Identification of tectonic units within Lhasa terrane in western Tibet by velocity structure along Hi-Climb and its indication for the evolution of the Tibetan Plateau
-
摘要:
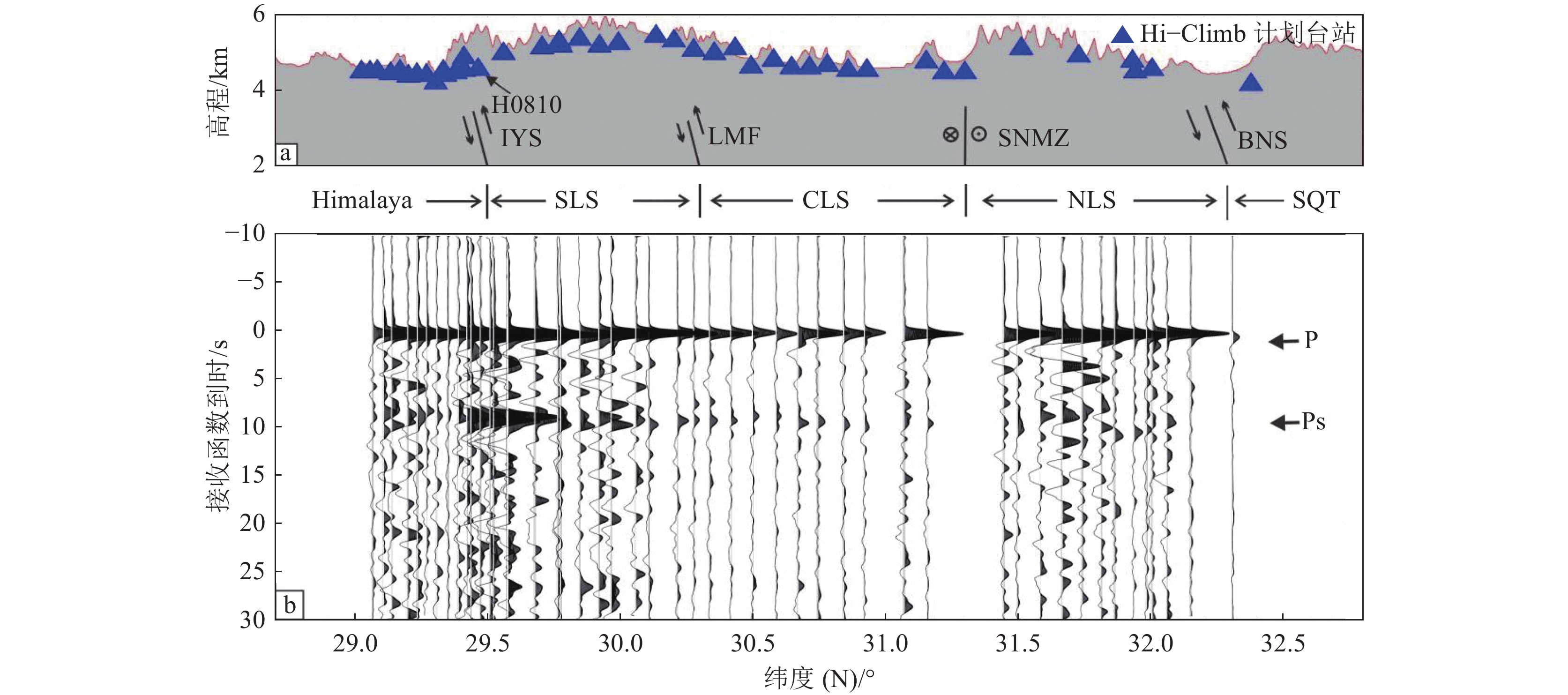
印度大陆板块北向俯冲及碰撞导致青藏高原快速隆升。在此过程中,高原内部物质组成及构造演化尤为复杂,其中高原内部低速层分布特征及其构造成因并不明确。收集了Hi−Climb计划北部台站的数据,利用接收函数复谱比非线性反演方法获取剖面的速度结构特征,与已有地球物理的研究结果结合,显示测线下地壳内部低速层被狮泉河-纳木错混杂岩带和班公湖-怒江缝合带(BNS)所分隔,且存在明显差异。研究结果表明,狮泉河-纳木错混杂岩带不仅是中拉萨地体与北拉萨地体间的深大断裂带,还是地幔顶部的重要转换边界带。上地壳低速层分布主要与地表区域构造及沉积层分布有关,中下地壳低速层分布不仅受地体边界的约束,且与青藏高原的隆升相关。
-
关键词:
- 青藏高原 /
- 接收函数分析 /
- 狮泉河-纳木错混杂岩带 /
- 低速层 /
- 拉萨地体
Abstract:The northward collision and subduction of the Indian continental plate have led to the rapid uplift of the Tibetan Plateau. During the uplift process, the material composition and tectonic evolution are highly complicated in the plateau, and the distribution characteristics and tectonic origin of the low−velocity layer within the plateau are not clear. In this paper, we collected data from the northern stations of the Hi−Climb and used the receiver function complex spectral ratio−based nonlinear inversion method to obtain 1−D shear velocity structure. Combining previous geophysical research results, our result show that the shear−wave low−velocity layer in the lower crust beneath the profile is separated by the Shiquanhe−Namco Melange suture zone (SNMZ) and the Bangong−Nujiang suture zone (BNS), and distinctly differ from each other. This result indicates that the SNMZ is a deep fault zone between the Central and North Lhasa terranes, and also an important transition zone at the uppermost mantle. Low−velocity layer in the upper crust is mainly related to the surface geological structure and the distribution of sedimentary layers. Horizontal distribution of the low velocity layer in the middle and lower crust is not only constrained by terrane boundaries, such as SNMZ and BNS, but also related to the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau.
-

-
[1] Ammon C J, Randall G E, Zandt G. 1990. On the nonuniqueness of receiver function inversions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 95(B10): 15303−15318.
[2] Bai D, Unsworth M J, Meju M A, et al. 2010. Crustal deformation of the eastern Tibetan plateau revealed by magnetotelluric imaging[J]. Nature Geoscience, 3(5): 358−362. doi: 10.1038/ngeo830
[3] Barron J, Priestley K. 2009. Observations of frequency−dependent Sn propagation in Northern Tibet[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 179(1): 475−488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04318.x
[4] Baxter A T, Aitchison J C, Zyabrev S V. 2009. Radiolarian age constraints on Mesotethyan ocean evolution, and their implications for development of the Bangong–Nujiang suture, Tibet[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 166: 689−694. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492008-128
[5] Boos W R, Kuang Z. 2010. Dominant control of the South Asian monsoon by orographic insulation versus plateau heating[J]. Nature, 463(7278): 218−222. doi: 10.1038/nature08707
[6] Brocher T M. 2005. Empirical Relations between Elastic Wavespeeds and Density in the Earth's Crust[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 95(6): 2081−2092. doi: 10.1785/0120050077
[7] Brown L D, Zhao W J, Nelson K D, et al. 1996. Bright spots, structure, and magmatism in southern Tibet from INDEPTH seismic reflection profiling[J]. Science, 274(6): 1688−1690.
[8] Chang C F, Zheng X L. 1973. The geological tectonic characteristics of the Qomolangma region in south Tibet of China and the formation of east−west mountain series on the Qinghai−Tibet plateau[J]. Science in China, 16(2): 82−93 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Chen S Y. 2010. The development of Sumdo suture in the Lhasa Block, Tibet[D]. PhD Dissertation of Chinese Academy of Geological Science: 10−187 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Chen Y, Li W, Yuan X. 2015. Tearing of the Indian lithospheric slab beneath southern Tibet revealed by SKS−wave measurements[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 413: 13−24. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.12.041
[11] Chen Z H, Liu Y, Li J L. 2006. The discovery and significance of the rapakivi granites in Gyisong, Tangra Yumco, Xizang[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 26(2): 16−20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Clark M K, Royden L H. 2000. Topographicooze: Building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow[J]. Geology, 28: 703−706.
[13] Cotte N, Pedersen H, Campillo M, et al. 1999. Determination of the crustal structure insouthern Tibet by dispersion and amplitude analy−sis of Rayleigh waves[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 138: 809−819. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.1999.00927.x
[14] Deng X, Wang F, Wu Y, et al. 2019. Review: Implications of vertebrate fossils for paleo−elevations of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Global Planet Change, 174: 58−69. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2019.01.005
[15] Dewey J F, Shackleton R M, Chang C F. 1988. The tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, 327: 379−413.
[16] Ding L, Lai Q Z. 2003. New geological evidence of crustal thickening in the Gangdese block prior to the Indo−Asian collision[J]. Chin. Sci. Bull., 48: 1604−1610. doi: 10.1007/BF03183969
[17] Ding L, Kapp P, Yue Y H. 2007. Postcollisional calc−alkaline lavas and xenoliths from the southern Qiangtang terrane, Central Tibet[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 254: 28–38.
[18] Ding L, Kapp P, Cai F L, et al. 2022. Timing and mechanisms of Tibetan Plateau uplift[J]. Nature Reviews Earth and Environment, 3(10): 652−667. doi: 10.1038/s43017-022-00318-4
[19] England P, Houseman G. 1986. Finite strain calculations of continental deformation: Comparison with the India−Asia collision zone[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 91(B3): 3664−3676. doi: 10.1029/JB091iB03p03664
[20] Fang X M, Dupont−Nivet G, Wang C S, et al. 2020. Revised chronology of central Tibet uplift (Lunpola Basin)[J]. American Association for the Advancement of Science, 50: 1−10.
[21] Gao R, Lu Z W, Klemperer S L, et al. 2016. Crustal−scale duplexing beneath the Yarlung Zangbo suture in the western Himalaya[J]. Nat. Geo. Sci., 9: 555–560.
[22] Haines S S, Klemperer S L, Brown L, et al. 2003. INDEPTH III seismic data: from surface observations to deep crustal processes in Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 22: 1−18.
[23] He R Z, Gao R, Zheng H W, et al. 2007. Matched−filter analysis of aeromagnetic anomaly in mid−western Tibetan Plateau and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 50(4): 1131−1140 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] He R Z, Liu G C, Golos E, et al. 2014. Isostatic gravity anomaly, lithospheric scale density structure of the northern Tibetan plateau and geodynamic causes for potassic lava eruption in Neogene[J]. Tectonophysics, 628: 218−227. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.04.047
[25] Hearn T M, Ni J F, Wang H Y, et al. 2019. Depth−dependent Pn velocities and configuration of Indian and Asian lithosphere beneath the Tibetan plateau[J]. Geography Journal International, 217: 179−189.
[26] Hou Z Q, Yang Z M, Lu Y J, et al. 2015. A Genetic Link age between Subduction and Collision Related Porphyry Cu Deposits in Continental Collision Zones[J]. Geology, 43(3): 247−250. doi: 10.1130/G36362.1
[27] Hou Z Q, Zheng Y C, Lu Z W, et al. 2020. Growth, thickening and evolution of the thickened crust of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(10): 2797−2815 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Hung S H, Che W P, Chiao L Y, et al. 2010. First multi−scale, finite−frequency tomography illuminates 3−D anatomy of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 37: 1−5.
[29] Jiang Y S, Zhou Y Y, Wang G M, et al. 2003. Characteristics and geological significance of Quaternary volcanic rocks in the central segment of the Gangdise area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 22(1): 16−20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Kapp P, Murphy M A, Yin A et al. 2003. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Shiquanhe area of western Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 22(3): 1−21.
[31] Kapp P, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. 2005. Cretaceous−Tertiary shortening, basin development, and volcanism in Central Tibet[J]. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 117: 865−878. doi: 10.1130/B25595.1
[32] Kapp P, DeCels P G, Leier A L, et al. 2007. The Gangdese retroarc thrust belt revealed[J]. GSA Today, 17(7): 4−9. doi: 10.1130/GSAT01707A.1
[33] Kern H. 1978. The effect of high temperature and high confining pressure on Compressional wave velocities in quartz−bearing and quartz−free Igneous and metamorphic rocks[J]. Tectonophysics, 44(1): 185−203.
[34] Kind R, Ni J, Zhao W, et al. 1996. Evidence from earthquake data for a partially molten crustal layer in southern Tibet[J]. Science, 274(5293): 1692−1694. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5293.1692
[35] Klemperer S L. 2006. Crustal flow in Tibet: geophysical evidence for the physical state of Tibetan lithosphere, and inferred patterns of active flow[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 268(1): 39−70. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2006.268.01.03
[36] Kong X R, Wang Q S, Xiong S B. 1996. Integrated geophysical and lithospheric structure of western Tibet Plateau[J]. Science in China, 16(4): 308−315 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Langston C A. 1977. Corvallis, Oregon, crustal and upper mantle receiver structure from teleseismic P and S waves[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 67: 713−724. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0670030713
[38] Li J, Song X. 2018. Tearing of Indian mantle lithosphere from high−resolution seismic images and its implications for lithosphere coupling in southern Tibet[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(33): 8296−8300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717258115
[39] Li S, Unsworth M J, Booker J R, et al. 2003. Partial melt or aqueous fluid in the mid−crust of southern Tibet? Constraints from INDEPTH magnetotelluric data[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 153: 289−304. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2003.01850.x
[40] Li Y H, Tian X B, Wu Q J, et al. 2006. The Poisson ratio and crustal structure of the central Qinghai−Xizang inferred from INDEPTH−Ⅲ teleseismic waveforms: Geological and geophysical implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(4): 1037−1044 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Li Y L, He R Z, Wang B S, et al. 2023. Pn velocity and anisotropy at the lithospheric mantle wedge beneath the middle−eastern Gangdese Metallogenic Belt, southern Tibet, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 258:105633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes. 2023.105633.
[42] Li Z X, He R Z, Ji Z B, et al. 2022. The focal mechanism and tectonic significance of the Ms 5.6 earthquake on July 24, 2009 in Ninna, Tibet[J]. Seismology and Geology, 44(4): 992−1010 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Liao S P, Chen Z H, Luo X C, et al. 2002. Discovery of leucite phonolite in the Tangra Yumco area, Tibet and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, (11): 735−738 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Liu Q Y, Shao X Z. 1985. Study on the dynamic characteristics of Ps converted waves[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, (3): 291−302 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Liu Q Y, Li S C. 1996. Maximal Likelihood estimation and nonlinear inversion of the complex receiver function spectrum ratio[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 39(4): 500−511(in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Mechie J, Sobolev S V, Ratschbacher L, et al. 2004. Precise temperature estimation in the Tibetan crust from seismic detection of the α−β quartz transition[J]. Geology, 32(7): 601−604. doi: 10.1130/G20367.1
[47] Molnar P, Tapponnier P. 1975. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: Effects of a continental collision: Features of recent continental tectonics in Asia can be interpreted as results of the India−Eurasia collision[J]. Science, 189: 419−426. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4201.419
[48] Murodov D, Zhao J M, Xu Q, et al. 2018. Complex N–S variations in Moho depth and Vp/Vs ratio beneath the western Tibetan Plateau as revealed by receiver function analysis[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 214: 895−906. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggy170
[49] Nábělek J, Hetenyi G, Vergne J, et al. 2009. Underplating in the Himalaya−Tibet collision zone revealed by the Hi−CLIMB experiment[J]. Science, 325: 1371−1374. doi: 10.1126/science.1167719
[50] Nelson K D, Zhao W, Brown L D, et al. 1996. Partially molten middle crust beneath southern Tibet: Synthesis of project INDEPTH results[J]. Science, 274(5293): 1684−1688. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5293.1684
[51] Niu X, Zheng H W, He R Z, et al. 2021. Study on the low velocity layer along INDEPTH−Ⅲ profile in the Central Qinghai−Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 42: 74−84 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[52] Niu X, He R, Zheng H, et al. 2022. In−situ central Qiangtang metamorphic belt in western Tibet as a typical suture zone: Evidence of crust−mantle structural footprints from P−wave receiver function analyses[J]. Tectonophysics, 838: 229484.
[53] Nowack R L, Chen W P , Tseng T L. 2010. Application of Gaussian−Beam Migration to Multiscale Imaging of the Lithosphere beneath the Hi−CLIMB Array in Tibet[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 100(4): 1743−1754.
[54] Nunn C, Roecker S W, Priestley K F, et al. 2014. Joint inversion of surface waves and teleseismic body waves across the Tibetan collision zone: the fate of subducted Indian lithosphere[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 198: 1526−1542.
[55] Owens T J, Zandt G. 1997. Implications of crustal property variations for model of Tibetan plateau evolution[J]. Nature, 387: 37−43. doi: 10.1038/387037a0
[56] Pan G T, Zhu D C, Wang L Q, et al. 2004. Bangong Lake−Nu River suture zone−the northern boundary of Gondwanaland: Evidence from geology and geophysics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(4): 371−382 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[57] Roger F, Tapponnier P, Arnaud N, et al. 2000. An Eocene magmatic belt across central Tibet: mantle subduction triggered by the Indian collision?[J]. Terra Nova, 12(3): 102−108. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3121.2000.123282.x
[58] Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, King R W, et al. 1997. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet[J]. Science, 276: 788−790. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5313.788
[59] Shang X F, De Hoop M V, Hilst R D. 2017. Common conversion point stacking of receiver functions versus passive−source reverse time migration and wavefield regularization[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 209: 923−934. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx069
[60] Sheng Y, Jin S, Comeau M J et al. 2023. Evidence for partial melting and alkali−rich fluids in the crust from a 3−D electrical resistivity model in the vicinity of the Coqen region, western Lhasa terrane, Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 619: 118316.
[61] Shi Z X, Gao R, Lu Z W, et al. 2022. Bidirectional subduction of the Bangong−Nujiang ocean revealed by deep−crustal seismic reflection profile[J]. Tectonophysics, 837: 229455.
[62] Shibutani T, Sambridge M, Kennett B. 1996. Genetic algorithm inversion for receiver functions with application to crust and uppermost mantle structure beneath Eastern Australia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 23(14): 1829−1832. doi: 10.1029/96GL01671
[63] Sun W C, Li S L, Luo L L, et al. 1987. A preliminary stydy on low velocity layer in the crust in north China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1: 17−26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[64] Tapponnier P, Xu Z Q, Roger F, et al. 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 294(5547): 1671−1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978
[65] Teng J W. 2010. Ponder and research on the genesis and occurrence of strong earthquakes and the prediction of their place, time and intensity[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 8: 1749−1766 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[66] Teng J W, Yuan X M, Zhang Y Q, et al. 2012. The stratificational velocity structure of crust and covering strata of upper mantle and the orbit of deep interaquifer substance locus of movement for Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(12): 4077−4100 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[67] Unsworth M J, Jones A G, Wei W, et al. 2005. Crustal rheology of the Himalaya and Southern Tibet inferred from magnetotelluric data[J]. Nature, 438(7064): 78−81. doi: 10.1038/nature04154
[68] Vinnik L P. 1977. Detection of waves converted from P to SV in mantle[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 15: 39−45. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(77)90008-5
[69] Wang B D, Liu H, Wang L Q, et al. 2020. Spatial−Temporal framework of Shiquanhe−Laguoco−Yongzhu−Jiali ophiolite mélange zone, Qinghai−Tibet Plateau and its Tectonic evolution[J]. Earth Science, 45(8): 2764−2784 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[70] Wei W, Unsworth M, Jones A, et al. 2001. Detection of Widespread Fluids in the Tibetan Crust by Magnetotelluric Studies[J]. Science, 292(5517): 716−718. doi: 10.1126/science.1010580
[71] Wei W B, Jin S, Ye G F, et al. 2006. Conductivity structure of crust and upper mantle beneath the northern Tibetan Plateau: Results of super−wide band Magnetotelluric sounding[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(4): 1215−1225 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[72] Wittlinger G, Vergne J, Tapponnier P, et al. 2004. Teleseismic imaging of subducting lithosphere and Moho offsets beneath western Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 221: 117−130. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00723-4
[73] Wu W, Liu Q Y, He R Z, et al. 2017. Waveform inversion of S−wave velocity model in the central Qiangtang in North Tibet and its geological implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(3): 941−952 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[74] Xiong S B, Liu H B. 1997. Crustal structure in western Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, (12): 1309−1312 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[75] Xu L, Rondenay S, Hilst R D. 2007. Structure of the crust beneath the southeastern Tibetan Plateau from teleseismic receiver functions[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 165(3): 176−193.
[76] Xu M J, Lan R, Wang P, et al. 2019. Zircon U−Pb dating of gabbro from Zhongcang ophiolitic mélange in Tibet and its geological implications[J]. Journal of Tianjin Chengjian University, 25(2): 128−132 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[77] Xu Q, Zhao J M, Pei S P, et al. 2011. The lithosphere−asthenosphere boundary revealed by S−receiver functions from the Hi−CLIMB experiment[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 187: 414−420. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05154.x
[78] Xu Z J, Song X , Zhu L. 2013. Crustal and uppermost mantle S velocity structure under Hi−CLIMB seismic array in central Tibetan Plateau from joint inversion of surface wave dispersion and receiver function data[J]. Tectonophysics, 584: 209−220.
[79] Xu W C, Zhang H F, Luo B J, et al. 2015. Adakite−like geochemical signature produced by amphibole−dominated fractionation of arc magmas: An example from the Late Cretaceous magmatism in Gangdese belt, south Tibet[J]. Lithos, 232: 197−210. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.07.001
[80] Xue S, Chen Y, Liang H D, et al. 2021. Deep electrical resistivity structure across the Gyaring Co Fault in Central Tibet revealed by magnetotelluric data and its implication[J]. Tectonophysics, 809: 228835. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.228835
[81] Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Li T F, et al. 2007. Oceanic subduction-type eclogite in the Lhasa block, Tibet, China: remains of the Paleo-Tethys ocean basin?[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(10): 1277-1287 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[82] Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Li Z L, et al. 2009. Discovery of an eclogite belt in the Lhasa block, Tibet: A new border for Paleo−Tethys?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34( 1): 76−89.
[83] Yan J Y, Zheng H W, He R Z, et al. 2019. Low velocity layer investigation in central Qiangtang in north Tibet and its dynamic implications[J]. Earth Science, 44(6): 1784−1796 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[84] Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Geng Q R, et al. 2006. A possible new HP/UHP metamorphic belt in China: discovey of eclogite in the Lasha terrane, Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(12): 1788−1796 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[85] Yang Y J, Ritzwoller M H, Zheng Y, et al. 2012. A synoptic view of the distribution and connectivity of the mid−crustal low velocity zone beneath Tibet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 117: B04303. doi: 10.1029/2011JB008810
[86] Yin A, Harrison T M. 2000. Geologic Evolution of the Himalayan−Tibetan Orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 28: 211−280.
[87] Yu C Q, Zheng Y C, Shang X F. 2017. Crazyseismic: a MATLAB GUI−Based Software Package for Passive Seismic Data Preprocessing[J]. Seismol. Res. Lett., 88: 410−415.
[88] Yu L F, Zhao W X, Chen J L, et al. 2012. Mineralogical Characteristics of the Sodium and Potassic−rich Alkaline Volcanic rocks at Tangra Yumco, SE Tibet: Implications for Petrogenesis[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 36(2): 274−283.
[89] Zeng R S, Lu H X, Ding Z F. 1988. Seismic refraction and reflection profilings across Tangshan epicentral region and their implication to seismogenic processes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 4: 383−398 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[90] Zhang J J, Ding L. 2003. East−West extension in Tibetan plateau and its significance to tectonic evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 38(2): 179−189 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[91] Zhang P Z, Shen Z, Wang M, et al. 2004. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data[J]. Geology, 32(9): 809−812.
[92] Zhang Z, Deng Y, Teng J. 2011. An overview of the crustal structure of the Tibetan plateau after 35 years of deep seismic soundings[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(4): 977−989. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.03.010
[93] Zhang Z J, Wang Y H, Houseman G A, et al. 2014. The Moho beneath western Tibet: Shear zones and eclogitization in the lower crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 408: 370−377.
[94] Zhao L S, Sen M K, Stoffa P. 1996. Application of very fast simulated annealing to the determination of the crustal structure beneath Tibet[J]. Geophys J . Int, 125: 355−370.
[95] Zhao J M, Neupane B, Liu H B, et al. 2020. Lithospheric structure of western Tibet – A brief review[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 198: 104159−104170. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104159
[96] Zhao L S, Sen M K, Stoffa P, et al. 2010. Application of very fast simulated annealing to the determination of the crustal structure beneath Tibet[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 125: 355−370.
[97] Zhao W, Mechie J, Brown L D, et al. 2001. Crustal structure of the central Tibet as derived from project INDEPTH wide−angle seismic data[J]. Geophys. J. Int., 145: 486−498. doi: 10.1046/j.0956-540x.2001.01402.x
[98] Zheng D, Yao T D, et al. 2004. Uplift and environmental effects of Tibetan Plateau[M]. Beijing: China Science Publishing and Media Ltd.: 1-560 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[99] Zheng H W, Li T D, He R Z, et al. 2020. Tomographic Imaging of the India−Asia Plate Collisional Tectonics and Mantle Upwelling Beneath the Western Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94: 1159−1166. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14563
[100] Zheng L L, Geng Q R, Ou C S, et al. 2003. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of Boninite in Yaluzangbujiang ophiolitic mélanges in Najiabawa[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 22(11): 908−911 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[101] Zhu D C, Mo X H, Zhao Z D, et al. 2008. Zircon U−Pb geochronology of Zenong Group volcanic rocks in Coqen area of the Gangdese, Tibet and tectonic significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(3): 401−412 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[102] Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. 2011. The Lhasa terane: Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Lettrs, 301: 241−255.
[103] Zhu D C, Li S M, Cawood P A, et al. 2016. Assembly of the Lhasa and Qiangtang terranes in central Tibet by divergent double subduction[J]. Lithos, 245: 7−17. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.023
[104] Zhu L P, Kanamori H. 2000. Moho depth variation in southern California from teleseismic receiver functions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 105: 2969−1980. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900322
[105] 常承法, 郑锡澜. 1973. 中国西藏南部珠穆朗玛峰地区地质构造特征以及青藏高原东西向诸山系形成的探讨[J]. 中国科学, 16(2): 82−93.
[106] 陈松永. 2010. 西藏拉萨地块中古特提斯缝合带的厘定[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文: 10−187.
[107] 陈振华, 刘云, 李均良. 2006. 西藏当惹雍错吉松环斑花岗岩的发现及地质意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, (2): 16−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2006.02.004
[108] 贺日政, 高锐, 郑洪伟, 等. 2007. 青藏高原中西部航磁异常的匹配滤波分析与构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 50(4): 1131−1140. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.04.020
[109] 侯增谦, 郑远川, 卢占武, 等. 2020. 青藏高原巨厚地壳: 生长、加厚与演化[J]. 地质学报, 94(10): 2797−2815. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.001
[110] 江元生, 周幼云, 王明光, 等. 2003. 西藏冈底斯山中段第四纪火山岩特征及地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 22(1): 17−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.01.003
[111] 孔祥儒, 王谦身, 熊绍柏. 1996. 西藏高原西部综合地球物理与岩石圈结构研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), (4): 308−315. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1996.04.004
[112] 李永华, 田小波, 吴庆举, 等. 2006. 青藏高原INDEPTH-Ⅲ剖面地壳厚度与泊松比: 地质与地球物理含义[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(4): 1037−1044. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.04.015
[113] 李宗旭, 贺日政, 冀战波, 等. 2022. 2009年7月24日西藏尼玛MS5.6地震的震源机制及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 44(4): 992−1010. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.04.011
[114] 廖思平, 陈振华, 罗小川, 等. 2002. 西藏当惹雍错地区白榴石响岩的发现及地质意义[J]. 地质通报, (11): 735−738. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.11.008
[115] 刘启元, 邵学钟. 1985. 天然地震PS转换波动力学特征的初步研究[J]. 地球物理学报, (3): 291−302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1985.03.007
[116] 刘启元, 李顺成. 1996. 接收函数复谱比的最大或然性估计及非线性反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 39(4): 500−511. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1996.04.008
[117] 牛潇, 郑洪伟, 贺日政, 等. 2021. 青藏高原中部INDEPTH-Ⅲ剖面低速层研究[J]. 地球学报, 42(1): 74−84. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.071801
[118] 潘桂棠, 朱弟成, 王立全, 等. 2004. 班公湖—怒江缝合带作为冈瓦纳大陆北界的地质地球物理证据[J]. 地学前缘, 11(4): 371−382. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.004
[119] 孙武城, 李松林, 罗力雷, 等. 1987. 初论华北地区的地壳低速层[J]. 地震地质, 1: 17−26.
[120] 滕吉文. 2010. 强烈地震孕育与发生的地点、时间及强度预测的思考与探讨[J]. 地球物理学报, 8: 1749−1766. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.08.001
[121] 滕吉文, 阮小敏, 张永谦, 等. 2012. 青藏高原地壳与上地幔成层速度结构与深部层间物质的运移轨迹[J]. 岩石学报, 28(12): 4077−4100.
[122] 王保弟, 刘函, 王立全, 等. 2020. 青藏高原狮泉河-拉果错-永珠-嘉黎蛇绿混杂岩带时空结构与构造演化[J]. 地球科学, 45(8): 2764−2784.
[123] 魏文博, 金胜, 叶高峰, 等. 2006. 藏北高原地壳及上地幔导电性结构——超宽频带大地电磁测深研究结果[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(4): 1215−1225. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.04.038
[124] 吴蔚, 刘启元, 贺日政, 等. 2017. 羌塘盆地中部地区地壳S波速度结构及构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(3): 941−952. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170309
[125] 熊绍柏, 刘宏兵. 1997. 青藏高原西部的地壳结构[J]. 科学通报, (12): 1309−1312.
[126] 徐梦婧, 兰锐, 王沛, 等. 2019. 西藏中仓蛇绿混杂岩中辉长岩锆石U−Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 天津城建大学学报, 25(2): 128−132.
[127] 严江勇, 郑洪伟, 贺日政, 等. 2019. 藏北羌塘盆地中部地壳低速层分布与动力学意义[J]. 地球科学, 44(6): 1784−1796.
[128] 杨经绥, 许志琴, 耿全如, 等. 2006. 中国境内可能存在一条新的高压/超高压变质带——青藏高原拉萨地体中发现榴辉岩带[J]. 地质学报, 80(12) : 1788−1792.
[129] 杨经绥, 许志琴, 李天福, 等. 2007. 青藏高原拉萨地块中的大洋俯冲型榴辉岩: 古特提斯洋盆的残留?[J]. 地质通报, (149): 1277−1287.
[130] 于丽芳, 赵文霞, 陈建林, 等. 2012. 西藏当惹雍错富钾和富钠碱性火山岩的矿物学研究及其成因指示[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 36(2): 274−283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.02.014
[131] 曾融生, 陆涵行, 丁志峰. 1988. 从地震折射和反射剖面结果讨论唐山地震成因[J]. 地球物理学报, 4: 383−398. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1988.04.003
[132] 张进江, 丁林. 2003. 青藏高原东西向伸展及其地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 38(2): 179−189. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2003.02.005
[133] 郑来林, 耿全如, 欧春生, 等. 2003. 藏东南迦巴瓦地区雅鲁藏布江蛇绿混杂岩中玻安岩的地球化学特征和地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 22(11): 908−911. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.11.013
[134] 郑度, 姚檀栋. 2004. 青藏高原隆升与环境效应[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1−560.
[135] 朱弟成, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等. 2008. 西藏冈底斯带措勤地区则弄群火山岩锆石 U−Pb 年代学格架及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 24(3): 401−412.
-




 下载:
下载: