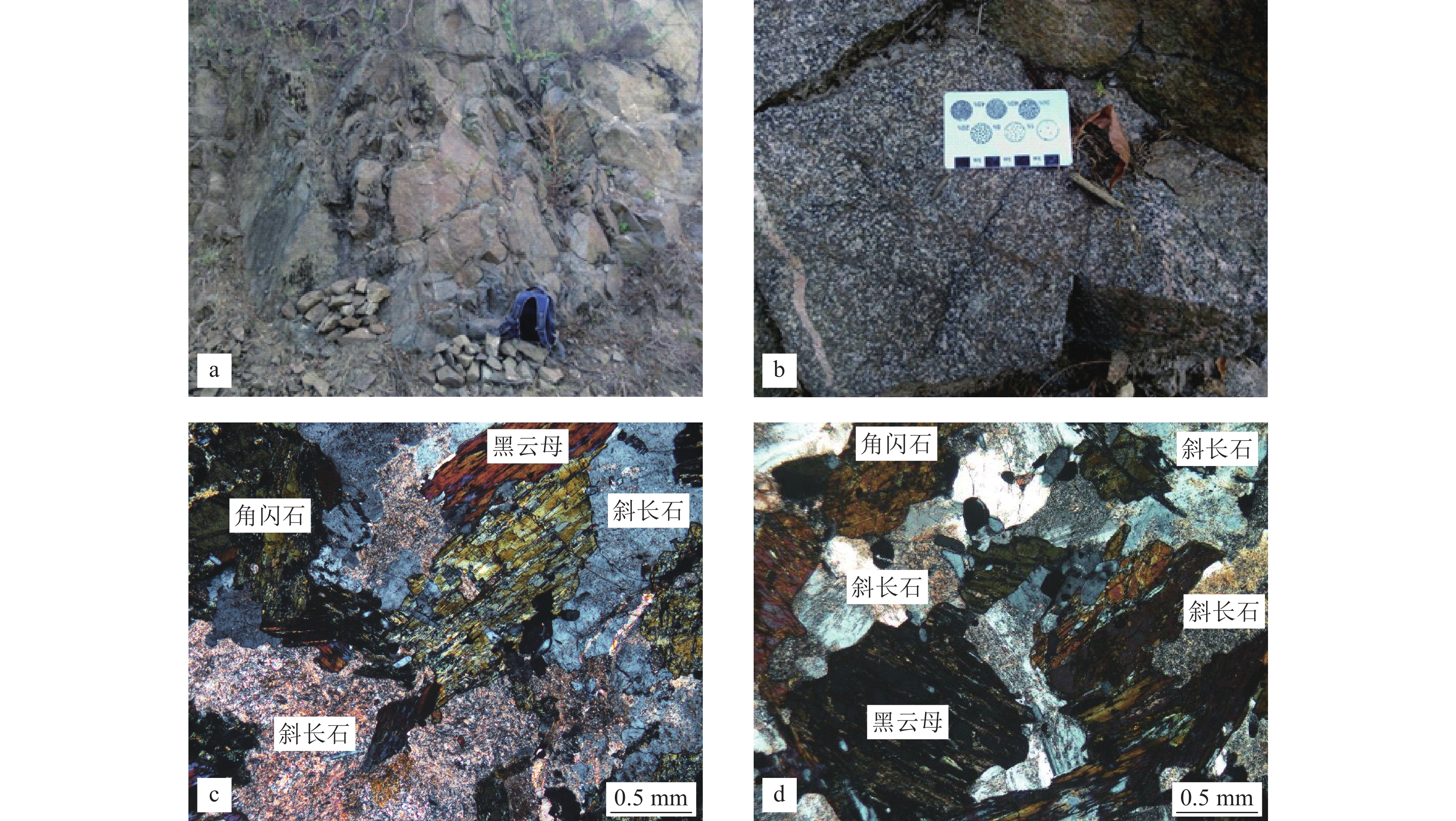
Geochemical characteristics of Early Cretaceous gabbro in Muzidian area, North Dabie and its indicative significance for tectonic environment
-
摘要:
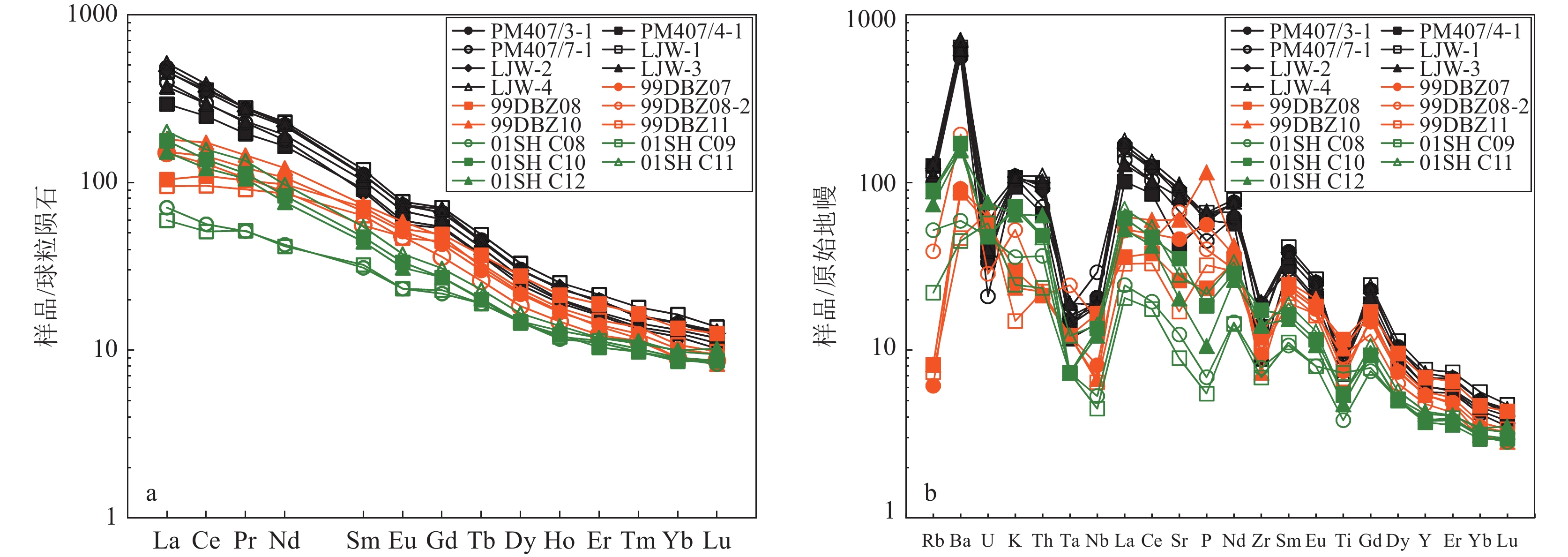
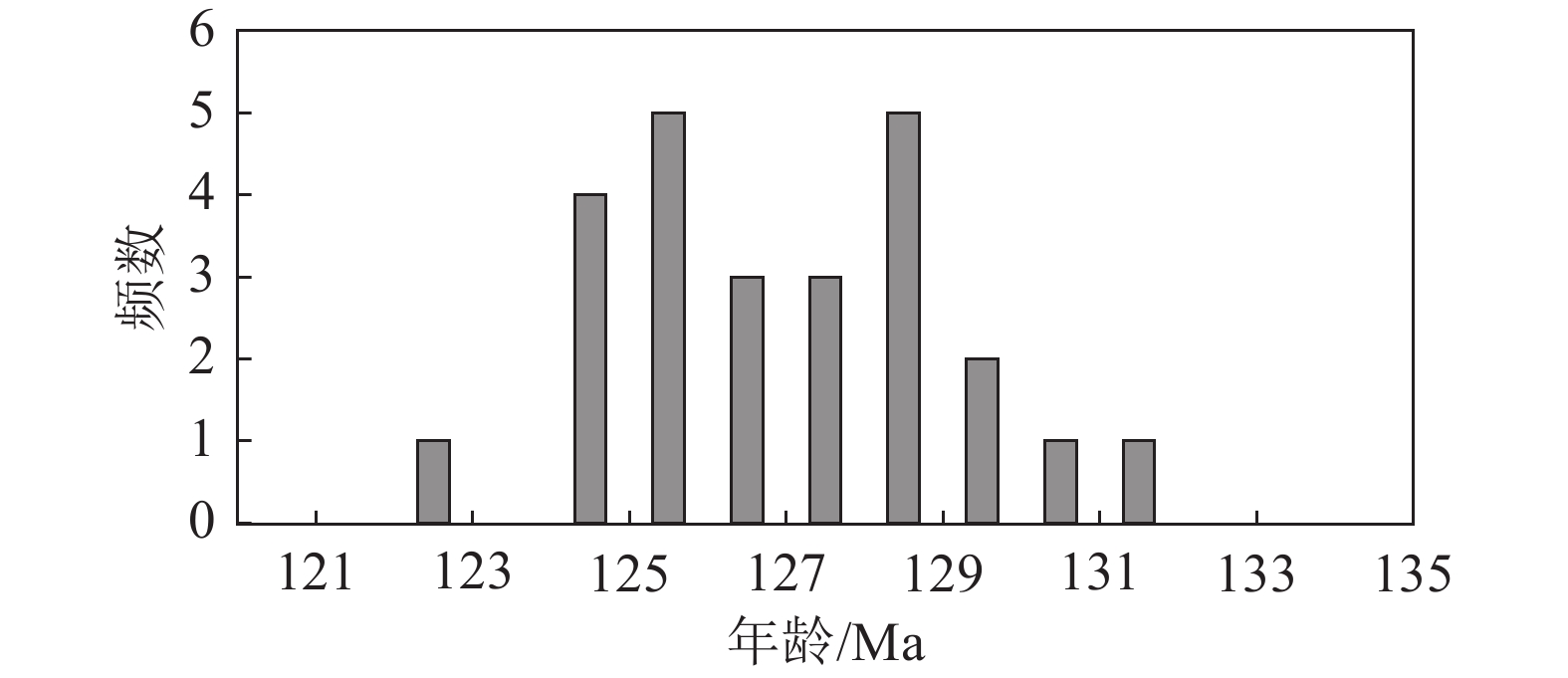
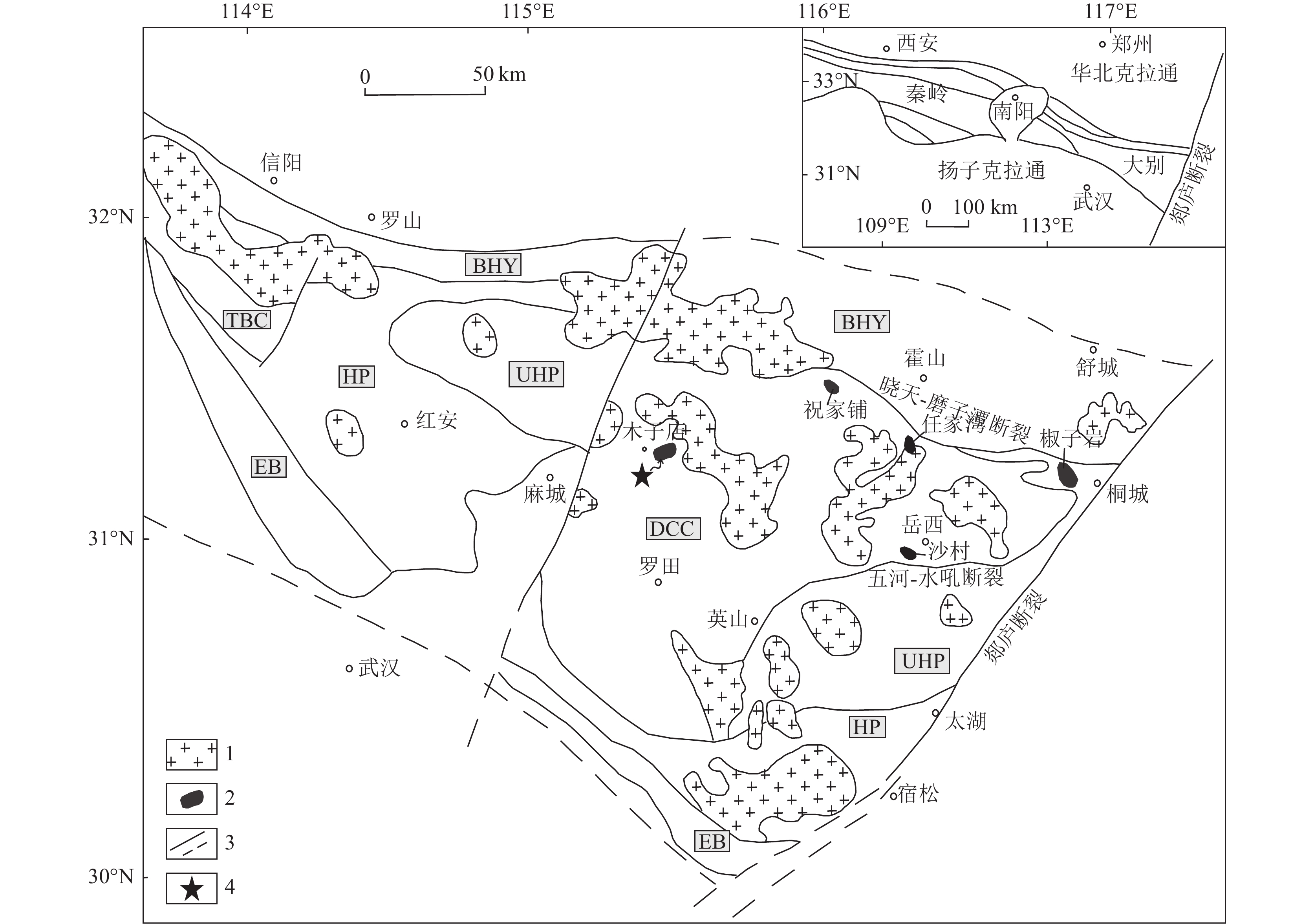
为揭示大别造山带基性岩的成因及构造背景,应用LA−ICP−MS锆石定年和地球化学分析,探讨了北大别木子店地区雷家湾辉长岩的成岩年龄、地球化学特征,并通过与安徽段基性—超基性岩对比,揭示了大别造山带基性—超基性岩成因和构造环境。结果显示,北大别木子店地区雷家湾辉长岩成岩年龄为122.3±1.0 Ma。雷家湾辉长岩的SiO2含量介于45.00%~50.69%之间,平均值为48.02%;Mg#值变化范围在45.62~53.49之间,平均值为47.86;K2O+ Na2O含量变化于4.68%~7.03%之间,平均值为6.31%,属于碱性系列;富集Rb、Ba、K、Sr等大离子亲石元素(LILE)和轻稀土元素,亏损Ta、Nb、Zr、Ti等高场强元素(HFSE)和重稀土元素;与安徽段基性—超基性岩具有相似的野外特征和岩石地球化学性质。岩石成因研究显示,雷家湾辉长岩的幔源母岩浆有地壳物质的加入,作用方式应该为源区的混合,地壳物质的加入可能与三叠纪以来扬子板块向华北板块俯冲后加厚岩石圈的拆沉作用有关。大别造山带130 Ma左右基性—超基性岩的出现可能暗示构造体制由挤压向伸展转换。
Abstract:In order to reveal the genesis and tectonic background of basic rocks in Dabie orogenic belt, LA−ICP−MS zircon dating and geochemical analysis were carried out to discuss the diagenetic age and geochemical characteristics of Leijiawan gabbro in Muzidian area, North Dabie, and by comparing with the basic−ultrabasic rocks in Anhui section, the genesis and tectonic environment of Dabie orogenic basic−ultrabasic rocks are revealed. The results show that the diagenetic age of the Leijiawan gabbro in the Muzidian area of North Dabie is 122.3 ± 1.0 Ma. The SiO2 content of the Leijiawan gabbro is between 45.00% and 50.69%, with an average of 48.02%. The Mg# value ranged from 45.62 to 53.49, with an average of 47.86.The content of K2O + Na2O varied from 4.68% to 7.03%, with an average of 6.31 %, belonging to the alkaline series. It is enriched in light rare earth elements and large ion lithophile elements ( LILE ) such as Rb, Ba, K and Sr, and depleted in heavy elements and high field strength elements ( HFSE ) such as Ta, Nb, Zr and Ti. It has similar field and geochemical characteristics to the mafic−ultramafic rocks of Anhui. The petrogenesis study shows that the mantle−derived magma of Leijiawan gabbro was added with crustal materials, and the mode of action is the mixing in magma source. The addition of crustal material may be related to the delamination of thickened lithosphere after subduction of Yangtze plate to North China plate since Triassic. The occurrence of mafic−ultramafic rocks at ca. 130 Ma in Dabie orogenic belt may imply the structural system transforms from compression to extension.
-

-
图 7 大别造山带中生代基性—超基性岩年龄频率图(资料来源见表3)
Figure 7.
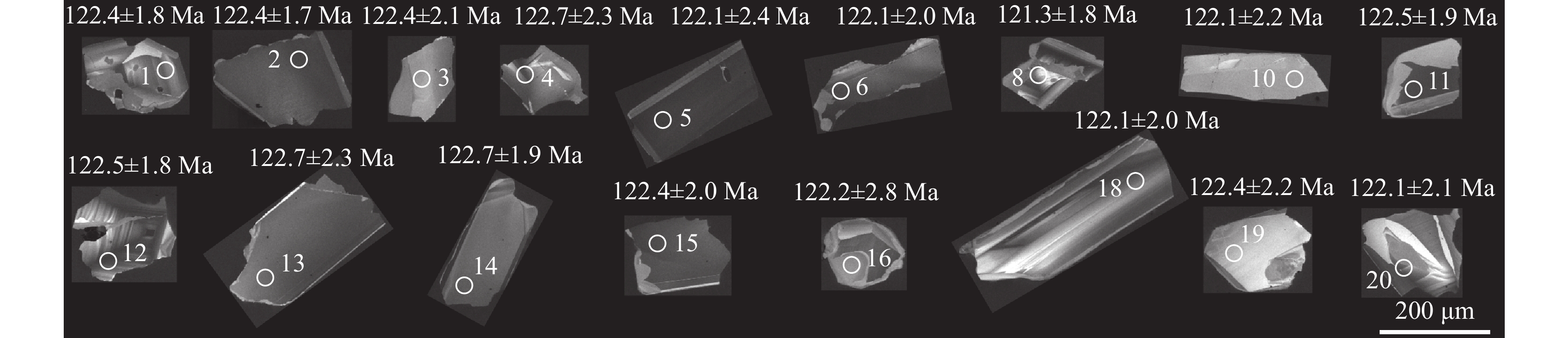
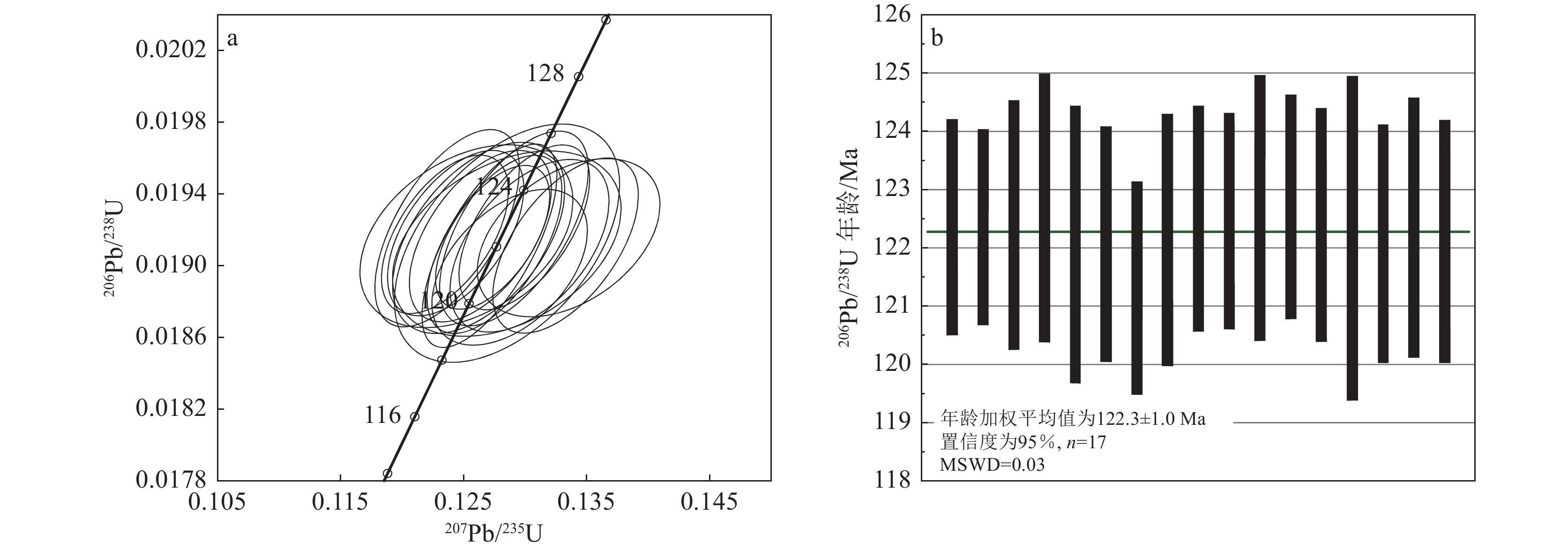
表 1 雷家湾辉长岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Th−Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1. Result of zircon LA−ICP−MS U−Th−Pb dating for the Leijiawan gabbro
分析号 含量/10−6 232Th/
238U同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma 谐和度 Total
Pb232Th 238U 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 206Pb/
238U1σ 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 206Pb/
238U1σ LJW-1-1 19.9 532 192 2.77 0.05060 0.0018 0.1335 0.0049 0.01916 0.00029 233.4 81.5 127.2 4.4 122.4 1.8 96% LJW-1-2 36.0 1082 451 2.40 0.04833 0.0011 0.1273 0.0031 0.01916 0.00026 122.3 53.7 121.7 2.8 122.4 1.7 99% LJW-1-3 8.9 236 139 1.70 0.04718 0.0019 0.1252 0.0057 0.01917 0.00034 57.5 92.6 119.7 5.2 122.4 2.1 97% LJW-1-4 22.5 654 211 3.10 0.04714 0.0016 0.1236 0.0039 0.01921 0.00036 57.5 74.1 118.4 3.5 122.7 2.3 96% LJW-1-5 50.0 1576 596 2.64 0.04815 0.0010 0.1271 0.0036 0.01911 0.00037 105.6 48.1 121.4 3.3 122.1 2.4 99% LJW-1-6 28.3 829 254 3.26 0.04949 0.0015 0.1303 0.0043 0.01912 0.00032 172.3 70.4 124.4 3.8 122.1 2.0 98% LJW-1-8 31.3 1014 274 3.70 0.04913 0.0015 0.1287 0.0042 0.01900 0.00029 153.8 76.8 122.9 3.8 121.3 1.8 98% LJW-1-10 6.4 72 129 0.56 0.04880 0.0023 0.1285 0.0061 0.01913 0.00034 200.1 104.6 122.7 5.5 122.1 2.2 99% LJW-1-11 30.1 937 359 2.61 0.04691 0.0012 0.1243 0.0036 0.01918 0.00030 42.7 63.0 119.0 3.3 122.5 1.9 97% LJW-1-12 53.3 1734 422 4.11 0.04685 0.0013 0.1235 0.0034 0.01918 0.00029 42.7 63.0 118.2 3.1 122.5 1.8 96% LJW-1-13 24.3 779 250 3.12 0.04875 0.0014 0.1291 0.0040 0.01921 0.00036 200.1 73.1 123.3 3.6 122.7 2.3 99% LJW-1-14 22.7 622 376 1.65 0.04901 0.0012 0.1299 0.0035 0.01922 0.00030 146.4 59.3 124.0 3.1 122.7 1.9 98% LJW-1-15 41.7 1316 362 3.63 0.04779 0.0013 0.1263 0.0038 0.01917 0.00031 100.1 58.3 120.8 3.4 122.4 2.0 98% LJW-1-16 4.7 85 97 0.88 0.04965 0.0024 0.1285 0.0060 0.01913 0.00044 189.0 119.4 122.7 5.4 122.2 2.8 99% LJW-1-18 24.9 778 230 3.38 0.05091 0.0015 0.1332 0.0039 0.01912 0.00032 235.3 66.7 127.0 3.5 122.1 2.0 96% LJW-1-19 14.2 385 225 1.71 0.04780 0.0016 0.1262 0.0046 0.01916 0.00035 100.1 77.8 120.7 4.2 122.4 2.2 98% LJW-1-20 31.5 1030 325 3.17 0.04847 0.0013 0.1275 0.0036 0.01912 0.00033 120.5 63.0 121.8 3.3 122.1 2.1 99% 表 2 雷家湾辉长岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2. Major, trace and rare earth elements data for the Leijiawan gabbro
样号 PM407/3-1 PM407/4-1 PM407/7-1 LJW-1 LJW-2 LJW-3 LJW-4 SiO2 48.13 43.20 49.12 46.71 46.58 45.37 47.38 TiO2 1.63 2.14 1.71 1.70 1.65 1.75 1.57 Al2O3 16.16 11.41 16.20 14.84 15.52 14.76 16.02 Fe2O3 4.68 6.20 3.34 5.11 5.06 5.77 4.88 FeO 6.87 9.44 6.60 7.63 7.53 7.98 7.06 TFeO 11.08 15.02 9.61 12.23 12.08 13.17 11.45 MnO 0.17 0.18 0.15 0.18 0.18 0.19 0.18 MgO 4.72 8.10 5.58 5.40 5.12 5.69 4.88 CaO 6.67 9.55 6.43 8.39 8.16 8.48 7.78 Na2O 3.55 1.64 3.56 2.89 3.05 2.79 3.18 K2O 3.28 2.85 3.23 3.21 3.24 3.14 3.30 P2O5 1.30 1.30 0.98 1.44 1.40 1.46 1.26 烧失量 3.21 4.12 3.88 1.94 2.20 2.20 2.14 总量 100.37 100.13 100.78 99.44 99.69 99.58 99.63 Mg# 45.75 51.64 53.49 46.65 45.62 46.10 45.76 La 115 69.6 93.6 108 109 88.1 122 Ce 222 152 182 218 212 180 236 Pr 26.3 18.6 21.6 26.5 25.2 22.0 26.2 Nd 103 77.0 83.6 107 101 89.7 104 Sm 17.1 14.0 13.5 18.3 16.9 15.7 17.0 Eu 4.26 3.44 3.28 4.46 4.28 3.93 4.26 Gd 13.6 11.2 11.0 14.6 13.6 12.4 14.3 Tb 1.70 1.39 1.37 1.83 1.67 1.53 1.69 Dy 7.70 6.58 6.24 8.38 7.56 6.91 7.62 Ho 1.31 1.12 1.08 1.43 1.34 1.14 1.31 Er 3.27 2.73 2.67 3.55 3.20 2.79 3.30 Tm 0.410 0.350 0.340 0.460 0.410 0.370 0.400 Yb 2.46 2.15 2.05 2.78 2.49 2.25 2.48 Lu 0.310 0.280 0.260 0.350 0.320 0.300 0.330 Y 31.1 27.9 25.6 34.9 31.4 27.6 33.2 ΣREE 518 360 423 516 499 427 541 LREE 488 335 398 482 468 399 509 HREE 30.8 25.8 25.0 33.4 30.6 27.7 31.4 LREE/HREE 15.9 13.0 15.9 14.4 15.3 14.4 16.2 LaN/YbN 33.5 23.2 32.8 27.9 31.4 28.1 35.3 δEu 0.854 0.840 0.823 0.834 0.863 0.861 0.835 Rb 63.5 79.8 78.4 74.7 76.6 82.2 70.0 Ba 4000 4320 3890 4460 4560 4950 4370 U 0.700 0.820 0.440 1.41 0.990 1.21 0.840 Th 8.03 5.54 6.08 8.29 7.54 8.62 9.34 Ta 0.570 0.480 0.730 0.650 0.630 0.780 0.580 Nb 14.7 10.3 20.8 13.7 13.1 13.4 13.0 Pb 11.2 9.8 11.8 12.1 12.9 12.5 12.4 Sr 1880 895 1420 1780 1960 1720 2050 Zr 154 99 212 154 214 217 196 Hf 4.14 3.23 4.80 3.98 4.89 4.99 4.50 注:TFeO=FeO+Fe2O3*0.8998;Mg#=100*MgO/[MgO+0.505*(FeO+0.9*Fe2O3)];δEu=Eu/Eu∗=2EuN/(SmN+GdN) ;主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10−6 表 3 大别造山带中生代基性—超基性岩年龄
Table 3. Isotope age of the Mesozoic mafic-ultramafic rocks from Dabie Orogenic belt
位置/岩体 岩性 年龄/Ma 定年方法 参考文献 小河口 闪长岩 127±6 TIMS锆石 李曙光等,1999 小河口 辉石岩 125.3±0.8 TIMS锆石 李曙光等,1999 祝家铺 闪长岩 130.2±1.4 TIMS锆石 李曙光等,1999 漆柱山 辉长岩 122.9±0.6 TIMS锆石 王江海等,2002 北大别 辉绿岩脉 128.3±0.1 全岩Ar−Ar Wang et al., 2005 北大别 煌斑岩 128.2±0.2 全岩Ar−Ar Wang et al., 2005 北大别 煌斑岩 129.6±0.2 全岩Ar−Ar Wang et al., 2005 北大别 辉绿岩脉 131.8±0.3 全岩Ar−Ar Wang et al., 2005 北大别 辉绿岩脉 127.6±0.2 全岩Ar−Ar Wang et al., 2005 沙村 辉长岩 128±2 TIMS锆石 Zhao et al., 2005 沙村 辉长岩 125±2 SHRIMP锆石 Zhao et al., 2005 沙村 辉长岩 125±3 SHRIMP锆石 Zhao et al., 2005 椒子岩 辉长岩 127±3 TIMS锆石 Zhao et al., 2005 金寨银沙畈 辉长岩脉 125.8±2.7 SHRIMP锆石 王世明等,2010 湖北大悟 闪斜煌斑岩脉 129.6±2.5 SHRIMP锆石 王世明等,2010 北淮阳 基性岩脉 129±1 SIMS锆石 Dai et al., 2011 道士冲 富斜长石角闪石岩 125±1 SIMS锆石 Dai et al., 2011 道士冲 富斜长石角闪石岩 129±1 LA−ICP−MS锆石 Dai et al., 2011 祝家铺 辉石岩 128±1 SIMS锆石 Dai et al., 2011 祝家铺 辉石岩 126±1 LA−ICP−MS锆石 Dai et al., 2011 祝家铺 富斜长石角闪石岩 126±2 SIMS锆石 Dai et al., 2011 祝家铺 富斜长石角闪石岩 126±1 LA−ICP−MS锆石 Dai et al., 2011 道士冲 角闪石岩 129±1 LA−ICP−MS锆石 Dai et al., 2012 祝家铺 角闪石岩 125±3 LA−ICP−MS锆石 Dai et al., 2012 道士冲 富斜长石角闪石岩 127±2 LA−ICP−MS锆石 Dai et al., 2012 祝家铺 角闪石岩 127±1 LA−ICP−MS锆石 Dai et al., 2012 -
[1] Chen D G, Wu Y B, Xia Q K, et al. 1997. The Sm-Nd age and Nd isotopic characterization of Jiaoziyan gabbroic intrusion[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 18: 9−11 ( in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Chen D G, Wang X, Deloule E, et al. 2001. Zircon SIMS ages and chemical compositions from Northem Dabie Terrain: Its implications for pyroxenite genesis[J]. Chinese Sci. Bull., 46(7): 586−590 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Dai L Q, Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, et al. 2011. Zircon Hf–O isotope evidence for crust–mantle interaction during continental deep subduction[J]. Earth and Planetary Sciense Letters, 308: 229−244. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2011.06.001
[4] Dai L Q, Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, et al. 2012. The nature of orogenic lithospheric mantle: Geochemical constraints from postcollisional mafic–ultramafic rocks in the Dabie orogen[J]. Chemical Geology, 344: 99−121.
[5] Gao S, Zhang B R, Jin Z M, et al. 1999. Lower crustal delamination in the Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt[J]. Science in China(series D), 29(6): 532−541 ( in Chinese with English abstract) .
[6] Ge N J, Hou Z H, Li H M, et al. 1999. Zircon U- Pb age of the Shacun gabbro body, Yuexi Dabie orogen and its geobgical implications[J]. Chinese Sci. Bull., 46(19): 2110−2114 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[7] Hacker B R, Wang. Q C. 1995. Ar/Ar geochronology of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in central China[J]. Tectonics, 14: 994−1006. doi: 10.1029/95TC00932
[8] Hacker B R, Ratschbacher L, Webb L. 1998. U/Pb zircon ages constrain the architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Qinling-Dabie Orogen, China[J]. Earth Planet. Lett., 161: 215−230. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00152-6
[9] Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Lo C H, et al. 1999. Crust–mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust: geochemical and Sr–Nd isotopic evidence from post-collisional mafic–ultramafic intrusions of the northern Dabie complex, central China[J]. Chemical Geology, 157: 119−146. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00197-1
[10] Kay R W, Kay S M. 1993. Delamination and delamination magmatism[J]. Tectonophys, 219: 177−189. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(93)90295-U
[11] Li C, Chen Y J. 2002. A review on petrologic evidences for Mesozoic lithosphere delamination in East Qinling Dabie Mountains[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 38(3): 431−441 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Li S G, Hart S R, Zheng S G, et al. 1989. Timing of collision between the North and South China Blocks: the Sm-Nd isotope age evidence[J]. Sci. China (B), 3: 312−319 ( in Chinese with English abstract) .
[13] Li S G, Nie Y H, Zheng S G, et al. 1997. Interaction between subducted continental crust and the mantle- I. Major and trace etement geochemistry of the syncollisional mafic-altrumafic intrusions in the Dabie Mountains[J]. Sci. China (D), 27: 488−493 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[14] Li S G, Nie Y H, Hart S R, et al. 1998. Interaction between sudutedcontinental crust and the mantle-II. Sr and Nd isotopic geochemistrv of the Syncollisional mafic-ultramafic intrusions in the Dabie Moutains[J]. Sci. China (D), 28: 18−22 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[15] Li S G, Hong J A, Li H M, et al. 1999. U−Pb zircon ages of the pyroxenite-gabbro intrusions in Dabie mountain and their geological implications[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 5(3): 351−355 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[16] Li S G. 2004. Exhumation mechanism of the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in the Dabie mountains and continental collision process between the North and South China blocks[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(3): 63−70 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[17] Li Q Z, Xie Z, Xu X S, et al. 2008. The isotopic characteristics of the Early-Cretaceous mafic rocks from Dabie Orogenic Belt and the contribution of the lower crust to the magma source[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8): 1771−1781 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[18] Lin W, Ji W B, Shi Y H, et al. 2013. Multi-stage exhumation processes of the UHP metamorphic rocks: Implications from the extensional structure of Tongbai-Hong’an-Dabieshan orogenic belt[J]. Chin. Sci. Bull., 58(23): 2259−2265 (in Chinese with English abstract) . doi: 10.1360/972013-636
[19] Liu Y S, Zong K Q, Kelemen P B, et al. 2008. Geochemistry and magmatic history of eclogites and ultramafic rocks from the Chinese continental scientific drill hole: Subduction and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism of lower crustal cumulates[J]. Chemical Geology, 247: 133−153. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.016
[20] Liu X C, Li S Z, Jahn B M. 2015. Tectonic evolution of the Tongbai-Hong’an orogen in central China: From oceanic subduction/accretion to continent-continent collision[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 45(8): 1008−1108 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[21] Ludwig K R. 2003. User's manual for Isoplot 3.00. A geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center: Special Publication, 4a.
[22] Ma C Q, Yang K G, Xu C H, et al. 1999. Mesozoic potassic magmatism in the Dabie Mountains Implication for exhumation mechanism of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic terranes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(3): 379−395 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[23] Ma C Q, Yang K G, Ming H L, et al. 2003. The time from shift to extrusion of Mesozoic crust of Dabie : Evidence from granite[J]. Science China (Series D), 33(9): 817−827 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[24] Ma C Q, Zhang C, She Z B, et al. 2007. The Dabie mountains and its southeast Yanshanian magmatic activity: Magmatic arc migration and extensional collapse[C]//2007 National Symposium on Petrology and Geody-namics and Chemical Geodynamics. China University of Geosciences Press, Wuhan: 106−109 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Nelson K D. 1992. Are crustal thickness variations in old mountain belts like the Appalachians a consequence of lithospheric delamination?[J]. Geology, 20: 498−502.
[26] Nie Y H, Li S G. 1997. Sm-Nd age of synolisional mafic-ultramafic intrusions in the Dabie Mountan[J]. Chinese Sci. Bull., 42(10): 1086−1088 (in Chinese with English abstract) . doi: 10.1360/csb1997-42-10-1086
[27] Nie Y H, Li S G. 1998. Rb-Sr chronologyand cooling history of the Renjiawan pyroxenite intrusion in north Dabie Terrane[J]. Chinese Sci. Bull., 43(11): 1195−1198 (in Chinese with English abstract) . doi: 10.1360/csb1998-43-11-1195
[28] Sacks P E, Secor J D. 1990. Delamination in collisional orogens[J]. Geology, 18: 999−1002.
[29] Suo S T, Zhong Z Q, Zhang H F, et al. 2001. High-pressure metamorphic belt and its tectonic pattern in Tongbai mountains, Central China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 25(6): 551−559 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Tsai C H, Lo C H, Liou J G, et al. 2000. Evidence against subduction-related magmatism for the Jiaoziyan Gabbro, northern Dabie Shan, China[J]. Geology, 28(10): 943−946. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<943:EASMFT>2.0.CO;2
[31] Tang J F, Hou M J, Li H K, et al. 2003. Multi-Superimposed deformation and their evolution in northeastern margin of Yangtze Block[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 27(4): 313−326 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Wang J H, Deng S X. 2002. Emplacement age for the mafic-ultramafic plutons in the northern Dabie Mts. (Hubei): Zircon U-Pb, Sm-Nd and 40Ar/39Ar dating[J]. Sci. China (D), 32(1): 1−9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Wang Q C. 2013. Exhumation of high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(5): 1607−1620 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[34] Wang Q, Wyman D A, Xu J F, et al. 2007. Early Cretaceous adakitic granites in the Northern Dabie Complex, central China: Implications for partial melting and delamination of thickened lower crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71: 2609−2636. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.03.008
[35] Wang S M, Ma C Q, Wang L Y, et al. 2010. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating, geochemistry and genesis of Early Cretaceous basic dykes from the Dabie Orogen[J]. Earth Science- Journal of China University of Geosciences, 35(4): 572−584 (in Chinese with English abstract) . doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.073
[36] Wu Y B. 2009. Multistage evolution of continental collision orogen: A case study for western Dabie orogeny[J]. Chinese Sci. Bull., 54(13): 1815−1825 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-13-1815
[37] Xu S T, Jiang L L, Liu Y C, et al. 1992. Tectonic framework and evolution of the Dabie mountains in Anhui, eastern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 66(1): 1−14(in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Wu Y B, Zheng Y F, Zhang S B. 2007. Zircon U–Pb ages and Hf isotope compositions of migmatite from the North Dabie terrane in China: constraints on partial melting[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 25: 991−1009. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2007.00738.x
[39] Wang Y J, Fan W M, Peng T P, et al. 2005. Nature of the Mesozoic lithospheric mantle and tectonic decoupling beneath the Dabie Orogen, Central China: Evidence from 40Ar/39Ar geochronology, elemental and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic compositions of Early Cretaceous mafic igneous rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 220: 165−189. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.02.020
[40] Wang Y S, Zhu G, Wang D X, et al. 2004. Relatin between P-T conditions of two phases of Tanlu strike-slip shear zones and delamination of the orogeic belts on the eastern margin of the Dabie Mountains[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 28(3): 228−238 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Xia Q K, Deloule E, Wu Y B, et al. 2002. Oxygen isotopic compositions of zircons from pyroxenite of Daoshichong, Dabieshan: Implications for crust mantle interaction[J]. Chinese Sci. Bull., 47(16): 1256−1260 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2002-47-16-1256
[42] Xie Q L, Li S Q, Fang B W, et al. 2016. Zircon ages and geological significances of intermediate mafic Dykes in Susong terrene of Dabie orogenic belt[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 38(3): 318−333 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[43] Xie Z, Zheng Y F, Zhao Z F. 2006. Mineral isotope evidence for the contemporaneous process of Mesozoic granite emplacement and gneiss metamorphism in the Dabie orogen[J]. Chemical Geology, 231: 214−235. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.01.028
[44] Xu H J, Ye K, Ma C Q. 2008. Early Cretaceous granitoids in the North Dabie and their tectonic implications: Sr-Nd and zircon Hf isotopic evidences[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(1): 87−103 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[45] Xu S T, Liu Y C, Jiang L L, et al. 1994. Tectonic regime and evolution of Dabie mountains[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 135−137 (in Chinese) .
[46] Xue F, Rowley D B, Tucker R D. 1997. U-Pb Zircon ages of granitoid rocks in the North Dabie Complex, Eastern Dabie Shan, China[J]. The Journal of Geology, 105: 744−753. doi: 10.1086/515984
[47] Xue H M, Dong S W, Liu X C. 2002. U/ Pb zircon dating for Cretaceous adakitic volcanic rocks in eastern part of the North Dabie Mountains[J]. Geochimica, 31(5): 455−463 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[48] Yang W R, Yang K G, Liu Z M, et al. 1999. Caledonian tectono-thermal event in Tongbai-Dabie orogenic belt and its singnificance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 6(4): 247−253 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[49] Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Wei C S, et al. 2003. Zircon U−Pb age, element and isotope geochemistry of Mesozoic mafic ultramafic rocks at Shacun and Jiaoziyan in North Dabie[J]. Geological Joumal of China Universities, 9(2): 139−162 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[50] Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Wei C S, et al. 2004. Zircon U-Pb age, element and oxygen isotope geochemistry of Mesozoic intermediate-felsic rocks in the Dahie Mountains[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(5): 1151−1174 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[51] Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Wei C S, et al. 2005. Zircon U–Pb age, element and C–O isotope geochemistry of post-collisional mafic-ultramafic rocks from the Dabie orogen in East-Central China[J]. Lithos, 83: 1−28. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.12.014
[52] Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F. 2009. Remelting of subducted continental lithosphere: Petrogenesis of Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the Dabie- Sulu orogenic belt[J]. Sci. China Ser. (D-Earth Sci.), 39(7): 888−909 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[53] Zheng Y F, Zhou J B, Wu Y B. 2005. Low-grade metamorphic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt: A Passive-margin accretionary wedge deformed during continent subduction[J]. Int. Geol. Rev., 47: 851−871. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.47.8.851
[54] 陈道公, 吴元保, 夏群科, 等. 1997. 椒子岩辉长岩体的Sm-Nd年龄及其Nd同位素特征[J]. 地球学报, 18(增刊): 9−11.
[55] 陈道公, 汪相, Deloule E, 等. 2001. 北大别辉石岩成因: 锆石微区年龄和化学组成[J]. 科学通报, 46(7): 586−590. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.07.014
[56] 高山, 张本仁, 金振民, 等. 1999. 秦岭-大别造山带下地壳拆沉作用[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 29(6): 532−541. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7240.1999.06.008
[57] 葛宁洁, 侯振辉, 李惠民, 等. 1999. 大别造山带岳西沙村镁铁-超镁铁岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 科学通报, 46(19): 2110−2114. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.19.020
[58] 李曙光, Hart S R, 郑双根, 等. 1989. 中国华北、华南陆块碰撞时代的钐-钕同位素年龄证据[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 3: 312−319.
[59] 李曙光, 聂永红, 郑双根, 等. 1997. 俯冲陆壳与上地幔的相互作用##Ⅰ. 大别山同碰撞镁铁#超镁铁岩的主要元素及痕量元素地球化学[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 27: 488−493.
[60] 李曙光, 聂永红, Hart S R, 等. 1998. 俯冲陆壳与上地幔的相互作用##Ⅱ. 大别山同碰撞镁铁-超镁铁岩的Sr, Nd同位素地球化学[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 28: 18−22.
[61] 李曙光, 洪吉安, 李惠民, 等. 1999. 大别山辉石岩−辉长岩体的锆石U−Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 5(3): 351−355.
[62] 李曙光. 2004. 大别山超高压变质岩折返机制与华北−华南陆块碰撞过程[J]. 地学前缘, 11(3): 63−70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.008
[63] 林伟, 冀文斌, 石永红, 等. 2013. 高压#超高压变质岩石多期构造折返: 桐柏-红安-大别造山带为例[J]. 科学通报, 58(23): 2259−2265.
[64] 李全忠, 谢智, 徐夕生, 等. 2008. 大别造山带早白垩世基性岩的同位素特征及下地壳物质对岩浆源区的贡献[J]. 岩石学报, 24(8): 1771−1781.
[65] 刘晓春, 李三忠, 江博明. 2015. 桐柏−红安造山带的构造演化: 从大洋俯冲/增生到陆陆碰撞[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 45(8): 1008−1108.
[66] 李超, 陈衍景. 2002. 东秦岭—大别地区中生代岩石圈拆沉的岩石学证据评述[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3): 431−441.
[67] 马昌前, 杨坤光, 许长海, 等. 1999. 大别山中生代钾质岩浆作用与超高压变质地体的剥露机理[J]. 岩石学报, 15(3): 379−395. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1999.03.007
[68] 马昌前, 杨坤光, 明厚利, 等. 2003. 大别山中生代地壳从挤压转向伸展的时间: 花岗岩的证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(9): 817−827. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2003.09.001
[69] 马昌前, 张超, 佘振兵, 等. 2007. 大别山及其东南燕山期岩浆活动: 岩浆弧迁移与伸展塌陷[C]//全国岩石学与地球动力学暨化学地球动力学研讨会论文集. 武汉: 中国地质大学: 106-109.
[70] 聂永红, 李曙光. 1997. 大别山同碰撞镁铁#超镁铁岩侵入体的Sm-Nd年龄及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 42(10): 1086−1088. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1997.10.018
[71] 聂永红, 李曙光. 1998. 北大别地体任家湾辉石岩的Rb-Sr年代学及冷却史[J]. 科学通报, 43(11): 1195−1198.
[72] 索书田, 钟增球, 张宏飞, 等. 2001. 桐柏山高压变质带及其区域构造型式[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 25(6): 551−559.
[73] 汤加富, 侯明金, 李怀坤, 等. 2003. 扬子地块东北缘多期叠加变形及形成演化[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 27(4): 313−326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2003.04.003
[74] 王勇生, 朱光, 王道轩, 等. 2004. 大别山东缘郯庐两期走滑剪切带形成的温压条件与造山带折返的关系[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 28(3): 228−238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2004.03.002
[75] 吴元保. 2009. 大陆造山过程的多期演化: 以西大别为例[J]. 科学通报, 54(13): 1815−1825.
[76] 王清晨. 2013. 大别山造山带高压-超高压变质岩的折返过程[J]. 岩石学报, 29(5): 1607−1620.
[77] 王世明, 马昌前, 王琳燕, 等. 2010. 大别山早白垩世基性脉岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地球科学, 35(4): 572−584.
[78] 王江海, 邓尚贤. 2002. 湖北北大别镁铁-超镁铁质侵入体的时代: 锆石U-Pb, Sm-Nd和40Ar/39Ar定年结果[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 32(1): 1−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7240.2002.01.001
[79] 徐树桐, 江来利, 刘贻灿, 等. 1992. 大别山区(安徽部分)的构造格局和演化过程[J]. 地质学报, 66(1): 1−14.
[80] 徐树桐, 刘贻灿, 江来利, 等. 1994. 大别山的构造格局和演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 135-137.
[81] 薛怀民, 董树文, 刘晓春. 2002. 北大别东部白垩纪埃达克质火山岩及其锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 地球化学, 31(5): 455−463. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2002.05.006
[82] 续海金, 叶凯, 马昌前. 2008. 北大别早白垩纪花岗岩类的Sm-Nd和锆石Hf同位素及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 24(1): 87−103.
[83] 谢清陆, 李双庆, 方博文, 等. 2016. 大别造山带宿松地体中—基性脉岩锆石年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 38(3): 318−333. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2016.03.003
[84] 夏群科, Deloule E, 吴元保, 等. 2002. 大别山道士冲地区辉石岩锆石的氧同位素组成: 壳幔相互作用的新信息[J]. 科学通报, 47(16): 1256−1260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.16.012
[85] 杨巍然, 杨坤光, 刘忠明, 等. 1999. 桐柏-大别造山带加里东期构造-热事件及其意义[J]. 地学前缘, 6(4): 247−253. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.04.007
[86] 赵子福, 郑永飞, 魏春生, 等. 2003. 大别山沙村和椒子岩基性#超基性岩锆石U-Pb定年、元素和碳氧同位素地球化学研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 9(2): 139−162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2003.02.001
[87] 赵子福, 郑永飞, 魏春生. 2004. 大别山中生代中酸性岩浆岩锆石U-Pb定年、元素和氧同位素地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 20(5): 1151−1174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2004.05.012
[88] 赵子福, 郑永飞. 2009. 俯冲大陆岩石圈重熔: 大别−苏鲁造山带中生代岩浆岩成因[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 39(7): 888−909.
-



 下载:
下载: