Geochemical characteristics and hydrocarbon generation potential of Eocene oil shale in Songxi Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin
-
摘要:
研究目的 近期在松西凹陷钻遇了一套厚层的始新统油页岩,是琼东南盆地首次钻遇油页岩。为进一步查明该源岩的生烃潜力,进而推动下步勘探。
研究方法 通过钻井记录、元素检测及系列地球化学测试,研究油页岩的特征及形成环境,并对这套油页岩资源潜力进行了预测。
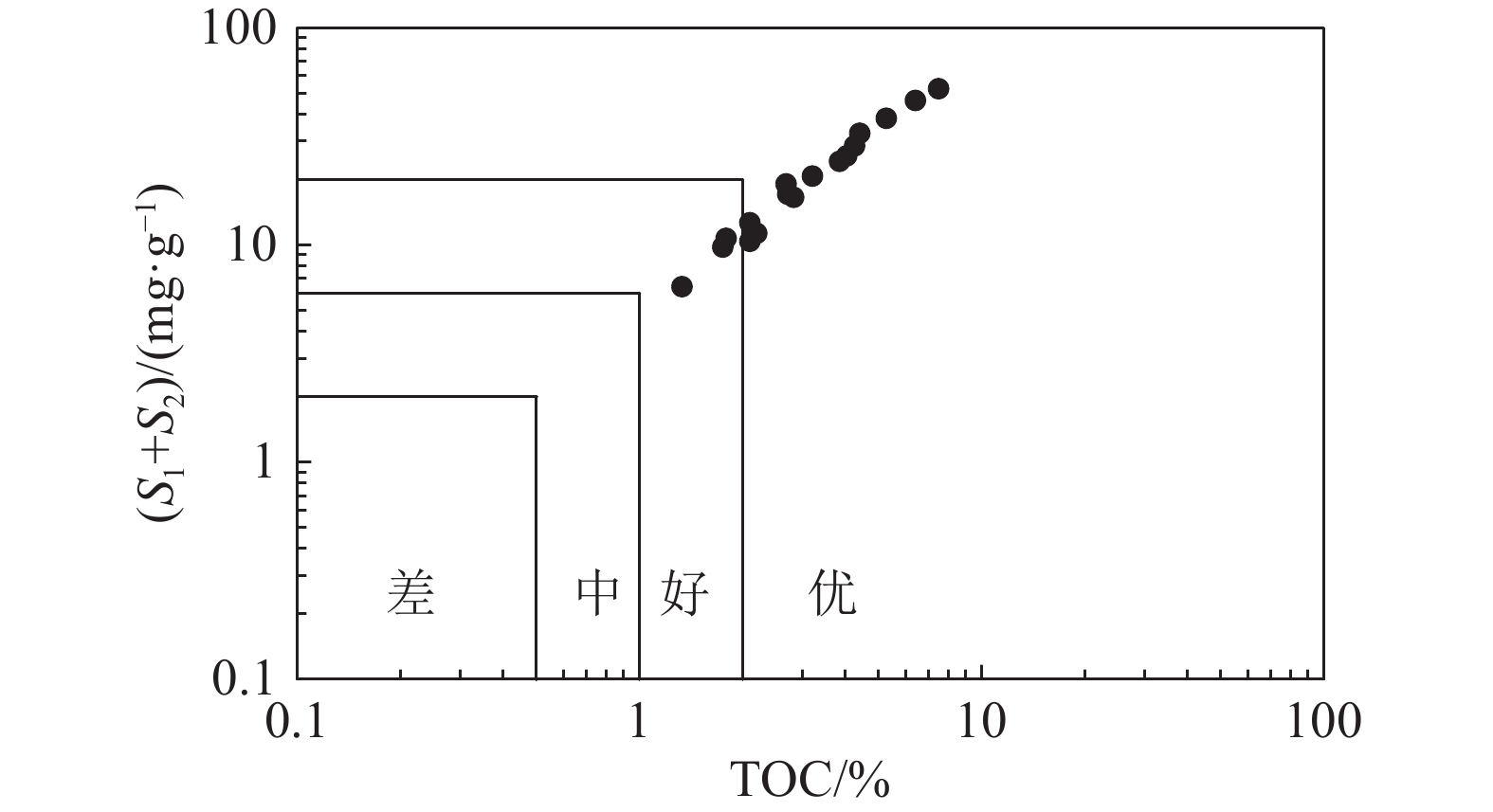
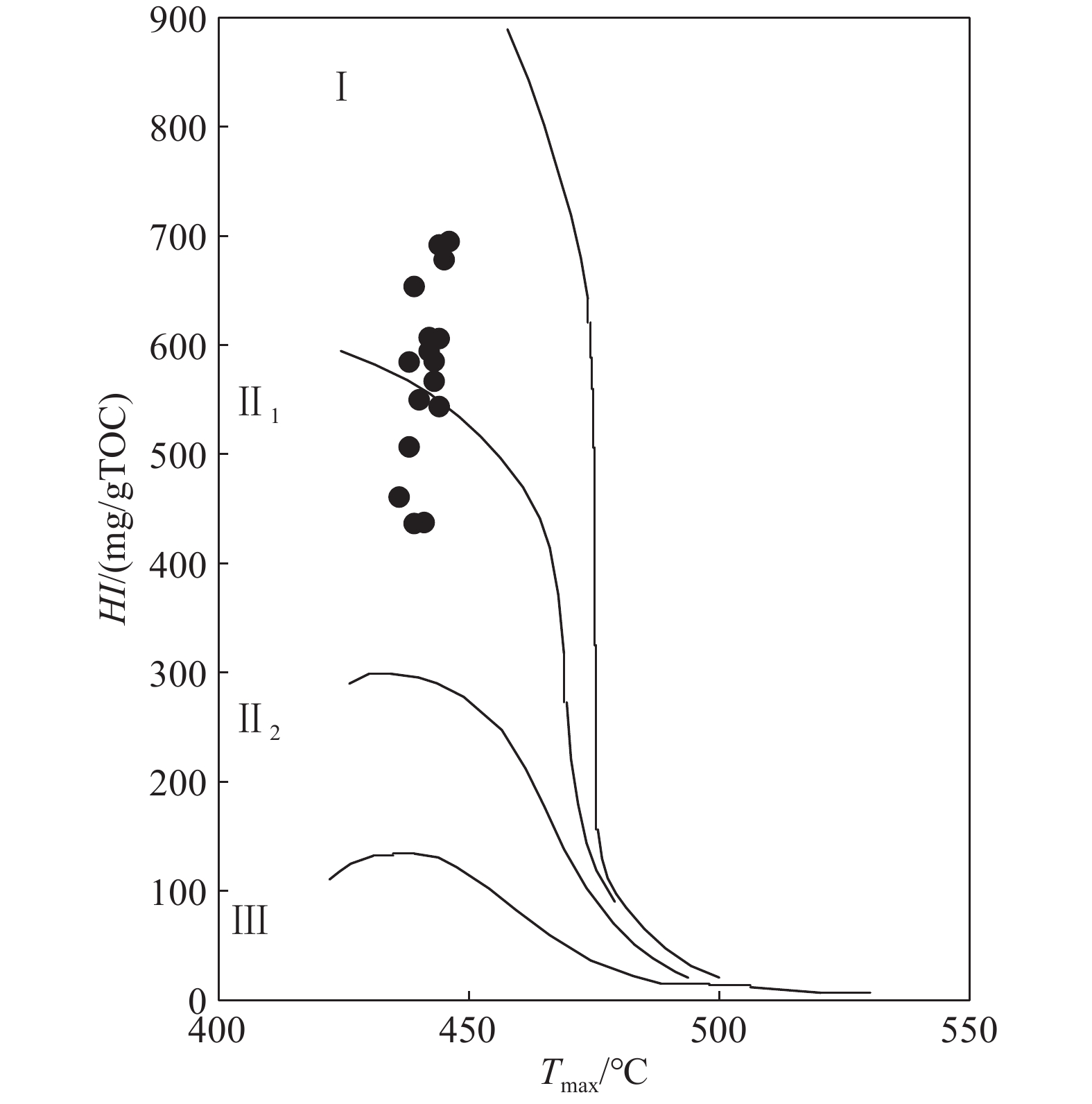
研究结果 分析显示,这套油页岩总有机碳含量(TOC)平均为3.33%,热解生烃潜量(S1+S2)平均为22.2 mg/g,氢指数(HI)平均606 mg/gTOC。沉积环境为温暖半湿润的还原淡水湖泊环境,具有低等水生生物和高等陆生植物混源输入的特征。
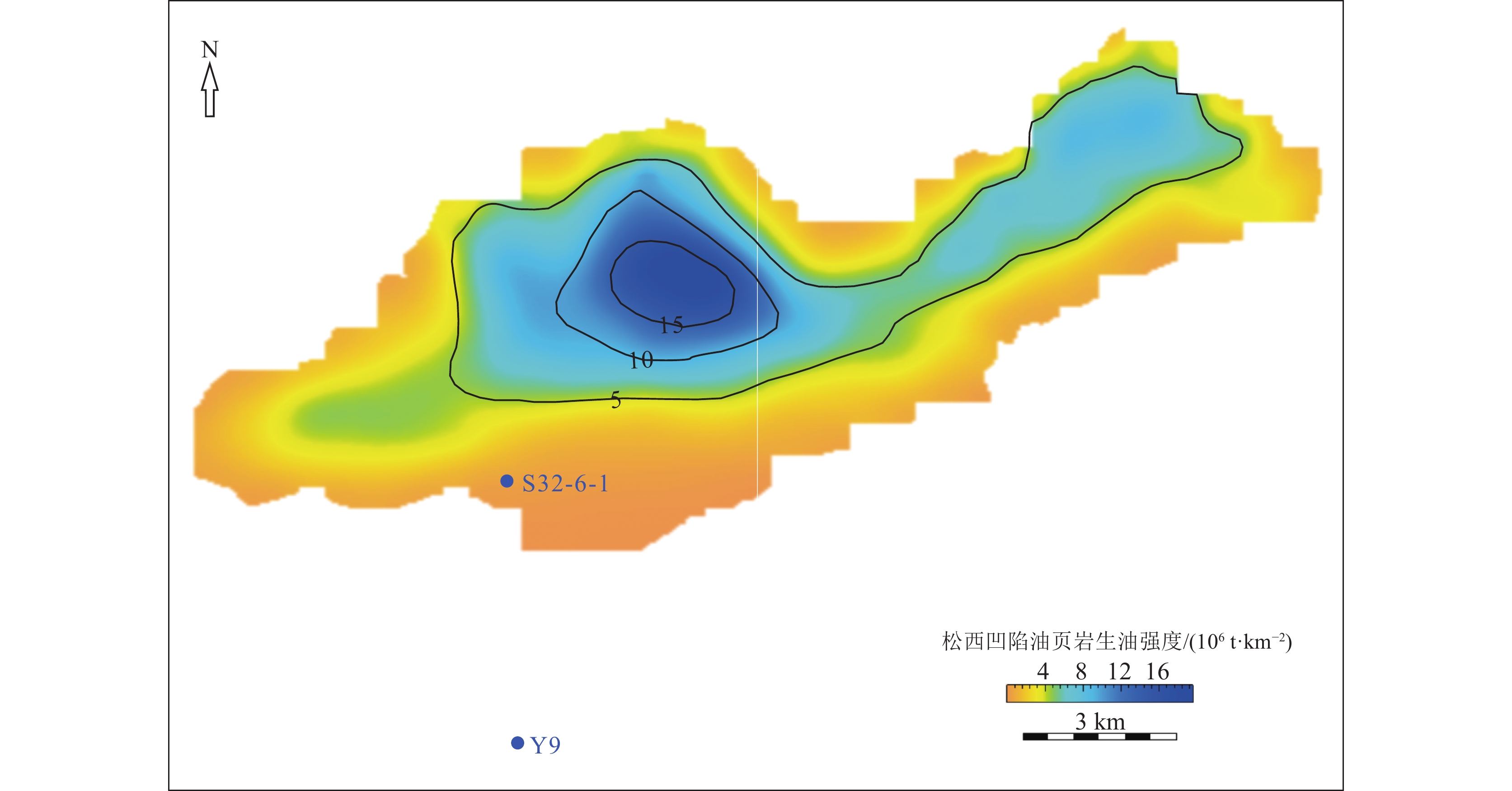
结论 研究表明,该套油页岩有机质丰度高、类型好、古生产力高,为好—优质烃源岩,其原油资源量约为4140×104 t,原油资源潜力巨大,常规油气和页岩油均有较大的勘探潜力。
Abstract:Objective Recently, a set of thick Eocene oil shale was drilled in Songxi Sag, which is the first time the oil shale was drilled in Qiongdongnan Basin. In order to implement the hydrocarbon generation potential of the Eocene oil shale and promote further exploration in songxi sag, Qiongdongnan Basin.
Methods this article is based on drilling records, elemental assays and a series of geochemical tests to study the characteristics and formation environment of oil shale and predict the resource potential of this oil shale.
Results The analysis results show that the average Total Organic Carbon (TOC) of this set of oil shale was 3.33%, the average pyrolysis hydrocarbon potential (S1+S2) was 22.2 mg/g, and the average Hydrogen Index (HI) was 606 mg/g TOC. The sedimentary environment of this oil shale is a warm semi−humid reduced freshwater lake environment, which has the characteristics of mixed input of lower aquatic organisms and higher terrestrial plants.
Conclusions It shows that the oil shale has high organic matter abundance, good type and high paleoproductivity, which is a good to high−quality source rock. Its crude oil resources are about 41.4 million tons, with huge potential for crude oil resources.Both conventional oil and gas and shale oil have great exploration potential.
-
Key words:
- oil shale /
- hydrocarbon generation potential /
- biomarker /
- Songxi Sag /
- Qiongdongnan Basin
-

-
表 1 陆相烃源岩有机质成烃演化阶段划分及判别指标(据SY/T 5735—1995)
Table 1. Hydrocarbon generation and evolution stages of organic matter in continental source rocks
演化阶段 未成熟 低成熟 成熟 高成熟 过成熟 Ro/% <0.5 0.5~0.7 0.7~1.3 1.3~2 >2 Tmax/℃ <435 435~440 440~450 450~580 >580 ɑɑɑ-C2920S/(20S+20R) <0.2 0.2~0.4 >0.4 — — C29ββ/(ββ+ɑɑ) <0.2 0.2~0.4 >0.4 — — 表 2 松西凹陷始新统油页岩生物标志化合物参数
Table 2. Biomarker parameters of Eocene oil shale in Songxi Sag
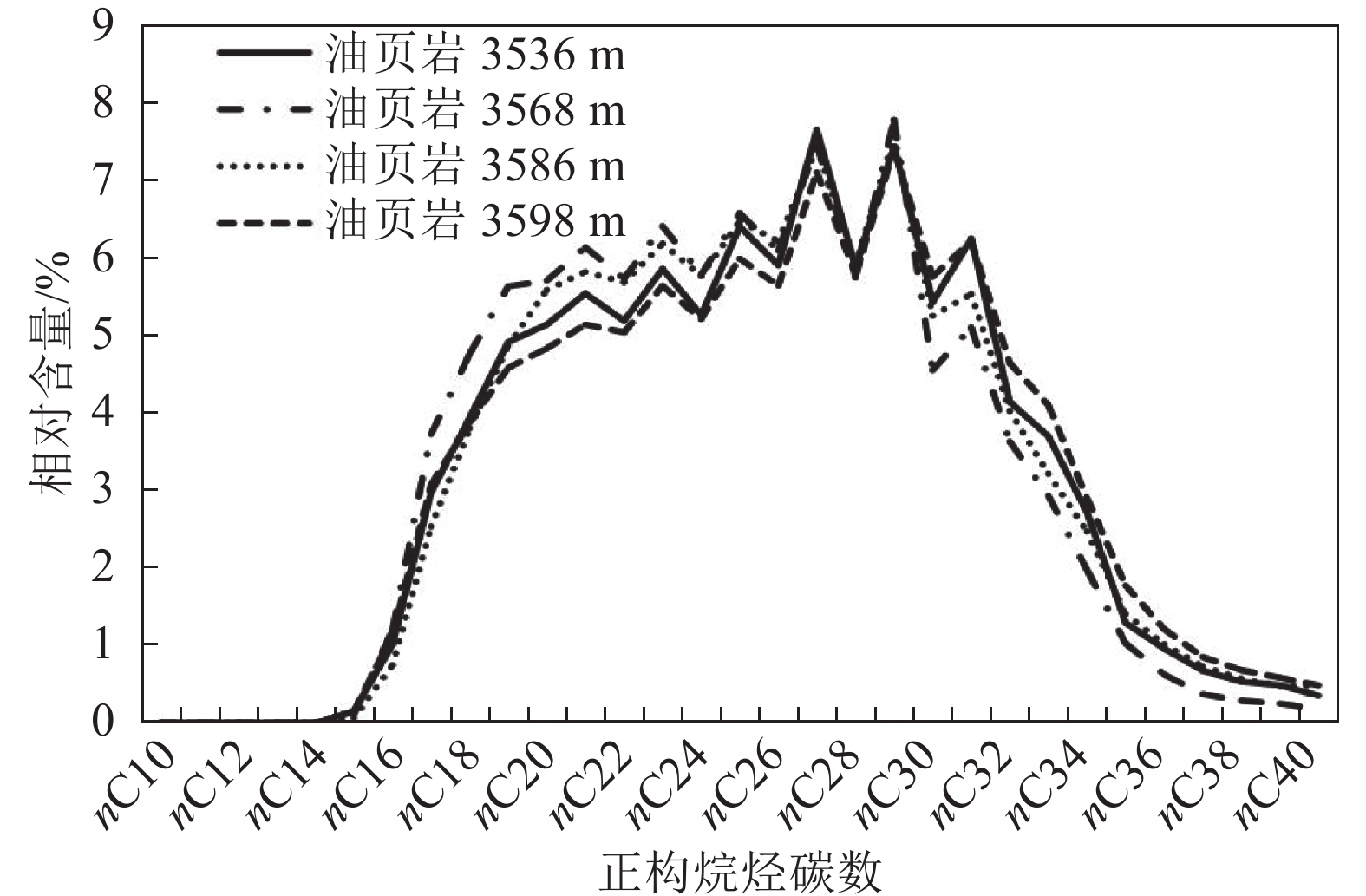
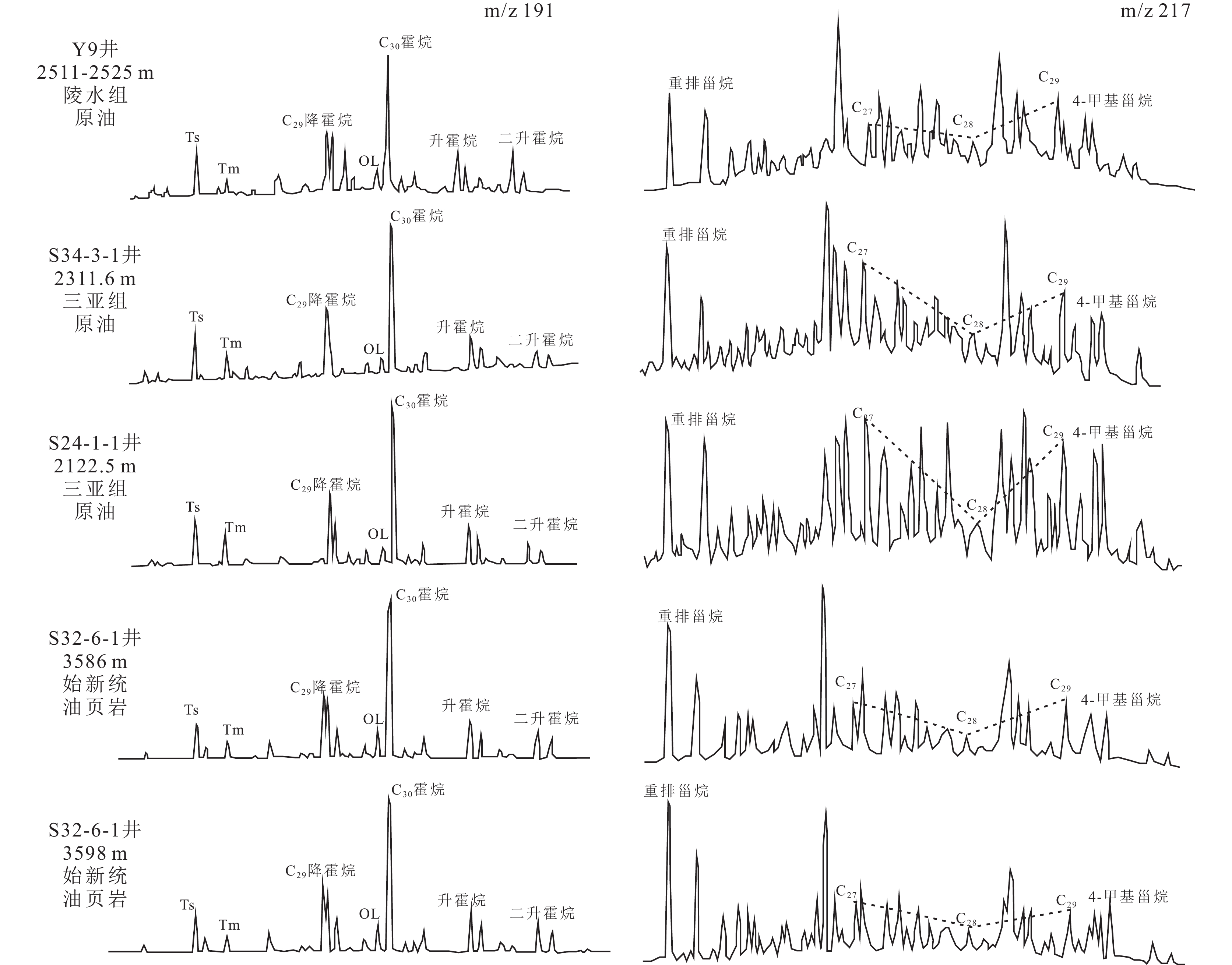
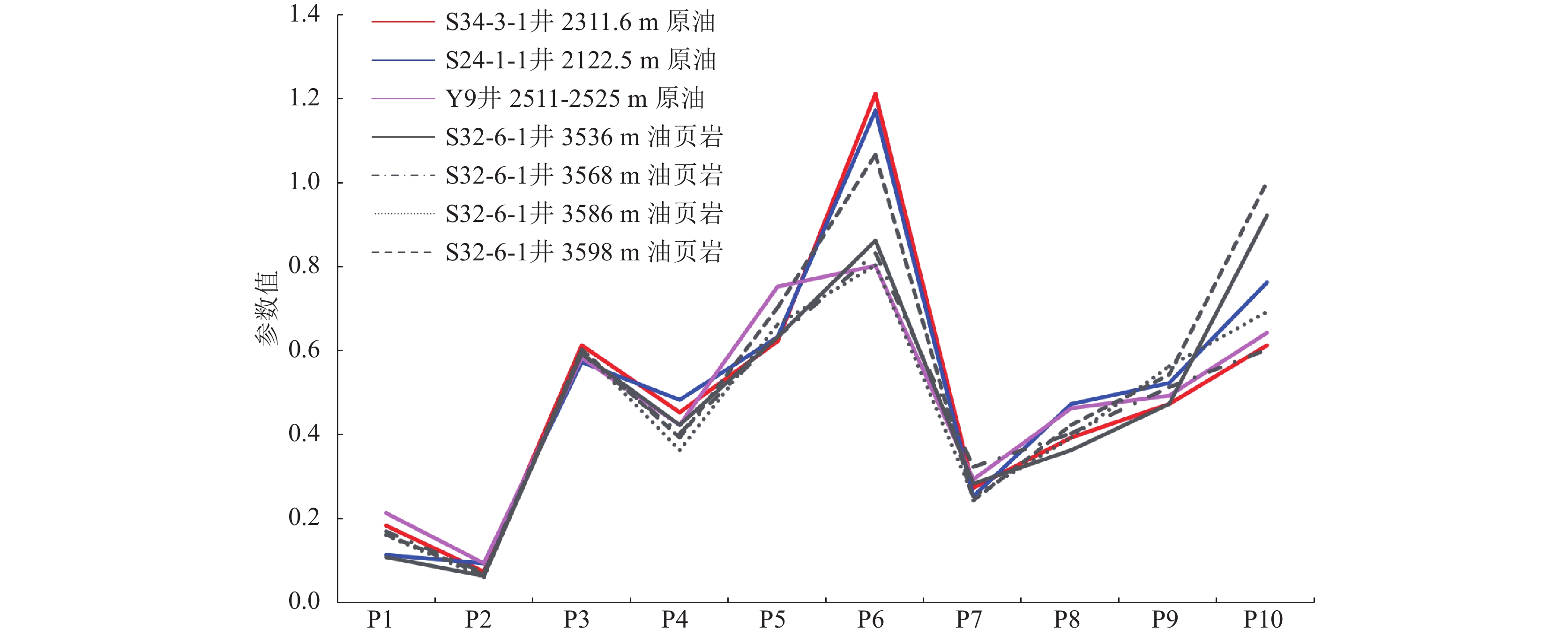
生标参数 深度/m 3536 3568 3586 3598 (nC21+nC22)/(nC28+nC29) 0.81 0.88 0.85 0.77 CPI 1.24 1.26 1.19 1.19 OEP 1.27 1.44 1.31 1.25 Pr/Ph 2.2 2.32 2.22 2.65 Pr/nC17 1.99 1.3 1.22 2.01 Ph/nC18 0.68 0.44 0.36 0.6 C19TT/C23TT 0.19 0.36 0.4 0.25 C24TeT/C26TT 0.77 1.4 1.22 0.91 OL/C30H 0.1 0.17 0.16 0.16 Ga/C30H 0.06 0.07 0.06 0.06 Ts/Tm 1.71 1.74 1.96 2.35 C27/C29ɑɑɑR 0.86 0.83 0.8 1.06 C2920S/(20S+20R) 0.36 0.4 0.39 0.42 C29ββ/(ββ+ɑɑ) 0.47 0.51 0.56 0.54 4-甲基甾烷/C29甾烷 0.92 0.6 0.69 1 -
[1] Bao J P, Zhu C S, Wang L Q. 2010. Geochemical characteristic comparison of crude oil samples from the western Qaidam Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 31(3): 353−359 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Cao T T, Liu H, Xiao J Y, et al. 2024. Paleoenviromental reconstruction and organic matter accumulation mechanism for Youganwo Formation oil shale in Maoming Basin[J]. Earth Science, 49(4): 1367−1384 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Chen J P, Wang X L, Deng C P, et al. 2016. Geochemical features of source rock and crude oil in the Junggar basin, Northwest China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(1): 37-67 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Fan C W, Hu L, Li M, et al. 2021. Evaluation method of trap effectiveness in deep water area of Qiongdongnan basin and its application[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 33(5): 1−13 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Hao F, Zhou X, Zhu Y, et al. 2011. Lacustrine source rock deposition in response to co−evolution of environments and organisms controlled by tectonic subsidence and climate, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 42(4): 323−339. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.01.010
[6] He J X, Li F Y, Wang H J, et al. 2020. Genetic mechanism of deep−water basin and their effects on oil and gas resources on the continental margin of the Northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 36(3): 1−11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Huang B J, Wang Z F, Liang G. 2014. Natural gas source and migration−accumulation pattern in the central canyon, the deep water area, Qiongdongnan basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 26(5): 8−14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Huang Q, Chen R T, Peng X B, et al. 2022. Characteristics and geological significance of bimarkers from the Paleogene source rocks in Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Techenology, 41(3): 180−192 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Kong Q Y, Zhou H, Li T, et al. 1987. Discussion on the indexes of biomarker compounds[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute, 11(3): 9−15(in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Liu X M, Zhang C. 2011. Numerical simulation study on the maturity history of source rocks in the Wan’an Basin in the southern South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 18(2): 34−37,113 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Lu S F, Zhang M. 2008. Petroleum Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press: 65−77 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Luo L R, Li J F, Yang W W, et al. 2022. Characteristics and hydrocarbon generation Potential of Chang 9 source rocks on Yishan Slope, Ordos Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 43(3): 278−284 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Mao X L, Zhu J T, Song P, et al. 2021. Preliminary study on the distribution pattern of gas hydrate stability zone in the deep−water areas of Qiongdongnan basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 37(10): 58−63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Moradi A V, Akkaya A S. 2016. Geochemistry of the Miocene oil shale (Hancili Formation) in the Cankiri−Corum Basin, Central Turkey: Implications for paleoclimate conditions, source−area weathering, provenance and tectonic setting[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 341(7): 289−303.
[15] Peters K E, Walters C C, Mokkwan J M. 2005. The Biomarker Guide: Biomarker and Isotopes in Petroleum and Earth History[M]. London: Cambridge University Press: 205−215.
[16] Sarki Yandoka B M, Abdullah W H, Abubakar M B, et al. 2014. Geochemical characterization of Early Cretaceous lacustrine sediments of Bima Formation, Yola Sub−basin, northern Benue Trough, NE Nigeria: Organic matter input, preservation, paleoenvironment and palaeoclimatic conditions[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 61(3): 82−94.
[17] Sun S S, Yao Y B, Lin W. 2015. Element geochemical characteristics of the oil shale and the paleo−lake environment of the Tongchuan area, southern Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 34(3): 642−645 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Wang T G, Zhong N N, Hou D J, et al. 1995. Genetic mechanism and occurrence of immature Hydrocarbon[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press: 32−54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Wang C J, Zhang H, Li S Y, et al. 2018. Selection of organic matter maturity evaluation parameters based on molecular markers and analysis of their scope of application[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 37(4): 202−211 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Wang Y, Li X Q, Wang G, et al. 2018. Geochemical characteristics and hydrocarbon generation potential of Miocene marine source rocks in the Ying−Qiong Basin[J]. Geoscience, 32(3): 500−510 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Xiao H, Li M J, Yang Z, et al. 2019. Distribution patterns and geochemical implications of C19~C23 tricyclic terpanes in source rocks and crude oils occurring in various depositional environments[J]. Geochimica, 48(2): 161−170 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Xu X D, Zhang Y Z, Liang G, et al. 2016. Hydrocarbon source condition and accumulation mechanism of natural gas in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 27(11): 1985−1992 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Yang Z G, Feng Z Q, Wang A G, et al. 2022. Characteristics and dominating genesis factors of main source rocks in Persian gulf basin[J]. Offshore Oil, 42(1): 1−12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Yu T T, Liu Z J, Wang J X, et al. 2022. Lower Permian Irati Formation oil shale geochemical features and geological significance in Parana Basin, Brazil[J]. Goal Geology of China, 34(8): 1−8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Zhang G C, Mi L J, Wu S G, et al. 2007. Deep water area: the new prospecting targets of northern continental margin of South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 28(2): 15−21 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Zhu W L, Zhang G C, Gao L. 2008. Geological characteristics and exploration objectives of hydrocarbons in the northern continental margin basin of South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 29(1): 1−9 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00742.x
[27] Zhu W L, Zhang G C, Yang S K, et al. 2007. Natural gas geology of continental margin basin in northern South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press: 1−15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] 包建平, 朱翠山, 汪立群. 2010. 柴达木盆地西部原油地球化学特征对比[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 31(3): 353−359. doi: 10.11743/ogg20100313
[29] 曹涛涛, 刘虎, 肖娟宜, 等. 2024. 茂名盆地油柑窝组油页岩古环境恢复与有机质聚集机制[J]. 地球科学, 49(4): 1367−1384.
[30] 陈建平, 王绪龙, 邓春萍, 等. 2016. 准噶尔盆地烃源岩与原油地球化学特征[J]. 地质学报, 90(1): 37−67.
[31] 范彩伟, 胡林, 李明, 等. 2021. 琼东南盆地深水区圈闭有效性评价方法及其应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 33(5): 1−13.
[32] 何家雄, 李福元, 王后金, 等. 2020. 南海北部大陆边缘深水盆地成因机制与油气资源效应[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 36(3): 1−11.
[33] 黄保家, 王振峰, 梁刚. 2014. 琼东南盆地深水区中央峡谷天然气来源及运聚模式[J]. 中国海上油气, 26(5): 8−14.
[34] 黄谦, 陈容涛, 彭晓波, 等. 2000. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷古近系烃源岩生物标志物特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 41(3): 180−192.
[35] 孔庆云, 周辉, 李铁, 等. 1987. 生物标志化合物指标的探讨[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 11(3): 9−15.
[36] 刘旭明, 张成. 2011. 南海南部万安盆地烃源岩成熟史数值模拟研究[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 18(2): 34−37,113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2011.02.008
[37] 卢双舫, 张敏. 2008. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 65−77.
[38] 罗丽荣, 李剑锋, 杨伟伟, 等. 2022. 鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡长9 烃源岩特征与生烃潜力[J]. 新疆石油地质, 43(3): 278−284.
[39] 毛雪莲, 朱继田, 宋鹏, 等. 2021. 琼东南盆地深水区天然气水合物稳定域分布特征与预测[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 37(10): 58−63.
[40] 孙莎莎, 姚艳斌, 吝文. 2015. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘铜川地区油页岩元素地球化学特征及古湖泊水体环境[J]. 岩石矿物地球化学通报, 34(3): 642−645.
[41] 王铁冠, 钟宁宁, 侯读杰, 等. 1995. 低熟油气形成机理与分布[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 32−54.
[42] 王崇敬, 张鹤, 李世宇, 等. 2018. 基于分子标志物的有机质成熟度评价参数选择及其适用范围分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 37(4): 202−211.
[43] 王元, 李贤庆, 王刚, 等. 2018. 莺琼盆地中新统海相烃源岩地球化学特征及生烃潜力评价[J]. 现代地质, 32(3): 500−510.
[44] 肖洪, 李美俊, 杨哲, 等. 2019. 不同环境烃源岩和原油中C19~C23三环萜烷的分布特征及地球化学意义[J]. 地球化学, 48(2): 161−170.
[45] 徐新德, 张迎朝, 梁刚, 等. 2016. 南海北部琼东南盆地深水区烃源条件及天然气成藏机制[J]. 天然气地球科学, 27(11): 1985−1992. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.11.1985
[46] 杨泽光, 冯志强, 王爱国, 等. 2022. 波斯湾盆地主力烃源岩特征及成因主控因素[J]. 海洋石油, 42(1): 1−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2022.01.001
[47] 于婷婷, 刘招君, 王君贤, 等. 2022. 巴西巴拉纳(Parana)盆地下二叠统伊拉蒂组(Irati)油页岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 34(8): 1−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2022.08.01
[48] 张功成, 米立军, 吴时国, 等. 2007. 深水区: 南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气勘探新领域[J]. 石油学报, 28(2): 15−21. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.02.003
[49] 朱伟林, 张功成, 高乐. 2008. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气地质特征与勘探方向[J]. 石油学报, 29(1): 1−9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.01.001
[50] 朱伟林, 张功成, 杨少坤, 等. 2007. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地天然气地质[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 1−15.
-




 下载:
下载: