Understanding the evolution of relationships among natural resource, social economy, and eco-environment
-
摘要:
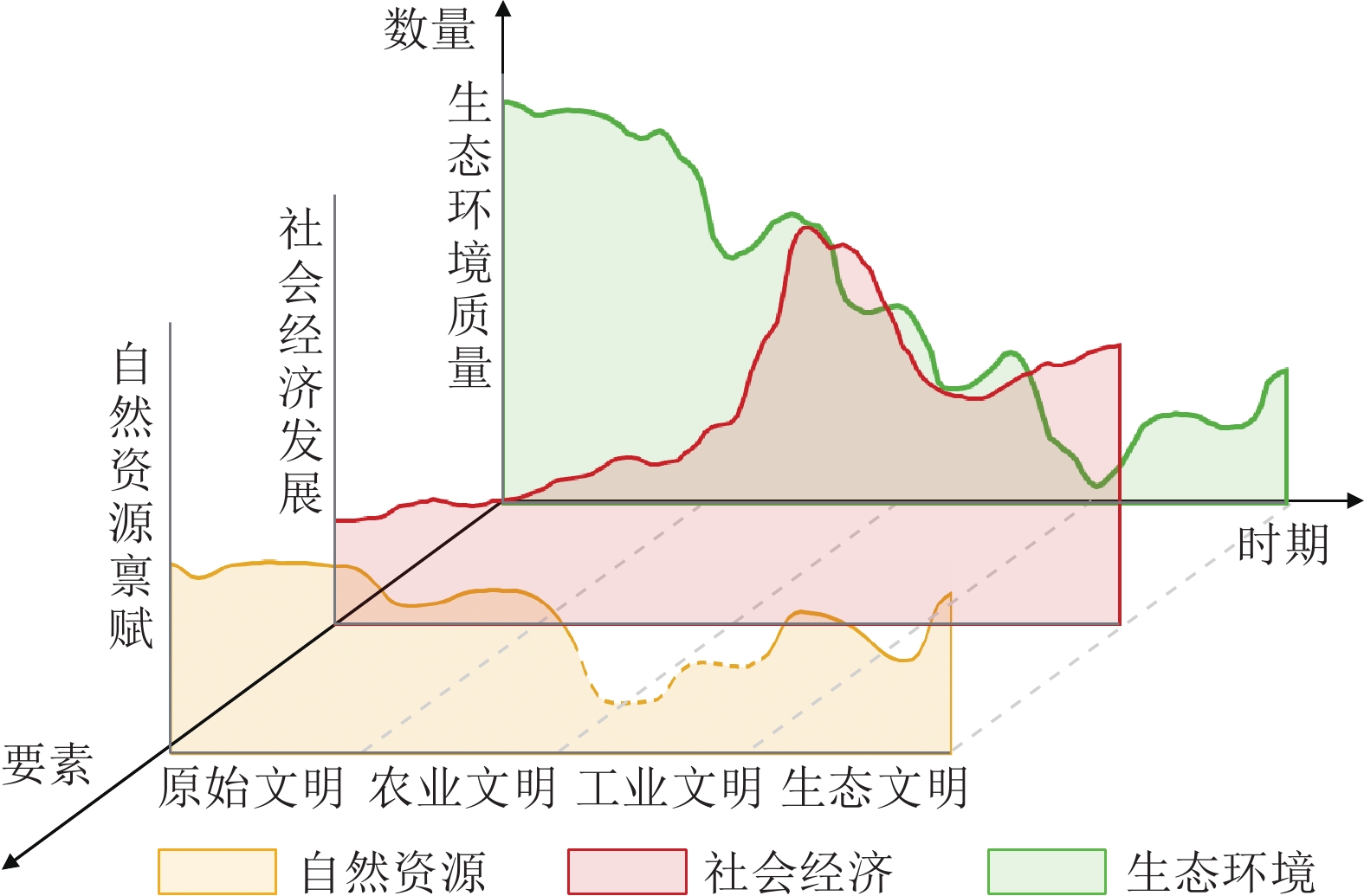
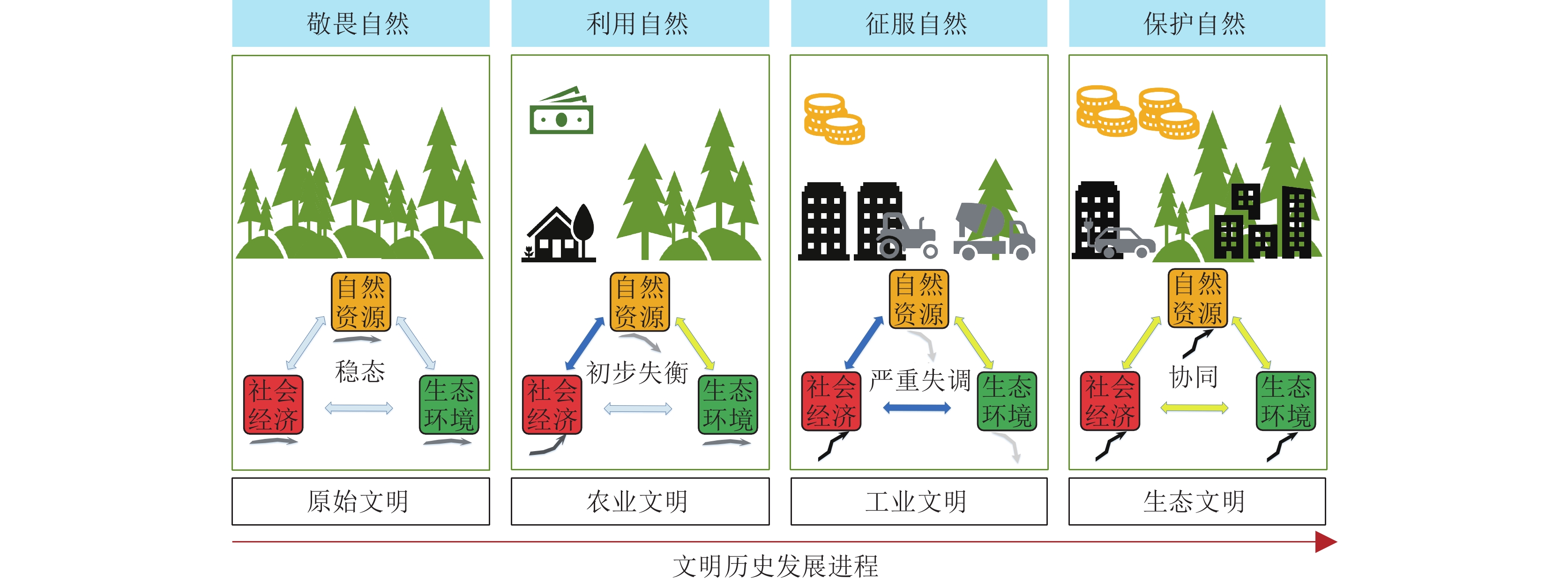
探讨了人与自然生命共同体理念下,自然资源、社会经济与生态环境三者之间的复杂关联及其演化机制。通过解析社会−生态系统的内涵,构建了涵盖自然资源、社会经济与生态环境复合体,旨在揭示三者间的相互作用与影响。进一步分析了从原始文明、农业文明、工业文明、生态文明的历史演进过程中,自然资源、社会经济与生态环境要素的演化路径,通过对历史阶段的深入分析,阐述了从工业文明到生态文明转型时期的启示,为人与自然和谐共生理念下研究三者耦合协调发展提供新的视角。
Abstract:The concept of human−nature community of life emphasizes the interdependent relationship between human and nature, and its intrinsic elements are universally linked and mutually influential. In this study, the interconnections and evolutionary mechanisms among natural resource, social economy, and eco−environment were delved, and then the interrelationship among the elements of the complex system was explored. Further analysis of the evolutionary paths of the elements of natural resources, socio−economic factors, and the ecological environment from primitive civilization, agricultural civilization, and industrial civilization to ecological civilization provides theoretical support and practical guidance for current ecological civilization transformation. This study initially explores the evolving relationships between natural resource, social economy, and eco−environment, providing scientific cognition for the concept of community of life between human and nature and theoretical support for promoting the construction of ecological civilization and achieving the goal of sustainable development.
-

-
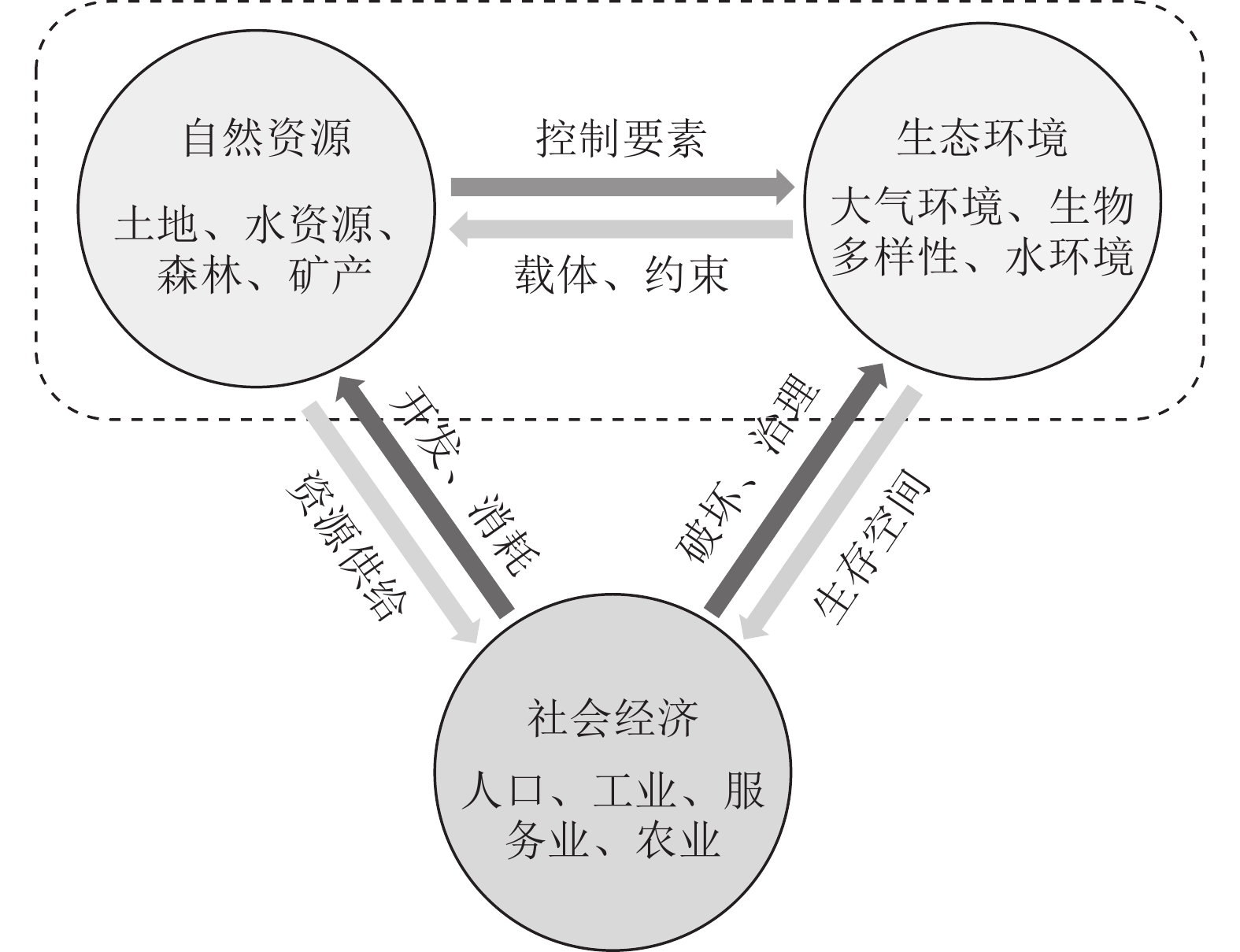
表 1 自然资源−社会经济−生态环境复杂系统的子系统要素
Table 1. Subsystem elements of natural resource-social economy- eco-environment complex system
子系统 组成要素 要素构成 自然
资源能源资源 化石燃料(如石油、天然气、煤炭)、可再生能源(如太阳能、风能、水能、生物能源) 水资源 河流、湖泊、地下水等供应给人类社会使用的水资源 矿产资源 金属矿产(如铁、铜、铝等)、非金属矿产(如石灰石、盐、石膏等) 土地资源 农田、森林、草地、城市用地等,供给农业、林业等 生物资源 野生动植物、海洋生物等 社会
经济生产要素 劳动力、资本、技术等 经济活动 农业、工业、服务业等各个领域的生产、交换和消费活动 生态
环境大气环境 空气质量、气候变化、温室气体排放等 水环境 河流、湖泊、海洋等水体的质量和生态状况 土壤环境 土壤质量、土地退化、土地污染等 生物多样性 地球上各种生物的多样性和物种丰富度 生态系统服务 生态系统为人类社会提供的服务,如水源保护、空气净化、景观游憩、食物生产等 -
[1] Adams D, Adams K, Ullah S, et al. 2019. Globalisation, governance, accountability and the natural resource ‘Curse’: Implications for socio−economic growth of oil−rich developing countries[J]. Resources Policy, 61: 128−140. doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.02.009
[2] Ahmed Z, Asghar M M, Malik M N, et al. 2020. Moving towards a sustainable environment: The dynamic linkage between natural resources, human capital, urbanization, economic growth, and ecological footprint in China[J]. Resources Policy, 67: 101677. doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101677
[3] Chen C, Tabssum N, Nguyen H P. 2019. Study on ancient Chu town urban green space evolution and ecological and environmental benefits[J]. Nature Environment & Pollution Technology, 18(5): 1733−1738.
[4] de Mello K, Taniwaki R H, de Paula F R, et al. 2020. Multiscale land use impacts on water quality: Assessment, planning, and future perspectives in Brazil[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 270: 110879. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110879
[5] Fu B. 2021. Several Key Points in Territorial Ecological Restoration[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 36(1): 64−69 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Fu B, Liu Y X. 2019. The theories and methods for systematically understanding land resource[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 64(21): 2172−2179(in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Fu Y J, Tan C H, Liu X H, et al. 2022. Definition, classification, observation and monitoring of natural resources and their application in territorial planning and governance[J]. Geology in China, 49(4): 1048−1063 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Ge J P, Wang Y B, Zhang H T, et al. 2023. Theoretical Analysis and System Reconstruction of Natural Resource Classification[J], Natural Resource Economics of China, 36(6): 4−13 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Goldberg L, Lagomasino D, Thomas N, et al. 2020. Global declines in human‐driven mangrove loss[J]. Global change biology, 26(10): 5844−5855. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15275
[10] Gu Y, Wu Y, Liu J, et al. 2020. Ecological Civilization and Government Administrative System Reform in China[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 155: 104654.
[11] Kong F B, Yang W C, Xu C Y, 2023. Coordinated relationship and influencing factors of ecological environment and socio−economic coupling of urban agglomeration around Hangzhou Bay in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(6): 2287−2297 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Hassan S T, Baloch M A, Mahmood N, et al. 2019a. Linking Economic Growth and Ecological Footprint through Human Capital and Biocapacity[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 47: 101516. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101516
[13] Hassan S T, Xia E, Khan N H, et al. 2019b. Economic growth, natural resources, and ecological footprints: Evidence from Pakistan[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26: 2929−2938. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3803-3
[14] Lin B, Zhou Y. 2022. Measuring the green economic growth in China: Influencing factors and policy perspectives[J]. Energy, 241: 122518. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.122518
[15] Liu C, Yang M, Hou Y, et al. 2021. Spatiotemporal evolution of island ecological quality under different urban densities: A comparative analysis of Xiamen and Kinmen Islands, Southeast China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 124: 107438. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107438
[16] Ma G X, Zhou X F, Peng F, et al. 2019. Cost of ecological degradation accounting in China in 2015[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 39(6): 1008−1015 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Mahtta R, Fragkias M, Güneralp B, et al. 2022. Urban land expansion: The role of population and economic growth for 300+ cities[J]. Npj Urban Sustainability, 2(1): 5. doi: 10.1038/s42949-022-00048-y
[18] Mcginnis M D, Ostrom E. 2014. Social−ecological system framework: Initial changes and continuing challenges[J]. Ecology and Society, 19(2): 374−386.
[19] Meng F, Guo J, Guo Z, et al. 2021. Urban ecological transition: The practice of ecological civilization construction in China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 755: 142633. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142633
[20] Nathaniel S P, Yalçiner K, Bekun F V. 2021. Assessing the environmental sustainability corridor: Linking natural resources, renewable energy, human capital, and ecological footprint in brics.[J]. Resources Policy, 70: 101924. doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101924
[21] Ostrom E. 2009. A general framework for analyzing sustainability of social−ecological systems[J]. Science, 325(5939): 419−422. doi: 10.1126/science.1172133
[22] Partelow S. 2018. A review of the social−ecological systems framework[J]. Ecology and Society, 23(4): https://www.jstor.org/ stable/26796887.
[23] Peng J, Li B, Dong J Q, et al. 2020. Basic logic of territorial ecological restoration[J]. China Land Science, 34(5): 18−26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Peng J, Lü D N, Zhang T, et al. 2019. Systematic cognition of ecological protection and restoration of mountains−rivers−forests−farmlands− lakes−grasslands[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica , 39(23): 8755−8762 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Shackleton C M, Mograbi P J, Drimie S, et al. 2019. Deactivation of field cultivation in communal areas of south Africa: patterns, drivers and socio−economic and ecological consequences[J]. Land Use Policy, 82: 686−699. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.01.009
[26] Soga M, Gaston K J. 2020. The ecology of human–nature interactions[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 287(1918): 20191882. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.1882
[27] Testa F, Pretner G, Iovino R, et al. 2021. Drivers to green consumption: A systematic review[J]. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23: 4826−4880.
[28] Whitburn J, Linklater W, Abrahamse W. 2020. Meta‐analysis of human connection to nature and proenvironmental behavior[J]. Conservation Biology, 34(1): 180−193. doi: 10.1111/cobi.13381
[29] Wang J, Ying L X, Zhong L N. 2020. Thinking for the transformation of land consolidation and ecological restoration in the new era[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 35: 26−36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Wang J, Zhong L N. 2019. Application of ecosystem service theory for ecological protection and restoration of mountain−river−forest− field−lake−grassland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(23): 8702−8708(in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Wang J Y, Bing L F, Yin Y, et al. 2021. Accounting for the cost of ecological degradation in Fuzhou City, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(11): 3781−3792 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Wang Y J, Liu Y X, Song S, et al. 2021. Research progress of the Water−Food−Energy−Ecosystem Nexus[J]. Advance in Earth Science, 36(7): 684−693 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Wei J Q, Zheng C, Cui M Y, et al. 2023. Analysis on the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem function in loess hilly region[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 31(5): 1490−1500(in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Xiao Y, Wang R, Wang F, et al. 2022. Investigation on spatial and temporal variation of coupling coordination between socioeconomic and ecological environment: A case study of the loess plateau, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 136: 108667. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108667
[35] Xu L, Ao C, Liu B, et al. 2023. Ecotourism and sustainable development: A scientometric review of global research trends[J]. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 25(4): 2977−3003.
[36] Yang Z, Chen Y, Guo G, et al. 2021. Characteristics of land surface temperature clusters: Case study of the central urban area of Guangzhou[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 73: 103140. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2021.103140
[37] Yang Z, Chen Y, Qian Q, et al. 2019. The coupling relationship between construction land expansion and high−temperature area expansion in China’s three major urban agglomerations[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40(17): 6680−6699. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1590877
[38] Yang Z, Chen Y B, Wu Z F, et al. 2018. The coupling between construction land expansion and urban heat island expansion in Guangdong−Hong Kong−Macao Greater Bay[J]. Journal of Geo−information Science, 20(11): 1592−1603 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Zafar M W, Zaidi S A H, Khan N R, et al. 2019. The impact of natural resources, human capital, and foreign direct investment on the ecological footprint: The case of the United States[J]. Resources Policy, 63: 101428. doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101428
[40] Zhang D, Mohsin M, Rasheed A K, et al. 2021. Public spending and green economic growth in Bri region: Mediating role of green finance[J]. Energy Policy, 153: 112256. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112256
[41] Zheng Z H, Wu Z F, Chen Y B, et al. 2021. Analyzing the ecological environment and urbanization characteristics of the Yangtze River delta urban agglomeration based on Google Earth Engine [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(2): 717−729 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] 傅伯杰. 2021. 国土空间生态修复亟待把握的几个要点[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 36(1): 64−69.
[43] 傅伯杰, 刘焱序. 2019. 系统认知土地资源的理论与方法[J]. 科学通报, 64(21): 2172−2179.
[44] 付宇佳, 谭昌海, 刘晓煌, 等. 2022. 自然资源定义、分类, 观测监测及其在国土规划治理中的应用[J]. 中国地质, 49(4): 1048−1063. doi: 10.12029/gc20220402
[45] 葛建平, 王艺博, 张洪涛, 等. 2023. 自然资源分类的学理解析与体系重构[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 36(6): 4−13.
[46] 孔凡斌, 杨文才, 徐彩瑶. 2023. 环杭州湾城市群生态环境与社会经济耦合协调关系及其影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 43(6): 2287−2297.
[47] 马国霞, 周夏飞, 彭菲, 等. 2019. 2015年中国生态系统生态破坏损失核算研究[J]. 地理科学, 39(6): 1008−1015.
[48] 彭建, 李冰, 董建权, 等. 2020. 论国土空间生态修复基本逻辑[J]. 中国土地科学, 34(5): 18−26. doi: 10.11994/zgtdkx.20200427.124442
[49] 彭建, 吕丹娜, 张甜, 等. 2019. 山水林田湖草生态保护修复的系统性认知[J]. 生态学报, 39(23): 8755−8762.
[50] 王军, 应凌霄, 钟莉娜. 2020. 新时代国土整治与生态修复转型思考[J]. 自然资源学报, 35(1): 26−36.
[51] 王军, 钟莉娜. 2019. 生态系统服务理论与山水林田湖草生态保护修复的应用[J]. 生态学报, 39(23): 8702−8708.
[52] 王娇月, 邴龙飞, 尹岩, 等. 2021. 福州市生态系统破坏损失评估[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(11): 3781−3792.
[53] 王奕佳, 刘焱序, 宋爽, 等. 2021. 水−粮食−能源−生态系统关联研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 36(7): 684−693. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2021.073
[54] 魏嘉琪, 郑诚, 崔梦莹, 等. 2023. 黄土丘陵区生物多样性与生态系统功能响应关系的分析[J]. 草地学报, 31(5): 1490−1500.
[55] 杨智威, 陈颖彪, 吴志峰, 等. 2018. 粤港澳大湾区建设用地扩张与城市热岛扩张耦合态势研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 20(11): 1592−1603. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2018.180242
[56] 郑子豪, 吴志峰, 陈颖彪, 等. 2021. 基于Google Earth Engine的长三角城市群生态环境变化与城市化特征分析[J]. 生态学报, 41(2): 717−729.
-



 下载:
下载: