Geochemical characteristics and driving factors of high-ammonium groundwater in the rapid urbanization of the Pearl River Delta
-
摘要:
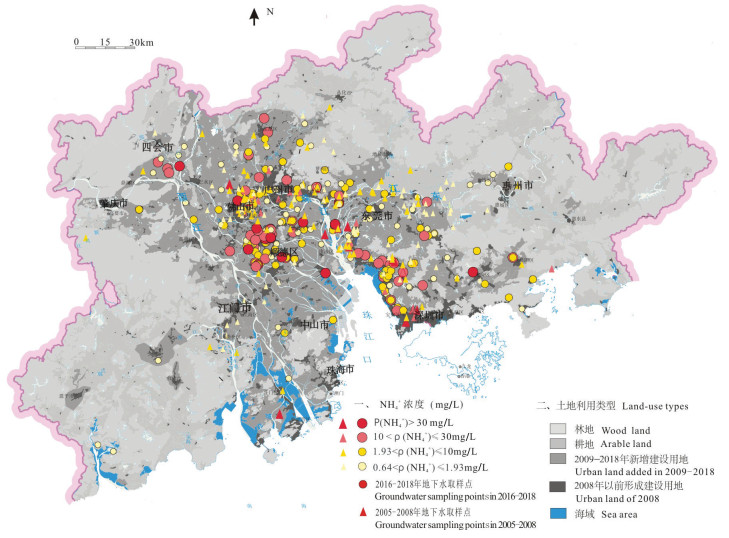
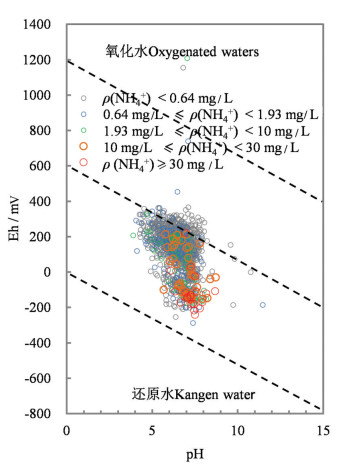
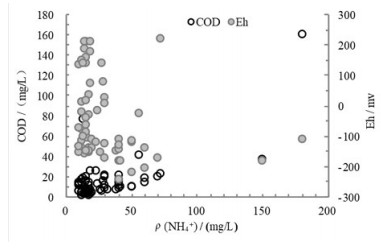
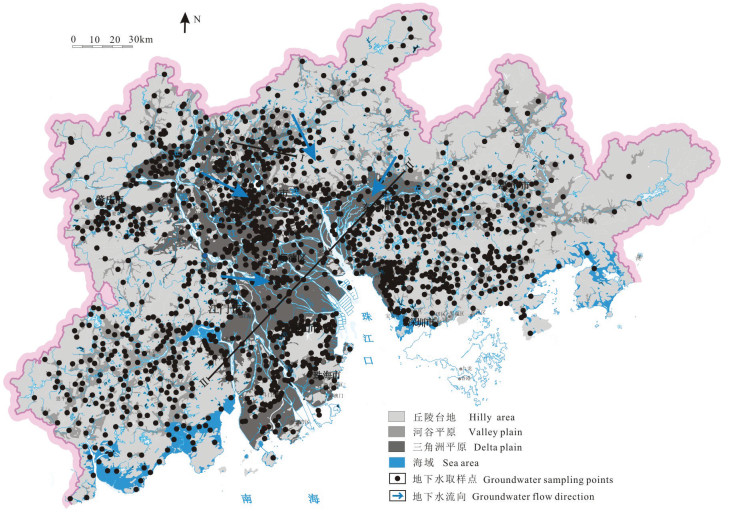
地下水中高浓度的铵态氮对生活饮用水安全及生态环境存在潜在威胁。相比较硝态氮,高浓度的铵态氮不仅有各种人为来源,天然沉积环境更是造成高铵地下水的主要成因。本文以城镇化快速发展的珠江三角洲为研究区,运用数理统计、主成分分析等方法深入探讨了研究区高铵地下水的赋存环境特征及驱动因素。结果表明,研究区地下水中NH4+质量浓度介于未检出~180 mg/L。研究区1539组地下水样品中,NH4+质量浓度大于10 mg/L的高铵地下水69组,其中含NH4+质量浓度大于30 mg/L的高铵"肥水"23组。对比2005-2008年历史水化学数据,2009-2018年新增建设用地孔隙含水层高铵地下水样品比例增加25%。高铵地下水呈斑块状分布于三角洲平原区第四系底部低洼的基底、洼地等退积层序发育的淤泥质含水层中。淤泥层等富含有机质和总有机碳的沉积层是珠江三角洲地区的"生铵层",有机氮的矿化是三角洲平原区城市化孔隙含水层中高铵地下水的主要驱动力。城镇化扩张引起生活污水及富铵工业废水的泄漏入渗是城乡结合部高铵地下水铵氮的重要来源。三角洲平原区中性至弱碱性富含有机质的还原环境是高铵地下水的主要成因。风化溶滤、阳离子交换吸附、海陆交互作用是珠江三角洲高铵地下水质演变的主要水文地球化学过程。
Abstract:High concentration of ammonium nitrogen in groundwater is a potential threat to drinking water safety and ecological environment. Compared with nitrate nitrogen, the high concentration of ammonium nitrogen not only has a variety of man-made sources, but also the natural sedimentary environment is the main cause of high ammonium groundwater. The rapid urbanization of the Pearl River Delta was taken as a case study to investigate the environmental characteristics and driving factors of high ammonium groundwater by means of mathematical statistics and principal component analysis methods. The results show that the concentration of ammonium in the groundwater in the study area is as high as-180 mg/L. Among 1539 groups of groundwater samples, 69 groups of high-ammonium groundwater with ammonium ion concentration greater than 10 mg/L, 23 groups of high-ammonium fertilizer water yield ammonium ion concentration greater than 30 mg/L. Compared with the historical hydrochemical data from 2005 to 2008, the proportion of high-ammonium groundwater sample sites in the pore aquifers of newly-added construction land from 2009 to 2018 is 6.5%, which is 1.25 times that of ten years ago. The high ammonium groundwater is distributed in the silty and silty aquifer developed in the low lying basement and depression at the bottom of Quaternary in the delta plain area. The sediments rich in organic matter and total organic carbon, such as silt layer, are the "ammonium producing layer" in the Pearl River Delta region, and the mineralization of organic nitrogen is the main driving force of the high ammonium groundwater in the urbanized pore aquifer in the delta plain region. The leakage and infiltration of domestic sewage from urbanization expansion and ammonium-rich industrial wastewater are the important sources of ammonium-nitrogen in high ammonium-rich groundwater in the urban-rural junction. The reduction environment rich in organic matter is the main cause of the high ammonium groundwater in the delta plain. Lixiviation, cation exchange adsorption and sea-land interaction are the main hydrogeochemical processes of the evolution of high-ammonium groundwater water quality in the Pearl River Delta.
-

-
表 1 研究区不同城镇化水平区地下水化学组分统计表(mg/L)
Table 1. Chemical composition of groundwater in various areas with different urbanization levels in the study area
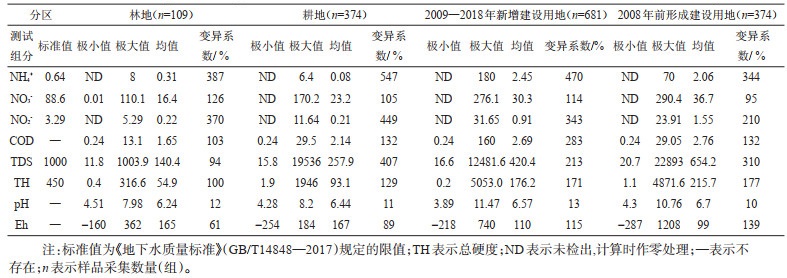
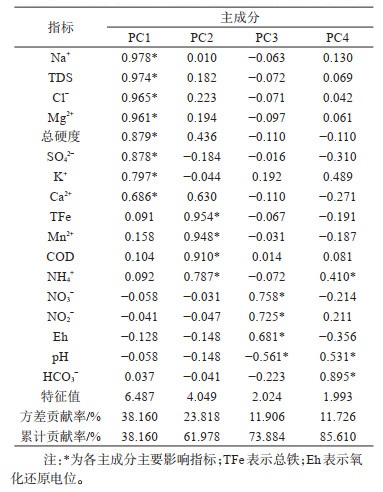
表 2 高铵地下水主要离子主成分分析
Table 2. Principal component analysis of the major ions
-
Du Y, Ma T, Deng Y M, Shen S, Lu Z. 2017a. Sources and fate of high levels of ammonium in surface water and shallow groundwater of the Jianghan Plain, Central China[J]. Environmental Science-Processes & Impacts, 19(2): 161-172. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039811074210_733f.html
Du Yao. 2017b. Surface Water-groundwater Interaction and its Effect on Ammonium Transport and Fate in Jianghan Plain, Central China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Fan B L, Zhao Z Q, Tao F X, Liu B J, Tao Z H, Gao S, Zhang L H. 2014. Characteristics of carbonate, evaporite and silicate weathering in Huanghe River basin: A comparison among the upstream, midstream and downstream[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 96: 17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.09.005
GB/T 8538-2008. 2008. Methods for examination of Drinking Natural Mineral Water[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press(in Chinese).
GB/T14848-2017. 2017. Environmental Quality Standards for Groundwater[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press(in Chinese).
Gibbs R J. 1970. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 170: 1088 -1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
Guangdong Provincial Bureau of statistics. 2020. Guangdong Statistical Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press(in Chinese).
He Jin, Zhang Youkuan, Zhao Yuqing, Han Shuangbao, Liu Yuanqing, Zhang Tao. 2019. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of groundwater in Xialatuo basin section of Xianshui River[J]. Environmental Science, 40(3): 1236-1244(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31087970
Hu K L, Huang Y F, Li H, Li B G, Chen D L, White R E. 2005. Spatial variability of shallow groundwater level, electrical conductivity and nitrate concentration, and risk assessment of nitrate contamination in North China Plain[J]. Environment International, 31(6): 896-903. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2005.05.028
Huang Guanxing, Sun Jichao, Zhang Ying, Chen Zongyu, Liu Fan. 2013. Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area, South China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 463-464: 209-221. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Guanxing_Huang/publication/243966802_Impact_of_anthropogenic_and_natural_processes_on_the_evolution_of_groundwater_chemistry_in_a_rapidly_urbanized_coastal_area_South_China/links/0046352822008e1b88000000
Huang Guanxing, Zhang Ming, Liu Chunyan, Li Liangping, Chen Zongyu. 2018. Heavy metal(loid)s and organic contaminants in groundwater in the Pearl River Delta that has undergone three decades of urbanization and industrialization: Distributions, sources, and driving forces[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 635: 913-925. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.210
Jiao J J, Wang Y, Cherry J A, Wang X S, Zhi B F, Du H Y, Wen D G. 2010. Abnormally high ammonium of natural origin in a coastal aquifer-aquitard system in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Environmental Science Technology, 44 (19): 7470-7475. doi: 10.1021/es1021697
Li Jiansen, Li Tingwei, Ma Haizhou, Peng Ximing. 2013. Investigation of the chemical characteristics and its geological significance of the tertiary oilfield brine in the western Qaidam basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Enineering Geology, 40(6): 208-36. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=83876871504849514854484855
Lingle D A, Kehew A E, Krishnamurthy R V. 2017. Use of nitrogen isotopes and other geochemical tools to evaluate the source of ammonium in a confined glacial drift aquifer, Ottawa County, Michigan, USA[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 78: 334-342. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.01.004
Liu Xingquan, Xu Jingyu, Jiang Lihua, Huang Jianxi, Wang Limin, Liu Jia, Zou Jinqiu. 2010. Spatial variability and distribution pattern of groundwater nitrate pollution in farming regions of Shandong Province, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 29(6): 1172-1179(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lü Xiaoli, Liu Jingtao, Zhou Bing, Zhu Liang. 2020. Fe and Mn distribution of groundwater and impact of human activities in the Tacheng basin, Xinjiang[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1765-1775(in Chinese with English abstract).
Miao Jinjie, Jin Jihong, Du Dong, Liu Hongwei, Bai Yaonan, Zhang Jing, Guo Xu. 2020. Valuation of groundwater environmental quality and causes of problems in the capital sub-center and key regions[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 43(3): 224-229, 286(in Chinese with English abstract).
Pu Junbing, Yuan Daoxian, Jiang Yongjun, Gou Pengfei, Yin Jianjun. 2010. Hydrogeochemistry and environmental meaning of Chongqing subterranean karst streams in China[J]. Advances in Water Science, 21(5): 628-636(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286993027_Hydrogeochemistry_and_environmental_meaning_of_Chongqing_subterranean_karst_streams_in_China
Scholler H. 1967. Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resource: Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development[J]. Water Research, 33: 44-52. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/298455180_Qualitative_evaluation_of_groundwater_resources_in_methods_and_techniques_of_groundwater_investigation_and_development
Sun Houyun, Mao Qigui, Wei Xiaofeng, Zhang Huiqiong, Xi Yuze. 2018. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation evolutionary mechanism of the groundwater system in the Hami basin[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 48-61(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiao J, Jin Z D, Zhang F, Jin W. 2012. Major ion geochemistry of shallow groundwater in the Qinghai Lake Catchment, NE Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 67(5): 1331-1344. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1576-4
Xu Jin, He Jiangtao, Peng Cong, Zeng Ying. 2018. Characteristics and genesis of NO3 type water in shallow groundwater in Liujiang basin[J]. Environmental Science, 39 (9): 4142-4149(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jing, Xiao Tianyun, Li Haibo, Wang Quanrong. 2018. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of the NO3-N concentration in groundwater in Jianghan Plain[J]. China Environmental Science, 38(2): 710-718(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGHJ201802041.htm
Zhang F E, Huang G X, Hou Q X, Liu C Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Q. 2019. Groundwater quality in the Pearl River Delta after the rapid expansion of industrialization and urbanization: Distributions, main impact indicators, and driving forces[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 577, doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124004.
Zhang Ming, Huang Guanxing, Liu Chunyan, Zhang Ying, Chen Zongyu, Wang Jincui. 2020. Distributions and origins of nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium in various aquifers in an urbanized coastal area, South China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 582, doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124528
Zhang Tao, He Jin, Li Jingjie, Cao Yueting, Gong Lei, Liu Jinwei, Bian Chao, Cai Yuemei. 2018. Major ionic features and possible controls in the groundwater in the Hamatong River basin[J]. Environmental Science, 39(11): 143-152(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30628220
Zhi Bingfa. 2015. Formation and evolution of high ammonium groundwater in the Pearl River Delta plain[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 22(4): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201504001.htm
Zhu B Q, Yang X P, Rioual P, Guang X. 2011. Hydrogeochemistry of three watersheds (the Erlqis, Zhungarer and Yili) in northern Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 26(8): 1535-1548. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.018
Zhu Danni, Zou Shengzhang, Zhou Changsong, Li Lujuan, Xie Hao. 2018. Identification of hydeochemical sensitive factors of karst groundwater in different functional urban areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 37(4): 484-492(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGYR201804002.htm
Zhu Liang, Liu Jingtao, Yang Mingnan, Lü Xiaoli, Xie Fei, Wei Yutao. 2020. Changes and driving factors of groundwater environment in Lanzhou since 1998[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1677-1687(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zuo Yuzheng, An Yanling, Wu Qixin, QU Kunjie, Fan Guanghui, Ye Zuxin, Qin Ling, Qian Juanting, Xu Chenglong. 2017. Study on the hydrochemical characteristics of Duliu River basin in Guizhou Province[J]. China Environmental Science, 37(7): 2684-2690(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/320550956_Study_on_the_hydrochemical_characteristics_of_Duliu_River_basin_in_Guizhou_Province
杜尧. 2017. 江汉平原地表水-地下水相互作用及其对铵氮迁移转化的影响[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学.
GB/T8538-2008. 2008. 饮用天然矿泉水检验方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
GB/T14848-2017.2017. 地下水质量标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
广东省统计局. 2020. 广东统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社.
何锦, 张幼宽, 赵雨晴, 韩双宝, 刘元晴, 张涛. 2019. 鲜水河断裂带虾拉沱盆地断面地下水化学特征及控制因素[J]. 环境科学, 40(3): 1236-1244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201903024.htm
李建森, 李廷伟, 马海州, 彭喜明. 2013. 柴达木盆地西部新近系和古近系油田卤水水化学特征及地质意义[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 40(6): 208-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201306007.htm
刘兴权, 许晶玉, 江丽华, 黄健熙, 王利民, 刘佳, 邹金秋. 2010. 山东省种植区地下水硝酸盐污染空间变异及分布规律研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 29(6): 1172-1179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201006026.htm
吕晓立, 刘景涛, 周冰, 朱亮. 2020. 新疆塔城盆地地下水中铁锰分布特征及人类活动的影响[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1765-1775. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200613&flag=1
苗晋杰, 靳继红, 杜东, 刘宏伟, 白耀楠, 张竞, 郭旭. 2020. 首都副中心及重点区域地下水环境质量评价与问题成因[J]. 地质调查与研究, 43(3): 224-229, 286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.03.005
蒲俊兵, 袁道先, 蒋勇军, 苟鹏飞, 殷建军. 2010. 重庆岩溶地下河水文地球化学特征及环境意义[J]. 水科学进展, 21(5): 628-636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201005008.htm
孙厚云, 毛启贵, 卫晓锋, 张会琼, 葸玉泽. 2018. 哈密盆地地下水系统水化学特征及形成演化[J]. 中国地质, 45(6): 48-61. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180604&flag=1
徐进, 何江涛, 彭聪, 曾颖. 2018. 柳江盆地浅层地下水硝酸型水特征和成因分析[J]. 环境科学, 39(9): 4142-4149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201809024.htm
杨静, 肖天昀, 李海波, 王全荣. 2018. 江汉平原地下水中硝酸盐的分布及影响因素[J]. 中国环境科学, 38(2): 710-718. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.02.036
张涛, 何锦, 李敬杰, 曹月婷, 龚磊, 刘金巍, 边超, 蔡月梅. 2018. 蛤蟆通河流域地下水化学特征及控制因素[J]. 环境科学, 39(11): 143-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2018.11.031
支兵发. 2015. 珠江三角洲平原高铵地下水的形成演化[J]. 安全与环境工程, 22(4): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201504001.htm
朱丹尼, 邹胜章, 周长松, 李录娟, 谢浩. 2018. 不同城镇功能区岩溶地下水化学敏感因子识别[J]. 中国岩溶, 37(4): 484-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201804002.htm
朱亮, 刘景涛, 杨明楠, 吕晓立, 解飞, 魏玉涛. 2020. 1998年以来兰州市地下水环境变化及驱动因素[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1677-1687. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200606&flag=1
左禹政, 安艳玲, 吴起鑫, 屈坤杰, 樊光辉, 叶祖鑫, 秦玲, 钱娟婷, 涂成龙. 2017. 贵州省都柳江流域水化学特征研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(7): 2684-2690. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.07.033
-



 下载:
下载: