Geochemical features of the Zoujiashan and Shazhou uranium ore deposits in the Xiangshan area, Jiangxi, China: Implications for hydrothermal source
-
摘要:
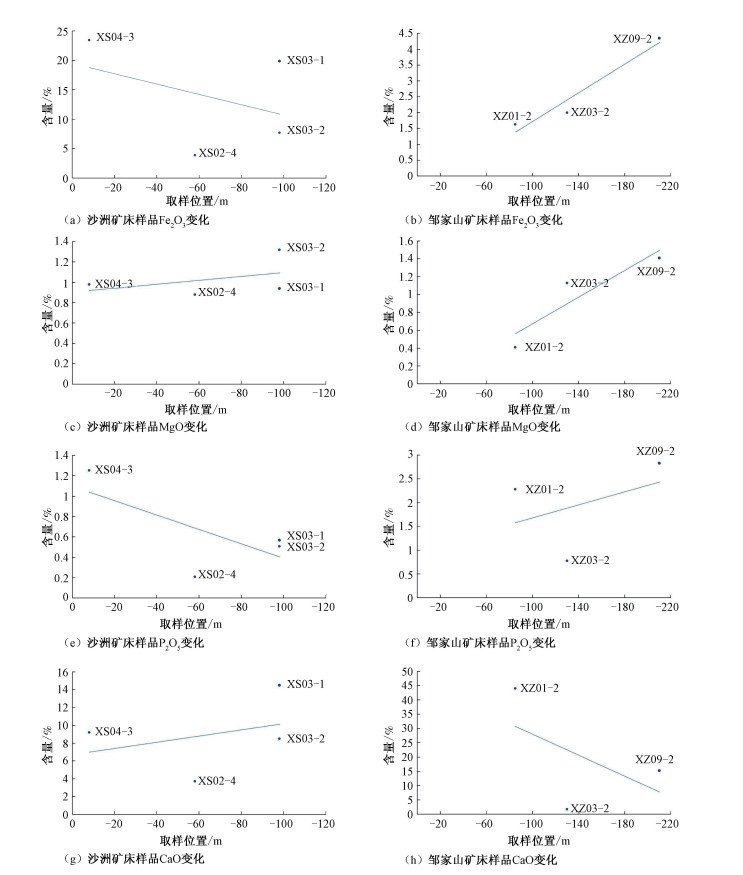
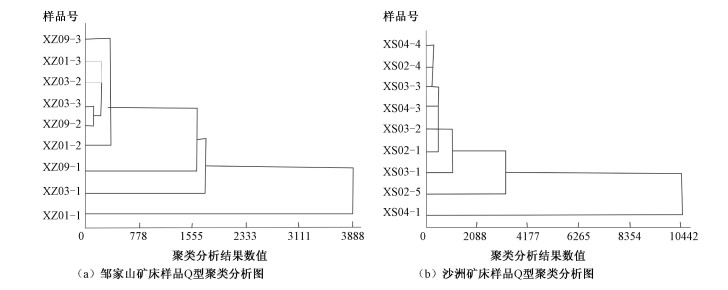
结合矿床的蚀变特征,对相山铀矿田邹家山矿床和沙洲矿床不同标高的赋矿围岩及矿石样品进行了常量和微量元素地球化学分析,以制约成矿物质和成矿流体的来源。典型常量元素的变化趋势研究表明,相山矿田垂向蚀变分带明显,邹家山矿床浅部出露的蚀变岩以"碱性"蚀变为主,而沙洲矿床出露的蚀变岩以"酸性"蚀变为主,证实了相山地区蚀变"北碱西酸"的特征。对邹家山和沙洲两个矿床的微量元素进行了相关分析和Q型聚类分析,结果表明两个矿床的地球化学特征相似,Mo、Sr、Th、Tl、U、V、La、Ba是与成矿作用密切相关的元素,微量元素相关分析、Q型聚类分析及正交因子载荷关系分析说明两个矿床成矿热液来源于同一深部流体;正交因子载荷关系分析还表明,流纹英安岩与矿石有极强的相关性,暗示成矿物质最可能来源于流纹英安岩岩浆。
Abstract:This article presents a geochemical analysis of the major and trace elements in the wall-rocks and ores at different elevations in the Zhoujiashan and Shazhou ore deposits of the Xiangshan uranium orefield. Combining the analysis results with alteration characteristics of the deposits, we aims to understand the source of ore-forming materials and fluids. The variation trend of the typical major elements shows that the Xiangshan orefield has obvious vertical alteration zonings. The alteration rocks exposed in the shallow part of the Zoujiashan deposit mainly show alkaline alteration, while those exposed in the Shazhou deposit mainly show acidic alteration, which confirms the alteration characteristics of "alkaline alteration in the north and acidic alteration in the west" in the Xiangshan area. Correlation analysis and Q-type cluster analysis of the trace elements in the two deposits show that the geochemical characteristics of the two deposits are similar. Mo, Sr, Th, Tl, U, V, La and Ba are closely related to mineralization. The above two analysis together with the study on loading relations of orthogonal factors reveal that the ore-forming hydrothermal fluids of the two deposits are derived from the same deep fluid. Moreover, the loading relations analysis of orthogonal factors also shows that rhyolite is strongly correlated with ore, suggesting that ore-forming materials are most likely derived from rhyolite magma.
-

-
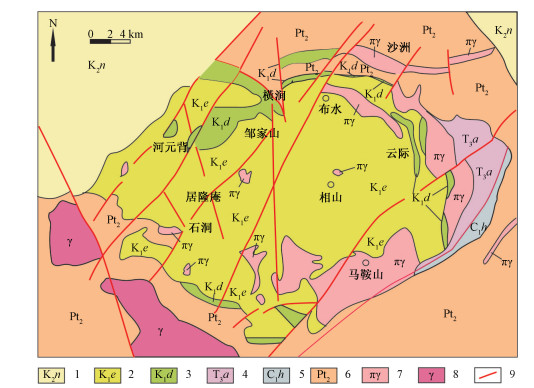
图 1 相山盆地火山构造简图(据温志坚等, 1999; 聂江涛, 2018修改)
Figure 1.
表 1 样品来源及性质简述
Table 1. Location and brief lithological description of the samples
样品号 样品性质 取样位置(标高/m) 岩性 样品号 样品性质 取样位置(标高/m) 岩性 沙洲矿床 XS04-1 围岩 -8 花岗斑岩 XS04-4 蚀变岩 -8 蚀变花岗斑岩 XS04-3 矿石 -8 矿化花岗斑岩 XS02-4 矿石 -58 矿化花岗斑岩 XS02-1 围岩 -58 花岗斑岩 XS03-1 矿石 -98 矿化花岗斑岩 XS02-5 围岩 -58 花岗斑岩 XS03-3 蚀变岩 -98 蚀变花岗斑岩 XS03-2 矿石 -98 矿化花岗斑岩 邹家山矿床 XZ01-1 围岩 -85 碎斑熔岩 XZ01-2 矿石 -85 矿化碎斑熔岩 XZ01-3 蚀变岩 -85 矿变碎斑熔岩 XZ03-1 蚀变岩 -130 蚀变碎斑熔岩 XZ03-2 矿石 -130 矿化碎斑熔岩 XZ03-3 蚀变岩 -130 蚀变碎斑熔岩 XZ09-1 围岩 -210 流纹英安岩 XZ09-2 矿石 -210 矿化流纹英安岩 XZ09-3 蚀变岩 -210 蚀变流纹英安岩 表 2 邹家山矿床和沙洲矿床不同标高样品常量元素表(%)
Table 2. Major elements of samples at different elevations in the Zoujiashan and Shazhou deposits (%)
样品号 样品性质 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO Na2O K2O TiO2 MnO P2O5 沙洲矿床 XS04-1 围岩 64.79 14.77 3.99 3.57 0.68 3.51 2.52 0.33 0.47 0.094 XS04-3 矿石 18.99 3.91 23.44 9.21 0.98 0.04 0.41 0.08 4.17 1.254 XS04-4 蚀变岩 67.66 14.89 3.34 1.93 0.73 2.35 5.33 0.38 0.11 0.104 XS02-1 围岩 61.09 16.57 3.89 4.15 1.00 6.49 1.18 0.51 0.28 0.158 XS02-4 矿石 63.52 15.31 3.88 3.72 0.88 4.08 3.35 0.48 0.14 0.208 XS02-5 围岩 64.56 15.97 3.52 2.94 0.72 4.54 2.99 0.47 0.12 0.164 XS03-1 矿石 24.61 10.74 19.87 14.51 0.94 1.42 1.77 0.40 0.36 0.568 XS03-2 矿石 48.63 16.26 7.71 8.51 1.32 5.95 1.06 0.52 0.27 0.508 XS03-3 蚀变岩 65.59 15.88 3.91 2.63 0.97 2.88 5.14 0.50 0.05 0.143 邹家山矿床 XZ01-1 围岩 82.57 9.22 1.17 0.20 0.24 0.83 3.89 0.05 0.01 0.016 XZ01-2 矿石 21.32 11.69 1.63 44.04 0.41 0.17 2.84 0.26 0.06 2.282 XZ01-3 蚀变岩 77.99 11.84 1.67 0.50 0.44 0.89 4.17 0.09 0.02 0.173 XZ03-1 围岩 72.20 12.90 1.17 1.87 0.67 0.34 6.70 0.10 0.03 0.043 XZ03-2 矿石 50.21 22.56 2.00 1.75 1.13 0.14 7.96 1.47 0.04 0.778 XZ03-3 蚀变岩 74.82 11.89 1.46 1.76 0.41 1.9 5.22 0.08 0.03 0.025 XZ09-1 围岩 68.41 14.40 2.51 2.75 0.82 1.95 3.84 0.41 0.08 0.151 XZ09-2 矿石 36.40 17.01 4.35 15.26 1.41 1.61 3.53 0.52 0.30 2.830 XZ09-3 蚀变岩 59.36 18.53 4.01 3.01 1.46 5.58 2.44 0.48 0.08 0.258 表 3 邹家山矿床和沙洲矿床不同标高样品微量元素表(×10-6)
Table 3. Trace elements of the samples at different elevations in the Zoujiashan and Shazhou deposits (×10-6)
样品号 Ba Sr Th Rb Nb Zr U Pb Tl Zn Y Ga V Cu Sm La Ta Mo ∑ XS04-1 396 91 24.1 194.0 15.7 254 7.65 60 1.0 20 23.5 16.7 22 5 8.73 84.7 1.1 4 1229 XS04-3 166 137 200.0 34.6 11.6 1050 1000.00 10000 5.2 8960 83.8 9.1 19 84 5.79 29.9 0.3 67 21863 XS04-4 590 134 26.0 228.0 16.9 277 87.10 208 1.0 70 23.6 17.2 26 5 8.81 87.2 1.1 3 1809 XS02-1 246 218 22.3 96.4 18.7 341 16.10 12 0.5 24 20.2 19.4 42 5 9.38 92.9 1.2 5 1190 XS02-4 557 291 24.8 159.0 17.8 348 398.00 18 0.7 36 24.3 17.3 43 5 8.85 81.8 1.1 3 2035 XS02-5 497 218 22.3 198.0 18.0 354 31.40 12 0.9 31 18.5 17.8 42 5 9.06 91.7 1.0 4 1572 XS03-1 125 318 640.0 139.0 22.2 628 1000.00 1300 14.2 3280 161.5 9.2 63 15 11.80 68.3 0.7 885 8681 XS03-2 314 379 64.0 94.3 20.4 421 1000.00 780 1.3 263 33.8 16.0 61 5 9.64 93.6 1.2 39 3596 XS03-3 790 337 25.0 193.0 18.4 350 96.00 31 0.7 67 24.4 18.9 42 5 8.86 83.0 1.2 8 2099 XZ01-1 464 42 23.0 62.8 21.2 63 17.80 46 2.0 24 28.4 14.1 6 5 3.84 14.6 2.0 31 1081 XZ01-2 82 1250 1000.0 339.0 27.3 450 1000.00 337 52.3 38 275.0 9.9 18 5 19.00 38.6 3.0 5250 10194 XZ01-3 287 271 32.5 378.0 12.9 97 143.00 21 4.1 29 30.4 17.5 11 5 3.85 11.1 2.2 193 1550 XZ03-1 132 96 54.7 607.0 15.0 100 79.20 28 5.0 37 46.1 15.6 10 5 5.53 21.2 2.7 33 1293 XZ03-2 145 271 1000.0 1005.0 114.0 494 1000.00 439 26.5 28 1480.0 25.5 32 36 74.40 111.0 9.4 1750 8009 XZ03-3 83 101 71.8 400.0 15.6 86 82.00 35 2.8 21 47.0 13.7 6 5 5.60 19.5 2.5 13 1011 XZ09-1 228 119 31.9 282.0 18.1 195 27.10 22 1.3 43 34.3 15.7 34 5 7.28 49.1 2.0 4 1119 XZ09-2 494 554 1000.0 319.0 24.7 356 1000.00 116 5.9 50 835.0 16.0 43 5 14.90 71.4 2.3 434 5341 XZ09-3 162 132 49.5 270.0 22.2 249 54.20 8 1.4 46 44.2 21.9 40 5 8.11 56.2 2.4 3 1176 表 4 成矿微量元素相关系数矩阵
Table 4. Correlation coefficient matrix of trace elements
Ba Ga La Mo Nb Rb Sm Sr Ta Th Tl U V Y Zr Cu Pb Zn Ba 1.0000 Ga 0.2535 1.0000 La 0.3845 0.5192 1.0000 Mo -0.3764 -0.2599 -0.0531 1.0000 Nb -0.2281 0.5463 0.4446 0.3517 1.0000 Rb -0.3206 0.4767 -0.0303 0.2882 0.7826 1.0000 Sm -0.2136 0.4968 0.4612 0.4097 0.9948 0.7594 1.0000 Sr -0.1226 -0.2888 0.0452 0.8832 0.1314 0.0248 0.1962 1.0000 Ta -0.3326 0.5434 0.1541 0.3839 0.9272 0.9327 0.9099 0.1281 1.0000 Th -0.3037 -0.1048 0.1531 0.7262 0.6062 0.4481 0.6538 0.6811 0.5584 1.0000 Tl -0.4507 -0.2335 -0.0534 0.9842 0.4649 0.3988 0.5179 0.8210 0.4893 0.7820 1.0000 U -0.3000 -0.3256 0.1739 0.5181 0.4133 0.0954 0.4585 0.5716 0.2592 0.7754 0.5783 1.0000 V 0.2095 0.1473 0.7210 -0.1036 0.1139 -0.3468 0.1120 0.1352 -0.1733 0.1478 -0.1138 0.3632 1.0000 Y -0.1692 0.3910 0.3424 0.3662 0.8969 0.7320 0.9089 0.2543 0.8497 0.8021 0.4704 0.5640 0.0931 1.0000 Zr -0.1587 -0.3502 0.2549 0.2170 0.1852 -0.2663 0.2312 0.2255 -0.0848 0.3691 0.2705 0.7094 0.3667 0.2207 1.0000 Cu -0.2163 -0.4789 -0.2390 -0.0722 -0.1299 -0.3067 -0.1051 -0.1209 -0.2460 0.0073 -0.0180 0.3792 -0.1154 -0.0648 0.7971 1.0000 Pb -0.2282 -0.4729 -0.2077 -0.0414 -0.0926 -0.2916 -0.0663 -0.0879 -0.2165 0.0374 0.0141 0.4325 -0.0906 -0.0329 0.8190 0.9962 1.0000 Zn -0.2583 -0.5552 -0.2097 -0.0538 -0.1292 -0.3392 -0.1048 -0.1041 -0.2796 0.0644 0.0108 0.4491 0.0051 -0.0675 0.8382 0.9739 0.9701 1.0000 表 5 正交因子载荷矩阵图
Table 5. Loaing matrix of orthogonal factors
因子1 因子2 因子3 因子4 公因子方差 Ba -0.2490 -0.2668 0.3066 0.5328 0.5111 Ga 0.6123 -0.4551 0.4262 0.3043 0.8564 La 0.3173 -0.0841 0.0346 0.8874 0.8964 Mo 0.1932 -0.0360 -0.9308 -0.1548 0.9290 Nb 0.9618 0.0138 -0.1790 0.1489 0.9794 Rb 0.8661 -0.2619 -0.0855 -0.3468 0.9463 Sm 0.9428 0.0389 -0.2431 0.1650 0.9767 Sr -0.0452 -0.0814 -0.9528 0.1071 0.9279 Ta 0.9516 -0.1623 -0.1753 -0.1625 0.9890 Th 0.5090 0.1494 -0.7645 0.0910 0.8741 Tl 0.3203 0.0395 -0.8982 -0.1864 0.9456 U 0.2825 0.5476 -0.6458 0.2482 0.8584 V -0.0434 0.0777 -0.1005 0.8964 0.8216 Y 0.8885 0.0771 -0.2952 0.1412 0.9025 Zr 0.0689 0.8907 -0.2677 0.3242 0.9749 Cu -0.1092 0.9646 0.0724 -0.1521 0.9708 Pb -0.0823 0.9722 0.0398 -0.1274 0.9698 Zn -0.1364 0.9804 0.0131 -0.0901 0.9880 方差贡献 5.3212 4.3560 4.1643 2.4764 累计方差贡献 0.2956 0.5376 0.7690 0.9066 -
CHEN B L, 2020. Development process of fault structure and formation and evolution of ore-controlling structure: a case study of the Zoujiashan uranium deposit[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(3): 285-298. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN G H, CHEN M Z, 1999. Analysis on metallogenic conditions of Xiangshan uranium ore-field[J]. Uranium Geology, 15(6): 329-337. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Y H, LI J H, 1995. The metallotectonic stress field in the west of the Xiangshan Uranium Orefield and its relations to Uranium mineralization[J]. Mineral Deposits, 14(3): 243-251. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Zh B, XIE Y X, WANG G L, et al., 1982. Uranium deposits in mesozoic volcanics in south-eastchina[J]. Actageologicasinica, (3): 235-243.
CHEN Z L, YANG N, WANG P A, et al., 2011. Analysis of the tectonic stress field in the Xiangshan Uranium ore field, Linchuan area, Jiangxi, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(4): 514-531. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DU L T, 2011. On the theory system of hydrothermal uranium metalization in China[J]. Uranium Geology, 27(2): 65-68, 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FAN H H, LING H F, WANG D Z, et al., 2003. Study on metallogenetic mechanism of Xiangshan Uranium ore-field[J]. Uranium Geology, 19(4): 208-213. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG X Q, CHEN Z L, WANG P A, et al., 2008. Fluid inclusion study of the Shazhou Uranium orefield in the Xiangshan deposit, Jiangxi[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 14(2): 176-185. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIAO Y Q, WU L Q, YANG Q, 2007. Uranium reservoir: a new concept of sandstone-type Uranium deposits geology[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 26(4): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LAI S Q, WANG T, LU X H, et al., 2008. Characteristics of trace elements of geothermal water in Fuzhou basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 27(2): 80-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI B D, 1993. The origin of porphyroclastic lava and its control over uranium deposits in Xiangshan, Jiangxi: a discussion[J]. Geological Review, 39(2): 101-110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI X L, SUN Z X, ZHOU W B, 1992. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of ore-forming fossil hydrothermal system in Xiangshan[J]. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 15(3): 234-242. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Z Y, 2010. Magmatism and uranium metallogeny in Guidong area of eastern Nanling mountains, South China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese)
LIU B, CHEN W F, GAO S, et al., 2019. Sulfur isotope and trace element geochemical characteristics of pyrite in Xiangshan uranium orefield and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 38(6): 1321-1335. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU G, 2020. Research progress of interaction of fluid with rock in the ductile shear zone[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(2): 175-186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU L, RUI H C, 2016. Present situation and development tendency of metallogenic prediction[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(2): 223-231. (in Chinese with English abstract)
MAO J W, XIE G Q, LI X F, et al., 2004. Mesozoic large scale mineralization and multiple lithospheric extension in South China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(1): 45-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
NIE J T, LI Z Y, WANG J, 2018. Isotopic Feature and Provenance of Lead-Zinc Mineralization Ores of the Scientific Drilling in Xiangshan Ore Field[J]. Uranium Geology, 34(6): 354-359.
QIU A J, GUO L Z, ZHENG D Y, et al., 1999. Constraints of Meso Cenozoic tectonic evolution on formation of rich and large Uranium deposits in Xiangshan, Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 5(4): 418-425. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SHAO F, XU H L, ZOU M Q, 2009. Metallogenic hydrothermal solution system of post volcanic magma in Xiangshan ore field[J]. Uranium Geology, 25(3): 137-143, 183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TIAN M M, LI Z Y, NIE J T, et al., 2020. A comparative study and its genesis of porphyroclastic rhyolite from Ehuling and Daguding formations in the Midwest of Xiangshan uranium Orefield, Jiangxi Province[J/OL]. Earth Science. (2020-07-14). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=DQKX2020071200B&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=6n79NuKJ8dLs3gl5MXbGNmqubDTBZ5RA9px1TrF9HoedYAdZIy7N3ryajFCwcDbJ. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG L, 2011. Application of fluid inclusions method in the research of uranium deposits: A case study of Zhoujiashan and Shazhou uranium deposits[J]. Uranium Geology, 27(6): 331-336, 369. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WEI X R, LIN G, LONG Q H, et al., 2006. Feature of Zoujiashan-Shidong structure and its controlling over uranium deposit[J]. Uranium Geology, 22(5): 281-289. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WEN Z J, DU L T, LIU Z Y, 1999. Ore-forming model of the extremely-rich ores in Xiangshan Uranium orefield, Jiangxi[J]. Geological Review, 45(S1): 763-767. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YAO H X, LV G X, NIE J T, et al., 2013. Characteristics of mineralizing alteration and hydrothermal sources in Zoujiashan uranium deposits in Xiangshan uranium ore field in Jiangxi Province[J]. Geoscience, 27(2): 332-338. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG B T, WU J Q, QIU Z L, et al., 1990. On the relationship between hydrothermal alteration and uranium enrichment[J]. Geological Review, 36(3): 238-244. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG X Q, JI S P, WANG S L, et al., 1982. Geochemical evolution of hydrothermal metallogenic in Xiangshan ore-field[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience(5): 412-416. (in Chinese)
ZHONG F J, PAN J Y, ZHANG W M, et al., 2019. Magmation, Tectonic activity and uranium mineralization events of southern Zhuguang uranium ore-concentrated district, Northern Guangdong, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(S1): 108-114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU G X, ZHAO E H, YUE M X, et al., 2014. Geological Significance of rare earth elements in Geochemical analysis[J]. Geology and Resources, 23(5): 495-499. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU W B, SHI W J, LV Y J, 1997. Geochemical modeling of mineralization processes for Xiangshan Uranium ore-field[J]. Geochimica, 26(5): 62-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
陈柏林, 2020. 断裂构造发育过程与控矿构造形成演化: 以邹家山铀矿床为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(3): 285-298. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.03.027
陈贵华, 陈名佐, 1999. 相山铀矿田成矿条件分析[J]. 铀矿地质, 15(6): 329-337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.1999.06.002
陈跃辉, 李建红, 1995. 相山铀矿田西部成矿构造应力场及与铀矿化关系[J]. 矿床地质, 14(3): 243-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ503.006.htm
陈肇博, 谢佑新, 万国良等, 1982. 华东南中生代火山岩中的铀矿床[J]. 地质学报(3): 235-243. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE198203004.htm
陈正乐, 杨农, 王平安, 等, 2011. 江西临川地区相山铀矿田构造应力场分析[J]. 地质通报, 30(4): 514-531. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.04.008
杜乐天, 2011. 中国热液铀矿成矿理论体系[J]. 铀矿地质, 27(2): 65-68, 80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2011.02.001
范洪海, 凌洪飞, 王德滋, 等, 2003. 相山铀矿田成矿机理研究[J]. 铀矿地质, 19(4): 208-213. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2003.04.003
黄锡强, 陈正乐, 王平安, 等, 2008. 江西相山铀矿田沙洲矿床流体包裹体研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 14(2): 176-185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2008.02.009 https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/article/id/688cbaf6-0733-4a3c-bb17-3e23510429b3
焦养泉, 吴立群, 杨琴, 2007. 铀储层: 砂岩型铀矿地质学的新概念[J]. 地质科技情报, 26(4): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200704000.htm
赖树钦, 王涛, 卢晓华, 等, 2008. 福州盆地地热水微量元素特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 27(2): 80-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2008.02.014
李邦达, 1993. 江西相山碎斑熔岩成因及其控矿作用的讨论[J]. 地质论评, 39(2): 101-110. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1993.02.002
李学礼, 孙占学, 周文斌, 1992. 相山成矿古水热系统的水文地球化学特征[J]. 华东地质学院学报, 1992, 15(3): 234-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ199203003.htm
李子颖, 2010. 南岭贵东岩浆岩与铀成矿作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
刘斌, 陈卫锋, 高爽, 等, 2019. 相山铀矿田黄铁矿微量元素、硫同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 38(6): 1321-1335. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201906008.htm
刘贵, 2020. 韧性剪切带内的流体与岩石相互作用研究进展[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(2): 175-186. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.02.017
刘林, 芮会超, 2016. 成矿预测的发展现状及趋势[J]. 地质力学学报, 22(2): 223-231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.02.004 https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/article/id/d2b2ef2d-8819-48f2-9cdc-9351e3fca51f
毛景文, 谢桂青, 李晓峰, 等, 2004. 华南地区中生代大规模成矿作用与岩石圈多阶段伸展[J]. 地学前缘, 11(1): 45-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.01.003
聂江涛, 李子颖, 王健等, 2018. 相山铀矿田铅锌矿化同位素特征及成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 铀矿地质, 34(6): 354-359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201806005.htm
邱爱金, 郭令智, 郑大瑜, 等, 1999. 江西相山地区中、新生代构造演化对富大铀矿形成的制约[J]. 高校地质学报, 5(4): 418-425. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX199904008.htm
邵飞, 徐恒力, 邹茂卿, 2009. 相山铀矿田火山岩浆期后成矿热液系统[J]. 铀矿地质, 25(3): 137-143, 183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2009.03.002
田明明, 李子颖, 聂江涛, 等, 2020. 江西相山铀矿田中西部鹅湖岭组与打鼓顶组碎斑流纹岩特征对比及其成因探讨[J/OL]. 地球科学. (2020-07-14). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=DQKX2020071200B&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=6n79NuKJ8dLs3gl5MXbGNmqubDTBZ5RA9px1TrF9HoedYAdZIy7N3ryajFCwcDbJ.
王蕾, 2011. 流体包裹体分析法在铀矿床研究中的应用: 以相山铀矿田邹家山、沙洲矿床为例[J]. 铀矿地质, 27(6): 331-336, 369. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2011.06.003
魏祥荣, 林舸, 龙期华, 等, 2006. 江西相山邹家山: 石洞断裂带及其控矿作用[J]. 铀矿地质, 22(5): 281-289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2006.05.004
温志坚, 杜乐天, 刘正义, 1999. 相山铀矿田特富矿成矿模式[J]. 地质评论, 45(S1): 763-767. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP1999S1110.htm
姚宏鑫, 吕古贤, 聂江涛, 等, 2013. 江西相山铀矿田邹家山铀矿床蚀变特征及热液来源[J]. 现代地质, 27(2): 332-338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.011
章邦桐, 吴俊奇, 丘志力, 等, 1990. 论热液蚀变与铀成矿富集作用的关系[J]. 地质评论, 36(3): 238-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199003005.htm
张学权, 季树藩, 王思龙, 等, 1982. 相山矿田热液成矿作用的地球化学演化[J]. 世界核地质学(5): 412-416. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ198205005.htm
钟福军, 潘家永, 张伟盟, 等, 2019. 粤北诸广南铀矿聚集区岩浆、构造与铀成矿活动[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(S1): 108-114. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.S1.018
周国兴, 赵恩好, 岳明新, 等, 2014. 稀土元素地球化学分析在地质学中的意义[J]. 地质与资源, 23(5): 495-499. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2014.05.016
周文斌, 史维浚, 吕跃进, 1997. 相山铀矿田成矿作用的地球化学模拟[J]. 地球化学, 26(5): 62-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1997.05.006
-



 下载:
下载: