Characteristics of structural deformation under Himalayan multi-periods movements in the Kuqa Depression
-
摘要:
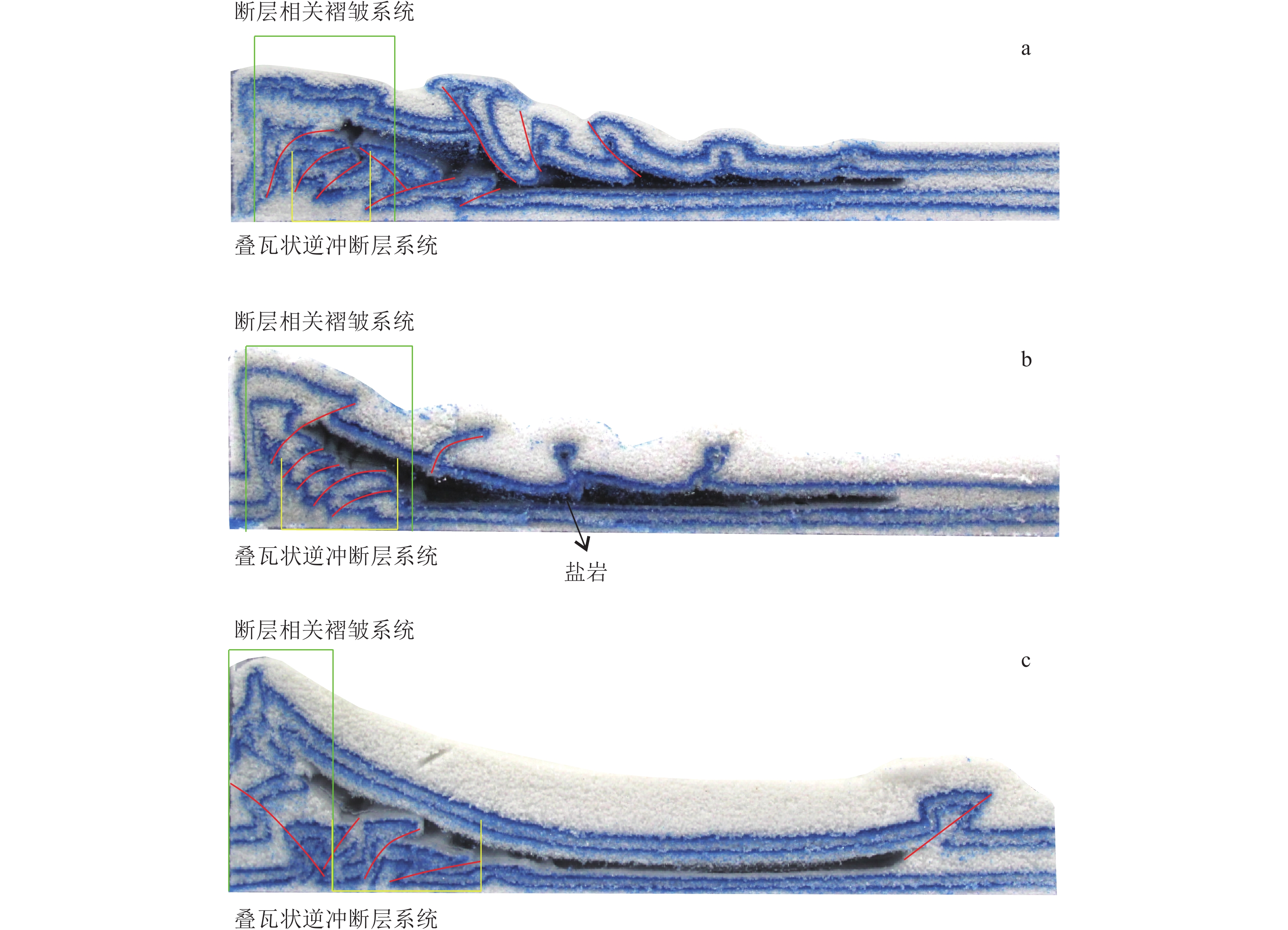
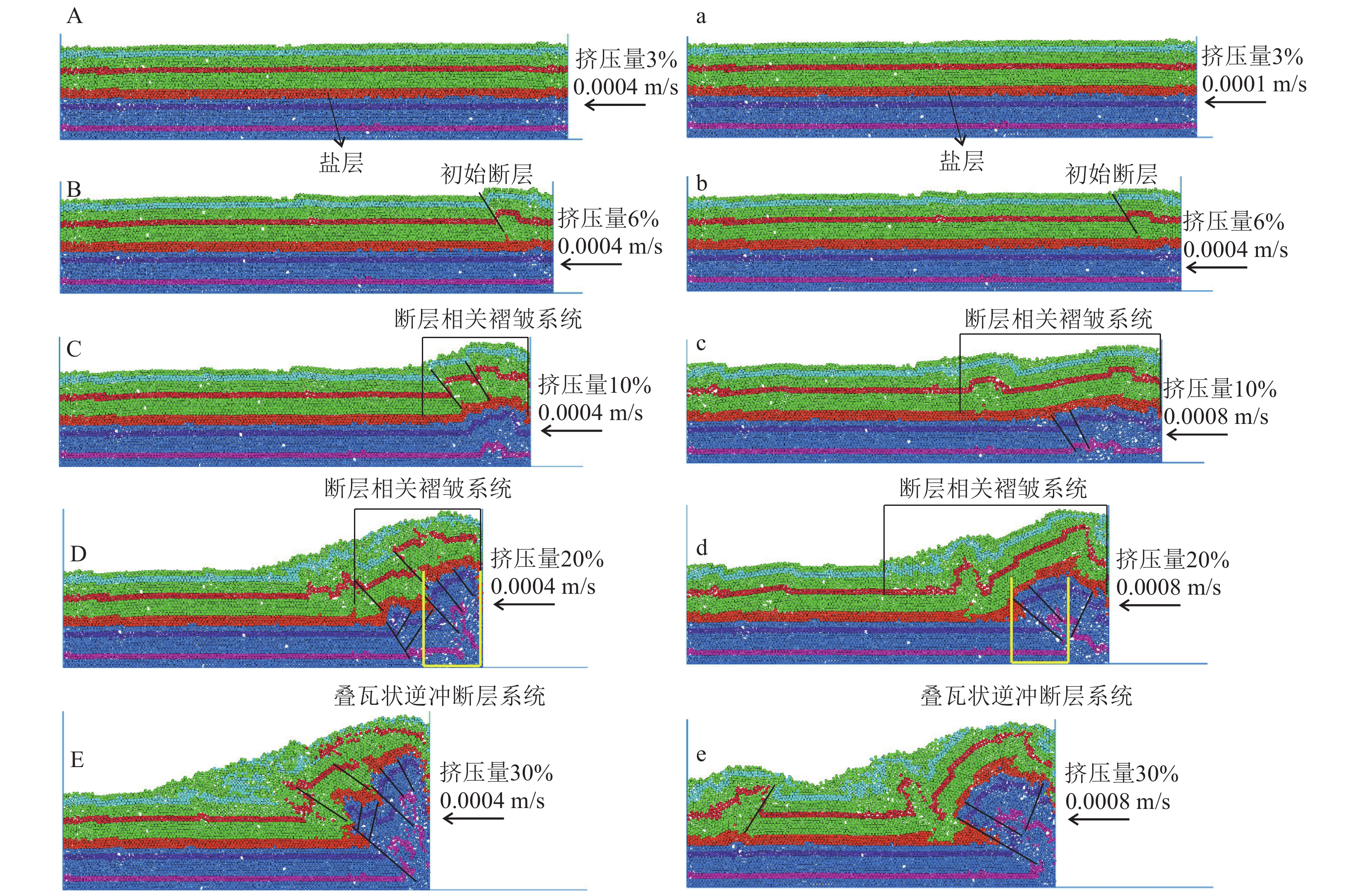
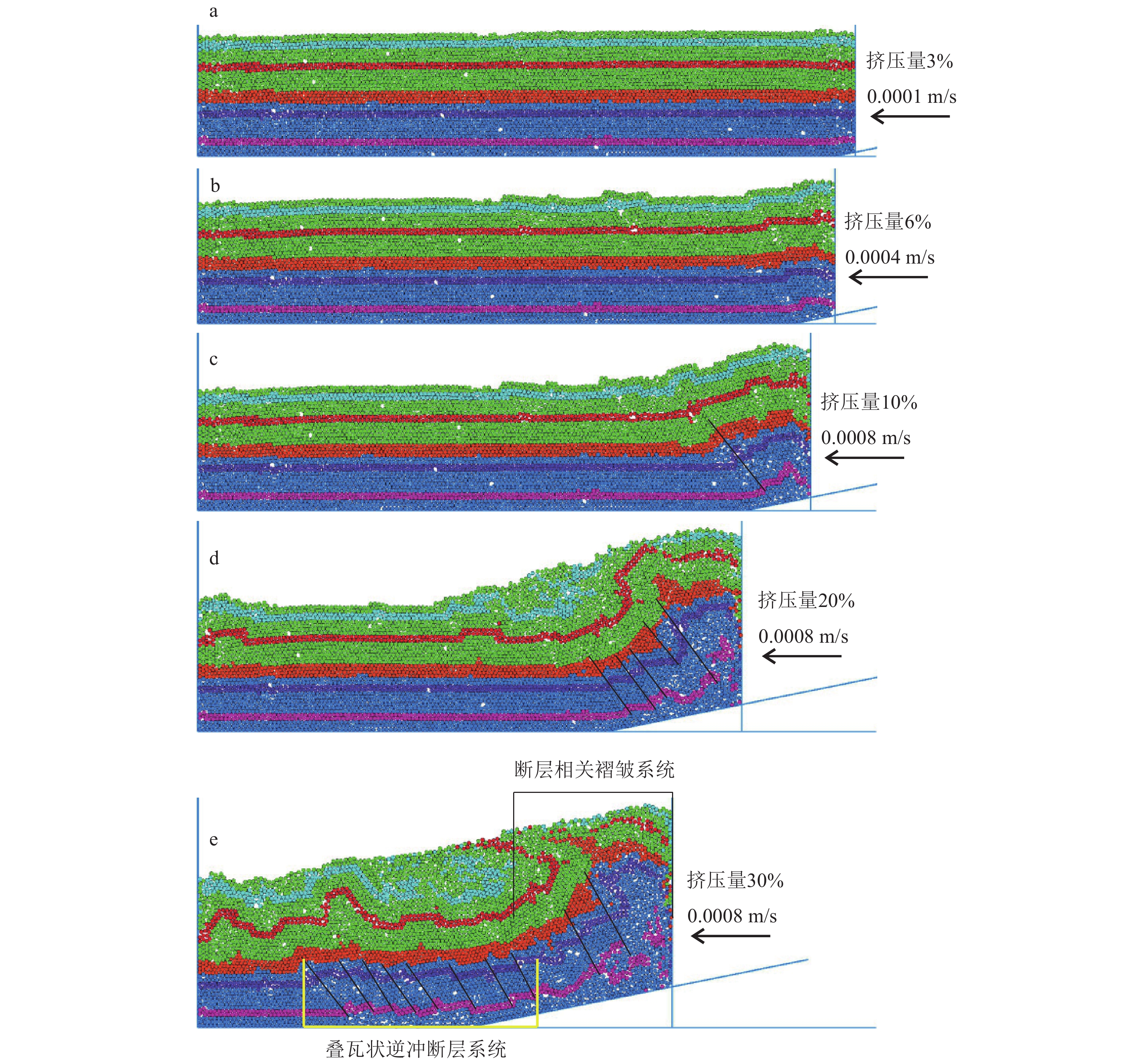
喜马拉雅期构造运动对中国西部地质地貌具有决定性影响,库车坳陷内的构造变形特征对其多期运动存在何种响应尚待解决。在库车坳陷克拉苏构造带地震剖面解译的基础上,采用离散元数值模拟、构造物理模拟等手段,探讨挤压背景下,喜马拉雅期构造活动造成的多期运动、垂向抬升、同构造沉积等因素对库车坳陷克拉苏构造带的构造变形响应特征与变形演化过程。克拉苏构造带对喜马拉雅多期运动的响应主要体现在,控制盐上层滑脱褶皱向前陆方向传播,挤压端褶皱隆升强度变弱;盐下层挤压端前展式叠瓦状逆冲断裂系统的倾角呈规律性变化,靠近挤压端的断裂倾角较大,远离挤压端断裂的倾角较小,但其逆冲的位移量大;同时,同构造沉积控制盐上层滑脱褶皱变形范围,垂向抬升主要控制盐下层叠瓦状逆冲断裂向前陆方向传播范围。构造变形过程研究显示,喜马拉雅多期运动导致克拉苏构造带构造分层的差异变形,盐上层滑脱褶皱变形范围更广,褶皱相关断层更发育,盐下层在发育前展式叠瓦状逆冲断层后会加强反冲构造的形成。研究结果揭示了喜马拉雅多期运动对克拉苏构造带动力学演化过程的影响,深化了对库车坳陷克拉苏构造带构造变形机理和演化过程的认识。
Abstract:The Himalayan movement has a decisive impact on the geology and geomorphology of western China. The response of the structural deformation characteristics in Kuqa Depression to its multi−periods movement remains unsolved. Based on the interpretation of the seismic section of Kelasu structural belt in Kuqa Depression, by means of discrete element numerical simulation and structural physical simulation, this paper discusses the response characteristics and deformation evolution process of the structural deformation of Kelasu structural belt caused by multi−periods movements, vertical uplift and syntectonic sedimentation caused by Himalayan multi−periods movement under the background of compressive stress. The results show that the response of Kelasu structural belt to multi−periods movements is mainly reflected in controlling the propagation of detachment folds in the upper salt layer in the foreland direction, and the uplift intensity of folds at the compression end becomes weaker; The dip angle of the pre−spreading imbricate thrust fault system at the extrusion end of the lower salt layer changes regularly. The dip angle of the fault near the extrusion end is large, and the dip angle away from the extrusion end is small, but its thrust displacement is large. At the same time, syntectonic sedimentation controls the deformation range of detachment fold in the upper salt layer, and vertical uplift mainly controls the forward land propagation range of laminated tile thrust fault under salt. The study of tectonic deformation process shows that the multi−periods movement of Himalaya leads to the differential deformation of structural stratification in Kelasu structural belt. The deformation range of detachment folds in the upper salt layer is wider, and fold related faults are more developed. After the development of forward spreading imbricate thrust faults in the lower salt layer, the formation of recoil structures will be strengthened. The results reveal the influence of Himalayan multi−periods movement on the dynamic evolution process of Kelasu structural belt, and deepen the understanding of structural deformation mechanism and evolution process of Kelasu structural belt in the Kuqa Depression.
-

-
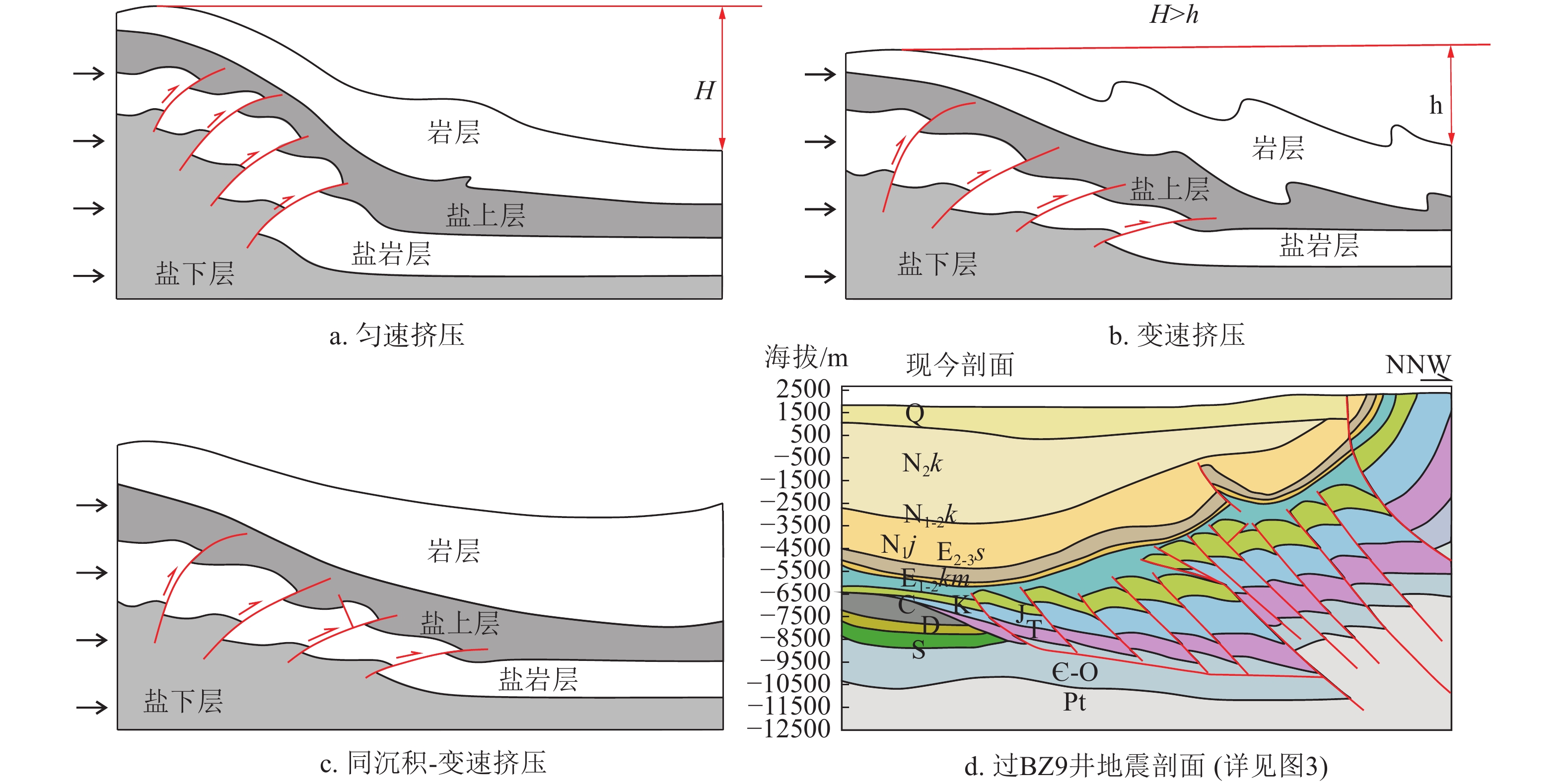
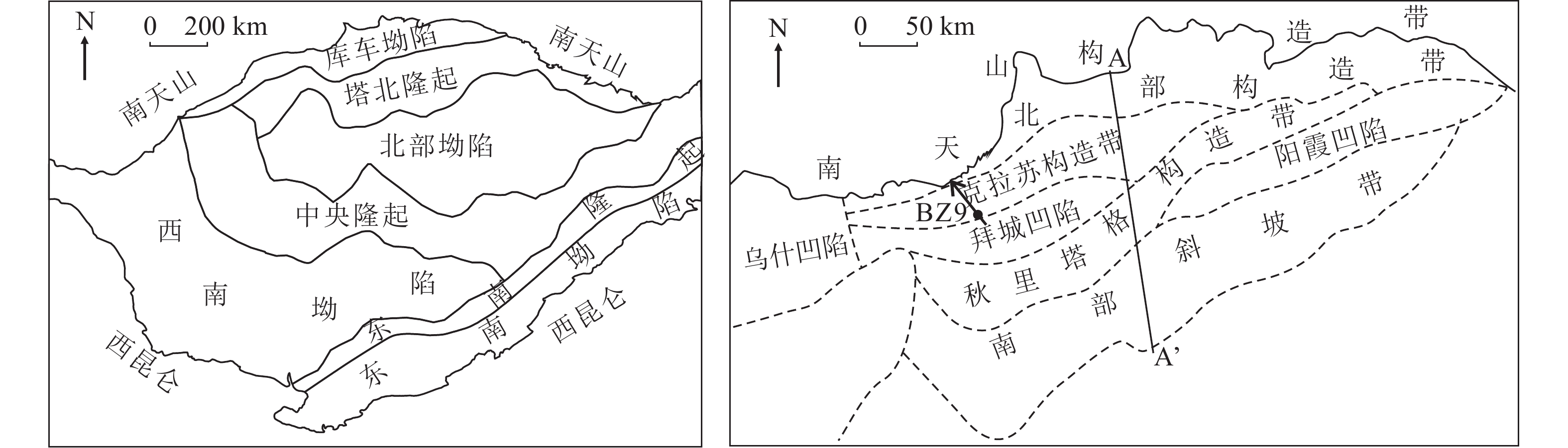
图 1 库车坳陷构造单元划分图和对应地震剖面位置(据贾承造等,2022修改)
Figure 1.
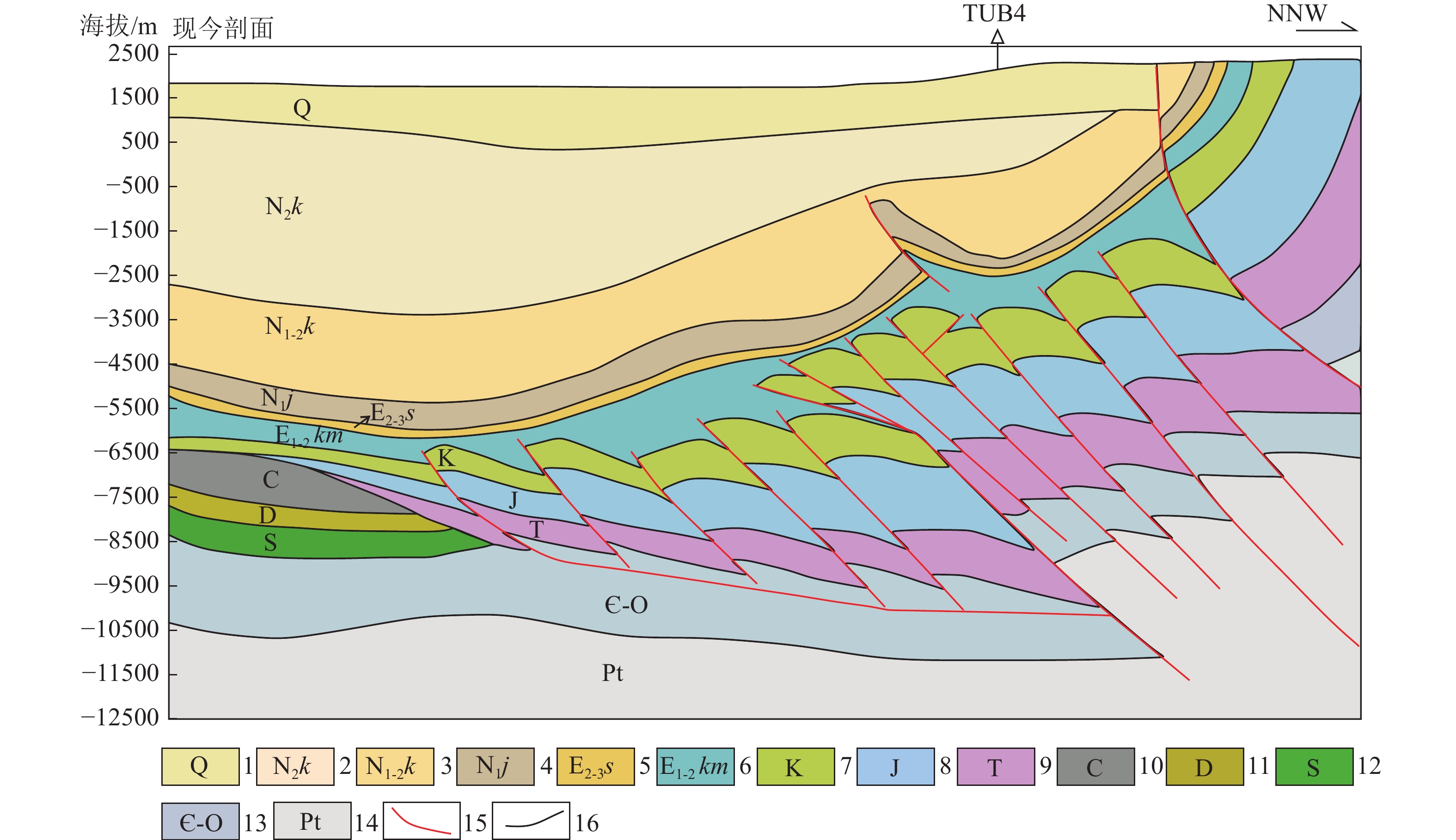
图 2 库车坳陷南北向结构剖面图(剖面位置见图1 A-A’)
Figure 2.
图 3 克拉苏构造带过BZ9井主干剖面地震解释剖面(剖面位置见图1)
Figure 3.
表 1 库车坳陷克拉苏构造带物理模拟模型参数
Table 1. Physical simulation model parameters of Kelasu structural belt in the Kuqa Depression
模型参数 单位 自然界(n) 模型(s) 相似系数(s/n) 重力加速度(g) m/s2 9.80 9.80 1 长度(l) m 40000 40×10−2 1×10−5 速度(v) m/s 1.38×10−10 4×10−6~8×10−6 2.9×104~5.8×104 石英砂密度(ρb) kg/m3 2400 1400 0.58 硅胶密度(ρd) kg/m3 2200 950 0.43 粘度(η) Pa·s 1×1019 8.8×103 8.8×10− 16 应力(σ) Pa 4.3×107~4.7×107 93.1~137.2 2.5×10−6 应变(ε) s−1 4.5×10−12 1.4×10−2 3.1×109 表 2 克拉苏构造带各层离散元(PFC2D)岩石微观物理学参数(据李维波等,2017)
Table 2. Rock microphysical parameters of discrete element (PFC2D) in each layer of Kelasu structural belt
参数 盐上层 盐下层 盐岩层 密度ρ/(kg·m−3) 2400 2600 2200 颗粒强度/Pa 1×108 1×108 1×107 粘结强度/Pa 1×106 1×106 1×106 粒间摩擦因素 0.7 0.7 0.1 重力加速度(g)/(m·s−3) 9.81 9.81 9.81 移动边界摩擦因素 / 0.7 / 底边界摩擦因素 / 0.2 / -
[1] Allen M B, Windley B F, Zhang C, et al. 1991a. Basin evolution within and adjacent to the Tien Shan range, NW China[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, London,148(2): 369−378.
[2] Allen P A, Crampton S L, Sinclair H D. 1991b. The inception and early evolution of the North Alpine foreland basin, Switzerland[J]. Basin Research, 3: 143−163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.1991.tb00124.x
[3] Allen M B, Windley B F, Zhang C. 1992. Palaeozoic collisional tectonics and magmatism of the Chinese Tien Shan, central Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 220: 89−115.
[4] Cao Z C, Tang D Q, Jiang Zhongzheng, et al. 2023. Evolution and characteristics of Mesozoic−Cenozoic faults in the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 42(1): 226−238 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Cundall P A, Strack O D L. 1979. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies[J]. Geotechnique, 29(1): 47−65. doi: 10.1680/geot.1979.29.1.47
[6] Finch Emma. 2005. Discrete element modelling of detachment folding[J]. Basin Research, 17(4): 507−520. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2005.00280.x
[7] He D f, Li D S, He J Y, et al. 2013. Comparison in petroleum geology between Kuqa depression and Southwest depression in Tarim Basin and its exploration significance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(2): 201−218(in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Hendrix M S. 2000. Evolution of Mesozoic sandstone compositions, southern Junggar, northern Tarim, and western Turpan basins, northwest China: a detrital record of the ancestral Tian Shan[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 70(3): 520−532.
[9] Huang S Y, Wang Y R, Wei H X, et al. 2009. Characteristies of salt structures and its evolution in Kuga Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 33(1): 117−123(in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Hubbert M K. 1937. Theory of scale models as applied to the study of geologic structures[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 48(9/12): 1459−1519.
[11] Jia C Z, Chen Z X, Lel Y L, et al. 2022. Deformation mechanisms and structural models of the fold thrust belts of central and western China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 29(6): 156−174 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Ju W, Hou G T, Huang S Y, et al. 2014. Constraints and controls of fault related folds on the development of tectonic fractures in sandstones[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 20(1): 105−113(in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Ju W, Hou G T, Huang S Y, et al. 2014. Structural fracture distribution and prediction of the Lower Jurassic Ahe Formation sandstone in the Yinan−Tuzi area, Kuga Depression[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 37(4): 592−602(in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Lei G L, Xie H W, Zhang J Z, et al. 2007. Structural features and natural gas exploration in the Kelasu structural belt, Kuga Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 28(6): 816−820,835(in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Li C S. 2019. Quantitative analysis and simulation of structural deformation in the fold and thrust belt based on discrete element method[D]. Nanjing University Ph. D. Academic Dissertation (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Li W B, Li J H, Wang H H, et al. 2017. Deformation mechanisms of Kelasu tectonic belt in Kuga foreland thrust belt: Insight from discrete element numerical simulation[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 41(6): 1001−1010.
[17] Li Y J, Yang H J, Z Y, et al. 2017. Tectonic framework and evolution of South Tianshan, NW China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 33(1): 94−104(in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Liu Z H, Wang G Q, Lu H F, et al. 1999. Nature and timing of the Kuqa Cenozoic structures[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 6(4): 215−221(in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Lu F H, Chen C M, Liu Z H, et al. 2000. The structural features and origin of the Kuqa rejuvenation foreland thrust belt[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 21(3): 18−24(in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Lu H F, J C Z, Jia D, et al. 2001. Features of the thrust wedge of deformation belt in Kuga rejuvenation foreland basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 7(3): 257−271(in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Lu H T, Zeng L B. 2004. Expression of the Himalayan orogeny in the Kuqa depression, Tarim basin ——evidence from the rock acoustic emission experiment[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(7): 676−679(in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Morgan J K. 2015. Effects of cohesion on the structural and mechanical evolution of fold and thrust belts and contractional wedges: Discrete element simulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 120(5): 3870−3896. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011455
[23] Neng Y, Qi J F, Xie H W, et al. 2009. Structural characteristics of northern margin of Kuga depression, Tarim basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(9): 1510−1519(in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Qi J F, Lei G L, Li M G, et al. 2009. A model of contractional structure for transition belt between Kuche depression and southern Tianshan Uplift[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(3): 120−128(in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Tang L J, Yu Y X, Yang W J. 2007. Paleo−uplifts and salt structures and their influence on hydrocarbon accumulations in the Kuga depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(2): 143−150(in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Tang P C. 2011. Cenozoic salt structures in the western Kuqa depression, Southern Tianshan: Structural analysis and physical modeling[D]. Zhejiang University Ph. D. Academic Dissertation (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Tian Z H, Sun J M, Brinan F, et al. 2016. Cenozoic detachment folding in the southern Tianshan foreland, NW China: Shortening distances and rates[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 84(1): 142−161.
[28] Wang X, Wang Z M, Xie W H, et al. 2010. Cenozoic salt tectonics and physical models in the Kuga depression of Tarim Basin, China[J]. Sci. Sin. Terrae., 40: 1655−1668(in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Wang Z M. 2013. Discussion of ceiling effect in foreland thrust belt of Kuga Depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 24(4): 671−677(in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Wu G H, Luo C S, Hu T P, et al. 2007. Fold−related faulting: An example from the Cenozoic salt overlying beds in the Kuqa depression[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 42(3): 496−505(in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Xu K, Tian J, Yang H J, et al. 2022. Effects and practical applications of present−day in−situ stress on reservoir quality in ultra deep layers of Kuga depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 33(1): 13−23(in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Yang H J, Sun X W, Pan Y Y, et al. 2020. Structural deformation laws and oil & gas exploration direction in the western Kelasu tectonic zone of the Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Geoscience Gas, 40(1): 31−37(in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Yin A, Nie S, Craig P, et al. 1998. Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the southern Chinese Tian Shan[J]. Tectonics, 17(1): 1−27. doi: 10.1029/97TC03140
[34] Yin H W, Wang Z, Wang X, et al. 2011. Characteristics and mechanics of Cenozoic salt−related structures in Kuqa foreland basins: Insights from physical modeling and discussion[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 17(2): 308−317(in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Yu Y X, Tang L J, Li J C, et al. 2006. Influence of basement faults on the development of salt structures in the Kuqa foreland fold and thrust belt in the northern Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(3): 330−336(in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Yu Y X, Tang L J, Yang W J, et al. 2007. Structural segmentation of salt structures in the frontal ranges of the Kuga foreland fold and thrust belt, northern Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(2): 166−173(in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Yu Y X, Zhou X H, Peng W X, et al. 2011. An overview on salt structures[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 35(2): 169−182(in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Zhang C H, Zhou H R, Liu B P, et al. 2002. New progress in the tectonostratigraphic study of the Paleozoic in the central sector of the South Tianshan Orogenic Belt[J]. Geological Review, 48(1): 9−14(in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Zhang J, Yin H W, Xu S J, et al. 2008. Influence of rock strength on fault patterns above active salt domes: Insights from 2D discrete element simulations[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 44(6): 642−652(in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] 曹自成, 唐大卿, 骆满嵩, 等. 2023. 塔里木盆地顺北地区中新生界断裂构造特征及演化[J]. 地质科技通报, 42(1): 226−238.
[41] 何登发, 李德生, 何金有, 等. 2013. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷和西南坳陷油气地质特征类比及勘探启示[J]. 石油学报, 34(2): 201−218.
[42] 黄少英, 王月然, 魏红兴. 2009. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷盐构造特征及形成演化[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 33(1): 117−123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.015
[43] 贾承造, 陈竹新, 雷永良, 等. 2022. 中国中西部褶皱冲断带构造变形机制与结构模型[J]. 地学前缘, 29(6): 156−174.
[44] 鞠玮, 侯贵廷, 黄少英, 等. 2014. 断层相关褶皱对砂岩构造裂缝发育的控制约束[J]. 高校地质学报, 20(1): 105−113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.01.010
[45] 鞠玮, 侯贵廷, 黄少英, 等. 2013. 库车坳陷依南-吐孜地区下侏罗统阿合组砂岩构造裂缝分布预测[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 37(4): 592−602.
[46] 雷刚林, 谢会文, 张敬洲, 等. 2007. 库车坳陷克拉苏构造带构造特征及天然气勘探[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 28(6): 816−820−835.
[47] 李维波, 李江海, 王洪浩, 等. 2017. 库车前陆冲断带克拉苏构造带变形影响因素分析——基于离散元数值模拟研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 41(6): 1001−1010.
[48] 李曰俊, 杨海军, 赵岩, 等. 2009. 南天山区域大地构造与演化[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 33(1): 94−104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.012
[49] 李长圣. 2019. 基于离散元的褶皱冲断带构造变形定量分析与模拟[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文.
[50] 刘洪涛, 曾联波. 2004. 喜马拉雅运动在塔里木盆地库车坳陷的表现——来自岩石声发射实验的证据[J]. 地质通报, 23(7): 676−679.
[51] 卢华复, 陈楚铭, 刘志宏. 等. 2000. 库车再生前陆逆冲带的构造特征与成因[J]. 石油学报, 21(3): 18−24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.03.004
[52] 卢华复, 贾承造, 贾东, 等. 2001. 库车再生前陆盆地冲断构造楔特征[J]. 高校地质学报, 7(3): 257−271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2001.03.002
[53] 卢华复, 贾东, 陈楚铭, 等. 1999. 库车新生代构造性质和变形时间[J]. 地学前缘, 6(4): 215−221. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.04.003
[54] 能源, 漆家福, 谢会文, 等. 2012. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷北部边缘构造特征[J]. 地质通报, 31(9): 1510−1519. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.09.014
[55] 漆家福, 雷刚林, 李明刚, 等. 2009. 库车坳陷-南天山盆山过渡带的收缩构造变形模式[J]. 地学前缘, 16(3): 120−128. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.03.008
[56] 汤良杰, 余一欣, 杨文静, 等. 2007. 库车坳陷古隆起与盐构造特征及控油气作用[J]. 地质学报, 81(2): 143−150.
[57] 唐鹏程. 2011. 南天山库车坳陷西段新生代盐构造: 构造分析和物理模拟[D]. 浙江大学博士学位论文.
[58] 汪新, 王招明, 谢会文, 等. 2010. 塔里木库车坳陷新生代盐构造解析及其变形模拟[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 40(12): 1655−1668.
[59] 王招明. 2013. 试论库车前陆冲断带构造顶蓬效应[J]. 天然气地球科学, 24(4): 671−677.
[60] 邬光辉, 罗春树, 胡太平, 等. 2007. 褶皱相关断层——以库车坳陷新生界盐上构造层为例[J]. 地质科学, 42(3): 496−505.
[61] 徐珂, 田军, 杨海军, 等. 2022. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷超深层现今地应力对储层品质的影响及实践应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 33(1): 13−23.
[62] 杨海军, 孙雄伟, 潘杨勇, 等. 2020. 塔里木盆地克拉苏构造带西部构造变形规律与油气勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 40(1): 31−37.
[63] 尹宏伟, 王哲, 汪新, 等. 2011. 库车前陆盆地新生代盐构造特征及形成机制: 物理模拟和讨论[J]. 高校地质学报, 17(2): 308−317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2011.02.016
[64] 余一欣, 汤良杰, 李京昌, 等. 2006. 库车前陆褶皱-冲断带基底断裂对盐构造形成的影响[J]. 地质学报, 80(3): 330−336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.03.003
[65] 余一欣, 汤良杰, 杨文静, 等. 2007. 库车前陆褶皱-冲断带前缘盐构造分段差异变形特征[J]. 地质学报, 81(2): 166−173. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.02.004
[66] 余一欣, 周心杯, 彭文绪, 等. 2011. 盐构造研究进展述评[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 35(2): 169−182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.02.001
[67] 张传恒, 周洪瑞, 刘本培, 等. 2002. 南天山造山带中段古生界构造地层研究新进展[J]. 地质论评, 48(1): 9−14. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2002.01.002
[68] 张洁, 尹宏伟, 徐士进. 2008. 用离散元方法讨论岩石强度对主动底辟盐构造断层分布模式的影响[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 44(6): 642−652. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0469-5097.2008.06.007
-



 下载:
下载: