Micropore structure and physical property of geothermal reservoir of Wumishan Formation in Beijing area
-
摘要:
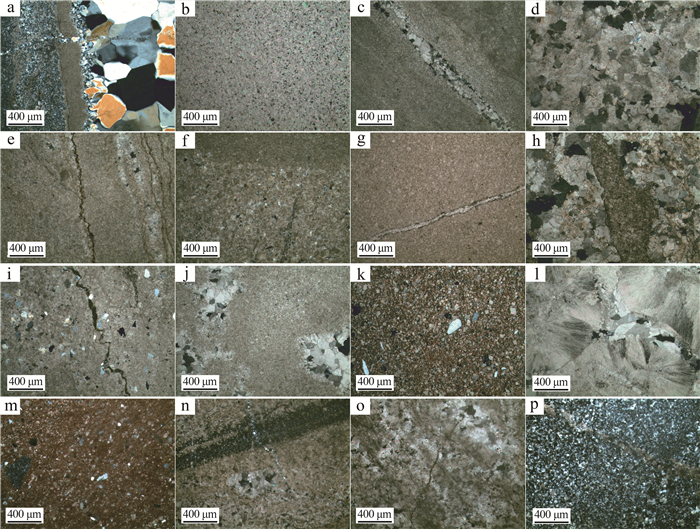
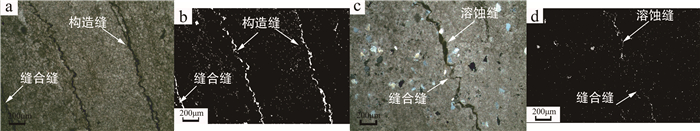
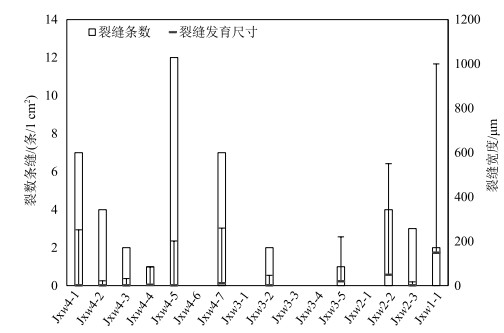
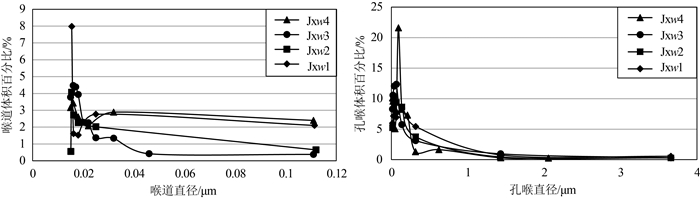
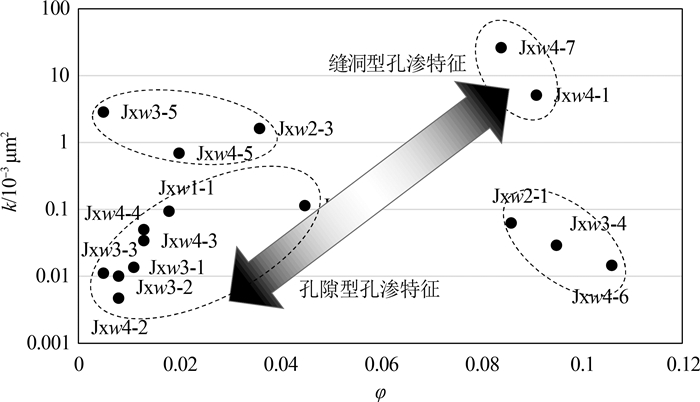
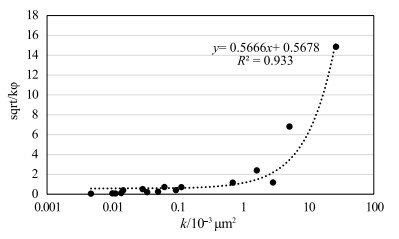
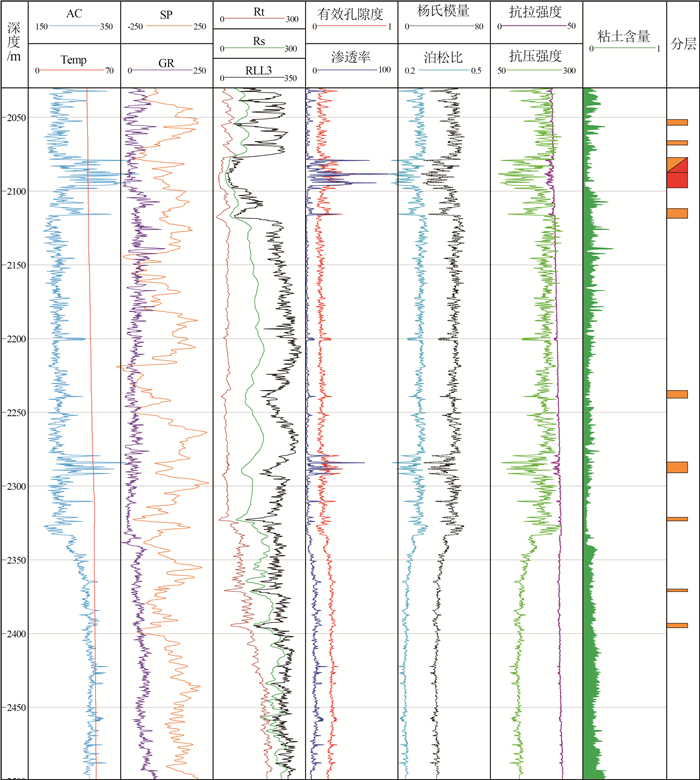
以北京地区中元古界蓟县系雾迷山组碳酸盐岩地热储层为研究对象,通过扫描电镜(SEM)和薄片鉴定,划分了样品微观孔隙类型,借助MATLAB图像处理技术,定量化表征微裂缝密度和尺寸发育特征; 联合毛管力测试与低温液氮吸附实验,定量化雾迷山组白云岩微-介-宏孔体积分布; 分析宏观孔渗测试结果,认为微裂缝越发育、透气孔越多、孔喉均质性越好,孔渗越大的微观-宏观作用规律,并拟合了孔渗经验关系式; 建立了基于测井资料划分有利开发层段的方法。雾迷山组白云岩基质孔隙连通性较差,微裂隙与溶蚀孔洞提供了主要渗流通道; 整体孔隙分布频率随孔径整体呈正态分布,最可能几率孔径分布于50~60 nm。研究成果可为华北地区雾迷山组地热资源开发提供基础数据支撑。
Abstract:Taking the carbonate geothermal reservoir in Wumishan Formation of Mesoproterozoic Jixian System in Beijing as the research object, the micro-pore types of samples are classified with SEM visualization and slice identification, and the density and size development characteristics of micro fractures are quantified with the help of MATLAB image processing technology.The micro-medium-macro pore volume distribution of dolomite in Wumishan Formation is quantified by combining capillary force test and low-temperature liquid nitrogen adsorption experiment.Based on the macro porosity and permeability test results, the analysis concluded that the more developed microfractures, the more gas permeable pores and the better pore throat homogeneity, the greater the influence law of porosity and permeability, and the empirical relationship between porosity and permeability is fitted.Finally, a method of dividing favorable development intervals based on logging data is established.The results show that the connectivity of matrix pores of dolomite in Wumishan Formation is poor, and micro fractures and dissolution pores provide the main seepage channels.The overall pore distribution frequency is normally distributed with the pore size, which distributes at 50~60 nm most likely.The research results can provide basic data support for the development of geothermal resources in the Wuzhishan Formation in North China.
-

-
表 1 实验样品编号及坐标
Table 1. Number and coordinates of the experimental samples
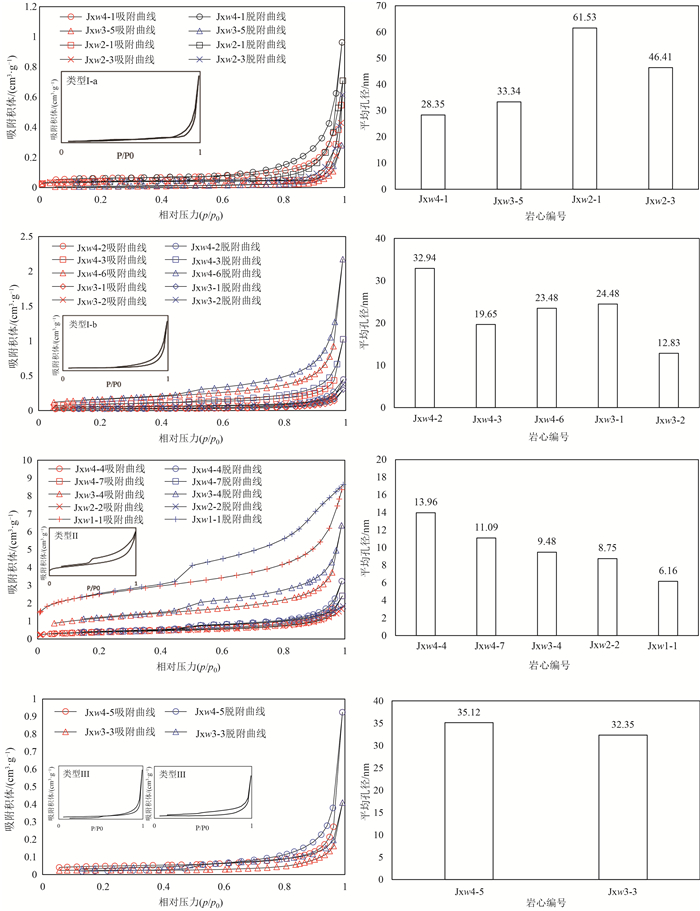
取样编号 经度 纬度 取样编号 经度 纬度 Jxw4-1 E117° 23′ 24.9″ N40° 06′ 47.0″ Jxw3-2 E117°24′ 23.2″ N40°06′ 57.6″ Jxw4-2 E117° 23′ 33.0″ N40° 06′ 52.5″ Jxw3-3 E117°24′ 21.5″ N40°07′ 03.3″ Jxw4-3 E117° 23′ 35.2″ N40° 06′ 52.2″ Jxw3-4 E117°24′ 24.4″ N40°07′ 04.9″ Jxw4-4 E117° 23′ 42.4″ N40° 06′ 50.9″ Jxw3-5 E117°24′ 29.7″ N40°07′ 15.0″ Jxw4-5 E117° 23′ 44.1″ N40° 06′ 51.4″ Jxw2-1 E117°24′ 25.79″ N40°07′ 18.92″ Jxw4-6 E117° 23′ 51.8″ N40° 06′ 51.4″ Jxw2-2 E117°24′ 36.11″ N40°07′ 25.43″ Jxw4-7 E117° 24′ 00.0″ N40° 06′ 52.4″ Jxw2-3 E117°24′ 41.86″ N40°07′ 38.06″ Jxw3-1 E117°24′ 14.7″ N40°06′ 59.1″ Jxw1-1 E117°24′ 44.00″ N40°07′ 57.62″ 表 2 雾迷山组白云岩孔隙度、渗透率测试结果
Table 2. Porosity and permeability test results of dolomite in the Wumishan Formation
样品编号 峰值个数 峰值孔径/nm 对应孔隙体积/cm3 孔隙度/% 渗透率/mD Jxw4-1 1 64.73 0.089 9.1 5.12 Jxw4-2 2 15.05 0.011 0.8 0.0047 35.72 0.010 Jxw4-3 1 42.84 0.025 1.3 0.0341 Jxw4-4 2 3.75 0.007 1.3 0.05 52.02 0.052 Jxw4-5 1 37.20 0.028 2 0.6919 Jxw4-6 1 46.44 0.032 10.6 0.0146 Jxw4-7 1 137.82 0.298 8.4 26.3 Jxw3-1 1 64.74 0.021 1.1 0.0136 Jxw3-2 1 37.05 0.012 0.8 0.01 Jxw3-3 1 35.30 0.015 0.5 0.0111 Jxw3-4 3 4.14 0.019 9.5 0.029 64.74 0.132 316.99 0.100 Jxw3-5 1 64.73 0.010 0.5 2.86 Jxw2-1 3 15.05 0.043 8.6 0.0624 28.22 0.064 64.74 0.029 Jxw2-2 5 15.05 0.012 4.5 0.1137 28.22 0.014 64.73 0.017 137.87 0.037 317.12 0.012 Jxw2-3 5 7.20 0.010 3.6 1.62 14.56 0.031 18.35 0.014 46.97 0.004 196.08 0.007 Jxw1-1 5 9.11 0.014 1.8 0.0937 22.00 0.021 47.64 0.064 126.74 0.026 317.66 0.041 -
[1] Jiurong L, Kun W. Experience of Geothermal Reinjection in Beijing and Tianjin[C]//Workshop for Decision Makers on Direct Heating Use of Geothermal Resources in Asia. 2008: 5.
[2] 刘东林, 李义曼, 庞忠和, 等. 碳酸盐岩热储对湖水回灌的响应[J]. 工程地质学报, 2019, 27(1): 178-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201901019.htm
[3] 阮传侠, 沈健, 李立亮, 等. 天津市滨海新区东丽湖地区基岩热储回灌研究[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(8): 1439-1449. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.08.013 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170813&flag=1
[4] Axelsson G. Sustainable geothermal utilization—Case histories, definitions, research issues and modelling[J]. Geothermics, 2010, 39(4): 283-291. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2010.08.001
[5] 柯柏林, 林天懿, 李文, 等. 北京西山谷积山背斜地热系统成因模式及远景区预测[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(8): 1378-1385. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190814&flag=1
[6] 刘凯, 王珊珊, 孙颖, 等. 北京地区地热资源特征与区划研究[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(6): 1128-1139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201706009.htm
[7] 于豪, 李劲松, 晏信飞, 等. 非均质碳酸盐岩储层微观孔隙结构表征与气藏检测——以阿姆河右岸灰岩气藏为例[J]. 石油物探, 2017, 56(4): 472-482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2017.04.002
[8] 张敏, 王正允, 张紫光, 等. 碳酸盐岩宏观储集空间研究——以冀北坳陷中元古界蓟县系雾迷山组和铁岭组为例[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2008, 22(5): 37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2008.05.010
[9] 李朋威, 何治亮, 罗平, 等. 华北北部地区蓟县系高于庄组-雾迷山组白云岩储层特征与形成主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(1): 26-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202001004.htm
[10] 金廷福. 天津蓟县雾迷山组微生物碳酸盐岩沉积与储层特征[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
[11] 韩宝平. 任丘油田雾迷山组白云岩储集层的渗透性试验研究[J]. 地质科学, 2000, (4): 396-403. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.04.002
[12] Xu S, Payne M A. Modeling elastic properties in carbonate rocks[J]. Geophysics: The Leading Edge of Exploration, 2009, 28(1): 66-68, 70-74. doi: 10.1190/1.3064148
[13] 张浩. 基于微观孔隙结构的碳酸盐岩渗透率计算方法研究[D]. 长江大学硕士学位论文, 2018.
[14] 柯柏林. 北京城区地热田西北部地热地质特征[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(1): 49-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.01.008
[15] 吕金波, 郑桂森, 李安宁, 等. 北京百年地质调查的传承与发展——《北京市区域地质志》修编[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(11): 1906-1917. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.11.013 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20161113&flag=1
[16] 天津市地质矿产局. 天津市区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992.
[17] 陈杰, 周改英, 赵喜亮, 等. 储层岩石孔隙结构特征研究方法综述[J]. 特种油气藏, 2005, (4): 11-14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2005.04.003
[18] 鲁洪江, 邢正岩, 王永诗. 压汞和退汞资料在储层评价中的综合应用探讨[J]. 油气采收率技术, 1997, (2): 53-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS702.008.htm
[19] 蔺亚兵, 贾雪梅, 马东民. 煤层气解吸滞后效应及其评判方法研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2016, 44(S1): 160-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ2016S1041.htm
[20] Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6): 1071-1098. doi: 10.1306/08171111061
[21] 侯科锋, 李浮萍, 罗川又, 等. 苏里格气田东南部碳酸盐岩储层特征及分类评价[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2019, 39(2): 276-285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB201902014.htm
-



 下载:
下载: