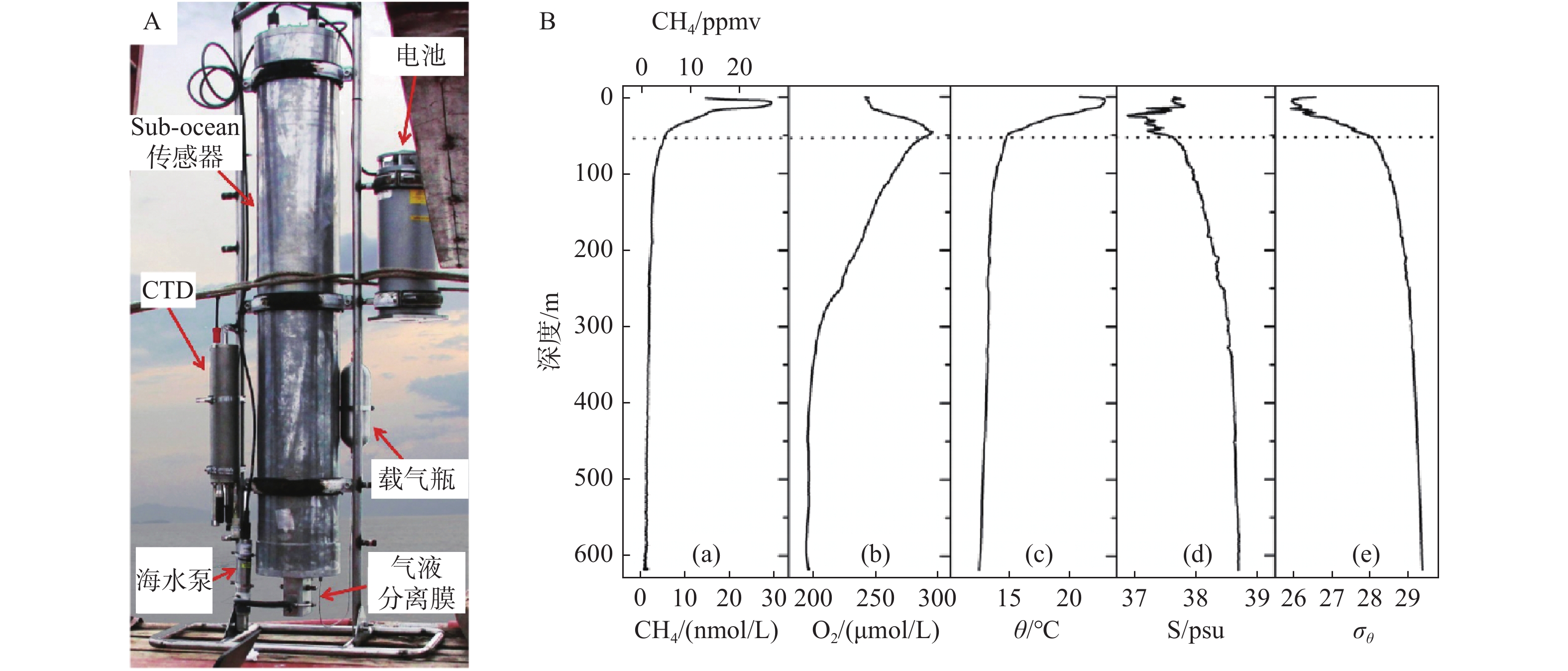
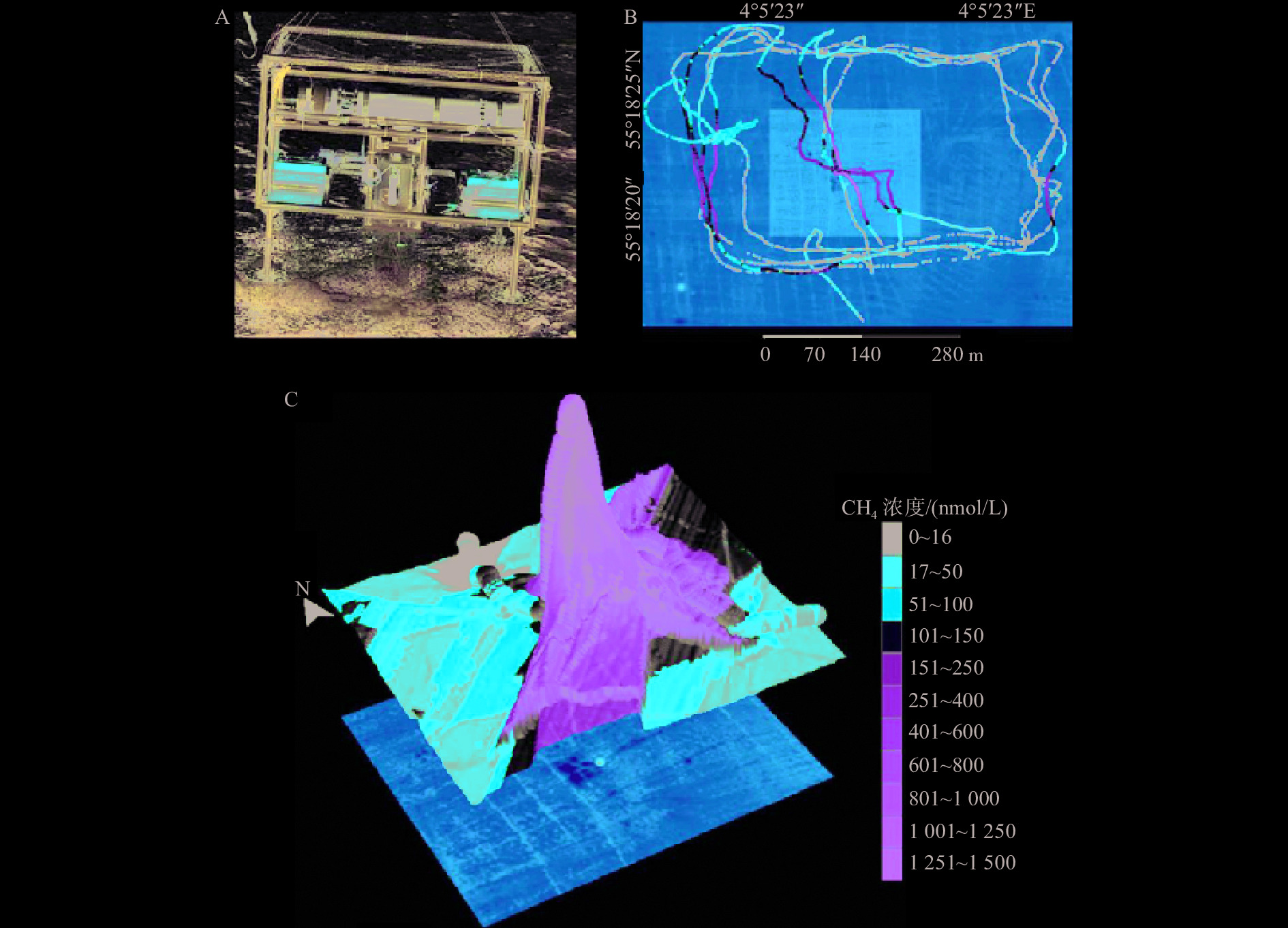
图 20 水下质谱仪及其应用[65]
Figure 20.
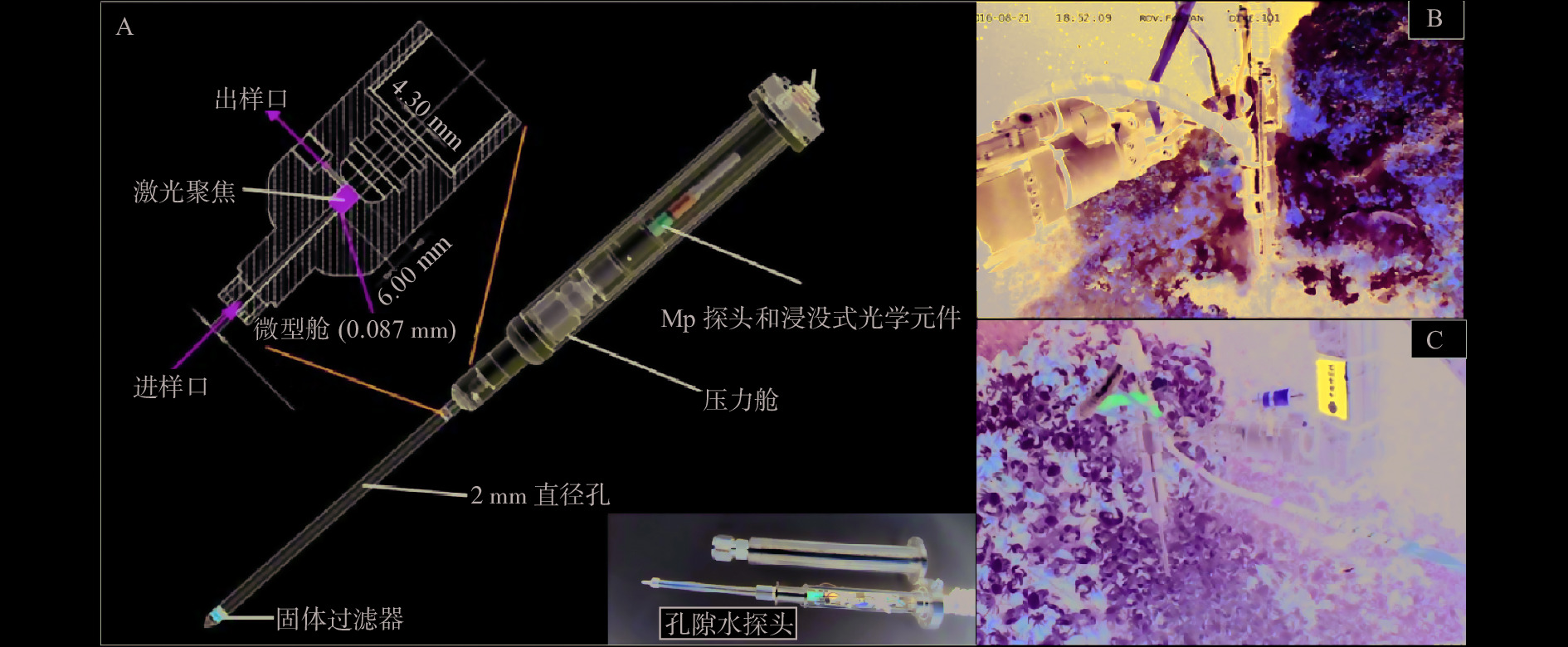
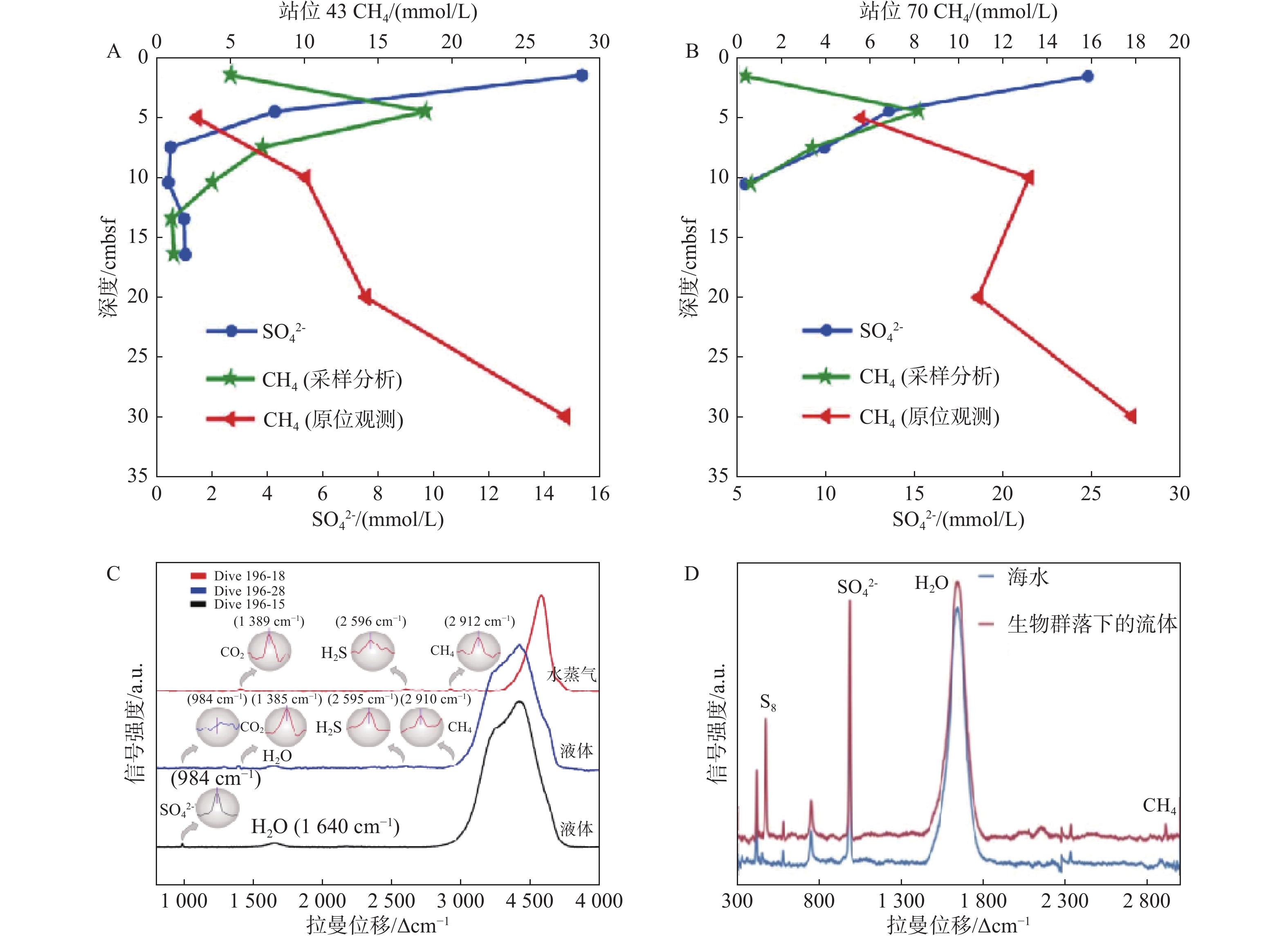
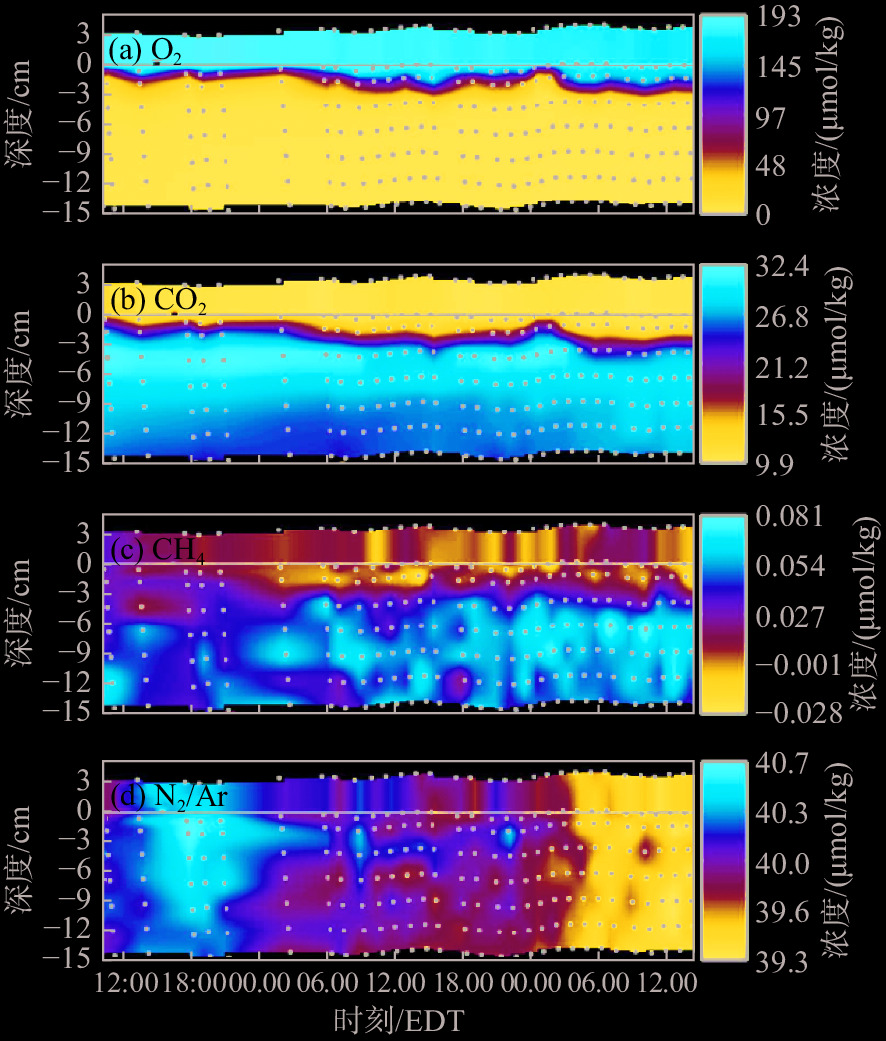
图 21 沉积物孔隙水中的溶解气体剖面[79]
Figure 21.
表 1 基于膜脱气和半导体气敏材料的电化学传感器比较
Table 1. The comparison of electrochemical sensors based on porous film and semiconductor gas sensing materials
表 2 基于光学技术的原位传感器比较
Table 2. The comparison of in situ sensors based on optical technology
仪器名称 检测原理 分析气体种类 测量范围/
(nmol/L)检出限/
(nmol/L)精度 响应时间/h 工作水深/m 功率 参考文献 Hydro CTM TDLAS CH4 0~56 700 <1 nmol/L 17~30 6 000 600 mA,12 V [25-27] NDIR CO2 0~200 000 <33.4 nmol/L 60 6 000 350 mA,12 V [26,28] 深水气体分析仪 OA-ICOS CH4
CO2
δ13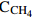
0.7~1 418.5
5 000~1 670 0000.001 nmol/L 33.4 nmol/L 1‰ 300 2 500 80 W,
115/230 V[30] 深海原位分析仪 OA-ICOS CH4
δ13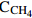
0.8‰ 3 000 120 VAC [22] 深海激光光谱仪 OA-ICOS CH4
δ13
CO2
δ13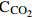
0.8‰
0.7‰3 000 70 W,24 V [31] Sub-Ocean OFCEAS CH4 0.1~106 0.035 30 4 000 50 W,24 V [32] 原位CH4
分析系统CRDS CH4 0.000 56 nmol/L 12 W,24 V [35] IR-ATR光谱仪 ATR CH4
CO21 100 [40] CH4传感器 SPR CH4 1~300 3~7 (6~7)×10−6 RIU/(nmol/L) 60 [42-44] 片状CH4传感器 马赫-曾德尔干涉 CH4 49 3.48×10−2
rad/(nmol/L)120 [41,46] DORISS 拉曼光谱 CH4
CO24×106
1075~20 4 000 [48-51] RiP 拉曼光谱 CH4
CO2106 6 000 [53-58] 表 3 基于质谱分析原理的原位传感器比较
Table 3. The comparison of in situ sensors based on mass spectrometry
-
[1] DI P,FENG D,CHEN D. The distribution of dissolved methane and its air-sea flux in the plume of a seep field,Lingtou Promontory,South China Sea[J]. Geofluids,2019:1-12.
[2] 汪思茹,殷克东,蔡卫君,等. 海洋酸化生态学研究进展[J]. 生态学报,2012,32(18):5859-5869.
[3] HARTMANN J F,GENTZ T,SCHILLER A,et al. A fast and sensitive method for the continuous in situ determination of dissolved methane and its δ13C‐isotope ratio in surface waters[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods,2018,16(5):273-285.
[4] SAUNOIS M,BOUSQUET P,POULTER B,et al. The global methane budget 2000–2012[J]. Earth System Science Data,2016,8(2):697-751. doi: 10.5194/essd-8-697-2016
[5] 于新生,李丽娜,胡亚丽,等. 海洋中溶解甲烷的原位检测技术研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2011,26(10):1030-1037.
[6] BEER D D,GLUD A,KUHL E M. A fast-responding CO2 microelectrode for profiling sediments,microbial mats,and biofilms[J]. Limnology and Oceanography,1997,42(7):1590-1600. doi: 10.4319/lo.1997.42.7.1590
[7] ZHAO P,CAI W J. An improved potentiometric pCO2 microelectrode[J]. Analytical Chemistry,1997,69(24):5052-5058. doi: 10.1021/ac970747g
[8] GARCIAL M L,MASSON M. Environmental and geologic application of solid-state methane sensors[J]. Environmental Geology,2004,46(8):1059-1063. doi: 10.1007/s00254-004-1093-1
[9] FUKASAWA T, HOZUMI S, MORITA M, et al. Dissolved methane sensor for methane leakage monitoring in methane hydrate production[C]//OCEANS 2006. IEEE, 2006: 1-6.
[10] FUKASAWA T, OKETANI T, MASSON M, et al. Optimized METS sensor for methane leakage monitoring [C]//OCEANS 2008- MTS/IEEE Kobe Techno-Ocean. IEEE, 2008: 1- 8
[11] ALEKSANYAN M S. Methane sensor based on SnO2/In2O3/TiO2 nanostructure[J]. Journal of Contemporary Physics (Armenian Academy of Sciences),2010,45(2):77-80. doi: 10.3103/S1068337210020052
[12] 申正伟,孙春岩,贺会策,等. 深海原位溶解甲烷传感器(METS)的原理及应用研究[J]. 海洋技术学报,2015,34(5):19-25.
[13] DI P,FENG D,CHEN D. In- Situ and On- Line Measurement of Gas Flux at a Hydrocarbon Seep from the Northern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2014,81:80-87. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.04.001
[14] NEWMAN K,CORMIER M,WEISSEL J,et al. Active methane venting observed at giant pockmarks along the US mid-Atlantic shelf break[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2008,267(1/2):341-352.
[15] 孙春岩,赵浩,贺会策,等. 海洋底水原位探测技术与中国南海天然气水合物勘探[J]. 地学前缘,2017,24(6):225-241.
[16] 一种海水中甲烷浓度原位探测系统 [P]. 中国, CN102288719A. 2013-09-25.
[17] 张志冰. 海水中甲烷浓度原位地球化学探测系统的研发与应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.
[18] 孙春岩,王栋琳,张仕强,等. 深海甲烷电化学原位长期监测技术及其在海洋环境调查和天然气水合物勘探中的意义[J]. 物探与化探,2019,43(1):1-16.
[19] ATHAVALE R,PANKRATOVA N,DINKEL C,et al. Fast potentiometric CO2 sensor for high-resolution in situ measurements in fresh water systems[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2018,52(19):11259-11266. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b02969
[20] 高红秀, 金萍, 周玉岩, 等. 近红外光谱分析原理、检测及定标技术简介[J]. 中国科技信息. 2014, (Z1): 59-61.
[21] 刘宏民. 实用有机光谱解析[M]. 郑州: 郑州大学出版社, 2008.
[22] WANKEL S D,HUANG Y W,GUPTA M,et al. Characterizing the distribution of methane sources and cycling in the deep sea via in situ stable isotope analysis[J]. Environmental Science andTechnology,2012,47(3):1478-1486.
[23] FIETZEK P, KRAMER S, ESSER D. Deployments of the HydroC™(CO 2/CH 4) on stationary and mobile platforms-Merging trends in the field of platform and sensor development[C]//OCEANS'11 MTS/IEEE KONA. IEEE, 2011: 1-9.
[24] FIETZEK P,FIEDLER,BJÖRN,STEINHOFF T,et al. In situ Quality Assessment of a Novel Underwater pCO2 Sensor Based on Membrane Equilibration and NDIR Spectrometry[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology,2014,31(1):181-196.
[25] BOULART C,CONNELLY D P,MOWLEM M C. Sensors and technologies for in situ dissolved methane measurements and their evaluation using Technology Readiness Levels[J]. Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2010,29(2):186-195. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2009.12.001
[26] CANNING A,FIETZEK P,REHDER G,et al. Seamless gas measurements across the land–ocean aquatic continuum–corrections and evaluation of sensor data for CO2,CH4 and O2 from field deployments in contrasting environments[J]. Biogeosciences,2021,18(4):1351-1373. doi: 10.5194/bg-18-1351-2021
[27] CONTROS HydroC® CH4 User manual[M]. Wischhofstrasse 1-3, Bld. 2, 24148 Kiel, Germany: Kongsberg Maritime AS, 2017.
[28] CONTROS HydroC® CO2 User manual[M]. Kongsberg Maritime AS, Wischhofstrasse 1-3, Bld. 2, 24148 Kiel, Germany: Kongsberg Maritime AS, 2017.
[29] GÜLZOW W,REHDER G,SCHNEIDER B,et al. A new method for continuous measurement of methane and carbon dioxide in surface waters using off-axis integrated cavity output spectroscopy (ICOS):an example from the Baltic Sea[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods,2011,9(5):176-184.
[30] LGR DWGA Datasheet[M/OL]. [2021-02-03]. http://www.lgrinc.com/documents/LGR_DWGA_Datasheet.pdf.
[31] MICHEL A,WANKEL S,KAPIT J,et al. In situ carbon isotopic exploration of an active submarine volcano[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2018,150:57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2017.10.004
[32] GRILLI R,TRIEST J,CHAPPELLAZ J,et al. Sub-ocean:subsea dissolved methane measurements using an embedded laser spectrometer technology[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2018,52(18):10543-10551. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b06171
[33] GRILLI R,DARCHAMBEAU F,CHAPPELLAZ J,et al. Continuous in situ measurement of dissolved methane in Lake Kivu using a membrane inlet laser spectrometer[J]. Geoscientific Instrumentation,Methods and Data Systems,2020,9(1):141-151. doi: 10.5194/gi-9-141-2020
[34] JANSSON P,TRIEST J,GRILLI R,et al. High-resolution under-water laser spectrometer sensing provides new insights to methane distribution at an Arctic seepage site[J]. Ocean Science Discussions,2019:1-21.
[35] YUAN F,HU M,HE Y,et al. Development of an in situ analysis system for methane dissolved in seawater based on cavity ringdown spectroscopy[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments,2020,91(8):083106. doi: 10.1063/5.0004742
[36] PEJCIC B,EADINGTON P,ROSS A. Environmental monitoring of hydrocarbons:a chemical sensor perspective[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2007,41(18):6333-6342. doi: 10.1021/es0704535
[37] 邓小红. 光纤消逝波吸收传感器的参数设计与分析[D]. 长春: 中国科学院研究生院(长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2005.
[38] PEJCIC B,MYERS M,ROSS A. Mid-infrared sensing of organic pollutants in aqueous environments[J]. Sensors,2009,9(8):6232-6253. doi: 10.3390/s90806232
[39] MIZAIKOFF B. Mid-infrared evanescent wave sensors-a novel approach for subsea monitoring[J]. Measurement Science and Technology,1999,10(12):1185. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/10/12/310
[40] SCHÄDLE T,PEJCIC B,MYERS M,et al. Portable mid-infrared sensor system for monitoring CO2 and CH4 at high pressure in geosequestration scenarios[J]. Acs Sensors,2016,1(4):413-419. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.5b00246
[41] LINDECRANTZ S M. Waveguide Mach-Zehnder interferometer for measurement of methane dissolved in water[D]. Tromso: The Arctic University of Norway, 2016.
[42] BOULART C,MOWLEM M C,CONNELLY D P,et al. A novel,low-cost,high performance dissolved methane sensor for aqueous environments[J]. Optics Express,2008,16(17):12607-12617. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.012607
[43] BENOUNIS M,JAFFREZIC-RENAULT N,DUTASTA J P,et al. Study of a new evanescent wave optical fibre sensor for methane detection based on cryptophane molecules[J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical,2005,107(1):32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2004.10.063
[44] BOULART C,PRIEN R,CHAVAGNAC V,et al. Sensing dissolved methane in aquatic environments:an experiment in the central Baltic Sea using surface plasmon resonance[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2013,47(15):8582-8590.
[45] SIARKOWSKI A L,HERNANDEZ L F,MORIMOTO N I,et al. Sensing based on Mach-Zehnder interferometer and hydrophobic thin films used on volatile organic compounds detection[J]. Optical Engineering,2012,51(5):054401. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.51.5.054401
[46] DULLO F T,LINDECRANTZ S,JÁGERSKÁ J,et al. Sensitive on-chip methane detection with a cryptophane-A cladded Mach-Zehnder interferometer[J]. Optics Express,2015,23(24):31564-31573. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.031564
[47] 陆同兴, 路秩群. 激光光谱技术原理及应用[M] . 北京: 中国科技大学出版社, 2006: 263 -279.
[48] BREWER P G,MALBY G,PASTERIS J D,et al. Development of a laser Raman spectrometer for deep-ocean science[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers,2004,51(5):739-753. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2003.11.005
[49] WHITE S N, DUNK R M, PELTZER E T, et al. In situ Raman analyses of deep-sea hydrothermal and cold seep systems (Gorda Ridge and Hydrate Ridge)[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(5): 123.
[50] WHITE S N. Laser Raman spectroscopy as a technique for identification of seafloor hydrothermal and cold seep minerals[J]. Chemical Geology,2009,259(3/4):240-252.
[51] HESTER K C,DUNK R M,WHITE S N,et al. Gas hydrate measurements at Hydrate Ridge using Raman spectroscopy[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2007,71(12):2947-2959. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.03.032
[52] ZHANG X,WALZ P M,KIRKWOOD W J,et al. Development and deployment of a deep-sea Raman probe for measurement of pore water geochemistry[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers,2010,57(2):297-306. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2009.11.004
[53] ZHANG X, HESTER K C, USSLER W, et al. In situ Raman-based measurements of high dissolved methane concentrations in hydrate-rich ocean sediments[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(8): L08605.
[54] ZHANG X,DU Z,ZHENG R,et al. Development of a new deep-sea hybrid Raman insertion probe and its application to the geochemistry of hydrothermal vent and cold seep fluids[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers,2017,123:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2017.02.005
[55] LI L,ZHANG X,LUAN Z,et al. In situ quantitative Raman detection of dissolved carbon dioxide and sulfate in deep-sea high-temperature hydrothermal vent fluids[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2018,19(6):1809-1823.
[56] LI L,ZHANG X,LUAN Z,et al. Hydrothermal Vapor‐Phase Fluids on the Seafloor:Evidence From In Situ Observations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2020,47(10):e2019GL085778.
[57] ZHANG X,LI L F,DU Z F,et al. Discovery of supercritical carbon dioxide in a hydrothermal system[J]. Science Bulletin,2020,65(11):958-964. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2020.03.023
[58] DU Z,ZHANG X,LUAN Z,et al. In situ Raman quantitative detection of the cold seep vents and fluids in the chemosynthetic communities in the South China Sea[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2018,19(7):2049-2061.
[59] 徐伟,马兆铭,王克家,等. 深海甲烷激光拉曼光谱原位探测器的研究[J]. 传感器与微系统,2008,27(6):66-68,72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9787.2008.06.021
[60] YANG D,GUO J,LIU Q,et al. Highly sensitive Raman system for dissolved gas analysis in water[J]. Applied Optics,2016,55(27):7744-7748. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.007744
[61] SCHMIDT H,HA N B,PFANNKUCHE J,et al. Detection of PAHs in Seawater Using Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2004,49(3):229-234. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.02.011
[62] SOWOIDNICH K, FERNÁNDEZ LÓPEZ M, KRONFELDT H D. Innovative Raman spectroscopic concepts for in situ monitoring of chemicals in seawater[C]//Proceeding of SPIE, 2013, 8718: 871802-1.
[63] MAHER S,JJUNJU F P M,Taylor S. Colloquium:100 years of mass spectrometry:Perspectives and future trends[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics,2015,87(1):113. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.87.113
[64] CAMILLI R,REDDY C M,YOERGER D R,et al. Tracking hydrocarbon plume transport and biodegradation at deepwater horizon[J]. Science,2010,330(6001):201-204. doi: 10.1126/science.1195223
[65] GENTZ T,SCHLÜTER M. Underwater cryotrap-membrane inlet system (CT-MIS) for improved in situ analysis of gases[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods,2012,10(5):317-328.
[66] CAMILLI R,DURYEA A N. Characterizing spatial and temporal variability of dissolved gases in aquatic environments with in situ mass spectrometry[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2009,43(13):5014-5021. doi: 10.1021/es803717d
[67] BELL R J,SAVIDGE W B,TOLER S K,et al. In situ determination of porewater gases by underwater flow-through membrane inlet mass spectrometry[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods,2012,10(3):117-128.
[68] CHUA E J,SAVIDGE W,SHORT R T,et al. A review of the emerging field of underwater mass spectrometry[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science,2016,3:209.
[69] HEMOND H,CAMILLI R. Nereus:engineering concept for an underwater mass spectrometer[J]. Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2002,21(8):526-533. doi: 10.1016/S0165-9936(02)00113-9
[70] CAMILI R,HEMOND H F. Nereis/kemonaut,a mobile autonomous underwater mass spectrometer[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2004,23(24):307-313.
[71] CAMILLI R,DURYEA A. Characterizing marine hydrocarbons with insitu mass spectrometry[J]. IEEE/MTS OCEANS'07,2007:1-7.
[72] CAMILLI R,NOMIKOU P,ESCARTÍN J,et al. The Kallisti Limnes,carbon dioxide-accumulating subsea pools[J]. Scientific Reports,2015,5(1):1-9. doi: 10.9734/JSRR/2015/14076
[73] SCHLÜTER M,GENTZ T. Application of membrane inlet mass spectrometry for online and in situ analysis of methane in aquatic environments[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry,2008,19(10):1395-1402. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2008.07.021
[74] GENTZ T,DAMM E,VON DEIMLING J S,et al. A water column study of methane around gas flares located at the West Spitsbergen continental margin[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2014,72:107-118. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.07.013
[75] BELOFF B. Lessons from the DeepWater Horizon debacle:a precautionary tale[J]. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy,2010,12(4):331-333. doi: 10.1007/s10098-010-0308-2
[76] BELL R J,SHORT R T,VAN AMEROM F H W,et al. Calibration of an in situ membrane inlet mass spectrometer for measurements of dissolved gases and volatile organics in seawater[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2007,41(23):8123-8128. doi: 10.1021/es070905d
[77] In-water mass spectrometry for characterization of light hydrocarbon seeps and leaks[M/OL]. [2021-02-03]. http://www.hems-workshop.org/10thWS/Talks/Short.pdf
[78] BELL R J,SHORT R T,BYRNE R H. In situ determination of total dissolved inorganic carbon by underwater membrane introduction mass spectrometry[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods,2011,9(4):164-175.
[79] BELL R J,SAVIDGE W B,TOLER S K,et al. In situ determination of porewater gases by underwater flow-through membrane inlet mass spectrometry[J]. Limnology and Oceanography Methods,2012,10(3):117-128.
[80] WANKEL S D,JOYE S B,SAMARKIN V A,et al. New constraints on methane fluxes and rates of anaerobic methane oxidation in a Gulf of Mexico brine pool via in situ mass spectrometry[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2010,57(21/23):2022-2029.
[81] WANKEL S D,GERMANOVICH L N,LILLEY M D,et al. Influence of subsurface biosphere on geochemical fluxes from diffuse hydrothermal fluids[J]. Nature Geoscience,2011,4(7):461-468. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1183
[82] APPOLINARIO L R,TSCHOEKE D,CALEGARIO G,et al. Oil leakage induces changes in microbiomes of deep-sea sediments of Campos Basin (Brazil)[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2020,740:139556. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139556
[83] SALVADOR J,KOPPER K,MITI A,et al. Multiplexed immunosensor based on the amperometric transduction for monitoring of marine pollutants in sea water[J]. Sensors,2020,20(19):5532. doi: 10.3390/s20195532
[84] WANG Q,YANG Q,WU W. Ensuring seafood safe to spoon:a brief review of biosensors for marine biotoxin monitoring[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2020(3):1-13.
[85] TIAN Y,DU L,ZHU P,et al. Recent progress in micro/nano biosensors for shellfish toxin detection[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2020,176(1):112899.
[86] DAMGAARD L R,REVSBECH N P. A microscale biosensor for methane containing methanotrophic bacteria and an internal oxygen reservoir[J]. Analytical Chemistry,1997,69(13):2262-2267. doi: 10.1021/ac9611576
[87] DAMGAARD L R,NIELSEN L P,REVSBECH N P. Methane microprofiles in a sewage biofilm determined with a microscale biosensor[J]. Water Research,2001,35(6):1379-1386. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00412-7
[88] WEN G,ZHENG J,ZHAO C,et al. A microbial biosensing system for monitoring methane[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology,2008,43(3):257-261. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2008.04.006
-



 下载:
下载: