Formation mechanism and stability analysis of a landslide in altered ophiolite in the upper reaches of Jinsha River: A case study of the Duirongtong landslide
-
摘要:
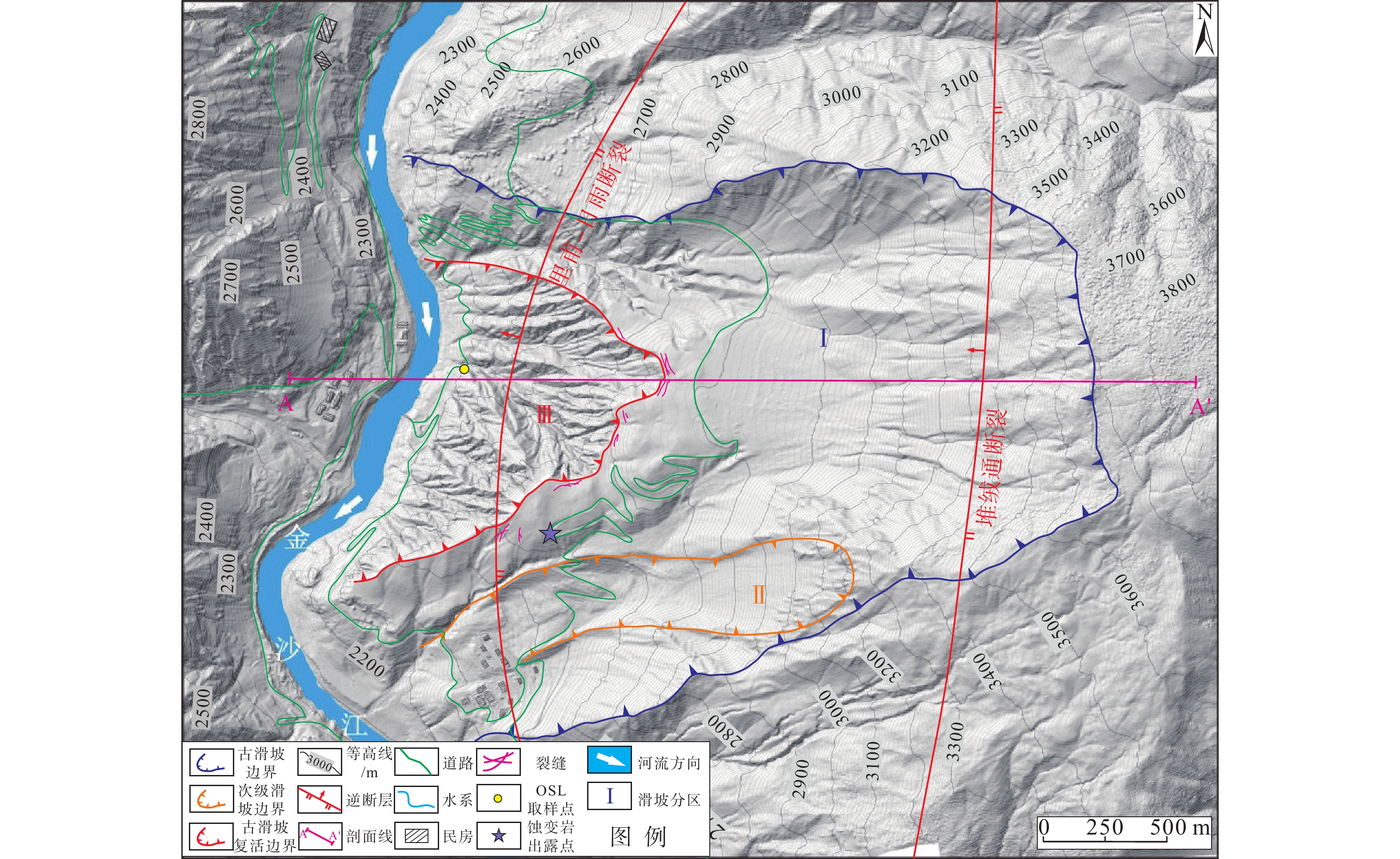
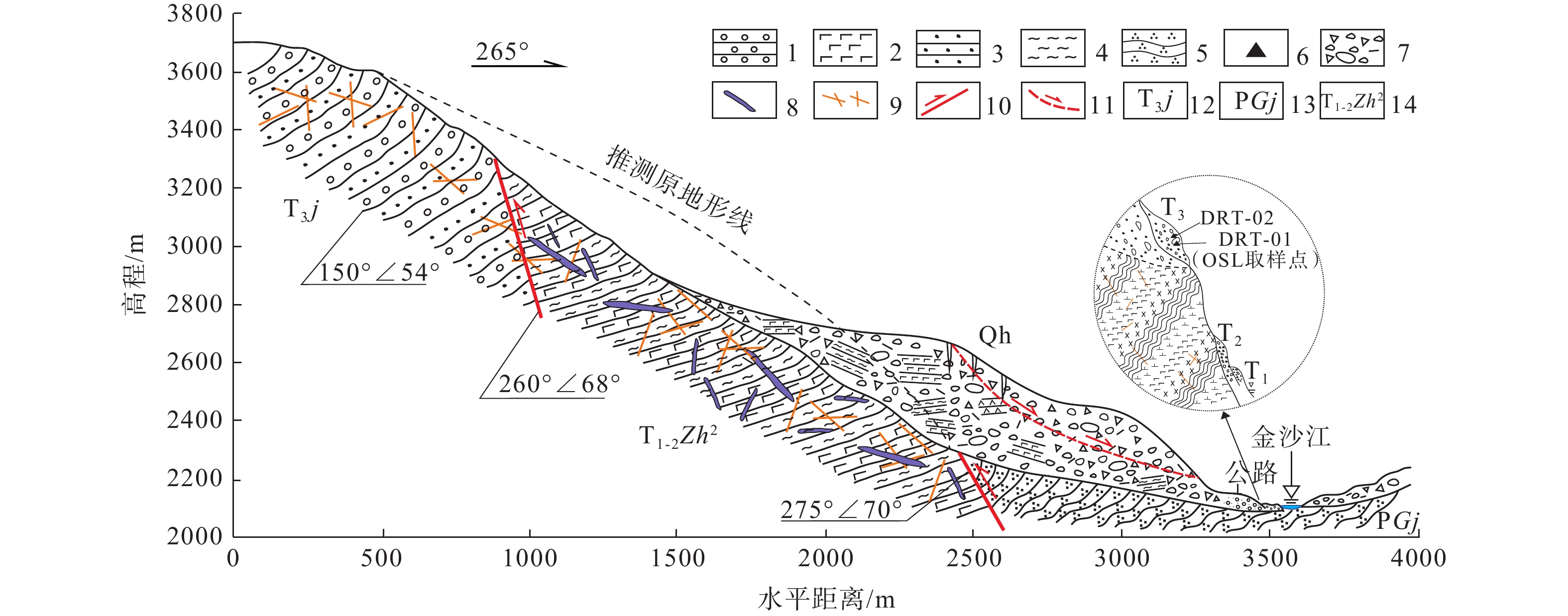
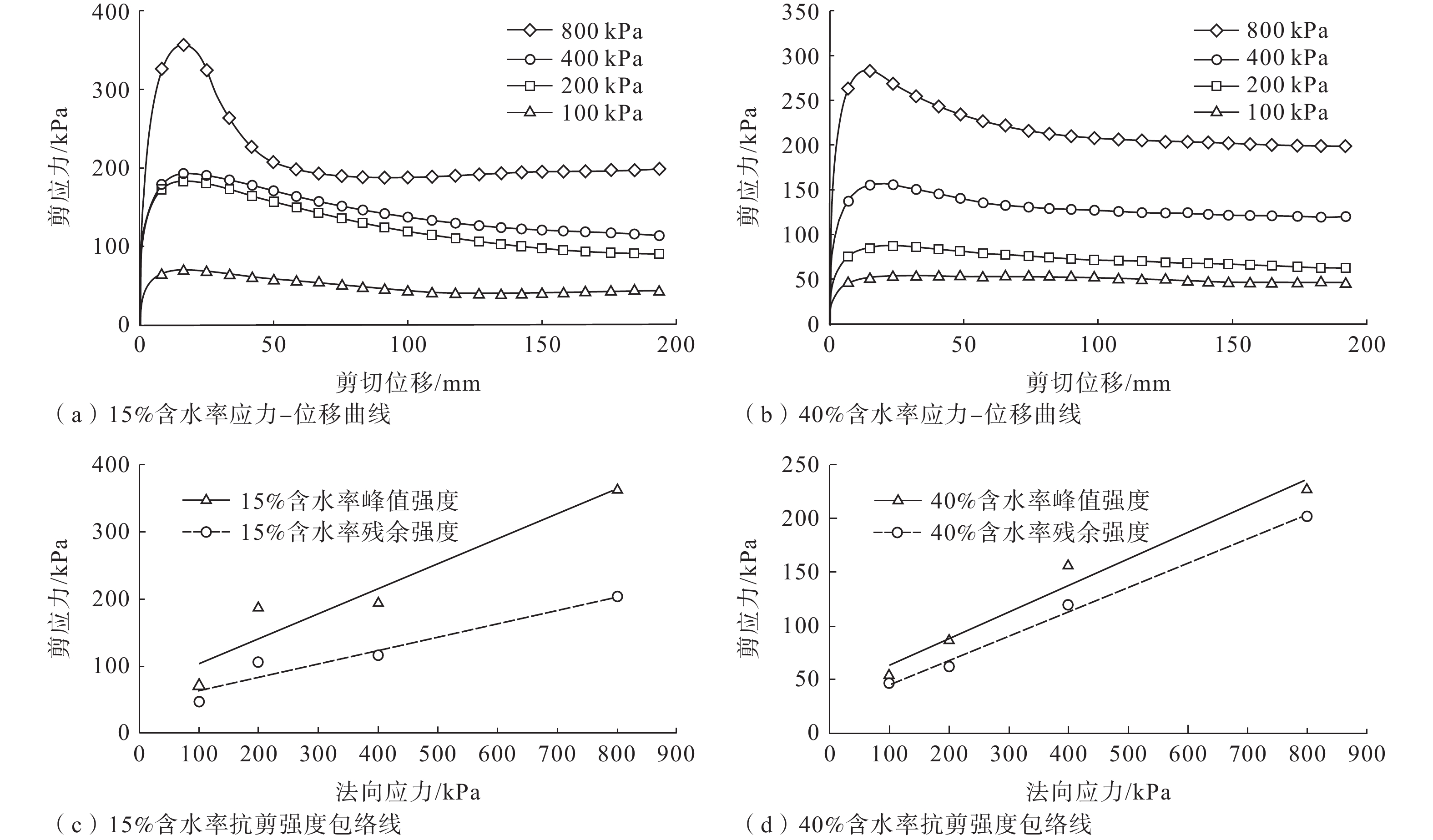
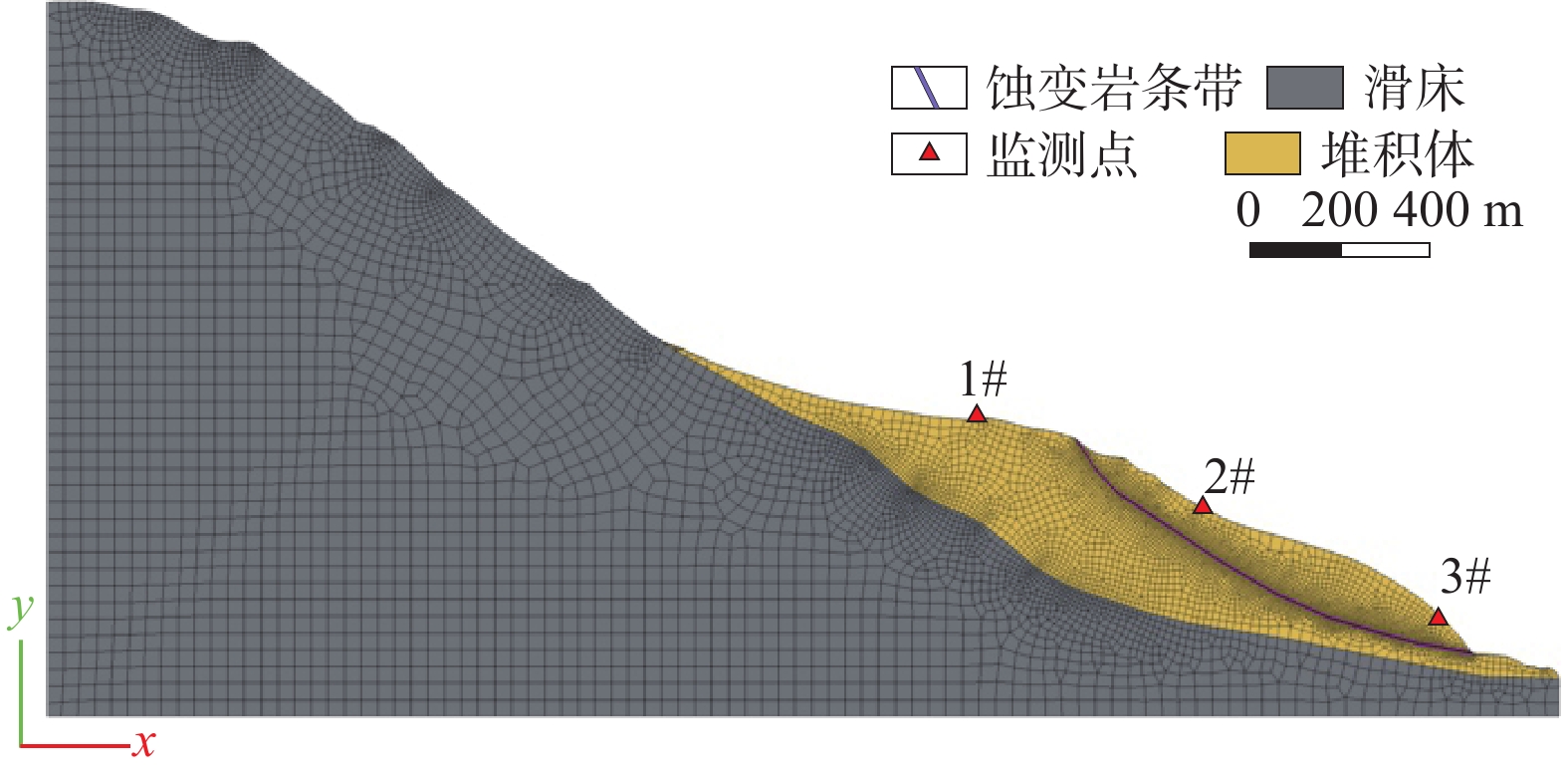
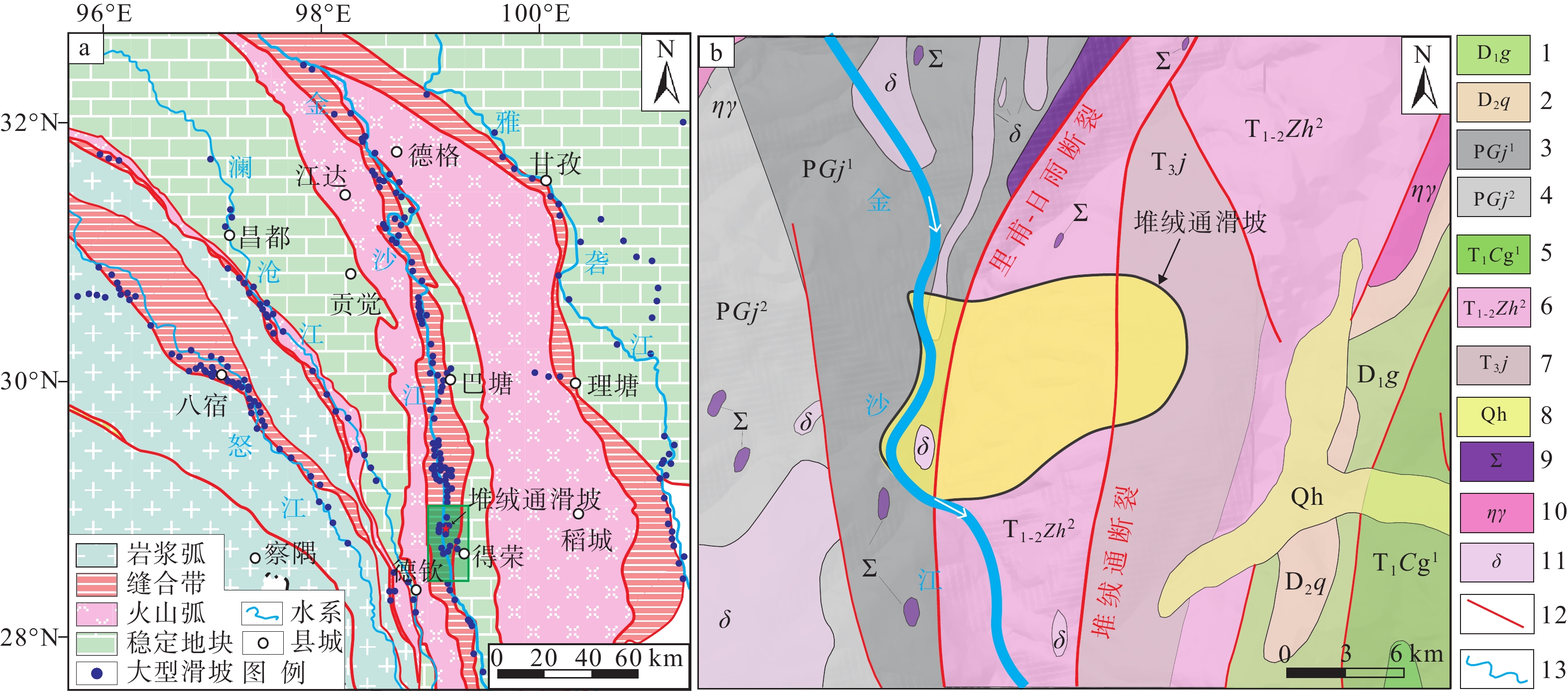
青藏高原构造缝合带具有复杂的岩体结构和特殊的岩性组合,是特大滑坡易发带,但蚀变蛇绿岩型滑坡形成演化涉及的影响因素较多,目前对其孕生机制尚不明晰,制约了灾害隐患有效判识和风险防范。以金沙江构造缝合带堆绒通滑坡为例,基于现场调查、无人机测绘、年代学测试和环剪试验等方法,剖析了蚀变蛇绿岩型滑坡的发育特征和形成机制,并对滑坡堆积体的稳定性进行了模拟分析。结果表明:堆绒通滑坡是形成于晚更新世的巨型滑坡,所在斜坡岩性以基性−超基性岩为主,内部发育多条黏土化蚀变蛇绿岩条带,构成易滑地质结构;黏土化蚀变蛇绿岩在天然状态下具有较低的抗剪强度,遇水强度急剧下降,天然状态下的黏聚力(c)、内摩擦角(φ)值分别为67.0 kPa和20.3°,饱和状态下的c、φ值分别为39.8 kPa和13.8°,软化效应显著;堆绒通滑坡堆积体目前整体稳定,但在强降雨条件下滑坡体前缘可能出现局部失稳,基于滑坡稳定性数值模拟结果提出了灾害风险防范对策。综合分析认为,岩体结构与黏土化蚀变岩联合控制了堆绒通滑坡的形成演化。相关认识对青藏高原构造缝合带斜坡稳定性分析和防灾减灾具有较好的启示意义。
Abstract:Objective The tectonic suture zone of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has a complex rock mass structure and special lithology combination and is thus prone for large landslides. However, many factors influence the formation and evolution of landslides in altered ophiolite. Their formation mechanism is not clear at present, which restricts an effective identification and disaster risk prevention.
Methods Taking the Duirongtong (DRT) landslide in the Jinsha River tectonic suture zone as an example, field investigations, UAV mapping, geochronological analysis, ring-shear testing, and numerical simulation were performed to analyze the formation mechanisms of the landslide and evaluate the stability of the landslide deposits.
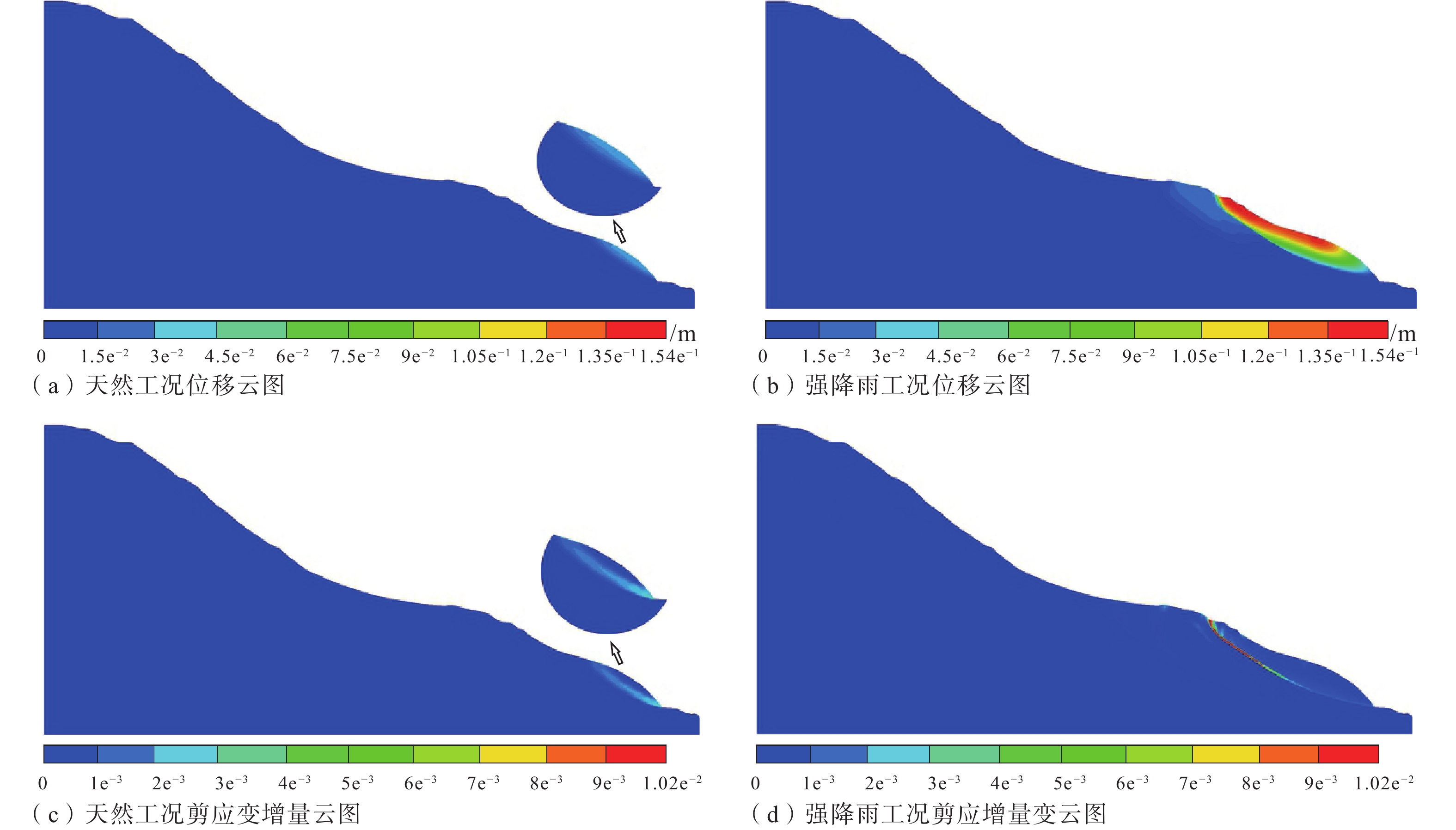
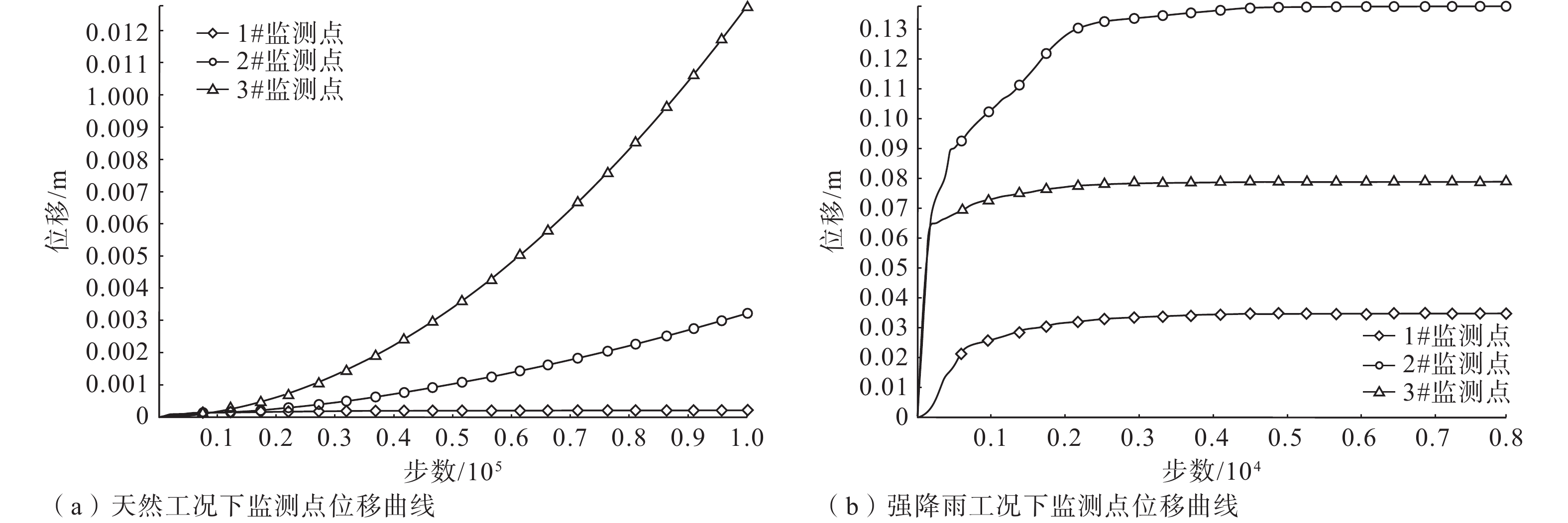
Results The results show that: (1) The DRT landslide is a giant landslide formed in the late Pleistocene. The slope is mainly composed of basic-ultrabasic rocks, and several clay-altered ophiolitic bands are developed, forming a sliding-prone geo-structure. (2) The clay-altered ophiolite has low shear strength under natural conditions, and its shear strength drops sharply when exposed to water. The natural values of c and φ are 67.0 kPa and 20.3°, and the water-saturated values of cohesion(c) and angle of internal friction(φ) are 39.8 kPa and 13.83°. The DRT landslide is currently stable as a whole, but the leading edge of the landslide may experience movement under heavy rainfall. Based on numerical simulation, some preventive recommendations are proposed.
Conclusion The study suggests that the formation and evolution of the DRT landslide are controlled by the combination of geological structure and clay-altered rock. [Significance] These findings have important implications for the slope stability analysis and disaster prevention in the tectonic suture zone of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
-
Key words:
- tectonic suture zone /
- landslip /
- ophiolites /
- clay-altered rock /
- sliding-prone geo-structure /
- stability analysis
-

-
表 1 光释光样品年龄测定结果
Table 1. Results of OSL age determination
样品号 埋深/m U/×10−6 Th/×10−6 K/% 等效剂量De(Gy) 年剂量Gy/ka 含水量/% 年龄/ka DRT-01 0.5 1.58 6.69 2.40 254.04±8.03 3.45±0.16 7±5 73.7±4.2 DRT-02 0.5 1.05 9.95 1.55 281.41±1.31 2.75±0.12 7±5 102.4±4.6 表 2 黏土化蚀变岩物质组成与滑带土粒度分析
Table 2. Material composition of clay-altered rock and particle size analysis of slip zone soil
天然含水率% 湿密度/(g·cm−3) 干密度/(g·cm−3) 塑限(WP)/% 液限(WL)/% 塑性指数(IP) 颗粒级配/% 矿物含量检测结果/% 粒径大小/mm % 15.0 2.1 1.8 19.9 62.4 42.5 <0.005 mm 16.0 蛇纹石 水菱镁矿 绿泥石 0.005~0.075 mm 25.3 0.075~2 mm 39.0 88 10 2 >2 mm 19.7 表 3 岩土体物理力学参数取值表
Table 3. Values of physical and mechanical parameters of rock and soil mass
岩性 杨氏模量/MPa 泊松比 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 天然密度/(g·cm−3) 天然 饱和 天然 饱和 滑坡堆积体 800 0.21 60.00 45.00 35.00 28.00 2.20 滑床 2810 0.20 460.00 400.00 40.00 30.00 2.50 蚀变岩条带 310 0.24 67.03 43.24 20.29 13.79 1.85 -
[1] BAI Y J, NI H Y, GE H, 2019. Advances in research on the geohazard effect of active faults on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6): 1116-1128. (in Chinese with English abstract
[2] BAI Y L, LV F J, SU H B, et al., 2023. Review of hyperspectral remote sensing altered mineral information extraction[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 38(1): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract
[3] BAO Y D, CHEN J P, SU L J, et al., 2023. A novel numerical approach for rock slide blocking river based on the CEFDEM model: a case study from the Samaoding paleolandslide blocking river event[J]. Engineering Geology, 312: 106949. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106949
[4] CHANG H, CHANG Z F, Liu C W, 2021. The relationship between activity of Jinsha River fault zone and large-scale landslides: a case study of the section between Narong and Rongxue along the Jinsha River[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(6): 1435-1458. (in Chinese with English abstract
[5] CHEN J, ZHOU W, CUI Z J, et al., 2018. Formation process of a large paleolandslide-dammed lake at Xuelongnang in the upper Jinsha river, SE Tibetan Plateau: constraints from OSL and 14C dating[J]. Landslides, 15(12): 2399-2412. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-1056-3
[6] CHEN J P, LI H Z, 2016. Genetic mechanism and disasters features of complicated structural rock mass along the rapidly uplift section at the upstream of Jinsha River[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 46(4): 1153-1167. (in Chinese with English abstract
[7] DARMAWAN H, TROLL V R, WALTER T R, et al., 2022. Hidden mechanical weaknesses within lava domes provided by buried high-porosity hydrothermal alteration zones[J]. Scientific Reports, 12(1): 3202. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06765-9
[8] DEL RODRIGO P, HÜRLIMANN M, 2009. The decrease in the shear strength of volcanic materials with argillic hydrothermal alteration, insights from the summit region of Teide stratovolcano, Tenerife[J]. Engineering Geology, 104(1-2): 135-143. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.09.005
[9] DENG J H, GAO Y J, YU Z Q, et al., 2019. Analysis on the formation mechanism and process of Baige landslides damming the upper reach of Jinsha River, China[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 51(1): 9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract
[10] DENG J H, LI H, DAI F C, et al., 2022. A gigantic paleo-dammed lake in the upper reaches of Jinsha River and its relevant issues[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 54(6): 75-84. (in Chinese with English abstract
[11] GAO Y, LI B, FENG Z, et al., 2017. Global climate change and geological disaster response analysis[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 23(1): 65-77. (in Chinese with English abstract
[12] HEAP M J, BAUMANN T S, ROSAS-CARBAJAL M, et al., 2021. Alteration-induced volcano instability at La Soufrière de Guadeloupe (eastern Caribbean)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 126(8): e2021JB022514. doi: 10.1029/2021JB022514
[13] LI J Q, ZHANG Y S, LI X, et al., 2023. Identification of clayey altered ophiolite in the Nujiang tectonic belt and new understanding of its impacts on engineering stability[J]. China Geology, 6(4): 754-758.
[14] LI J Q, ZHANG Y S, REN S S, et al., 2024. Catastrophic mechanical behavior of clay-altered rock in the Baige landslide upstream of the Jinsha River[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 56(3): 72-82. (in Chinese with English abstract
[15] LIU K, ZHOU X P, SHI Y, et al,2023. Basic characteristics and mechanisms of the giant Shaweitaizi paleo-landslide dammed the Jinsha River[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,54(8):167-177.
[16] LIU Z, LI B, HE K, et al., 2020. An analysis of dynamic response characteristics of the Yigong landslide in Tibet under strong earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 471-480. (in Chinese with English abstract
[17] PAN G T, REN F, YIN F G, et al., 2020. Key zones of Oceanic Plate geology and Sichuan-Tibet railway project[J]. Earth Science, 45(7): 2293-2304. (in Chinese with English abstract
[18] POLA A, CROSTA G, FUSI N, et al., 2012. Influence of alteration on physical properties of volcanic rocks[J]. Tectonophysics, 566-557: 67-86.
[19] REN S S, ZHANG Y S, XU N X, et al. , 2021. Mobilized strength of sliding zone soils with gravels in reactivated landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 42(3): 863-873, 881. (in Chinese with English abstract
[20] REN S S, ZHANG Y S, LI J Q, et al., 2023. A new type of sliding zone soil and its severe effect on the formation of giant landslides in the Jinsha River tectonic suture zone, China[J]. Natural Hazards, 117(2): 1847-1868. doi: 10.1007/s11069-023-05931-0
[21] SCHAEFER L N, KERESZTURI G, KENNEDY B M, et al., 2023. Characterizing lithological, weathering, and hydrothermal alteration influences on volcanic rock properties via spectroscopy and laboratory testing: a case study of Mount Ruapehu volcano, New Zealand[J]. Bulletin of Volcanology, 85(8): 43. doi: 10.1007/s00445-023-01657-w
[22] SHAO S, SHAO S J, LI N, et al., 2021. Dynamic centrifugal model tests on seismic subsidence of loess slopes under earthquake action[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 43(2): 245-253. (in Chinese with English abstract
[23] TANG Y, QIN Y D, GONG X D, et al., 2022. Determination of material composition of Jinshajiang tectonic mélange belt in Gonjo-Baiyu area, eastern Tibet[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 42(2): 260-278. (in Chinese with English abstract
[24] TONG Peng, WU Shangqian, XIE Meng, et al, 2023. Remote Sensing Interpretation and Risk Assessment of Landslide Hazards in Newly Built High-speed Railway[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 49(6): 56-63.
[25] WANG W, WANG Z L, LI Z Q, et al., 2006. Study of effect of rock softness-hardness on evolution of 1-D stress waves[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 33(1): 11-15. (in Chinese with English abstract
[26] WU X G, CAI C X, 1992. The neotectonic activity along the central segment of Jinshajiang fault zone and the epicentral determination of Batang M6.5 earthquake[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 15(4): 401-410. (in Chinese with English abstract
[27] XU Q, ZHENG G, LI W L, et al., 2018. Study on successive landslide damming events of Jinsha River in Baige village on Octorber 11 and November 3, 2018[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 26(6): 1534-1551. (in Chinese with English abstract
[28] YOUSUFI A, AHMADI H, BEKBOTAYEVA A, et al., 2023. Integration of remote sensing and field data in ophiolite investigations: a case study of Logar ophiolite complex, SE Afghanistan[J]. Minerals, 13(12): 234.
[29] ZHANG W, WANG J, CHEN J P, et al., 2022. Mass-wasting-inferred dramatic variability of 130, 000-year Indian summer monsoon intensity from deposits in the Southeast Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 49(6): e2021GL097301. doi: 10.1029/2021GL097301
[30] ZHANG Y S, BA R J, REN S S, et al., 2020. An analysis of geo-mechanism of the Baige landslide in Jinsha River, Tibet[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1637-1645. (in Chinese with English abstract
[31] ZHANG Y S, LI J Q, REN S S, et al., 2022. Development characteristics of clayey altered rocks in the Sichuan-Tibet Traffic corridor and their promotion to large-scale landslides[J]. Earth Science, 47(6): 1945-1956. (in Chinese with English abstract
[32] ZHANG Y S, REN S S, LI J Q, et al., 2023. Prone sliding geo-structure and high-position initiating mechanism of Duolasi landslide in Nu River tectonic mélange belt[J]. Earth Science, 48(12): 4668-4679. (in Chinese with English abstract
[33] ZHANG Y S, WANG D B, LI X, et al., 2024. Research on hazard prone geological genes and major engineering geological problems in tectonic mélange belts of Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 98(3): 992-1005. (in Chinese with English abstract
[34] 白杨林,吕凤军,苏鸿博,等,2023. 高光谱遥感蚀变矿物信息提取研究综述[J]. 遥感信息,38(1):1-10.
[35] 白永健,倪化勇,葛华,2019. 青藏高原东南缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究现状[J]. 地质力学学报,25(6):1116-1128. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.06.095
[36] 常昊,常祖峰,刘昌伟,2021. 金沙江断裂带活动与大型滑坡群的关系研究:以金沙江拿荣—绒学段为例[J]. 地震地质,43(6):1435-1458.
[37] 陈剑平,李会中,2016. 金沙江上游快速隆升河段复杂结构岩体灾变特征与机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),46(4):1153-1167.
[38] 邓建辉,高云建,余志球,等,2019. 堰塞金沙江上游的白格滑坡形成机制与过程分析[J]. 工程科学与技术,51(1):9-16.
[39] 邓建辉,李化,戴福初,等,2022. 金沙江上游超大古堰塞湖及其相关问题[J]. 工程科学与技术,54(6):75-84.
[40] 高杨,李滨,冯振,等,2017. 全球气候变化与地质灾害响应分析[J]. 地质力学学报,23(1):65-77.
[41] 李金秋,张永双,任三绍,等,2024. 金沙江上游白格滑坡黏土化蚀变岩的灾变力学行为研究[J]. 工程科学与技术,56(3):72-82.
[42] 刘科,周小棚,施炎,等,2023. 金沙江杀威台子巨型堵江古滑坡基本特征与成因机理研究[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文),54(8):167-177.
[43] 刘铮,李滨,贺凯,等,2020. 地震作用下西藏易贡滑坡动力响应特征分析[J]. 地质力学学报,26(4):471-480.
[44] 潘桂棠,任飞,尹福光,等,2020. 洋板块地质与川藏铁路工程地质关键区带[J]. 地球科学,45(7):2293-2304.
[45] 任三绍,张永双,徐能雄,等,2021. 含砾滑带土复活启动强度研究[J]. 岩土力学,42(3):863-873,881.
[46] 邵帅,邵生俊,李宁,等,2021. 地震作用下黄土边坡震陷破坏的动力离心模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,43(2):245-253.
[47] 唐渊,秦雅东,巩小栋,等,2022. 藏东贡觉—白玉地区金沙江构造混杂岩带物质组成的厘定[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,42(2):260-278.
[48] 童鹏,伍尚前,谢猛,等,2023. 新建高速铁路滑坡隐患遥感解译及风险评估[J]. 铁道勘察,49(6):56-63.
[49] 王伟,王志亮,李振强,2006. 岩体软硬度对一维应力波演化影响研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,33(1):11-15.
[50] 伍先国,蔡长星,1992. 金沙江断裂带新活动和巴塘6.5级地震震中的确定[J]. 地震研究,15(4):401-410.
[51] 许强,郑光,李为乐,等,2018. 2018年10月和11月金沙江白格两次滑坡-堰塞堵江事件分析研究[J]. 工程地质学报,26(6):1534-1551.
[52] 张永双,巴仁基,任三绍,等,2020. 中国西藏金沙江白格滑坡的地质成因分析[J]. 中国地质,47(6):1637-1645.
[53] 张永双,李金秋,任三绍,等,2022. 川藏交通廊道黏土化蚀变岩发育特征及其对大型滑坡的促滑作用[J]. 地球科学,47(6):1945-1956.
[54] 张永双,任三绍,李金秋,等,2023. 怒江构造混杂岩带多拉寺滑坡的易滑地质结构及高位启滑运动机制[J]. 地球科学,48(12):4668-4679.
[55] 张永双,王冬兵,李雪,等,2024. 青藏高原构造混杂岩带的孕灾地质基因与重大工程地质问题研究[J]. 地质学报,98(3):992-1005.
-



 下载:
下载: