Feasibility Study of Synthesizing PGE-Bearing Sulfide Reference Material by Remelted Nickel Sulfide Fire Assay Button
-
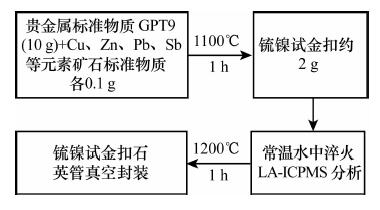
摘要: 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱(LA-ICP-MS)适合于直接分析硫化物矿物中痕量元素的含量及空间分布,但硫化物矿物的激光剥蚀特性与硅酸盐及氧化物不同,受到的干扰也更严重,且由于硫化物标准物质(尤其是含铂族元素、Au、Ag等贵金属元素标准物质)极度缺乏,限制了LA-ICP-MS技术在硫化物微区分析中的广泛应用。本文以贵金属标准样品GPT-9和矿石标准物质为原料合成锍镍试金扣,并封入真空管中重熔,利用背散射电子图像和LA-ICP-MS分析元素分布的均匀性,探讨真空重熔锍镍试金扣制备硫化物原位微区分析标准样品的可行性。背散射电子图像(BSE)显示真空重熔后锍镍试金扣由单相S、Ni化合物组成。LA-ICP-MS线扫描和点扫描分析表明,锍镍试金扣中S、Ni、Cr、Co、Cu、Pb、Sb、Cd、Bi等主量及微量元素分析精密度(RSD)均小于10%,均匀分布;在镍扣制备过程中Zn相对于Cu、Pb、Sb更难进入硫化物相;贵金属元素Au、Ag、Pt均一性较好,其余贵金属元素由于含量低、仪器波动及质谱干扰等影响因素造成分析数据的RSD相对较大,但可通过提高原料中贵金属元素含量、降低熔融样品淬火温度等方法进一步提高其均匀性。锍镍试金扣的组成元素对铂族元素分析的质谱干扰研究表明,重铂族元素(Os、Ir、Pt)和Au受到的干扰可忽略不计;轻铂族元素(Ru、Rh、Pd)受金属氩化物干扰较为严重,需进行干扰校正。研究认为,真空重熔技术可有效提高锍镍试金扣中各元素(包括贵金属)的均一性,达到硫化物原位微区分析标准样品的要求,利用真空重熔锍镍试金扣制备LA-ICP-MS原位微区痕量及贵金属硫化物分析标准样品具可行性。
-
关键词:
- 锍镍试金法 /
- 真空重熔 /
- 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱法 /
- 含PGEs硫化物微区分析标准样品
Abstract: Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) is suited to analyze the abundances and spatial distributions of trace elements in sulfide. However, the spread use of the technology on micro area analysis has been hampered by the different characteristics of sulfides from silicates and oxides and the lack of sulfide reference material, especially PGE-bearing reference material. In this study, a PGE-bearing sulfide (SRMD-1) is synthesized by remelted nickel sulfide fire assay button in AN evacuated quartz tube. The examination by BSE imaging revealed that the nickel button SRMD-1 was completely of monosulfide composition. Homogeneity testing by LA-ICP-MS shows that the RSDs of elements, such as S, Ni, Cr, Co, Cu, Pb, Sb, Cd, Bi, are less than 10%. The data suggest the homogeneous distribution of these elements inside SRMD-1, but elements Mn, Zn, Sn, Tl are not as homogeneous with relatively larger RSDs. Elements Ag, Au and Pt are homogeneous inside SRMD-1, but RSDs of other noble metal elements are relatively larger according to low element content, instrument fluctuations or mass spectrometry interference. The homogeneity of the nickel button will be improved by increasing the content for the noble metal elements and lowering the quenching temperature for the molten samples. During the analysis of the nickel sulfide fire assay button, the spectral interferences in light PGEs (Ru, Rh and Pd) by argides is serious, and must be corrected, while the interferences to Os, Ir, Pt and Au can be ignored. Compared to the button which is not remelted, the homogeneity of the elements improved significantly. According to the work documented here, it is possible to synthesized PGE-bearing sulfide reference material for LA-ICP-MS by remelted nickel sulfide fire assay button. -

-
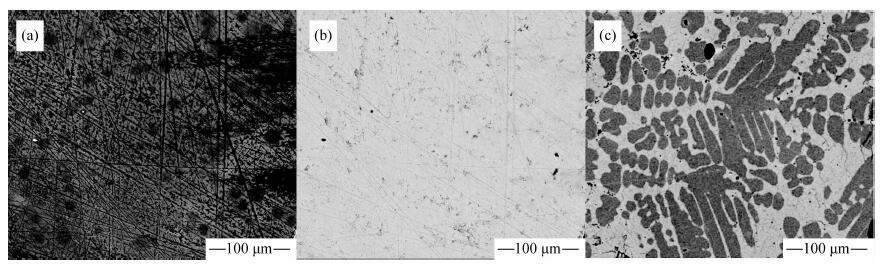
图 2 (a) SRMD-1二次电子图像(SEM);(b) SRMD-1背散射电子图像(BSE);(c) Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser等[16]合成Ni、S化合物的BSE图像,深色NiS,浅色Ni6-xS5
Figure 2.
表 1 SRMD-1的LA-ICP-MS分析数据RSD值
Table 1. RSD values of SRMD-1 analyzed by LA-ICP-MS
待测元素 第Ⅰ次 第Ⅱ次 第Ⅲ次 第Ⅳ次 第Ⅴ次 重熔前
(n=22)A
(n=10)A
(n=13)A
(n=25)B
(n=20)T
(n=45)A
(n=51)B
(n=80)T
(n=130)A
(n=60)B
(n=110)T
(n=170)F MASS-1
(n=23)34S - - - - - - - - 2.9 5.0 4.4 0.03 11 0.0 52Cr 4.6 2.5 2.8 4.7 3.9 2.7 4.1 5.8 2.7 4.2 3.8 1.87 5.1 6.3 55Mn 3.9 6.7 3.9 6.1 5.1 8.8 31 31 21 185 41 16.6 1.7 9.8 57Fe 2.9 2.0 3.2 3.4 3.6 2.8 3.1 3.1 - - - - - 5.3 59Co 2.6 2.5 3.0 3.7 3.4 2.9 2.5 2.7 2.2 3.2 2.9 0.29 2.2 6.3 60Ni 3.3 2.8 3.9 3.4 3.8 2.6 2.8 2.7 2.2 3.1 2.9 2.61 7.5 4.1 65Cu 3.5 3.6 3.7 7.6 5.7 4.5 5.8 5.5 3.1 5.4 4.8 2.04 3.1 11 66Zn 9.5 5.5 13 128 12 4.0 6.0 7.0 12 19 13.7 0.02 5.9 11 99Ru 28 23 19 20 20 29 37 34 70 136 118 0.02 - 59 101Ru 10 8.2 10 9.9 10 8.0 14 12 19 25 23 2.19 - 10 102Ru 6.2 6.4 7.2 6.9 7.7 4.7 8.6 7.6 13 25 21 0.48 - 11 103Rh 9.8 7.8 7.0 7.5 7.7 7.6 13 11 15 22 20 0.11 - 11 105Pd 7.0 4.5 5.1 8.5 7.0 5.4 8.8 7.7 11 19 17 6.36 - 9.6 106Pd 7.1 4.1 11 8.0 10 13 28 23 41 79 61 3.37 - 21 108Pd 5.2 4.4 7.4 10 8.8 9.3 20 16 31 91 73 1.04 - 27 107Ag 4.8 3.9 5.4 9.6 7.7 4.8 5.4 7.0 4.8 7.2 6.5 0.07 9.9 9.5 111Cd 11 6.0 13 11 14 8.0 7.3 11 7.5 12 10 0.05 23 12 118Sn 15 7.7 7.2 15 13 11 20 19 25 54 45 0.92 5.5 24 121Sb 5.6 3.9 5.6 5.2 5.4 7.5 9.5 10 7.8 7.9 7.9 0.04 10 - 189Os 12 9.7 12 15 13 18 26 25 27 52 44 5.73 - 25 192Os 8.3 4.3 8.9 7.5 8.3 12 15 17 17 28 25 18.9 - 16 191Ir 16 14 13 17 15 18 31 27 32 75 54 0.74 - 29 193Ir 8.6 12 15 8.5 13 12 24 21 33 71 58 5.27 - 24 194Pt 6.2 5.6 6.1 11 8.9 7.7 7.3 10 6.4 9.4 8.7 0.36 - 19 195Pt 4.8 5.0 6.6 10 8.6 6.8 7.4 10 6.5 9.5 10 2.07 - 14 197Au 4.8 6.0 5.0 9.8 7.4 6.1 6.8 9.8 9.4 9.4 9.3 0.21 - 16 205Tl 5.7 4.3 5.4 11 8.2 9.1 7.9 15 9.1 15 14 10.0 - 11 207Pb 3.3 5.0 3.5 9.4 6.7 9.3 4.8 14 6.4 7.9 7.4 0.06 - 10 209Bi 4.9 4.1 3.7 7.7 5.8 10 4.8 16 7.1 7.1 7.1 0.04 14 10 表 2 PGEs主要质谱干扰及SRMD-B贵金属空白样品分析信号
Table 2. Mass interference of PGEs and signal intensity of SRMD-B
待测元素 主要干扰 信号强度/cps 背景 SRMD-B贵金属空白样品 99Ru 59Co40Ar 25 24 101Ru 61Ni40Ar 15 691 102Ru 62Ni40Ar,102Pd 126 2469 103Rh 63Cu40Ar,206Pb2+ 150 522 105Pd 65Cu40Ar 53 170 106Pd 66Zn40Ar,106Cd 1854 1950 108Pd 68Zn40Ar,108Cd 837 743 189Os 173Yb16O 0 0 192Os 176Hf16O,192Pt 0 7 191Ir 175Lu16O 0 5 193Ir 177Hf16O 0 11 194Pt 178Hf16O 10 0 195Pt 179Hf16O 8 3 -
[1] Axelsson M D, Rodushkin I. Determination of major and trace elements in sphalerite using laser ablation double focusing sector field ICP-MS [J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2001,72(2):81-89. doi: 10.1016/S0375-6742(00)00166-7
[2] Houghton J, Shanks W, Seyfried W. Massive sulfide deposition and trace element remobilization in the Middle Valley sediment-hosted hydrothermal system, northern Juan de Fuca Rdge [J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004,68(13):2863-2873. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.12.023
[3] Cook N J, Ciobanu C L, Pring A, Skinner W, Shimizu M, Danyushevsky L, Saini-Eidukat B, Melcher F. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite:A LA-ICPMS study [J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009,73(16): 4761-4791. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.05.045
[4] 周涛发,张乐骏,袁峰,范裕, Cook D R. 安徽铜陵新桥Cu-Au-S矿床黄铁矿微量元素LA-ICP-MS原位测定及其对矿床成因的制约[J].地学前缘, 2010,17(2):306-319. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002035.htm
[5] Piña R, Gervilla F, Barnes S J, Ortega L, Lunar R. Distribution of platinum-group and chalcophile elements in the Aguablanca Ni-Cu sulfide deposit (SW Spain): Evidence from a LA-ICP-MS study [J].Chemical Geology, 2012,302: 61-75.
[6] Bockrath C, Ballhaus C, Holzheid A. Fractionation of the platinum-group elements during mantle melting [J].Science, 2004,305(5692): 1951-1953. doi: 10.1126/science.1100160
[7] Lorand J P, Luguet A, Alard O, Bezos A, Meisel T. Abundance and distribution of platinum-group elements in orogenic lherzolites; a case study in a Fontete Rouge lherzolite (French Pyrénées) [J].Chemical Geology, 2008,248(3): 174-194.
[8] Lorand J P, Luguet A, Alard O. Platinum-group element systematics and petrogenetic processing of the continental upper mantle: A review [J].Lithos, 2013,164-167: 2-21. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.08.017
[9] Alard O. Nonchondritic distribution of the highly sider-ophile elements in mantle sulfides [J].Nature, 2000,407: 891-894. doi: 10.1038/35038049
[10] McDonald I. Development of sulphide standards for the in-situ analysis of platinum-group elements by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS)[C]//10th Intern Platinum Symp, 2005: 468-471.
[11] Jarvis K E, Williams J G, Parry S J, Bertalan E. Quantitative determination of the platinum-group elements and gold using NiS fire assay with laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS ) [J].Chemical Geology, 1995,124(1 2): 37-46.
[12] Norman M, Robinson P, Clark D. Major-and trace-element analysis of sulfide ores by laser-ablation ICP-MS, solution ICP-MS, and XRF: New data on international materials [J].The Canadian Mineralogist, 2003,41: 293-305. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.41.2.293
[13] Barnes S J, Cox R A, Zientek M L. Platinum-group element, gold, silver and base metal distribution in compositionally zoned sulfide droplets from the Medvezky Creek Mine, Noril′sk, Russia [J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006,152(2): 187-200. doi: 10.1007/s00410-006-0100-9
[14] Godel B, Barnes S J. Platinum-group elements in sulfide minerals and the whole rocks of the J-M Reef (Stillwater Complex): Implication for the formation of the reef [J].Chemical Geology, 2008(248): 272-294.
[15] Wilson S A, Ridley W I, Koenig A E. Development of sulfide calibration standards for the laser ablation inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry technique [J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2002,17(4): 406-409. doi: 10.1039/B108787H
[16] Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser C C, Ballhaus C, Berndt J, Stotternée P V, Meisel T. Synthesis of PGE sulfide standards for laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) [J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007,154(5): 607-617. doi: 10.1007/s00410-007-0212-x
[17] 袁继海,詹秀春,范晨子,赵令浩,孙冬阳,贾泽荣,胡明月,蒯丽君. 玻璃标样结合硫内标归一定量技术在激光剥蚀-等离子体质谱分析硫化物矿物中的应用[J].分析化学, 2012,40(2): 201-207. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201202008.htm
[18] 袁继海,詹秀春,樊兴涛,胡明月. 硫化物矿物中痕量元素的激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体质谱微区分析进展 [J].岩矿测试, 2011,30(2): 121-130. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201102003.htm
[19] Perkins W T, Pearce N J G, Westgate J A. The development of laser ablation ICP-MS and calibration strategies: Examples from the analysis of trace elements in volcanic glass shards and sulfide minerals [J].Geostandards Newsletter, 1997,21: 175-190. doi: 10.1111/ggr.1997.21.issue-2
[20] Figueiredo A M, Enzweiler J, Sarkis J E, Jorge A P, Shibuya E. NAA and UV laser ablation ICP-MS for platinum group elements and gold determination in NiS fire assay buttons: A comparison between two methods [J].Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2000,244(3): 623-625. doi: 10.1023/A:1006725618998
[21] Gros M, Lorand J P, Luguet A. Analysis of platinum group elements and gold in geological materials using NiS fire assay and Te coprecipitation; the NiS dissolution step revisited [J]. Chemical Geology, 2002,185(3): 179-190.
[22] Sylvester P, Cabri L, Tubrett M, McMahon G, Laflamme J, Peregoedova A. Synthesis and evaluation of a fused pyrrhotite standard reference material for platinum group element and gold analysis by laser ablation-ICPMS[C]//10th International Platinum Symposium. Finland: Geological Survey of Finland, 2005: 16-20.
[23] Wang X, Zeng Z, Yin X, Wang X. Study on the constituents of nickel sulfide assay button [J].Precious Metals, 2007,28(4): 45-49.
[24] Q/GD 008—2002,岩石、土壤、水系沉积物中铂族元素的锍镍试金-电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)法测定[S].
[25] Sylvester P. A practical guide to platinumgroup element analysis of sulphides by laser ablation ICPMS[M].Toronto: Mineralogical Association of Canada, 2001: 203-211.
[26] Shibuya E K, Sarkis J E S, Enzweiler J, Jorge A P S, Figueiredo A M G. Determination of platinum group elements and gold in geological materials using an ultraviolet laser ablation high-resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric technique [J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,1998,13(9): 941-944. doi: 10.1039/a801477i
-



 下载:
下载: