The characteristics of in-situ stress and its application in the fault-controlled fracture-vug reservoirs in the Fuman Oilfield, Tarim Basin
-
摘要:
研究目的 为了明确断控缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层地应力分布特征,提高碳酸盐岩油气的勘探效率和开发效益,
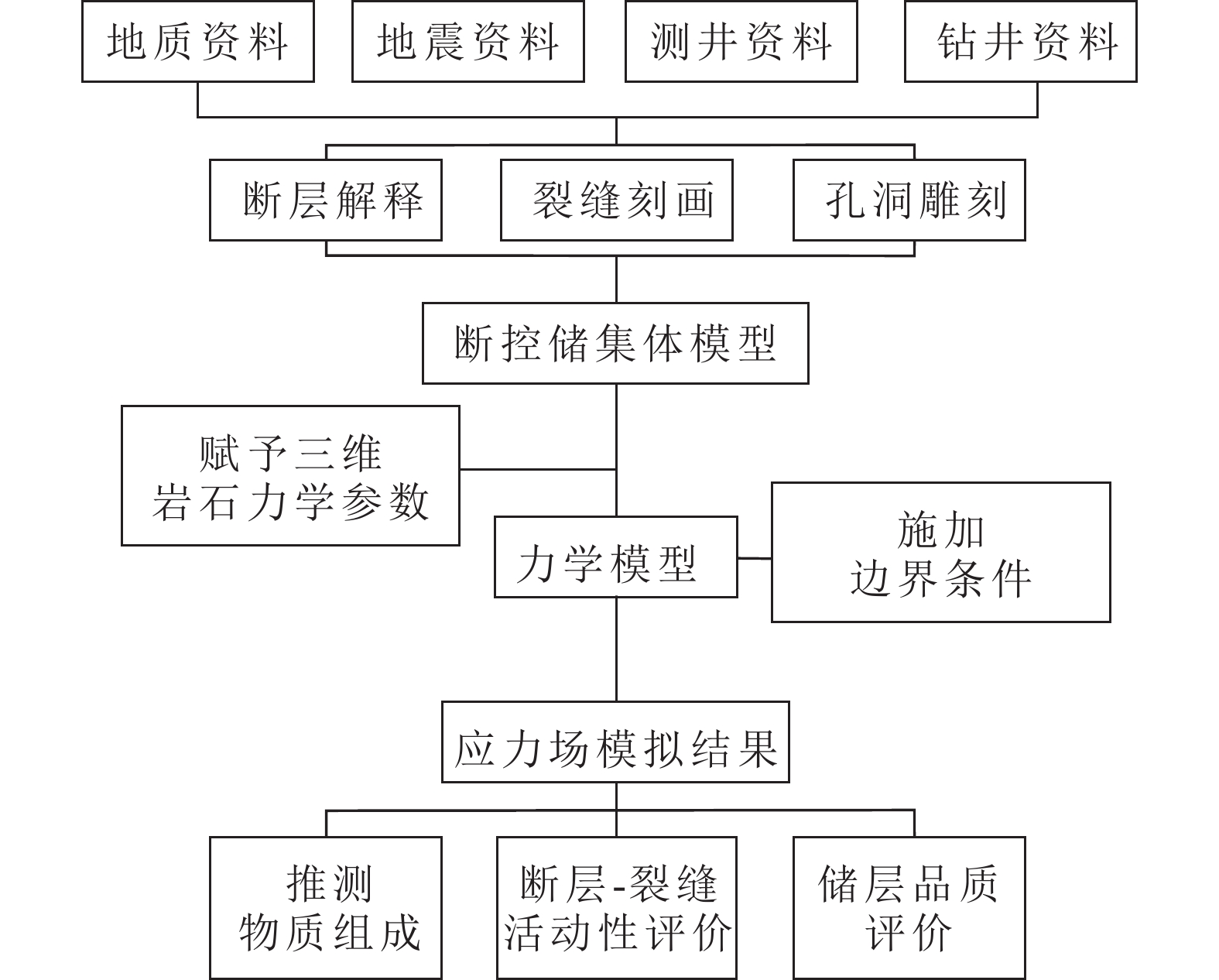
研究方法 基于地质信息、钻井信息、地震资料及地震属性分析,以塔里木盆地富满油田FY210断裂带为例,开展地应力场建模,明确地应力分布模式,分析断裂力学有效性,并提出基于地应力分析的储层品质评价方法和提产对策。
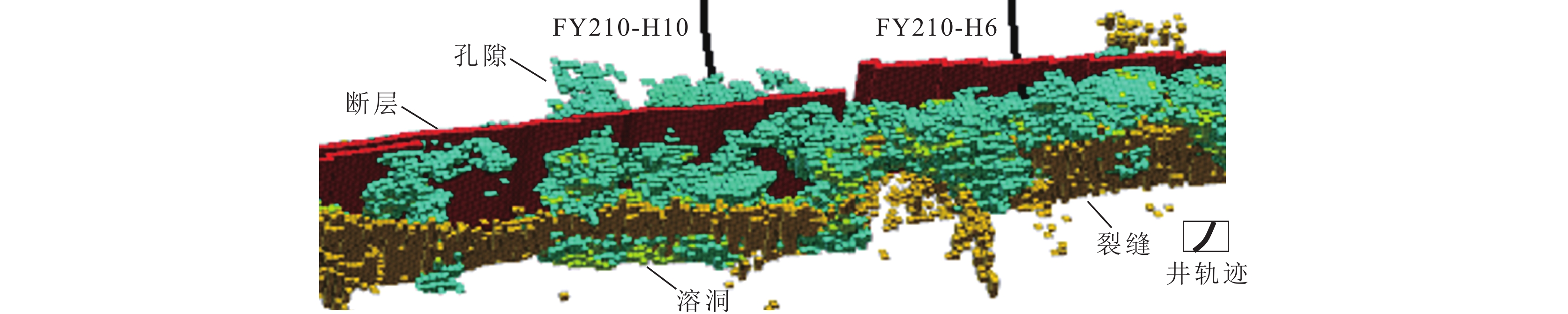
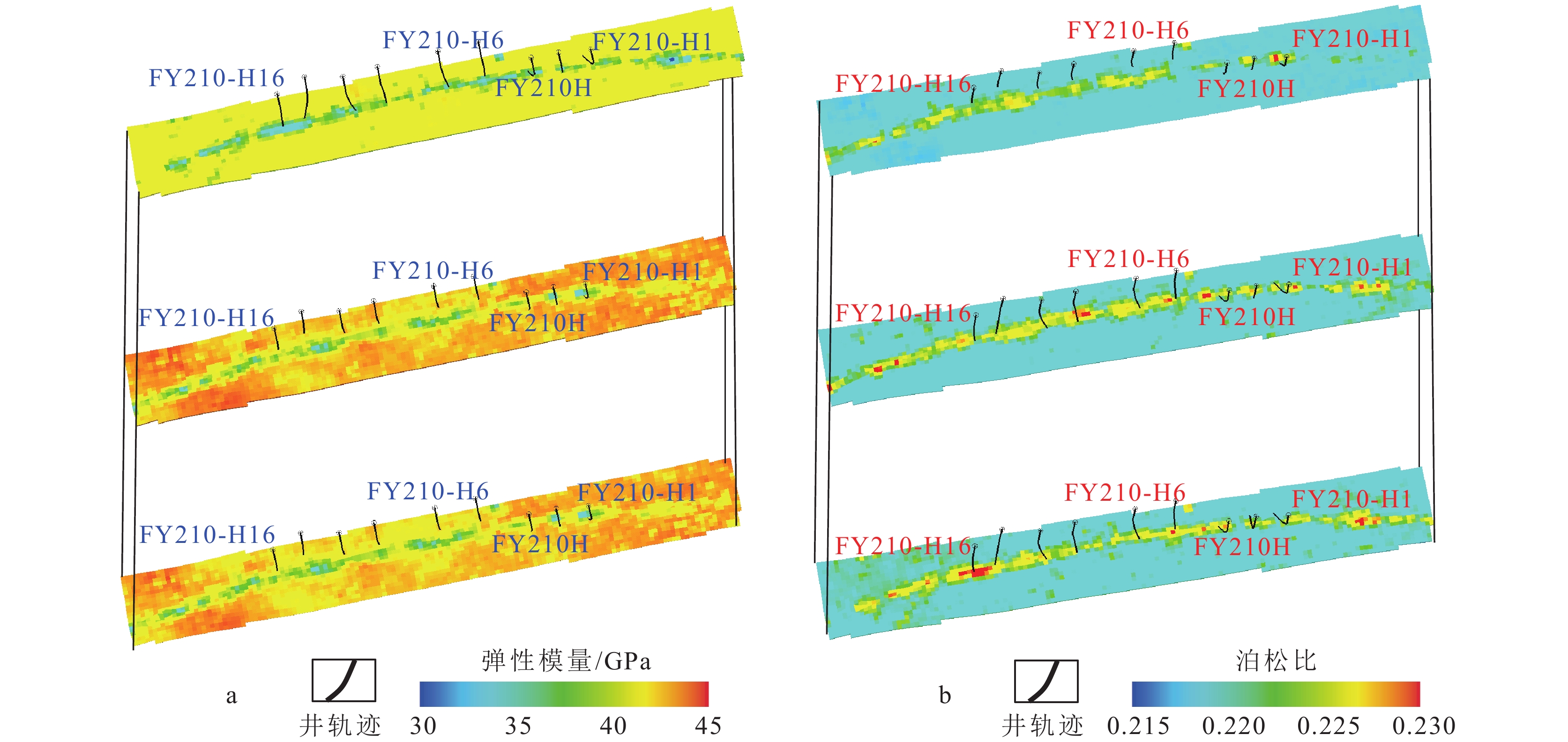
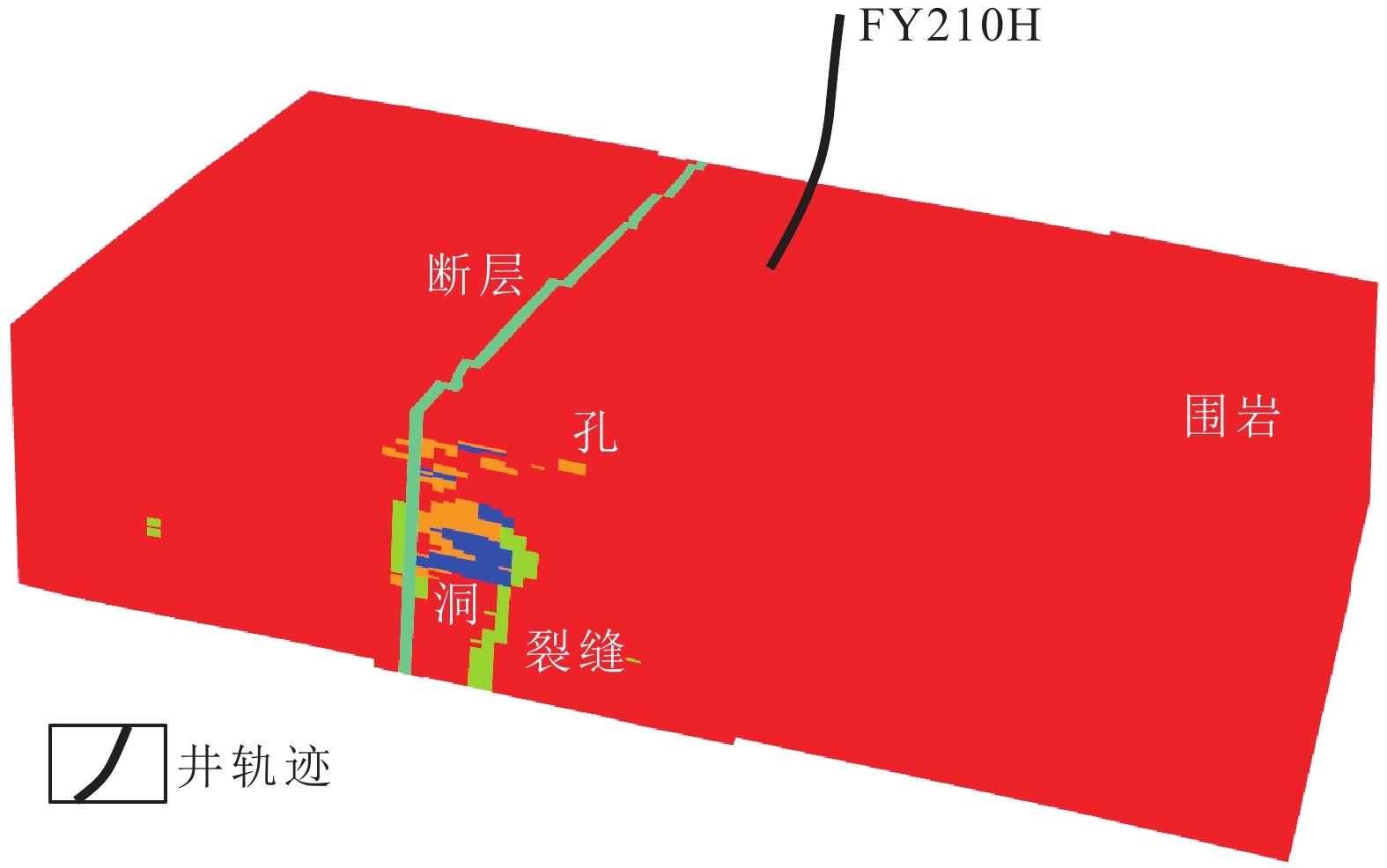
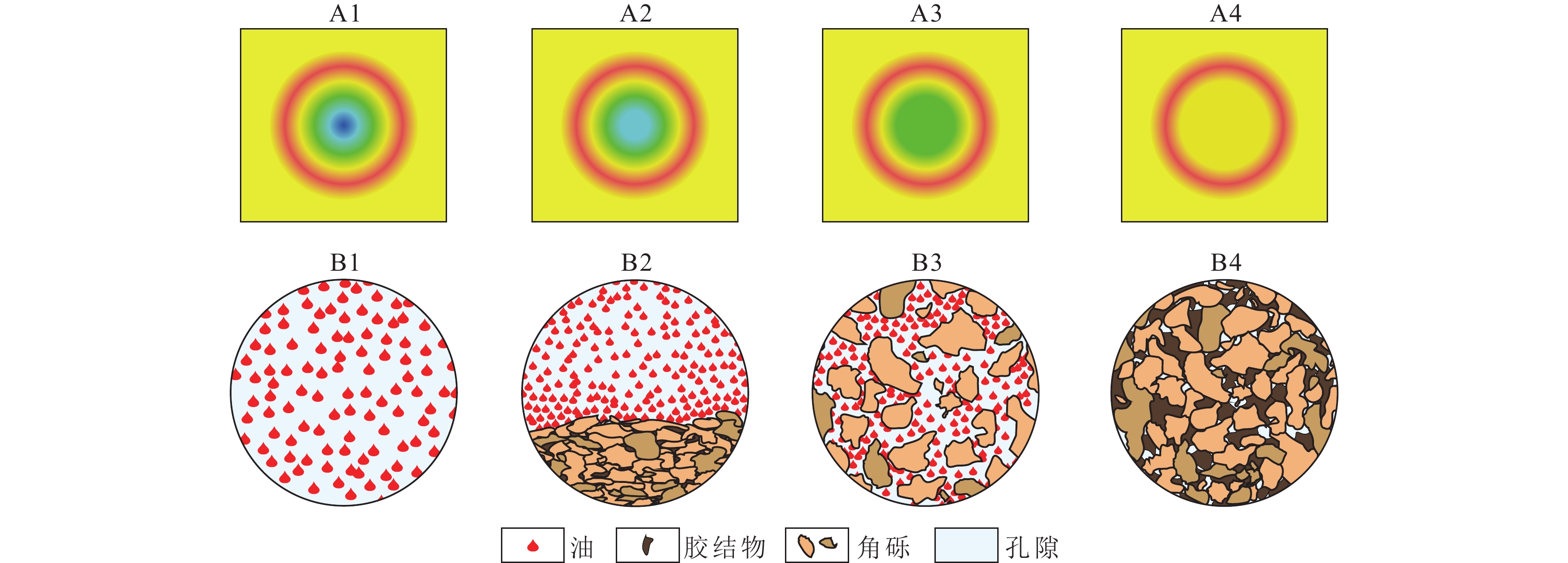
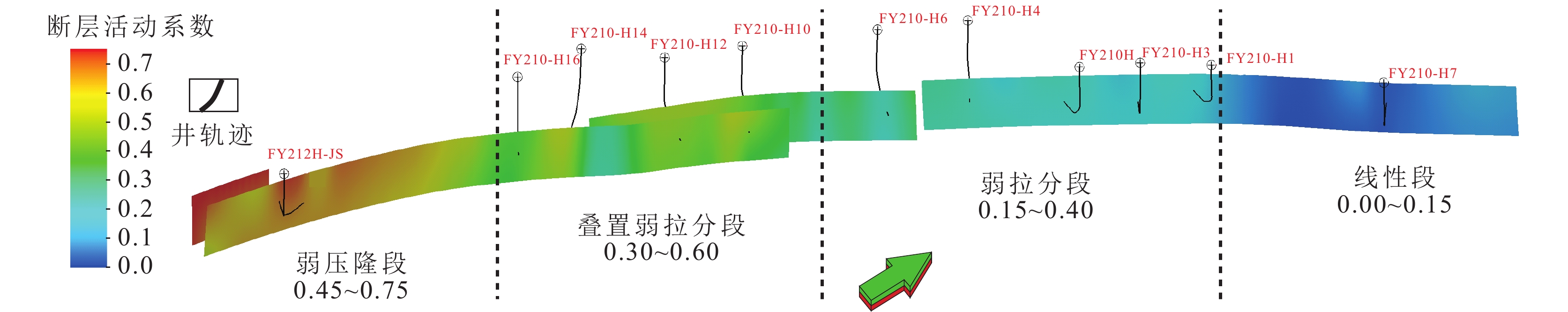
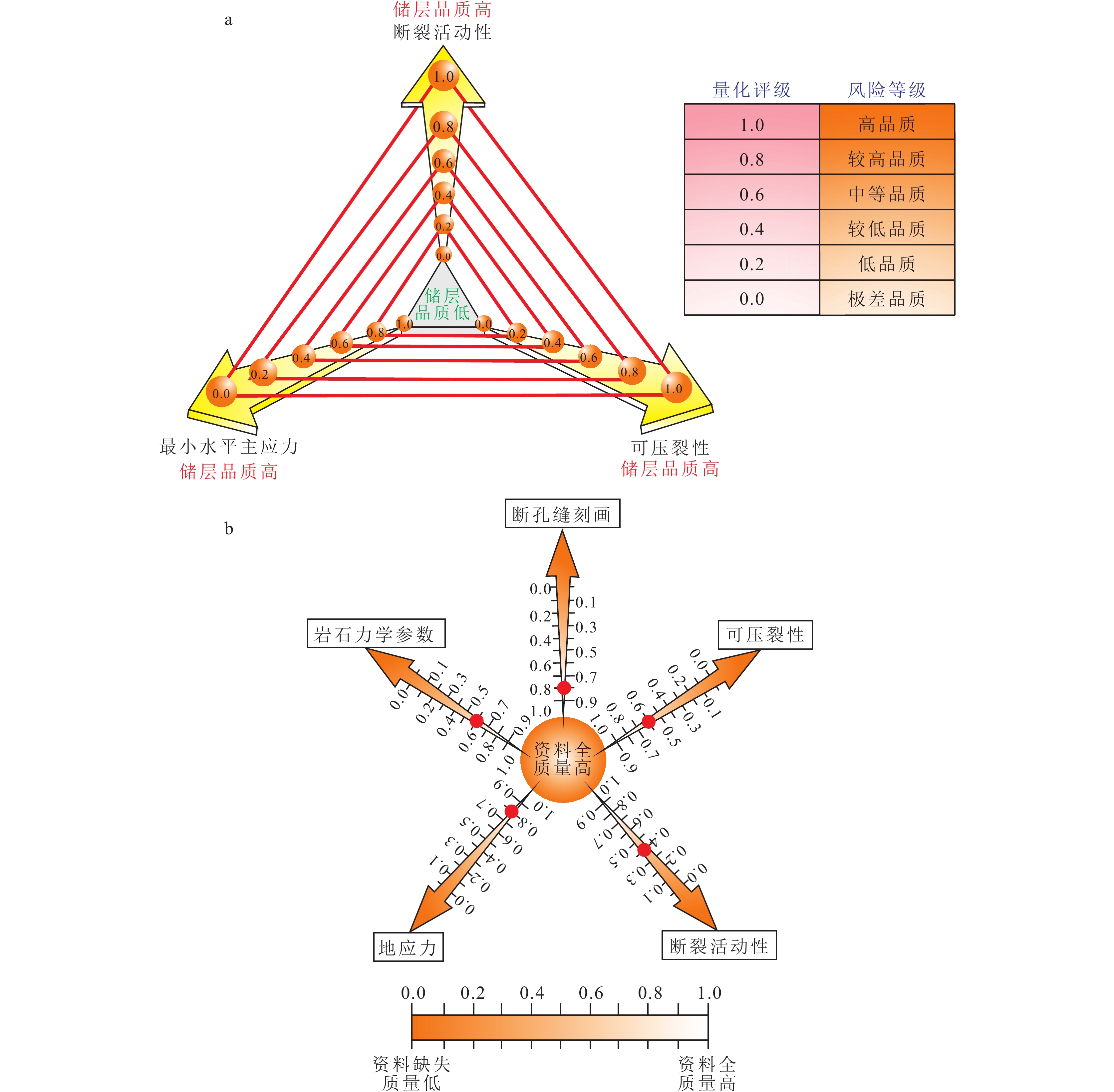
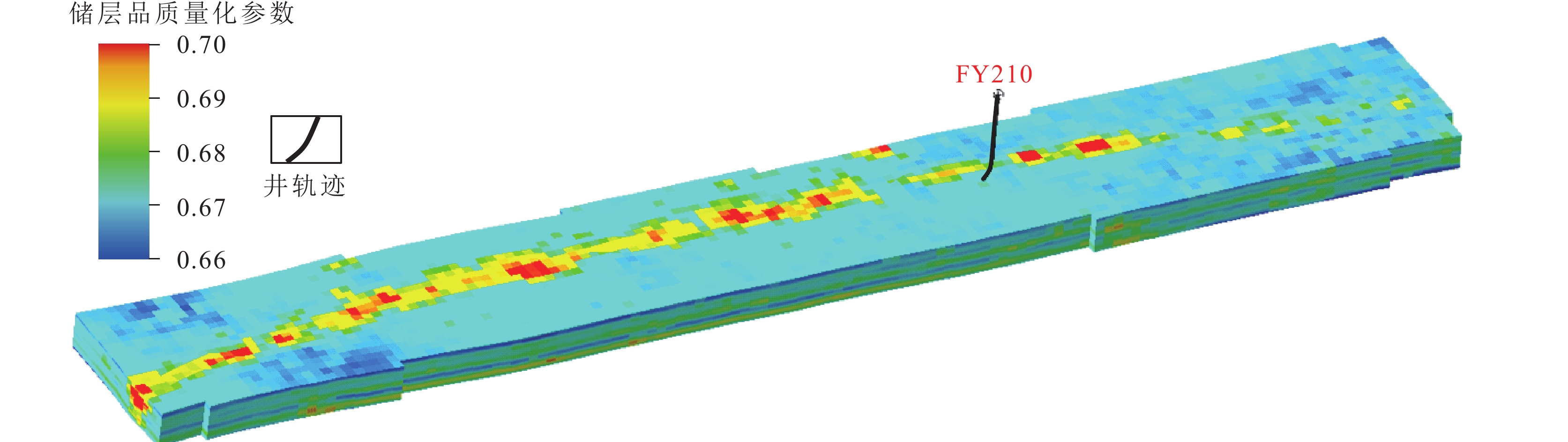
研究结果 结果表明:①断控缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层的非均质性强,断层、裂缝、孔洞造成局部应力场发生异常变化,洞体的地应力场呈“壳式”分布特征,外部强应力壳体表现为应力集中,内部低值区为有利储层体,可根据地应力变化反推断层-裂缝-孔洞发育情况;②高应力部位属于不利的钻探目标,具高应力特征的储层渗透性较差,且钻井过程中会出现井壁垮塌,应通过大规模改造、加深或者侧钻方式避开这类部位;③除常规岩石物理参数外,地应力、断裂活动性、可压裂性等地质力学属性也是影响断控缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层品质和产能的重要因素。
结论 超深断控油气藏井位部署和井轨迹优化应充分考虑地应力相关因素,并兼顾储层改造效率,促进单井提产和油藏效益开发。
Abstract:In order to clarify the distribution characteristics of in−situ stress in fault−controlled fracture−vug reservoirs and improve the exploration efficiency and development benefits of carbonate reservoir. Based on geological information, drilling information, seismic data, and seismic attribute analysis, this article conducts a modeling of the in situ stress field in the FY210 fault zone of the Fuman Oilfield, clarifies its in situ stress distribution mode, analyzes the effectiveness of fracture mechanics, and proposes a reservoir quality evaluation method and production improvement strategy based on in situ stress analysis. The results indicate that: ① the heterogeneity of fault−controlled fracture−vug reservoirs is strong, and faults, fractures, and pores cause abnormal changes in local stress fields. The in situ stress field of the cave body shows a "shell like" distribution feature, and the external strong stress shell shows stress concentration. The low value area inside is a favorable reservoir body, and the development of fractures, pores, and caves can be inferred based on the changes of in situ stress. ② High stress areas are unfavorable drilling targets, and reservoirs with high stress characteristics have poor permeability. During drilling, wellbore collapse may occur, and such areas should be avoided through large−scale renovation, deepening, or lateral drilling. ③ In addition to conventional petrophysical parameters, geomechanical properties such as in−situ stress, fracture activity, and fracturability are also important factors that affect the quality and productivity of fracture−controlled vuggy carbonate reservoirs. Well placement and well trajectory optimization should fully consider factors related to in−situ stress, while also taking into account reservoir reconstruction efficiency to promote single well production and reservoir benefit development.
-

-
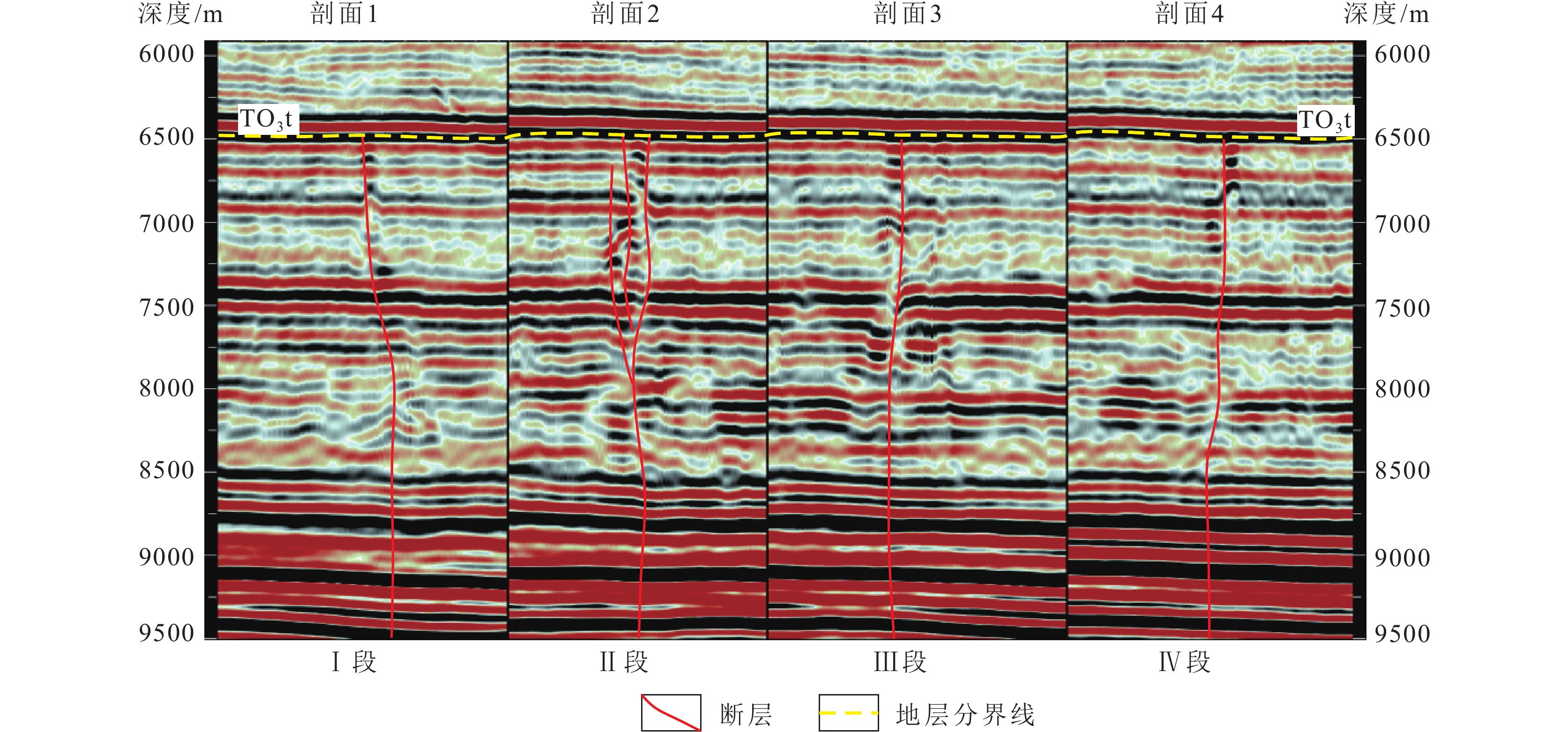
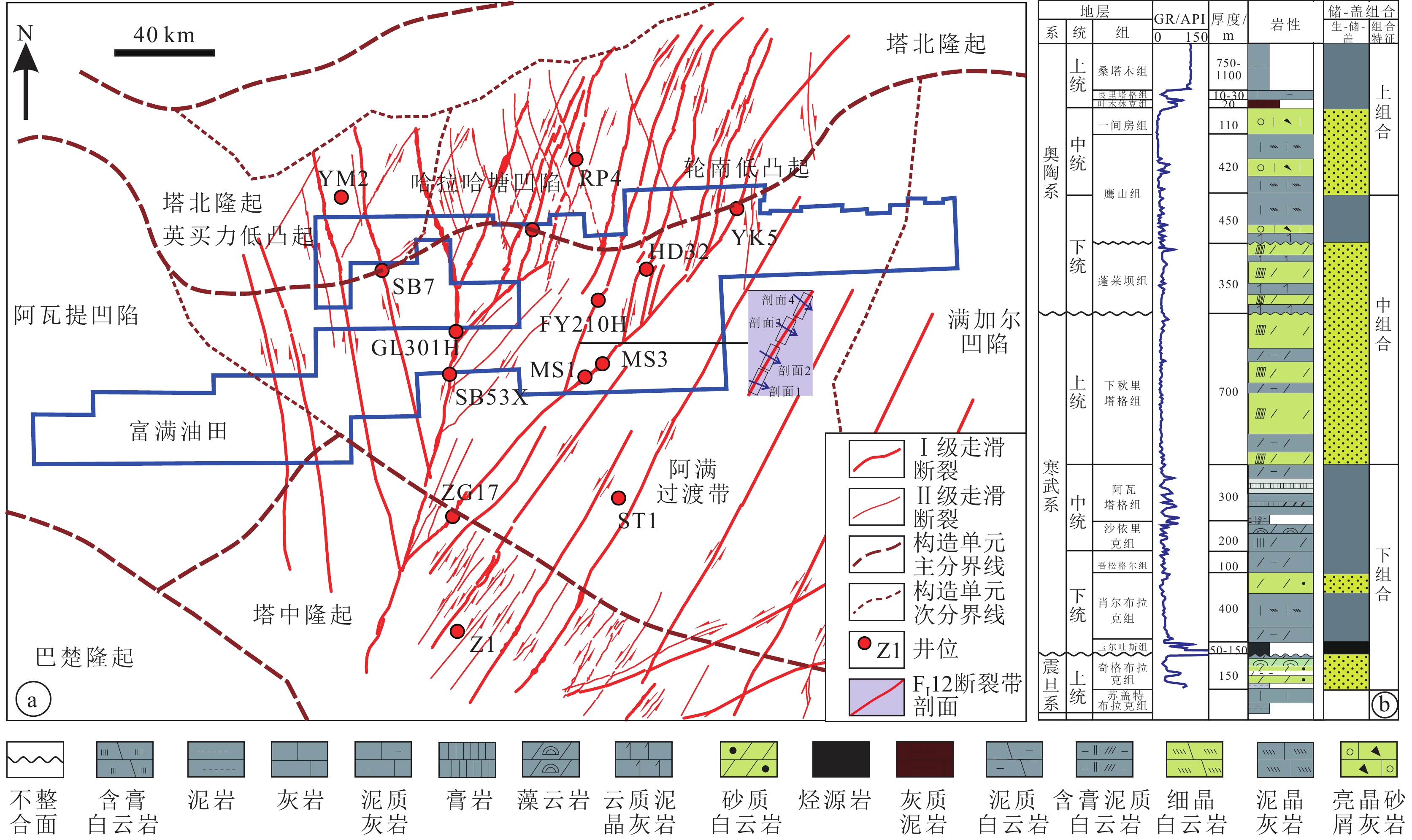
图 1 富满油田构造位置、断裂体系分布(a)和下古生界地层柱状图(b,据宋兴国等,2023)
Figure 1.
表 1 FY210断裂带现今地应力数值模拟结果
Table 1. Statistics of numerical simulation results of in situ stress in the FY210 fault
井号 预测Shmin值/ MPa 井筒Shmin值/ MPa 误差/ % FY210-H16 149 158 5.69 FY210-H14 147 156 5.77 FY210-H12 144 150 4.00 FY210-H10 140 143 2.10 FY210-H6 143 140 2.14 FY210-H3 148 137 8.03 FY210H 146 156 6.41 -
[1] Deng M Z, Cai P R, Lu J L, et al. 2023. Characterization parameters of the evolution degree of strike−slip faults[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 45(5): 1007−1015 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Deng S, Li H, Zhang Z, et al. 2019. Structural characterization of intracratonic strike−slip faults in the central Tarim Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 103(1): 109−137. doi: 10.1306/06071817354
[3] Feng J W, Guo H H, Wang R J, et al. 2023. Segmentation genesis mechanism of strike−slip fracture of deep carbonate rocks in Tabei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science, 48(7): 2506−2519 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Han J F, Su Z, Chen L X, et al. 2023. Reservoir−controlling and accumulation controlling of strike−slip faults and exploration potential in the platform of Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 40(11): 1296−1310 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Han J F, Wang P, Zhu G Y, et al. 2023. Petroleum geology and distribution law of high efficiency areas in ultra−deep kiloton wells in Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 34(5): 735−748 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] He Z L, Zhu C H, Xu W Y, et al. 2023. Seismic characterization of multi−type deep/ultra−deep carbonate reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 66(1): 65−82 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Jia C Z, Ma D B, Yuan J Y, et al. 2021. Structural characteristics, formation & evolution and genetic mechanisms of strike–slip faults in the Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 41(8): 81−91 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Jiang T W, Zhang H, Xu K, et al. 2021. Technology and practice of quantitative optimization of borehole trajectory in ultra−deep fractured reservoir: A case study of Bozi A gas reservoir in Kelasu structural belt, Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 26(4): 149−161 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Jiao F Z. 2017. Significance of oil and gas exploration in NE strike−slip fault belts in Shuntuoguole area of Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 38(5): 831−839 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Li B, Deng S, Li W P, et al. 2019. Strike−slip fault system activity and hydrocarbon geology understanding in Tahe of Tarim Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 26(4): 45−51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Li G H, Li S Y, Li H Y, et al. 2021. Distribution pattern and formation mechanism of the strike−slip fault system in the central Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 41(3): 30−37 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Li W, Ping M M, Zhou D H, et al. 2018. Estimation of the Cenozoic strike−slip displacement for major faults in the Liaodong Bay depression and its geological significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 42(3): 445−454 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Liu J, Li W, Gong W, et al. 2021. Seismic identification and description of ultra−deep fault−controlled reservoirs in Shunbei area[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 42(3): 445−454 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Lu X B, Hu W G, Wang Y, et al. 2015. Characteristics and development practice of fault−karst carbonate reservoirs in Tahe area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 36(3): 347−355 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Ma Y S, Cai X Y, Yun L, et al. 2022. Practice and theoretical and technical progress in exploration and development of Shunbei ultra−deep carbonate oil and gas field, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 49(1): 1−17 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(22)60001-6
[16] Song X G, Chen S, Xie Z, et al. 2023. Strike−slip faults and hydrocarbon accumulation in the eastern part of Fuman oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 44(2): 335−349 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Sun Q, Fan T, Gao Z, et al. 2021. New insights on the geometry and kinematics of the Shunbei 5 strike−slip fault in the central Tarim Basin, China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 150: 104400. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2021.104400
[18] Teng C, Cai Z, Hao F, et al. 2020. Structural geometry and evolution of an intracratonic strike−slip fault zone: A case study from the north SB5 fault zone in the Tarim Basin, China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 140: 104159. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2020.104159
[19] Tian J, Yang H J, Zhu Y F, et al. 2021. Geological conditions for hydrocarbon accumulation and key technologies for exploration and development in Fuman oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 42(8): 971−985 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Wang Q H, Yang H J, Li Y, et al. 2022. Control of strike−slip fault on the large carbonate reservoir in Fuman, Tarim Basin—a reservoir model[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 29(6): 239−251.
[21] Wang Q H, Yang H J, Wang R J, et al. 2021. Discovery and exploration technology of fault−controlled large oil and gas fields of ultra−deep formation in strike slip fault zone in Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 26(4): 58−71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Wu G H, Pang X Q, Li Q M, et al. 2016. The structural characteristics of carbonate rocks and their effects on hydrocarbon exploration in Craton Basin: A case study of the Tarim Basin[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1−344 (in Chinese).
[23] Xu K, Cai Z, Zhang H, et al. 2023a. Geomechanical modeling of ultradeep faultcontrolled carbonate reservoirs and its application: A case of the Fuman Oilfield in Tarim Basin[J]. Energy Science and Engineering, 11(10): 3332−3343. doi: 10.1002/ese3.1552
[24] Xu K, Tian J, Yang H J, et al. 2022. Effects and practical applications of present−day in−situ stress on reservoir quality in ultra−deep layers of Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 33(1): 13−23 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Xu K, Wang B F, Fu X L, et al. 2019. Smart prediction of the three−dimensional stress field of Block Yi 176 of the Bonan oilfield[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 41(5): 75−84 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Xu K, Yang H, Zhang H, et al. 2023b. Geomechanical characteristics and stimulation of Dibei deep tight sandstone reservoirs in the Kuqa depression of Tarim Basin[J]. Geofluids, 4270521.
[27] Yang H J, Zhang H, Yin G Q, et al. 2018. Geomechanics−based geology−engineering integration boosting high−efficiency exploration of fractured−vuggy carbonate reservoirs − A case study on West Yueman block, northern Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 23(2): 27−36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Yang X W, Wang R J, Deng X L, et al. 2022. Theoretical exploration of water injection gravity flooding oil in ultra−deep fault−controlled fractured−cavity carbonate reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 49(1): 116−124 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Yin G, Zhang H, Xin Y, et al. 2022. Ultra−deep dolomite reservoir quality classification and its effect on acid−fracturing based on natural fracture activity analysis: A case study of the Cambrian subsalt reservoir in northern uplift of Tarim Basin[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10: 904064. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.904064
[30] Yun L. 2021. Controlling effect of NE strike−slip fault system on reservoir development and hydrocarbon accumulation in the eastern Shunbei area and its geological significance, Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 26(3): 41−52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Zhang B X, Zhang G J, Liu J S, et al. 2024. Research progress on identification and carving methods of carbonate fracture−cavity reservoirs[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 39(2): 580−593 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Zhang H, Yin G Q, Wang Z M, et al. 2019. Fracability evaluation of deep−burial fractured sandstone gas reservoir in Kuqa depression[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 40(1): 108−115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Zhang T J. 2021. Restraining and releasing effect of strike−slip transition structure and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation in the East Bohai Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Petroleum: 35−45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Zhu G Y, Jiang H, Huang S P, et al. 2024. New progress of marine hydrocarbon accumulation theory and prediction of super large oil and gas areas in China[J/OL]. Acta Petrolei Sinica: 1−25. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2128.TE.20230625.1736.002.html (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] 邓铭哲, 蔡芃睿, 陆建林, 等. 2023. 走滑断裂演化程度的表征参数研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 45(5): 1007−1015.
[36] 冯建伟, 郭宏辉, 汪如军, 等. 2023. 塔里木盆地塔北地区深层走滑断裂分段性成因机制[J]. 地球科学, 48(7): 2506−2519.
[37] 韩剑发, 苏洲, 陈利新, 等. 2019. 塔里木盆地台盆区走滑断裂控储控藏作用及勘探潜力[J]. 石油学报, 40(11): 1296−1310. doi: 10.7623/syxb201911002
[38] 韩剑发, 王彭, 朱光有, 等. 2023. 塔里木盆地超深层千吨井油气地质与高效区分布规律[J]. 天然气地球科学, 34(5): 735−748.
[39] 何治亮, 朱成宏, 徐蔚亚, 等. 2023. 深层—超深层碳酸盐岩多类型储集体地震预测[J]. 地球物理学报, 66(1): 65−82. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0432
[40] 贾承造, 马德波, 袁敬一, 等. 2021. 塔里木盆地走滑断裂构造特征、形成演化与成因机制[J]. 天然气工业, 41(8): 81−91.
[41] 江同文, 张辉, 徐珂, 等. 2021. 超深层裂缝型储层最佳井眼轨迹量化优选技术与实践: 以克拉苏构造带博孜 A 气藏为例[J]. 中国石油勘探, 26(4): 149−161.
[42] 焦方正. 2017. 塔里木盆地顺托果勒地区北东向走滑断裂带的油气勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 38(5): 831−839.
[43] 李兵, 邓尚, 李王鹏, 等. 2019. 塔里木盆地塔河地区走滑断裂体系活动特征与油气地质意义[J]. 特种油气藏, 26(4): 45−51.
[44] 李国会, 李世银, 李会元, 等. 2021. 塔里木盆地中部走滑断裂系统分布格局及其成因[J]. 天然气工业, 41(3): 30−37.
[45] 李伟, 平明明, 周东红, 等. 2018. 辽东湾坳陷新生代主干断裂走滑量的估算及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 42(3): 445−454.
[46] 刘军, 李伟, 龚伟, 等. 2021. 顺北地区超深断控储集体地震识别与描述[J]. 新疆石油地质, 42(2): 238−245.
[47] 鲁新便, 胡文革, 汪彦, 等. 2015. 塔河地区碳酸盐岩断溶体油藏特征与开发实践[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 36(3): 347−355.
[48] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 云露, 等. 2022. 塔里木盆地顺北超深层碳酸盐岩油气田勘探开发实践与理论技术进展[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 49(1): 1−17.
[49] 宋兴国, 陈石, 谢舟, 等. 2023. 塔里木盆地富满油田东部走滑断裂发育特征与油气成藏[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 44(2): 335−349.
[50] 田军, 杨海军, 朱永峰, 等. 2021. 塔里木盆地富满油田成藏地质条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 42(8): 971−985.
[51] 王清华, 杨海军, 李勇, 等. 2022. 塔里木盆地富满大型碳酸盐岩油气聚集区走滑断裂控储模式[J]. 地学前缘, 29(6): 239−251.
[52] 王清华, 杨海军, 汪如军, 等. 2021. 塔里木盆地超深层走滑断裂断控大油气田的勘探发现与技术创新[J]. 中国石油勘探, 26(4): 58−71.
[53] 邬光辉, 庞雄奇, 李启明, 等. 2016. 克拉通碳酸盐岩构造与油气: 以塔里木盆地为例[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1−344.
[54] 徐珂, 田军, 杨海军, 等. 2022. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷超深层现今地应力对储层品质的影响及实践应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 33(1): 13−23.
[55] 徐珂, 汪必峰, 付晓龙, 等. 2019. 渤南油田义176区块三维应力场智能预测[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 41(5): 75−84.
[56] 杨海军, 张辉, 尹国庆, 等. 2018. 基于地质力学的地质工程一体化助推缝洞型碳酸盐岩高效勘探——以塔里木盆地塔北隆起南缘跃满西区块为例[J]. 中国石油勘探, 23(2): 27−36.
[57] 杨学文, 汪如军, 邓兴梁, 等. 2022. 超深断控缝洞型碳酸盐岩油藏注水重力驱油理论探索[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 49(1): 116−124.
[58] 云露. 2021. 顺北东部北东向走滑断裂体系控储控藏作用与突破意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 26(3): 41−52.
[59] 张滨鑫, 张冠杰, 刘敬寿, 等. 2024. 碳酸盐岩缝洞型储层识别与雕刻方法研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 39(2): 580−593.
[60] 张辉, 尹国庆, 王志民, 等. 2019. 库车坳陷深层裂缝性砂岩气藏可压裂性评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 40(1): 108−115.
[61] 张同杰. 2021. 渤海海域东部走滑转换构造的增、释压效应及其控藏作用[D]. 中国石油大学(华东)硕士学位论文: 35−45.
[62] 朱光有, 姜华, 黄士鹏, 等. 2023. 中国海相油气成藏理论新进展与超大型油气区预测[J/OL]. 石油学报: 1−25. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2128.TE.20230625.1736.002.html.
-



 下载:
下载: