Database of 1∶50 000 Mineral Geological Map of the Hongshi Map-sheet in Kalatage Copper (-Zinc) Deposit, Hami, Xinjiang
-
摘要:
新疆哈密卡拉塔格铜(锌)矿红石幅(K46E009008)1∶50 000矿产地质图数据库是根据《固体矿产地质调查技术要求(1∶50 000)》(DD2019–02)和行业其他标准及要求,在充分利用1∶200 000、1∶50 000等区域地质调查工作成果资料的基础上,采用数字填图系统进行野外地质专项填图,并应用室内与室外填编图相结合的方法完成。本数据库将中–上奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组、下志留统红柳峡组和卡拉塔格组的建造类型进行了重新划分,把图幅内侵入岩时代划分为志留纪、泥盆纪、二叠纪等3期,建立了岩浆岩演化序列。图幅区内有大中小型矿床和矿点共8个,成矿时代集中分布在志留纪、石炭纪,赋矿围岩为火山碎屑岩和次火山岩,该区优势矿产以铜锌金为主,矿床类型以VMS型和次火山热液脉型矿床为主,分布在图幅东南一带。除金属矿产外,尚有膨润土矿床产出,具有较好的找矿潜力。本数据库包含5个地层单位和3期岩浆岩资料,数据量约为 15.1 MB。这些数据充分反映了该图幅 1∶50 000 矿产地质调查示范性成果,对该区矿产资源研究和勘查等具有参考意义。
Abstract:The database of 1∶50 000 mineral geological map of Hongshi Map-sheet (K46E009008) in Kalatage Copper (-Zinc) Deposit, Hami, Xinjiang (also referred to as the Database) was developed through field geology-specific mapping using the digital mapping system in accordance with the Technical Requirements of Solid Mineral Geological Survey (1∶50 000) (DD2019-02) and other standards and requirements in the geological industry. Meanwhile, the results of previous 1∶200 000 and 1∶50 000 regional geological surveys were fully utilized, and indoor and outdoor mapping/compilation was also carried out during database building. In this database, the suites of the Daliugou Formation of Middle-Upper Ordovician Huangcaopo Group as well as Lower Silurian Hongliuxia and Kalatage formations were reclassified. Moreover, the formation time of intrusive rocks in the map-sheet area was determined as Silurian, Devonian, and Permian, and the evolutionary sequence of magmatic rocks was established. There are eight large, medium and small mineral deposits and ore occurrences in the map-sheet area, the metallogenic epoch of which is concentrated in the Silurian and Carboniferous. The ore-hosted wall rocks are pyroclastic and subvolcanic rocks. The dominant mineral resources in this area are copper, zinc and gold, and their deposit types are mainly VMS type and subvolcanic hydrothermal vein type, which are distributed in the southeastern zone of the map-sheet area. In addition to metallic minerals, there are bentonite deposits with good prospecting potential. With a data size of about 15.1 MB, this database contains the data of five stratigraphic units and three stages of magmatic rocks. These data fully reflect the demonstration results of 1∶50 000 mineral geological survey of this map-sheet and provide references for the research and exploration of mineral resources in the survey area.
-

-
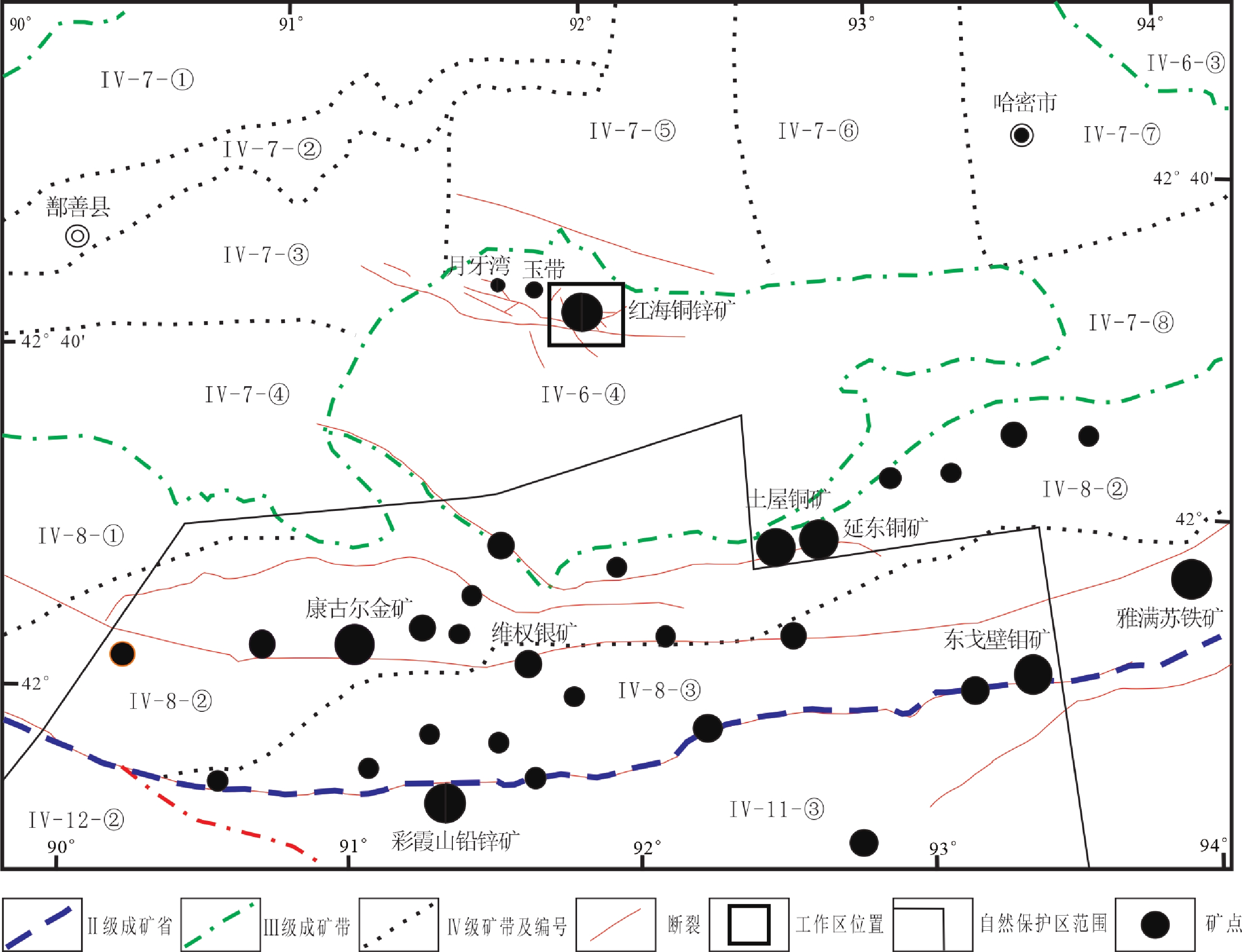
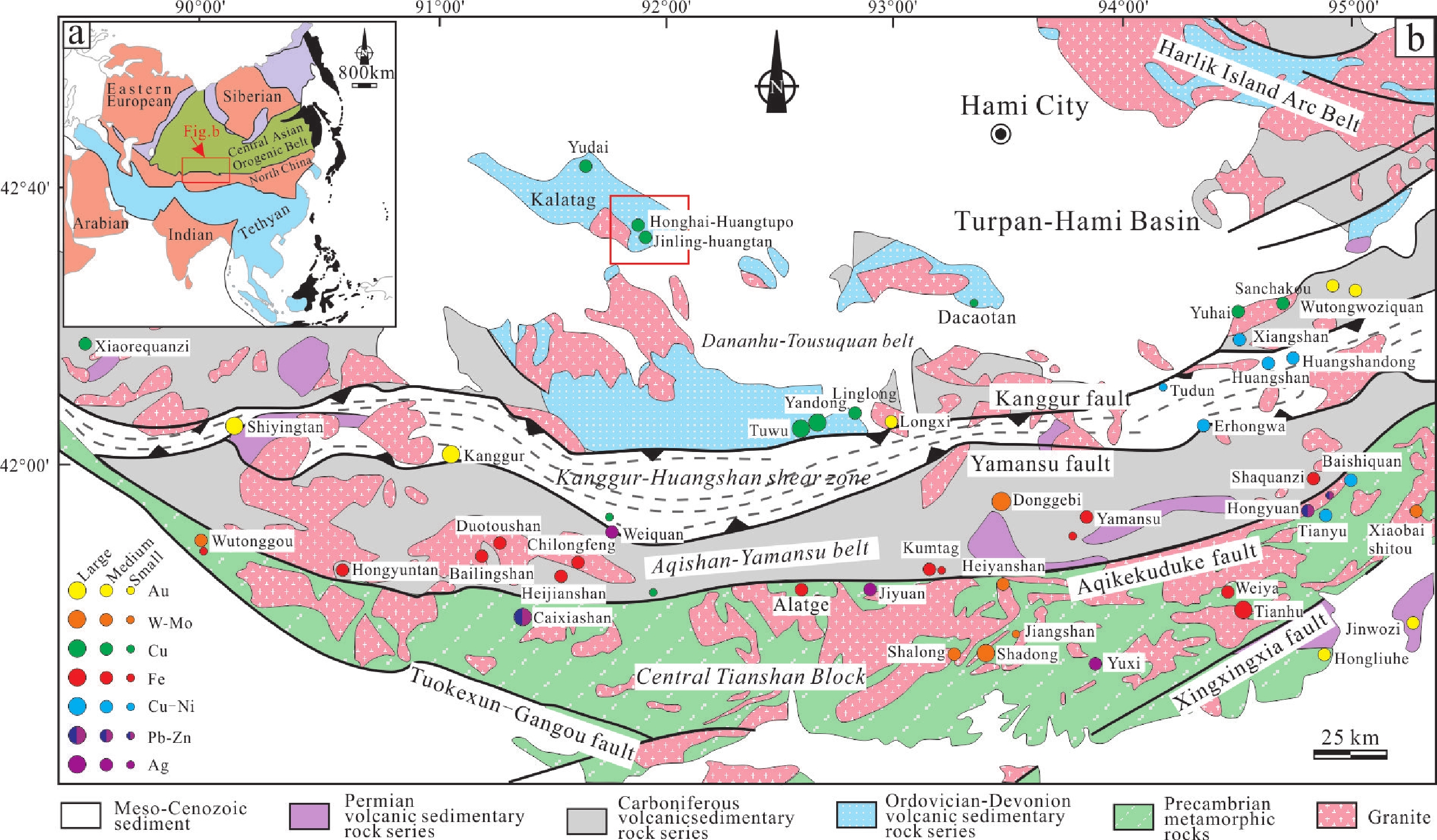
图 1 中亚造山带构造简图(a,修改自Sengor et al., 1993)和东天山构造及矿床分布图(b,修改自王京彬等,2006)
表 1 数据库(集)元数据简表
条目 描述 数据库(集)名称 新疆红石幅1∶50 000矿产地质图数据库 数据库(集)作者 王丰丰,北京矿产地质研究院
邓小华,北京矿产地质研究院
李德东,北京矿产地质研究院
卫晓锋,北京矿产地质研究院
吕晓强,北京矿产地质研究院
王燕超,北京矿产地质研究院数据时间范围 2017—2018年 地理区域 东经91°45′~92°00′,北纬42°30′~42°40′ 数据格式 *.wl, *.wt, *.wp; *.pm, *.lm, *.tm 数据量 15.1 MB 数据服务系统网址 http://dcc.cgs.gov.cn/ 基金项目 中国地质调查局地质调查项目“整装勘查区找矿预测与技术应用示范”(项目编号: 121201004000160901–66) 语种 中文 数据库(集)组成 数据库包括: 1∶50 000地质图库、角图和整饰。地质图库包括沉积岩、侵入岩、火山岩、构造、地质界线、产状、矿床(点)、矿化蚀变、同位素地质年龄取样点及取样点测年数据、岩性花纹、各类岩性代号等;角图包括综合建造柱状图、沉积岩建造柱状图、侵入岩建造柱状图、火山岩建造柱状图、构造、火山岩相、地质剖面图、图切剖面、典型矿床(区)平面图、矿产图例、矿产地名录、矿化蚀变图例、成矿区带位置图;整饰部分包括接图表、中国地质调查局局徽、图名、比例尺、坐标参数、责任签等 表 2 红石幅矿产地名录
序号 名称 规模 类型 主要含矿
建造构造1 新疆维吾尔自治区哈密市卡拉塔格红山铜金矿 小型 次火山热液 次火山岩 2 新疆维吾尔自治区哈密市卡拉塔格红山东铜金矿 矿点 次火山热液 次火山岩 3 新疆维吾尔自治区哈密市卡拉塔格梅岭铜锌矿 中型 次火山热液 次火山岩 4 新疆维吾尔自治区哈密市卡拉塔格红石铜矿 小型 次火山热液 次火山岩 5 新疆维吾尔自治区哈密市卡拉塔格碧玉山铜金矿 矿点 次火山热液 次火山岩 6 新疆维吾尔自治区哈密市卡拉塔格红海铜锌矿 大型 VMS型 火山碎屑岩 7 新疆维吾尔自治区哈密市卡拉塔格金岭金锌铜矿 中型 VMS+次火山热液 火山碎屑岩 8 新疆维吾尔自治区哈密市卡拉塔格沙尔湖膨润土矿 中型 风化蚀变 次火山岩 表 3 成矿区带划分一览表
二级成矿省及编号 三级成矿区带及编号 四级矿带及编号 古亚洲成矿域Ⅰ–1 准噶尔成矿省Ⅱ–2 Ⅲ–6准噶尔南缘(复合岛弧带) Cu–Mo–Au–Ag–Pb–Zn–W–Fe–Cr–Mn–RM–Pt–Sb–U–Ni–高岭土–硫铁矿–膨润土–重晶石–玉石–石墨–钠硝石–泥炭–盐类–重晶石成矿带 Ⅳ–6–③哈尔里克(复合岛弧带) Cu–Au–Ag–Pb–Zn–W–RM–Mo–多金属–石墨–钠硝石–芒硝–泥炭–白云母–重晶石矿带 Ⅲ–7吐哈盆地(地块) U–Fe–石油–天然气–煤–耐火黏土–钠硝石–盐类–膨润土成矿带 Ⅳ–7–①胜金口–小草湖(凹陷)石油–天然气–煤–钠硝石–石膏矿带 Ⅳ–7–②中央隆起带Fe–Mn–U–煤–石油–天然气–钠硝石矿带 Ⅳ–7–③托克逊–鄯善(凹陷) Fe–Mn–石油–天然气–煤–钠硝石–岩盐矿带 Ⅳ–7–④艾丁湖(斜坡) U–石油–天然气–煤–石盐–芒硝矿带 Ⅳ–7–⑤了墩(隆起)煤–钠硝石矿带(区) Ⅳ–7–⑥三道岭(凹陷) U–煤–耐火黏土矿带(区) Ⅳ–7–⑦哈密–骆驼圈子(隆起)芒硝矿带(区) Ⅳ–7–⑧大南湖–卡特卡尔(凹陷) Fe–U–煤矿带 古亚洲成矿域Ⅰ–1 准噶尔成矿省Ⅱ–2 Ⅲ–8觉罗塔格(裂陷槽) Cu–Ni–Fe–Mn–V–Ti–Au–Ag–Mo–W–RM–钠硝石–石膏–硅灰石–煤–硫铁矿–玉石成矿带 Ⅳ–8–①小热泉子(夭折裂谷) Cu–Pb–Zn–Au
矿带Ⅳ–8–②康古尔–土屋–黄山(裂陷槽) Cu–Ni–Ti–Au–Ag–Mo–Pb–Zn–RM–硫铁矿–硅灰石–玉石矿带 Ⅳ–8–③阿齐山–雅满苏–沙泉子(裂陷槽) Fe–Mn–Co–V–Ti–Au–Cu–石膏–煤–硫铁矿矿带 塔里木成矿省Ⅱ–4 Ⅲ–11那拉提–巴伦台–卡瓦布拉克(微陆块群/结合带) Fe–Pb–Zn–Ag–Cu–Ni–Pt族–Cr–V–Ti–REE–MR–U–W–硅灰石–水晶–滑石–萤石–盐类–白云母–磷灰石–宝玉石–煤矿带 IV–11–③卡瓦布拉克–星星峡(地块/结合带) Fe–Pb–Zn–Ag–Cu–Ni–Cr–V–Ti–REE–MR–U–W–硅灰石–盐类–白云母–磷灰石–宝玉石矿带 Ⅲ–12塔里木板块北缘(复合沟弧带) Fe–Ti–Mn–Cu–Ni–Mo–Pb–Zn–Sn–Pt族–菱镁矿–铝土矿–石墨–硅灰石–红柱石–磷灰石–石油–天然气–煤–硫铁矿–盐类–宝玉石–滑石–石棉–蛇纹岩–萤石–重晶石–泥炭成矿带 IV–12–②艾尔宾山(残余海盆) Fe–Mn–Cu–Au–W–Sn–Pb–Zn–U–菱镁矿–石墨–硅灰石–红柱石–石棉–滑石–蛇纹岩–硫铁矿–盐类矿带 表 4 火山岩建造柱状图一览表
岩石地层单位 建造单元特征 系 统 群 组 代号 建造类型 厚度/m 岩性组合 矿化蚀变特征 同位素年龄/Ma 火山机构 二叠系 中二叠统 卡拉岗组 P2k2a 中基性—中酸性火山岩建造 1451.4 英安岩–玄武岩–杏仁状安山岩 膨润土矿、蒙脱石化、高岭石化、碳酸盐化 253±1.2 破火山口 P2k2b P2k2c P2k1a 火山碎屑岩
建造晶屑岩屑凝灰岩–集块岩–玄武质晶屑岩屑凝灰岩 P2k1b P2k1c 泥盆系 下泥盆统 大南湖组 D1d3a 碎屑岩夹安山质火山岩建造 1995.71 晶屑岩屑凝灰岩–角砾凝灰岩–火山灰凝灰岩 含锰菱铁
矿化D1d3b D1d3c D1d2a 玄武质角砾熔岩、火山碎屑岩建造 凝灰岩–玄武质角砾熔岩夹砂岩 D1d2b D1d2c 志留系 下志留统 卡拉塔格组 S1k2a 流纹斑岩建造 300~
600英安质凝灰岩–含角砾晶屑岩屑凝灰岩–晶屑岩屑凝灰岩–英安岩 次火山岩热液型铜金
矿床439±7 S1k2b (黄铁)霏细岩建造 S1k1a 含角砾晶屑岩屑凝灰岩建造 S1k1b 英安质凝灰岩建造 S1k1c 英安岩建造 S1k1d 晶屑岩屑凝灰岩建造 S1k1e 火山角砾岩
建造志留系 下志留统 红柳峡组 S1ha 含矿沉凝灰岩建造 0~>400 沉凝灰岩–条带状凝灰岩 VMS型铜锌金多金属
矿床440.4±2.9 S1hb 黄铁绢英岩化凝灰岩建造 S1hc 条带状凝灰岩建造 434.2±3.9 奥陶系 中–上奥陶统 荒草坡群 大柳沟组 O2–3Hda 安山岩建造 >800 安山岩–玄武岩 446.4±4.6 O2–3Hdb 玄武岩建造 表 5 侵入岩建造一览表
时代 建造单元特征 代 纪 世 期 代号 建造类型 岩性组合 同位素年龄/Ma 晚古生代 二叠纪 ψνP 基性–超基性侵入岩 辉长岩–辉绿岩–橄榄辉石岩 280~270 νP βνP βμP 泥盆纪 δD 中酸性侵入岩 正长花岗岩–二长花岗岩–闪长岩–石英闪长玢岩 390~380 δμD ξγD ηγD 早古生代 志留纪 γS 中酸性侵入岩 英云闪长岩–花岗闪长岩–石英闪长岩组合 450~426 γδS δοS γδοS Table 1. Metadata Table of Database (Dataset)
Item Description Database (dataset) name Database of 1∶50 000 Mineral Geological Map of the Hongshi Map-sheet in Xinjiang Database (dataset) authors Wang Fengfeng, Beijing Institute of Geology for Mineral Resources
Deng Xiaohua, Beijing Institute of Geology for Mineral Resources
Li Dedong, Beijing Institute of Geology for Mineral Resources
Wei Xiaofeng, Beijing Institute of Geology for Mineral Resources
Lyu Xiaoqiang, Beijing Institute of Geology for Mineral Resources
Wan Yanchao, Beijing Institute of Geology for Mineral ResourcesData acquisition time 2017–2018 Geographical area 91°45′−92°00′E, 42°30′−42°40′N Data format *.wl, *.wt, *.wp; *.pm, *.lm, *.tm Data size 15.1 MB Data service system URL http://dcc.cgs.gov.cn Fund project The project entitled Prospecting Prediction and Technological Application Demonstration of Integrated Exploration Areas (No.: 121201004000160901–66) initiated by the China Geological Survey Language Chinese Database (dataset) composition The Database consists of a map library, corner maps, and map decorations of 1∶50 000 geological map. The map library covers sedimentary rocks, intrusive rocks, volcanic rocks, structures, geological boundaries, attitude, mineral deposits (ore occurrences), mineralized alternation, samples for isotopic dating and their dated ages, lithologic patterns, and various lithologic codes. The corner maps include histograms of comprehensive suites, sedimentary rock suites, intrusive rock suites, and volcanic rock suites. Besides, they cover structures, volcanic rock facies, geological sections, cross-sections, plans of typical deposits (mining areas), mineral legends, mineral deposit list, mineralized alternation legends, and the map of metallogenic zone/belt location. The map decorations include an index map, the logo of the China Geological Survey, map name, scale, coordinate parameter, and signature Table 2. List of mineral deposits in the Hongshi Map-sheet area
No. Mineral deposit name Scale Type Main ore-bearing suite 1 Hongshan copper-gold deposit in Kalatag region, Hami, Xinjiang Small Subvolcanic hydrothermal Subvolcanic rocks 2 East Hongshan copper-gold deposit in Kalatag region, Hami, Xinjiang Ore occurrence Subvolcanic hydrothermal Subvolcanic rocks 3 Meiling copper-zinc deposit in Kalatag region, Hami, Xinjiang Medium Subvolcanic hydrothermal Subvolcanic rocks 4 Hongshi copper deposit in Kalatag region, Hami, Xinjiang Small Subvolcanic hydrothermal Subvolcanic rocks 5 Biyushan copper-gold deposit in Kalatag region, Hami, Xinjiang Ore occurrence Subvolcanic hydrothermal Subvolcanic rocks 6 Honghai copper-zinc deposit inKalatag region, Hami, Xinjiang Large VMS Pyroclastic Rocks 7 Jingling gold-zinc-copper deposit in Kalatag region, Hami, Xinjiang Medium VMS+Subvolcanic hydrothermal Pytoclastic Rocks 8 Shaerhu bentonite deposit in Kalatag region, Hami, Xinjiang Medium Weathering alteration Subvolcanic rocks Table 3. Classification of metallogenic zones/belts
Level Ⅱ metallogenic province and no. Level Ⅲ metallogenic belt and no. Level Ⅳ ore belt and no. Paleo-Asian metallogenic domain I–1 Junggar metallogenic province II–2 III–6:Cu–Mo–Au–Ag–Pb–Zn–W–Fe–Cr–Mn–RM–Pt–Sb–U–
Ni–kaolin–pyrite–bentonite–barite–jade–graphite–nitratine–
peat–salts–barite metallogenic belt on the southern margin of Junggar (composite island arc belt)IV–6–③: Halierke (composite island arc belt) Cu–Au–Ag–Pb–Zn–W–RM–Mo–
polymetal–graphite–nitratine–mirabilite–peat–muscovite–barite metallogenic beltIII–7: U–Fe–petroleum–natural gas–coal– chamotte–nitratine–
salts–bentonite metallogenic belt in Turpan–Hami Basin (Block)IV–7–①: Shengjinkou–Xiaocaohu (sag) petroleum–natural gas–coal–nitratine–
gypsum ore beltIV–7–②: Fe–Mn–U–coal–petroleum–natural gas–nitratine ore belt of central uplift belt IV–7–③: Toksun–Shanshan (sag) Fe–Mn–petroleum–natural gas–coal–
nitratine–rock salt ore beltIV–7–④: Aydingkol (slope) U–petroleum–natural gas–coal–rock salt–mirabilite ore belt IV–7–⑤: Liaodun (uplift) coal–nitratine ore belt (zone) IV–7–⑥: Sandaoling (sag) U–coal–chamotte ore belt (zone) IV–7–⑦: Hami–Luotuojuanzi (uplift) mirabilite ore belt (zone) IV–7–⑧: Dananhu–Katekar (sag) Fe–U–coal ore belt III–8: Jueluotage (rift trough) Cu–Ni–Fe–Mn–V–Ti–Au–
Ag–Mo–W–RM–nitratine–gypsum–wollastonite–coal–
pyrite–jade metallogenic beltIV–8–①: Xiaorequanzi (failed rift) Cu–Pb–Zn–Au ore belt IV–8–②: Kanggur–Tuwu–Huangshan (rift trough) Cu–Ni–Ti–Au–Ag–Mo–Pb–
Zn–RM–pyrite–wollastonite–jade ore beltIV–8–③: Aqishan–Yamansu–Shaquanzi (rift trough) Fe–Mn–Co–V–Ti–Au–
Cu–gypsum–coal–pyrite ore beltTarim metallogenic province II–4 III–11: Nalati–Baluntai–Kawabulake (microcontinental group/junction zone) Fe–Pb–Zn–Ag–Cu–Ni–Pt family–
Cr–V–Ti–REE–MR–U–W–wollastonite–crystal–talc–
fluorite–salts–muscovite–apatite–gem–coal metallogenic beltIV–11–③: Kawabulake–Xingxingxia (block/junction zone) Fe–Pb–Zn–Ag–Cu–
Ni–Cr–V–Ti–REE–MR–U–W–wollastonite–salt–muscovite–apatite–gem ore beltIII–12: Fe–Ti–Mn–Cu–Ni–Mo–Pb–Zn–Sn–Pt group–magnesite–
bauxite–graphite–wollastonite–andalusite–apatite–petroleum–
natural gas–coal–pyrite–salts–gem–talc–asbestos–serpentine–
fluorite–barite–peat metallogenic belt on the northern margin of Tarim plate (composite trench arc belt)IV–12–②: Aierbin (residual basin) Fe–Mn–Cu–Au–W–Sn–Pb–Zn–U–
magnesite–graphite–wollastonite–andalusite–asbestos–talc–serpentine–
pyrite–salt ore beltTable 4. Histogram of volcanic rock suites
Lithostratigraphic unit Characteristics of a suite unit System Series Group Formation Code Suite type Thickness/m Lithologic association Mineralized alteration characteristics Isotopic age/Ma Volcanic edifice Permian Middle Permian Kalagang P2k2a Intermediate-basic – intermediate-acid volcanic rock suites 1451.4 Dacite-basalt-amygdaloidal andesite Bentonite ore, montmorillonitization, kaolinitization, and carbonation 253±1.2 Calderas P2k2b P2k2c P2k1a Volcanic clastic rock suites Crystal lithic tuff-agglomerate-basaltic crystal lithic tuff P2k1b P2k1c Devonian Lower Devonian Dananhu D1d3a Suites consisting of clastic rocks interbedded with andesitic volcanic rocks 1995.71 Crystal lithic tuff-breccia tuff - lapilli tuff Manganese-bearing sideritization D1d3b D1d3c D1d2a Suites consisting of basaltic breccia lava and pyroclastic rocks Tuff - basaltic breccia lava interbedded with sandstone D1d2b D1d2c Silurian Lower Silurian Kalatage S1k2a Rhythmic porphyry suites 300–600 Dacitic tuff-breccia-bearing crystal lithic tuff-crystal lithic tuff-dacite Subvolcanic hydrothermal copper-gold deposit 439±7 S1k2b (Pyrite) felsite suites S1k1a Suites consisting of crystal lithic tuff bearing breccia S1k1b Dacitic tuff suites S1k1c Dacite suites S1k1d Crystal lithic tuff suites S1k1e Volcanic breccia suites Silurian Lower Silurian Hongliuxia S1ha Ore-bearing sedimentary tuff suites 0–>400 Sedimentary tuff-banded tuff VMS copper-zinc-gold polymetallic deposit 440.4±2.9 S1hb Beresitized tuff suites S1hc Banded tuff suites 434.2±3.9 Ordovician Middle–
Upper OrdovicianHuangcaopo Daliugou O2–3Hda Andesite suites >800 Andesite-basalt 446.4±4.6 O2–3Hdb Basalt suites Table 5. Histogram of intrusive rock suites
Time Characteristics of a suite unit Era Period Epoch Stage Code Suite type Lithologic association Isotopic age/Ma Late Paleozoic Permian ψνP Mafic-ultramafic intrusive rocks Gabbro-diabase-olivine pyroxenite 280–270 νP βνP βμP Devonian δD Intermediate-acid intrusive rocks Orthogranite-monzogranite-diorite-quartz diorite porphyrite 390–380 δμD ξγD ηγD Early Paleozoic Silurian γS Intermediate-acid intrusive rocks Tonalite-granodiorite-quartz diorite association 450–426 γδS δοS γδοS -
[1] Deng X H, Wang J B, Pirajno F, Wang Y W, Li Y C, Li C, Zhou L M, Chen Y J. 2016. Re-Os dating of chalcopyrite from selected mineral deposits in the Kalatag district in the Eastern Tianshan Orogen, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 77: 72−81. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.01.014
[2] Deng Y F, Song X Y, Hollings P, Chen L M, Zhou T F, Yuan F, Xie W, Zhang D Y, Zhao B B. 2017. Lithological and geochemical constraints on the magma conduit systems of the Huangshan Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, NW China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 52(6): 845−862. doi: 10.1007/s00126-016-0703-7
[3] Deng X H, Wang J B, Pirajno F, Mao Q G, Long L L. 2020. A review of Cu- dominant mineral systems in the Kalatag district, East Tianshan, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 117: 103284. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103284
[4] Du L, Zhang Y Y, Huang Z Y, Li X P, Yuan C, Wu B, Long X P. 2019. Devonian to carboniferous tectonic evolution of the Kangguer Ocean in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Insights from three episodes of granitoids[J]. Lithos, 350–351: 105243. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105243
[5] Han C M, Xiao W J, Zhao G, Mao J W, Yang J M, Wang Z L, Yan Z, Mao Q G. 2006. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Tuwu porphyry copper deposit, Hami, Xinjiang, Central Asia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 29(1): 77−94. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.07.032
[6] He X H, Deng X H, Bagas L, Zhang J, Li C, Zhang W D. 2020. Geology, geochronology, and fluid inclusion studies of the Xiaorequanzi VMS Cu–Zn deposit in the East Tianshan Terrane, China[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 57(12): 1392–1410.
[7] Li D F, Chen H Y, Zhang L, Hollings P, Chen Y J, Lu W J, Zheng Y, Wang C M, Fang J, Chen G, Zhou G. 2016. Ore geology and fluid evolution of the giant Caixiashan carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposit in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 72(1): 355−372. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.08.007
[8] Li D F, Chen H Y, Sun X M, Fu Y, Liu Q F, Xia X P, Yang Q. 2019. Coupled trace element and SIMS sulfur isotope geochemistry of sedimentary pyrite: Implications on pyrite growth of Caixiashan Pb-Zn deposit[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 10(6): 2177−2188. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.05.001
[9] Mao Q G, Wang J B, Xiao W J, Windley B F, Schulmann K, Yu M J, Fang T H, Li Y C. 2019. Mineralization of an intra-oceanic arc in an accretionary orogen: Insights from the Early Silurian Honghai volcanogenic massive sulfide Cu-Zn deposit and associated adakites of the Eastern Tianshan (NW China)[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 131(5–6): 803−830. doi: 10.1130/B31986.1
[10] Mao Q G, Wang J B, Yu M J, Ao S J, Deng X H, Lü X Q, Li Y C. 2020. Re-Os and U-Pb geochronology for the Xiaorequanzi VMS deposit in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Constraints on the timing of mineralization and stratigraphy[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 122: 103473. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103473
[11] Sengör A M C, Natalin B A, Burtman V S. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid Tectonic Collage and Paleozoic Crustal Growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 364(6435): 299−307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
[12] Shen P, Pan H D, Zhou T F, Wang J B. 2014. Petrography, geochemistry and geochronology of the host porphyries and associated alteration at the Tuwu Cu deposit, NW China: a case for increased depositional efficiency by reaction with mafic hostrock?[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 49(6): 709−731. doi: 10.1007/s00126-014-0517-4
[13] Sun Y, Wang J B, Lv X Q, Yu M J, Li Y C, Mao Q G, Wang Y W, Long L L. 2019. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the newly discovered Cu-Ni sulfide-mineralized Yueyawan gabbroic complex, Kalatag district, north-western Eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 109: 598−614. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.05.009
[14] Wang Y F, Chen H Y, Xiao B, Han J S, Fang J, Yang J T, Jourdan F. 2018. Overprinting mineralization in the Paleozoic Yandong porphyry copper deposit, Eastern Tianshan, NW China-Evidence from geology, fluid inclusions and geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 100: 148−167.
[15] Wu C Z, Xie S W, Gu L X, Samson I M, Yang T, Lei R X, Zhu Z Y, Dang B. 2018. Shear zone-controlled post-magmatic ore formation in the Huangshandong Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 100: 545−560. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.015
[16] Xiao B, Chen H Y, Wang Y F, Han J S, Xu C, Yang J T. 2018. Chlorite and epidote chemistry of the Yandong Cu deposit, NW China: metallogenic and exploration implications for Paleozoic porphyry Cu systems in the Eastern Tianshan[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 100: 168−182. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.03.004
[17] Xiao W J, Zhang L C, Qin K Z, Sun S, Li J L. 2004. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China): Implications for the continental growth of central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 304(304): 370−395.
[18] Zhang L C, Xiao W J, Qin K Z, Zhang Q. 2006. The adakite connection of the Tuwu-Yandong copper porphyry belt, eastern Tianshan, NW China: trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope geochemistry[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 41(2): 188−200. doi: 10.1007/s00126-006-0058-6
[19] 龙灵利, 王京彬, 王玉往, 邓小华, 毛启贵, 孙燕, 孙志远, 张忠义. 2019. 东天山古弧盆体系成矿规律与成矿模式[J]. 岩石学报, 35(10): 3161−3188. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.10.13
[20] 毛启贵, 方同辉, 王京彬, 王书来, 王宁. 2010. 东天山卡拉塔格早古生代红海块状硫化物矿床精确定年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 26(10): 3017−3026. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201010013.htm
[21] 毛启贵, 王京彬, 方同辉, 于明杰, 孙燕. 2017. 新疆东天山卡拉塔格地区中泥盆世玉带斑岩铜(金)矿发现的地质找矿意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 53(1): 1−11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.01.001
[22] 秦克章, 方同辉, 王书来, 王旭东. 2001. 吐哈盆地南缘古生代“天窗”卡拉塔格铜金矿化区的发现及其成矿潜力[J]. 中国地质, 28(3): 16−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2001.03.004
[23] 秦克章, 方同辉, 王书来, 朱宝清, 冯益民, 于海峰, 修群业. 2002. 东天山板块构造分区?演化与成矿地质背景研究[J]. 新疆地质, 20(4): 302−307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2002.04.002
[24] 唐俊华, 顾连兴, 郑远川, 方同辉, 张遵忠, 高军辉, 王福田, 汪传胜, 张光辉. 2006. 东天山卡拉塔格钠质火山岩岩石学?地球化学及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 22(5): 1150−1166. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.05.008
[25] 王丰丰, 邓小华, 李德东, 卫晓锋, 吕晓强, 王燕超. 2020. 新疆红石幅1∶50 000矿产地质图数据库[DB/OL].地质科学数据出版系统.(2020-12-30). DOI:10.35080/data.C.2020.P35.
[26] 王京彬, 王玉往, 和志军. 2006. 东天山大地构造演化的成矿示踪[J]. 中国地质, 33(3): 461−469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.03.002
[1] Deng X H, Wang J B, Pirajno F, Wang Y W, Li Y C, Li C, Zhou L M, Chen Y J. 2016. Re-Os dating of chalcopyrite from selected mineral deposits in the Kalatag district in the Eastern Tianshan Orogen, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 77: 72−81. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.01.014
[2] Deng Y F, Song X Y, Hollings P, Chen L M, Zhou T F, Yuan F, Xie W, Zhang D Y, Zhao B B. 2017. Lithological and geochemical constraints on the magma conduit systems of the Huangshan Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, NW China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 52(6): 845−862. doi: 10.1007/s00126-016-0703-7
[3] Deng X H, Wang J B, Pirajno F, Mao Q G, Long L L. 2020. A review of Cu-dominant mineral systems in the Kalatag district, East Tianshan, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 117: 103284. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103284
[4] Du L, Zhang Y Y, Huang Z Y, Li X P, Yuan C, Wu B, Long X P. 2019. Devonian to carboniferous tectonic evolution of the Kangguer Ocean in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Insights from three episodes of granitoids[J]. Lithos, 350-351: 105243. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105243
[5] Han C M, Xiao W J, Zhao G, Mao J W, Yang J M, Wang Z L, Yan Z, Mao Q G. 2006. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Tuwu porphyry copper deposit, Hami, Xinjiang, Central Asia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 29(1): 77−94. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.07.032
[6] He X H, Deng X H, Bagas L, Zhang J, Li C, Zhang W D. 2020. Geology, geochronology, and fluid inclusion studies of the Xiaorequanzi VMS Cu-Zn deposit in the East Tianshan Terrane, China[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 57(12): 1392−1410. doi: 10.1139/cjes-2019-0067
[7] Li D F, Chen H Y, Zhang L, Hollings P, Chen Y J, Lu W J, Zheng Y, Wang C M, Fang J, Chen G, Zhou G. 2016. Ore geology and fluid evolution of the giant Caixiashan carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposit in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 72(1): 355−372.
[8] Li D F, Chen H Y, Sun X M, Fu Y, Liu Q F, Xia X P, Yang Q. 2019. Coupled trace element and SIMS sulfur isotope geochemistry of sedimentary pyrite: Implications on pyrite growth of Caixiashan Pb-Zn deposit[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 10(6): 2177−2188. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.05.001
[9] Long Lingli, Wang Jingbin, Wang Yuwang, Deng Xiaohua, Mao Qigui, Sun Yan, Sun Zhiyuan, Zhang Zhongyi. 2019. Metallogenic regularity and metallogenic model of the paleo arc-basin system in eastern Tianshan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(10): 3161−3188 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.10.13
[10] Mao Qigui, Fang Tonghui, Wang Jingbin, Wang Shulai, Wang Ning. 2010. Geochronology studies of the Early Paleozoic Honghai massive sulfide deposits and its geological significance in Kalatage area, eastern Tianshan Mountain[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(10): 3017−3026 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Mao Qigui, Wang Jingbin, Fang Tonghui, Yu Mingjie, Sun Yan. 2017. Discovery of the middle Devonian Yudai porphyric Cu (Au) deposit in the Kalatage area of eastern Tianshan Mountain, Xinjiang and and its geological prospecting significance[J]. Geology and Exploration, 53(1): 1−11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Mao Q G, Wang J B, Xiao W J, Windley B F, Schulmann K, Yu M J, Fang T H, Li Y C. 2019. Mineralization of an intra-oceanic arc in an accretionary orogen: Insights from the Early Silurian Honghai volcanogenic massive sulfide Cu-Zn deposit and associated adakites of the Eastern Tianshan (NW China)[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 131(5-6): 803−830. doi: 10.1130/B31986.1
[13] Mao Q G, Wang J B, Yu M J, Ao S J, Deng X H, Lü X Q, Li Y C. 2020. Re-Os and U-Pb geochronology for the Xiaorequanzi VMS deposit in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Constraints on the timing of mineralization and stratigraphy[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 122: 103473. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103473
[14] Qin Kezhang, Fang Tonghui, Wang Shulai, Wang Xudong. 2001. Discovery of the Kalatage Cu-Au mineralized district and its prospecting potentiality at the south margin of the Tu-Ha basin[J]. Geology in China, 28(3): 16−23 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Qin Kezhang, Fang Tonghui, Wang Shulai, Zhu Baoqing, Feng Yimin, Yu Haifeng, Xiu Qunye. 2002. Plate tectonics division, evolution and metallogenic settings in eastern Tianshan mountains, NW China[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 20(4): 302−308 (in Chinese with English abstract
[16] Sengör A M C, Natalin B A, Burtman V S. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid Tectonic Collage and Paleozoic Crustal Growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 364(6435): 299−307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
[17] Shen P, Pan H D, Zhou T F, Wang J B. 2014. Petrography, geochemistry and geochronology of the host porphyries and associated alteration at the Tuwu Cu deposit, NW China: a case for increased depositional efficiency by reaction with mafic hostrock?[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 49(6): 709−731. doi: 10.1007/s00126-014-0517-4
[18] Sun Y, Wang J B, Lv X Q, Yu M J, Li Y C, Mao Q G, Wang Y W, Long L L. 2019. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the newly discovered Cu-Ni sulfide-mineralized Yueyawan gabbroic complex, Kalatag district, north- western Eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 109: 598−614. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.05.009
[19] Tang Junhua, Gu Lianxing, Zheng Yuanchuan, Fang Tonghui, Zhang Zunzhong, Gao Junhui, Wang Futian, Wang Chuansheng, Zhang Guanghui. 2006. Petrology, geochemistry and genesis of the Na-rich volcanic rocks of the Kalatag area, eastern Tianshan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1150−1166 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Wang Fengfeng, Deng Xiaohua, Li Dedong, Wei Xiaofeng, Lyu Xiaoqiang, Wang Yanchao. 2020. Database of 1∶50 000 Mineral Geological Map of the Hongshi Map-sheet in Xinjiang[DB/OL]. Geoscientific Data & Discovery Publishing System. (2020-12-30). DOI: 10.35080/data.C.2020.P35.
[21] Wang Jingbin, Wang Yuwang, He Zhijun. 2006. Ore deposits as a guide to the tectonic evolution in the east Tianshan mountains, NW China[J]. Geology in China, 33(3): 461−469 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Wang Y F, Chen H Y, Xiao B, Han J S, Fang J, Yang J T, Jourdan F. 2018. Overprinting mineralization in the Paleozoic Yandong porphyry copper deposit, Eastern Tianshan, NW China-Evidence from geology, fluid inclusions and geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 100: 148−167. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.04.013
[23] Wu C Z, Xie S W, Gu L X, Samson I M, Yang T, Lei R X, Zhu Z Y, Dang B. 2018. Shear zone-controlled post-magmatic ore formation in the Huangshandong Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 100: 545−560. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.015
[24] Xiao B, Chen H Y, Wang Y F, Han J S, Xu C, Yang J T. 2018. Chlorite and epidote chemistry of the Yandong Cu deposit, NW China: metallogenic and exploration implications for Paleozoic porphyry Cu systems in the Eastern Tianshan[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 100: 168−182. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.03.004
[25] Xiao W J, Zhang L C, Qin K Z, Sun S, Li J L. 2004. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China): Implications for the continental growth of central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 304: 370−395. doi: 10.2475/ajs.304.4.370
[26] Zhang L C, Xiao W J, Qin K Z, Zhang Q. 2006. The adakite connection of the Tuwu-Yandong copper porphyry belt, eastern Tianshan, NW China: trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope geochemistry[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 41(2): 188−200. doi: 10.1007/s00126-006-0058-6
-




 下载:
下载: