Removal Performance of Phosphorus from Water by High Temperature Modified Iron Ore Tailing
-
摘要:
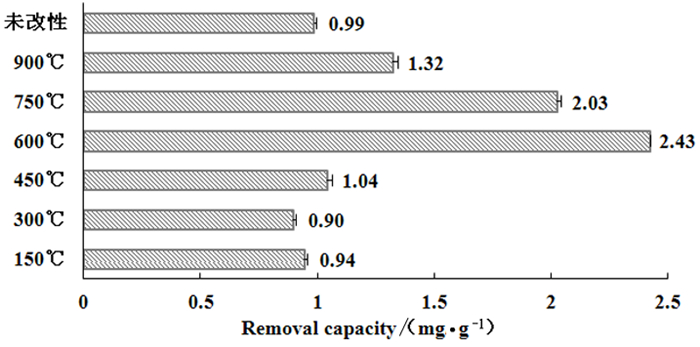
为探究铁尾矿对水体中磷去除能力与过程,并进一步提高其去除性能,采用高温方法对铁尾矿进行改性。以温度、恒温时间、升温速率为试验因素,以单位去除量为响应值设计响应面试验,并在此基础上依据动力学、等温线、热力学分析铁尾矿改性前后的除磷过程与性能。结果表明,经高温600℃改性的铁尾矿对水体中磷的单位去除量最大为2.43 mg/g,是未改性前的2.46倍。并结合文献和铁尾矿XRD矿物成分分析推测Fe3O4对水体中磷的去除起主要作用。回归模型极显著(P < 0.0001),该模型的决定系数R2大于0.99,说明建立的回归方程可靠。从响应面试验得到的最优条件为改性温度627.84℃,恒温时间得3.00 h,升温速率为9.82℃/min,预测最大单位去除量为17.43 mg/g。铁尾矿改性前后对磷的去除均属于非均匀表面的化学吸附,水中磷的去除过程更接近Freundlich等温模型,根据Langmuir等温模型估算改性前后铁尾矿对水体中磷的最大去除量分别为0.19 mg/g和149.97 mg/g,铁尾矿对磷的去除均较易发生。△H0>0反应需要吸热,温度升高可提高铁尾矿对水中磷的去除作用。
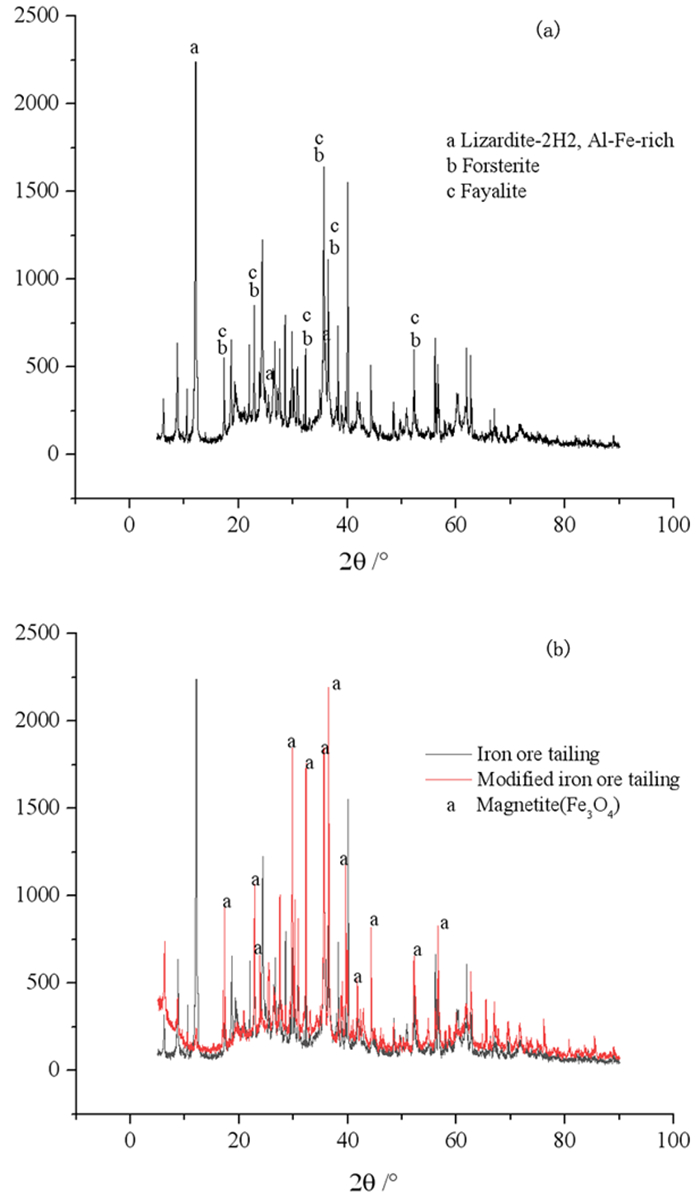
Abstract:In order to improve the phosphorus removal capacity and investigate the process of iron ore tailing in water, the iron ore tailing was modified by heating. With the aim of phosphorus removal capacity, the response surface test was designed by taking temperature, time of constant temperature and heating rate as factors value. Moreover, the phosphorus removal process and performance of iron ore tailing before and after modification were analyzed by kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics. The results shown that the maximum removal capacity of phosphorus by modified iron ore tailings is 2.43 mg/g at 600 ℃, which was 2.46 times that unmodified. Furthermore, It was concluded that Fe3O4 played a major role in increasing phosphorus removal capacity combined with literature and tailing sand composition analysis. The response surface regression model was significant (P < 0.0001) and the determination coefficient R2 was greater than 0.99, indicated that the regression model was reliable. The optimal modification conditions obtained from response surface test were as follows temperature 627.84 ℃, constant temperature 3.00 h, heating rate 9.82 ℃/min, which predicted maximum removal capacity of 17.43 mg/g. The removal of phosphorus by iron ore tailing before and after modification was chemisorbed on non-uniform surface. The removal process of phosphorus from water were closer to Freundlich isothermal model. Moreover, the maximum removal amount of phosphorus in Langmuir isothermal model by iron ore tailing before and after modification were estimated as 0.19 mg/g and 149.97 mg/g, respectively. Meanwhile, the removal of phosphorus by iron ore tailing was easy to occur, △H0>0 shown that removal process was endothermic and the removal capacity of phosphorus by iron ore tailing could be improved by increasing the temperature.
-
Key words:
- iron ore tailings /
- phosphorus removal /
- the response surface /
- dynamics /
- thermodynamics
-

-
表 1 铁尾矿主要成分含量
Table 1. Main component content of iron ore tailings
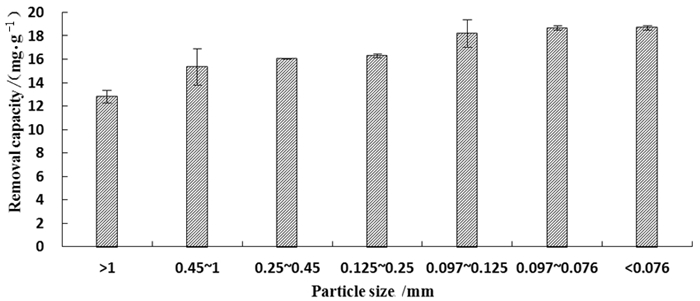
组分 SiO2 MgO Fe2O3 MnO Al2O3 CaO 含量/% 41.92 36.26 4.32 0.42 2.56 4.87 表 2 响应面设计与因素水平表
Table 2. Response surface design and factor level table
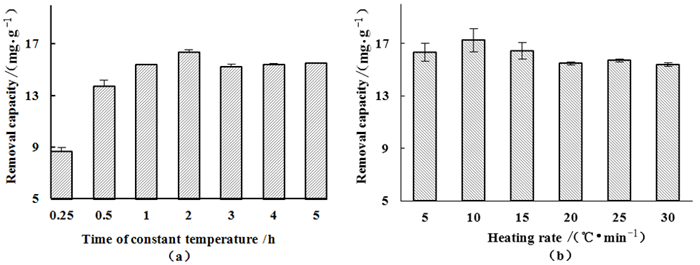
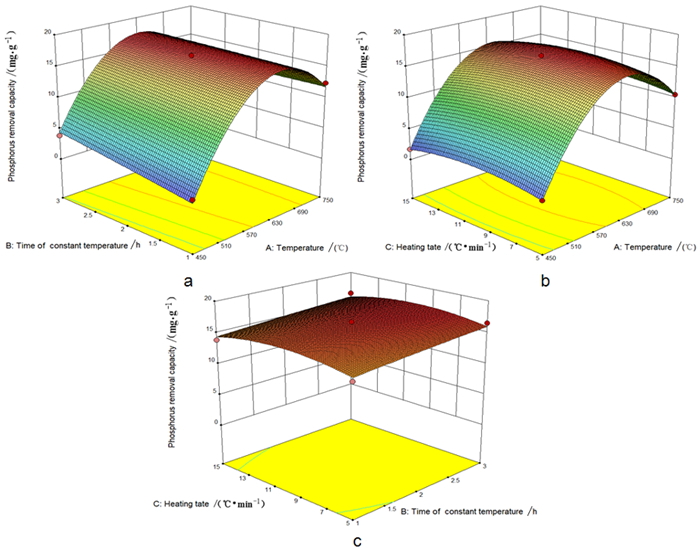
因素 水平 高水平 低水平 A改性温度/℃ 600 750 450 B恒温时间/h 2 3 1 C升温速率/(℃·min-1) 10 15 5 表 3 响应面试验方差分析表
Table 3. Analysis of variance of response surface tests
因素 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 Model 534.07 9 59.34 113.20 < 0.0001 ** A-改性温度 152.94 1 152.94 291.74 < 0.0001 ** B-恒温时间 3.99 1 3.99 7.62 0.0281 * C-升温速率 0.021 1 0.021 0.041 0.8453 AB 3.62 1 3.62 6.90 0.0341 * AC 0.025 1 0.025 0.047 0.8342 BC 2.318E-003 1 2.318E-003 4.422E-003 0.9488 A2 359.34 1 359.34 685.45 < 0.0001 ** B2 0.026 1 0.026 0.049 0.8307 C2 6.27 1 6.27 11.96 0.0106 * Residual 3.67 7 0.52 Lack of Fit 2.46 3 0.82 2.71 0.1796 Pure Error 1.21 4 0.30 Cor Total 537.74 16 R2=0.9932 AdjR2=0.9844 CV%=0.9233 表 4 铁尾矿对磷吸附的动力学模型参数
Table 4. Kinetic model parameters of phosphorus adsorption by iron ore tailings
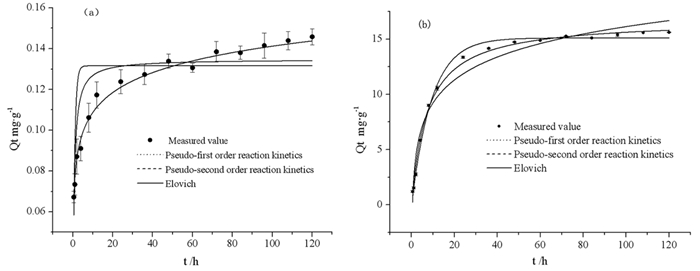
方程
变量准一级动力学方程 准二级动力学方程 Elovich方程 Qe K1 R2 Qe K2 R2 αe βe R2 改性前 0.1316 1.1734 0.8026 0.1348 0.1168 0.9665 3.1035 70.7977 0.9914 改性后 15.1050 0.1063 0.9944 16.7667 0.0081 0.9960 0.7233 0.3336 0.9696 表 5 铁尾矿对磷吸附的吸附等温参数
Table 5. Adsorption isothermal parameters of phosphorus adsorption by iron ore tailings
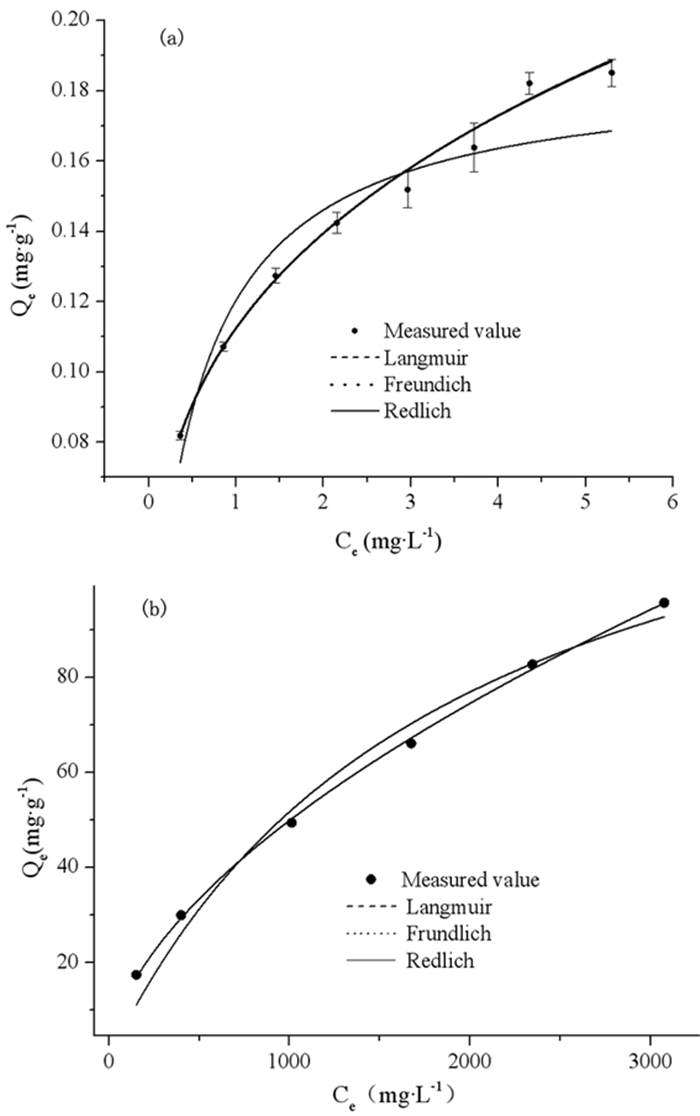
方程
变量Langmuir模型 Freundlich模型 Redlich模型 Qm KL RL2 Kf n Rf2 A B g Rr2 改性前 0.1858 1.8380 0.9240 0.1125 3.2220 0.9972 11.7395 103.2240 0.6956 0.9972 改性后 149.97 5.26E-4 0.9757 0.9145 1.7274 0.9990 364.31 398.17 0.4212 0.9986 表 6 铁尾矿对磷吸附热力学参数
Table 6. Thermodynamic parameters of phosphorus adsorption from iron ore tailings
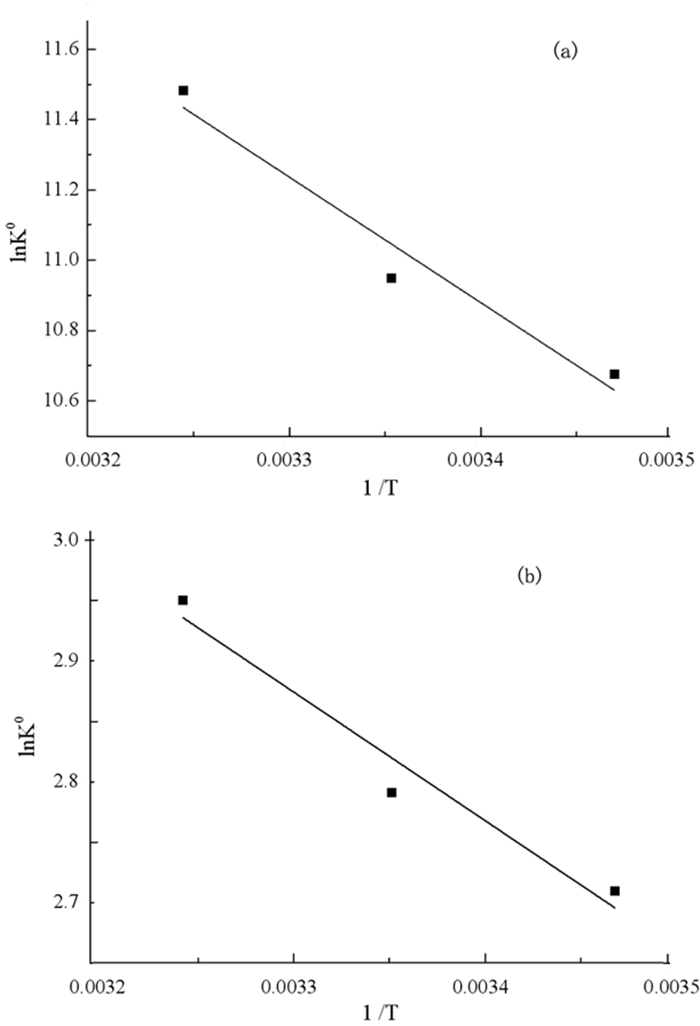
变量 温度/℃ △G0/(kJ·mol-1) Qm/(mg·g-1) KL/(L·mg-1) R2 △H0/(kJ·mol-1) △S0/(J·mol-1·K-1) 改性前 15 -0.8052 0.1816 1.3995 0.8928 29.63 191.26 25 -1.5088 0.1858 1.8380 0.9240 35 -2.9277 0.2193 3.1354 0.9443 改性后 15 -6.4889 144.7585 4.8480×10-4 0.9716 8.85 53.12 25 -6.9170 149.9769 5.2616×10-4 0.9757 35 -7.5563 151.8507 6.1690×10-4 0.9735 -
[1] 衡忠暄, 单超, 花铭, 等. 不同价态无机磷在金属氧化物表面吸附的第一性原理研究[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2021, 51: 591-600. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JEXK202105009.htm
[2] 何强, 何璇, 洪毅怡晖, 等. 铁盐辅助生物除磷工艺研究进展[J/OL]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文): 1-8[2021-06-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1218.TU.20210525.1048.004.html.
[3] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 2020中国生态环境状况公报[EB/OL]. [2021-5-24], http://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202105/P020210526572756184785.pdf.
[4] 路畅, 陈洪运, 傅梁杰, 等. 铁尾矿制备新型建筑材料的国内外进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021(5): 5011-5026. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB202105002.htm
[5] 陈虎, 沈卫国, 单来, 等. 国内外铁尾矿排放及综合利用状况探讨[J]. 混凝土, 2012(2): 88-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2012.02.028
[6] 潘德安, 逯海洋, 刘晓敏, 等. 铁尾矿建材化利用的研究进展与展望[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2019(10): 3162-3169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201910021.htm
[7] 王海军, 王伊杰, 李文超, 等. 全国矿产资源节约与综合利用报告(2019)[M]. 北京: 中国地质出版社, 2020.
[8] TIE JX., NIU YF, XIAO H, et al. Performance of phosphorus adsorption by acid-activated iron-based waterworks sludge adsorbent[J]. Nature environment and pollution technology, 2021, 20(2): 747-751. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/352110244_Performance_of_Phosphorus_Adsorption_by_Acid-Activated_Iron-Based_Waterworks_Sludge_Adsorbent
[9] 张小宇, 张世熔, 王新月, 等. 镧改性农业废弃秸秆对养殖废水中磷的去除[J]. 环境化学, 2021(4): 1274-1284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202104032.htm
[10] 杨天雪. 热处理赤泥对水体Cd(Ⅱ)和Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附特性及吸附机理研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2019.
[12] 国家环境保护局, GB 11893-89, 水质总磷的测定(钼酸铵分光光度法)[S]. 北京, 国家环境保护局, 1990.
[13] 张冰倩, 李咏梅. 污泥中铁磷化合物分析方法的研究进展[J]. 四川环境, 2019(2): 115-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ201902022.htm
[14] 杨颂, 上官炬, 杜文广, 等. 印尼某低品位红土镍矿的热解性能[J]. 金属矿山, 2016(8): 98-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2016.08.020
[15] 李博, 魏永刚, 王华. 干燥过程中硅镁镍矿的作用机制及其相变特征[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 2(5): 1440-1446. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201305036.htm
[16] 王洪阳, 包焕均, 张文韬, 等. 铁橄榄石的氧化分解及碱浸溶硅[J]. 金属矿山, 2020(10): 167-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS202010023.htm
[17] 胡小莲. 磁性纳米四氧化三铁及其复合材料吸附磷性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2018.
[18] 谢晶晶, 庆承松, 陈天虎, 等. 几种铁(氢)氧化物对溶液中磷的吸附作用对比研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2007(6): 535-538. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2007.06.011
[19] 高晓雯. 铁盐化学强化三种吸附材料的除磷特性研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳建筑大学, 2019.
[20] 李一兵, 呼瑞琪, 张彦平, 等. 给水厂含铝污泥对含磷废水的吸附特性研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2018(5): 30-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYSC201805007.htm
[21] 周宏光. 载纳米水合氧化铁复合半焦的研制及其除磷性能研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2014.
[22] 常春, 刘天琪, 廉菲, 等. 不同热解条件下制备的秸秆炭对铜离子的吸附动力[J]. 环境化学, 2016(5): 1042-1049. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201605026.htm
[23] ADVA ZACH-MAOR, RAPHAEL SEMIAT, HILLA SHEMER. Adsorption-desorption mechanism of phosphate by immobilized nano-sized magnetite layer: Interface and bulk interactions[J]. Journal of colloid and interface science, 2011, 363(2): 608-614. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2011.07.062
[24] CHEN X, WU L, LIU F, et al. Performance and mechanisms of thermally treated bentonite for enhanced phosphate removal from wastewater[J]. Environmental science and pollution research international, 2018, 25(16): 15980-15989. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1794-8
[25] JIN HY, LIN L, MENG XY, et al. A novel lanthanum-modified copper tailings adsorbent for phosphate removal from water[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 281: 1-11.
[26] SAMARAWEERA HASARA, SHARP ABIGAIL, EDWARDS JOHN, et al. Lignite, thermally-modified and Ca/Mg-modified lignite for phosphate remediation[J]. The Science of the total environment, 2021, 773: 1-14. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969721006999
[27] 张玉洁. 改性赤泥吸附除磷性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2014.
[28] 彭莎. 改性沸石吸附水中典型污染物的性能与机理研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2016.
[29] 王春芳. 活性炭理化特性对饮用水中有机物吸附特性的影响研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2015.
[30] 那立艳, 张丽影, 张凤杰, 等. 固液界面吸附热力学参数的计算[J]. 材料导报, 2020(22): 22030-22035. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19080096
[31] 熊炜平. 基于铁金属有机骨架材料的水中典型抗生素去除行为机理研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2019.
-



 下载:
下载: