Fluorine enrichment pattern of groundwater in the lower reaches of the Yellow River in southwestern Shandong Province and influencing factors
-
摘要:
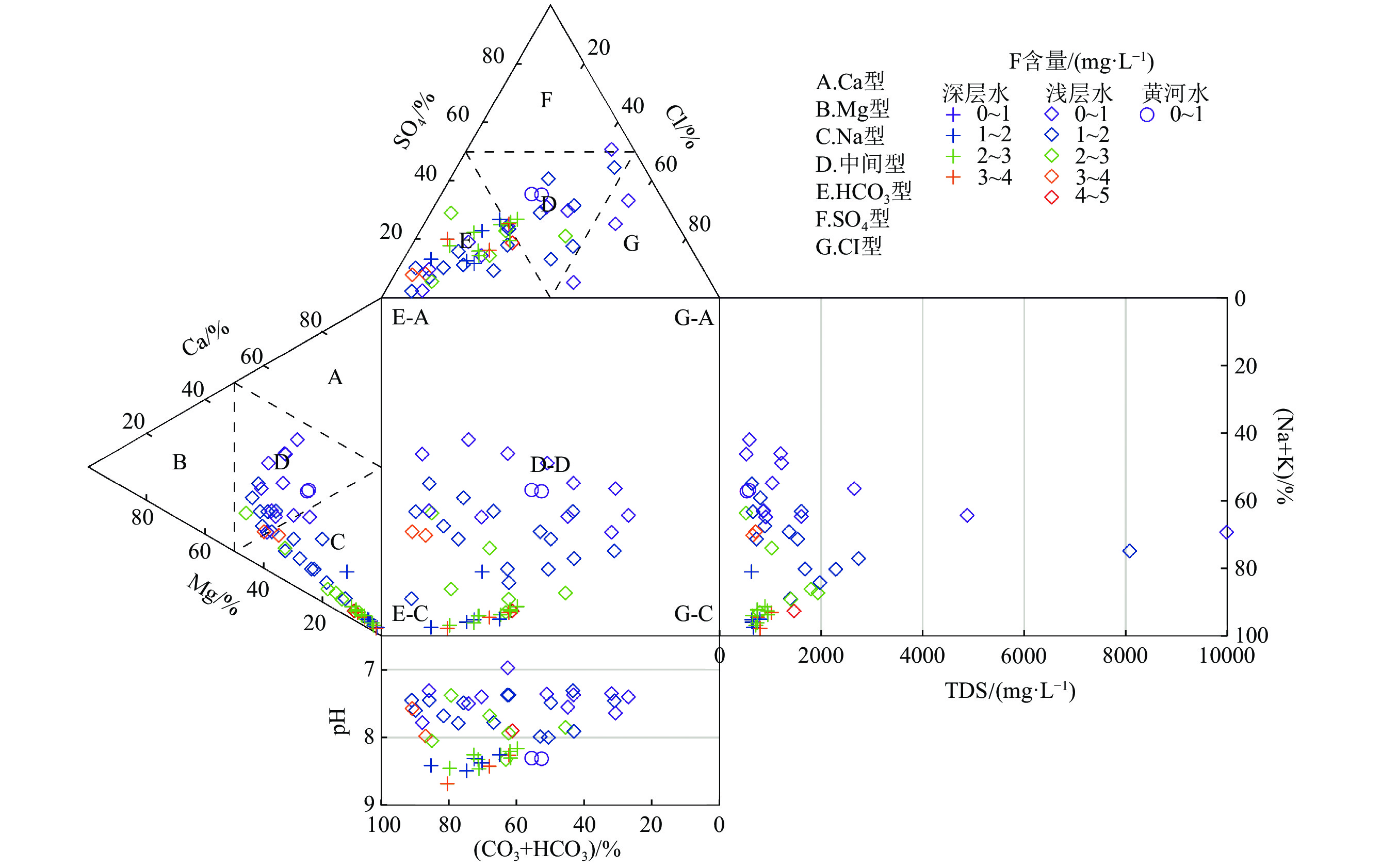
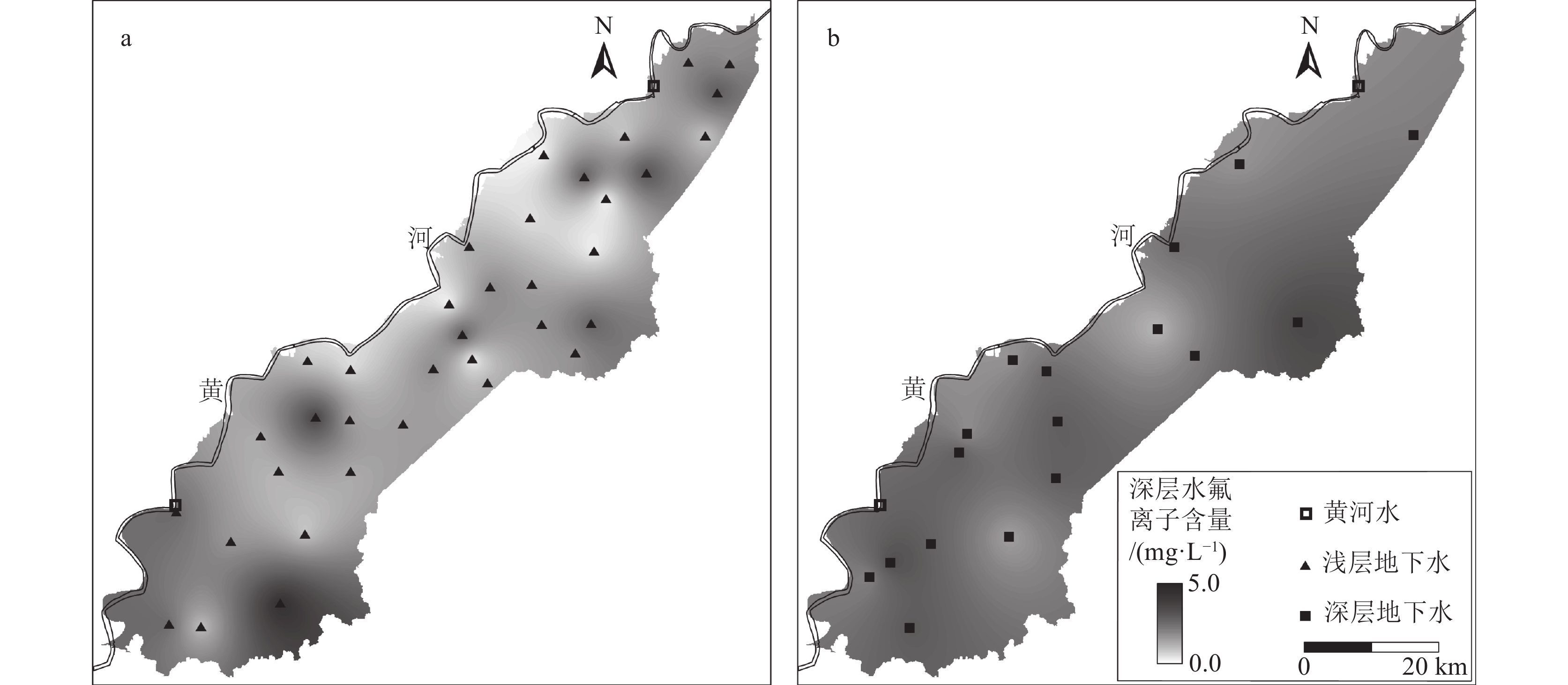
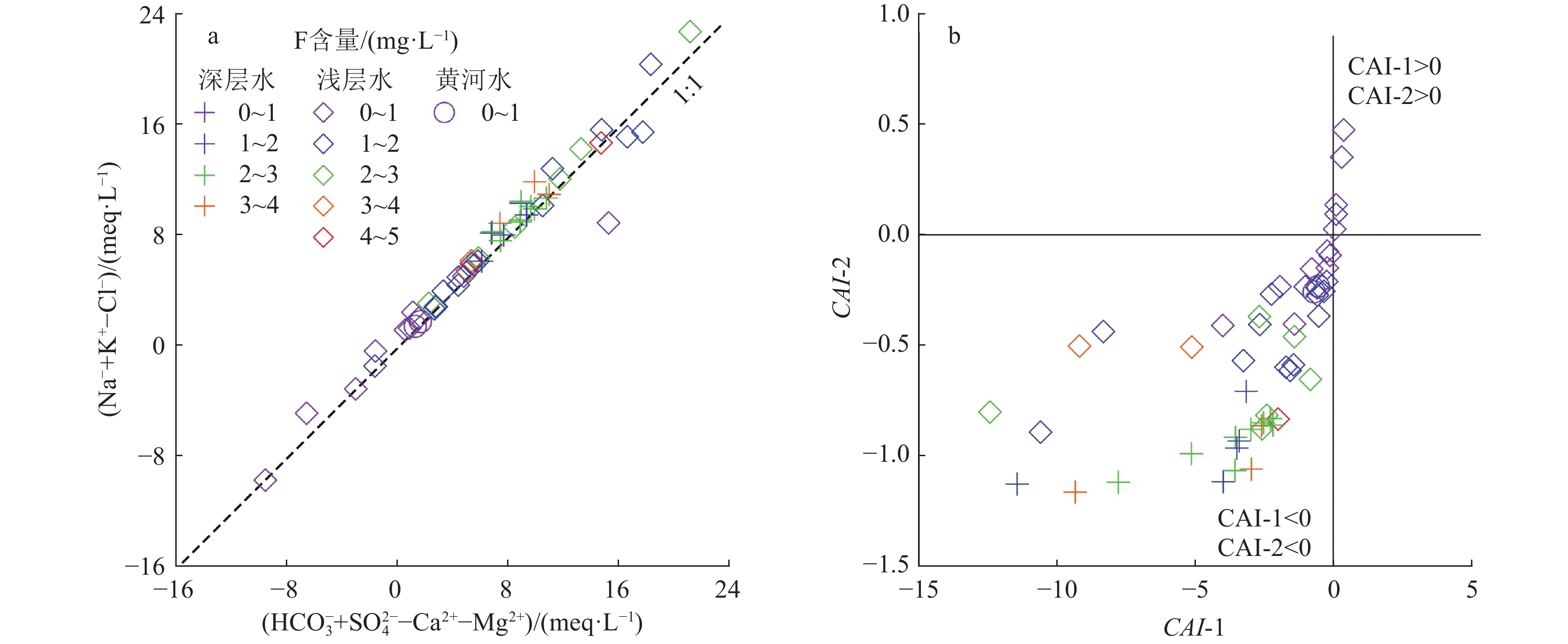
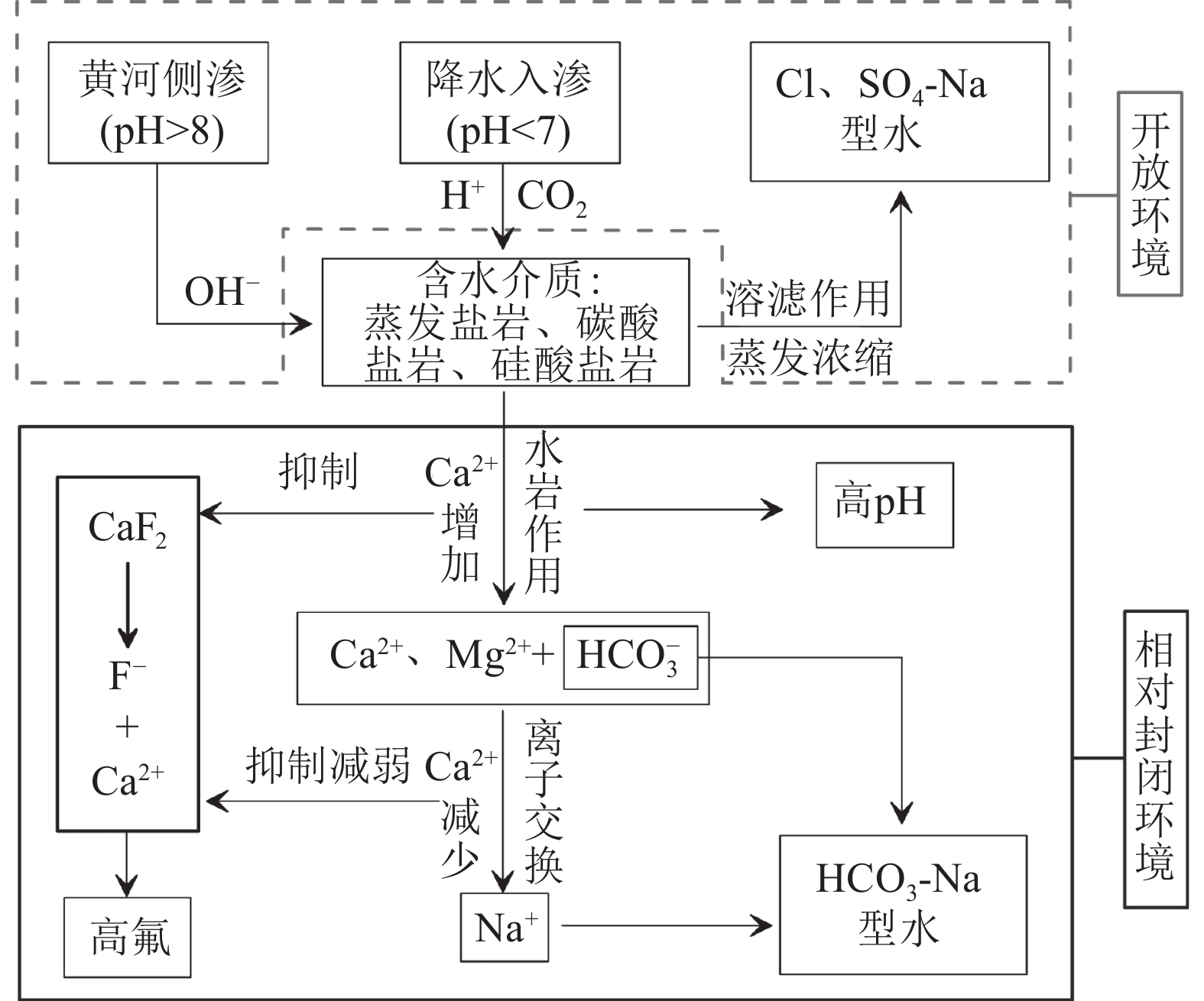
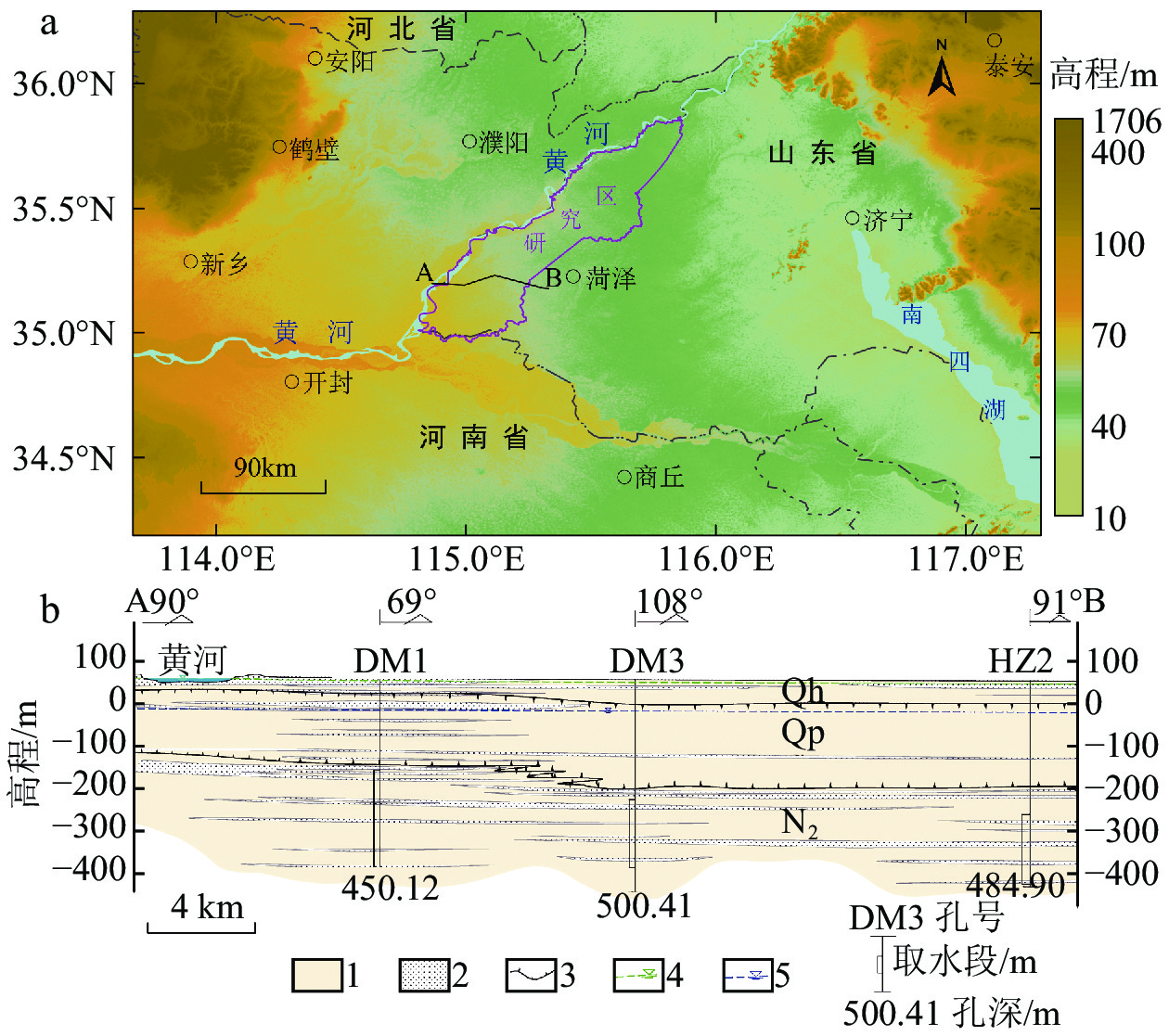
鲁西南平原位于黄河下游,现阶段对该区地下水水化学成因及其对地下水中F元素富集影响机理的研究较少。该研究以鲁西南平原沿黄河地带地下水为主要研究对象,采集浅层地下水样品36件,深层地下水样品16件,黄河水样品2件进行全分析测试;通过统计、相关性分析、水化学模拟等方法手段,计算氯碱指数(CAI),绘制Durov图、Gibbs图、Ca2+/Na+–Mg2+/Na+图、log10(Ca2+)activity–log10(F−)activity图等图件,分析了研究区地下水水化学成因及其富氟机理。结果显示,鲁西南沿黄区浅层及深层地下水化学类型均以HCO3−Na为主,整体偏碱性,地下水氟含量分别为1.59 mg/L、2.35 mg/L,深层水氟含量水平变化程度低于浅层;区内浅层地下水氟与Ca2+含量呈显著负相关,与pH值呈显著正相关,深层地下水中氟与Na+、TDS值呈显著正相关。鲁西南沿黄区地下水氟含量主要来源于萤石(CaF2)的溶解,受水岩作用和阳离子交换作用共同控制下的Ca2+含量制约。此研究揭示了黄河下游主要地下水含水层中氟富集规律和影响因素。
Abstract:The southwestern plain of Shandong Province is located in the lower reaches of the Yellow River, and there are few studies on the chemical genesis of groundwater in this region and the mechanism of its influence on fluorine enrichment in groundwater at this stage. In this study, 36 shallow groundwater samples, 16 deep groundwater samples and 2 Yellow River water samples were collected for comprehensive analysis and testing. By means of statistical, correlation analysis and water chemistry simulation, the chlor−alkali index (CAI) , Durov diagram, Gibbs diagram, Ca2+/Na+−Mg2+/Na+ diagram, log10(Ca2+)activity−log10(F−) activity diagram were constructed, and then the causes of groundwater chemistry and its fluoride enrichment mechanism in the study area were analyzed. The results showed that the chemical types of both shallow and deep groundwater in the study area were mainly HCO3−Na, indicating the overall alkaline, the fluorine content of groundwater was 1.59 mg/L and 2.35 mg/L, respectively, and the level of fluorine content in deep water varied less than that in shallow water. The fluorine content in shallow groundwater in the area was significantly negatively correlated with Ca2+ content and positively correlated with pH value. The fluorine content in deep groundwater was significantly and positively correlated with Na+ and TDS values. The chemical composition of groundwater in the study area is mainly controlled by water−rock action and cation exchange, and the fluorine content of groundwater mainly comes from the dissolution of fluorite (CaF2), and is controlled by Ca2+ content. This study revealed the fluorine enrichment laws and influencing factors in the main groundwater aquifers in the lower reaches of the Yellow River.
-

-
表 1 研究区主要水体化学组分统计
Table 1. Statistics of chemical components of main water bodies in the study area
ρB/
(mg·L−1)黄河水 浅层地下水(n=36) 深层地下水(n=16) 上游 下游 最大值 最小值 平均值 变异系数 最大值 最小值 平均值 变异系数 K+ 3.68 4.21 2.75 0.04 0.74 0.77 1.88 0.41 0.66 0.51 Na+ 96.74 91.37 1853.12 68.44 391.64 1.03 350.53 184.83 274.29 0.14 Ca2+ 59.59 55.18 361.57 8.45 86.39 0.95 28.31 3.47 8.27 0.68 Mg2+ 29.16 28.09 766.19 12.40 115.71 1.24 18.52 1.96 9.53 0.55 Cl− 89.55 93.49 2542.55 21.26 381.45 1.51 150.74 32.14 92.52 0.38 SO42− 160.54 150.21 4085.37 11.67 420.59 1.90 206.97 59.57 125.21 0.39 HCO3− 224.62 195.00 1404.46 419.61 695.03 0.30 530.69 375.18 449.35 0.10 CO32− 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 - 55.84 0.00 14.28 1.38 F− 0.23 0.32 4.52 0.19 1.59 0.64 3.52 1.08 2.35 0.28 CO2 0.00 0.00 15.21 0.00 6.99 0.50 0.00 0.00 0.00 - TDS 573.38 538.13 9986.68 520.96 1767.28 1.11 1018.90 627.64 768.59 0.15 pH 8.31 8.32 8.33 6.97 7.62 0.04 8.69 8.17 8.36 0.02 表 2 研究区地下水氟含量与主要化学指标相关性
Table 2. Correlation between fluoride content and main chemical indexes of groundwater in the study area
水体 相关性参数 Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− pH H2SiO3 TDS 浅层地下水
n=36r −0.07 −0.60 −0.31 −0.30 −0.22 0.30 0.55 −0.17 −0.23 p 0.70 0.00 0.07 0.08 0.21 0.08 0.00 0.32 0.19 深层地下水
n=16r 0.69 −0.34 0.22 0.45 0.41 0.27 0.13 0.15 0.61 p 0.00 0.19 0.40 0.08 0.12 0.31 0.63 0.57 0.01 注: r值带符号“−”,代表负相关关系,否则为正相关关系。相关性统计学显著水平:p≥0.05,不显著;p<0.05,显著;p<0.01,非常显著 表 3 研究区各主要水体矿物饱和指数模拟结果(模拟温度20℃)
Table 3. Statistics of simulation results of mineral saturation index of main water bodies in the study area
水体 SI方解石 SI白云石 SI石膏 SI萤石 黄河水 上游 0.85 1.64 −1.54 −2.37 下游 0.78 1.51 −1.59 −2.10 浅层地下水
(n=36)最大值 0.90 2.29 −0.19 −0.29 最小值 0.18 0.58 −2.81 −2.26 平均值 0.53 1.38 −1.70 −1.13 变异系数 0.38 0.29 −0.35 −0.49 深层地下水
(n=16)最大值 0.86 1.73 −2.00 −1.03 最小值 0.11 0.28 −3.03 −1.93 平均值 0.28 0.90 −2.61 −1.35 变异系数 0.59 0.39 −0.11 −0.20 注: SI为矿物饱和指数 -
[1] Aghapour S, Bina B, Tarrahi M J, et al. 2018. Distribution and health risk assessment of natural fluoride of drinking groundwater resources of Isfahan, Iran, using GIS[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(3): 1–13.
[2] Amini M, Mueller K, Abbaspour K C, et al. 2008. Statistical modeling of global geogenic fluoride contamination in groundwaters[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(10): 3662–3668.
[3] An L S, Zhao Q S, Ye S Y, et al. 2012. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 33(2): 370−378(in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Chen Y. 2020. Spatial evolution characteristics of the Yellow River sediments and the significance of provenance tracing[D]. Doctoral Thesis of Chang’an University: 99–116 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, National Standardization Administration. 2017. Standard for groundwater quality (GB/T 14848—2017)[S](in Chinese).
[6] Gong J S, Ye N J, Ge W Y, et al. 2010, The relationship between fluorine in geological environment and endemicfluorosis in Huaihe River basin[J]. Geology in China, 37(3): 633–639(in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Habuda-Stanić M, Ergović Ravančić M, Flanagan A. 2014. A Review on Adsorption of Fluoride from Aqueous Solution[J]. Materials, 7(9): 6317–6366.
[8] Han S, Han J Z, Zhao X, et al. 2019. A Pearson correlation coefficient improved by spatial weight[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 54(6): 1363−1370,1177 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] He J, Zhang F C, Han S B, et al. 2010. The distribution and genetic types of high - fluoride groundwater in northern China[J]. Geology in China, 37(3): 621−626 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Liu C H, Wang W, Yang L Z, et al. 2021. Driving mechanisms of fluorine ennrichment characteristics in groundwater, Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(6): 1962−1972(in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Liu H Y, Liu M H, Zhang W M, et al. 2022. Distribution and fractionation of rare earth elements in high - fluoride groundwater from the North China Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 29(3): 129−144(in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Liu J, Peng Y, Li C, et al. 2021. A characterization of groundwater fluoride, influencing factors and risk to human health in the southwest plain of Shandong Province, North China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 207: 111512.
[13] Liu H, Guo H, Xing L, et al. 2016. Geochemical behaviors of rare earth elements in groundwater along a flow path in the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 117: 33–51.
[14] Liu J J, Gao Z J, Wang M, et al. 2019. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls in the groundwater of the Yarlung Zangbo River Valley, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78: 76.
[15] Luo W T, Gao X B, Zhang X. 2018. Geochemical processes controlling the groundwater chemistry and fluoride contamination in the Yuncheng Basin, China: An area with complex hydrogeochemical conditions[J]. Plos One, 13(7): e0199082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199082
[16] Mao R Y, Guo H M, Jia Y F, et al. 2016. Distribution characteristics and genesis of fluoride groundwater in the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(2): 260–268(in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Mo B B, Lian B. 2010. Study on feldspar weathering and analysis of relevant impact factors[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(3): 281−289(in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Nordstrom D K, Smedley P L. 2022. Fluoride-in-Groundwater[M]. Canada, Guelph, Ontario: The Groundwater Project: 10–11.
[19] Pan H Y, Zou C J, Bi J B, et al. 2021. Hydrochemical characteristics and fluoride enrichment mechanisms of high-fluoride groundwater in a typical piedmont proluvial fan in Aksu area, Xinjiang, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 40(3): 194−203(in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Pang X G, Gao Z J, Bian J C, et al. 2010. The Correlation Between Endemic Diseases and Eco-geochemical Environment in the Lower Yellow River Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 37(3): 824−830(in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Scholler H. 1967. Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources: in methods and technics of groundwater investigation and development[J]. Water Research, 33: 44−52.
[22] Song X G, Lu Y, Liang S K, et al. 2022. Analysis of high-fluoride groundwater formation mechanisms and assessment of health risk in Baxia region, Zhangjiakou[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 41(1): 240−250, 259(in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] State Administration for Market Regulation, National Standardization Administration. 2022. Standards for drinking water quality (GB 5749—2022)[S] (in Chinese).
[24] Wang X X, Sun M H. 2017. Chemical characteristics analysis on precipitation in Jinan[J]. Journal of Environmental Management College of China, 27(1): 53−56(in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Wu C, Wu X, Zhang Y S, et al. 2018. Distribution characteristics and genesis of high-fluoride groundwater in the Niuxin Mountain, Qinhuangdao[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 25(4): 307−315(in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Wu Y F, Li H X, Sun D Y, et al. 2022. Mechanism of high fluorine groundwater in the groundwater over-exploitation area of North China Plain[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 29(3): 127−135(in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Xing L N, Guo H M, Wei L, et al. 2012. Evolution Feature and Gensis of Fluoride Groundwater in Shallow Aquifer from North China Plain[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environmen, 34(4): 57−67 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Xu X, Xiao P P, Sun Y P, et al. 2020. Study on the Characteristics and Physical Causes of Groundwater Fluoride and Iodide Over the Yellow River Alluvial Plain in the Southwest of Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 36(2): 186−192 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Yan J Y, Hu J M, Wang D M, et al. 2021. The critical geological events in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain during the Late Cenozoic[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 40(5): 623−648(in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Yan Z W, Liu H L, Tao Z T. 2011. Temperature effect on carbonic acid balance in water[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 30(2): 128−131(in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Yang L Z, Lin S H, Tong Z H, et al. 2013. Discussion about the causation of sodium bicarbonate type watercome into being in the midland of Huabei Plain[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering. 24(6): 34–37, 42(in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] 安乐生, 赵全升, 叶思源, 等. 2012. 黄河三角洲浅层地下水化学特征及形成作用[J]. 环境科学, 33(2): 370−378.
[33] 陈垚. 2020. 黄河泥沙沉积物演化特征及物源示踪[D]. 长安大学博士学位论文: 99–116.
[34] 龚建师, 叶念军, 葛伟亚, 等. 2010. 淮河流域地氟病环境水文地质因素及防病方向的研究[J]. 中国地质, 37(3): 633−639. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.014
[35] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 2022. 生活饮用水卫生标准(GB 5749—2022)[S].
[36] 韩晟, 韩坚舟, 赵璇, 等. 2019. 距离权重改进的Pearson相关系数及应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 54(6): 1363−1370,1177.
[37] 何锦, 张福存, 韩双宝, 等. 2010. 中国北方高氟地下水分布特征和成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 37(3): 621−626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.012
[38] 刘春华, 王威, 杨丽芝, 等. 2021. 山东省地下水氟富集规律及其驱动机制[J]. 地质学报, 95(6): 1962−1972. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.06.020
[39] 刘海燕, 刘茂涵, 张卫民, 等. 华北平原高氟地下水中稀土元素分布和分异特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(3): 129–144.
[40] 毛若愚, 郭华明, 贾永锋, 等. 2016. 内蒙古河套盆地含氟地下水分布特点及成因[J]. 地学前缘, 23(2): 260−268.
[41] 莫彬彬, 连宾. 2010. 长石风化作用及影响因素分析[J]. 地学前缘, 17(3): 281−289.
[42] 潘欢迎, 邹常健, 毕俊擘, 等. 2021. 新疆阿克苏典型山前洪积扇内高氟地下水的化学特征及氟富集机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 40(3): 194−203.
[43] 庞绪贵, 高宗军, 边建朝, 等. 2010. 山东省黄河下游流域地方病与生态地球化学环境相关性研究[J]. 中国地质, 37(3): 824−830. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.040
[44] 宋晓光, 芦岩, 梁仕凯, 等. 2022. 张家口坝下地区高氟地下水成因分析与健康风险评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 41(1): 240−250,259.
[45] 王秀秀, 孙明虎. 2017. 济南市大气降水化学特征分析[J]. 中国环境管理干部学院学报, 27(1): 53−56.
[46] 吴初, 武雄, 张艳帅, 等. 2018. 秦皇岛牛心山高氟地下水分布特征及成因[J]. 地学前缘, 25(4): 307−315.
[47] 吴艳飞, 李和学, 孙丹阳, 等. 2022. 华北平原超采区高氟地下水形成机理探究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 29(3): 127−135.
[48] 邢丽娜, 郭华明, 魏亮, 等. 2012. 华北平原浅层含氟地下水演化特点及成因[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 34(4): 57−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2012.04.008
[49] 徐雄, 肖培平, 孙艳亭, 等. 2020. 鲁西南黄河冲积平原地下水氟碘特征及成因分析[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 36(2): 186−192.
[50] 闫纪元, 胡健民, 王东明, 等. 2021. 黄淮海平原晚新生代重大地质事件[J]. 地质通报, 40(5): 623−648.
[51] 闫志为, 刘辉利, 陶宗涛. 2011. 温度对水中碳酸平衡的影响浅析[J]. 中国岩溶, 30(2): 128−131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.02.002
[52] 杨丽芝, 林尚华, 佟照辉, 等. 2013. 华北平原中部重碳酸钠型水的成因探讨[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 24(6): 34−37,42. doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2013.06.008
[53] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 2017. 地下水质量标准(GB/T 14848—2017)[S].
-



 下载:
下载: